804 BCH Week 2 - DNA, RNA, Transcription
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
112 Terms
R5P and ATP
PRPP is a molecule produced from ___ and ___
IMP
___ is the first purine nucleotide synthesized
PRPP, amino acids, folate, ATP
What 4 things are used to synthesize purines
IMP
AMP and GMP are synthesized from ___
reciprocally
The biosynthesis of ATP and GTP are ____ regulated by the concentration of the other
ATP and GTP
Kinases convert AMP and GMP to ___
feedback inhibition and feedforward activation
Purine synthesis is regulated by ___ and ___ to maintain concentration of purines
Branchpoint
___ control regulation is used to maintain a balance of each purine
pyrimidine biosynthesis
The photos are "ingredients" for

developmental delay, seizures, ataxia, language deficits, mental retardation, anemia, hypouricosuria, high levels of uracil and thymine in urine
What are some disorders of pyrimidine metabolism
pyrimidine base on PRPP
pyrimidine nucleotides are synthesized by placing an assembled ____
OMP
___ is the first pyrimidine nucleotide synthesized
UTP, glutamine, ATP, H20
UMP synthesized from OMP & CTP is made from what 4 things
UTP
Kinases convert UMP to ___
substrate (PRPP), energy levels (ATP; activates), and product levels (UDP, UTP; inhibits)
Pyrimidine synthesis is regulated by what 3 things
2' deoxy-forms
thymine nucleotides are only synthesized as ___
Synthesized
TMP, TDP, TTP are not ___
ATP, PRPP
Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase II is activated by ___
UTP, UDP
Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase II is inhibited by ___
dADP, dGDP, dCDP, dUDP
Ribonucleotide Reductase (RR): one enzyme produces 2'-deoxyribonucleoside diphosphate - what are 4 examples
2' hydroxyl
RR removes what
1- catalyzed by ribonucleotide reductase (RR)
2- NDP is reduced (2' position) to form dNDP
3- NADPH provides reducing power via thioredoxin (protein intermediate)
what are the 3 steps of synthesis of 2'-deoxy-ribonucleotides for DNA
glutaredoxin
___ can be used in place of thioredoxin in synthesis of 2'-deoxy-ribonucleotides for DNA
produce correct ratios of 4 dNDPs
what is the goal of ribonuleotide reductase enzyme
