characterisation of solid state
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
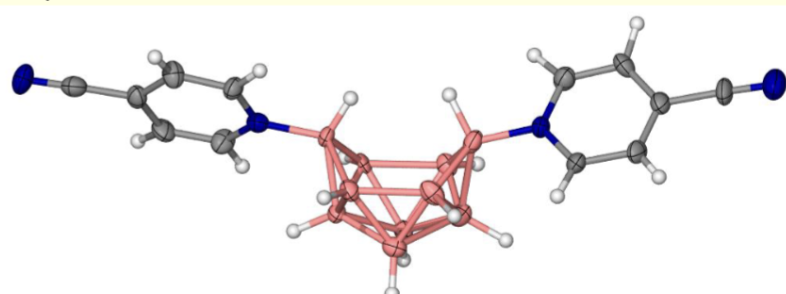
what is do ellipsoid figures show and represent?
atoms shown as cross hatched ellipsoids
represents an area where there is 50% probability that electron density of that atom is contained within its boundary
what is the unit cell an average of? how does this vary for ordered vs disordered structures?
average structure across entire crystal lattice and across all crystallites
ordered - no significant variations across unit cells
disordered - randomly dispersed variations across unit cells
what is disorder?
what are the sites like?
when sites within unit cells may be one type of element in some, and another type in other unit cells
this gives sites of mixed elemental character
what is non-stoichiometry?
what are 2 reasons for this?
compounds have elemental composition and proportion cannot be represented by integers
sites have mixed elemental character due to doping
sites have low occupancy as some unit cells are missing ions
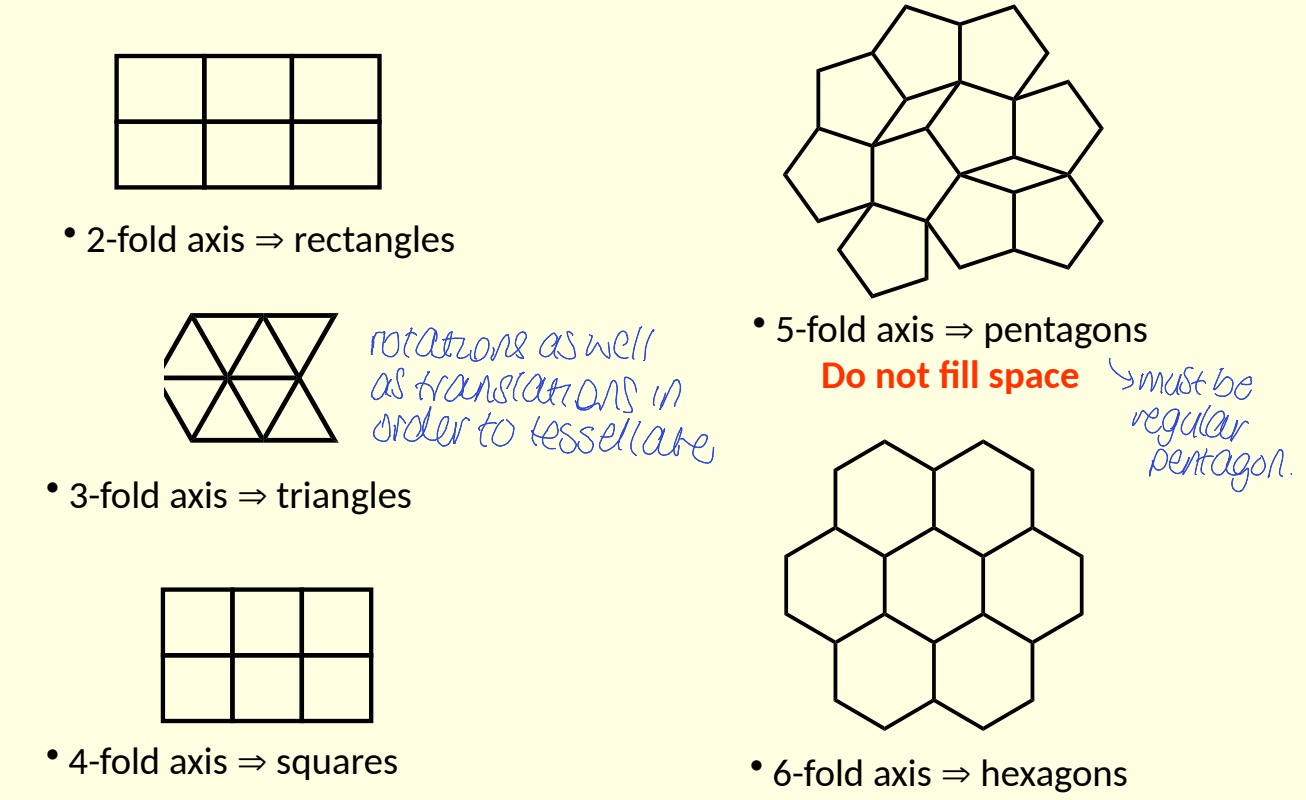
what are crystallographic rotation axes limited to?
