direct current & iontophoresis
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
direct current
galvanism (medical) / constant current
mA: 1 mA = 6.24 × 10²1 electrons per second
unidirectional flow through a conductor
electron flow: (-) to (+)
current flow: (+) to (-)
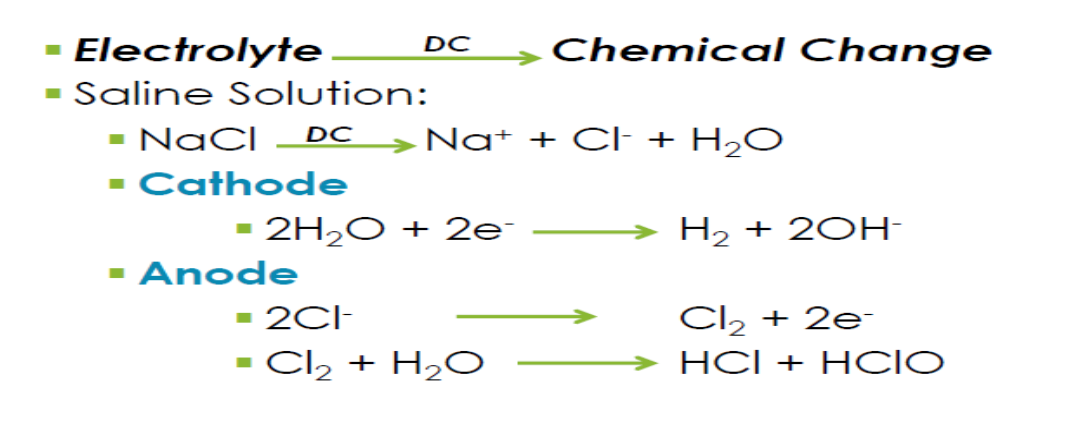
electrolysis
polarity testing
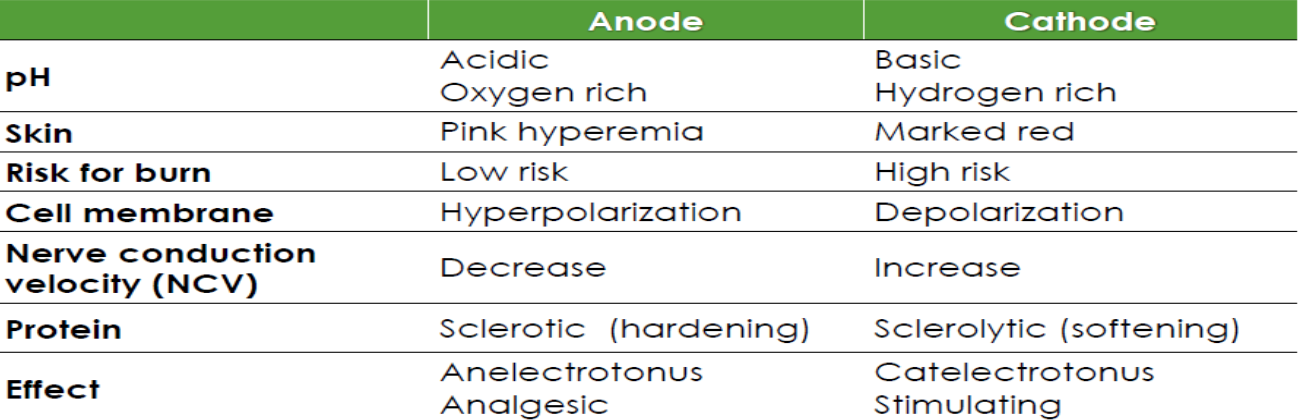
physiologic effects
hyperemia
counter-irritant → pain relief
sedation
at the ANODE, analgesic
DC reduces NCV
Pfleuger’s (Erb’s) law
“polar formula”
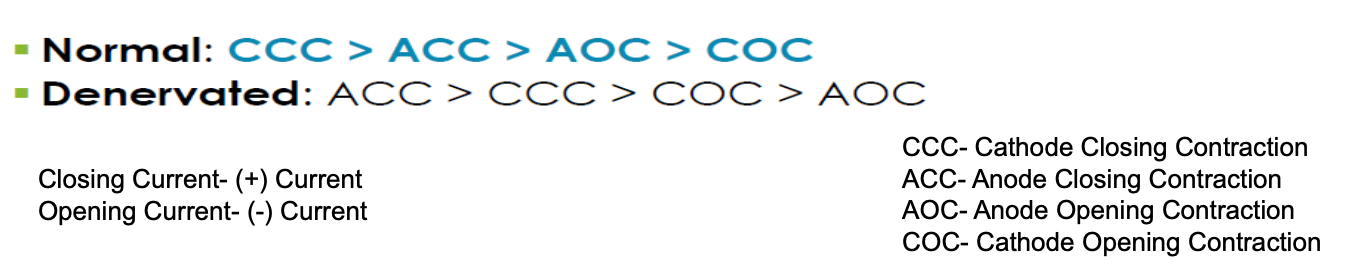
continuous direct current
ionthoporesis
high risk for chemical burn
rarely used today
