W4 Neuroscience 2
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
Nueraxis
an imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the bottom of the spinal cord to the front of the forebrain
- level of the head = dorsal up
- level of the spinal cord = dorsal back
Dorsal
back of the axis
Ventral
to the belly/front of the axis
Rostral
top of the axis
Caudal
towards the bottom of the axis
Medial
central/towards the midline
Lateral
regions outside the brain
what are Lesion studies
creating damage to a brain region and observing different brain behavior
advantage of Lesion studies
direct measure of a brain structures function
disadvantage of Lesion studies
hard to selectively target particular regions and draw conclusions
solution to Lesion studies
specific brain lesions can be studied in animal models
how does a CT scan work?
produces structural slices of the brain by taking a series of x-ray slices of brain and pieced together to create an image
CT scan advantage & limitation?
- helpful to diagnose brain injuries
- low resolution
how does an MRI work?
powerful magnetic fields are generated, aligning hydrogen atoms found throughout the brain
MRI advantage and limitation?
- used to localize tissue very percisely throughout the brain, clearer imagery compared to CT
- takes longer & more expensive
how does a PET scan work?
radioactive tracer of glucose or oxygen is injected into bloodstream, radioactive molecules make their way to brain and are used in metabolic processes
PET scan advantage and limitation?
- shows how brain function relates to cognitive tasks
- requires radioactive tracer to be injected = invasive
how does an fMRI work?
measures the blood oxygen dependent signal and uses many of the same principles as MRI
fMRI advantage and limitation?
- produces clear image of the brain activity without need for radioactive tracer
- oxygen used by the brain spikes a few seconds later than spikes of functional activity in the brain (not percise)
how does an EEG work?
electrical activity of the brain can be recorded through the scalp by wearing a cap of very sensitive electrodes, recording from a population of neurons to provide rough image of brain's overall activity
what are the 3 distinct regions of the brain?
1) Hindbrain
2) Midbrain
3) Forebrain
Hindbrain
all information into and out of the brain travels through the cranial nerves and spinal cord at the base of the skull, forced with regulating bodily functions
what does the hindbrain consist of?
(RCMP) reticular formation, cerebellum, medulla, pons
what does the Reticular formation control?
arousal & motivation, aircadian rhythms, posture & balance
what does the Cerebellum control?
coordinated movement
what does the Medulla control?
breathing, digestion, heart rate and autonomic reflexes
what does Pons control?
movement auditory perception, emotional processing
Midbrain
small region including two major subdivisions involved in a variety of functions including perception, arousal, and motor control
what are the 2 major subdivisions of the midbrain?
1) Tectum
2) Tegmentum
Tectum function
perception & action
what are 2 primary Tectum structures
1) Superior Colliculi
2) Inferior Colliculi
what is the function of the Superior Colliculi?
eye movements, visual reflexes
what is the function of the Inferior Colliculi?
auditory integration
what are the Tegmentum structures?
1) Red nucleus
2) Substantial nigra
what is the Red nucleus' function?
motor control
what is the Substantial nigra function?
reward related behaviour through release of the neurotransmitter, dopamine
Forebrain function
largest region of the brain, involved in emotion, memory, perception, and thought
what are the 2 sections in the forebrain
1) Limbic System
2) Cortex
what are structures are in the Limbic system?
(PHAT-H) pituitary gland, hypothalamus, amygdala, thalamus - hippocampus
what does the Hypothalamus do?
directing stress responses, regulating energy metabolism by influencing feeding, digestion, and metabolic rate, regulating production through hormonal control of mating, pregnancy and lactation
what is the function of the Pituitary gland?
regulates and releases vital hormones
what are the 2 sub regions of the Pituitary gland?
1) Anterior
2) Posterior
what is the function of the Anterior PG?
receives signals from the brain via hypothalamus and releases stimulating hormones to regulate other important endocrine glands
what is the Postpperituitary?
extension of the hypothalamus and releases oxytocin and vasopressin
what does Oxytocin do?
lactation and uterine contractions in women, bonding, love, trust
what does Vasopressin do?
regulates levels of thirst by interacting with kidneys to regulate glucose levels
what is the function of the Amygdala?
almond shaped structure below temporal lobe, receiving sensory information and plays a role in decoding emotions, particularly stimuli that may be threatening
what is the function of the Hippocampus?
horseshoe shaped structure in the temporal lobe, involved in the process of memory, spatial mapping, neurogenesis
what does the Cortex do?
controls information processing and cognition
when the cortex folds over itself what does it form?