restricted to those than product shapes that fill space
no gaps
what are examples of shapes with 2-fold, 3-fold, 4-fold, 5-fold and 6fold?
do they all fill space?
what are unit translations?
how is a crystal lattice generated?
translations of whole unit cell lengths
unit translations in 3D generate crystal lattice
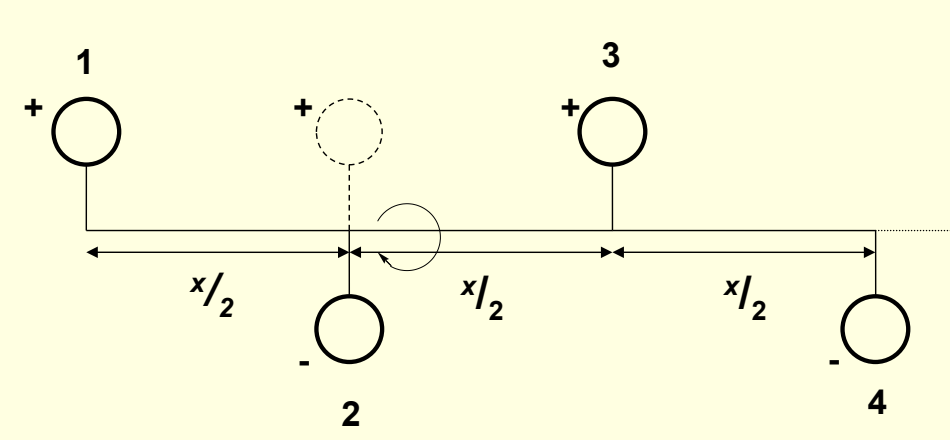
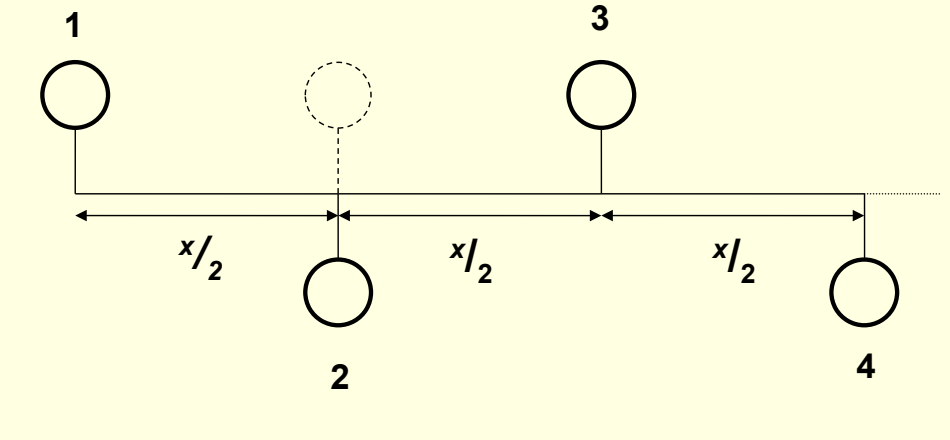
what is a screw axis?
what is nm?
translation plus rotation
nm - translate m/n of unit x, rotation 360/n around direction of translation
show 21 screw axis?
what is a glide plane?
show example
translation of half the unit x plus reflection across mirror plane parallel with translation direction
what is crystal structure defined by? 3
unit cell parameters (e.g. a, b, c, alpha etc)
space group - braves lattice type, symmetry elements
atom types and fractional coordinates of asymmetric unit
what is an asymmetric unit?
part of structure that can’t be related to another part by symmetry elements
wavelength range of X-rays?
