Autonomic Pharmacology & the Peripheral Nervous System
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
HNI 333-Pharmacology Lecture 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
neuropharmacology
the study of drugs that alter processes controlled by the nervous system
– designed to enhance(agonists)/block(antagonists) normal physiologic processes
– most alter synaptic transmission (enhances selectivity)
normal synaptic transmission
process of __ __ __
1. Neurotransmitter synthesized in pre-synaptic neuron
2. NTM^ stored in vesicle until needed
3. NTM released into synapse upon stimulation by action potential
4. NTM crosses synapse & binds w post-synaptic receptor (reversible)
5. Termination- NTM separates from receptor
6. Removal of free neurotransmitter from synapse
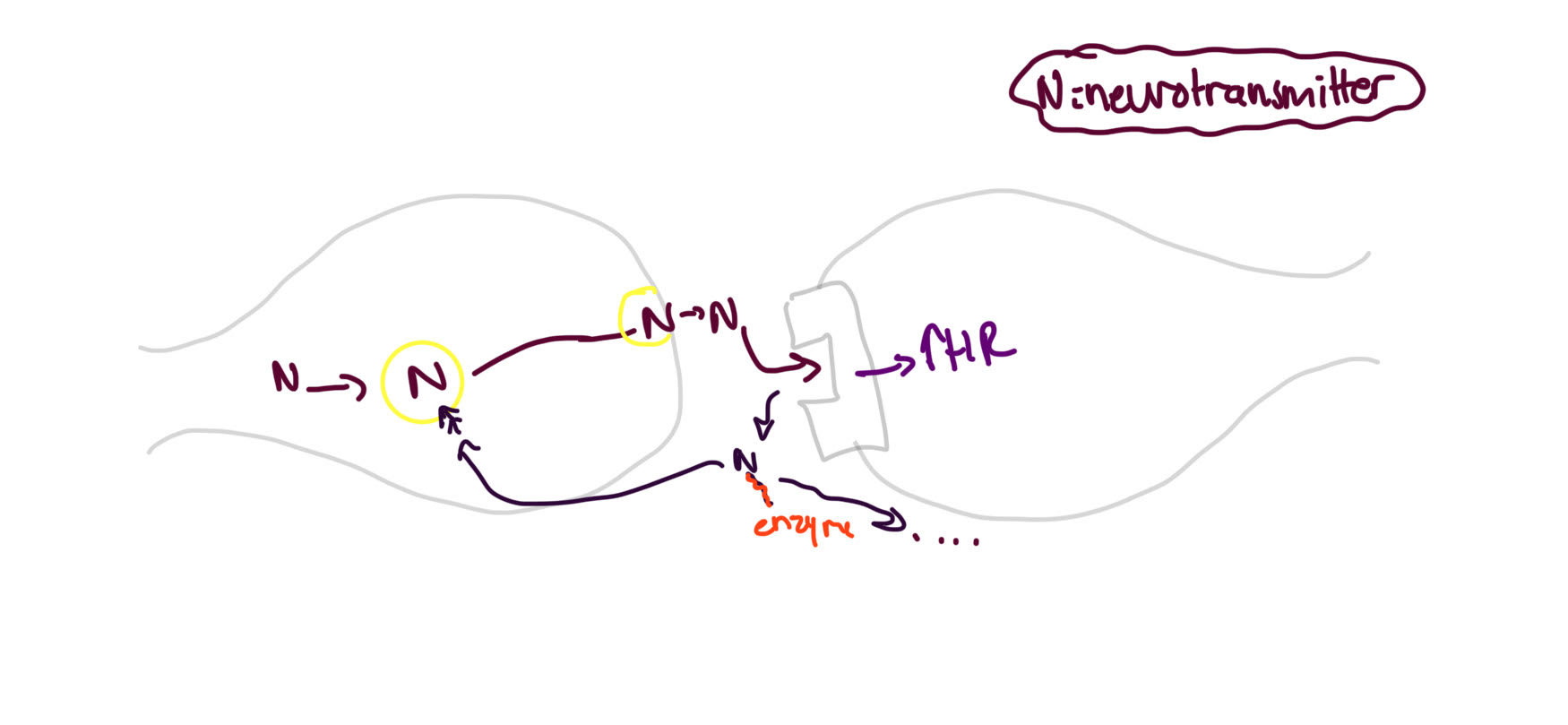
re-uptake
removal of neurotransmitter from synapse process: Pumps in the pre-synaptic neuron transport the neurotransmitters back into pre-synaptic neuron
– neurotransmitter may be re-packaged for re-use or degraded by enzymes
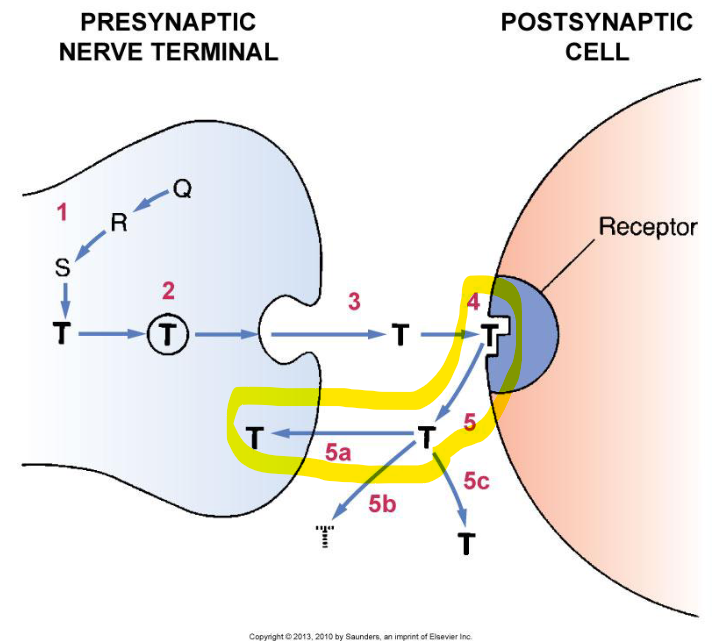
enzymatic degradation
way of removing neurotransmitters from synapse: the synapse contains degrading enzymes
– alternative method: diffusion
transmitter synthesis
how drugs influence synaptic transmission:
– by ↑ synthesis of neurotransmitter or by ↓ synthesis of neurotransmitter
– or by synthesizing a neurotransmitter that is more effective than the naturally-occurring neurotransmitter
transmitter storage
how drugs influence synaptic transmission:
– reduces number of vesicles available for storage and reducing the drug’s availability for release
transmitter release
how drugs influence synaptic transmission:
– Drugs can either promote or inhibit release
– ex: amphetamines enhancing release or botulinum toxins inhibiting release
receptor binding
how drugs influence synaptic transmission: works by
– Binding to receptor and causing activation (agonists) [epinephrine/insulin]
– Binding to receptor and block activation (antagonists) [narcan/antihistamines]
– partially bind to receptor and enhance activation by naturally-occurring neurotransmitter [benzos/valium]
termination of action
how drugs influence synaptic transmission:
– blocks reuptake [SSRIs]
– inhibit degradation
cholinergic
receptor in the peripheral NS: stimulated by acetylcholine (ACh)!
– types: Muscarinic, NicotinicN, and NicotinicM
adrenergic
receptor in peripheral NS: stimulated by epinephrine and norepinephrine!
