Axial Skeleton (Skull)
1/107
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lab 6
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
Human Skeleton # bones
206
Axial Skeleton
Bones lying on the body’s longitudinal axis (80 bones)
Skull
22 bones (Cranial and Facial)
Cranial
8 bones
Facial bones
14 bones
Hyoid bone
U-shaped bone in neck
No direct joint with other bones
Supports tongue, aids swallowing & speech
Between mandible & larynx
Cervical
7 bones
Thoracic
12 bones
Lumbar
5 bones
Sacrum 1 bone
Triangular bone at the base of the spine
Formed by the fusion of 5 vertebrae
Connects spine to pelvis
Supports weight in sitting & standing
Coccyx 1 bone
Also called the tailbone
Small, triangular bone at the spine’s base
Formed by 3-5 fused vertebrae
Provides attachment for ligaments & muscles
Helps support body weight when sitting
Sternum 1 bone
Flat, breastbone in the chest
Located in the center of the ribcage
Consists of manubrium, body, and xiphoid process
Protects vital organs (heart, lungs)
Attachment point for ribs and clavicles
Ribs 24 bones
12 pairs of curved bones in the chest
Protect vital organs (heart, lungs)
True ribs (1-7): directly attach to sternum
False ribs (8-10): connect to cartilage of rib 7
Floating ribs (11-12): no anterior attachment
Auditory ossicles 6 bones
Three small bones in the middle ear
Malleus (hammer), Incus (anvil), Stapes (stirrup)
Transmit sound vibrations from the eardrum to the inner ear
Smallest bones in the human body
Appendicular skeleton
Bond of the limbs & girdles which anchor the limbs to the axil skeleton (126 bones)
Pectoral girdle
4 bones (clavicle and scapula)
Clavicle
2 bones
Scapula
2 bones
Upper extremities (60 bones)
Humerus (2), radius (2), ulna(2), carpals (16), Meta carpals (10), phalanges (28)
Pelvic girdle
2 coxal bones
Lower extremities (60 bones)
Femur (2), Tibia (2), Fibula (2), patella (2), Tarsals (14), Metatarsals (10), Phalanges (28)
The cranium consists of 8 cranial bones:
1 frontal, 2 parietal, 1 occipital, 2 temporal, 1 ethmoid, 1 sphenoid
Cranial cavity
fluid filled chamber housing and protecting the brain
Sutures
The articulation points where one cranial bone meets another, clear bone unions
Frontal bone
Forms the forehead, roof of the orbits and most of the anterior portion of the cranial floor
Frontal squama
flattened expanse commonly referred to as the forehead
Supraorbital foramen or notch
of forehead
superior margin of the orbit, passage for blood vessels & nerves. of the forehead
Lacrimal fossa
Location of the lacrimal (tear) gland. Located in the superior- lateral boarder of orbit
*A 2nd lacrimal fossa exists in the lacrimal bone of the face to accommodate the lacrimal duct
Frontal Sinus
Air filled cavity. Mucus membrane lined cavities (not visible in all skulls)
Parietal bones (2)
Forms most of the lateral/posterior wall of cranium. Functions as muscle attachment site for temporalis muscle
Occipital bone (1)
Forms posterior, lateral and inferior surfaces of the cranium
Foramen Magnum
Large hole in the base of the skull- allows for the passage of spinal chord, lower brain regions and vertebral &spinal arteries (connects the cranial & spinal cavities
Occipital condyles
Convex surfaces on either side of foremen magnum- articulates w. first vertebrae (Atlas C1)
External occipital protuberance
prominent projection o back of skull- serves as attachment for ligaments and muscles
Hypoglossal canal
Small passage present along lateral boarder of foramen magnum- allows passage of the hypoglossal nerve (CN XII) innervating the tongue
Temporal bones (2)
Form inferior, lateral walls of cranium
External structures (7 of them)
Temporal squama
External auditory canal
zygomatic process
mandibular fossa
mastoid process
Styloid process
stylomastoid foreman
Temporal squama
Flattened lateral portion of skull, provides attachment site for muscle (temporalis)
External auditory canal
Ear canal. Opening into interior of ear, conducting sound waves to the interior of the ear (ends at eardrum- tympanic membrane)
mandibular fossa
Depression anterior to external auditory canal which articulates w/ mandible (lower jaw)
mastoid process
Breast shaper, posterior- ventral process just posterior to external auditory canal serves as site for neck muscle attachment