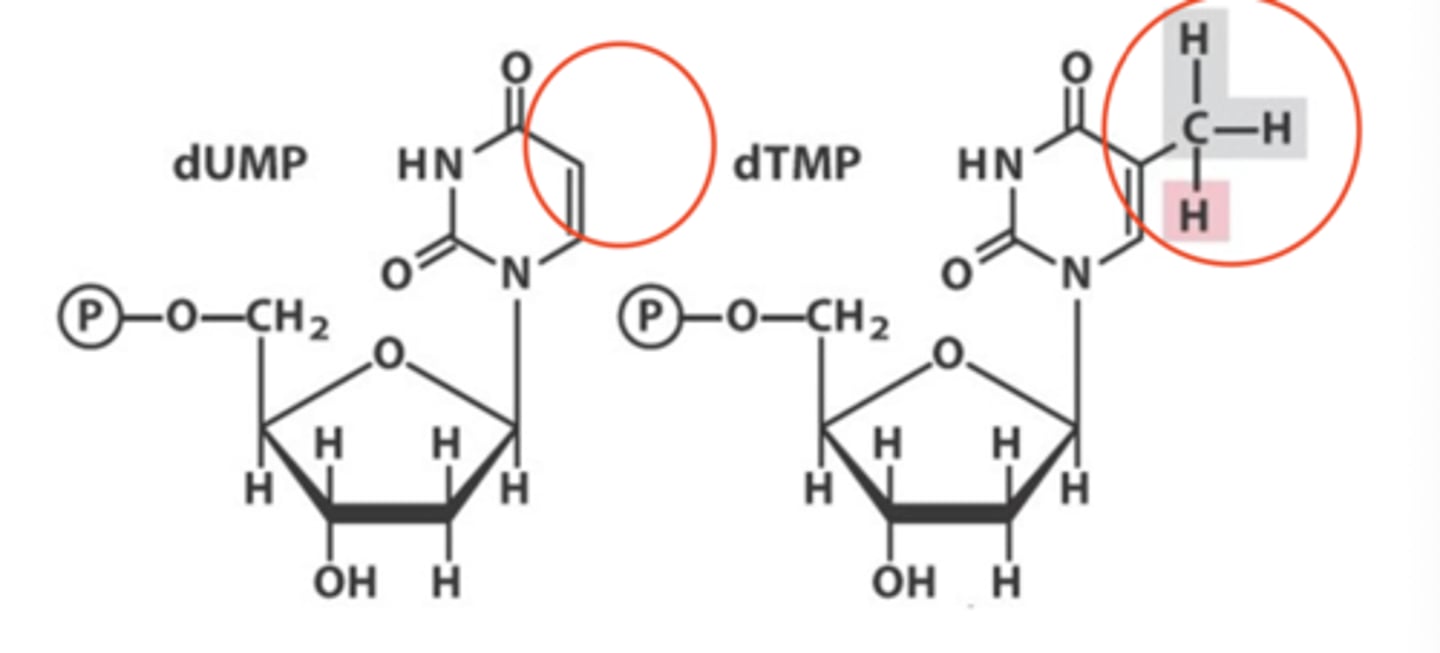
dTTP from dUMP
thymidylate synthase and thymidine kinase together make ____
add a methyl group to dUMP
How is deoxythymidine produced
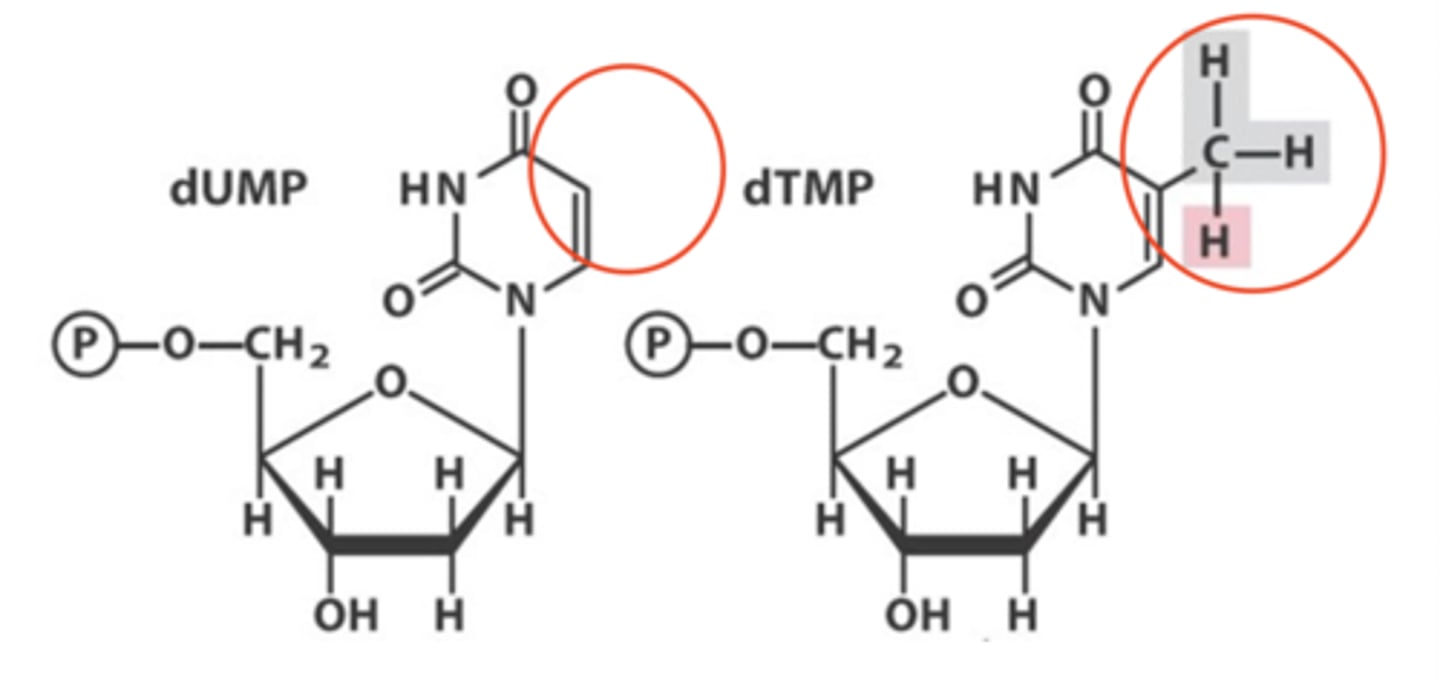
thymidylate synthase
What is is deoxythymidine production catalyzed by
dihydrofolate reductase (key enzyme in biosynthetic production of dTMP)
N5, N10 - methylene-tetrahydrofolate must be regenerated by ___
reuse of bases
what is nucleotide salvage
catabolizes bases
what is nucleotide degradation
cell turnover, dietary nucleic acids, pathogens
3 sources of nucleotide salvage and degradation
intestine; nucleosides and nucleoside phosphorylases
nucleosides are absorbed through the ___ OR further degraded by ___
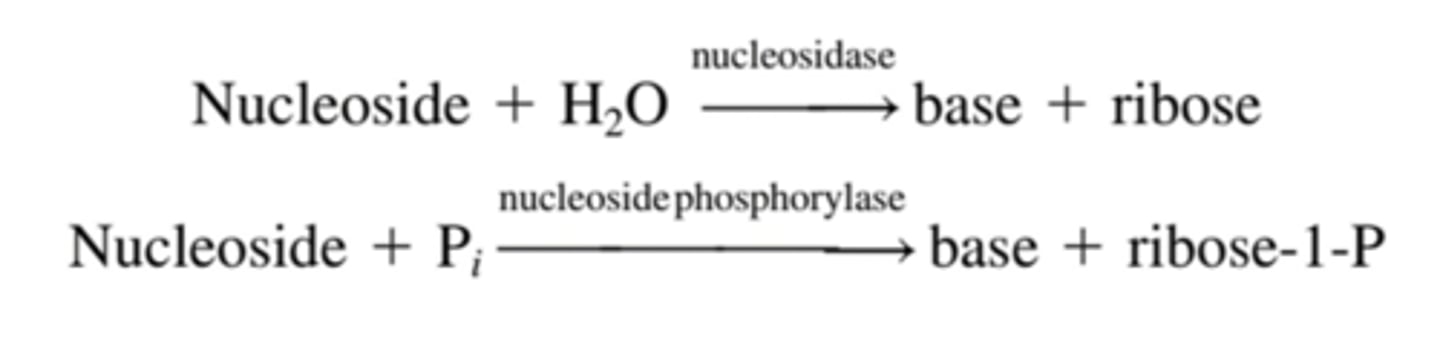
uric acid
in nucleotide degradation, purines are broken down to ___
removing base from nucleotides, then sugars
in purine degradation, degradation proceeds by ___
adenosine deaminase
in purine degradation, deficiency of ____ causes SCIDS
HGPRT (HPRT)
in purine salvage, bases are added to PRPP by ___
Lesch-Nyhan syndrome
