CH4: The pieces of the body puzzle
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
parts of the skull/calvaria
frontal
parietal (2)
sphenoid
temporal
occipital
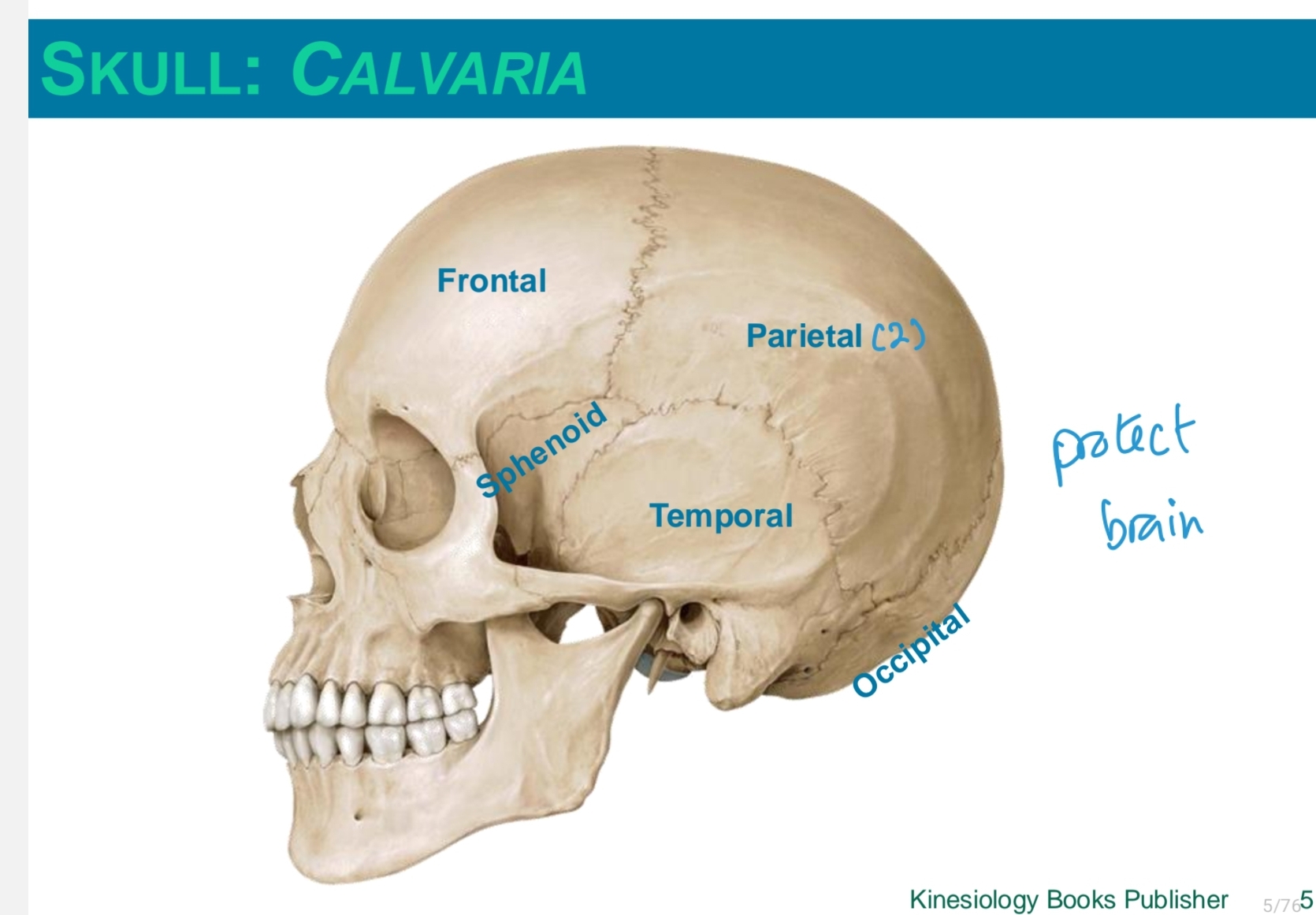
skull: facial bones
lacrimal
nasal
zygomatic
maxilla
mandible
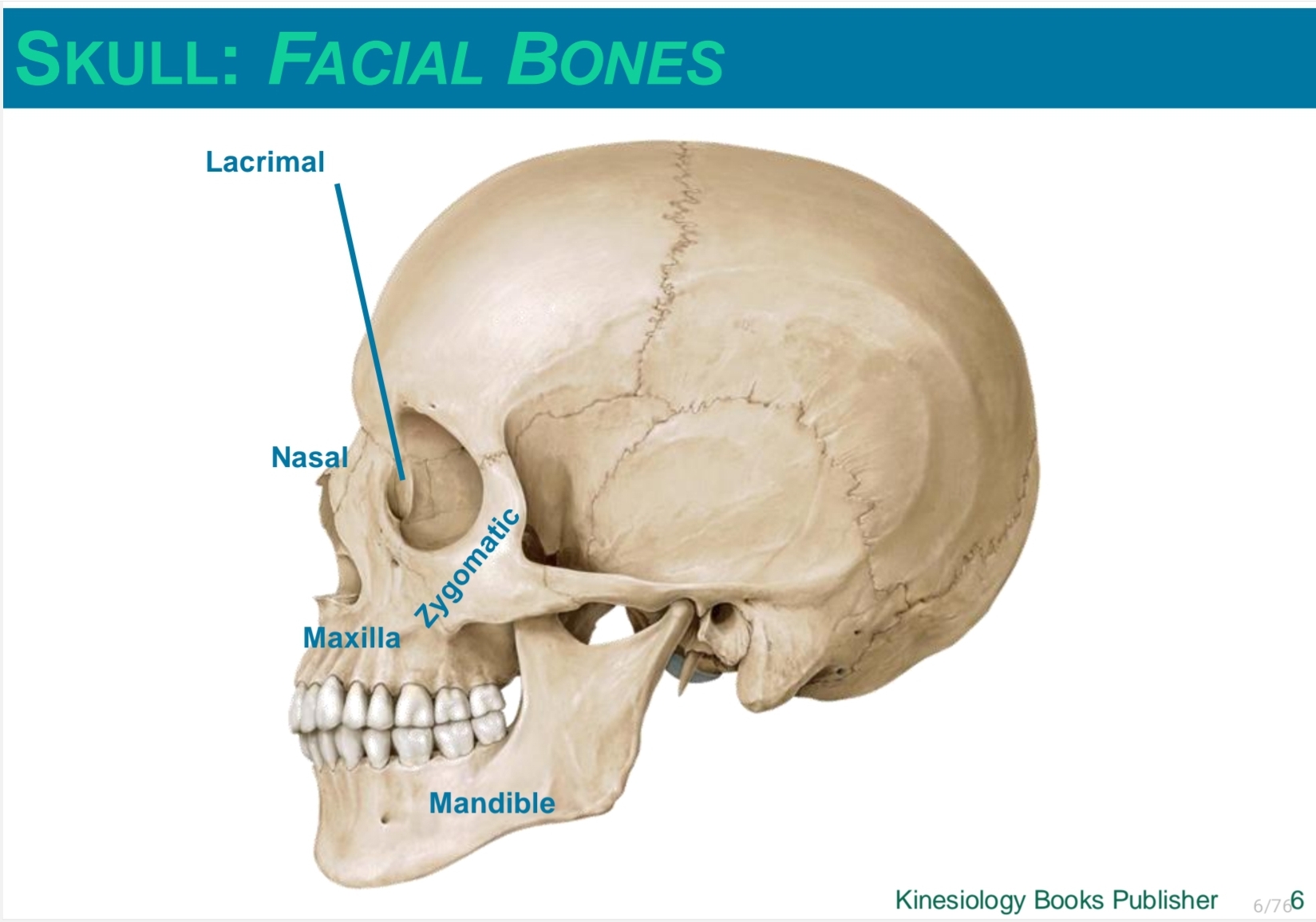
facial muscles
Orbicularis oculi
Orbicularis oris
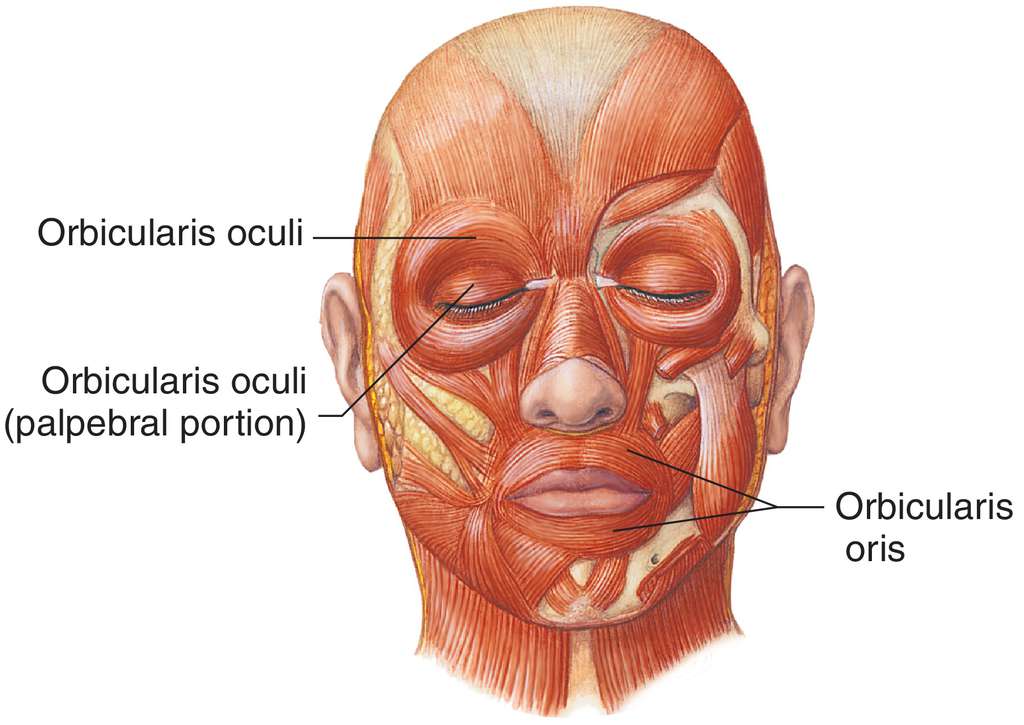
vertebral column
7 cervical vertebrae (neck)
12 thoracic vertebrae (chest)
5 lumber vertebrae (lower back)
1 sacrum = 5 fused vertebrae (midline region of buttocks)
1 coccyx = 3 or 4 fused vertebrae (tail bone)
how many pairs of ribs are in the body?
and what are their categories?
