Unit 3: Ancient Greek Astronomy
1/184
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
185 Terms
What was Ancient Greece’s time period?
3000 B.C.E. ↔ 300 C.E.
What happened at around 3000 B.C.E?
Greeks arrived at Aegean Peninsula
What happened at around 750 B.C.E?
started recorded history
founded Rome
wrote alphabet
What time period was set in between 750 B.C.E. & 480 B.C.E?
Archaic Period
What characterized the time period set in between 750 B.C.E. & 480 B.C.E?
city states loosely united & expanded to new territories
What time period was set in between 480 B.C.E. & 323 B.C.E?
Classical Period
What characterized the time period set in between 480 B.C.E. & 323 B.C.E?
Macedonia dominated
Alexander the Great expanded to Egypt & Babylon
What time period was set in between 323 B.C.E. & 156 B.C.E?
Hellenistic Period
What characterized the time period set in between 323 B.C.E. & 156 B.C.E?
culture expanded to Middle East & Egypt
What time period was set in between 156 B.C.E. & 30 B.C.E?
Greco-Roman Period
What characterized the time period set in between 156 B.C.E. & 30 B.C.E?
Greek empire joined Roman Republic
last Egyptian Greek ruler Cleopatra VVI died
True or False: Ancient Greece is the 1st documented group taking astronomy beyond tracking time & astrology & religion.
True.
What were some possible reasons for Greeks taking astronomy beyond tracking time & astrology & religion?
fragmented geography
decentralized rule
established first higher education
What are the word origins of “academy?”
1st school location
just outside Athens
What is the identity of the 1st school’s creator?
Plato
What philosopher group originated in 600 B.C.E?
Ionian
What philosopher group originated in 500 B.C.E?
Pythagorean
What are some examples of geocentrists?
Plato
Eudoxus
Aristotle
Appollonius
Hipparchus
Ptolemy
What are some examples of heliocentrists?
Philolaus
Herakleides
Aristarchus
What were the featured Ionian philosophers’ birthplace?
Miletus, Ionia
Which featured Ionian philosopher taught the other Ionian philosopher?
Thales taught Anaximander
What was Thales’ birth date?
625 B.C.E.
What method did Thales use to learn about science?
travel
Middle East
Egypt
What did Thales recognize about Greek & Egyptian / Babylonian explanations?
explained phenomena with different god & mood
sought explanation beyond god
What did Greeks associate with earthquakes?
angry Poseidon
What did Egyptians associate with earthquakes?
laughing Geb
What did Thales associate with earthquakes?
Earth floated on water
What was the reason for Thales’ association with earthquakes?
large wave moved ground
What was Thales’ method for gaining popularity?
demonstrating natural events’ predictability
What was the start date of the Medes & Lydians war?
600 B.C.E.
What ended the Medes & Lydians war on 585 B.C.E?
eclipse
What did Thales say to both army generals?
solar eclipse’s going to occur
What did Greeks associate with solar eclipses?
Zeus randomly blocked sun
What was the identity of the observer that wrote the legend on 585 B.C.E?
Herodotus
What was Anaximander’s birth date?
610 B.C.E.
What is the identity of the 1st cosmologist?
Anaximander
What does “cosmology” mean?
universe study explaining origin & method by creating model organizing known universe & motion pattern
What was Anaximander’s cosmology?
wheels around cylinder Earth
What did Anaximander believe about Earth’s absolute position?
finite ground
floating in space
True or False: Anaximander explained the reason for Earth’s absolute position.
False: Anaximander did not explain why Earth was floating in space.
What astronomical concepts did Anaximander’s cosmology explain?
day cycle
moon cycle
eclipse cycle
season cycle
What revolution did Anaximander have about the thought process?
model could be proposed & tested
What was the identity of Pythagoras’ teacher?
Anaximander
What date was Pythagoras being taught by his teacher?
550 B.C.E.
What is Pythagoras’ birth date?
570 B.C.E.
What is Pythagoras’ birthplace?