0.1-10Å
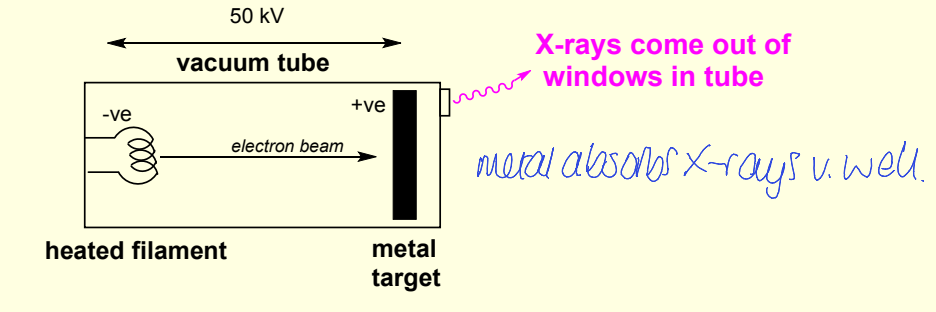
conventional source of X-rays
where? what produces them? how?
diagram of electron movement?
in X-ray tube, electron beam hitting metal target
electron beam ionises core electron from atom in metal. upper shell electron relaxes to fill hole - X-rays emitted
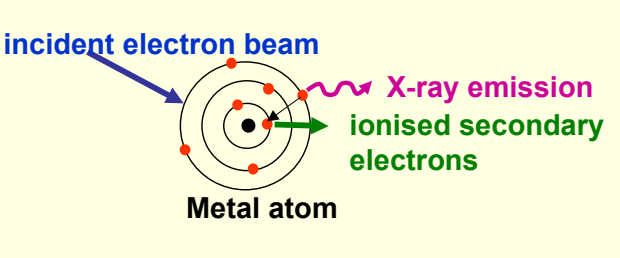
diagram of X ray tube and metal target
what produces electrons? where do x rays go?
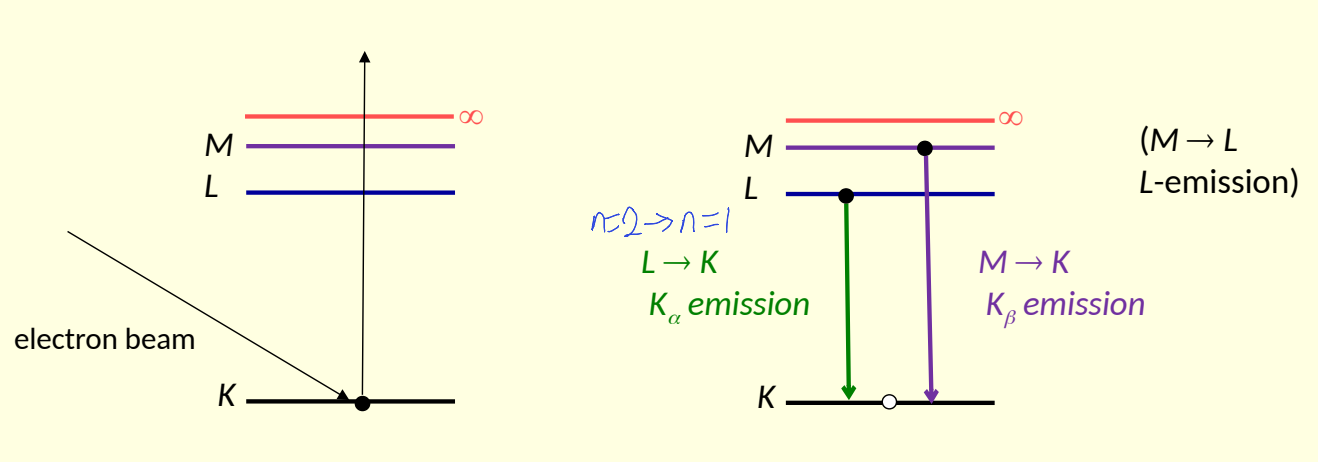
what is K, L and M shell?