12 pairs of ribs
1 to 7; true ribs
8 to 10 false ribs
11 and 12 floating ribs
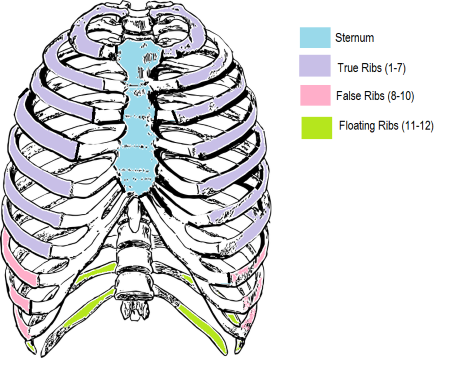
true ribs
1 to 7
they directly attach to the sternum
false ribs
8 to 10
their cartilage does not connect to the sternum directly
floating ribs
11 to 12
do not attach to the sternum and have no cartilage
costal cartilage
cartilage on the ribs that give them more expansion
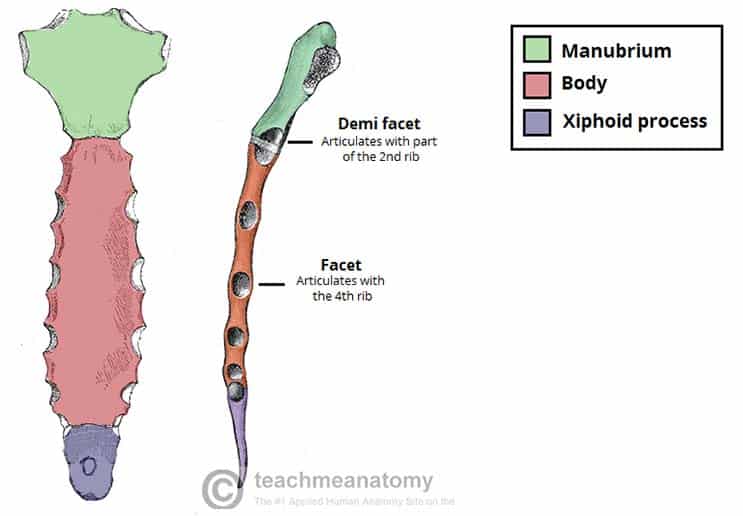
manubrium
top part of the sternum
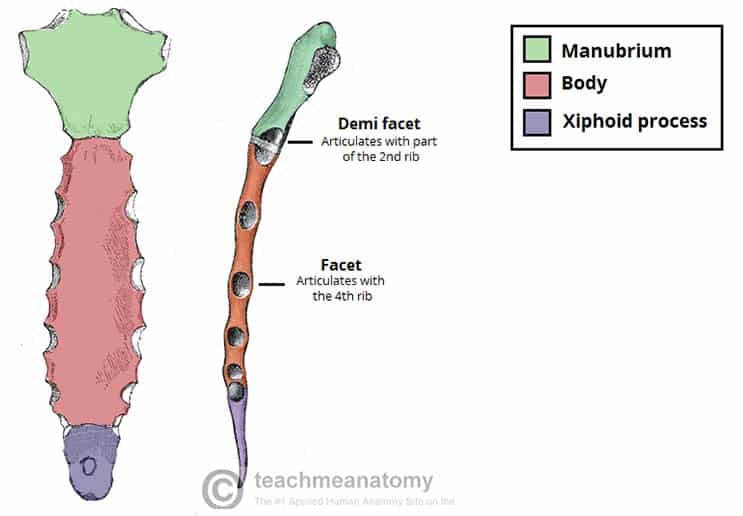
sternal body
body of the sternum
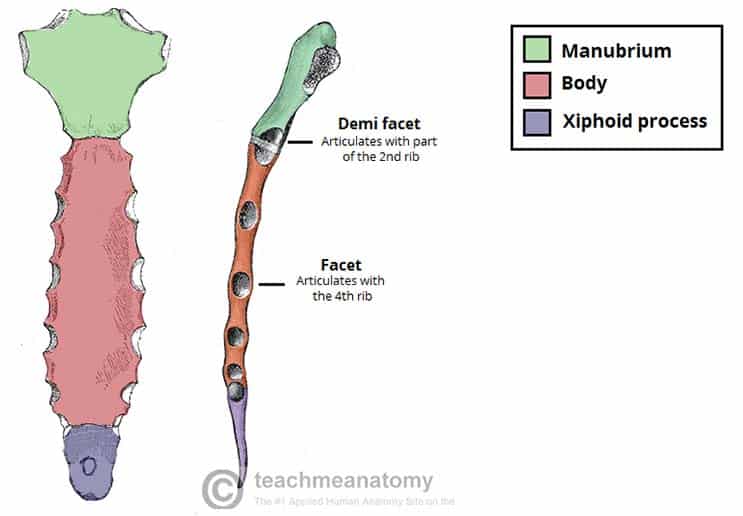
xiphoid process
lower part of the sternum
atlas (C1)
the first cervical vertebrae the head sits on
what maintains the heads position on the atlas
muscles posterior, lateral and anterior to the neck or cervical region
sternocleidomastoid
runs from the mastoid to the sternum
erector spinae
keeps the spine erect
spinal extension
connected in 3 segments