1) Gyri
2) Sulci
Gyri
ridge on cortex/bulge outward
what is the point of the Gyri?
linked on cortex/buldge outward
Sulci
shallow grooves that separate the gyri
what is the point of the Sulci?
useful in indicating where neural tissue responsible for one function ends and the next function begins
what are the 4 lobes the cortex is organized into?
1) Frontal
2) Occiptial
3) Parietal
4) Temporal
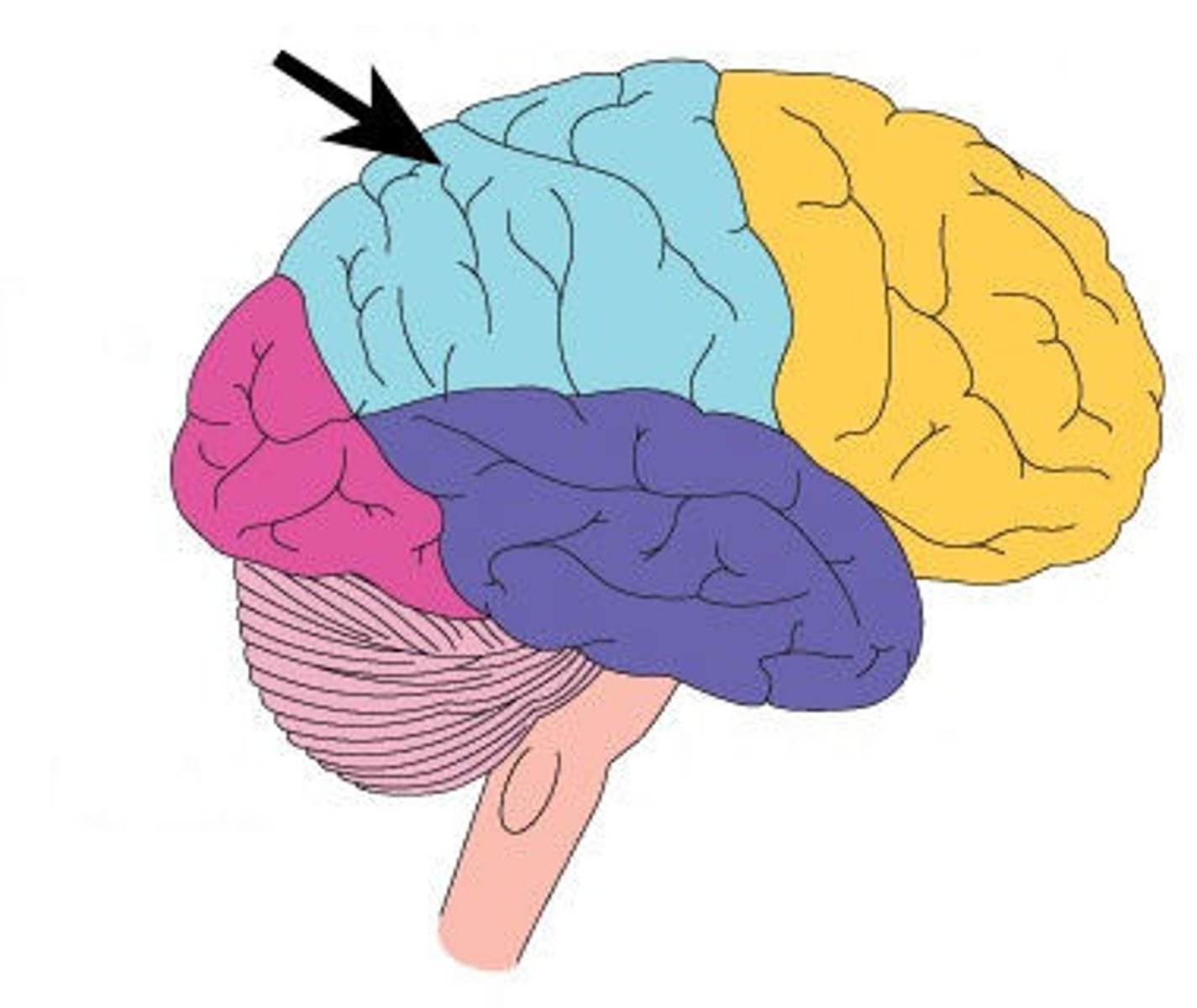
Frontal lobe function?
