Bio-Energy Notes
1/48
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Photosynthesis is the process..
in which green plants
use the energy of sunlight to convert water and
carbon dioxide into glucose (sugar) and oxygen.
6CO2 + 6H2O C6H12O6 + 6O2
carbon dioxide + water light——>sugars + oxygen
Autotrophs
Autotrophs are organisms that can make
their own food and sustain themselves without eating
other organisms
Plants, algae, certain other protists, and some prokaryotes
(bacteria) are autotrophs
Photoautotrophs…
are autotrophs that produce food using
light energy (photosynthesis)
Chloroplasts
Chloroplasts are concentrated in the cells of the mesophyll, the
green tissue in the interior of the leaf
Carbon dioxide enters the leaf and oxygen exits through pores called
stomata (singular—stoma).
Water absorbed by the roots is delivered to the leaves in veins
Chloroplast innermembrane
The inner membrane surround a
space filled with thick fluid called
stroma
Sugars are made from carbon
dioxide and water in the stroma
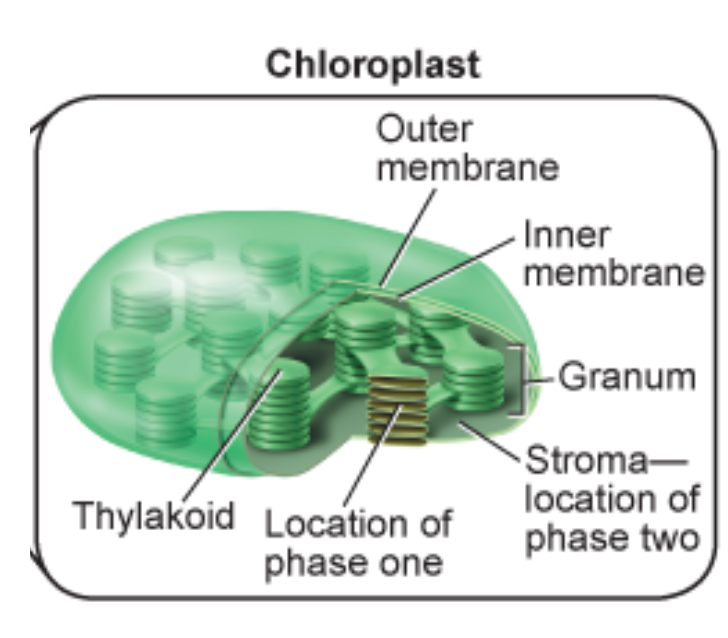
Inside the stroma are thylakoids,
which are..
flattened disc-shaped sacs.
The membranes of the thylakoid
contain chlorophyll molecules
that capture light energy.
Thylkaoids are stacked together into
stacks called grana
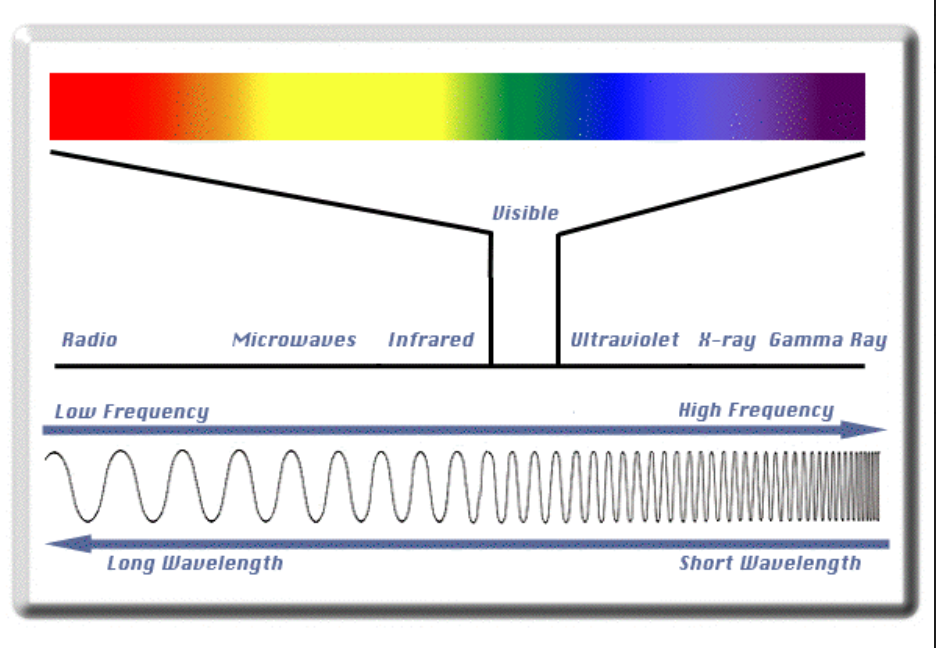
(Sunlight)Electromagnetic Energy
Light energy travels in waves and the distance between the crests of
two adjacent waves are called wavelength
Some light waves are shorter and have more
energy (violet waves), and other lights are longer and
have less energy (red
waves)
Pigments
light-absorbing molecules inside the thylakoid membrane
Pigments absorb some wavelengths of light and reflect/transmit
other wavelength
Different pigments absorb light of different wavelengths
Chlorophyll a
absorbs mainly blue-violet and red light and reflects
green light
Chlorophyll b
absorbs mainly blue and orange light and reflects
