Chapter 11 Pro
1/139
Earn XP
Description and Tags
powerpoint
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
140 Terms
40”
100cm
72”
180cm
Diagnostic –type protective tube housing:
lead lined
type protective tube housing is required to protect patient and imaging personnel from off focus, or
leakage radiation
type protective tube housing protects by restricting the emission of x-rays to the area of
primary beam
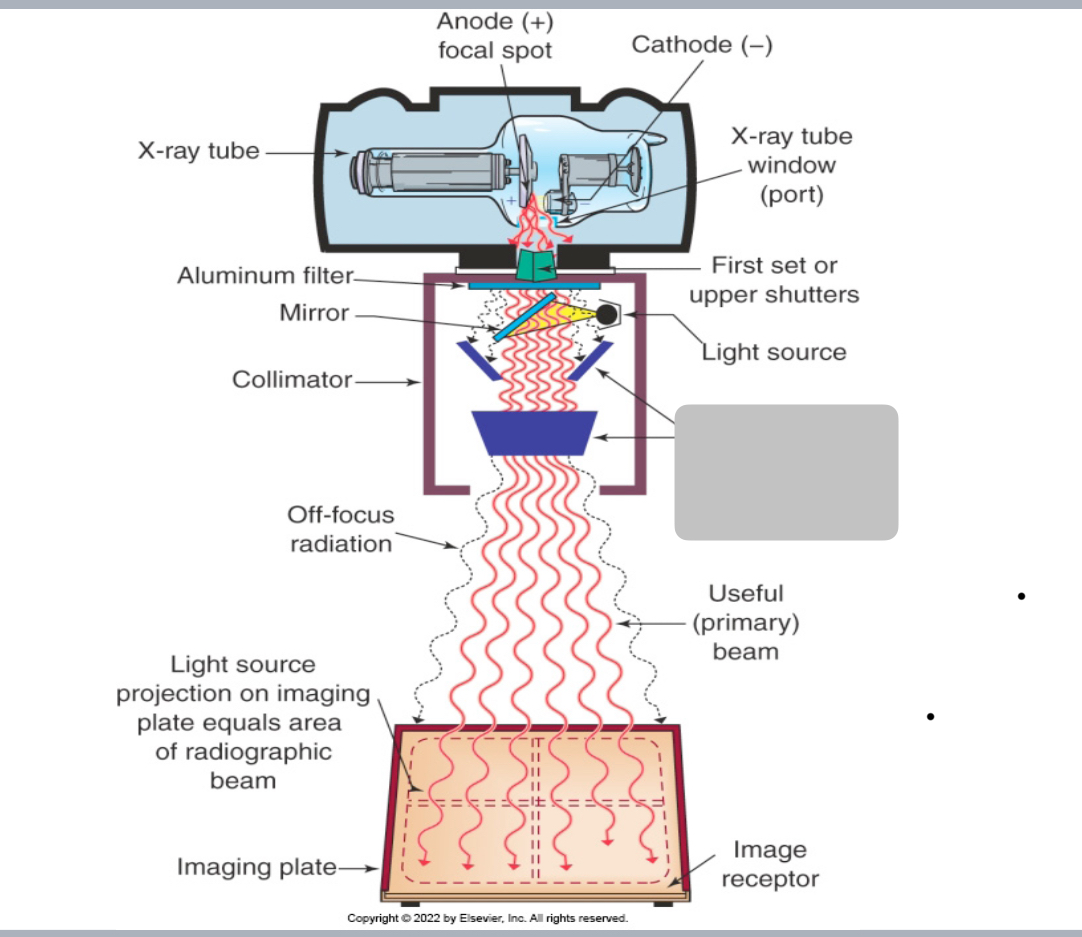
What’s the grey out area
Second shutters 🥈
type protective tube housing: housing must not allow leakage radiation measured at 1 meter from the x-ray source to exceed ____mGy/hr.
0.88
when tube is operated at ___voltage at the ___ current that allows for continuous
operation
highest, highest
must be located behind a suitable protective
barrier with a radiation absorbent window that
permits observation of patient
Control panel
Control panel
~ Must indicate conditions of exposure
~ must ____ indicate when the x-ray tube is energized
~ the audible sound indicates tube is energized
positively
~ strong and support patient
~ uniform thickness
~ carbon fiber is common
Radiographic Examination Table
Radiographic Examination Table is ___ to absorb very little radiation
radiolucent
~a measure from the distance of the anode focal spot to IR
~tape measure or laser
SID indicator
SID indicator: distance and centering indicators must be accurate to
within ________ of the SID respectively
2% and 1%
primary beam is adequately collimated so it isn’t larger than the size of the IR
X-ray beam limitation device
X-ray beam limitation device:
light localizing variable aperture rectangular collimator
- to adjust the ____ and shape of the x-ray beam automatically or manually
size
X-ray beam limitation device:
______
- currently the predominant x-ray beam limitation device
collimator
1.Confines the useful beam
2.Limits the quantity of body tissue irradiated
3.Reduces the amount of scatter
some characteristics of X-ray beam limitation devices
Useful beam=primary beam=
umbra
is all the radiation that arises from the
interaction of an x-ray beam with the atoms of any object in the path of the beam
Scatter
- the most versatile device for defining the size & shape of the beam.