– types: Alpha1, Alpha2, Beta1, Beta2
nicotinic M receptor
cholinergic receptor: stimulate contraction of skeletal muscle
nicotinic N receptor
cholinergic receptors: ganglionic synapse only
– function: transmission of impulse from pre-ganglionic neuron to post-ganglionic neuron in parasympathetic+sympathetic nervous syst
– stimulation of adrenal gland to release epinephrine
muscarinic receptor
cholinergic receptors: affects end organs&sweat glands only
– ↑ sweat gland activation
– miosis + ciliary muscle contraction=focused near vision
– bronchoconstriction + ↑pulmonary glandular secretion
– slowed HR
– ↑ GI peristalsis + GI glandular secretion
– Bladder voiding
– erection in males

alpha 1 receptor
adrenergic receptor-THE TIGER..: affects eyes, blood vessels, GU
– Mydriasis
– Vasoconstriction (skin, mucous membr, visceral organs)
– Urinary sphincter & Prostate contraction
– Ejaculation
applications: hemostasis (from vasoconstriction), nasal decongestion, BP elevation but adverse effects= HTN, necrosis from infiltration, bradycardia
beta 1 receptor
adrenergic receptor-THE TIGER..: affects heart and kidney
– ↑HR and heart contraction
– ↑cardiac conduction speed
– release of renin from kidney
applications: heart failure+shock+AV block+cardiac arrest (effective blood flow+contraction) but adverse effects= tachycardia+angina
beta 2 receptor
adrenergic receptor-THE TIGER..: affects lungs, uterus, glucose
– Bronchial dilation
– Relaxation of uterine smooth muscle
– Promotion of glycogenolysis by liver
applications: asthma, delay of preterm labor but adverse effects= hyperglycemia and tremor
muscarinic agonists DRUGS
Bethanechol (Urecholine)
– also: Pilocarpine (Salagen, Isopto, Pilocar)- used to treat glaucoma (relaxes iris) and dry mouth
muscarinic agonists
aka parasympathomimetic: this class binds reversibly to muscarinic receptors, stimulates muscarinic response, and create a cholinergic response
– ↑ sweating, ↑ salivation, miosis, bronchial constriction (+↑ secretions), ↓HR, ↑GI motility(↑ secretions), urination and hypotension
muscarinic agonist uses
uses for __ __: treatment of urinary retention
- adverse effects: hypotension+bradycardia, excessive salivation+diarrhea, ↑bladder pressure, exacerbation of asthma (bronchial constriction)
– use __ antagonist for treatment^
muscarinic antagonists DRUG
Atropine (Atropen)
– also Oxybutinin(Ditropan)- treats overactive bladder, Ipratropium Bromide (Atrovent)- treats asthma+COPD
– treatment if toxic: cholinesterase inhibitor(physostigmine)
muscarinic antagonist
aka parasympatholytics (anticholinergics) – binds reversibly to muscarinic receptors and BLOCKS the effect of ACh, yielding a blocked musca response
– ↓sweating, ↓salivation, mydriasis, bronchial dilation(↓secretions), ↑HR, ↓GI motility(↓secretions), and urinary retention
muscarinic antagonist USES
uses for __ __ are dose dependent (lungs+GI need higher doses for impact)
– treatment for symptomatic bradycardia, pupillary dilation during eye exam, increased GI motility, and overactive bladder
– adverse effects: HTN+tachycardia, dry mouth+urinary retention, ↓respiratory secretions→viscous thick secretions
cholinesterase inhibitors
drugs(enzymes) that prevent breakdown of ACh by acetylcholinesterase
– act like cholinergic agonists (🤽♂), allows prolonged availability of ACh in synapse, and broad activty=non selective for a cholinergic receptor
– two categories: Irreversible (4 insecticides+chem warfare) and Reversible (treats myasthenia gravis)
cholinesterase inhibitor DRUGS
Neostigmine(Prostigmin), Edrophonium (Tensilon/Reversol)
– they bind to cholinesterase preventing breakdown of acetylcholine. resulting in prolonged ACh action (esp at NicotinicM receptors—increases force of skeletal muscle contraction+CNS stimulation)
– treatment if toxic: mechanical ventilation and muscarinic antagonist (atropine)
neuromuscular blocking agents
agents that prevent ACh from activating NicotinicM receptors on skeletal muscle
– relaxes muscles during surgery/procedures
– two types: depolarizing and competitive
competitive neuromuscular blocking
__ __ __ agents that compete with ACh for binding to NicotinicM receptors on effector muscle, do NOT cause depolarization, and prevent ACh from binding→ muscle relaxation, dependent on drug conc
– doesnt alter consciousness or pain pain bc it doesnt pass BBB
– adverse effects= hypotension likely due to partial blockade of NicM in ganglia and respiratory arrest
competitive neuromuscular blocking DRUGS
Rocuronium (Zemuron), Cisatracurium, Pancuronium, Vecuronium
– muscle relaxation during surgery/intubation/etc.