stylomastoid foreman
Between the styloid and mastiod process is a small passage. It allows passage of the facial nerves (CN VII)
Styloid process
process serves as attachment for muscles of the tongue & neck
Internal Structures (5 of them)
Petrous portion
Internal acoustic canal
Jugular foramen
Carotid canal
Foramen lacerum
Petrous portion
Large raised region on cranial floor, contains inner & middle ear structures
Internal acoustic canal
Small canal on the posterior medial surface of the petrous portion; carries auditory nerve (CN VIII) and facial nerve (CN VII)
Carotid canal
Medium sized canal seen from both the cranial floor and the inferior skull surface. From the inferior skulls surface, the canal lies anterior to the jugular foramen. The canal runs in a lateral inferior to the medial superior directions. Carries internal carotid artery
Foramen lacerum
Jagged opening inferior to the exit of the carotid canal on the medial surface. Extends between occipital & temporal bone
Normally filled w/ hyaline cartilage in living skull
Jugular foramen
Medium sized jagged hole visible from both the cranial floor and the inferior skull surface. From the inferior skull surface, the passage lies between the mastoid process and the occipital condyles
Allows passage of jugular vein, glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX), vagus nerve (CN X) & spinal accessory nerve (CN XI)
Sphenoid bone (1)
Lies at the base of cranium, “Keystone” of skull as it articulates with all other cranial bones. Connects to facial and cranial bones displays distinct bat like shape
Sphenoid bones Lesser wing
The anterior margin of the sphenoid is the bat shaped lesser wings. Most superior projection of bones anterior to Sella Turcica
Sphenoid bones Greater wing
Lying posterior to the lesser wing, the greater wing contributes to the anterior floor of the cranium and forms back of eye orbits
Pterygoid process
Sharp process off of greater wings- serves as attachment sites for jaw & tongue muscles
Sella turcica Hypophyseal fossa
“turkish saddle” middle portion of sphenoid.
Supports the pituitary gland
Body of sphenoid
Cube shaped central mass of bone between the occipital and ethmoid bones
optic canal
paired canals inferior to the lesser wing carriers optic nerve CN II
Superior orbital fissure
Superior elongated opening in the orbit. Carries nerves
3 foramen on the lateral sides of the sella turcica
Foramen rotundum
Foramen ovale
Foramen spinosum
Foramen rotundum
Small paired passages on the surface of the greater wing just inferior to the superior orbital fissure. Allows passage of the maxillary division of the trigeminal nerve (CN V2)
Foramen ovale
Paired medium sized oval foramen in the posterior region of greater wing. Allows passage of the mandibular division of trigeminal nerve (CN V3)
Foramen spinosum
Paired small holes posterior to foremen ovale. Allows for passage of blood vessels
Ethmoid bone (1)
Sponge like bones forms majority of nasal structure.majority of this bone lies within the nasal cavity, but a prominent projection through the frontal bone (crista galli) communicates with the cranium. The ethmoid is directly behind the nasal bones and medial to the eye orbits.
Crista galli
Vertical projection, site for attachment of the
brain's coverings (meninges: brain CT)
Cribriform plate
Superior porous bone projection through the frontal bone. Allows
entrance of olfactory nerves (CN I). Small olfactory foramina allow passage of olfactory nerves.
Lateral masses (2)
delicate scrolled bones called conchae or turbinates; function to circulate inhaled air.
The lateral masses are a combination of the superior and middle nasal conchae.
perpendicular plate
Superior nasal septum. Thin sheet of bone dividing the nasal cavity in half.
Sutures
The tight immovable joints found only in the skull. Sutures bind cranial bones together with dense irregular CT.
1. coronal suture 2. sagittal sutures 3. lambdoid suture 4. squamosuture.
(Metopic suture: fusion line within frontal bone; disappears ~ 8 years of age)
Fontanels
Temporary fibrous connections between adjacent cranial bones in the infant skull. A newborn infant has six fontanels; the anterior and posterior, two mastoid, and two sphenoid.