in purine salvage, deficiency of HGPRT (HPRT) causes ___
corresponding nucleotides
in purine salvage, free purines are reconverted to ___

CoA
in nucleotide degradation, pyrimidines are converted to ___ derivates for catabolism
an excess of uric acid
gout is ___
allopurinol
____ treats gout by irreversibly inhibiting xanthine oxidase
urea
in pyrimidine degradation or salvage, pyrimidines degrade to ___
cytotoxic (kills dividing cells); targeted (kills cancer cells by targeting unique molecular properties)
Chemotherapy is ___ and ___
antimetabolite drugs
The following drugs are what
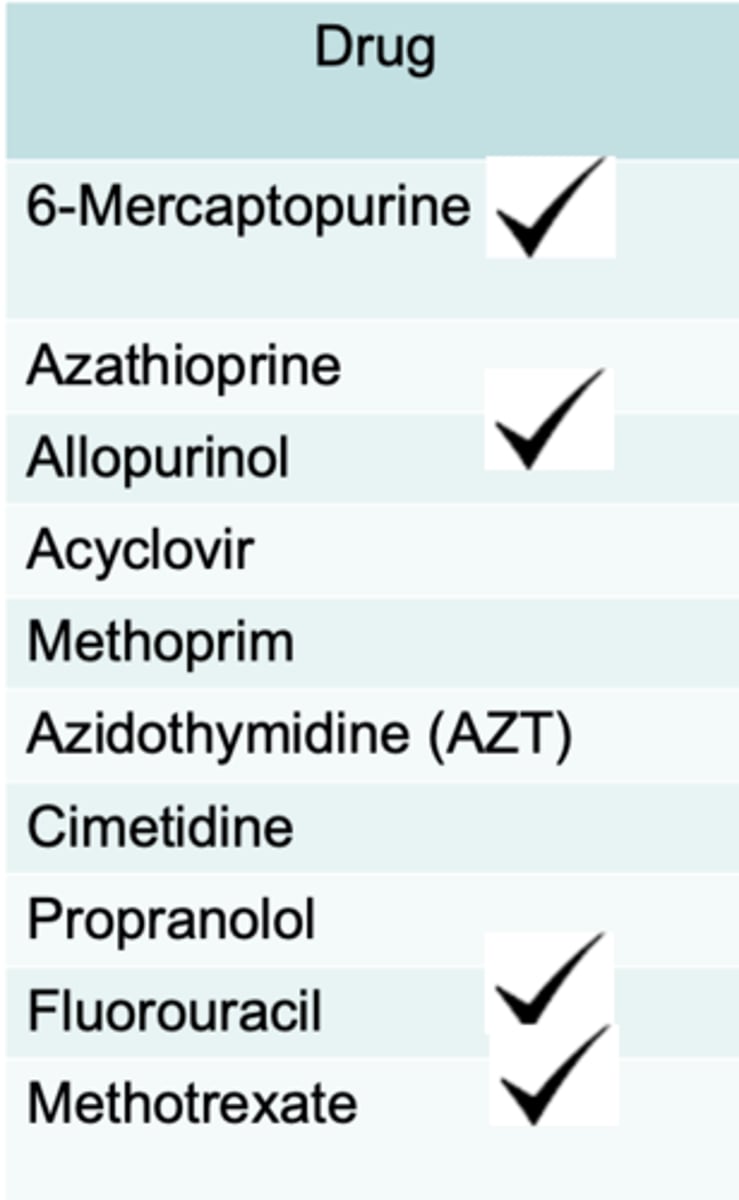
antimetabolite used to treat cancer
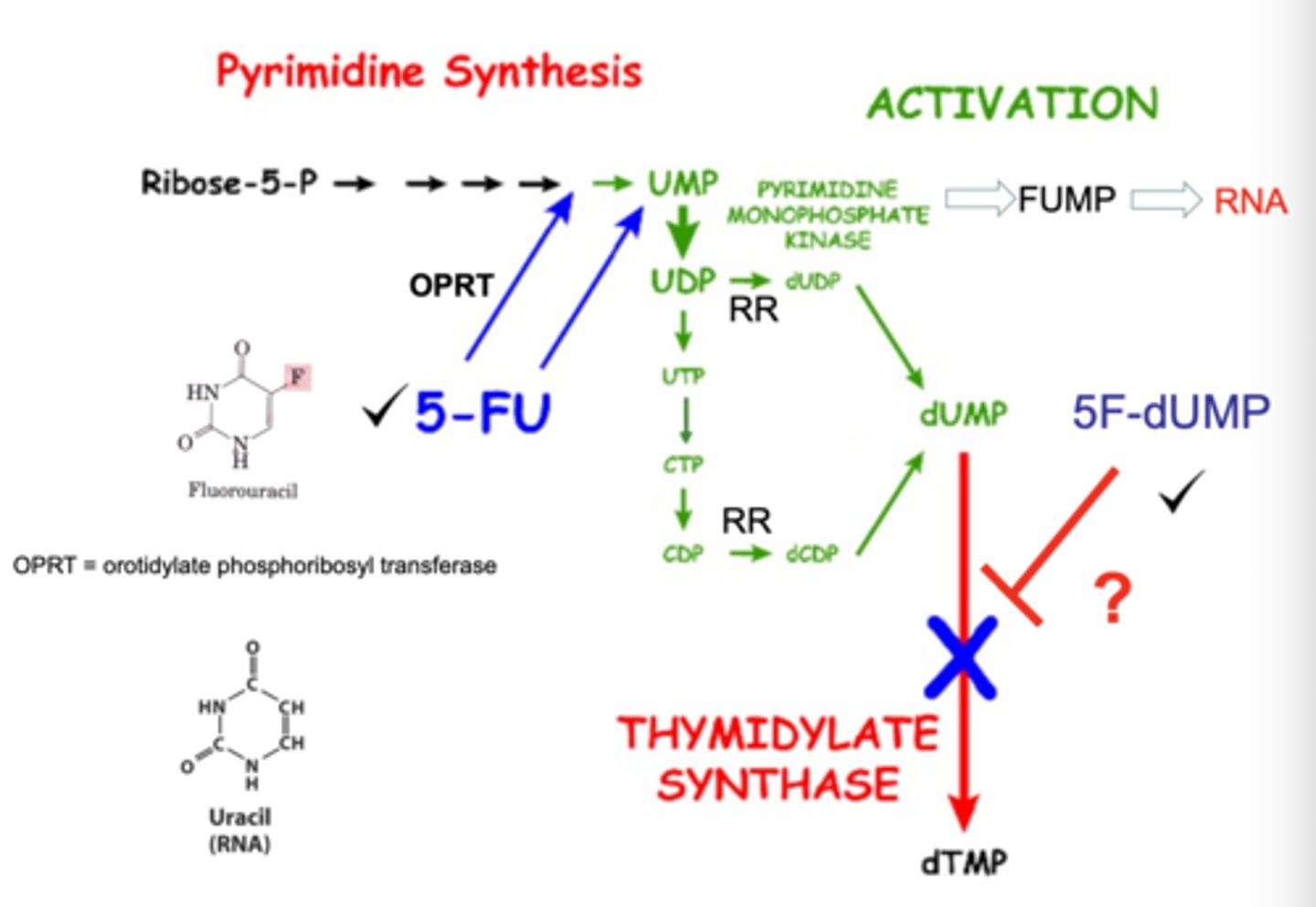
5-fluorouracil is __
thymidylate synthase
5FU (5F-uridine) inhibits ___
5-FU metabolism
the following is a photo of
false; multi-drug cocktails are used to treat cancer
true or false: only one drug at a time is used to treat cancer
apoptosis and DNA repair
two common results from DNA damage are
therapeutic index greater than 1
what therapeutic index value for a drug is best for killing cancer cells?