interrupted direct current
flows in the same direction intermittently
strength reduces to 0 between each period of flow
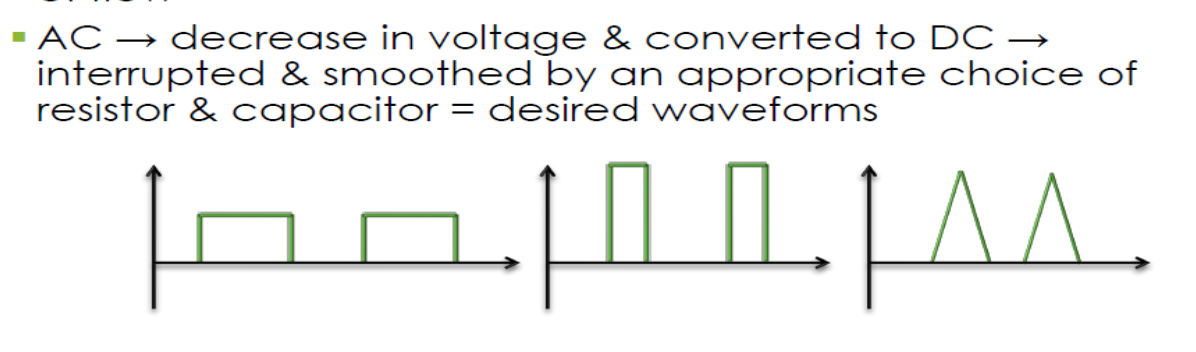
pulsed current
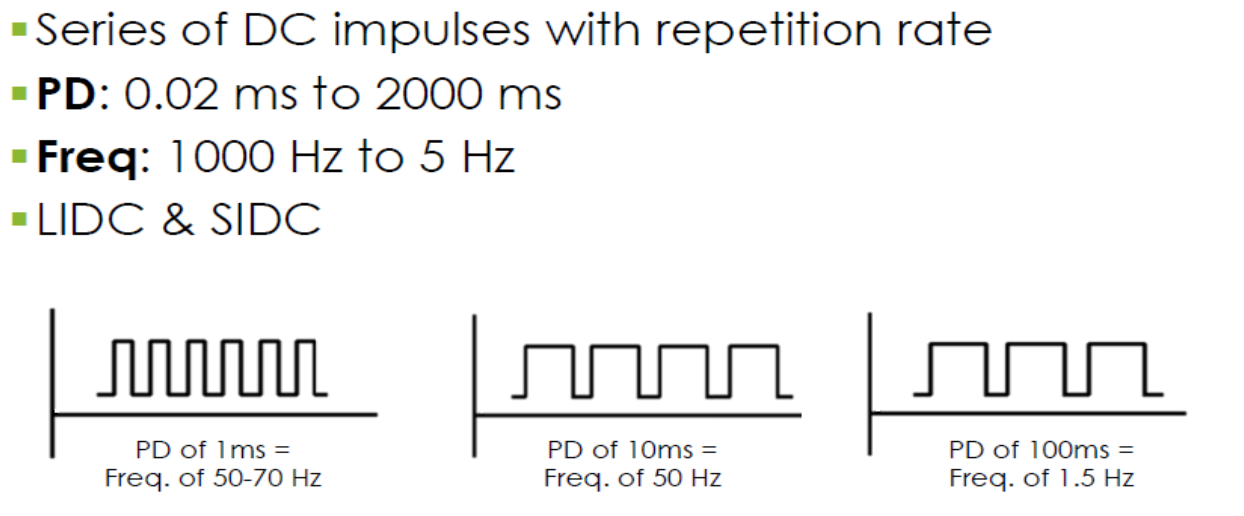
long interrupted direct current
unidirectional, interrupted at regular intervals
for denervated mm
modulation
intensity is cyclically reduced to 0
interrupted modulation: current is turned on & off
waveform
exponential progressive pulses
factors
strength & duration of stimulus
rheobase
5-35 V (2-18 mA)
minimal voltage, prolonged PD
produces bare minimal & palpable contraction
cathode / bipolar technique
Chronaxie
0.05-0.5 ms