Samos
What did Pythagoras’ followers believe?
math cult
understand science = understand god
What were some examples of Pythagorean rules?
communal
vegetarian
specific on science
men = women
What was the reason for Pythagoras’ leadership?
only one hearing celestial music
What comprises the Pythagoras & Blacksmith legend?
walked past blacksmith forge & wondered why some sounds were harmonious / unharmonious
method: measured dimensions
result: bar length determined sound, musical pitch followed natural law so universe followed natural law
if 2 bar lengths were simple ratio, harmonious
if 2 bar lengths were not simple ratio, unharmonious
What did “cosmos” mean to Pythagoras?
universe follows equation laws
What is the word origin of “cosmos?”
order
Greek
What Pythagorean legend connected music and celestial motion?
music equation = celestial motion equation
What beliefs did Pythagoreans have about perfection?
celestial bodies move in perfect circles
Earth = sphere
What reason did Pythagoreans have to choose a perfect shape?
simplest & purest geometric shape
What evidence did Pythagoreans have for a round Earth?
horizon disappearance
lunar eclipse
star shift
What is the reason that horizon disappearance is Pythagorean evidence?
if flat Earth, decrease size then fall off of edge / fade to 1 point
v.s.
if round Earth, disappear bottom-first
on curved surface, top remains visible as object goes over horizon
What is the reason that a lunar eclipse is Pythagorean evidence?
Earth’s round shadow on Moon
What is the reason that a star shift is Pythagorean evidence?
if flat Earth, specific rate based on walk speed
v.s.
if round Earth, different rate based on walk speed
constellation shift = travel distance
True or False: It is a misconception that European colonizers in the 1500s were worried that they would fall off of the edge of Earth.
True.
What was the Pythagorean persecution time period?
500 B.C.E. ↔ 400 B.C.E.
Which philosopher group followed Anaximander?
eliocentrism
What is the identity of the 1st person to suggest Earth moves through space?
Philolaus
What does Philolaus suggest Earth orbits, and at what frequency?
Central Fire 1x a day
True or False: Greece faced the celestial body that Earth orbited.
False: Greece faced away from the Central Fire.
What did Aristotle claim about the celestial body in between the Central Fire & Earth?
added to bring celestial body number to 10
What was Philolaus’ cosmology?
Central Fire → Counter-Earth & Earth orbit Central Fire once a day → Sun orbits Central Fire once a year → fixed stars
[image]
What did Herakleides change about Herakleides’ cosmology?
rid Central Fire
other side of Earth did not see Central Fire
rid Counter-Earth
put Mercury & Venus in orbit around Sun
What was Herakleides’ reason for orbiting celestial bodies around the Sun?
Mercury & Venus make nearer loop to rising / setting sun → motion & brightness
What was Aristarchus’ birth date?
310 B.C.E.
What was Aristarchus’ birthplace?
Samos
What are Aristarchus’ famous texts?
“On the sizes & distances of the Sun & Moon”
heliocentric universe
What text gained Aristarchus fame?
“On the sizes & distances of the Sun & Moon”
True or False: Aristarchus’ results were incorrect but his methods were correct.
True.
