Complement System
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
the complement system is made up of how many distinct proteins?
more than 40
the complement system is activated at sites of …?
infection
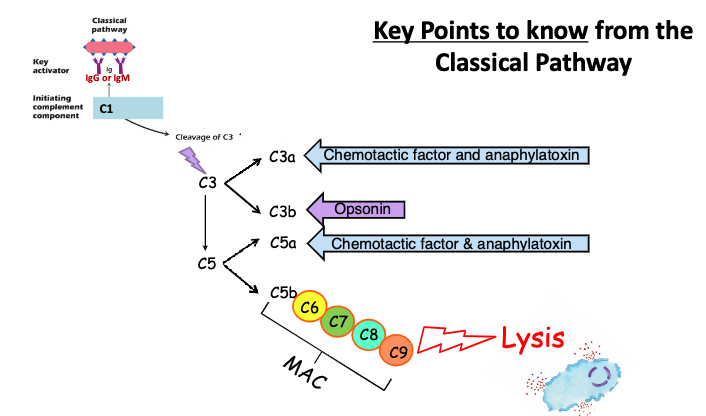
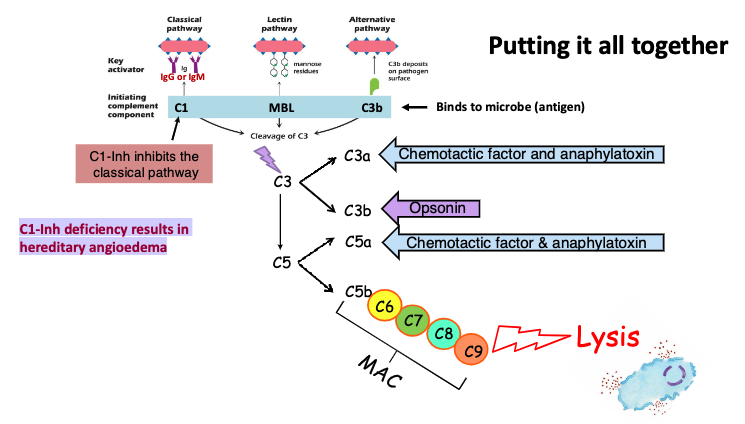
complement system induces a series of inflammatory responses that help to fight infection. the different series of responses are…?
opsonization (C3b)
Chemotaxis (C3a & C5a)
Mast cell activation (C3a & C5a)
Cell lysis (C5b - C9)
complement proteins are always present where?
blood and tissue fluids
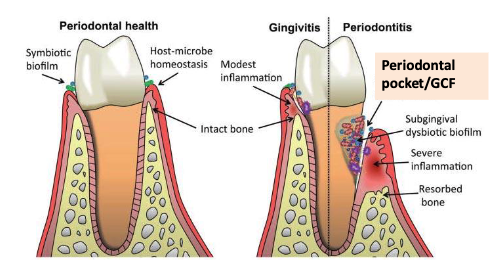
where might we find high concentrations of complement fragments?
Gingival crevicular fluid (GCF) from patients with periodontitis
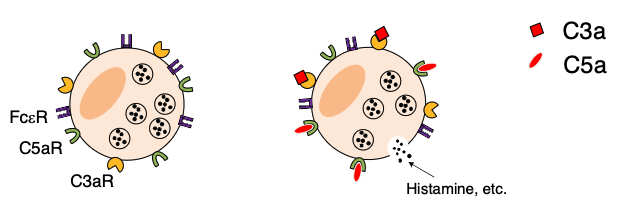
what are C3a and C5a?
Chemotactic factors and anaphylatoxins (mast cell degranulation)
C3a and C5a are chemotactic factors that recruit neutrophils to the site of complement activation (infection). They are also anaphylatoxins because they activate mast cells to release histamine and other inflammatory agents
what is C3b?
opsonin
C3b binds to antigen (pathogen) and is recognized by phagocytes (neutrophils and macrophages)
what does the membrane attack complex (C5b-C6-C7-C8-C9 complex) do?
punches holes (aka form pores) in membrane (for example, bacterial membranes) → lysis
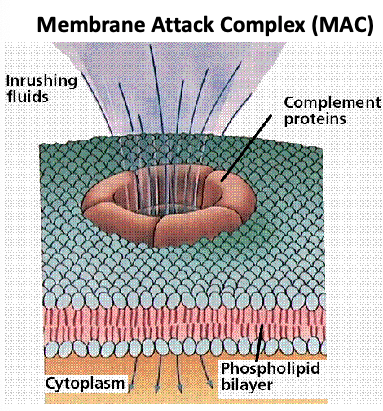
The activation of complement results in…?
biologically active protein fragments C3a, C5a and C3b and formation of the MAC
the classical complement pathway requires which antibodies?