minimal time, stimulus twice the strength of rheobase
physiological effects of EPC

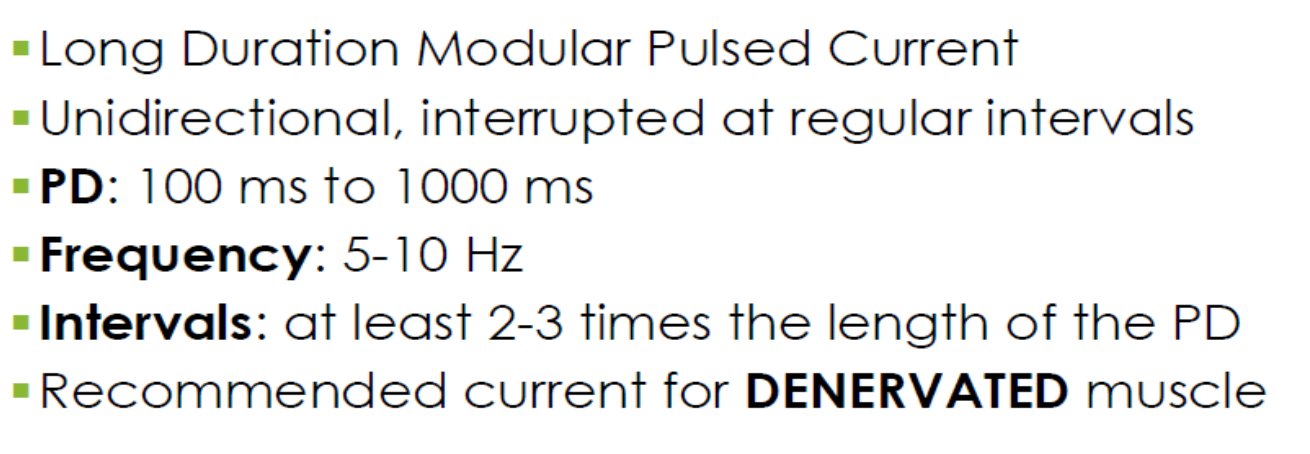
long IDC: denervated mm
normal : (+) accommodation
denervated: (-) accommodation
to stimulate: ↓ intensity, ↑ time (rheobase?)
effects of LIDC on denervated mm

effects of SIDC
sensorimotor: minimal stimulation of sensory fibers
ionic mov’t of IC & EC fluid
through & through faradism
surged interrupted DC
peak intensity ↓, ↓ gradually
no fixed current intensity — modulated
depolarized interrupted DC
definite positive polarity
intensity flows on reverse during interval between impulses → reduce chemical effects
