EXSS 155: The Nervous System--Overview and Divisions, Neurons and Synapses, The Brain, The Spinal Cord, Reflex Arcs, Cranial Nerves, and Neurophysiology and Action Potentials
1/182
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
183 Terms
Conus medularis
true end of the spinal cord
Cauda equina
"horse's tail", branching of nerve fibers below the spinal cord
Filum terminale
anchors spinal cord to coccyx
Map of Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
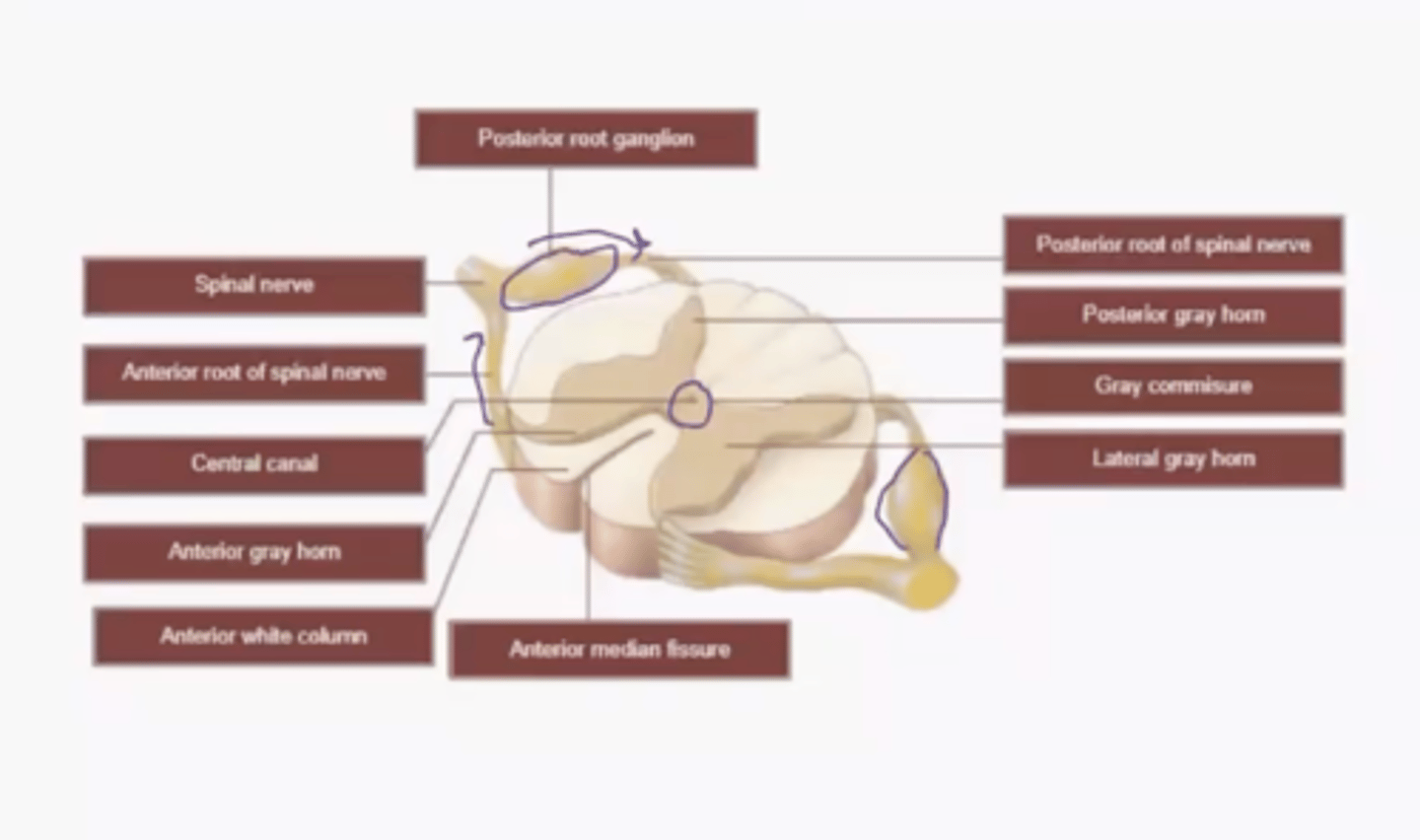
Gray matter in the Spinal Cord
processing
White matter in the Spinal Cord
the "two and from". While because of myelin.
Nerve Pairs: Cranial
8 pairs
Nerve Pairs: Thoracic
12 pairs
Nerve Pairs: Lumbar
5 pairs
Nerve Pairs: Sacral
5 pairs
Nerve Pairs: Coccygeal
1 pair
Cervical Nerve Pairs...
above vertebrae (except C8)
Thoracic and Lumbar Nerve Pairs...
below vertebrae
Cervical Plexus
C1-C5
Brachial plexus
C5-T1
Lumbar Plexus
L1-L4
Sacral Plexus
L4-S4
Cervical Plexus: Hypoglossal (CN XII)
1st branch; vertical
Cervical Plexus: Lesser occipital
2nd branch; vertical
Cervical Plexus: Greater Auricular
3rd branch; vertical
Cervical Plexus: Transverse Cervical
Straight across big loop
Cervical Plexus: Superior root of ansa cervicalis
Upper big loop
Cervical Plexus: Inferior root of ansa cervicalis
Lower big loop
Cervical Plexus: Supraclavicular
2nd lowest; pitchfork
Cervical Plexus: Phrenic
Lowest branch; going to diaphragm
Brachial Plexus: Musculocutaneous
Letter M; Upper
Brachial Plexus: Axillary
Letter V; Upper
Brachial Plexus: Median
Letter M; middle
Brachial Plexus: Radial
Letter V; lower
Brachial Plexus: Ulnar
Letter M; lower
Lumbar Plexus: Iliohypograstric
1st branch; fork
Lumbar Plexus: Ilioinguinal
2nd branch
Lumbar Plexus: Genitofemoral
Drapes over Lateral cutaneous nerve of thigh
Lumbar Plexus: Lateral cutaneous nerve of thigh
Genitofemoral crosses this nerve
Lumbar Plexus: Femoral
Lower; thick
Lumbar Plexus: Obturator
Most inferior
Sacral Plexus: Sciatic
Huge!
Common Fibular (posterior): lateral side
Tibial (anterior): medial side
Sacral Plexus: Superior gluteal
Most superior branching off sciatic
Sacral Plexus: Inferior gluteal
Middle branching off sciatic
Sacral Plexus: Nerve to piriformis
Most inferior branching off sciatic
Reflex: Definition
fast, predictable, automatic response to changes in the environment that helps to maintain homeostasis
- Simplest type of pathway
- Level of brain involvement varies
- How ANS operates
- Some inborn (touch hot stove)
- Some learned (driving)
Gray vs. White Matter in Brain
Gray: integration center for reflexes
White: highways for nerve impulse propagation
Reflexes: Necessary Components
1. Receptor
2. Sensory Neuron (posterior)
3. Integrating Center (brain or spinal cord)
4. Motor neuron (movement; anterior)
5. Effector (muscles or glands)
Sensory Receptors in Muscle: Muscle Spindle
1. Senses muscle length (how much stretch)
2. Muscles attached to spindle stretch
3. Neurons "report" stretch to CNS
4. Muscles contract (reflex) to resist further stretching
Sensory Receptors in Muscle: Golgi Tendon Organs (GTO)
1. Sense changes in muscle tension
2. Located close to tendon and muscle attachment
3. Inhibit agonist muscle contraction and excite antagonist muscles to prevent injury
Mechanoreceptors:
respond to mechanical force such as touch, pressure, vibration, and stretch
Theromoreceptors:
respond to changes in temperature
Photoreceptors:
respond to light to allow vision
Chemoreceptors:
respond to chemical stimuli from foods, odors, and changes in blood concentrations
Osmoreceptors:
respond to changes in the osmotic pressure of body fluids
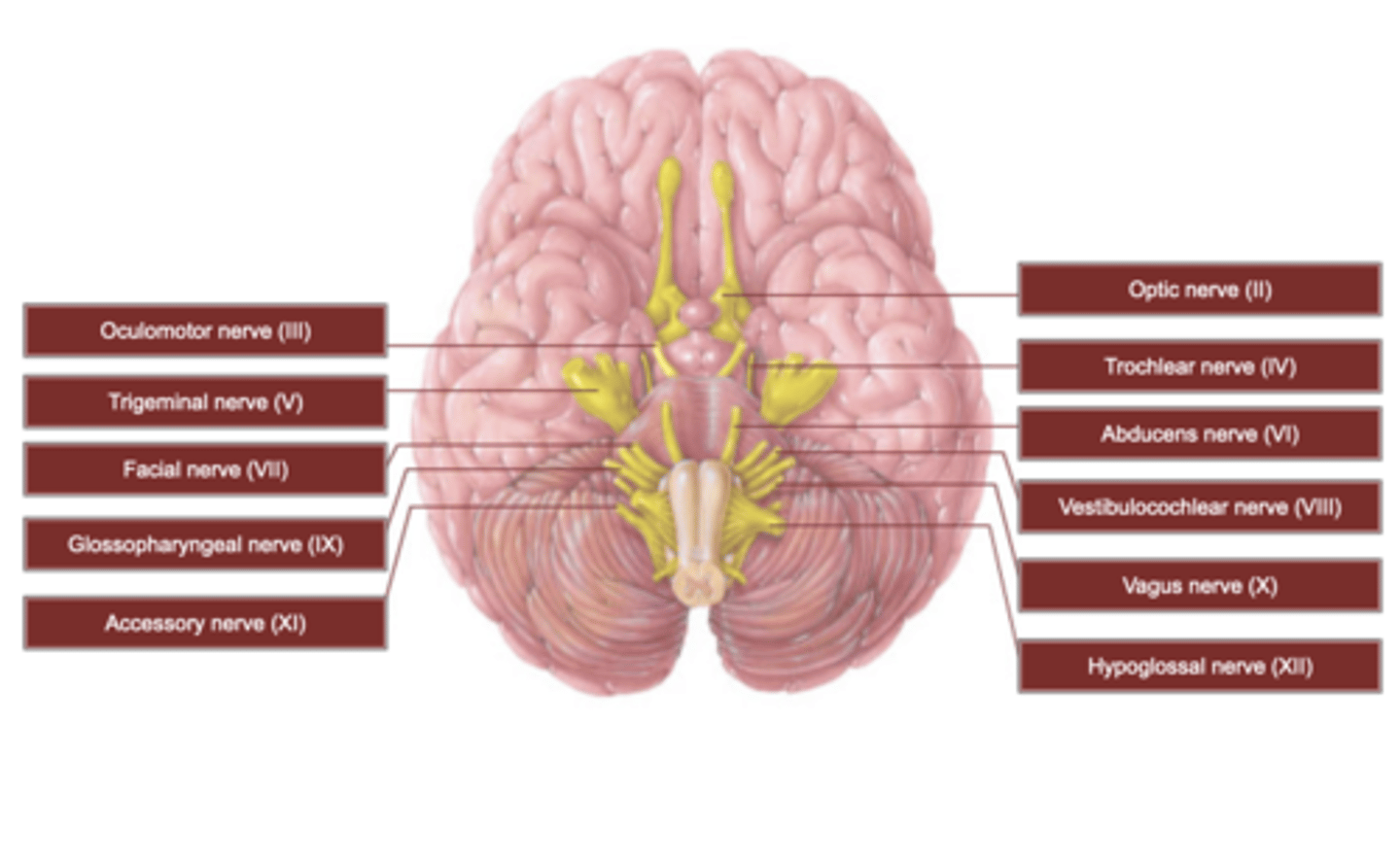
Cranial Nerves: Map and Basic Information
Sensory, motor, and mixed nerves
Name and roman numerals to identify
Cranial Nerves: How many pairs?