Facial bones (14)
Mandible (1)
Maxillary bones (2)
Zygomatic bones (2)
Nasal bones (2)
Lacrimal bones (2)
vomer (1)
INferior nasal conchae (2)
Palatine bones (2)
Mandible
Foramen spinosum
Mandible body
U-shaped horizontal portion bending posteriorly at the angle to 2 lateral raised walls (ramus)
Mandible ramous
2 lateral raised "walls". Perpendicular portions serve as muscle
attachment sites (masseter muscle)
Mandible
Coronoid process
2 lateral raised "walls". Perpendicular portions serve as muscle
attachment sites (masseter muscle)
Mandible
Condylar process
Posterior-superior rounded process - Articulates w/ temporal bone forming the temporomandibular joint (TMJ at the mandibular fossa, the ONLY synovial joint in the skull
Mandible
Alveolar processes
Oral margins accommodating the teeth within the superior surface of the body
Mental foramen:
Small holes on the lateral-anterior surfaces of the mental region. Allow passage of mental nerve (chin & lips)
7. Mandibular foramen (canal):
Medium sized hole on the medial aspect of the ramus: Allows passage of mandibular nerve and blood vessels to the teeth & gums
Maxillary Bones
(2): Bones unite to form the upper jaw. Articulates w/ every bone in face except the mandible
Maxillary
Alveolar processes:
Oral margins accommodating the teeth (alveoli)
Maxillary sinus:
Mucus membrane lined cavity within maxillary bone. Lateral to nasal cavity. Drains fluids into nasal cavity
Maxillary
Palatine process:
forms anterior 3/4 of hard palate
Maxillary
Inferior orbital fissure:
Inferior elongated hole in the inferior aspect of the orbit (formed by union with sphenoid bone within the orbit)
Maxillary
teeth
"Bilateral" dental formula - Adult: 2, 1, 2, 3. On top and bottom, right and left, from midline, teeth are:
2 incisors, 1 cuspid (canine), 2 bicuspid (premolars), 3 tricuspid (molars)
Incisors:
Blade-shaped teeth with a single root found at the front of the mouth. Incisors are useful in nipping and cutting. First teeth to appear at ~ 7.5 - 9 months and then at 7-9
Cuspids (canines):
Conical- shaped teeth with one root, lateral to incisors. Used for tearing or slashing.
First appear at 18 months and then at 11-12 yrs.
bicuspids
(premolars): Flat wide teeth with usually 2 roots, just posterior to cuspids. Useful for grinding, crushing, and tearing. First appear at 14 months and then at 10-12 years
Tricuspids (molars_
Flat wide teeth with usually 3-4 roots. Useful for grinding crushing and tearing.
First appear at 24 months and then at 6 - 21 yrs (with the third molar - wisdom tooth cutting at ~21 yrs).
Zygomatic bones (2)
"cheek bones"; Form the lateral wall of orbit & anterior portion of zygomatic arch
1. Temporal process: Articulation with temporal bone. Forms anterior portion of the zygomatic arch
Nasal bones (2)
Paired bones forming the bridge of nose (most of nose is hyaline & elastic cartilage)
Lacrimal bones (2)
Smallest bones in skull. Forms the medial, anterior portion of orbit
Smallest bones in skull. Forms the medial, anterior portion of orbit
1. Lacrimal foramen:
2. Lacrimal fossa:
Lacrimal foramen:
Passages located at the inferior medial aspect of the eyes orbit. Allows passage of nasolacrimal duct - "tear duct". Functions to drain eye fluids into the nasal cavity
Lacrimal fossa:
Depression almost encompassing the whole bone, allows passage of lacrimal duct into nasal cavity
Vomer (1):
Inferior portion of nasal septum. Thin triangle or "plow"-shaped bone. Unites
with the perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone.
Inferior nasal conchae (2):
Lateral, inferior fold of scroll-shaped bone projecting into nasal cavity (turbinates). Inferior to the middle and superior nasal conchae of the ethmoid bone. Similar structure and function, but are considered paired facial bones (not part of any cranial bone).
Palatine bones (2)
Paired "L" shaped bones; Form the posterior 1/3 of the hard palate, contribute to floor and lateral walls of nasal cavity, and to the floor of the orbits.
Hyoid bone:
Unique "U-shaped"
inferior to the skull, provides attachment for muscles of tongue, neck, and pharynx to aid in tongue movement and swallowing. The hyoid does NOT articulate with any other bones.
Middle ear ossicles
located within the middle ear, in the petrous portion of the temporal bone.