IgG or IgM (part of adaptive immunity)
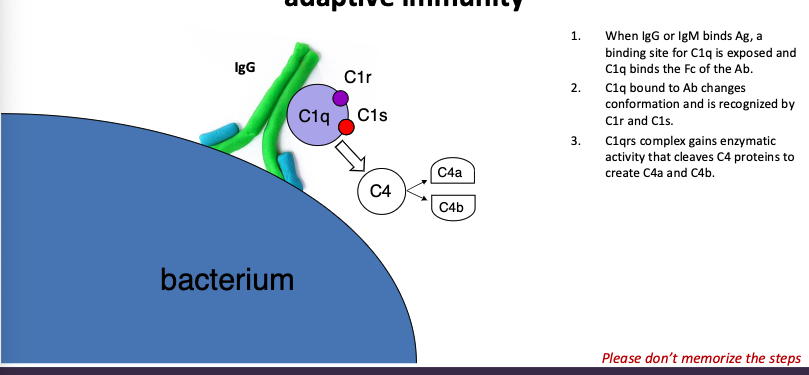
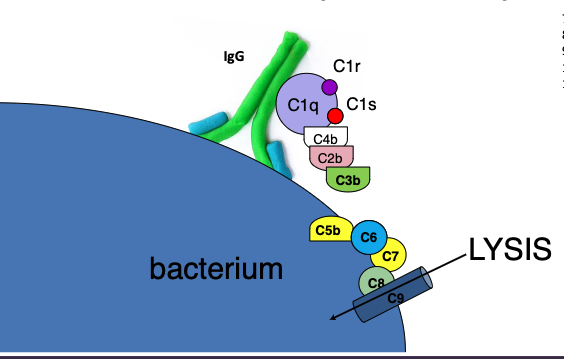
walk through the classical pathway
When IgG or IgM binds Ag, a binding site for C1q is exposed and C1q binds the Fc of the Ab.
C1q bound to Ab changes conformation and is recognized by C1r and C1s.
C1qrs complex gains enzymatic activity that cleaves C4 proteins to create C4a and C4b.
C4b binds C1qrs, resulting in enzymatic activity that cleaves C2 molecules, forming C2a and C2b.
C2b binds C1qrs4b, resulting in enzymatic activity that cleaves C3 molecules, forming C3a and C3b
C3b binds C1qrs4b2b, resulting in enzymatic activity that cleaves C5 molecules, forming C5a and
C5bC5b molecules bind to the antigen
C6 binds to C5b\C7 binds to C6
C8 binds to C7
C9 binds to 8
what are the key points to know from the classical pathway
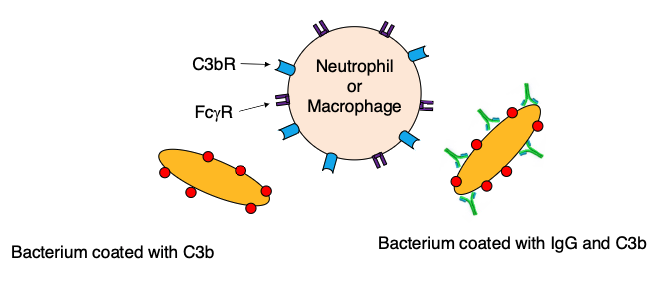
what can opsonization be mediated by?