~It is boxed-shaped and contains the radiographic beam devices.
Collimation
Beam Limitation Devices/Collimation: This system consists of two sets of adjustable _________ mounted within the device at different levels, a light source to illuminate the x-ray field and permit it to be centered over the area of clinical interest, and a mirror to deflect the light beam toward the patient to be radiographed
lead shutters
The upper shutters are mounted as ___ as possible to the tube window to reduce the amount of off-focus radiation (x-rays are
emitted from parts of the tube other than the focal spot of the tube)
~ This ___ patient’s dose
close, reduces
Not all off-focus radiation can be removed because ____ of shutters
can not be placed right under the actual focal spot.
1st set
The ________ of collimator shutters are mounted below the level of
the light source and mirror and function to confine further the
radiographic beam to the area of interest.
2nd set
This set of shutters consists of two pairs of lead plates oriented at
right angles to each other
Second
Each set can be ____independently
adjusted
to minimize skin exposure to electrons produced by photon interaction with the collimator, the patient’s skin must be at least 15 cm below collimator
Skin sparing
Portable or mobile units are required to maintain SSD of
a minimum of ___
30 cm/ 12 inches
a scientific term referring to the brightness of a surface
Luminance
Luminance
~ quantifies the _____of a light source
~ is determined by measuring the concentration of light over a
particular field of view
intensity
The primary unit is the candela per square meter, or a __
“nit”
One ____ = billions photons per second being emitted
from a light source through a specific field of view.
candela
If the luminance of the collimator light source is ___, the localizing light beam will ____outline the margins of the radiographic beam on the area of interest on all patients
adequate, adequately
Coincidence between the radiographic beam and the
localizing light beam
~ when using light localizing variable aperture rectangular
collimator the physical size and alignment between the
radiographic beam and the localizing light beam is essential
to eliminate collimator ________of the body structures being radiographed
cut off
Both alignment and length and width dimensions of the
radiographic and light beams must correspond to within
___ of the SID
2%
Coincidence between the radiographic beam and the
localizing light beam- This coincidence requirements are collectively known as:
1. alignment 2. congruence
The maximum allowable total difference in length and
width alignments of the projected light field with the
radiographic beam at the level of the IR MUST be no more
than_________ or 40” which equals 2cm or 0.8”
2% of 100cm
~ radiographic collimators that are part of fixed radiographic
equipment manufactured in the US generally include this limitation
device
Positive beam limitation (automatic collimation)
The ____ consists of electronic sensors in the cassette holder that send
signals to the collimator housing
PBL
When PBL is activated, the collimators are automatically adjusted so
that the radiation field _____ the size of the IR
matches
The PBL feature may be deactivated by?
turning a key
The radiographer must ensure that collimation is adequate by
collimating the radiographic beam so that it is __________!
no larger than the IR
What is the purpose of filtration?
reduces exposure to the patient’s skin and superficial tissue
by absorbing most of the lower-energy photons from the
beam.
Removes long wavelength or soft x-rays (or hardens the
beam)This increases the energy/quality of the beam.
Purpose of filtration
A purpose of filtration: absorbs some of the photons in the beam, it ______the overall intensity (quantity) of radiation
decreases
Filtration: The photons that remain are ____penetrating and less
likely to be absorbed in the body tissue
more
The absorbed dose to the patient decreases when the correct amount and type of filtration are placed in the path of the beam
decreases*
Two types of filtration:
1. Inherent filtration 2. Added filtration
1. the glass envelope encasing the tube
2. the insulating oil
3. the glass window in the tube housing.
-1 – 3 makes up 0.5 mm thickness of aluminum
4. reflective surface of the collimator mirror
-provides almost 1mm aluminum equivalent
Inherent filtration
0.5 mm+1 mm=
1.5 mm of aluminum filtration
consists of sheets of aluminum of appropriate thickness located outside the glass window of the tube housing above the collimator shutters.