motor processing, decision making & higher-order thought
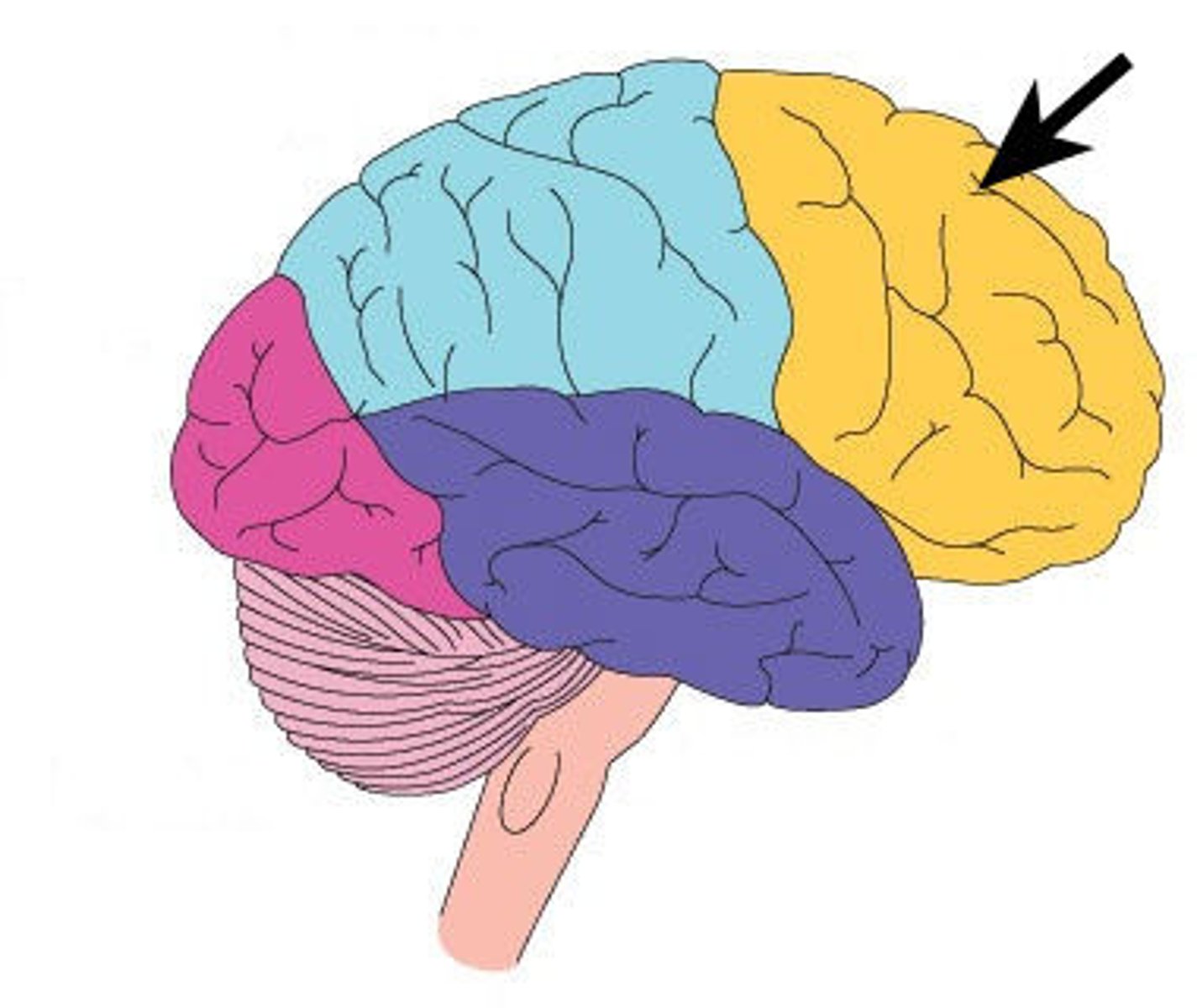
Occipital lobe function?