is a posture muscles
intervertebral disc
absorbs shock along the vertebral column
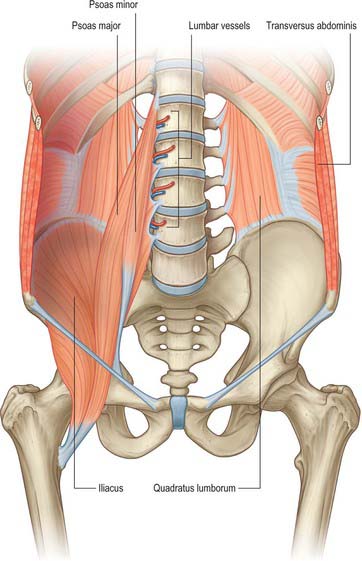
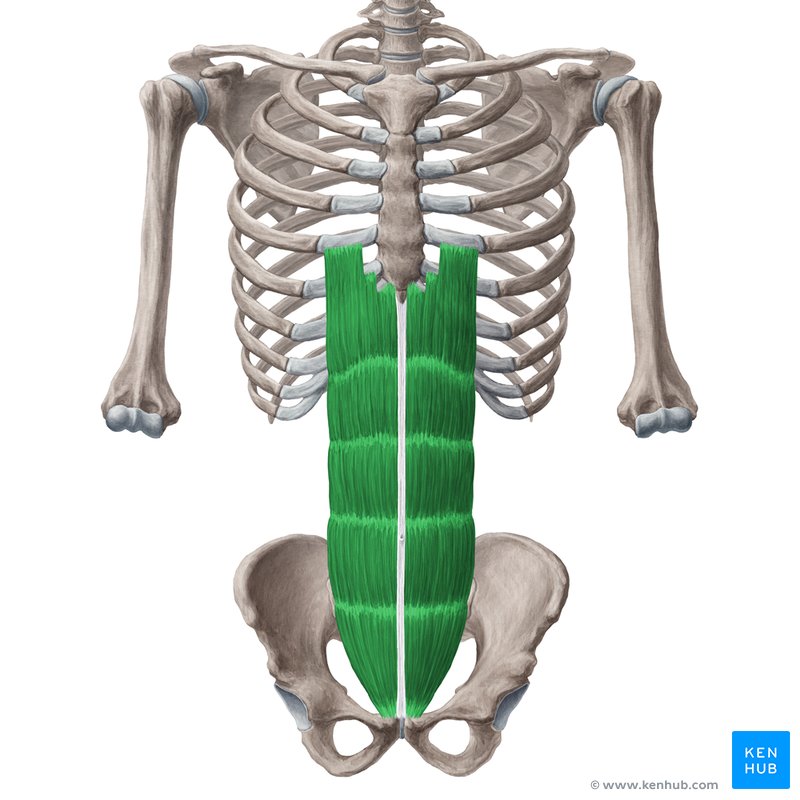
where abdominal muscles attach posteriorly
vertebral column
ribs
hip bone
where abdominal muscles attach anteriorly
linea alba
linea alba
white line where abdominal muscles connect anteriorly
it is a mix of connective tissues
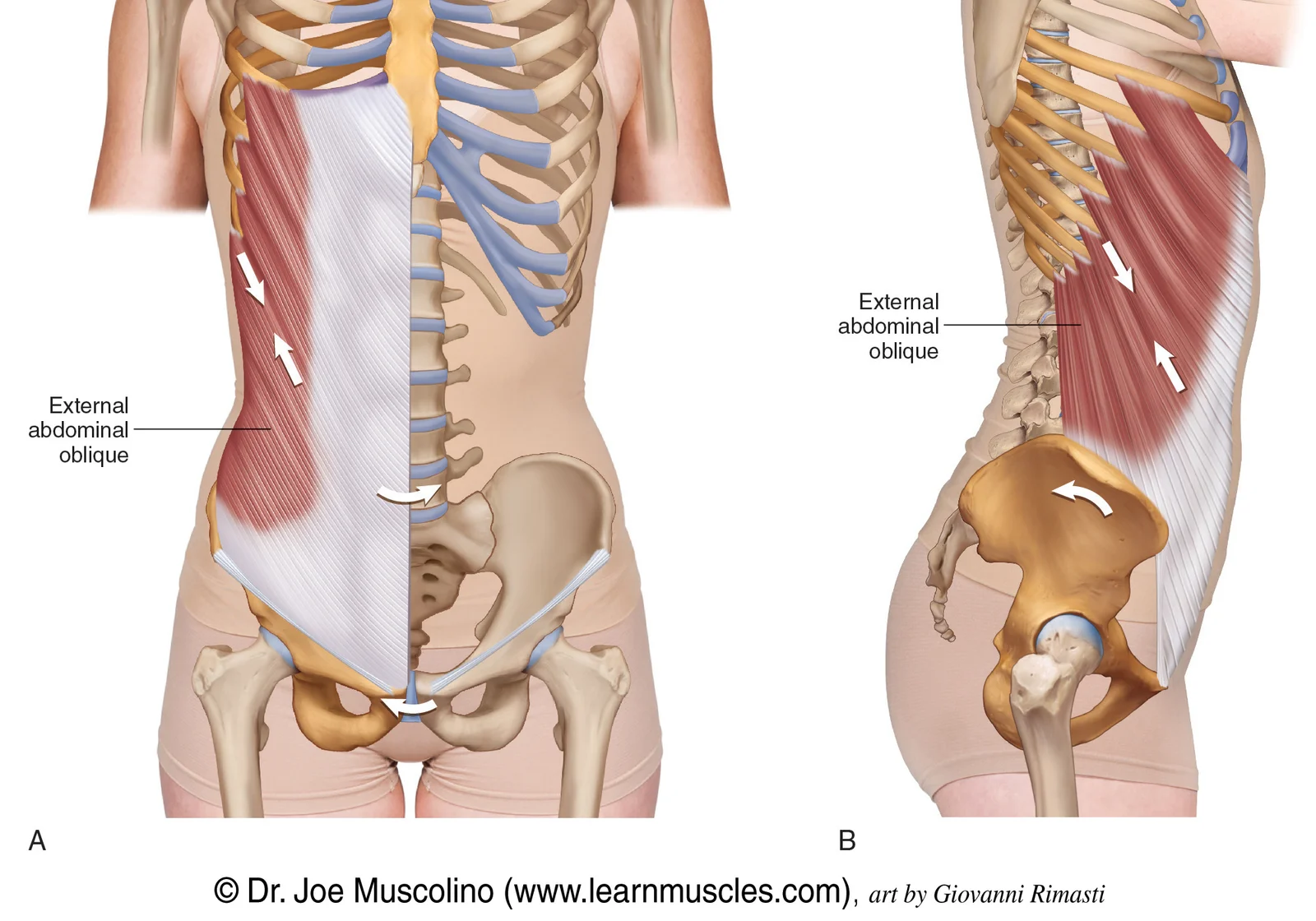
external oblique
lateral bending
rotation
flexes the spine forward
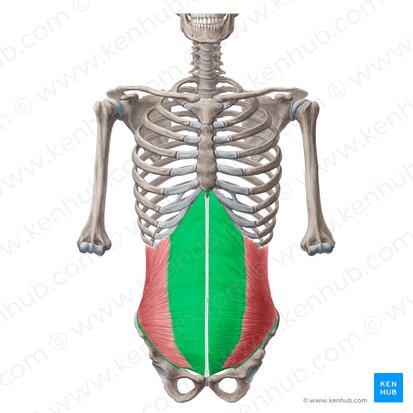
internal oblique
lateral flexion and rotation
underneath the external oblique
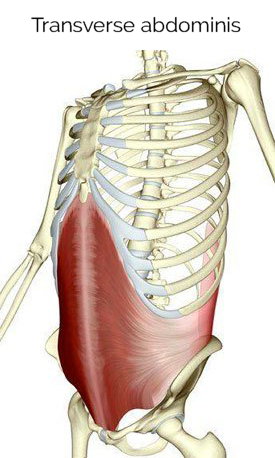
transversus abdominis
runs along the transverse plane
does not move the spine
sucks/pulls in the abdominal region
rectus abdominis
attach to pubic bone
flexion of the spine
pectoral girdle
connects upper limb to the axial skeleton
suspends the upper limb away from the chest wall