– positively charge drugs, administered by IV, cannot cross membranes (BBB, placenta)
– administer if toxic:
depolarizing neuromuscular blocking
__ __ __ agents: binds to NicoM receptors and causes depolarization, doesnt release from receptor, and prevents repolarization→ paralysis (cells must depolarize→ repolarize→ depolarize→ repolarize to cause sustained muscle contraction)
– initial contractions followed by paralysis, doesnt cross BBB→ doesnt alter consciousness or pain perception
depolarizing neuromuscular blocking DRUG
Succinylcholine (Anectine)
– adverse effects of __ __ __ drug:
– Malignant hyperthermia- due to constant metabolism in muscle cells & release of Ca during depolarization
– Post-op muscle pain- from initial contractions
– Hyperkalemia- release of potassium stimulated by Succinylcholine
muscle contraction
1. Action potential reaches end of somatic motor neuron
2. Acetylcholine released into synapse
3. ACh binds with Nicotinic M receptor on motor end plate (reversible)
4. Membrane of motor end plate depolarizes
5. Wave of depolarization moves along muscle membrane (action potential in the muscle)
6. Calcium released from sarcoplasmic reticulum
7. Ca causes actin and myosin to interact causing muscle contraction
8. Rapid release of ACh from Nicotinic M receptor
9. Muscle repolarizes
10. Ca detaches from actin and myosin and moves back to sarcoplasmic reticulum
11. Muscle relaxes
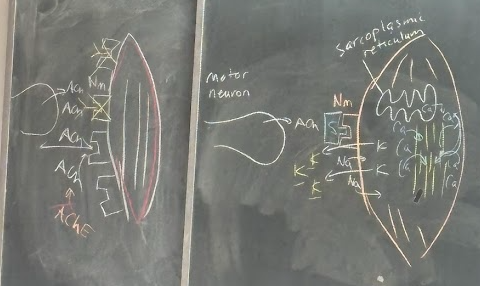
sustained contraction
1. Continuous series of motor neuron action potentials is necessary
2. Continuous release of ACh into synapse
3. Continuous depolarization/repolarization of motor end plate and skeletal muscle
4. Continuous release of calcium and reuptake of calcium by sarcoplasmic reticulum
–—If end plate remains depolarized, the signal to release Ca from the sarcoplasmic reticulum stops →Calcium eventually releases and goes back to sarcoplasmic
reticulum & muscle relaxes
Dantrolene
treatment of malignant hyperthermia! works by reducing metabolism in skeletal muscle and suppressing release of Ca from sarco reti
– also ice packs, cold IV saline,
adrenergic agonists
aka sympathomimetics: this class activates adrenergic receptors(alpha1+beta1&2)
mechanisms:
– 1. Direct receptor binding, 2. Norepinephrine release promotion, 3. Blockade of norepinephrine reuptake (prolonged stay in synapse), 4. Inhibition of norepinephrine inactivation by monoamine oxidase (MAO)
1-5mcg
__/kg/min= low dose of dopamine that stimulates only dopaminergic receptors
– dilates renal vasculature and improves renal perfusion+urinary output
6-10mcg
