Topic 2.4 - Properties of Period 3 Elements and their Oxides
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
Appearance and physical
properties of sodium?
Metallic, shiny, conducts electricity (worst
conductor out of the metals)
Reaction of sodium with
acid?
Na + acid → H 2 + salt
Reaction of sodium with
cold water - equation and
observations?
Vigorous reaction, floats on water, fizzes, melts
due to -ΔH of the reaction. NaOH is pH 13-14.
2Na + 2H 2
O → 2NaOH + H 2
Reaction of sodium with
oxygen (equation and
observations)?
Bright yellow flame, forms white powder of Na 2
O
2Na + ½ O 2 → Na 2
O
Appearance and physical
properties of magnesium?
Metallic, shiny, conducts electricity (between Na
and Al in terms of how well it does).
Reaction of Mg with cold
water (observations and
equation)?
Very slow reaction. pH = 10 as Mg(OH) 2 is
sparingly soluble
Mg + 2H 2
O → H 2 + Mg(OH) 2
Reaction of Mg with steam
(observations and
equation)?
Much faster.
Mg + H 2 O → MgO + H 2
Reaction of Mg with oxygen
(observations and
equation)?
Bright white flame, forms white powder of MgO
2Mg + O 2 → 2MgO
Appearance and physical
properties of aluminium?
Metallic, shiny, best conductor of
electricity in period 3
Reaction of Al with cold
water?
no reaction
Reaction of Al with oxygen
(equation and
observations)?
Heat and lower into jar of O 2 → bright flame,
forms white powder.
4Al + 3O 2 → 2Al 2
O 3
Why is aluminium
considered unreactive even
though the metal itself is
reactive?
Covered by Al 2 O 3 from where oxygen has oxidised the
surface of the Al. Al 2 O 3 is unreactive. Makes it useful for
saucepans, window frames etc.
If Al 2 O 3 is scratched off, Al reacts rapidly with air to form a
new coat.
Appearance and physical
properties of silicon?
Semimetal (metalloid), semiconductor (conducts electricity to an extent and in certain conditions)
Reaction of silicon with
oxygen (observations and
equation)?
Heat strongly
Si + O 2 → SiO 2 (white powder)
Appearance and physical
properties of phosphorus?
Non-metal, low m.p. And b.p., does not conduct
electricity.
Red Phosphorus as a crystal structure
White Phosphorus as P 4
Reaction of phosphorous in
excess oxygen
(observations and
equation)?
Red P needs to be heated significantly first, white
P ignites spontaneously in air
Phosphorus pentoxide (white crystalline solid)
formed
4P + 5O 2 → P 4
O 10
Reaction of phosphorous in
limited oxygen
(observations and
equation)?
Incomplete combustion: colourless liquid
phosphorus trioxide is formed.
4P + 3O 2 → P 4
O 6
Appearance and physical
properties of sulfur?
Non-metal, low mp and bp, does not conduct electricity.
Reaction of sulfur with
oxygen (observations and
equation)?
Need to heat and lower into a jar of oxygen.
Colourless gas sulfur dioxide formed. Some SO 3
also formed.
S + O 2 → SO
What are the different types
of structure and bonding
displayed by the period 3
oxides?
Na ionic lattice
Mg ionic lattice
Al ionic lattice with covalent character; Al 3
+ distorts O 2
- electron cloud
Si giant covalent
P simple molecular covalent
S simple molecular covalent
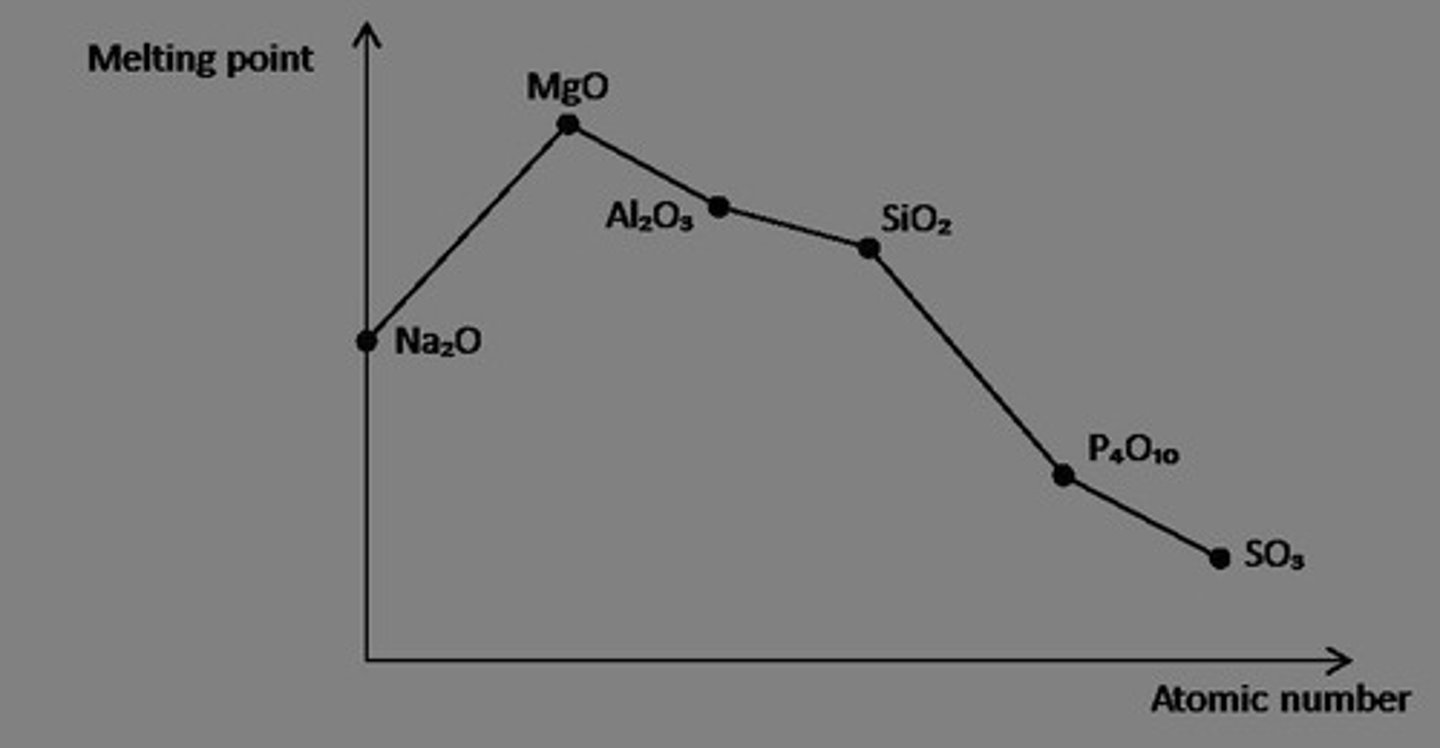
What is the trend in melting
points for period 3 oxides
(state highest and lowest
and why and draw graph)?