enables a great range of movement
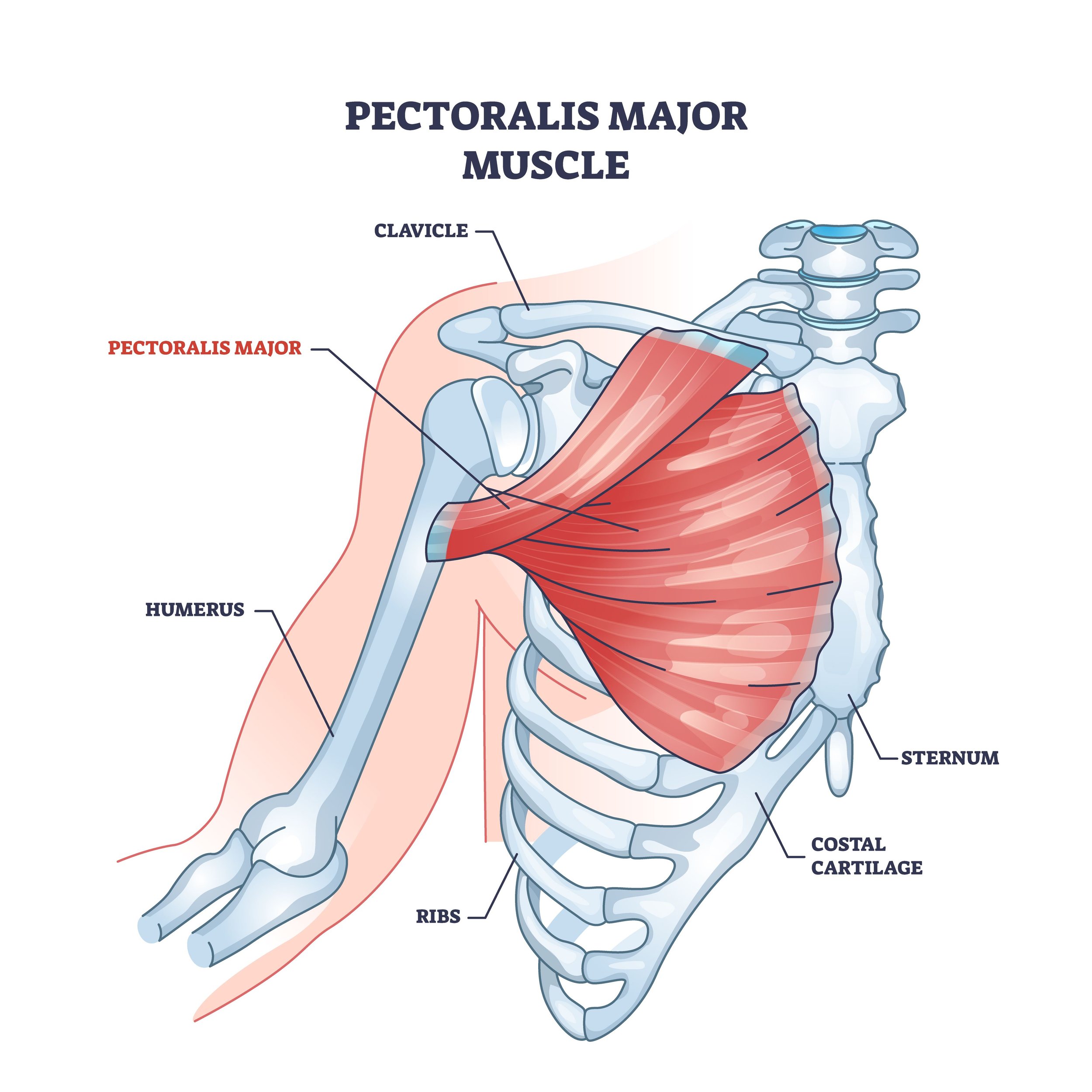
pectoralis major
the chest muscles
moves the shoulder joint (shoulder flexion and medial rotation)
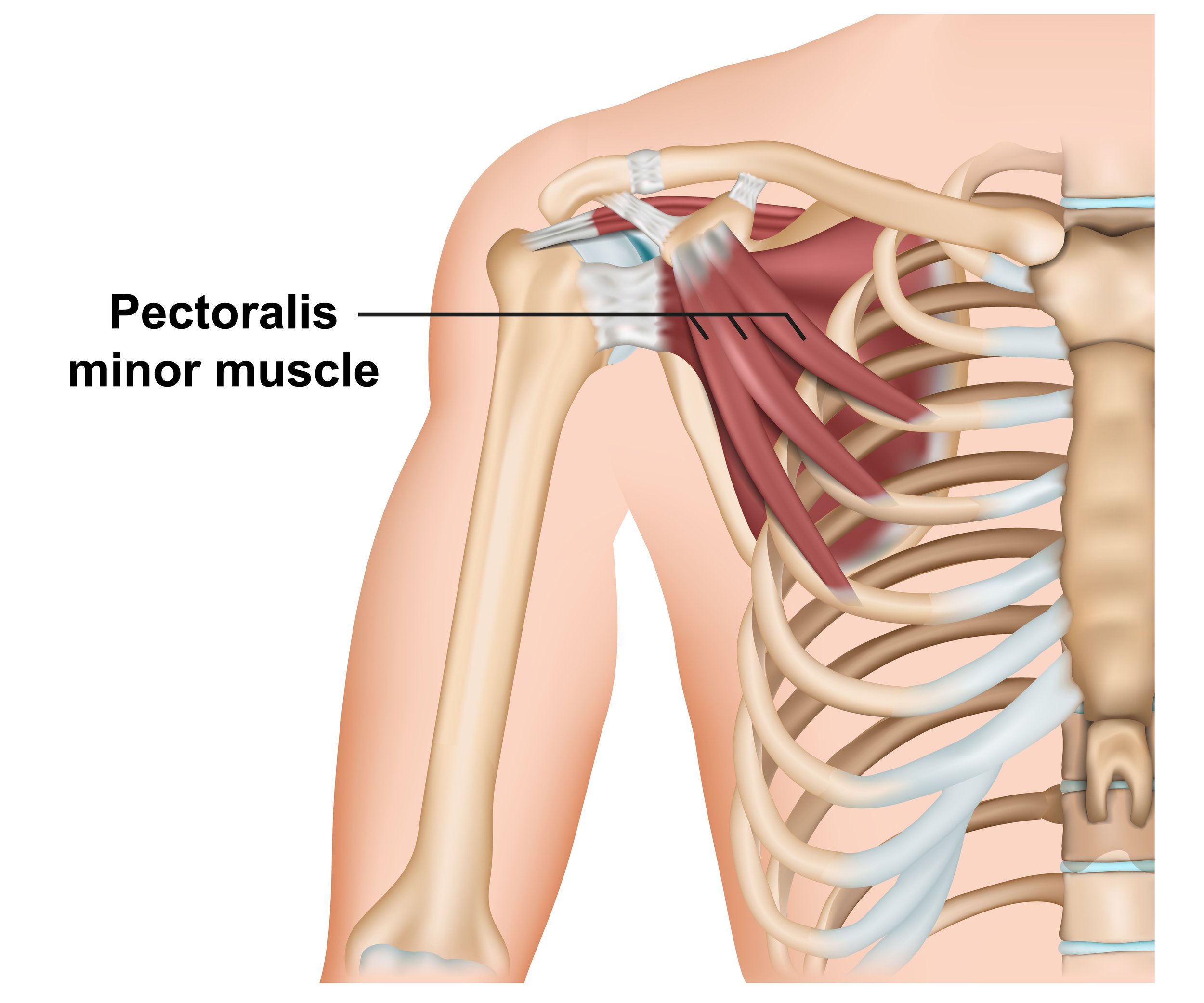
pectoralis minor
attaches the scapula to the ribs
depresses the scapula
protects and stabilizes scapula
serratus anterior
connects scapula and rib cage
keeps scapula against rib cage
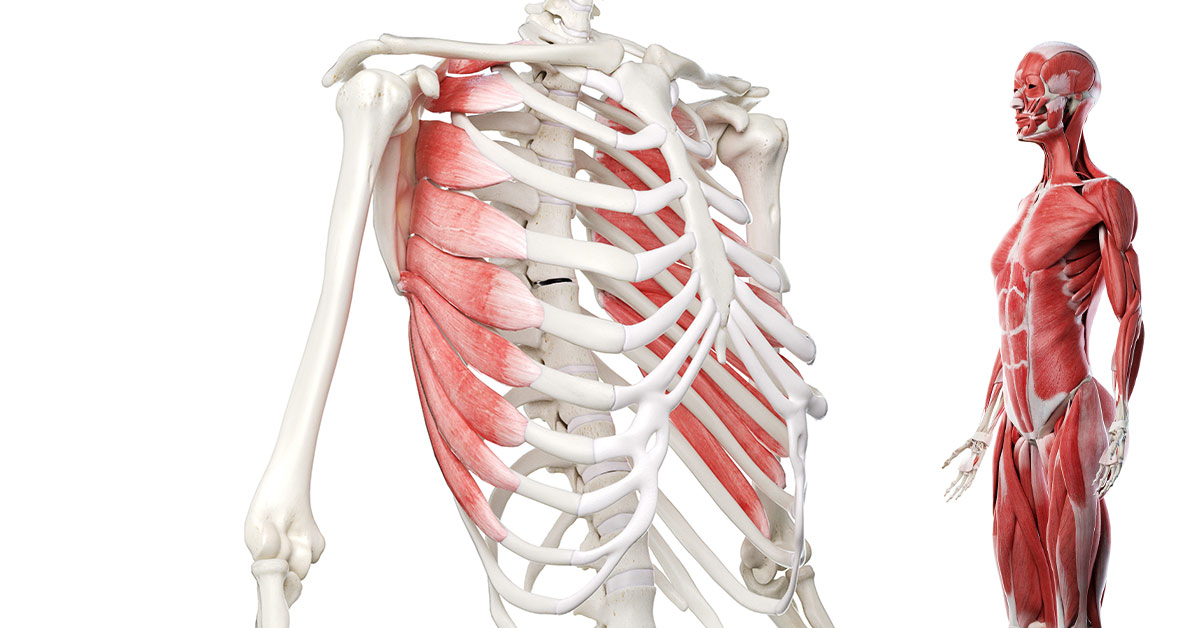
trapezius
runs from skull to T12
upper trapezius: scapula elevation
middle trapezius: scapula retraction
lower trapezius: scapula depression
the trapezius does not attach to the humerus so it does not move the shoulder
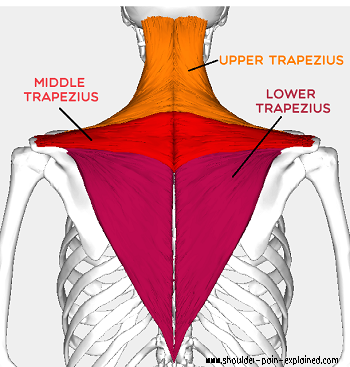
latissimus dorsi
lat pull down
shoulder extension
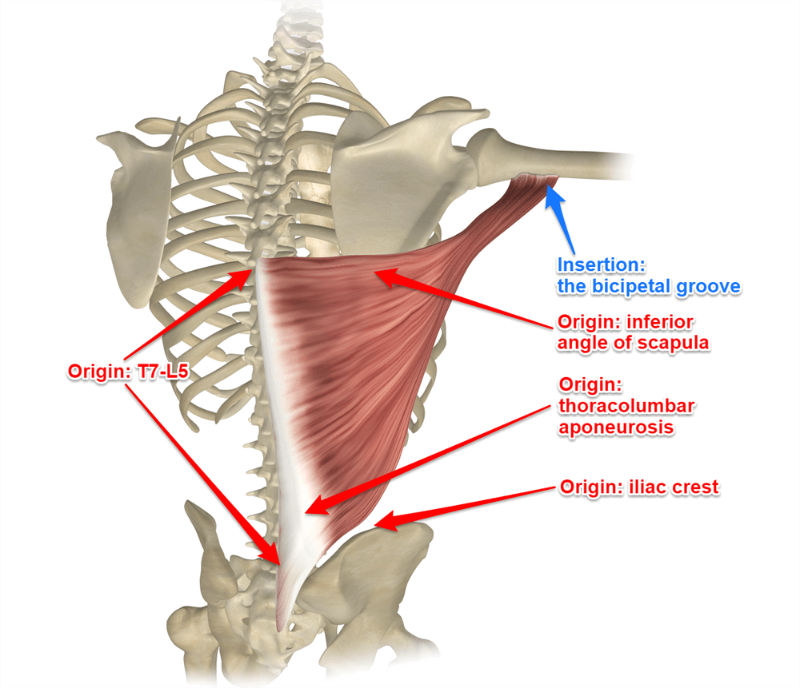
levator scapulae
elevates scapula
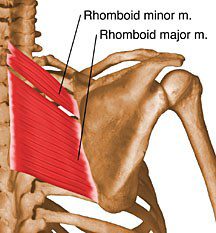
rhomboid major
rhomboid minor
scapula retraction
sternoclavicular joint