12
Cranial Nerve 1
Olfactory Nerve
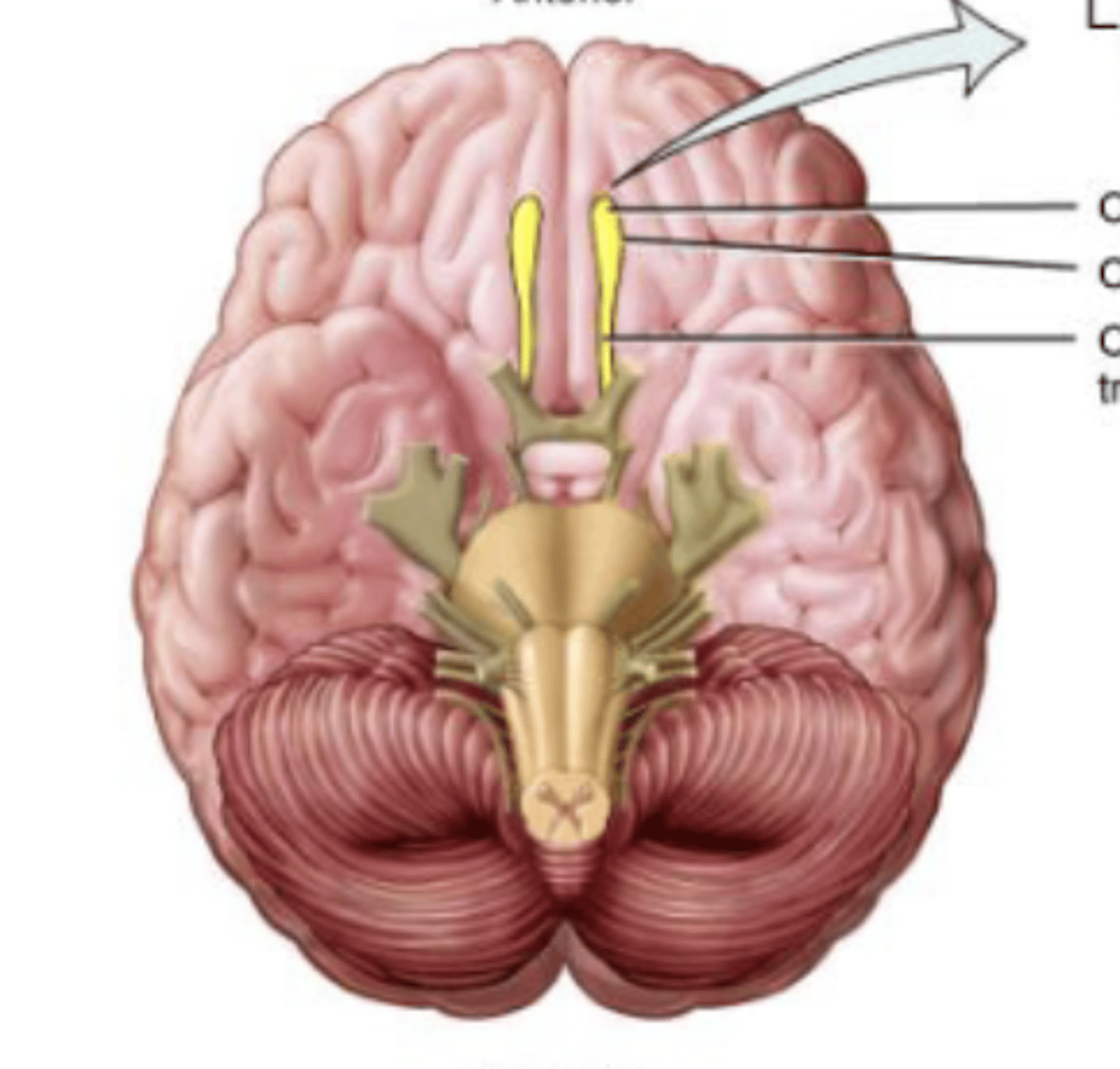
Olfactory (I) Nerve
Sense of smell
Sensory nerve
Olfactory cells converge to become nerve
Cranial Nerve 2
Optic
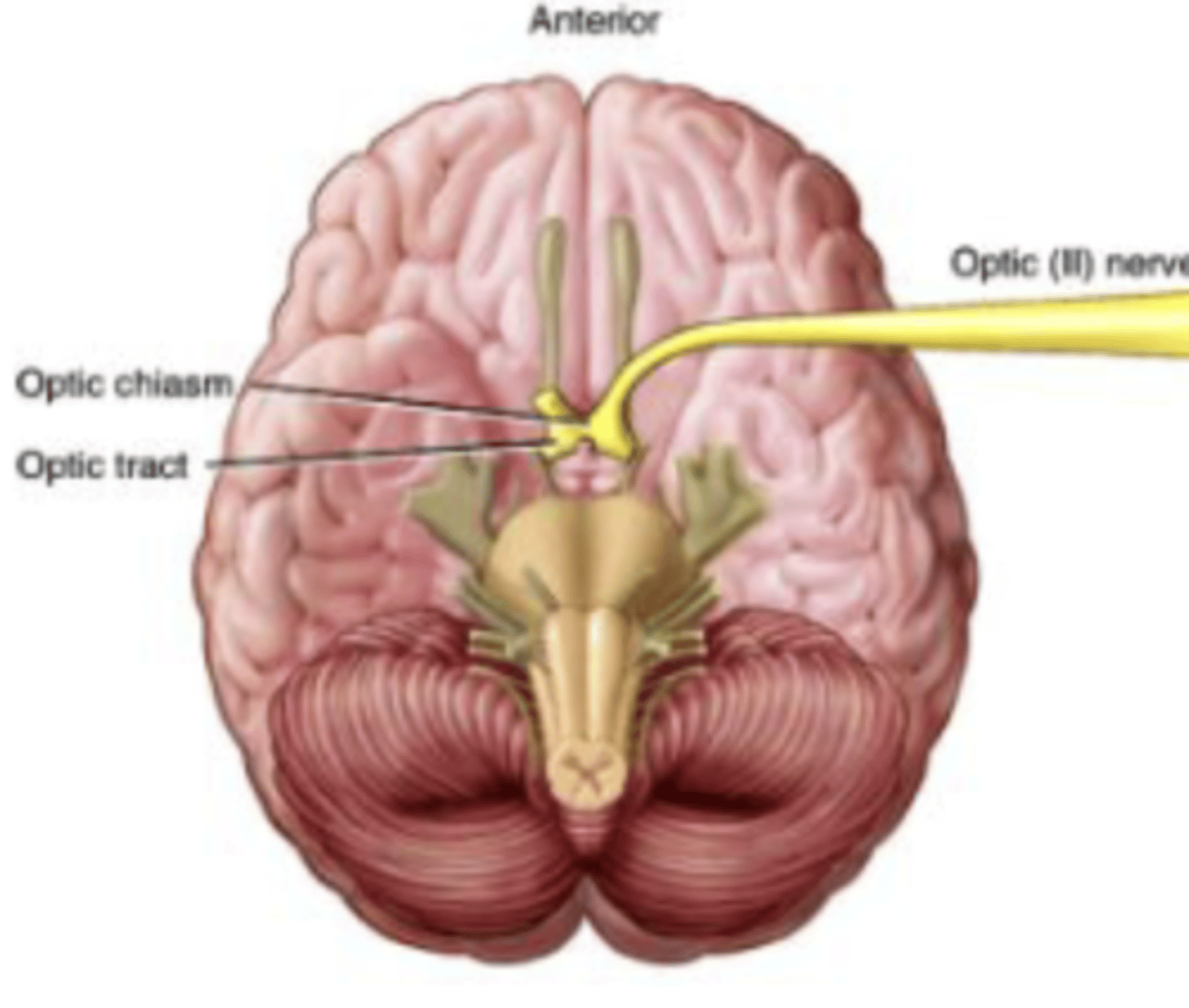
Optic (II) Nerve
Vision
Sensory Nerve
Ganglion cells in retina of each eye join to form
Cranial Nerve 3
Oculomotor
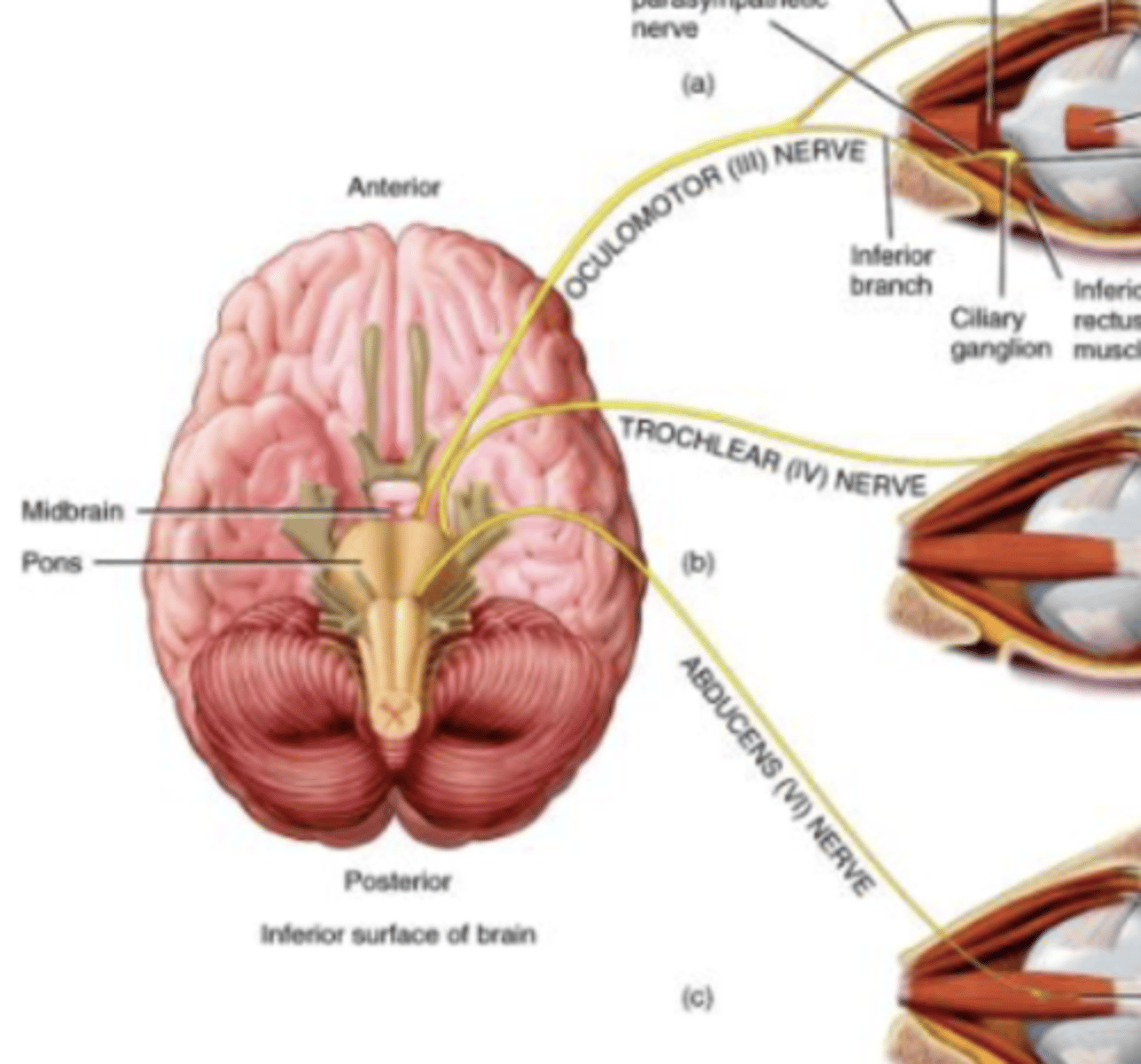
Oculomotor (III) Nerve