visual processing
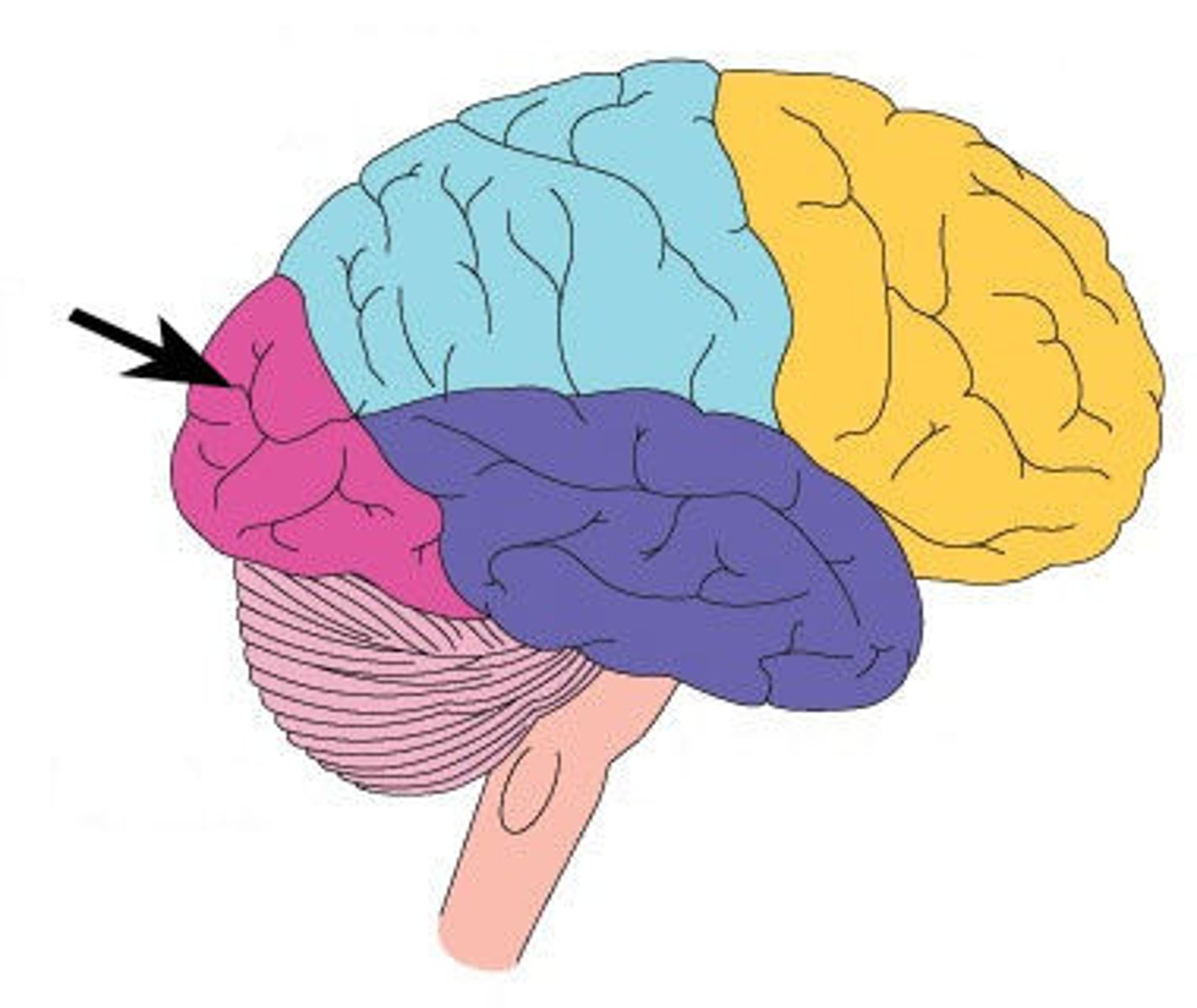
Parietal lobe function?