synovial saddle joint
acromioclavicular joint
gliding joints
scapulohumeral regions
anterior muscles: subscapularis
superior and posterior muscles: Supraspinatus, infraspinatus and teres minor
lateral muscles: deltoid, anterior fibres, middle fibres, posterior fibres
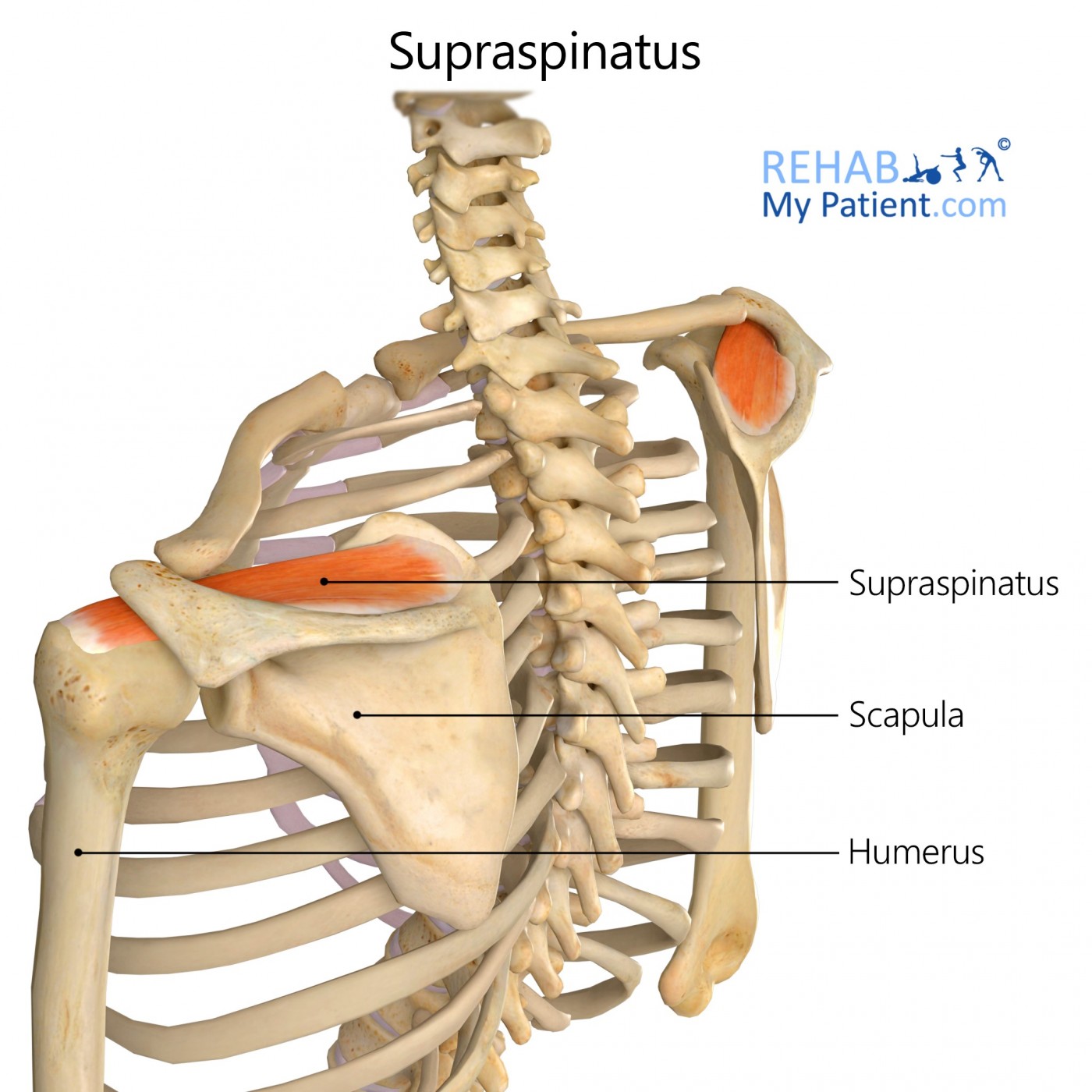
supraspinatus
exists above the spine of the scapula
assists with the abduction of the arm
infraspinatus
extension of shoulder joints
below the spine of the scapula
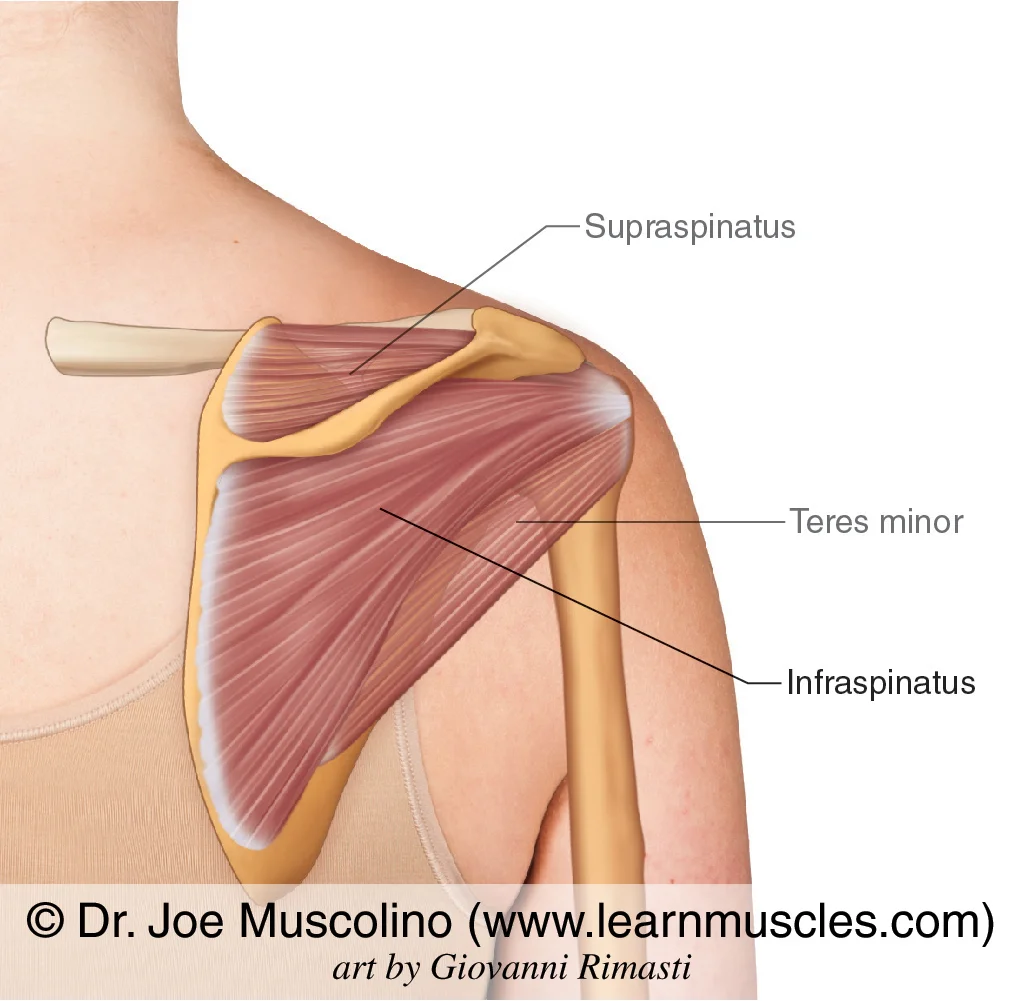
teres minor
copies the infraspinatus to extend shoulder joints
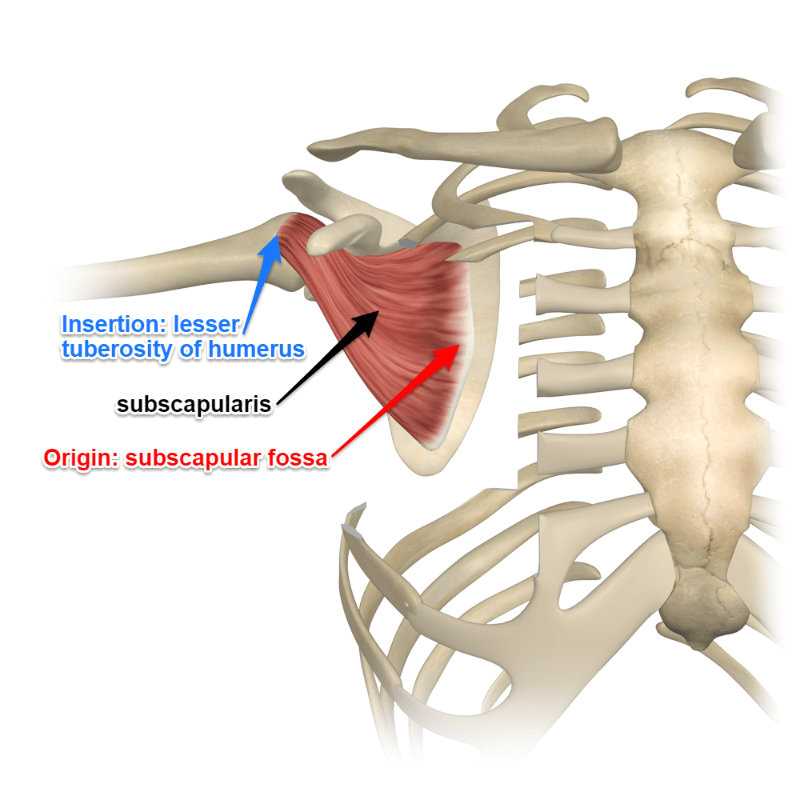
subscapularis
shoulder adduction
underneath the scapula
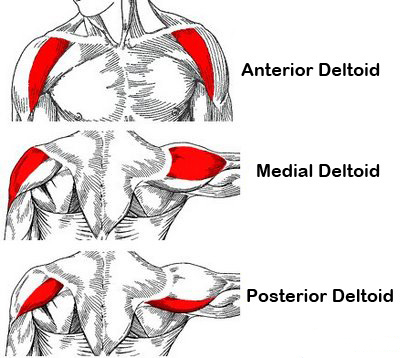
deltoid
shoulder muscles
anterior fibres
flexion and medial rotation
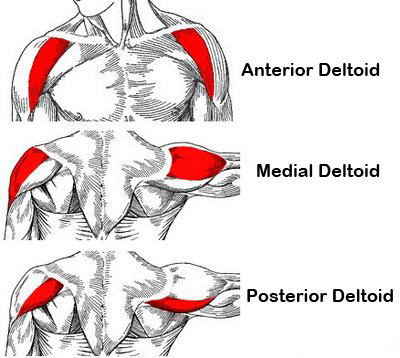
middle fibres
lateral raise and shoulder abduction
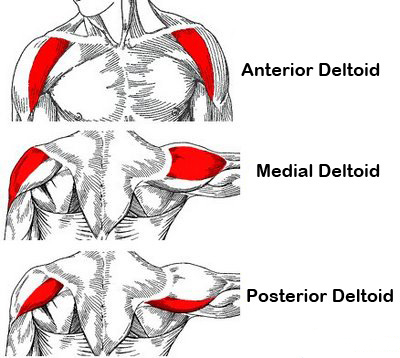
posterior fibres