IgG and/or C3b
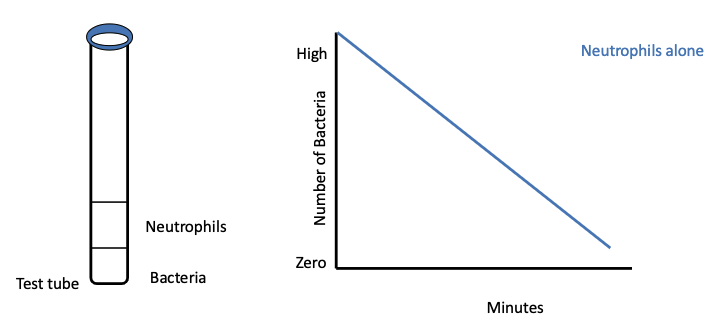
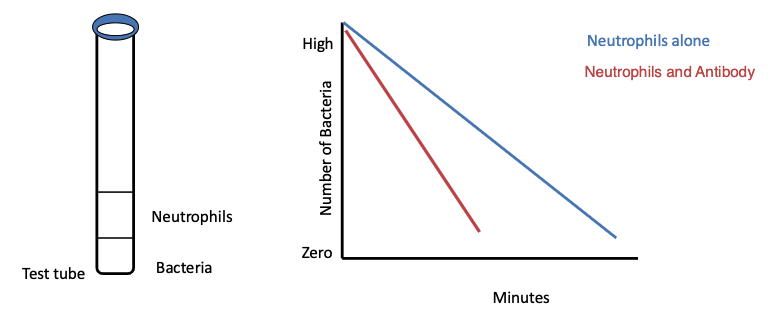
describe the phagocytic activity of neutrophils alone
slow (ingest organisms slowly)
describe the phagocytic activity of neutrophils with antibody
Phagocytosis is markedly increased
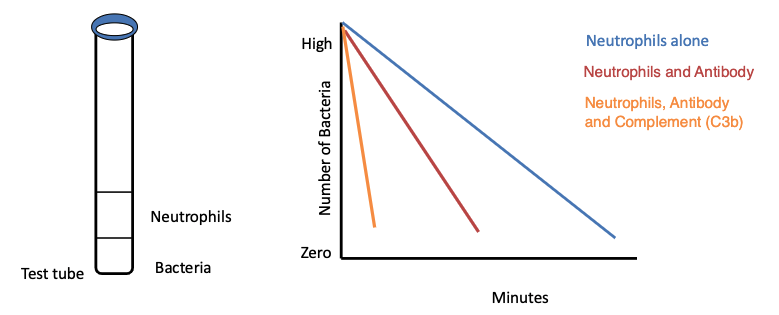
describe the phagocytic activity of neutrophils with antibody AND complement
Phagocytosis is extremely efficient and 90% of organisms are
phagocytosed in 10 minutes
what are chemotactic factors that recruit neutrophils to the site of infection?
C3a and C5a
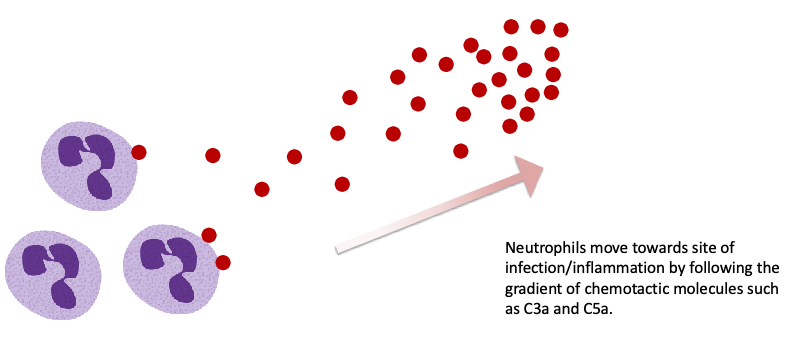
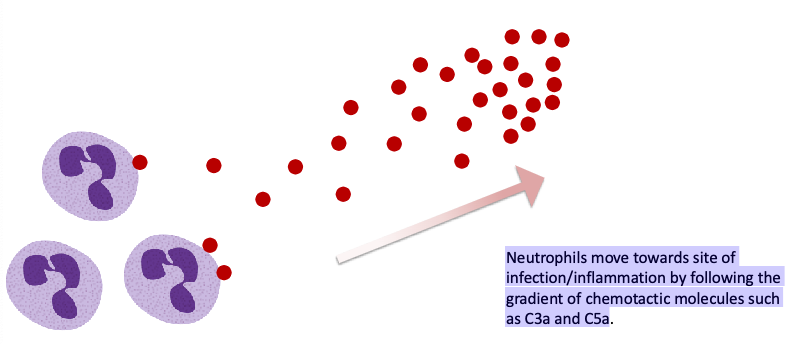
Neutrophils move towards site of infection/inflammation by following the…?
gradient of chemotactic molecules such as C3a and C5a
what are also anaphylatoxins because they activate mast cells and basophiles to release histamine and other inflammatory agents?