yellow-green
Photosynthesis light-dependent reactions
The light-dependent reactions take place within the thylakoid
and traps sunlight energy
Photosynthesis light-independent reactions (Calvin cycle)
The Calvin cycle takes place in the stroma and produces
high-energy sugars from carbon dioxide
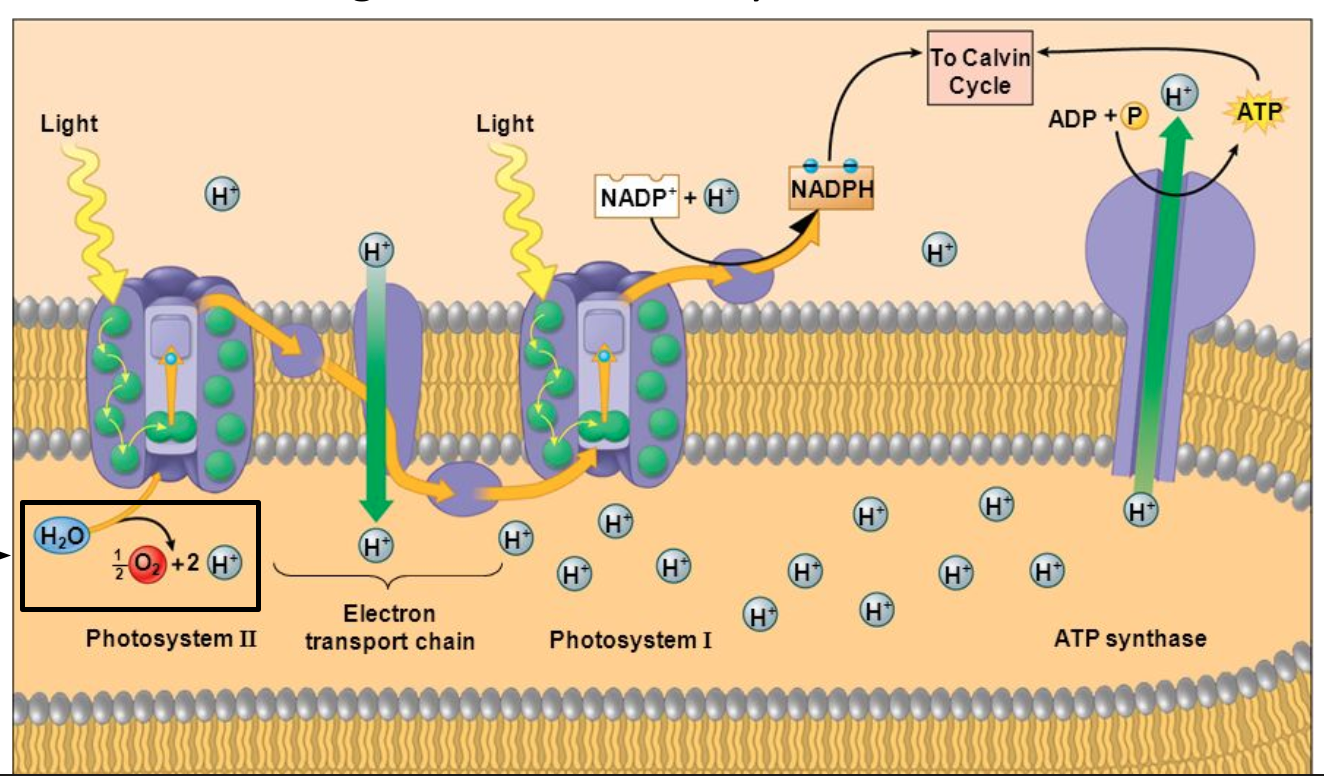
Photosynthesis Phase 1: Light Reactions
The absorption of light is the first
step in photosynthesis.
Chloroplasts capture light energy
and converts it to chemical
energy and produces O2 gas as a
waste product
Water molecules are split to
create O2 gas
ATP and an electron carrier
called NADPH are also created
The light reactions occurs in the
thylakoid membrane
Photosystems
In the thylakoid membrane, chlorophyll and other pigments and
proteins are arranged into clusters called photosystems
Photosystem I and Photosystem II
Light energy is absorbed by the photosystems, which excites the
electrons of chlorophyll molecules
The electrons are then passed down an electron transport chain and
then to an electron carrier called NADPH
NADPH will bring these electrons to the Calvin cycle
Water & ATP
As electrons are being passed down, water is split into oxygen and H+ ions
H+ ions diffuse down an enzyme called ATP synthase
ATP synthase phosphorylates ADP to create ATP
ATP is then brought to the Calvin Cycle
Phase 2: Calvin Cycle
Takes place in the stroma of the chloroplast
It takes CO2 from the air and converts it to
glucose.
To do this, it uses the energy in ATP and the
electrons in NADPH (which were both made
in the Light Reactions)
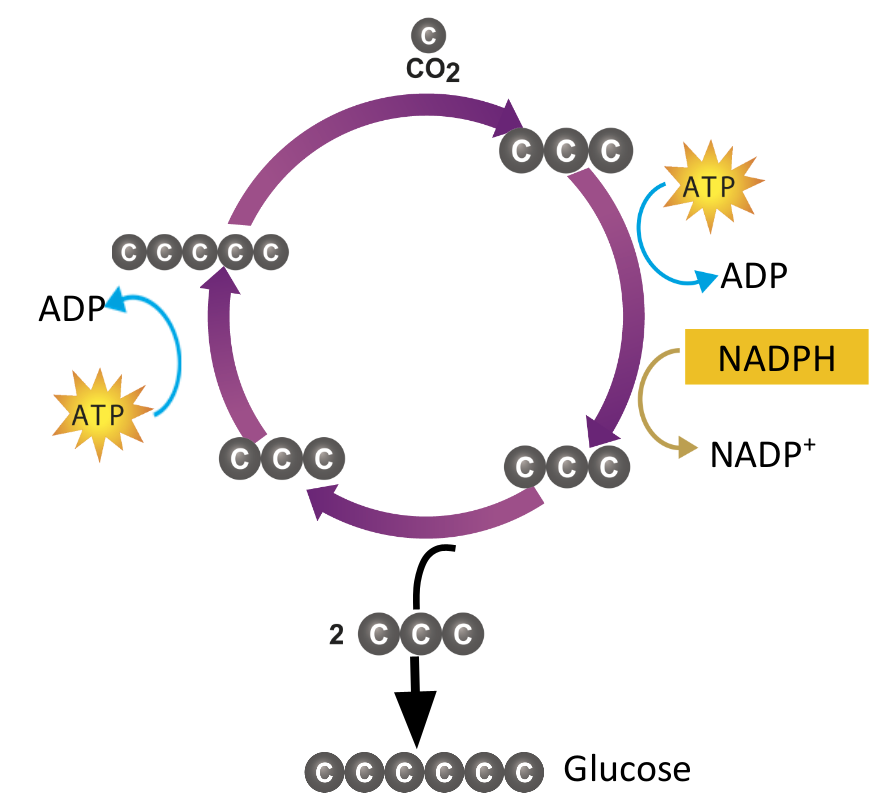
The 1st sets of photosynthetic reactions work together
The light-dependent reactions trap sunlight energy in chemical form
(ATP & NADPH)
The 2nd sets of photosynthetic reactions work together
The light-independent reactions use that chemical energy to
produce high-energy sugars (glucose) from carbon dioxide.