extension and lateral rotation
arm
shoulder to elbow
forearm
elbow to wrist
joined by a sheet of fibrous tissue
radius and ulna
radius runs along the thumb
ulna along the pinky
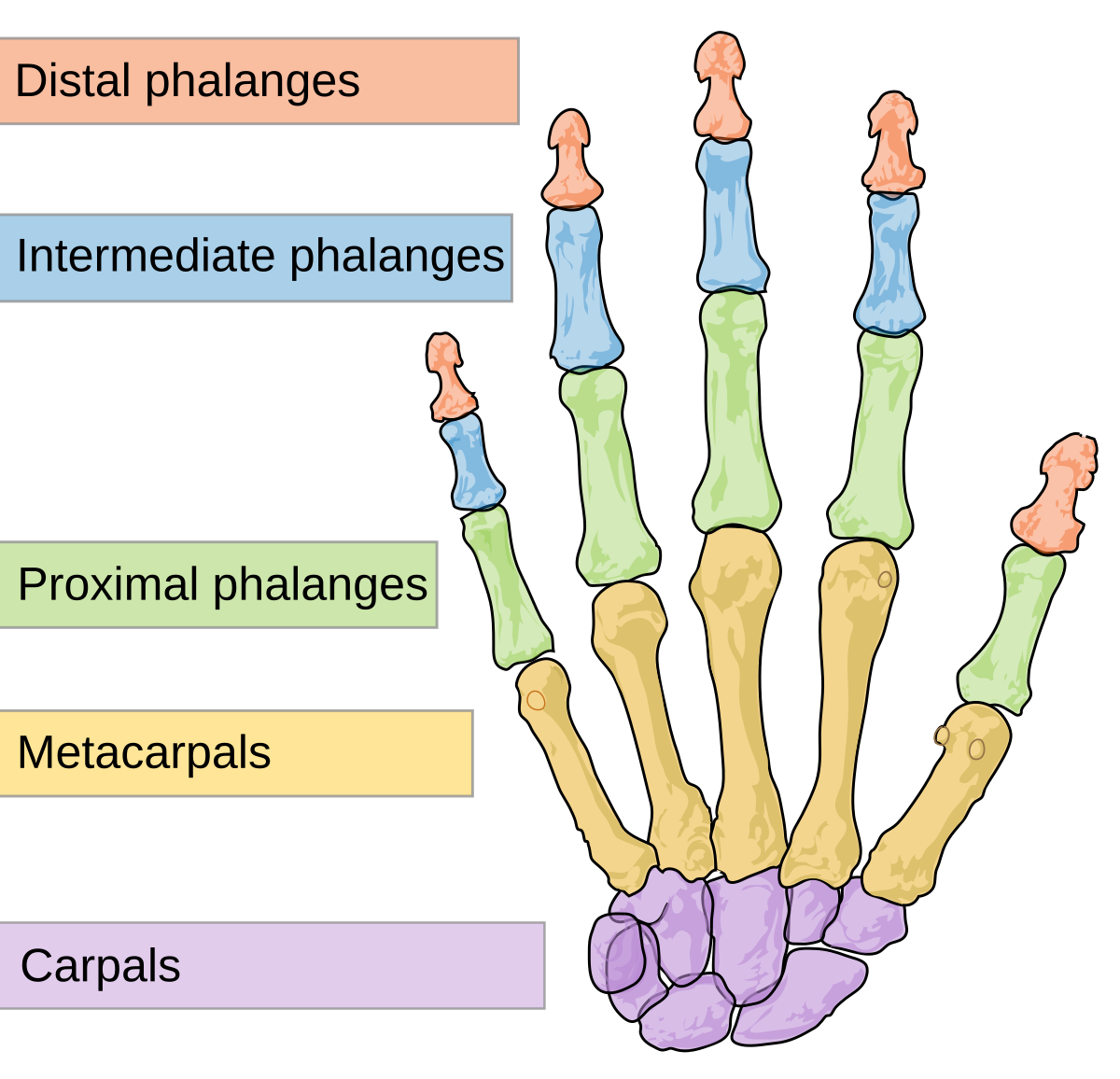
how many carpals in a finger
8 carpals
proximal row of carpals
scaphoid
lunate
triquetrum
pisiform (sesamoid bone)
distal row of carpals
trapezium
trapezoid
capitate
hamate (by the thumb)
metacarpals
5
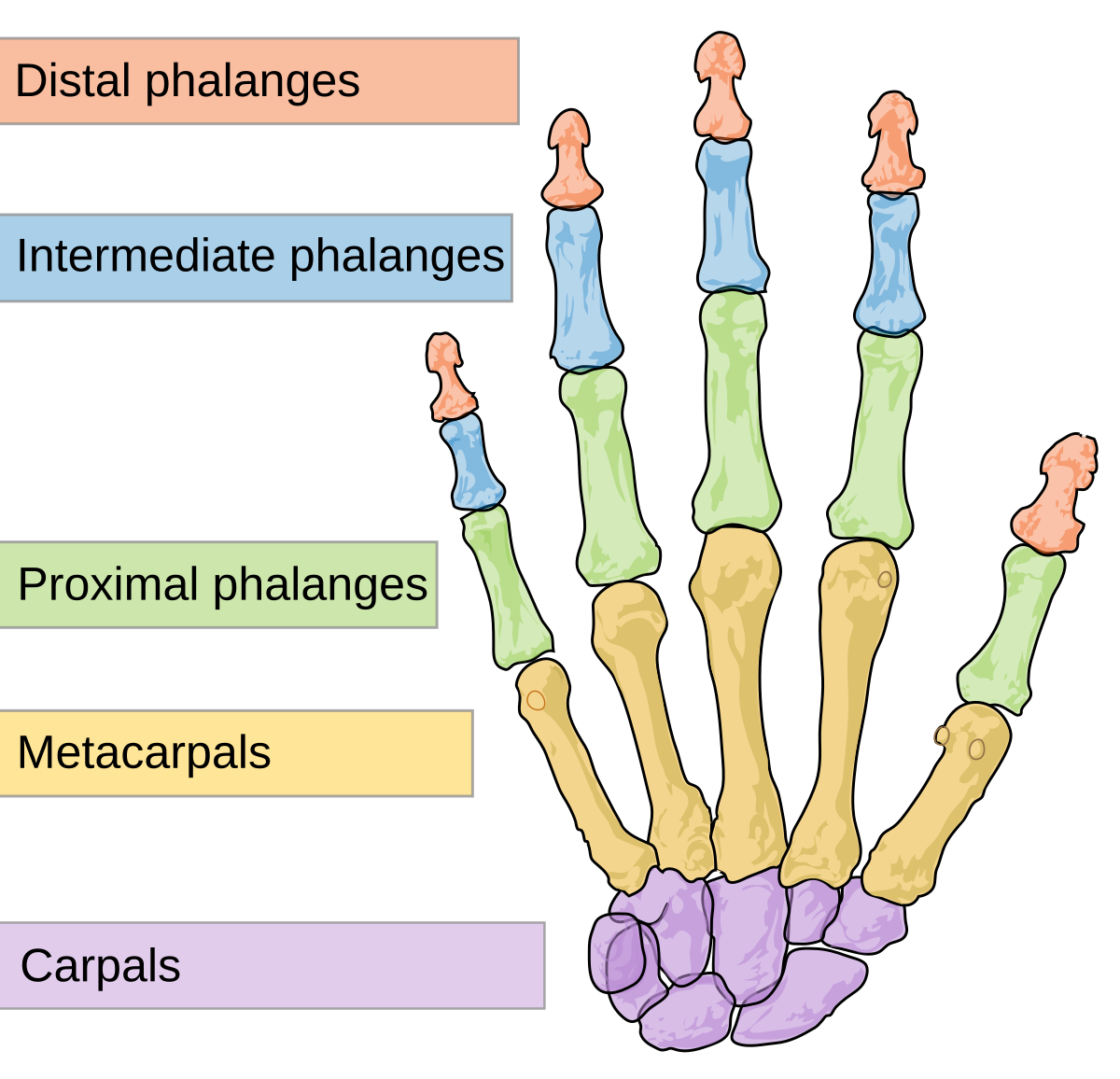
phalanges
14
3 phalanges per finger
2 phalanges per thumb
flexors
anterior
extensors
posterior
coracobrachialis
shoulder flexion
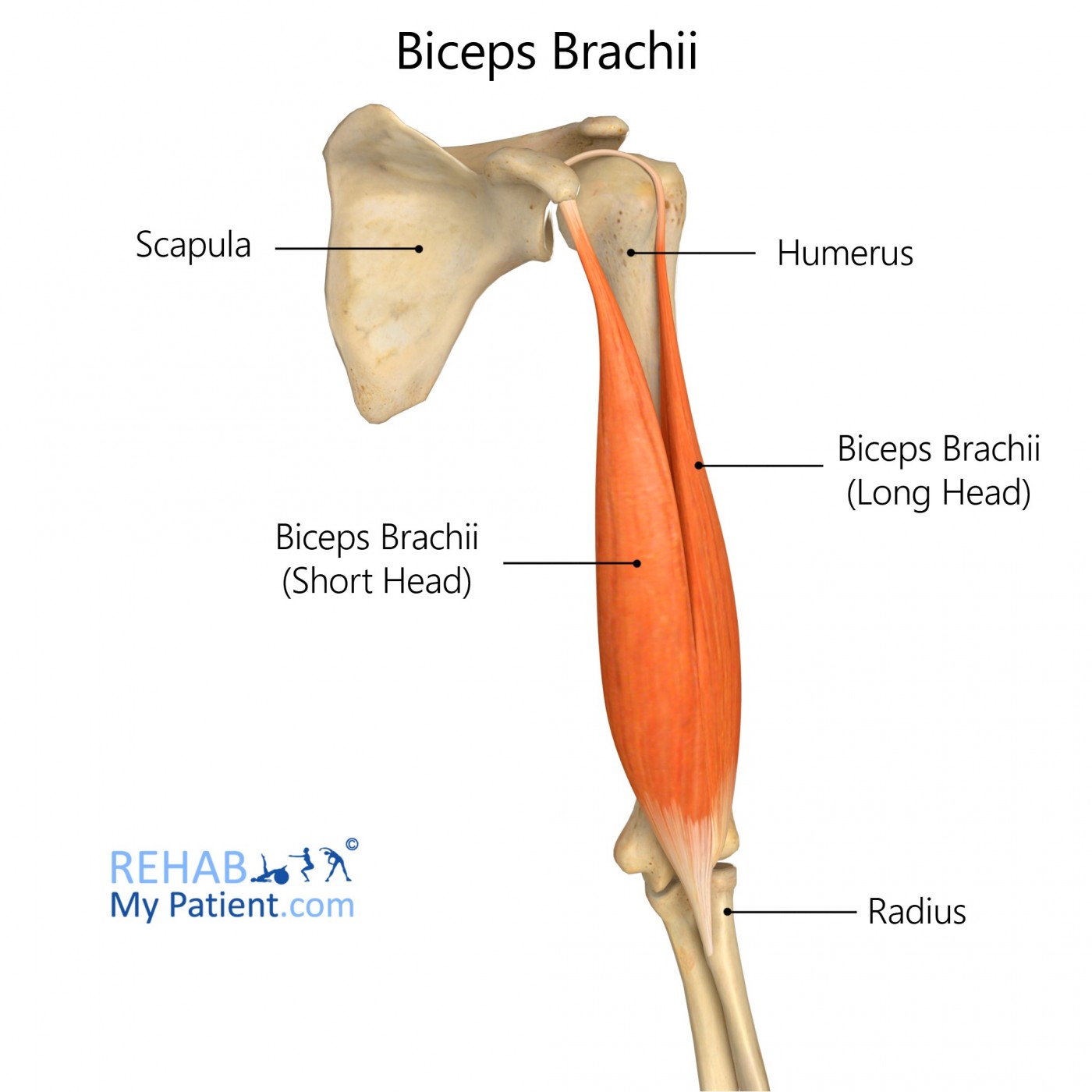
biceps brachii
supination
elbow flexor
shoulder flexor
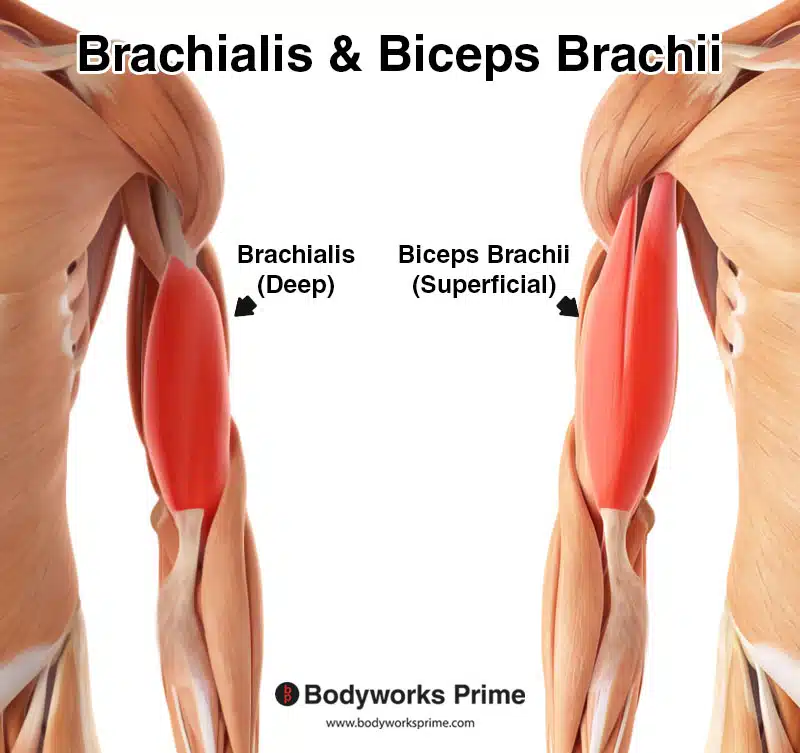
brachialis
elbow flexion
attaches to ulna
triceps
extension of shoulders and elbows
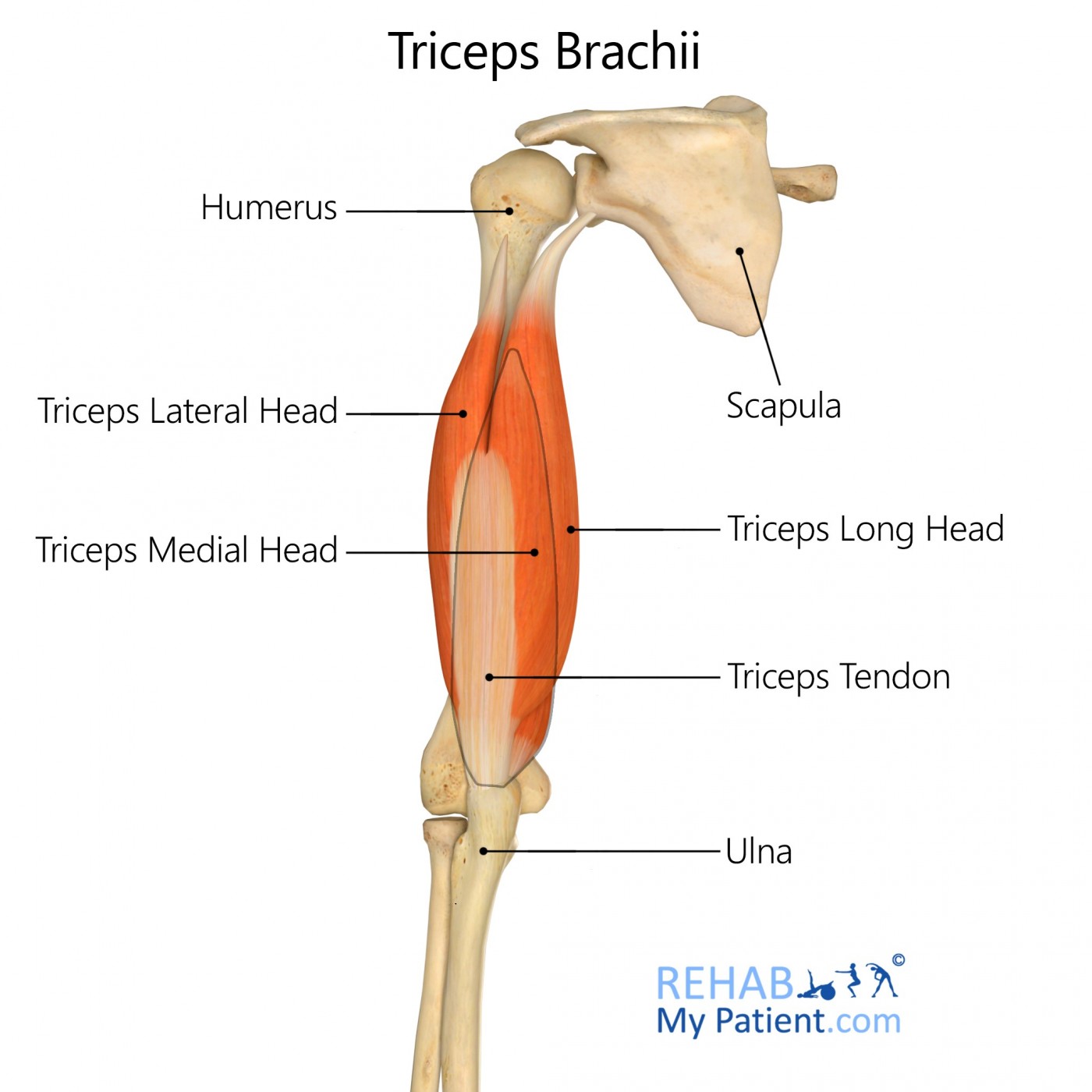
flexor-pronator group
anterior
extensor-supinator group
posterior
thenar group