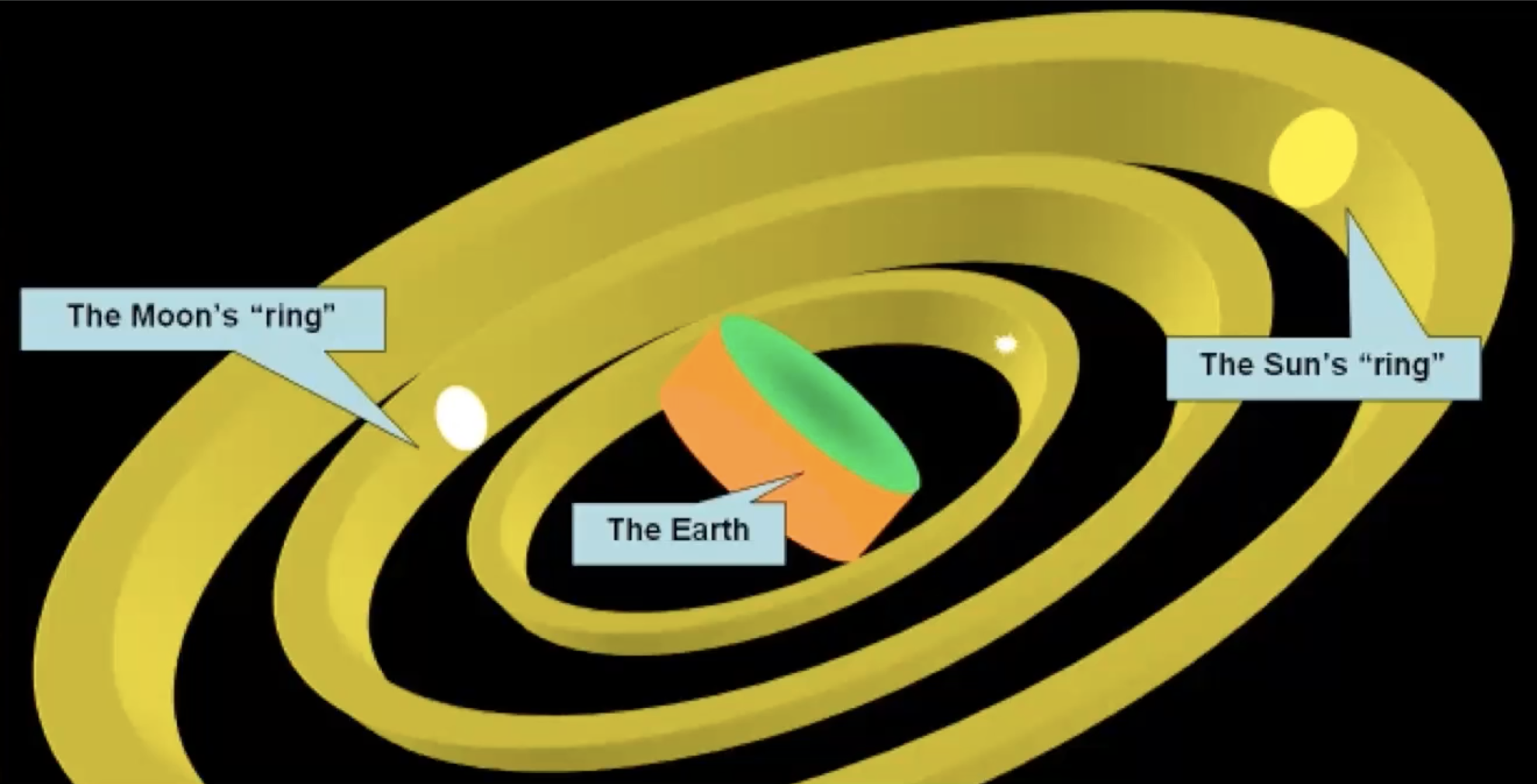
What did Aristarchus do with a lunar eclipse?
monitored Earth’s shadow size on Moon
What did Aristarchus determine with a lunar eclipse?
Moon size < Earth size
What was the Moon’s size relative to Earth, according to Aristarchus?
1/2 of Earth
What is the Moon’s size relative to Earth?