Added filtration
Added filtration is ______to service personnel.
accessible
The peak kilovoltage of a given x-ray unit determines the________ of filtration required
total amount
inherent + added filtration=
Total filtration
Total filtration of 2.5mm aluminum equivalent for fixed x-
ray units operating above ____is the required standard
70kVp
Stationary radiographic equipment requires a total
filtration of 1.5mm aluminum equivalent for
machines operating from
50-70kVp
Stationary units operating __________ only
require .5mm aluminum equivalent
below 50kVp
___________equipment require a
minimum of 2.5mm aluminum equivalent total permanent filtration
Mobile and fluoroscopic
the thickness of a designated absorber required to decrease the
intensity of the primary beam by 50% of its initial value
HVL
When should radiologic physicist obtain HVL measurement?
1. at least once a year
2. after an x-ray tube is replaced
3. following repairs that have been made on the housing or
collimator
for diagnostic x-ray beams, the HVL is expressed in
mm of Al
HVL is a measure of beam ____ of effective energy of the x-ray
beam
quality
are used for dose reduction and uniformity of
image. The body parts that may vary in thickness considerably may
be made uniform with a filter constructed of aluminum or lead-
acrylic.
Compensating Filters
Compensating Filters: The device partially attenuate x-rays that are directed toward the__________ area while permitting more x-ray to strike the
thicker or more dense area
thinner, or less dense
_____ filter may be used to improve the image of the toes on a foot
x-ray, the thickest part is over the toes and the thinner part over the
heel
Wedge
The __________ filter, is used in some dedicated chest
radiographic units. This filter is thin in the center to permit adequate
penetration of the mediastinum and thick laterally to reduce
exposure to aerated lung fields.
Trough, or bilateral wedge
consistency in output in radiation intensity for identical
generator settings from one individual exposure to
subsequent exposures
Exposure Reproducibility
Exposure Reproducibility: x-ray unit must have the ability to ______ certain
radiographic exposures for any given combination of kVp, mA
and time
duplicate
Exposure Reproducibility: variance of ______ is acceptable
5% or less
consistency in output radiation intensity at selected kVp
settings when settings are changed from one mA and time
combo to another
Exposure linearity
Exposure linearity: mA X time=
mAs
Exposure linearity, also the ratio difference in
mSv/mAs
Exposure linearity: values between two successive generator stations must be
less than
0.1
linearity can vary only __%
10
AEC is also known as
“Phototiming”
system of a radiographic unit is
essentially an x-ray exposure termination
device that ends the radiation when a
predetermined amount is received by the
sensors
AEC
are designed to produce an acceptable diagnostic image
while limiting the total amount of radiation exposure to the patient
Automatic exposure systems
a device made of parallel radiopaque strips alternated with low attenuation
strips of aluminum, plastic, or wood.
Radiographic grid
Radiographic grid: Placed between _________ to
remove scattered x-ray photons.
patient and image receptor
Most often this device is used when the thickness
of the body part is greater than ___.
10 cm
The use of grids _____patient dose, the benefit
of improved quality of the recorded image is a good
compromise
increase
In new DR equipment, an electronic grid is used.
-it does not require ____ in technique
an increase
~ x-rays pass through an object, and some photons are
scattered
~ radiographic quality is higher when scatter is not
recorded on the radiograph
function of grid
What does this function of grid improve?
grid is designed to block the passage of photons that
have been scattered at some angle from their original path
this improves radiographic contrast & visibility of
detail
Grid ratio and patient dose:
~ grid requires an increase
in mAs
Grid ratio and patient dose:
What happens to patient does when a grid is used?
pt. dose increases when a grid is used
Grid ratio and patient dose:
higher grid ratio (more lead) does what to patient dose?
increases*
Minimal SSD for mobile radiography
~ SSD (source –skin distance) of at ________
is imperative 40” is recommended
least 12” (30cm)
When should portable units be used?
portable units should only be used on patients
who can not be transported to a radiographic room
when SSD is small, pt entrance exposure is
higher
Digital radiography:
~ _____image formed by x-ray photons on a radiation detector – an
electronic image
latent
Digital radiography: since its produced by a ____ - digital image
computer
Digital radiography:
numeric values of a digital image are aligned in a fixed number of
rows and columns –
image matrix
each small box is called a
pixel
_____collectively produce a 2 dimensional representation of the
information contained in a volume of tissue
“pixel”
In DR, the radiographic _____ appear as levels of brightness
associated with shades of gray.
densities
is the amount of luminance of a display monitor.
Brightness
The shades of gray that are displayed constitute the _____ in the
image.
contrast
Digital image permits adequate visualization of anatomic structures
because it has better contrast and density, and contrast can be
manipulated to improve overall ___
quality