abducts thumb and its metacarpals
hypothenar group
abducts little finger and its metacarpal
interossei and lumbrical muscles
move digits
glenohumeral joint
ball and socket shoulder joint
2 elbow joints
humeroradial and humeroulnar
radioulnar joints
pronation and supination
pivot joints
radiocarpal
joint between radius and all carpals
metacarpophalangeal
joints between metacarpals and phalanges
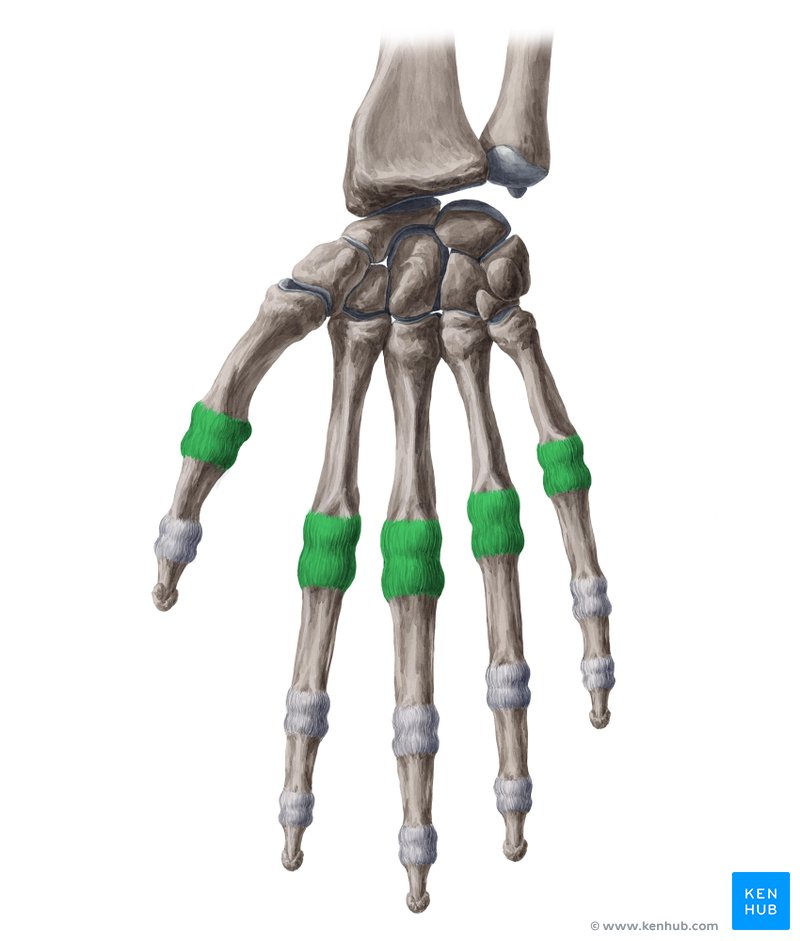
interphalangeal
joints between phalanges
pelvic girdle
weight bearer
supports bladder and abdominal contents
sacrifices mobility for stability and strength
innominate bones and what its made up of
it is a paired hip bone made up of
Ilium
pubis
Ischium
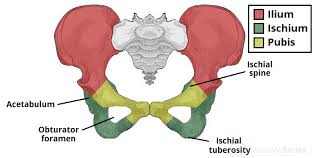
acetabulum
cup-shaped cavity in the pelvic bone that forms a joint with the head of the femur
lliopsoas
hip flexors formed by psoas major and lliacus

gluteal muscles
gluteus maximus: hip extensor