Highest is MgO, lowest is SO 2 ;
increases along group for metals for
Na 2 O and MgO due to stronger ionic
bonding, but Al 2 O 3 is lower due to the
covalent character of the bonding.
Decreases with size for simple
molecular molecules
Which period 3 oxides are
basic?
Na2O and MgO
Reaction of Na oxide with
water? pH?
Na2O + H2O → 2Na+ + 2OH-
pH = 14
Reaction of Mg oxide with
water? pH?
MgO + H2O → Mg2+ + 2OH- ⇌ Mg(OH)2 pH = 9-10 as Mg(OH)2 is sparingly soluble
What are the products if
Na 2 O and MgO are reacted
with acid?
Salt and water only
Is aluminium oxide acidic or basic?
It is amphoteric; can act as either an acid or a base
Is aluminium oxide soluble?
not water
Reaction of aluminium oxide
with HCl?
Al2O3 + 6HCl → 3H2O + 2AlCl3
Reaction of aluminium oxide
with NaOH?
Al2O3 + 2NaOH + 3H2O → 2NaAl(OH)4 ; sodium aluminate is formed
Is silicon dioxide soluble in
water?
No
In what conditions will
silicon dioxide act as an
acid?
In what conditions will silicon dioxide act as an acid?
Reacts as a weak acid with a strong
base (e.g. hot, conc NaOH)
Reaction of silicon dioxide
with hot, conc NaOH?
SiO2 + 2NaOH → H2O + Na2SiO3 - sodium silicate
How is silicon dioxide used
in the production of Fe?
SiO 2 + CaO → CaSiO 3 - calcium silicate
Reaction of Phosphorus
pentoxide with water? pH?
P4O10 + 6H2O → 4H3PO4 ; pH = 1-2
Dissociation of the acid
formed (H 3 PO 4 )?
H 3 PO 4 → H + + H 2 PO 4
-
Reaction of P 4 O 10 with
NaOH?
3NaOH + H 3 PO 4 → Na 3 PO 4 + 3H 2 O
Reaction of SO 2 with water?
pH?
SO 2 + H 2
O → H 2
SO 3 ; weak acid → pH = 2-3
Reaction of SO 3 with water?
pH?
SO 3 + H 2 O → H 2 SO 4
strong acid → pH = 0-1
Reaction of SO 2 with
NaOH? (2 stages)
SO 2 + NaOH → NaHSO 3
NaHSO 3 + NaOH → Na 2 SO 3 + H 2 O
How can flue gases be
removed by CaO?
CaO + SO 2 → CaSO 3 (calcium sulfite)
Draw the structure of
H 3 PO 4 ?
How many electrons does P
have in its outer shell in
H 3 PO 4 ?
10
What is the shape and
bonding in PO 4
3- ?
Electrons delocalise to give tetrahedral structure
with 109.5 o bond angle. Each P-O bond is the
same length
Draw the structure and
bonding of H 2 SO 4 ?
What is the structure,
bonding and shape of
SO 4
2- ?
Electrons delocalise → tetrahedral with 109.5 o
bond angle. Each S-O bond is the same
What is the structure,
bonding and shape of
SO 3
2- ?
Bond angle = 106 o (trigonal pyramid shape),
each S-O bond is the same, S has one lone pair
of electrons.
Uses of MgO?
Additive for cattle feed
How useful is Al 2 O 3 ?
Oxide layer on Aluminium makes it very useful as
it is unreactive and returns quickly if it is
scratched off
Uses of SO 2 ?
Reactant in contact process (making H 2
SO 4
)
Would Lithium oxide or
sodium oxide have a higher
melting point? Why?
Li 2
O has a higher m.p., since Li + is a smaller ion
than Na + , so the O 2- and Li + charge centres are
closer together and there is a greater
electrostatic force of attraction between the
oppositely charged ions.