Supply extrinsic eye muscles to control adduction and downward movement of eyeball, movement of upper eyelid, and reaction to light
Motor nerve
Originates in Midbrain
Cranial Nerve 4
Trochlear
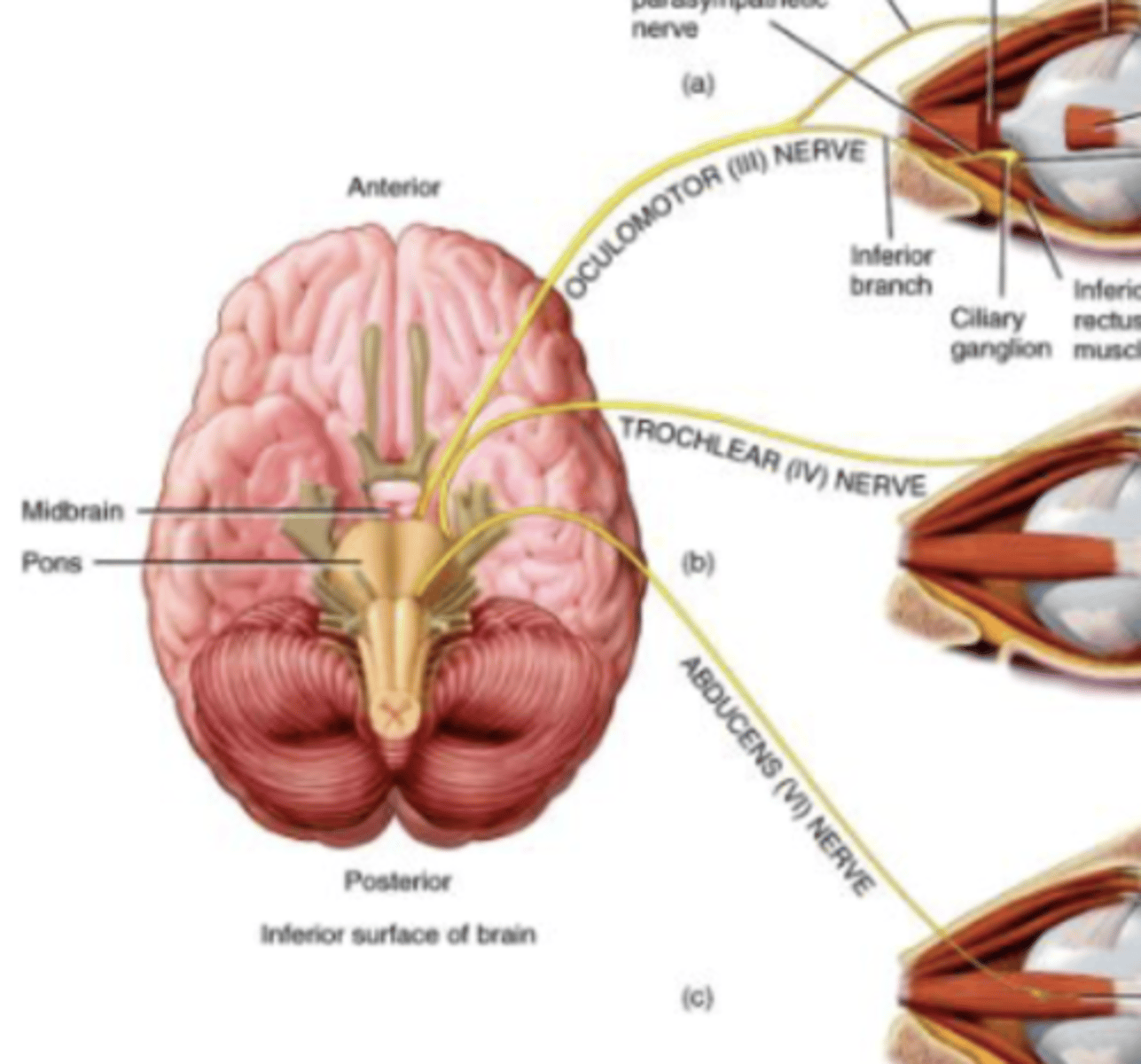
Trochlear (IV) Nerve
Downward movement of eyeball
Motor nerve
Originates in Midbrain
Smallest of cranial nerves
Cranial Nerve 5
Trigeminal
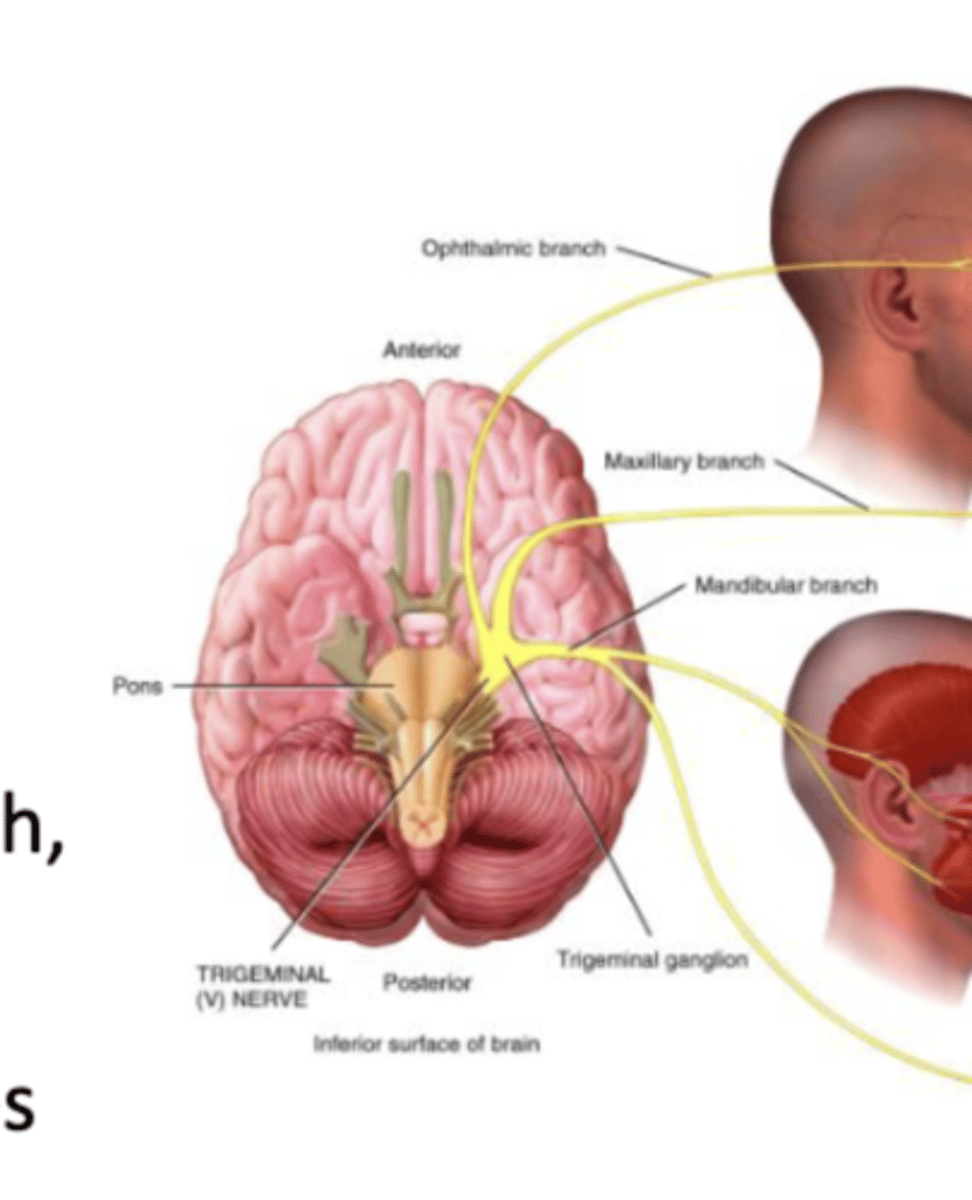
Trigeminal (V) Nerve
Touch, pain, temperature. Chewing (mastication) muscles.