Interrupted modulated DC
intensity is cyclically reduced to zero at regular intervals
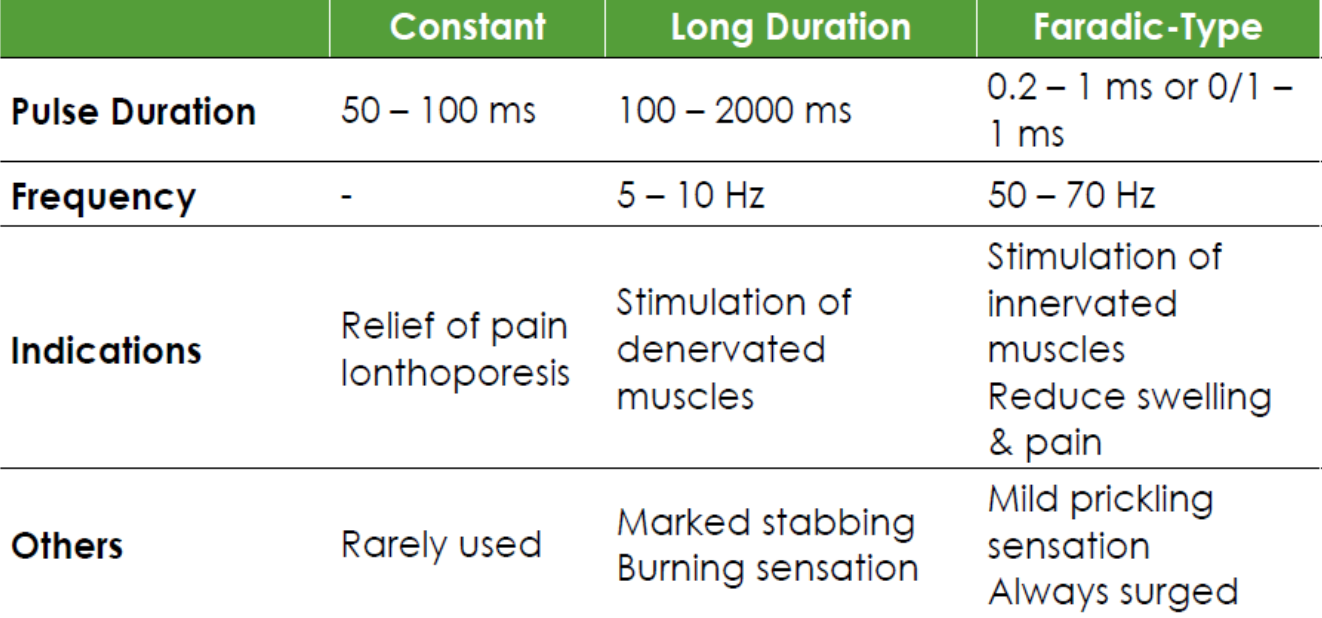
iontophoresis
continuous DC to transfer ions
used to avoid GI upset
electrophoresis: movement of ions in solution
principles:
ionisation
like charges repel
deeper penetration
wave form: monophasic
modulation: constant
# of ions transferred is directly related to:
duration of tx
current density
ion concentration
Selecting the ion
must be soluble in both fat & water
relatively superficial, generally <1mm
indication for DC & ionthophoresis
relief of pain
cathodal galvanism
chronic pain due to adhesion, swelling, or pressure on nerves