C4 Plants
C4 Pathway helps plants maintain photosynthesis while
minimizing water loss
Keep their stomata closed during hot days, but can still
keep CO2 levels high to do photosynthesis
Ex: Sugarcane and Corn
CAM Plants
CO2 enters leaves only at night when it’s much cooler
Then, photosynthesis is completed during the day with
the stomata closed
Ex: Water-conserving plants
that live in deserts and other
places where water is limited
Cactus, Orchids, Pineapple
Cellular Respiration stages:
Glycolysis, the Krebs cycle(Citric acid cycle), Electron Transport Cycle (ETC:Oxidative Phosphorylation)
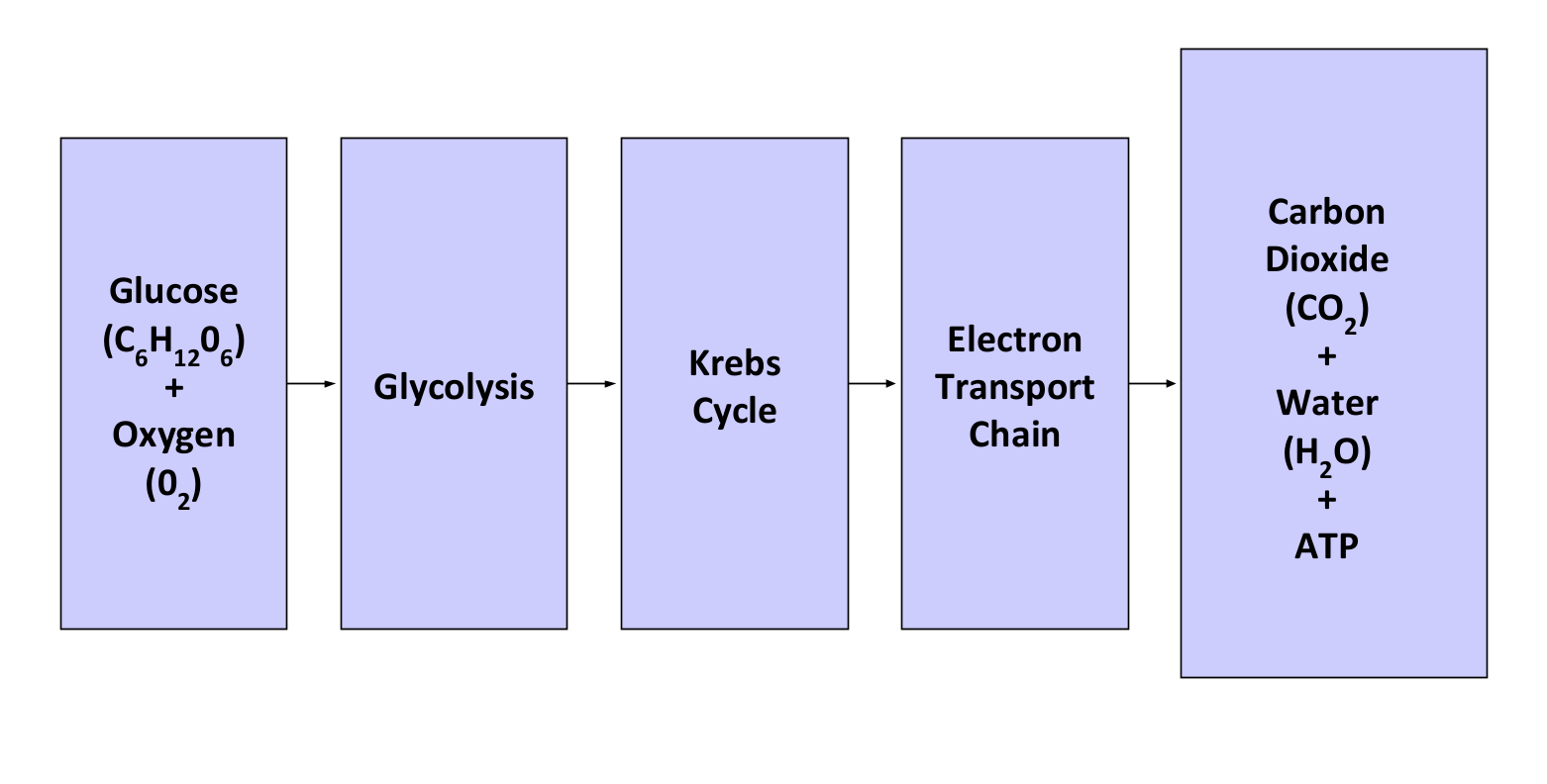
Step 1 of Cellular Respiration:Glycolysis-
an anaerobic process (does not use oxygen).
During glycolysis, glucose is broken down into 2 molecules of pyruvate (pyruvic acid)
Glyco = sugar, Lysis = break down
Glycolysis happens in the cytoplasm of cells.