Mixed Nerve
Branches: Opthalmic, maxillary, mandibular
Largest Nerve
Cranial Nerve 6
Abducens
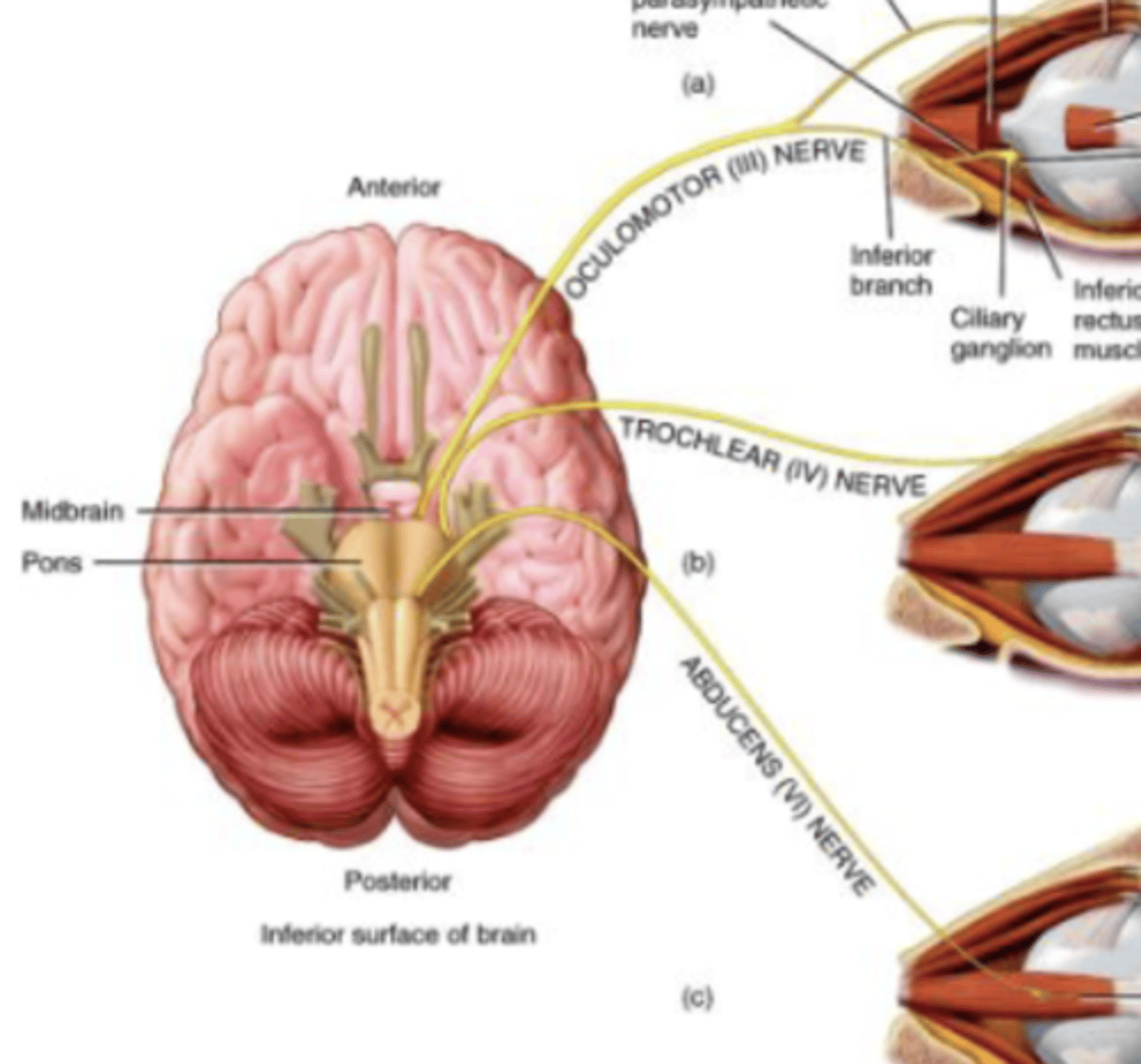
Abducens (VI) Nerve
Abduction of eyeball
Motor nerve
Originates from pons
Cranial Nerve 7
Facial
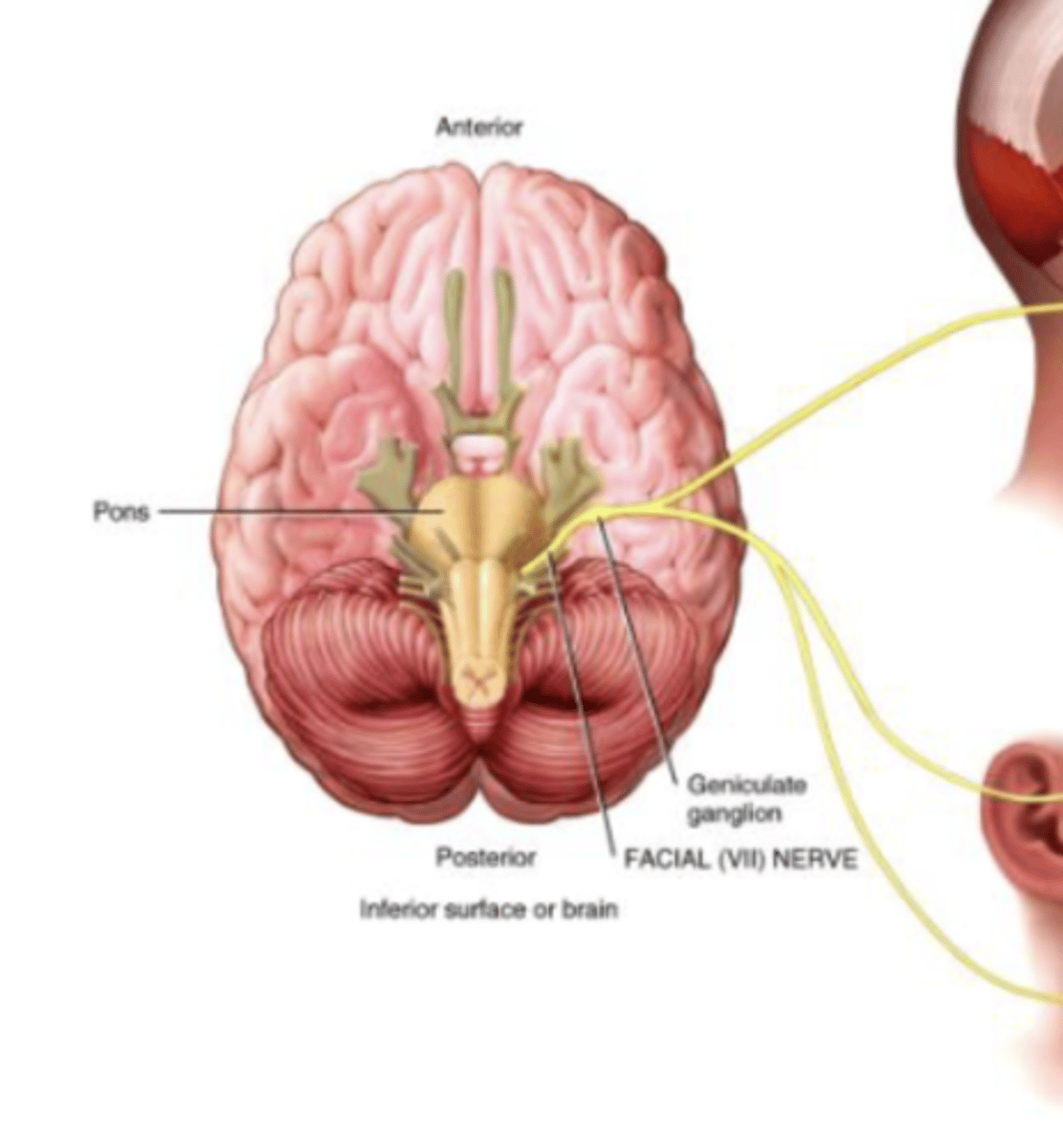
Facial (VII) Nerve
Sensory: Taste
Motor: Facial Expression
Mixed Nerve
Cranial Nerve 8
Vestibulocochlear
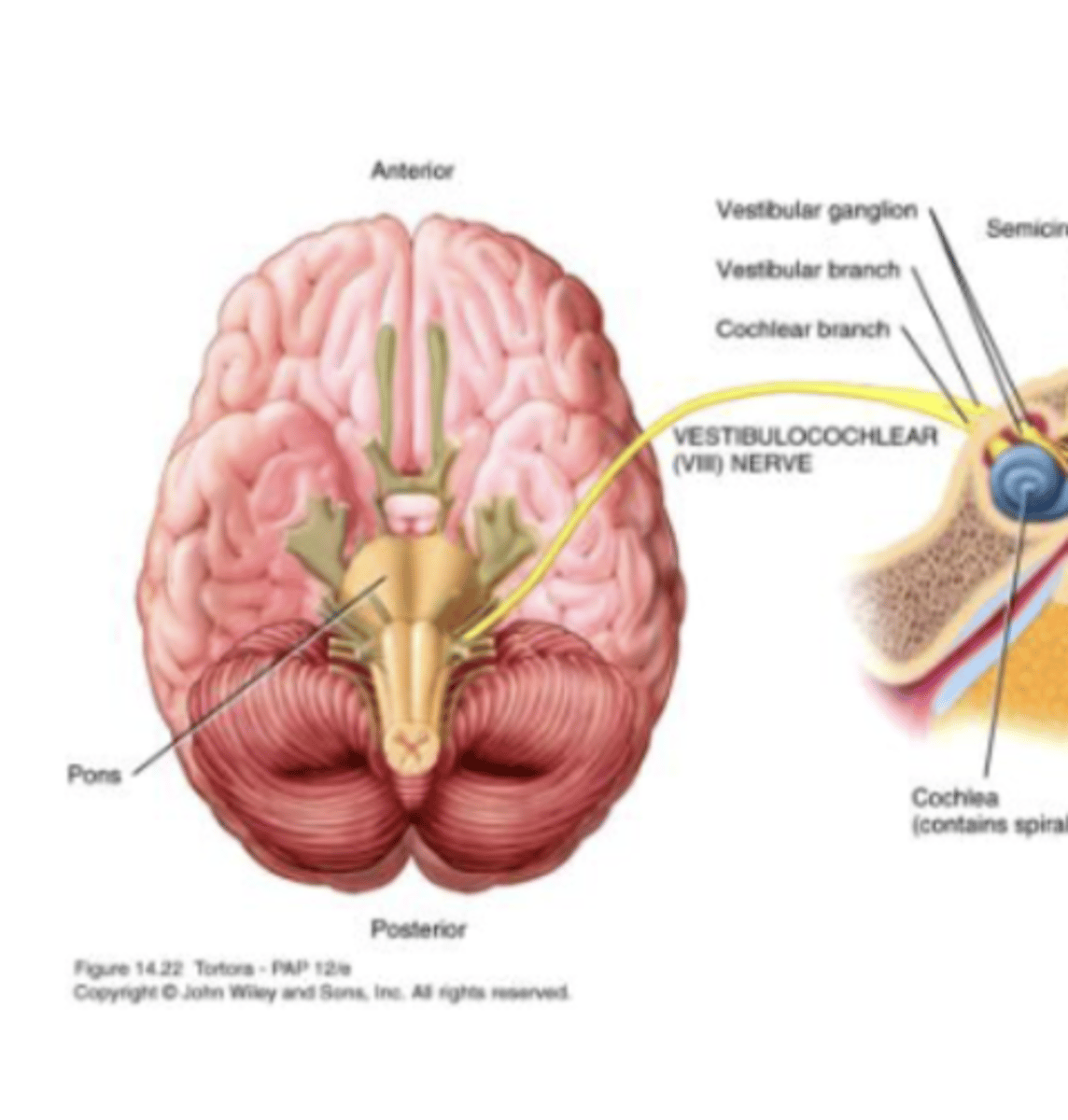
Vestibulocochlear (VIII) Nerve
Vestibular branch: equilibrium
Cochlear branch: hearing
Sensory Nerve
Originates in inner ear
Cranial Nerve 9
Glossopharyngeal
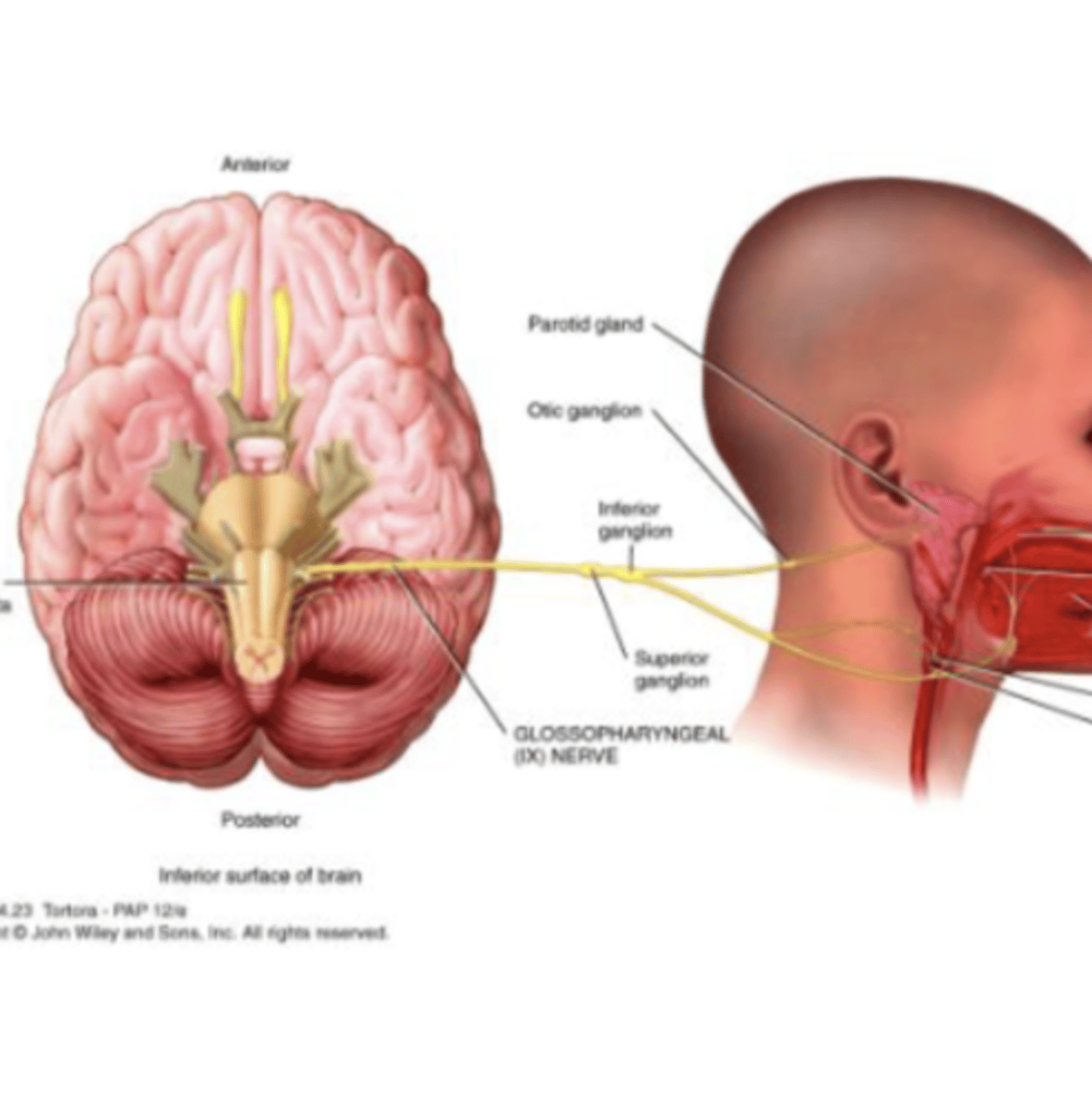
Glossopharyngeal (IX) Nerve
Sensory: Taste
Motor: Saliva
Mixed Nerve
Cranial Nerve 10
Vagus