C3a and C5a
why are C3a and C5a are also considered anaphylatoxins?
because they activate mast cells and basophiles to release histamine and other inflammatory agents
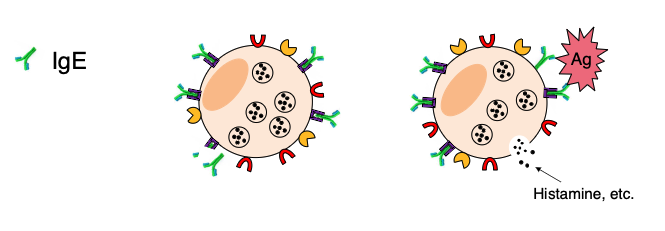
This IgE mechanism is important in
parasite immunity and allergy.
what are 2 pathways for mast cell degranulation?
IgE binds to the Fcε-receptors of mast cells and basophils. When IgE is crosslinked, the cells degranulate (antigen specific)
C3a and C5a are also anaphylatoxins because they activate mast cells and basophiles to release histamine and other inflammatory agents
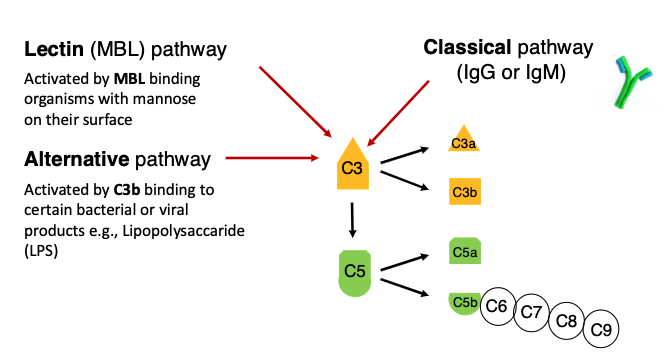
what 3 pathways can activate complement?
lectin (MBL) pathway)
alternative pathway (C3b)
classical pathway
what is the lectin (MBL) pathway activated by?
Activated by MBL binding organisms with mannose on their surface
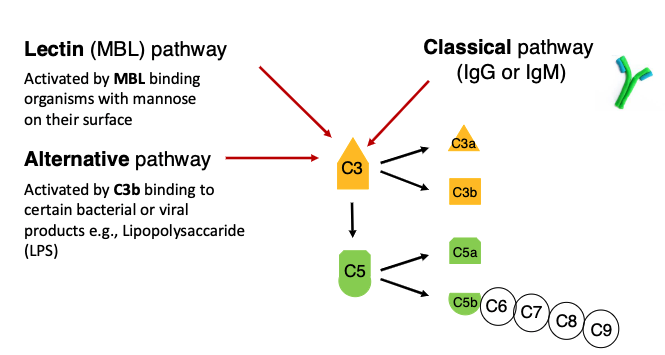
what is the alternative pathway activated by?
Activated by C3b binding to certain bacterial or viral products e.g., Lipopolysaccaride (LPS)
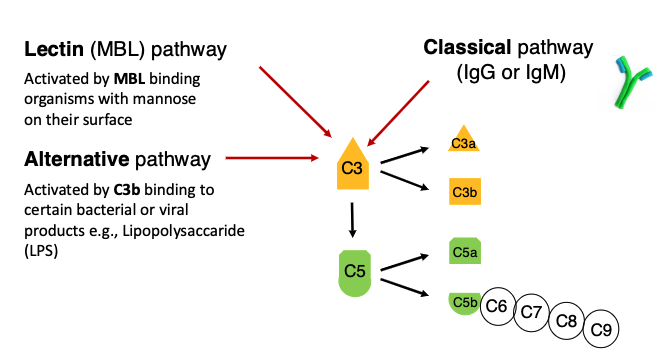
what is the classical pathway activated by?