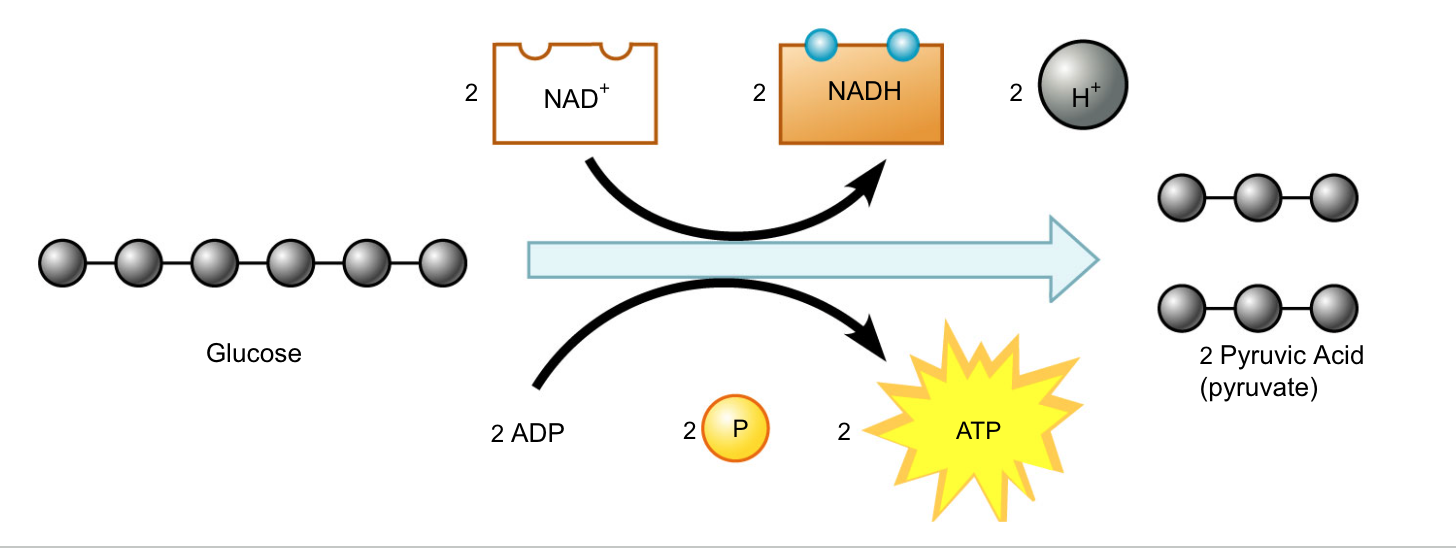
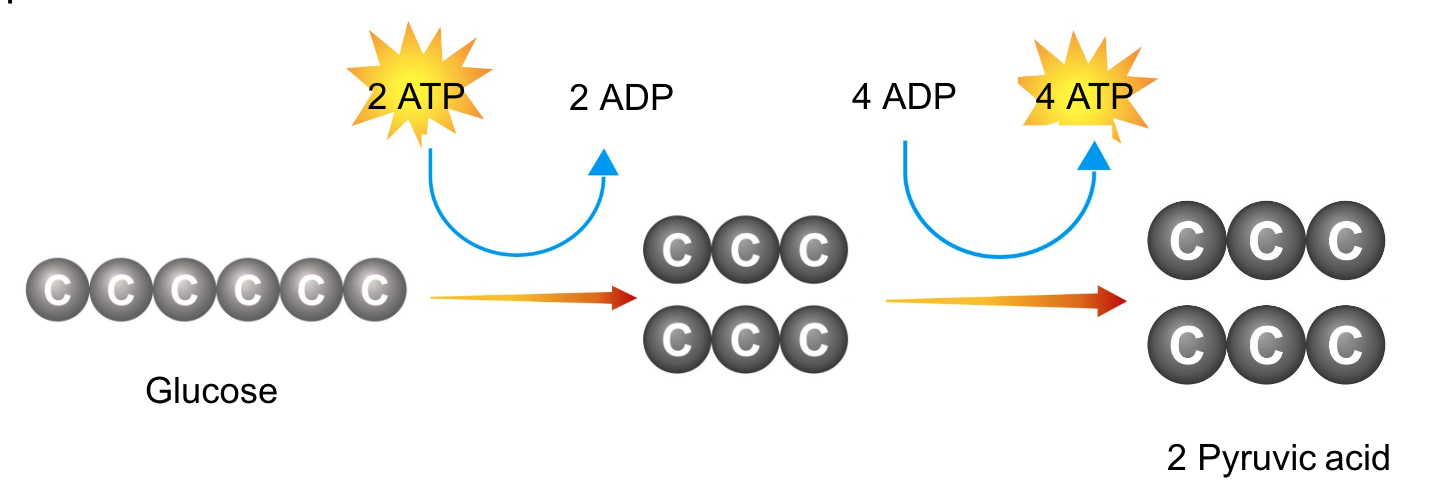
Glycolysis uses….ATP to make … ATP
At the beginning of glycolysis, the cell uses up 2 molecules of ATP to start the reaction.