counter-irritant → VD
max dosage (chronaxie?), short time
0.5 to 0.8
10 min, 1st tx → progress by 5 min to 20 min
tx on alternate days
anodal galvanism
relieve pain by removing H & K ions (MPS)
low dosage, max time (rheobase?)
0.15 to 0.25
15 mins, 1st tx → progress by 5 to 30 mins
can be given daily for a few days

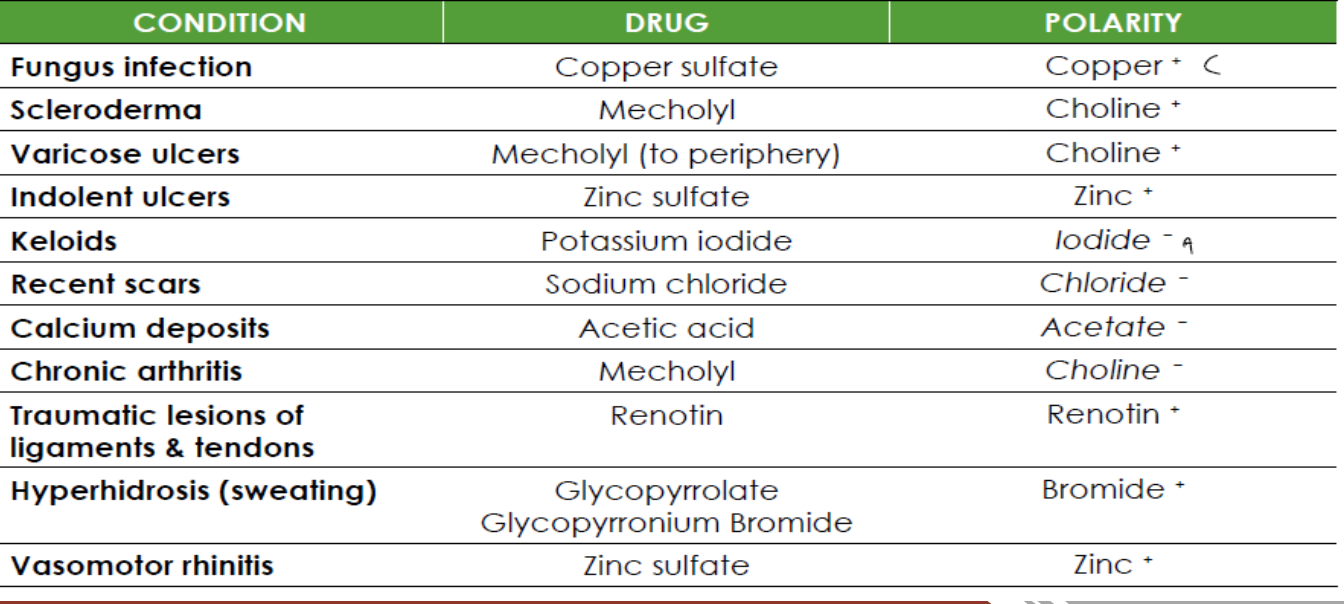
common drugs
contraindication
open skin
infection
bony areas
can produce burn, impedance
loss of sensation
dry scaly skin
skin lesions
dangers
shock
burns
chemical
alkaline — cathode
acidic — anode
due to: overdosage & skin lesions
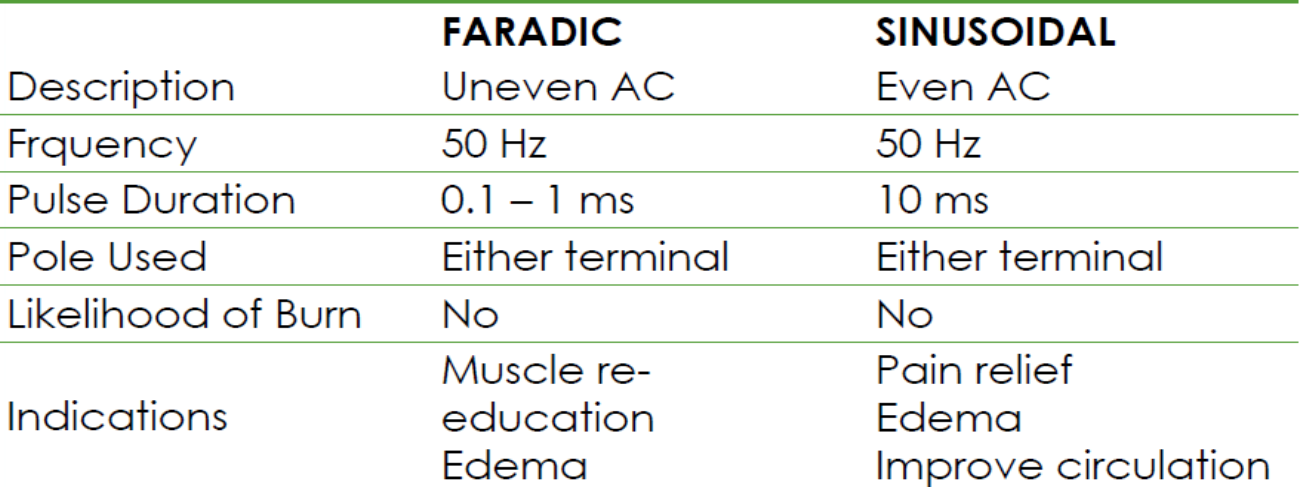
alternating current