INCREASED DNA REPAIR, decreased drug uptake, increased drug export, increased drug detoxification, reduced activation of pro-drug
what are some chemoresistance mechanisms (DNA repair)
(the first one being the most important to remember)
DNA
this photo shows common damaging agents of ___

linear energy transfer
x-rays have low ___ that may cause ionizing radiation DNA damage
FALSE - a non-damaged chromosome CAN be used to repairs its double strand DNA damaged homologous chromosome
true or false: a non-damaged chromosome cannot be used to repairs its double strand DNA damaged homologous chromosome
BRCA 1 or BRCA 2
inherited mutations in what genes give an increased risk of breast/ovarian cancer
single and double strand
ionizing radiation can cause ___ break repair
regulated DNA-dependent biochemical process that results in synthesis of RNA
transcription
regulated RNA-dependent biochemical process that results in the synthesis of amino acid sequences or polypeptides
translation
the synthesis of amino acid sequences or polypeptides
translation results in __
RNA synthesis done by rewriting information contained in DNA
Transcription is essentially
RNA polymerases
RNA synthesis is catalyzed by DNA dependent
initiation, elongation, termination
3 key steps in transcription
TRUE - there is no proofreading or repair
true or false: RNA polymerases do not edit DNA
FALSE - no primer required to start synthesis
true or false: there is a primer required to start synthesis of RNA
the gene promoter
the starting site of transcription Is controlled by ___
One - single RNA polymerase
bacteria have how many RNA polymerases
3 -
know RNA Polymerase II - mRNA, snRNA, miRNA
eukaryotes have how many RNA polymerases
located at 5' of and approximately 10 bases from the transcription start site (TSS)
Pribnow box
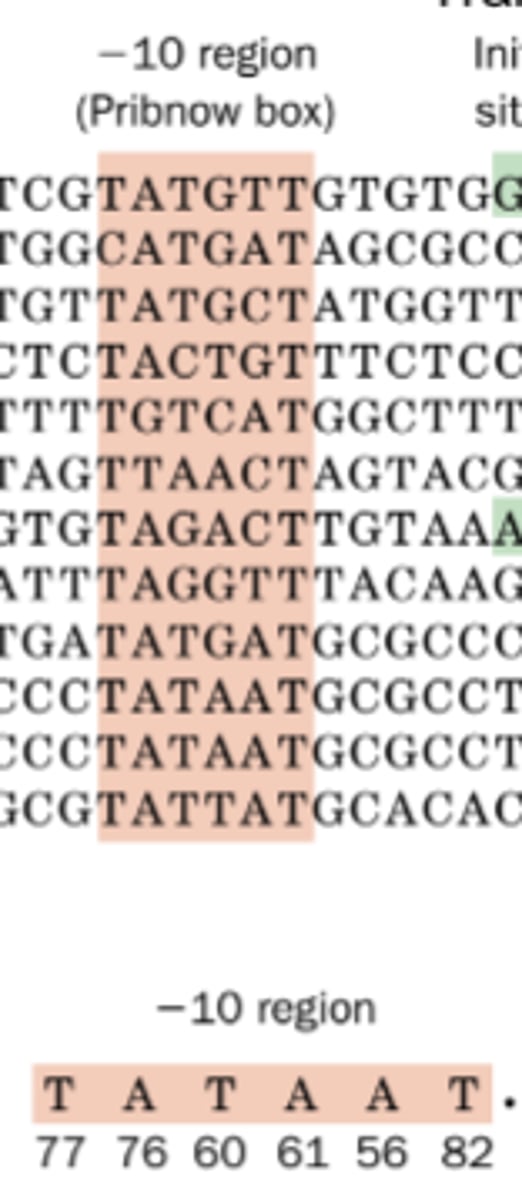

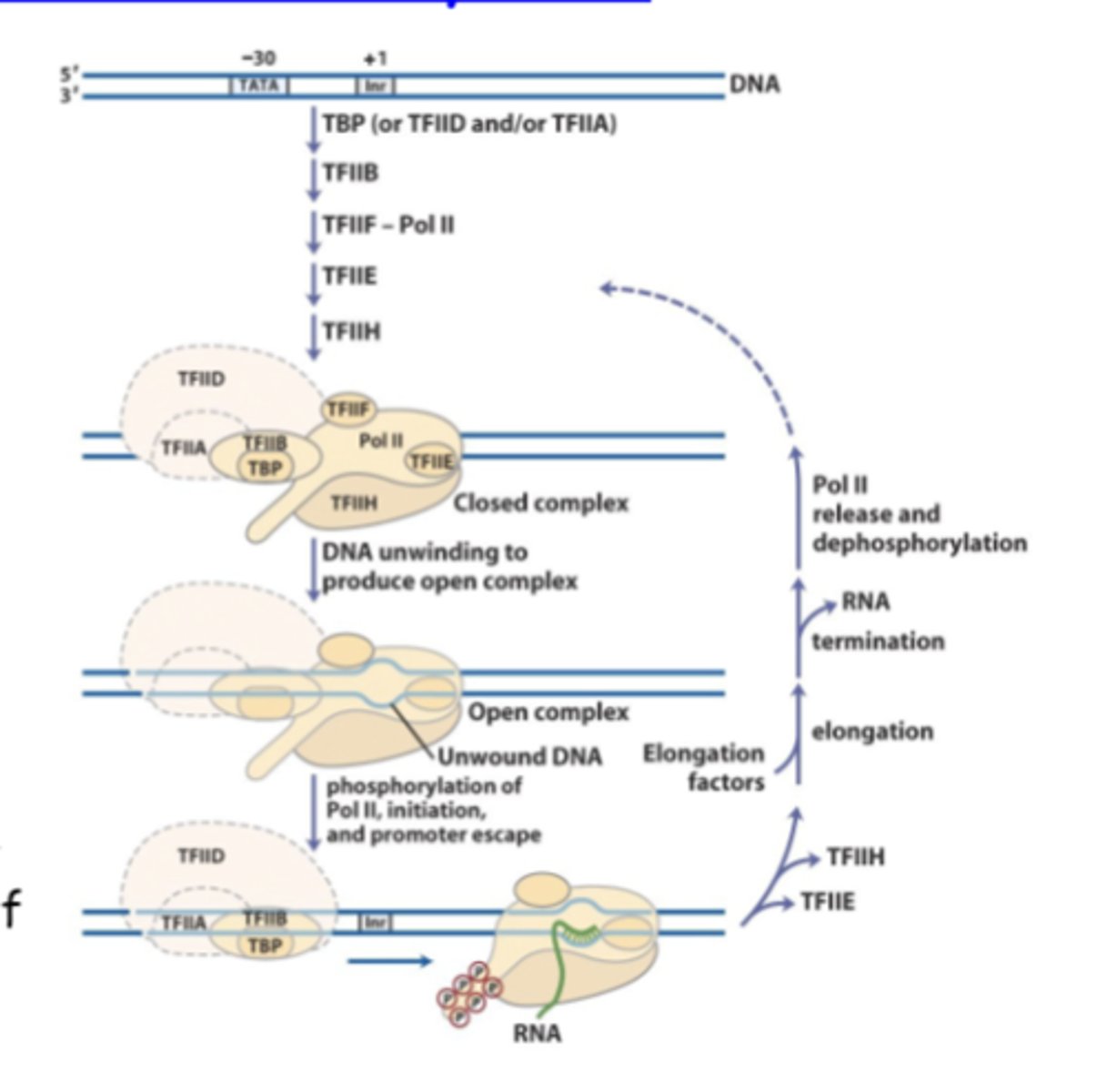
initiation
RNAP sigma factor has a major function in transcription ___
5' to 3'
RNA synthesis occurs in ___ direction
eukaryotic gene promoter
RNA pol II is a ___ of transcription
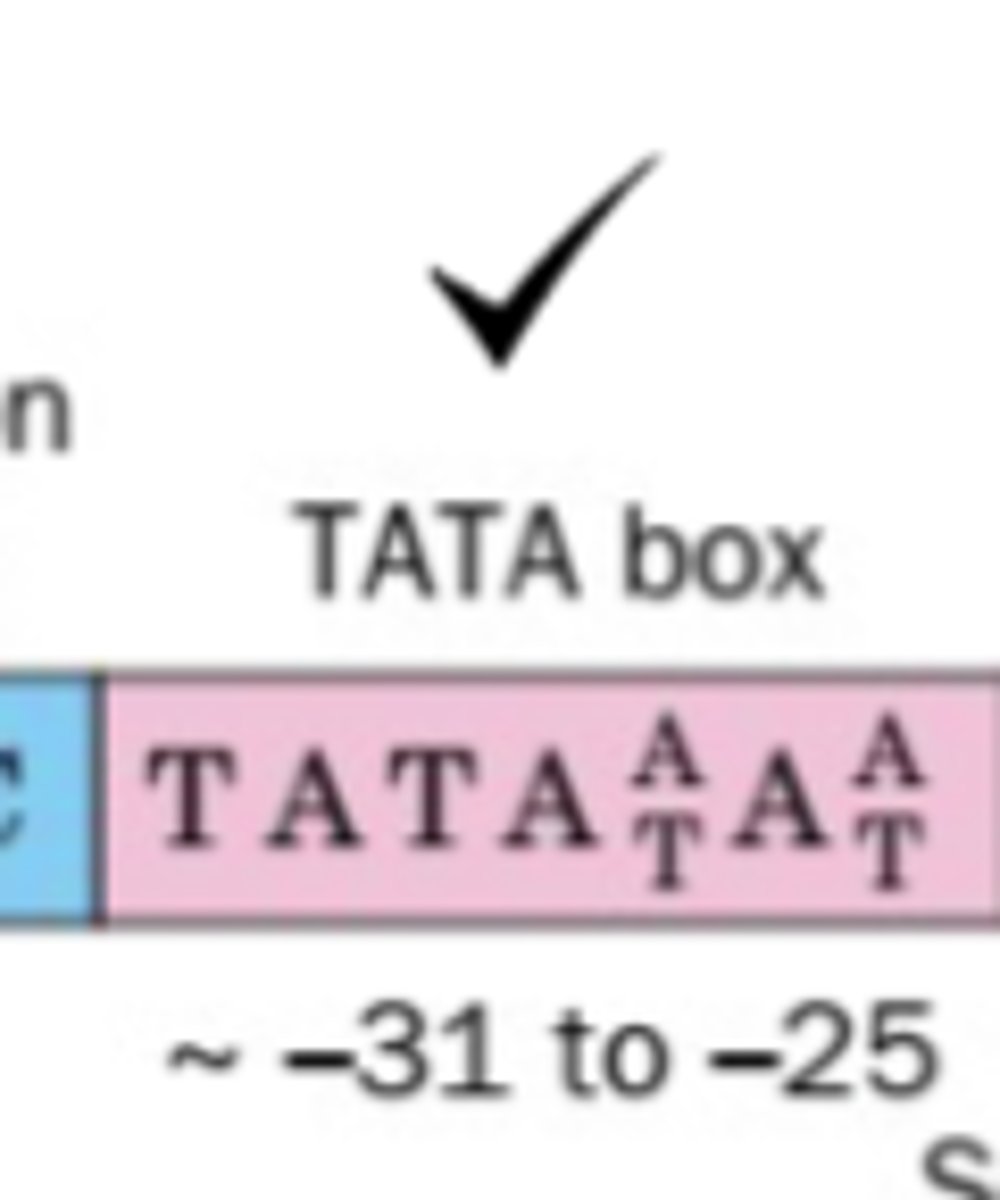
50 - 60%
what percent of genes gave an upstream TATA box element at -30 to -100