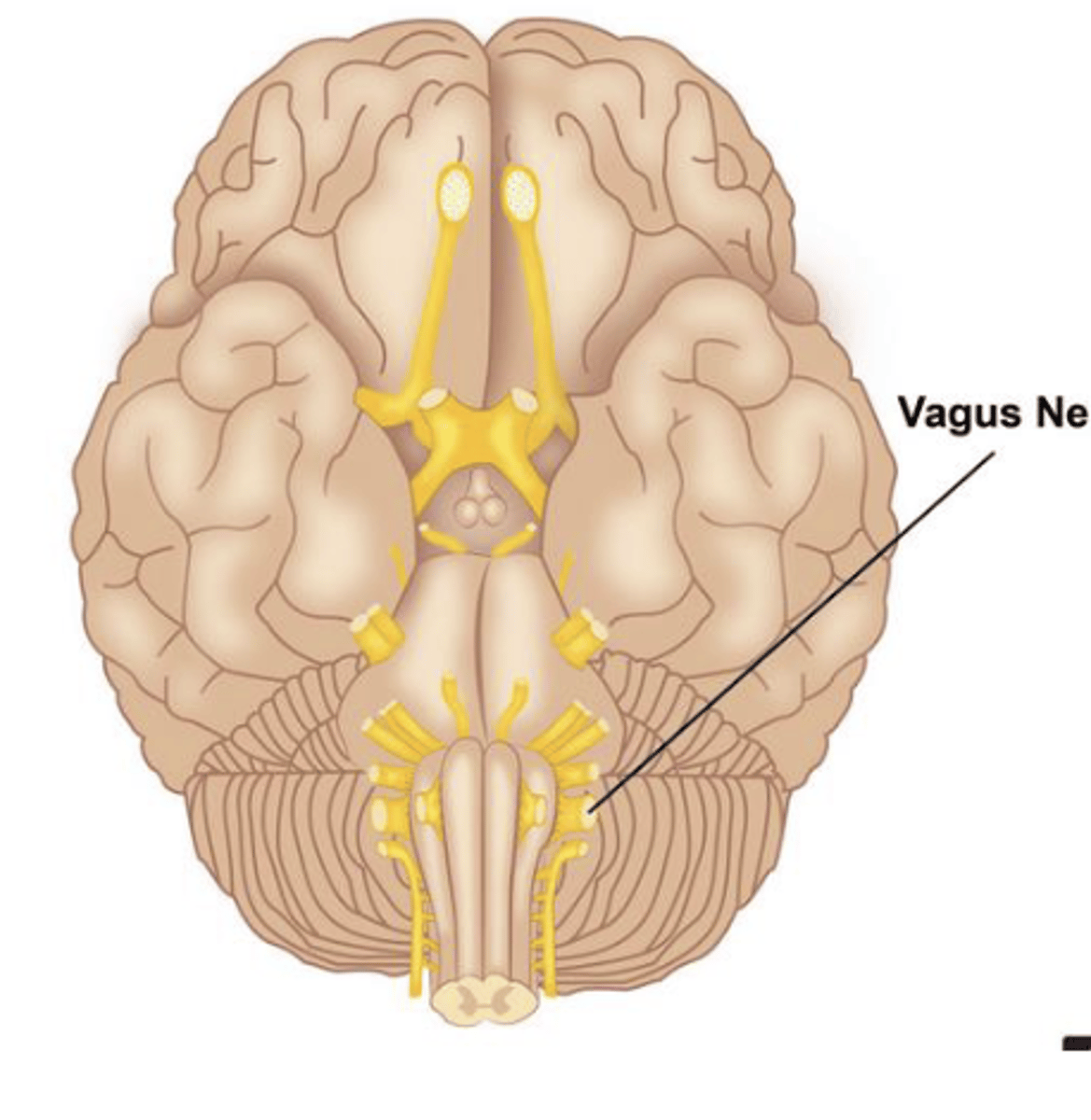
Vagus (X) Nerve
Sensory: proprioception (where we are in space), stretching
Motor: swallowing, vocalization
Mixed Nerve
Main nerve of Parasympathetic Nervous System (rest/digest)
Cranial Nerve 11
Spinal Accessory Nerve
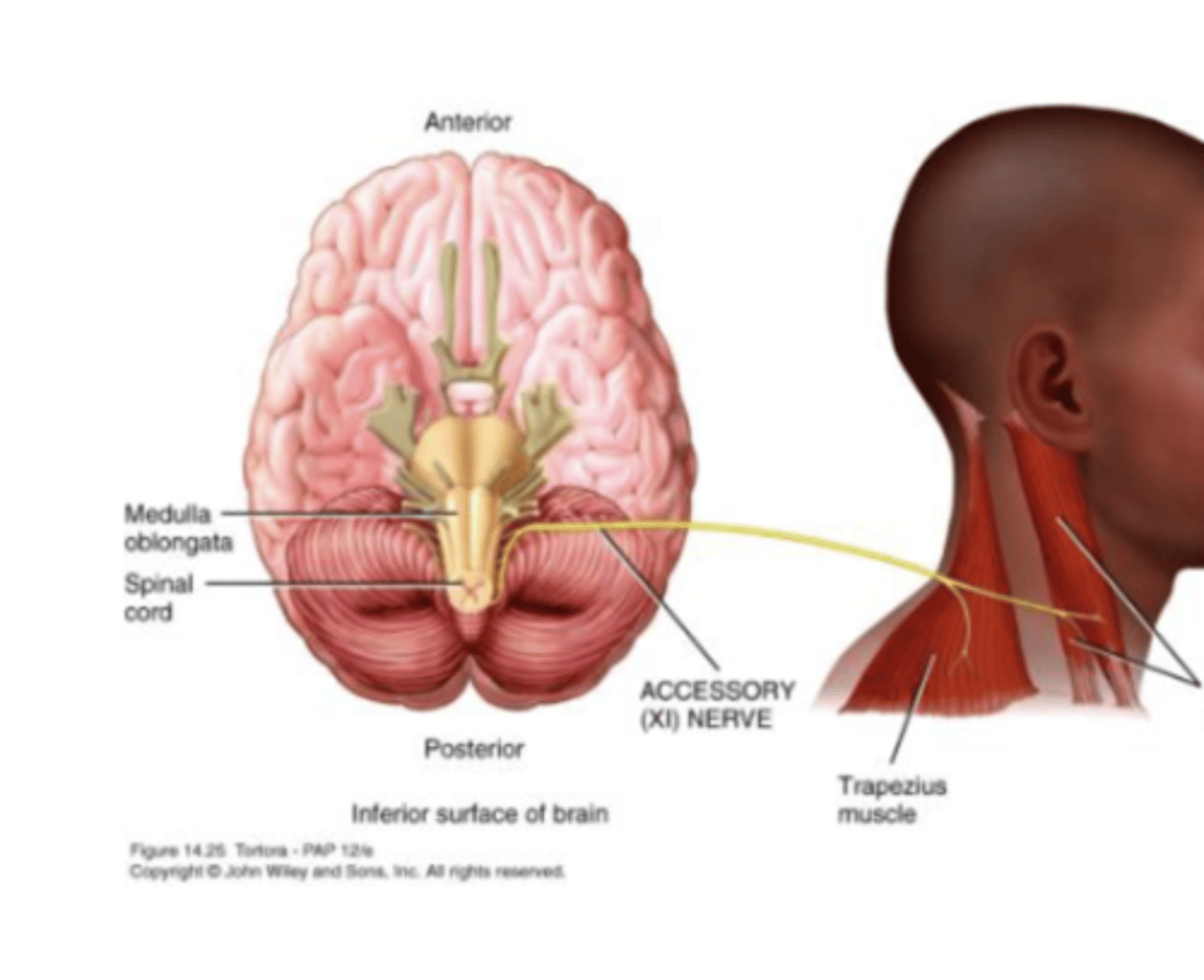
Spinal Accessory (XI) Nerve
Supplies Sternocleidomastoid and Trapezius
Motor Nerve
Cranial Nerve 12
Hypoglossal
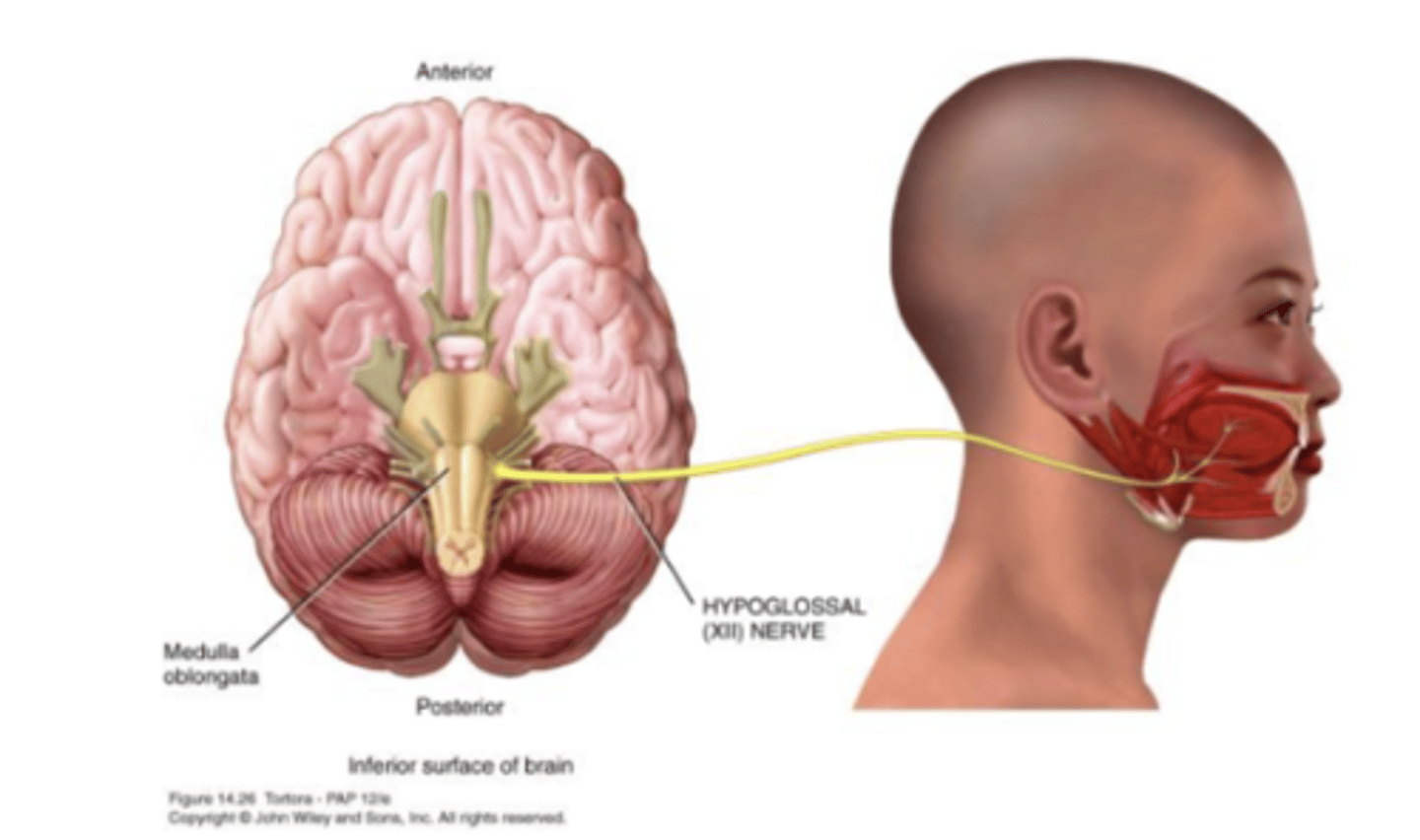
Hypglossal (XII) Nerve
Speech and swallowing
Motor Nerve
Cranial Nerve Map
Resting Membrane Potential (RMP)
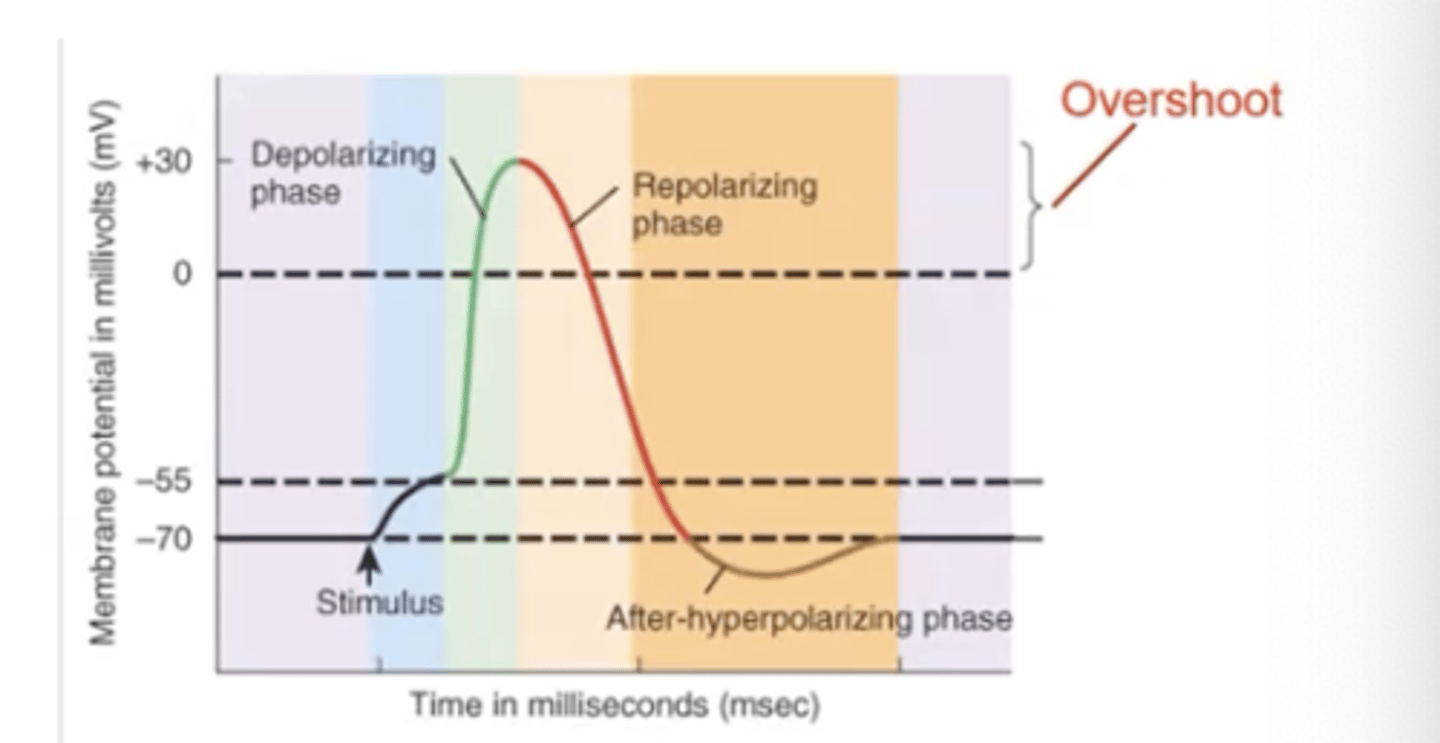
- Accumulation of negative ions inside the cell (cytosol), and positive ions outside the cell (extracellular fluid)
- RMP: Negative charge difference inside compared to outside: -70mV (maintained by Na/K pump
- Changes in membrane potential occur when ion gates in the membrane open, permitting ions to move from one side to the other
If membrane potential becomes less negative (by 15-20 mV) then it reaches the threshold and it results in an action potential
*Threshold value is -55. If we become more positive (-55), it is considered a meaningful change = action potential
Graded Potentials
small, localized deviations from the RMP of -70mV
Characteristics:
- vary in amplitude
- localized
- depend upon the strength of the stimulus
- occur most often in the dendrites and cell body of a neuron
Graded Potentials: the amplitude of a graded potential depends on the...