1/4 of Earth
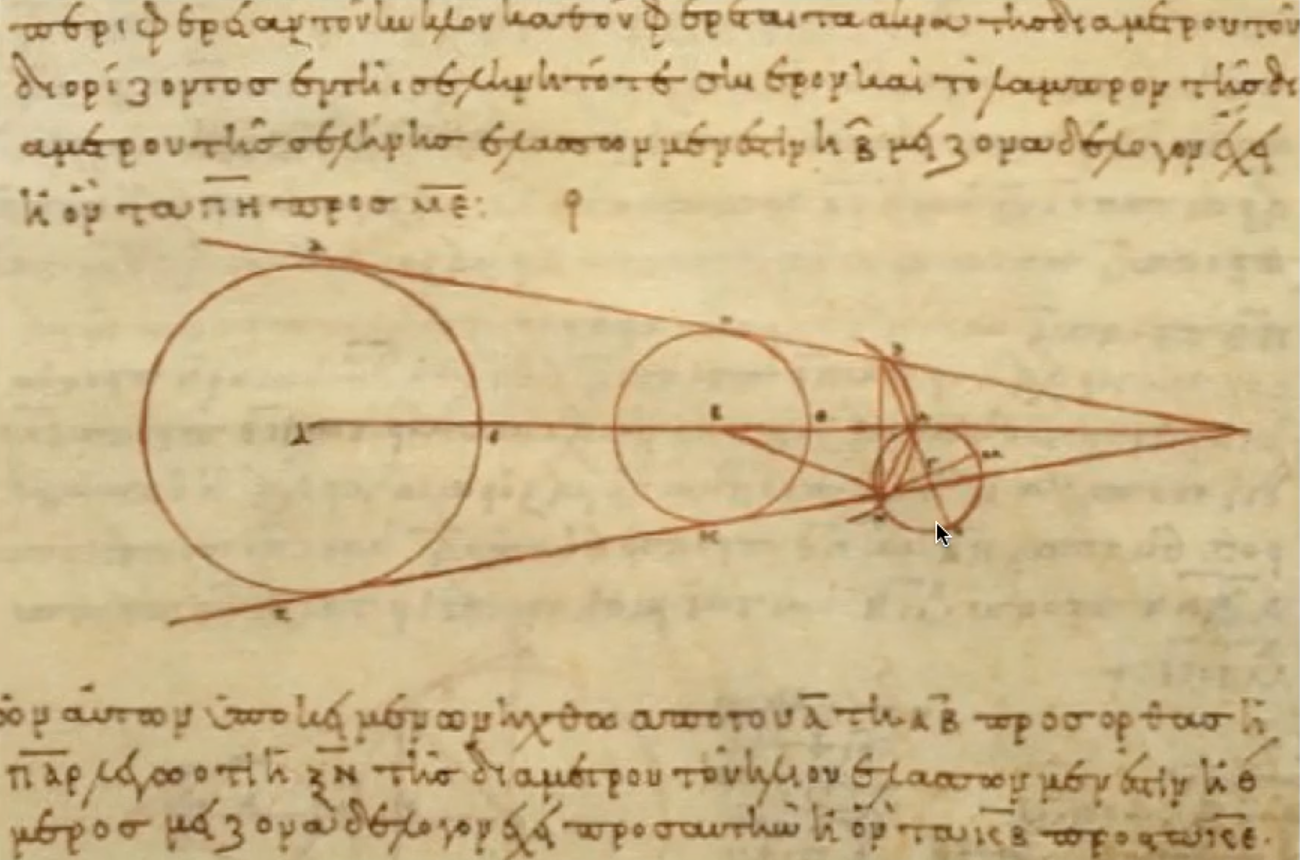
What did Aristarchus do with Sun’s distance compared to the Moon?
waited for 3rd quarter moon phase
because Sun’s in lit direction
solved right triangle
measured ∠A (Sun ↔ Moon angle) using quadrant
used Pythagorean theorem
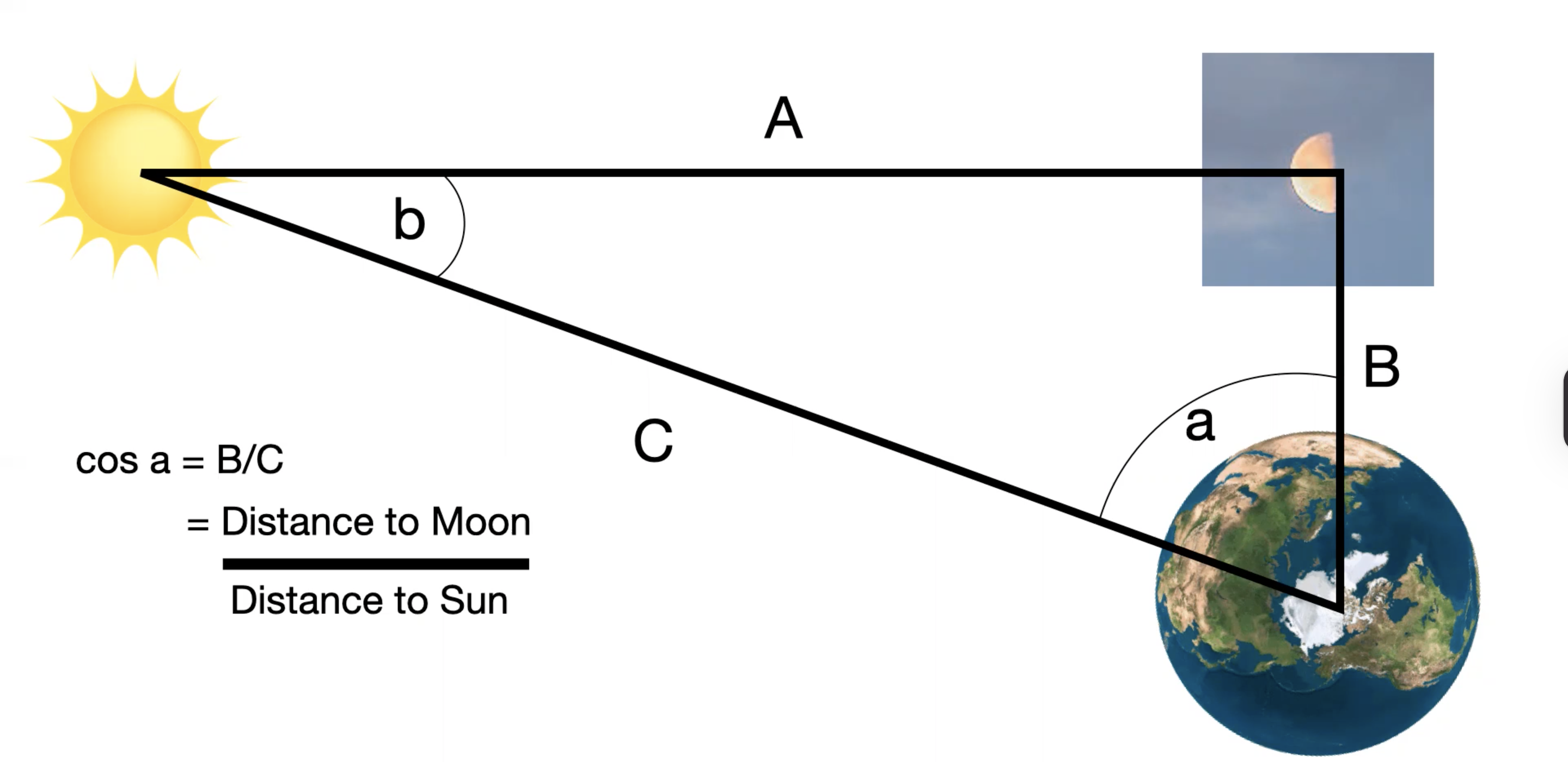
What did Aristarchus determine with Sun’s distance compared to the Moon?
Sun’s farther than Moon
What was Earth’s angle in between the Sun & Moon, according to Aristarchus?
87°
What is Earth’s angle in between the Sun & Moon?
89.9°
What was the Moon’s distance from Earth relative to the Sun, according to Aristarchus?
1/19 of Sun’s distance
What is the Moon’s distance from Earth relative to the Sun?
1/382 of Sun’s distance
True or False: Aristarchus determined the Moon’s & the Sun’s distances.
False: Aristarchus did not determine the Moon’s or the Sun’s distances.
What was Earth’s size relative to the Sun, according to Aristarchus?
1/10 of Sun
What is Earth’s size relative to the Sun, according to Aristarchus?
1/100 of Sun
What method did Aristarchus to determine Sun’s size relative to Earth?
Sun > Moon
Moon < Earth
Sun & Moon have similar apparent size
so
Sun > Earth
What happened to Aristarchus’ 2nd famous text?
lost but spoken / written about for centuries
What question does Aristarchus’ 2nd famous text answer?
“Is Earth at centre if Sun is the largest celestial body?”
What answer does Aristarchus’ 2nd famous text have for the question it asks?
no
Moon orbits Earth
only celestial body that doesn’t have weird pattern
What date did the heliocentric track end?
100 B.C.E.
What was the reason for the heliocentric track end?
Aristarchus wasn’t interested in followers