mRNAs
RNA poll II is required for synthesis of
basal transcription factors (common to all genes transcribed by pol II)
TATA-binding protein binds, followed by other proteins called ___
phosphorylated
Once transcription complex is assembled, RNAP II is ____, beginning elongation
removing introns and joining exons to make mature mRNA
Define RNA splicing
site-specific cleavage and ligation
spliceosome accomplishes
snRNAs
spliceosomes contain
1-cleavage by endonuclease 2- addition of polyA by polyadenylate polymerase
polyA is added at consensus sequence in 2 steps:
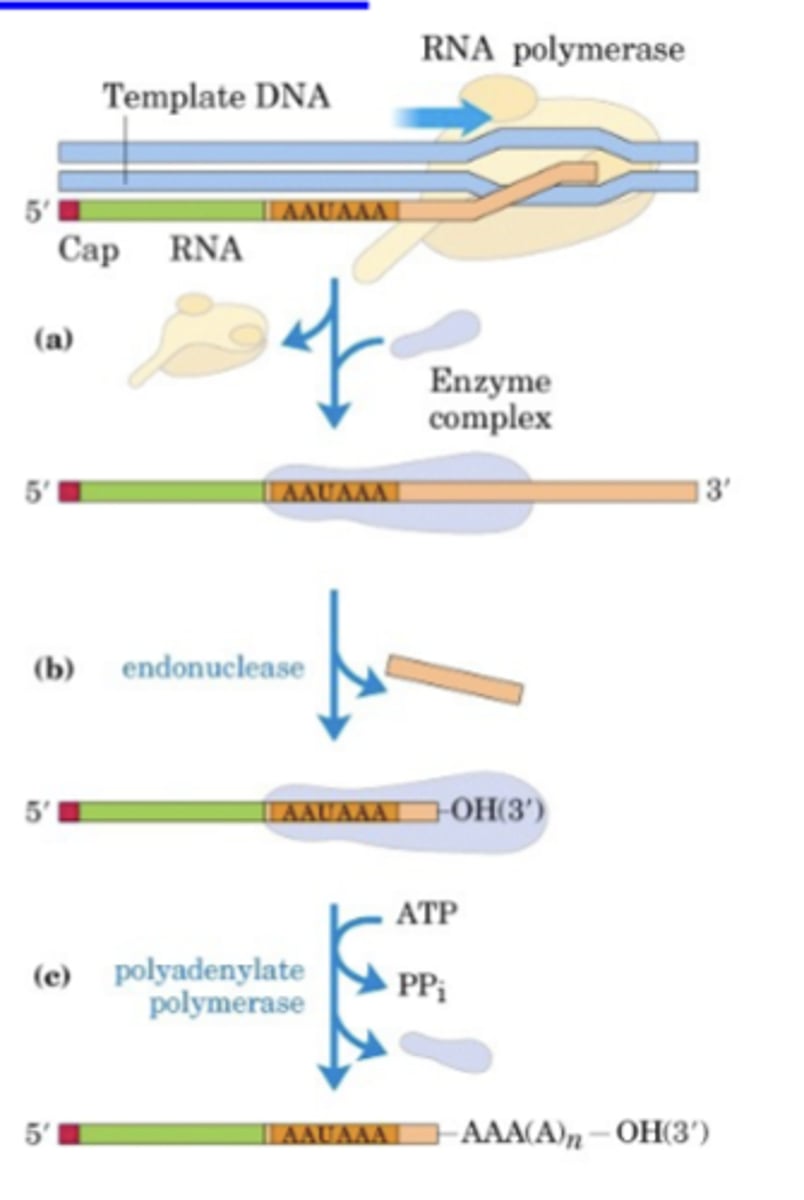
AAUAAA
consensus sequence
immediately proximal to RNA transcription start site
gene promoter
increased diversity in proteins produced
alternative splicing allows for
translate information stored in DNA into proteins
the genetic code is used to
evolutionarily conserved
the genetic code is ___
genes that perform certain functions in lower animals have been maintained even in the human DNA script, though sometimes the genes have been modified for more complex functions.