stimulus strength
Graded Potentials: Shifts in Membrane Potential
Polarization/
Hyperpolarization: membrane potential becoming more negative
Depolarization: becoming less negative (more positive)
EPSP: Excitatory Postsynaptic Potential
- excitatory
- depolarizing (Na influx)
- one doesn't usually initiate a nerve impulse (aka graded potential, takes more than 1)
IPSP: Inhibitory Postsynaptic Potential
- inhibitory
- hyperpolarizing (K outflux)
- makes harder to generate action potential
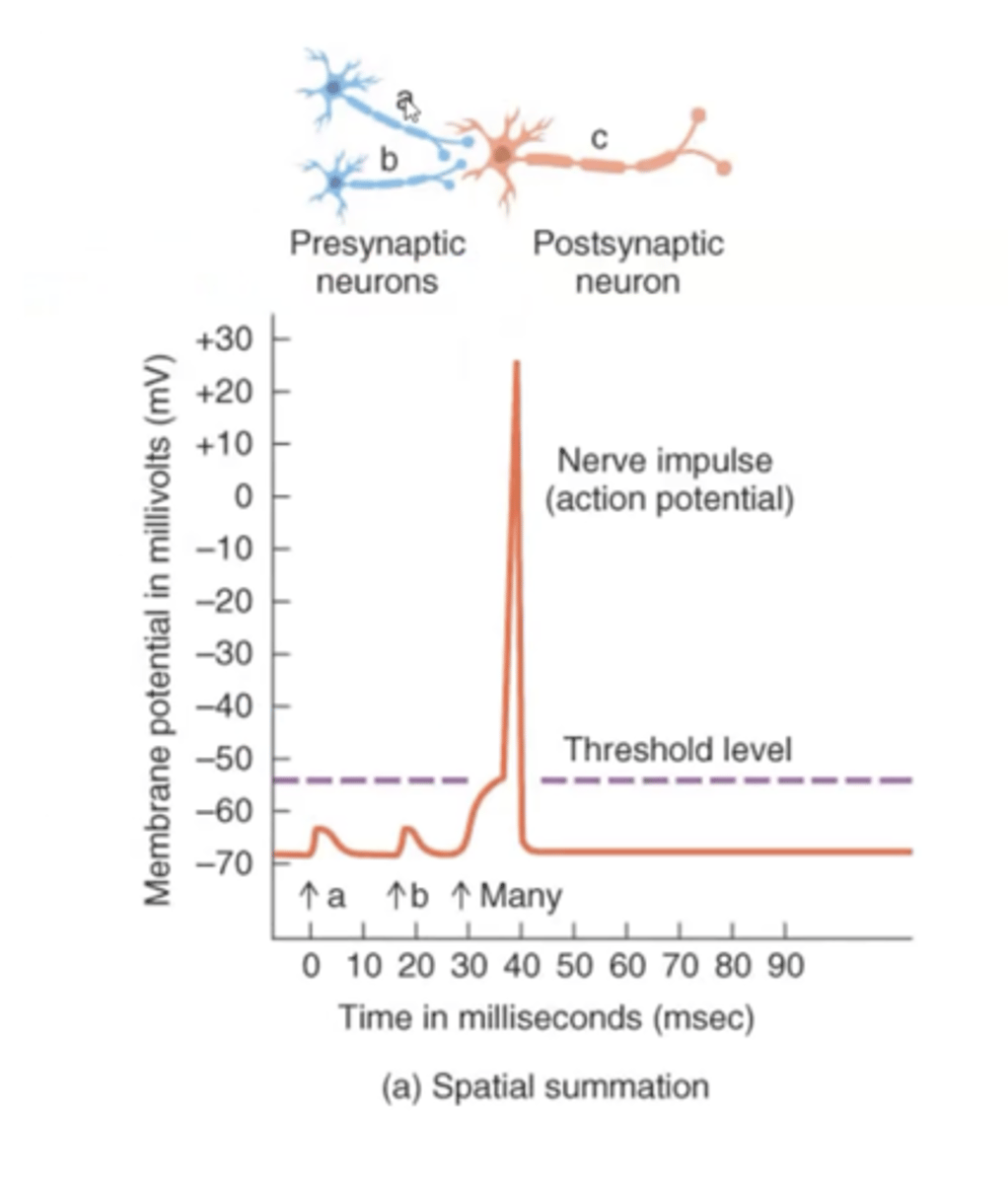
Summation
effects of presynaptic neurons may be combined to generate a nerve impulse
Integrator
postsynaptic neuron that recieves and integrates signals, then responds
Summation may be:
1. Spatial
2. Temporal
Spatial Summation
neurotransmitters released from several presynaptic end bulbs onto 1 postsynaptic neuron
"space" issue
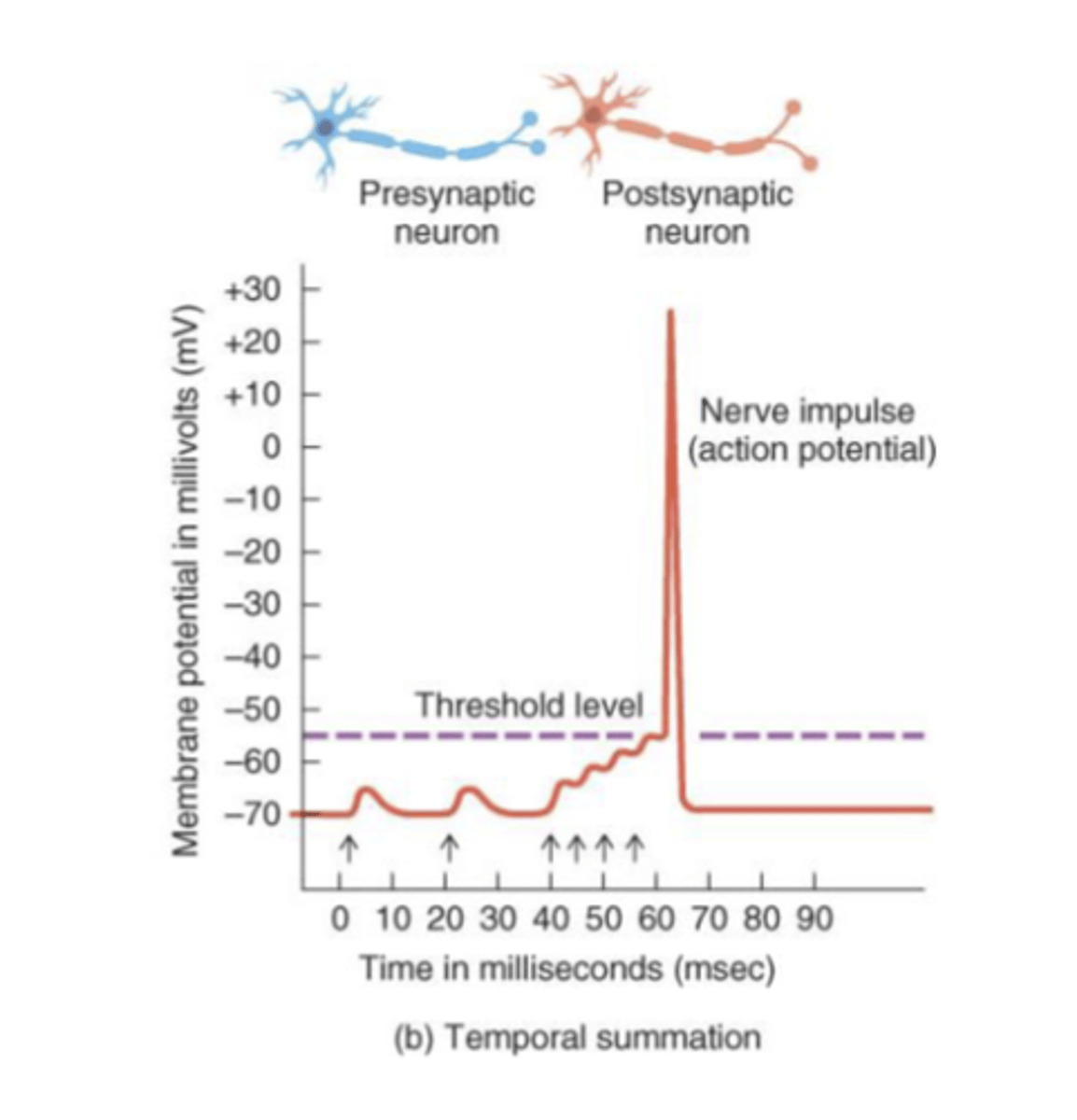
Temporal Summation
neurotransmitters released from 2 or more firings of the same end bulb in rapid succession onto a neuron
"time" issue
What is an Action Potential?