gluteus medius and minimus: hip abductors
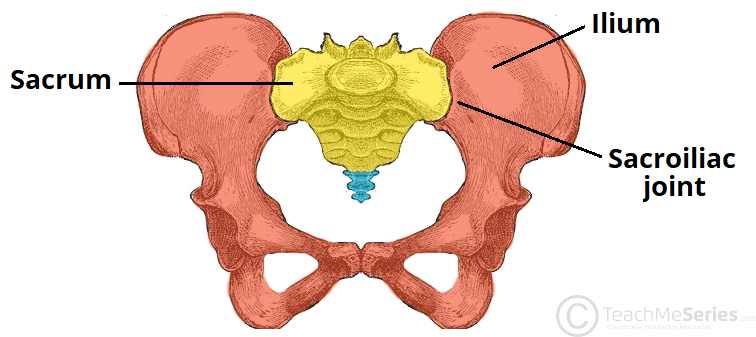
sacroiliac
compound joint made of fibrous (posterior) and synovial (anterior) joints
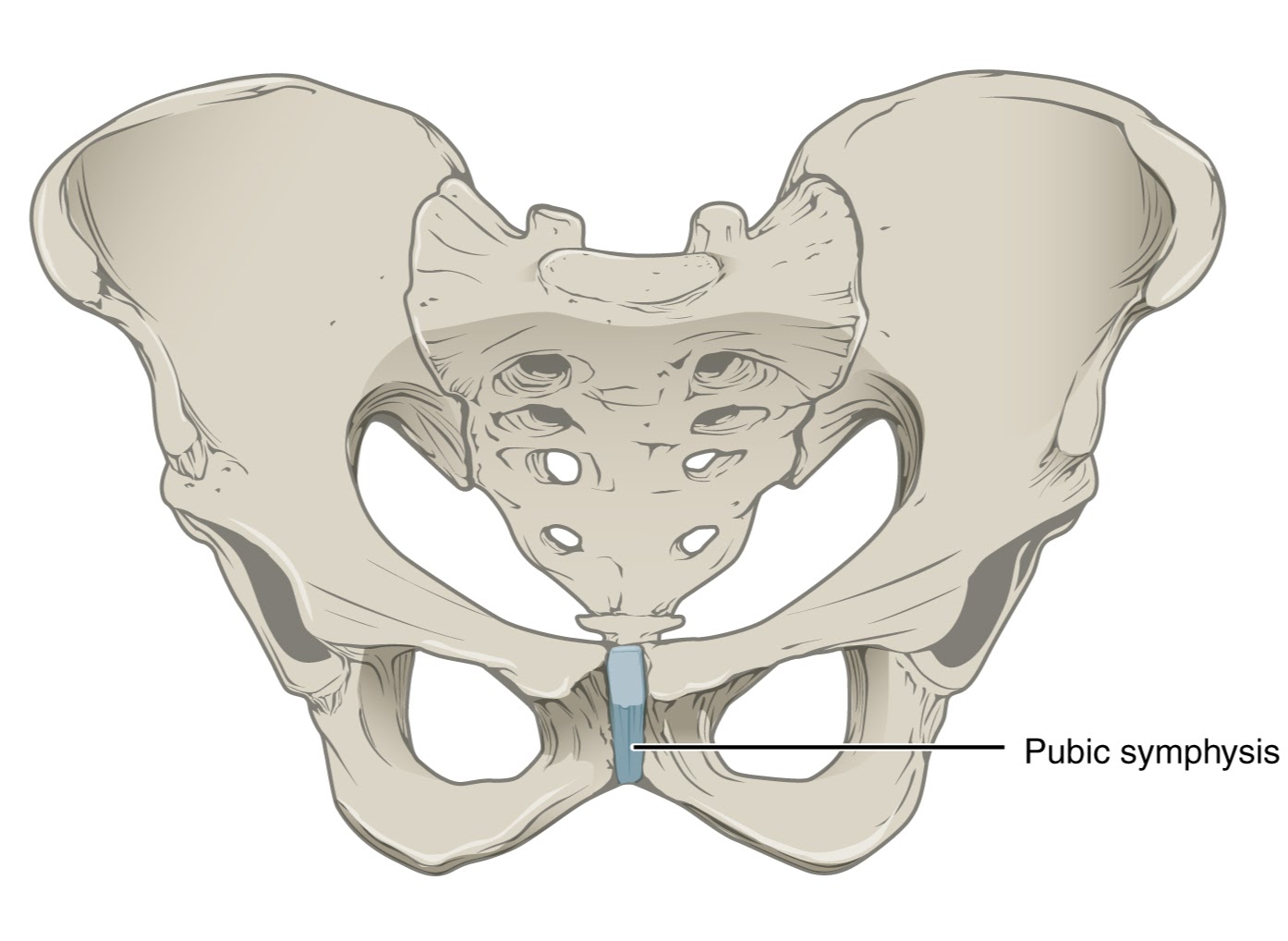
pubic symphysis
cartilagenous joint
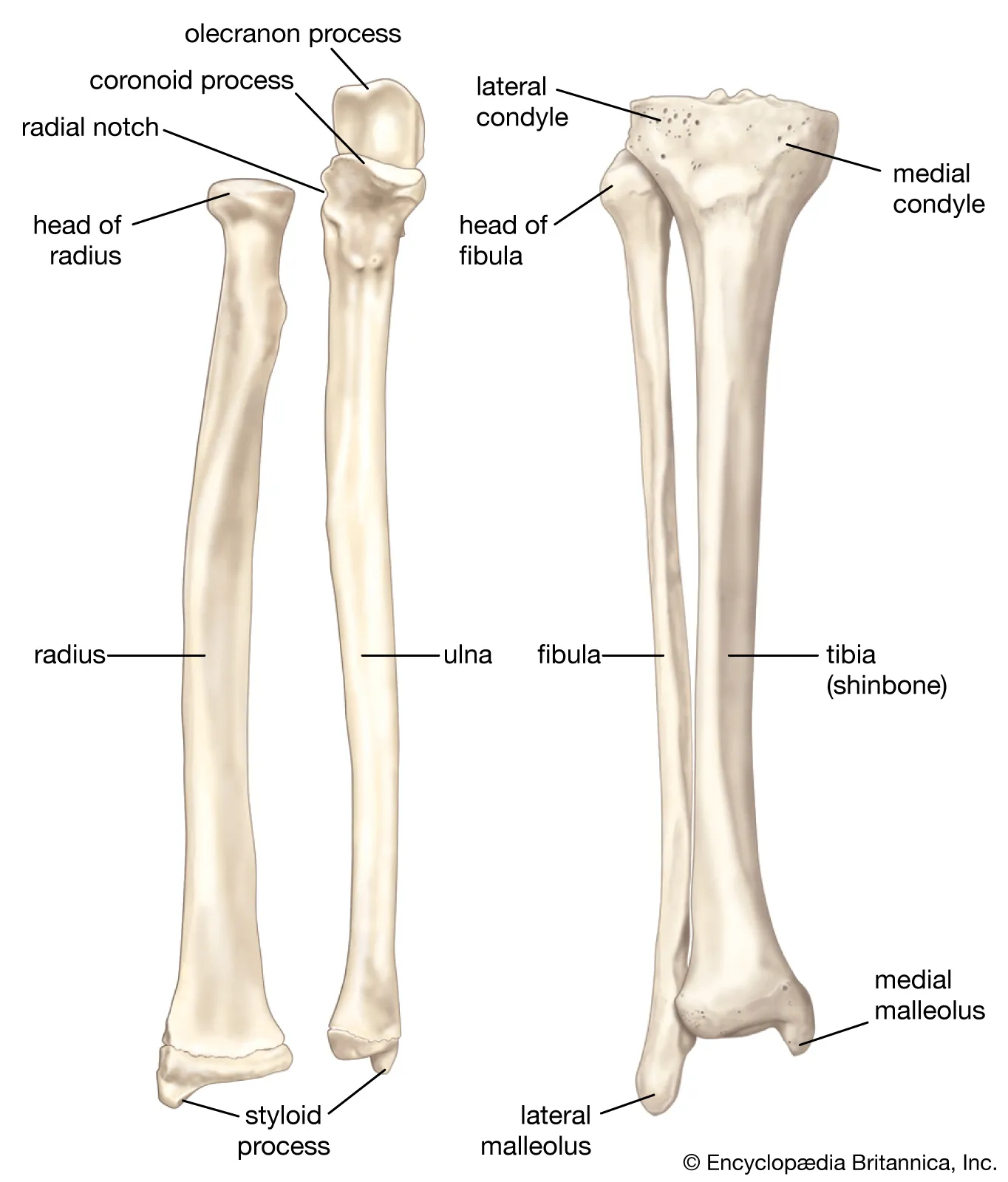
lower limbs
thigh: hip to knee
leg: knee to ankle
thigh consists of
femur and patella
leg bones
tibia: medial malleolus
fibula: lateral malleolus
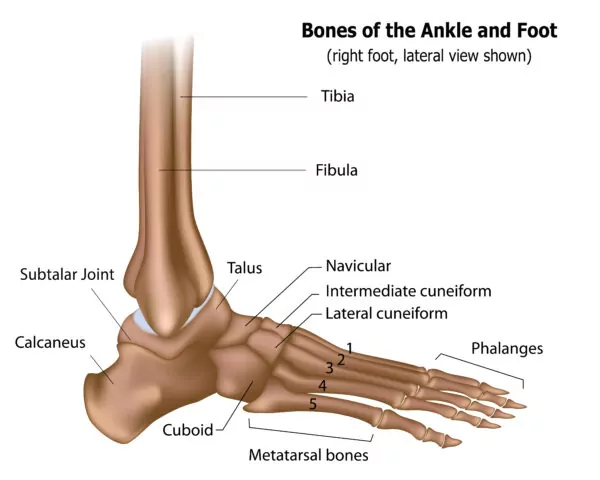
parts of ankle
calcaneus
talus
cuboid
navicular
1st (medial), 2nd (intermediate) and 3rd (lateral) cuneiform
quadriceps femoris
rectus femoris: hip flexor
medial thigh muscles
adductors
adductor inner thigh/medial thigh
adductor longus
adductor brevis
adductor magnus
hamstrings
flexors and abductors
biceps femoris: headed femur muscles
tibialis anterior
foot invertor and dorsiflexor
fibularis longus and brevis
long and short muscles in the lateral leg muscles
eversion