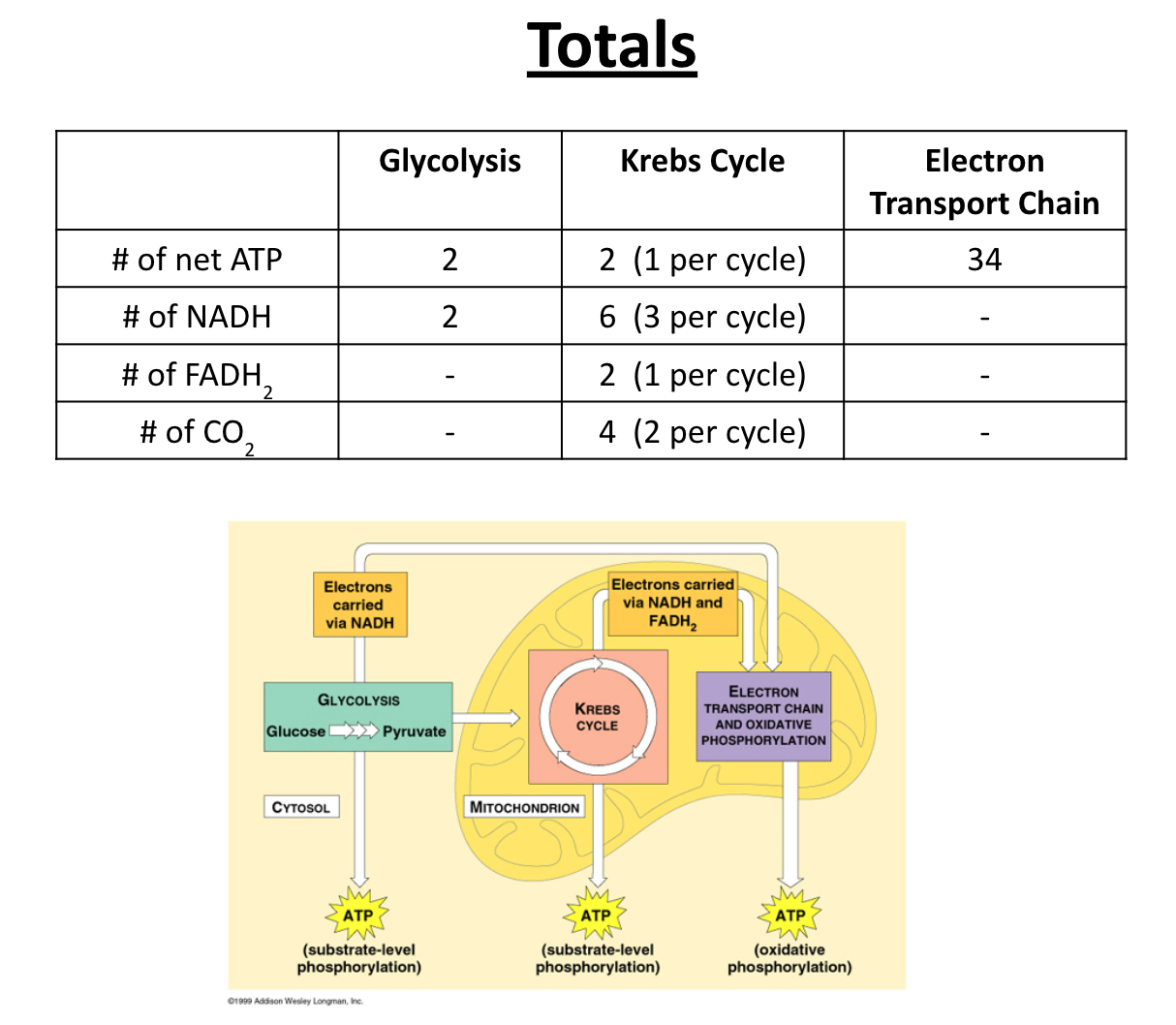
When glycolysis is complete, 4 ATP molecules have been produced.
This gives the cell a net gain of 2 ATP molecules (since 2 ATP were used to help make the pyruvic acid).
This means that glycolysis produces 2 ATP for the cell.
NADH production
Electrons from glucose are given to an electron carrier called NADH, which brings the electrons to the Electron Transport Chain
After glycolysis is finished, it will have produced:
2 ATP (net gain)
2 NADH (carrying high energy electrons)
2 pyruvate (to get ready to enter the Krebs cycle)
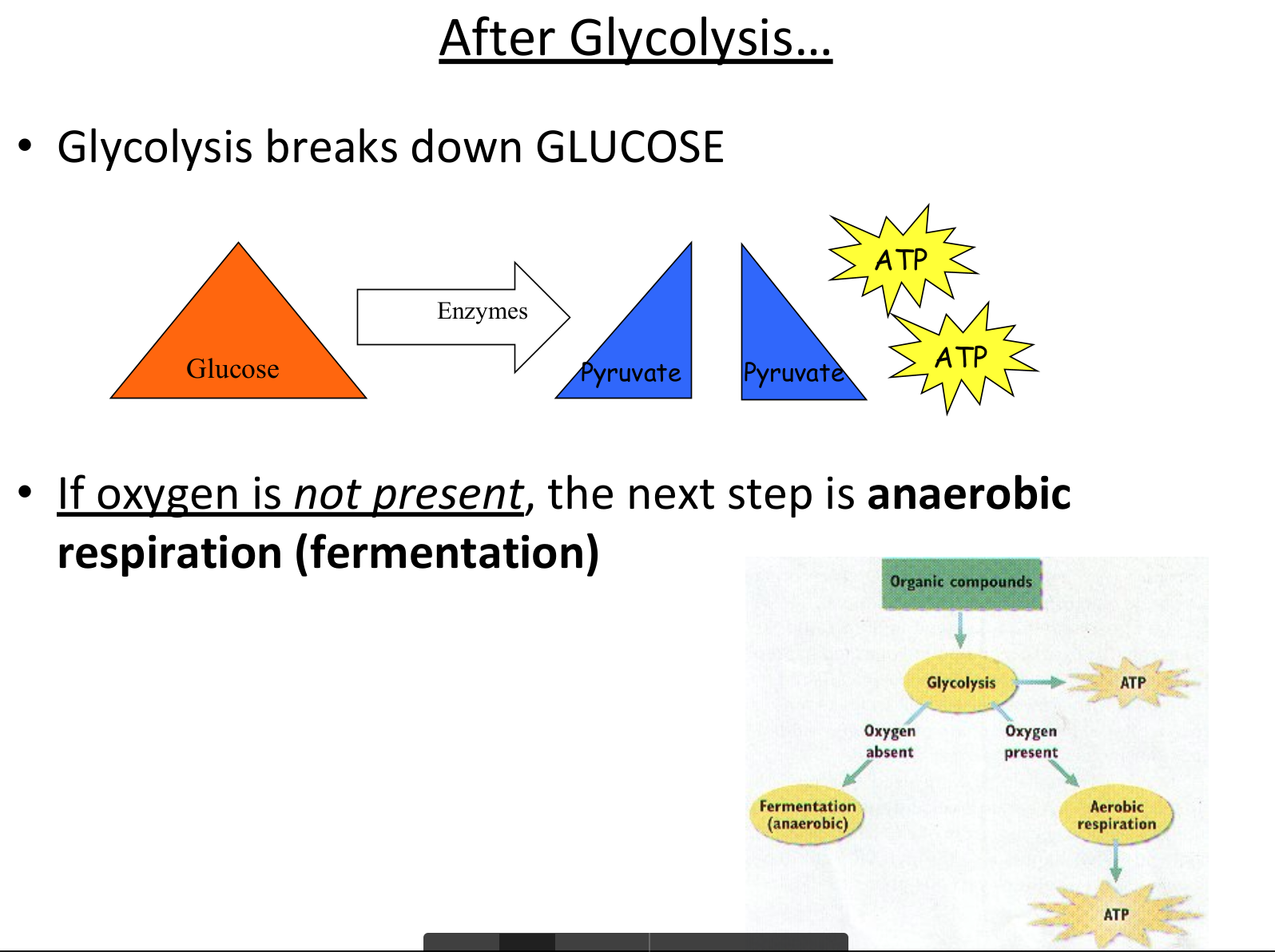
Where does the pyruvic acid and NADH go if oxygen is present?