IgG or IgM
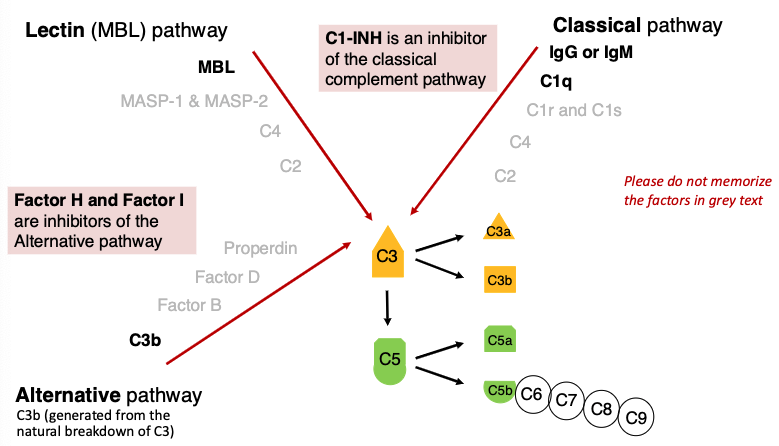
what is an inhibitor of the classical complement pathway?
C1-INH
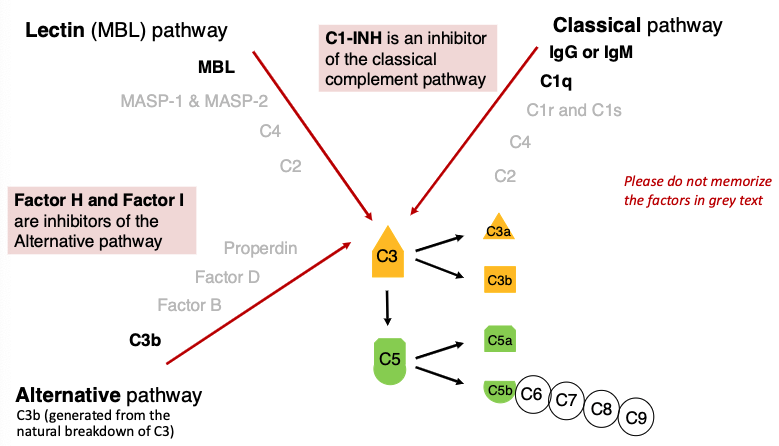
what are inhibitors of the Alternative pathway?
Factor H and Factor I
C1-Inh deficiency results in…?
hereditary angioedema
WHICH OF THE THREE COMPLEMENT PATHWAYS REQUIRES ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY?
classical pathway (lectin and alternative are part of innate)
WHICH WOULD YOU EXPECT TO BE MORE SEVERE:
A - C3 DEFICIENCY
B – C5 DEFICIENCY
A - C3 DEFICIENCY
Absence of C3 would lead to…?
Severe recurrent bacterial infections
Absence of C5 would lead to…?
Recurrent bacterial infections
Absence of C6, C7 or C8 would lead to…?
Overwhelming Neisserial infections (N.meningitidis and N.gonorrhea
Absence of alternative pathway components would lead to…?
recurrent bacterial infections
Absence of Lectin pathway proteins- would lead to…?
infection in childhood
what is Hereditary angioedema (HAE)?
rare autosomal dominant genetic disorder resulting from an inherited deficiency or dysfunction of C1-INH (C1 inhibitor)
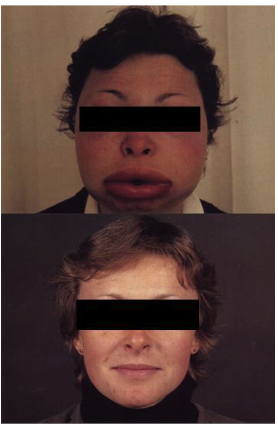
what is Hereditary angioedema (HAE) characterized by?
recurrent episodes of angioedema, which most often affect the
skin and mucosal tissues of the upper respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts
Although the swelling is self-limited, laryngeal involvement may cause fatal
asphyxiation.
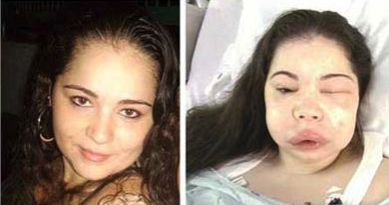
Hereditary angioedema (HAE) can be triggered by?
trauma, including dental procedures
what should be given to patients with C1-INH deficiency prior
to dental procedures?
C1-INH