The National Grid
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
What is the national grid?
The infrastructure used to transport electricity across the UK from the power stations where its produced to the consumers using a network of cables and transformers
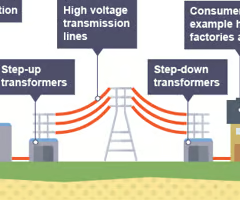
What are the component parts of the National Grid?
Power Station -> Step up transformer -> Overhead cables -> Step down transformers -> Consumers
What does the power station do?
Transfers the energy generated by resources into electrical energy.
What do step-up transformers do?
Step-up transformers increase the voltage and decrease the current. They do this to minimise the amount of energy lost in distribution because a high current results in wires heating up and thermal energy being lost to the surroundings.
What are the overhead cables for?
The overhead cables are to transport the electrical energy to the next part of the grid.
What do step-down transformers do?
Step-down transformers decrease the voltage and increase the current. This is to ensure the voltage is at a useable safe level.
How does demand work?
Throughout the day electricity usage (demand) changes. Power stations have to produce enough electricity for everyone to have it when they need it. The minimum demand over a period of time is called the base load.
Main factors affecting demand on the supply of electricity are..
Time of day
Weather
Seasons
How does the National Grid meet demand?
Some power stations have a short start up time so that they can quickly respond to changes in demand. Power stations also run at well below their maximum power output so that if demand increases and another power station stops working there is spare capacity to cope
Is it reliable?
The National Grid is very reliable in that there are multiple power stations to fill in if something goes wrong. There are many smaller ones kept for times when bigger power stations shut down.
What about if theres not enough/too much energy?
If there's not enough, extra energy will be imported from other countries. If theres too much, we will export our energy to them.