If oxygen is present, the pyruvic acid molecules get ready to finish cellular respiration and enter the Krebs cycle (aerobic respiration).
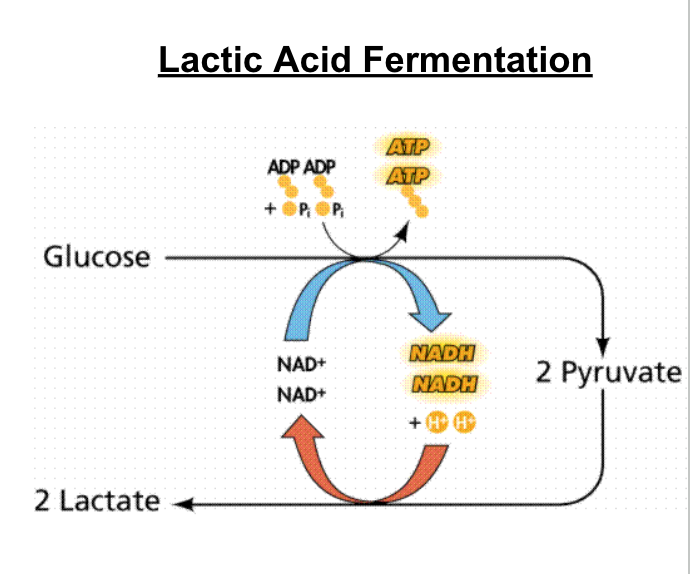
Where does the pyruvic acid and NADH go if oxygen is not present?
If oxygen is absent, the pyruvic acid molecules begin fermentation (anaerobic process)
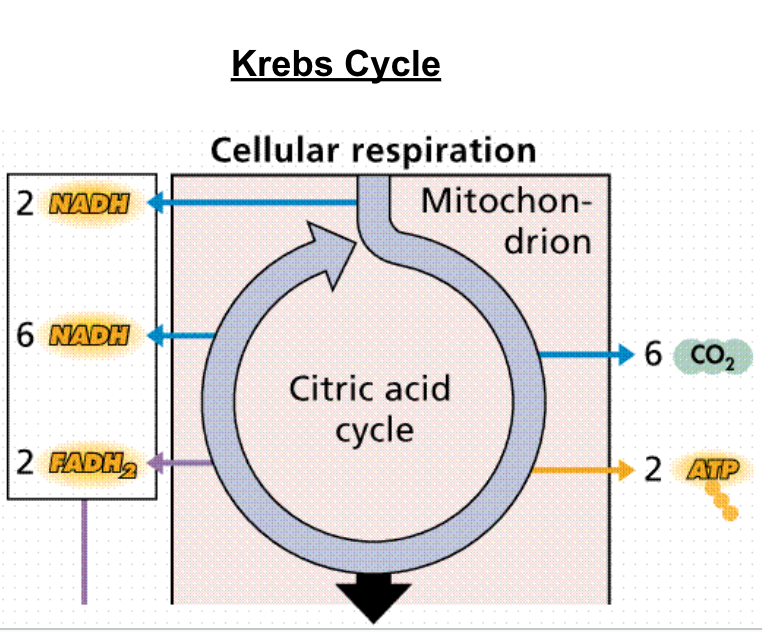
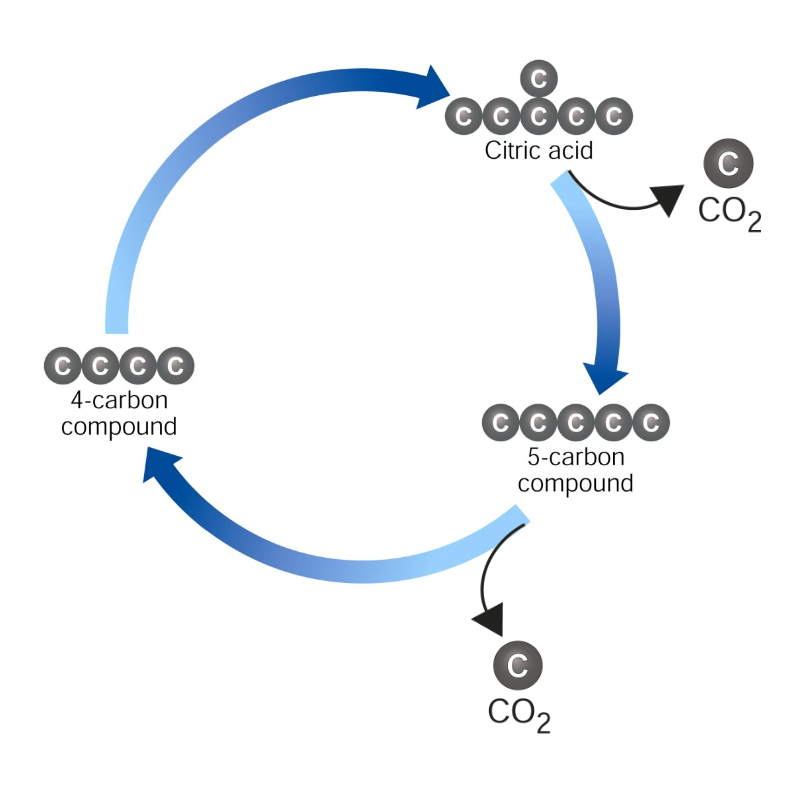
Step 2:The Krebs Cycle
During the Krebs Cycle, the pyruvic acid is broken down into carbon dioxide
The Krebs Cycle occurs in the mitochondrial matrix
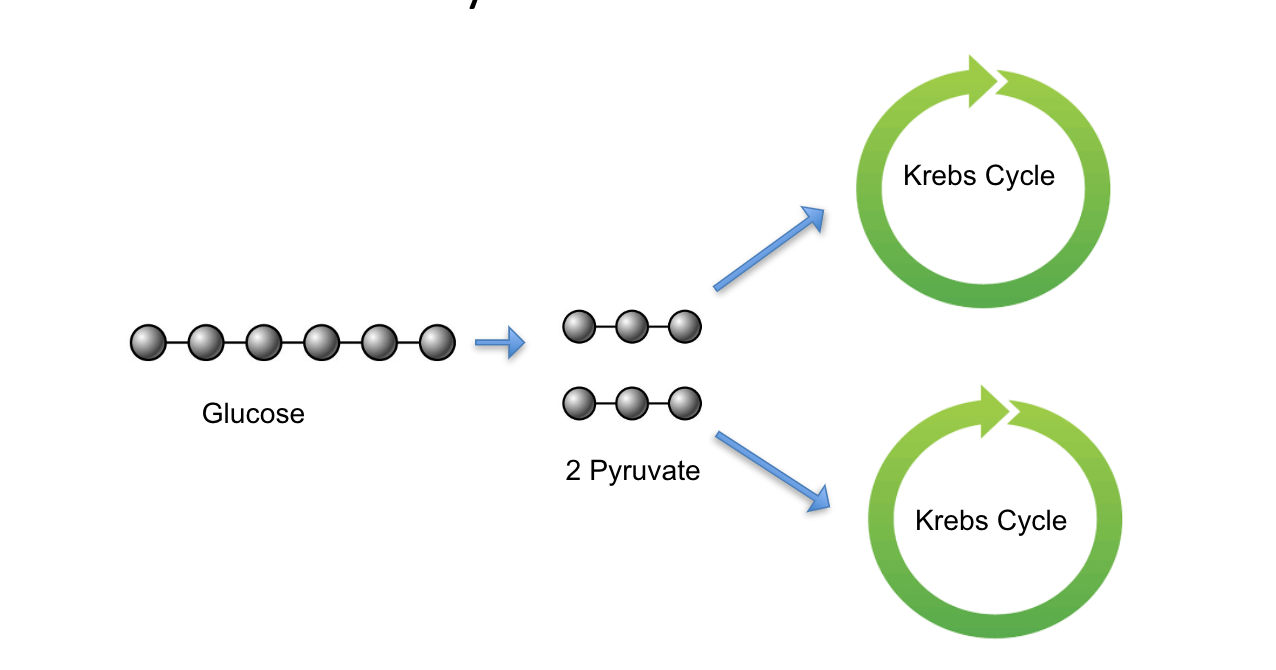
Two Turns of the Krebs Cycle:
Remember, 1 glucose molecules turns into 2 pyruvates
Each pyruvate enters the Krebs Cycle, one at a time
Therefore, for each glucose molecule, there must be 2 turns of the Krebs Cycle
Electron Carriers
The Krebs Cycle produces more electron carriers that will bring electrons over to the Electron Transport Chain
These electron carriers are called NADH and FADH2
For one turn of the Krebs Cycle, it produces 3 NADH and 1 FADH2
-Therefore, in total, for 2 turns of the cycle, it produces 6 NADH and 2 FADH2-
Krebs Cycle Produces:
The Krebs Cycle also produces one of the main products of cellular respiration, carbon dioxide
For one turn of the Krebs Cycle, it produces 2 molecules of CO2
Kreb Cycle ATP
The Krebs Cycle also produces 1 ATP molecule for each turn
So, for each turn of the Krebs Cycle:
2 CO2 molecules are released
The energy yield is
1 ATP
3 NADH
1 FADH2
So how many energy molecules does the Krebs cycle make for ONE pyruvic acid?
The energy tally from 1 molecule of pyruvic acid is
1 ATP
3 NADH
1 FADH2
2 CO2
However, each glucose produces 2 pyruvic acids… So how many of each molecule is made for each GLUCOSE?