Mnemonic: lateral→ medial; "MIS"
1. Malleus: "hammer"
2. Incus: "anvil"
3. Stapes: "stirrup"
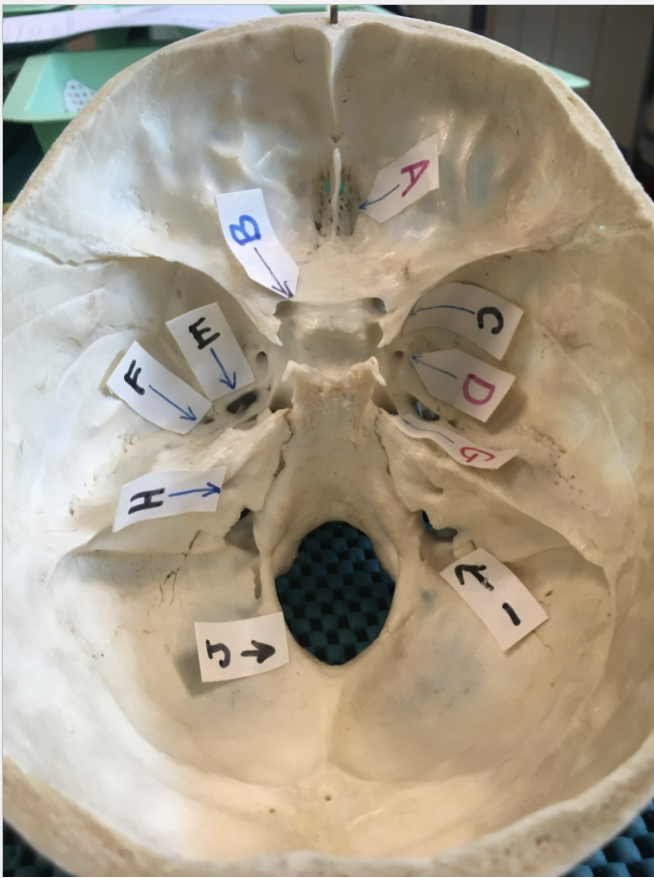
A:
olfactory foramina
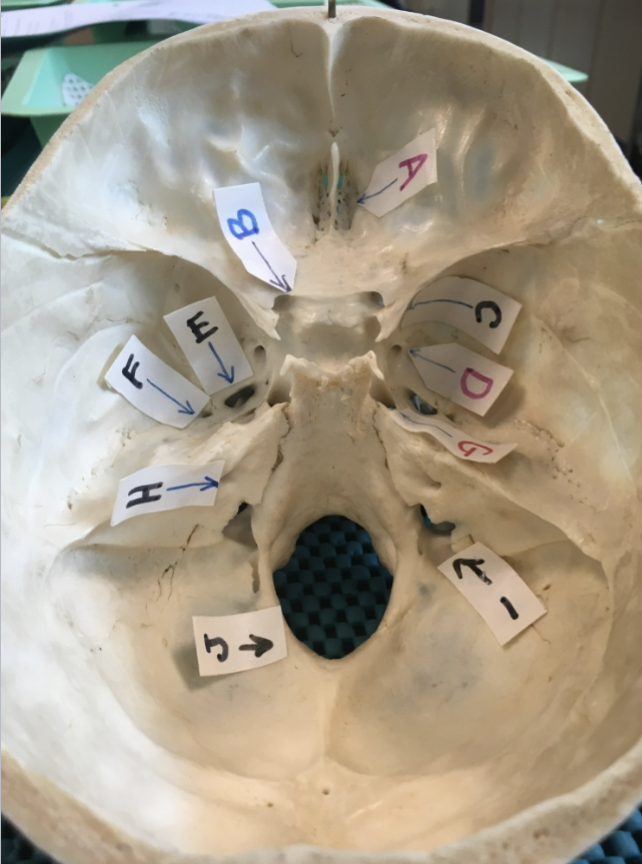
B:
B: optic canal
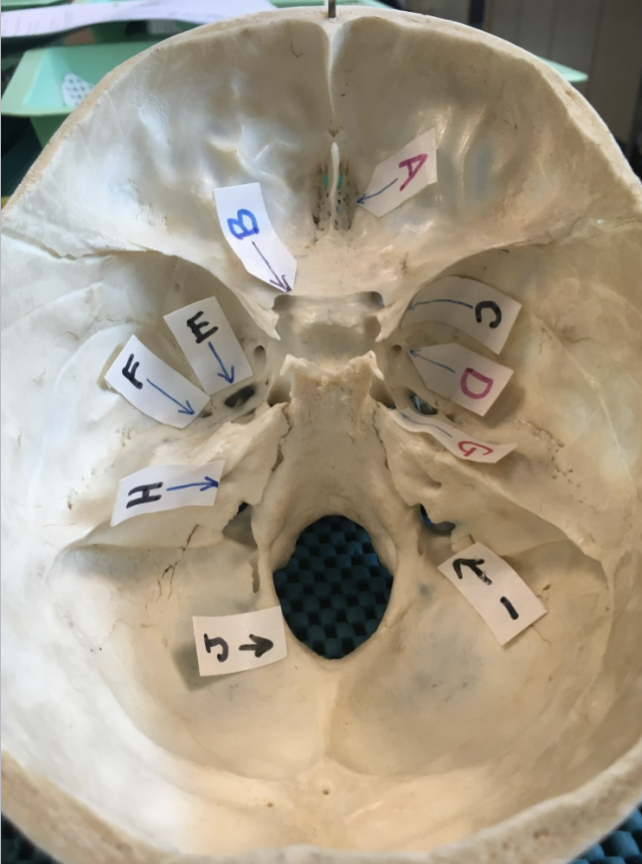
C
Superior orbital fissure