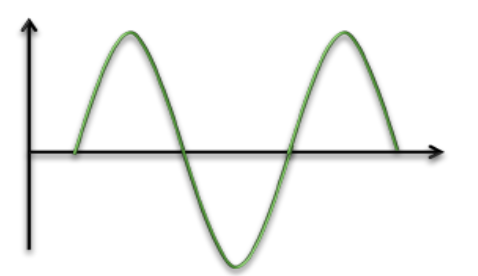
sinusoidal currents
direction of flow changes in rhythmically at a specific frequency per second
medicine = 50 Hz
surged AC
magnitude gradually increased or decreased
length: varies, 1-10 ms
pulse — sine wave of each polarity
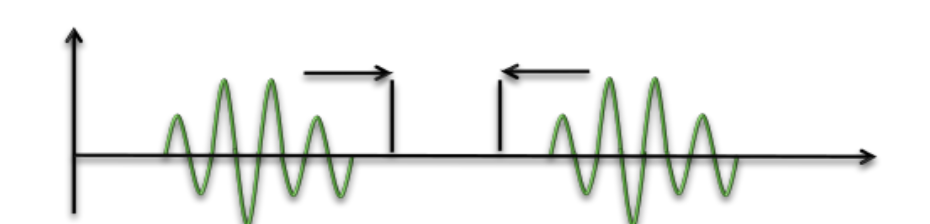
types of surged ac
sinusoidal currents
even AC, 50 Hz
PD: 100 ms, sine pulse
may be surged or unsurged
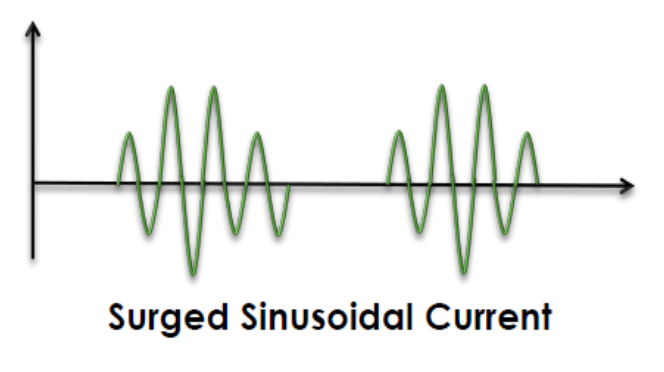
physiological effects of SC
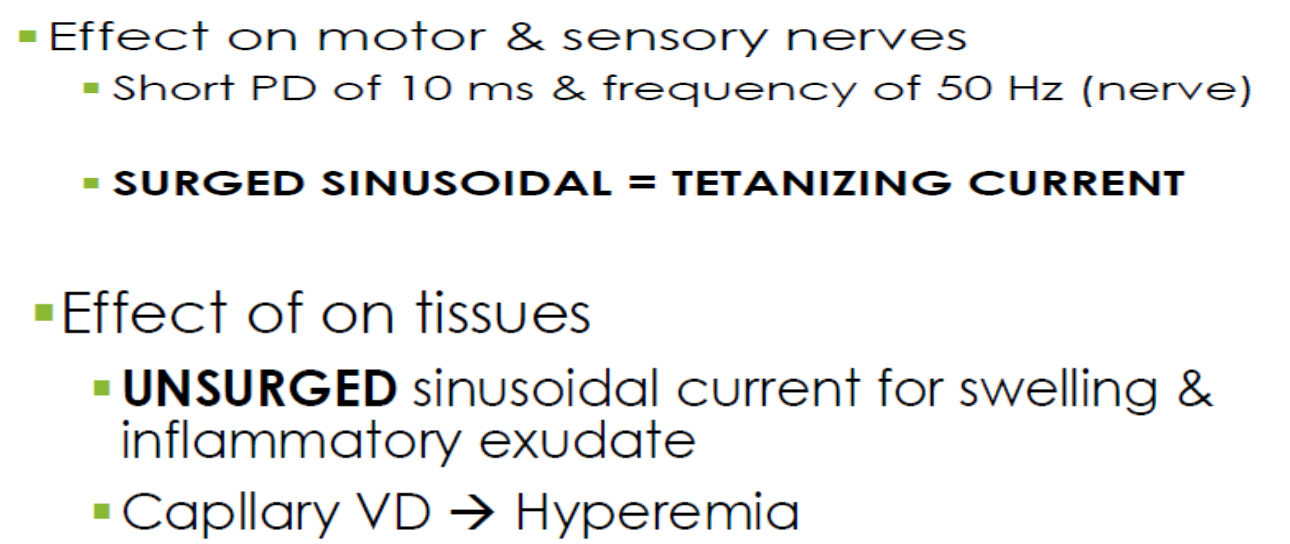
SC indication & contraindication

faradic currents
uneven AC, 50 Hz
PD: 1 ms, hand surged current
produced by a faradic / induction coil