2___ATP
6__ NADH
2__ FADH2
4__ CO2
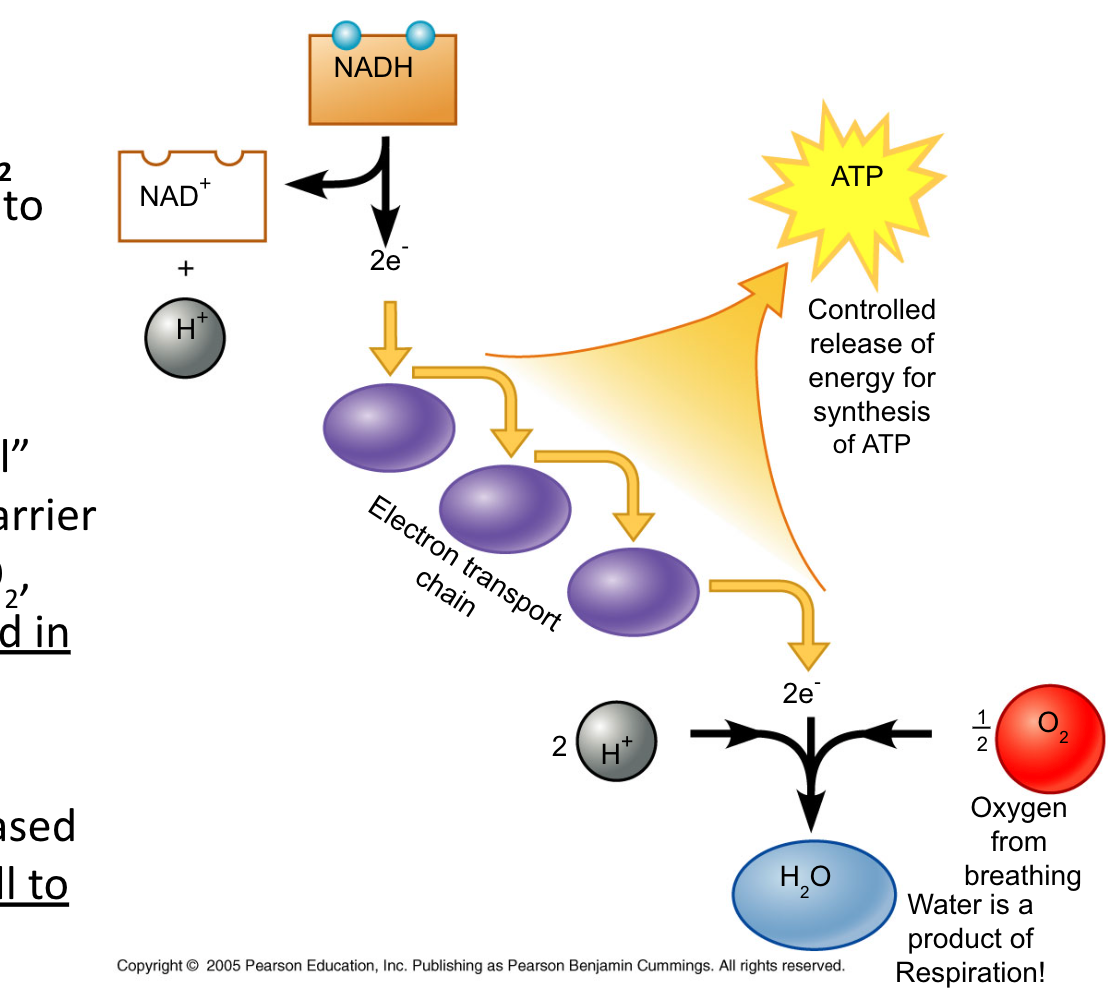
Step 3:The Electron Transport Chain
Electron carrier NADH and FADH2 passes electrons to the electron transport chain
As electrons “fall” from carrier to carrier and finally into O2, energy is released in small quantities
The energy released is used by the cell to make 34 ATP!
Electron Transport Chain & Production of Water
The electron transport chain is built into the inner membrane of the mitochondria
The electrons from NADH and FADH2 get passed down to O2, the final electron acceptor
Each oxygen atom combines with 2 electrons and 2 hydrogen ions (H+) to produce water, one of the products of cellular respiration
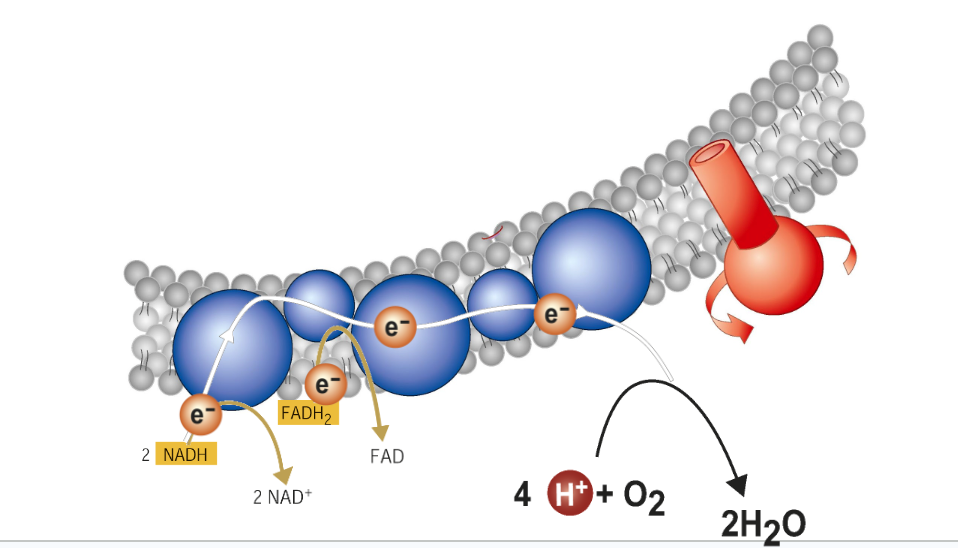
ATP Synthase: Production of ATP-
As electrons are being passed down, the ATP Synthase produces 34 molecules of ATP
The breakdown of glucose to produce ATP can be either:
Anaerobic or Aerobic
Anaerobic Respiration
does not require oxygen
Glycolysis & Fermentation
are anaerobic processes
Aerobic Respiration
requires oxygen
The Krebs Cycle and Electron
Transport Chain are aerobic processes
There are 2 types of Anaerobic Respiration(Fermentation)
Lactic Acid Fermentation
Alcohol Fermentation
Fermentation only produces 2 ATPS
2 ATPs are enough to keep your muscles contracting for
a short while when the need for ATP outpaces the delivery of O2