1. "Sequence of rapidly occuring events that starts with depolarization (rushing in of Na) and then restore it to the resting state (repolarization, with outflux of K)"
2. Rapid, transient change in started with depolarization
3. Starts as graded potential in response to stimuli
4. Requires depolarization of the membrane
5. Once threshold is met, the all or none principle applies
Events during AP:
1. Resting state (RMP)
2. Depolarization
3. Propagation of an action potential
4. Repolarization
5. Return to the resting state with help from the Na/K pump
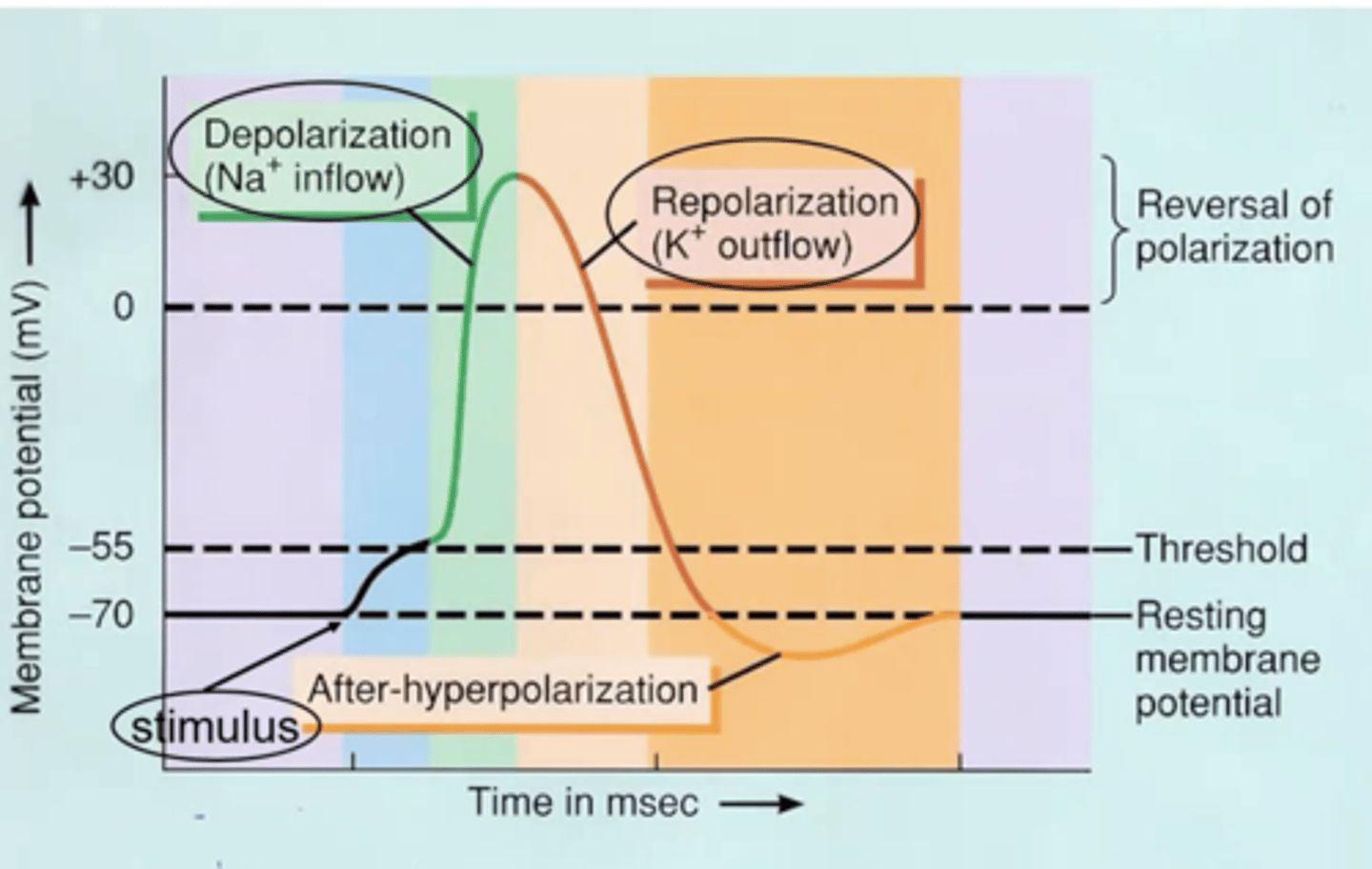
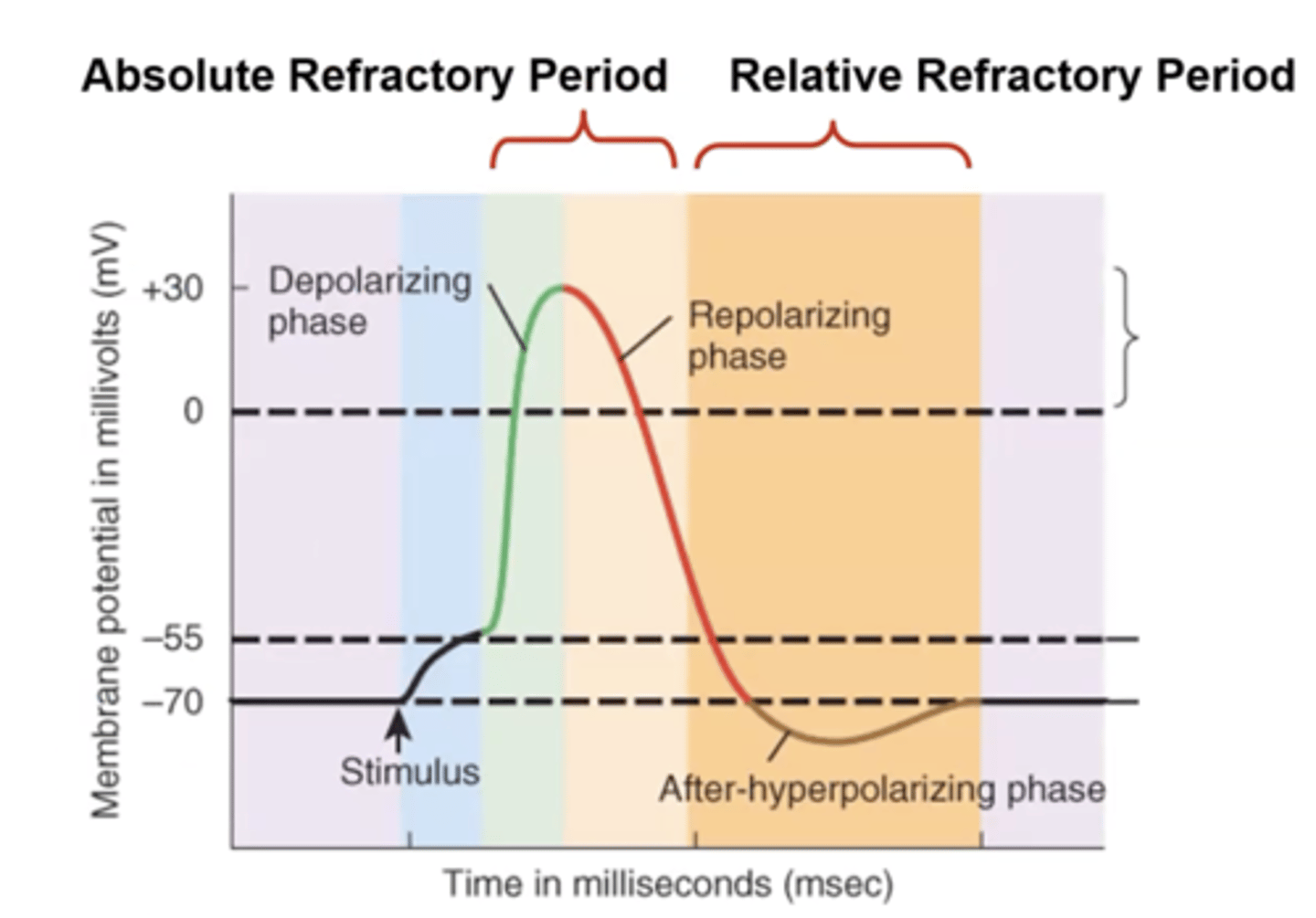
Depolarizing Phase
- Upstroke
- Stimulus causes a graded potential to reach at least 55mV or threshold
- Voltage-gated Na+ channels open & Na+ rushes into cell
- Gate closes again in few ten-thousandths of second
- Positive feedback process
Action Potential Propagation (Spreading)
- Spreads over cell surface without dying
- Na+ flows in during depolarization, the voltage of adjacent areas is affected and their voltage-gated Na+ channels open
- Self-propagates along the membrane
- Traveling action potential is called a nerve impulse
Action Potential Conduction Velocity: Depends on...
Diameter of nerve fiber (larger=faster)
Myelination of fibers
Nerves (motor=fast, sensory=slow)
Temperature (higher=faster)
*Not related to stimulus strength
Continuous Conduction
slow conduction that occurs in nonmyelinated axons
Saltatory Conduction
Rapid transmission of a nerve impulse along an axon, resulting from the action potential jumping from one node of Ranvier to another, skipping the myelin-sheathed regions of membrane.
Repolarizing Phase
- Downstroke
- When threshold is reached, voltage-gated K+ channels open
- K+ channels open much slower than Na+ channels
- K+ outflow returns membrane potential back to -70mV
- If enough K+ leaves cell it reaches a -90mV membrane potential (hyperpolarization)
All-or-none principle
if a stimulus reaches threshold, the action potential is always the same
*A stronger stimulus will not cause a larger impulse
Amplitude
change from RMP
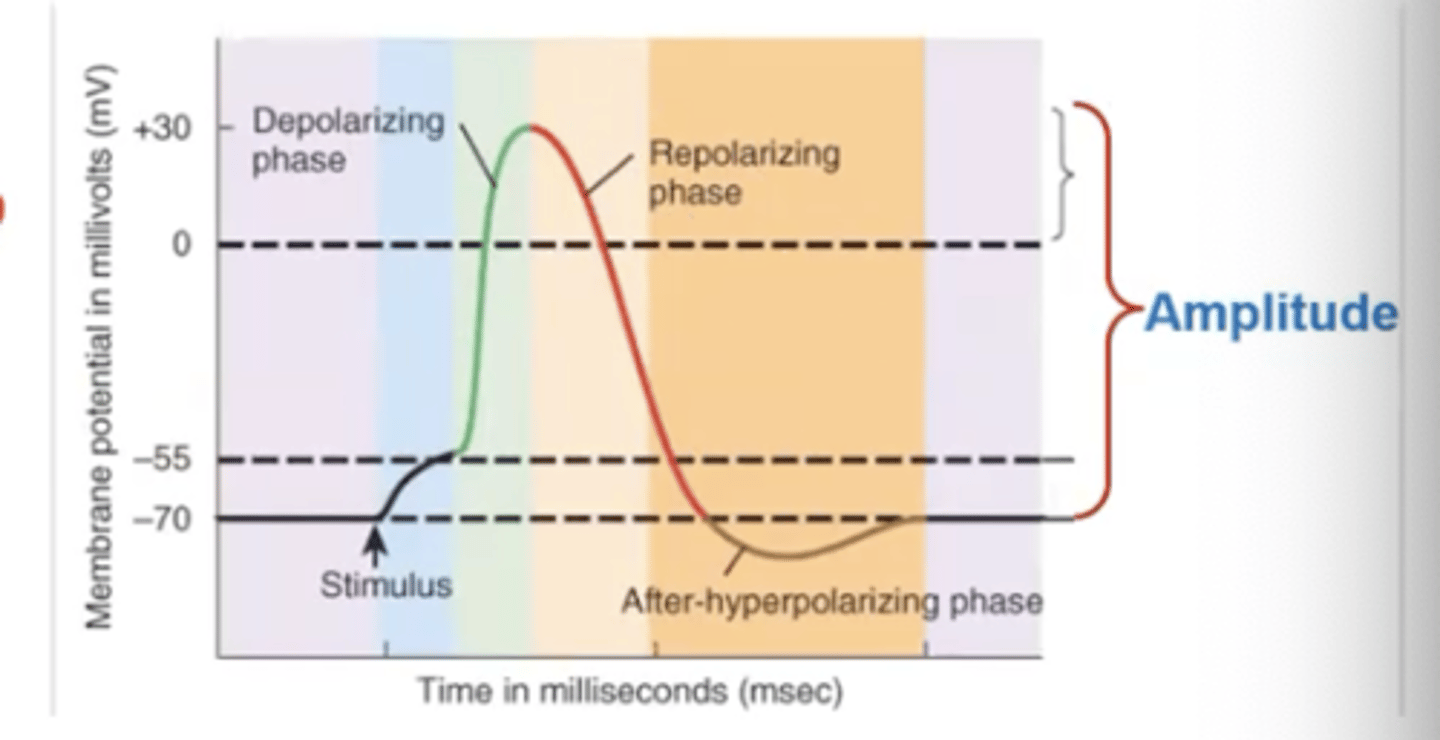
Overshoot
change from zero
Absolute refractory period
- even a very strong stimulus cannot initiate a second action potential
- inactivated Na+ channels cannot open
"Absolutely no way to have another AP"