touch processing, spatial representation
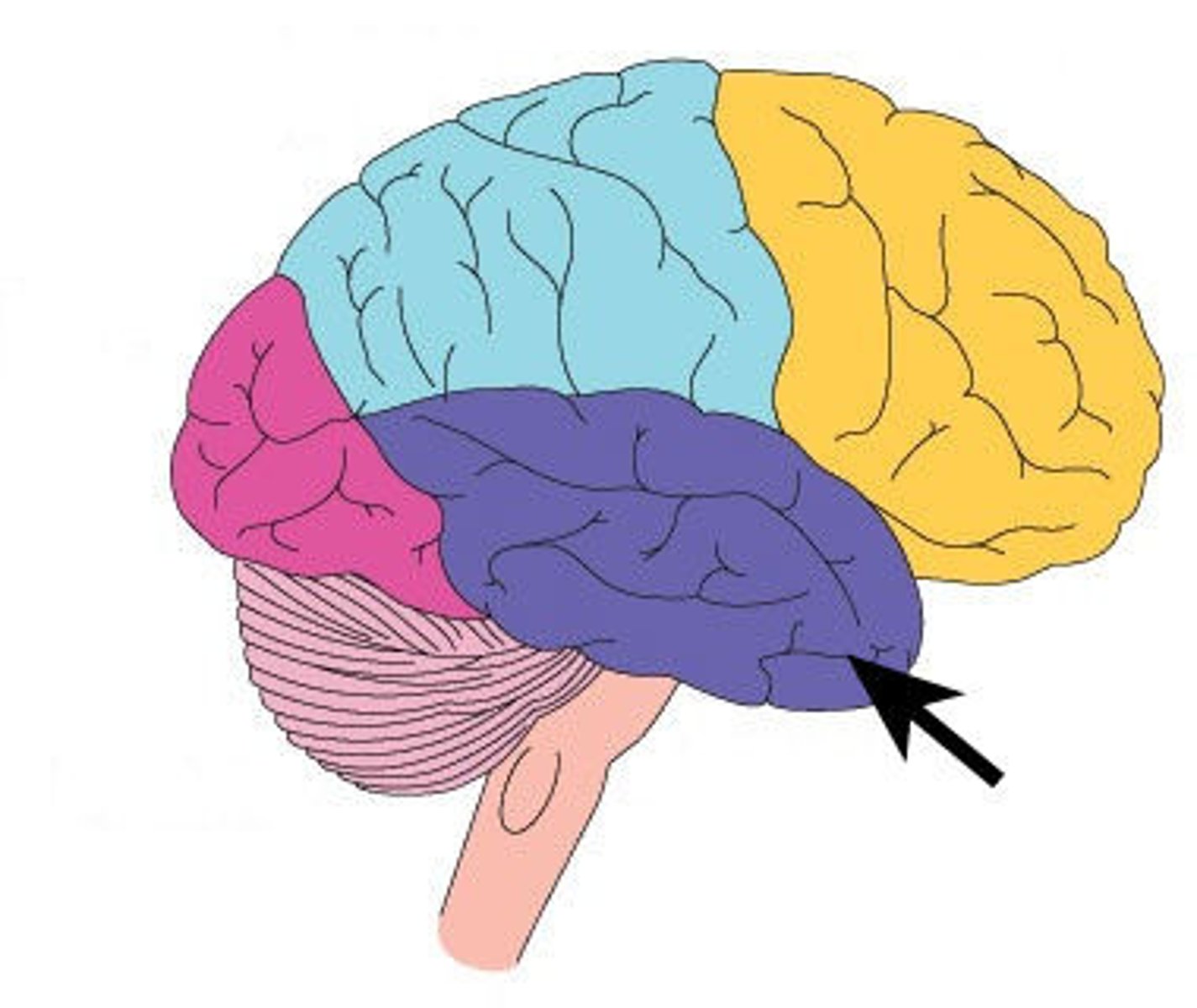
Temporal lobe function?
higher visual processing, basic auditory processing, memory & language
Broca's Area
motor production of speech
what happens when the Broca's Area is damaged?
expressive aphasia
when Broca is broke, he uses broken words
Wernicke's Area
language comprehension
what happens when the Wernicke's Area is damaged?
receptive aphasia:
when Werncike won't work, we wonder 'what'?
what does the Corpus Callsum do?
carries information between the two hemispheres of the brain
what can a severed corpus callosum lead to?
Split Brain Syndrome