what does "evolutionarily conserved" mean
3
each mRNA has how many potential reading frames
a different protein
each mRNA reading frame produces
always methionine
first amino acid in open reading frame (ORF) is
linearly; N; C
polypeptide chains are assembled ___ from ___ terminus to ___ terminus
multiple codons result in addition of the same amino acid --> a single tRA must be capable of recognizing multiple codons
what does it mean that the genetic code is degenerate
anticodon
tRNAs base pair with mRNA using a
32
how many tRNAs are there
recognize more than one codon in mRNA
because there are only 32 anticodons and 61 codons, tRNA anticodons must
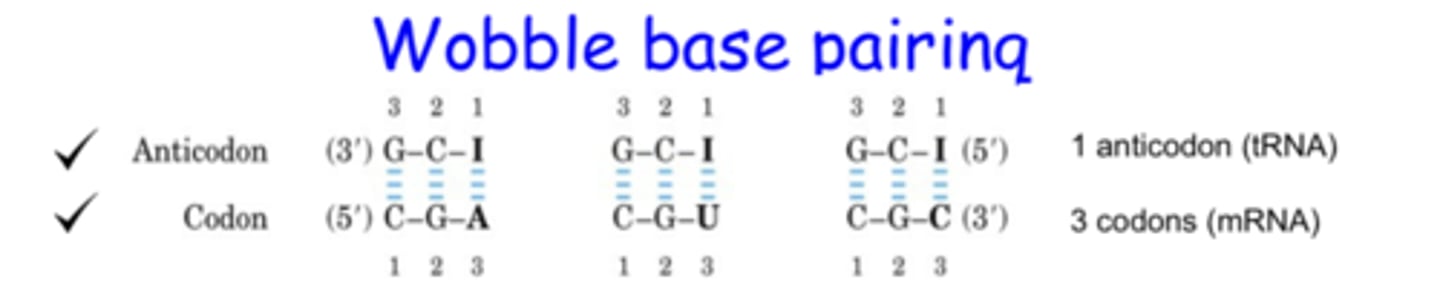
wobble base pairing in 3rd position of the codon
why is it possible for anticodons to recognize more than one codon
1-activation of amino acids
2-initiation
3-elongation
4-termination
5-folding and processing of protein
5 steps of translation protein synthesis
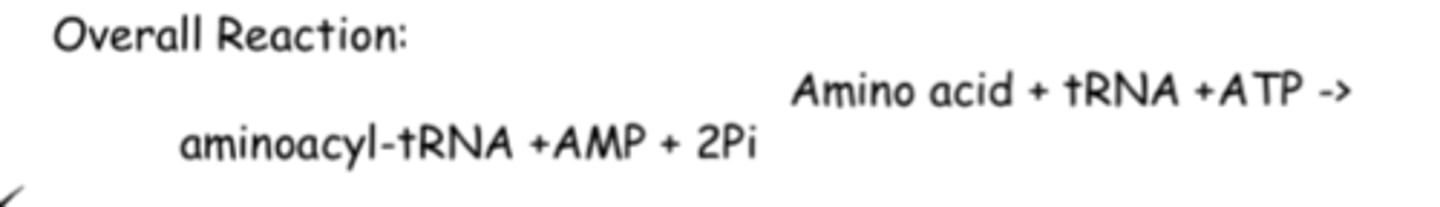
aminoacyl tRNA synthetase.
this reaction is catalyzed by
1-position next tRNA
2-form peptide bond between amino acids
3-translocate ribosome
3 steps of elongation
end of polypeptide synthesis and release of new synthesized protein
termination
FALSE - protein synthesis on ribosomes is similar
(small differences exist and are important in use of antibiotics)
true or false: the process of protein synthesis on ribosomes is different between prokaryotes and eukaryotes
upstream of AUG, initiates translation by aligning codon over the P site
shine-dalgarno sequence