__/kg/min= mid-range dose of dopamine stimulating dopaminergic receptors and beta 1 receptors
– ↑HR, conduction velocity, contractility, and CO
>10 mcg
__/kg/min= high dose of dopamine stimulating dopaminergic receptors and beta 1 and alpha 1 receptors
– peripheral vasoconstriction,↑ BP, peripheral ischemia
adrenergic receptor specificity
Every Nurse Panics Daily And Is Drained
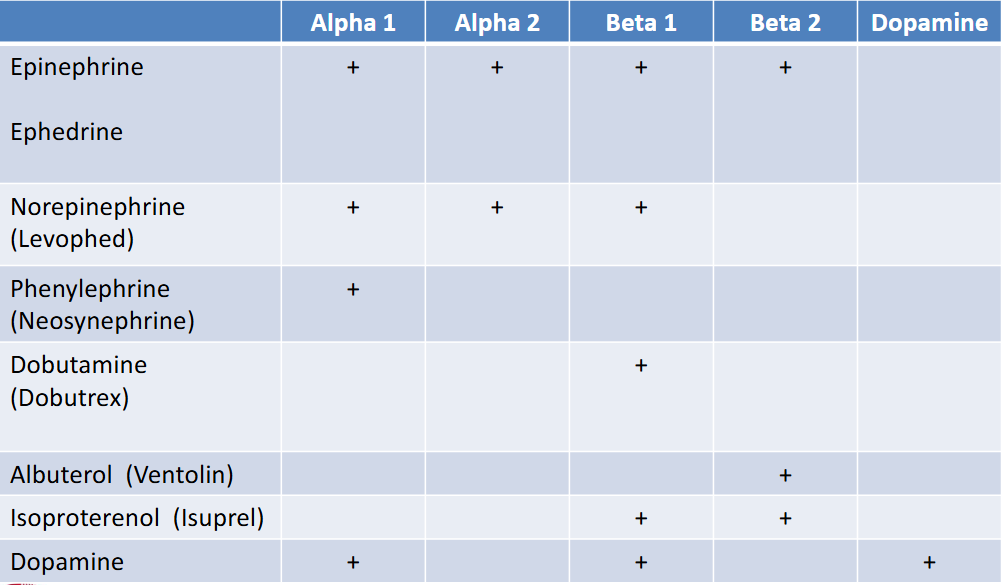
epinephrine
adrenergic agonist— stimulates Alpha 1 & Beta 1+2= broad spectrum of sympathomimetic effect
– essential drug in cardiac arrest and anaphylactic shock
norepinephrine
adrenergic agonist drug— stimulates alpha 1+beta 1
– used to treat hypotension
– aka Levophed
dobutamine
adrenergic agonist—stimulates beta 1 only
– used for heart failure (promotes faster+strong heart)
– aka Dobutrex
phenylephrine
adrenergic agonists—stimulates alpha 1
– treats nasal congestion and hypotension (due to vasoconstriction)
– aka Neo-synephrine
albuterol
adrenergic agonists—stimulates beta 2
– acts as bronchodilation for asthma patients
– better than isoproterenol due to specificity but adverse effects= tremor, tachycardia, hyperglycemia
– aka Ventolin
isoproterenol
adrenergic agonists—stimulates beta 1+2
– delays preterm labor, used for asthma and to support hemodynamics
– adverse effects= tachycardia, chest pain, hyperglycemia
– aka Isuprel
dopamine
adrenergic agonists—dose dependent effect
– Low dose – Stimulates dopamine receptors only
– Mid-range dose – Stimulates dopamine receptors AND Beta 1 receptors
– High dose - Stimulates dopamine receptors AND Beta 1 AND alpha 1 receptors
– treats shock, HF, acute renal failure
adrenergic antagonists
class of which all cause reversible blockade of adrenergic receptors, most are specific
– two classes: Alpha and Beta __ __
alpha 1 antagonists
Mechanism: Reversible blockade of alpha 1 receptors only; eye dilation, vasodilation, relaxed prostate, ↑urinary output
Indications: essential hypertension, reversal of alpha 1 agonist overdose, benign prostatic hyperplasia, pheochromocytoma
alpha 1 antagonist DRUGS
Prazosin (Minipress), Doxazosin (Cardura) treats HTN and BPH
Tamsulosin (Flomax) treats BPH and the bladder neck
beta adrenergic antagonists
Propranolol (Inderal), Nadolol (Corgard), Carvedilol (Coreg) – Non-specific: blocks beta 1+2
Metoprolol (Lopressor), Atenolol (Tenormin)– Blocks beta 1 only
beta blocker
aka beta adrenergic antagonist- beta 1 blockade has most benefits= reduce HR, contraction and conduction velocity
– indications: treats angina pectoris, HTN, Dysrhythmias, MI, Hyperthyroidism, Stage fright
– adverse effects: bradycardia, reduced CO, AV block, bronchoconstriction, hypoglycemia