K n =1
L n =2
M n=3
show M, L, K and ∞ energy levels - show electron beam causing ionisation and then electrons moving down, what the names of L→K, M→K and M→L emissions?
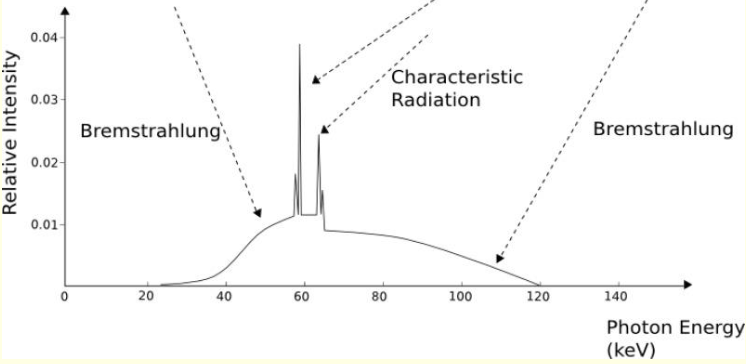
what is a broad hump on X ray emission spectrum?
white radiation
accelerate/decelerate charged particles and need to relax KE so white radiation is released
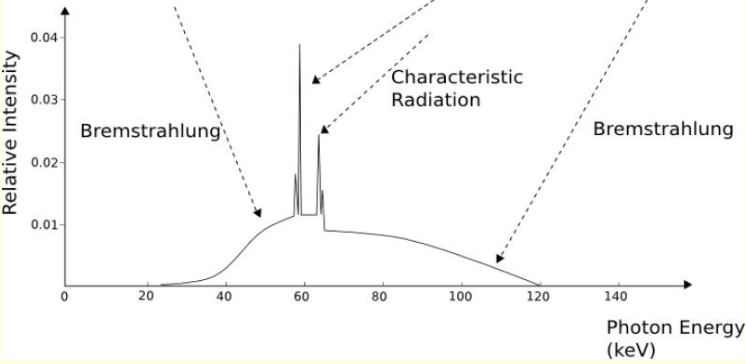
what are characteristic radiation spikes? (specific and show diagram)
quantised electronic transitions - Kɑ and Kβ
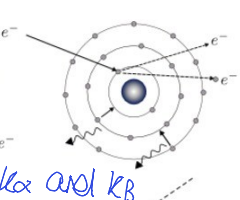
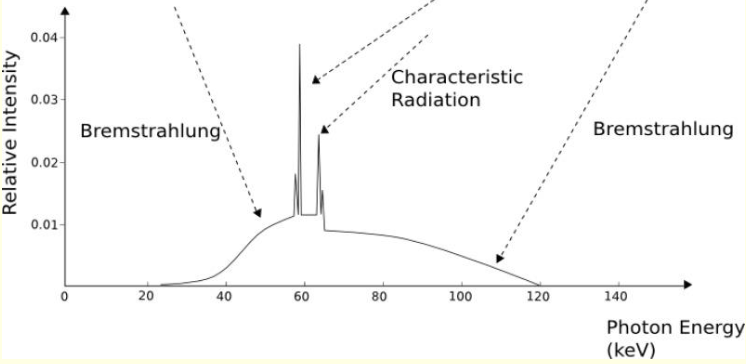
why is there more than two peaks when it shows Kɑ and Kβ?
coming from 2s or 2p, and 3s or 3p
what energy is wanted for diffraction experiments?
what is used to achieve this?
just one energy of X-rays
use metal filters or monochromators to remove white radiation, or any less intense emission wavelengths
what is synchrotron radiation?
speed? what type of radiation? energy?
when charged particles travel in curved paths
speeds close to speed of light
white/ broadband radiation
energy ranges from microwave to X-rays
single slit experiment - what does slit do?
show diagram of X rays approaching slit and after
slit acts as secondary scattering source for light
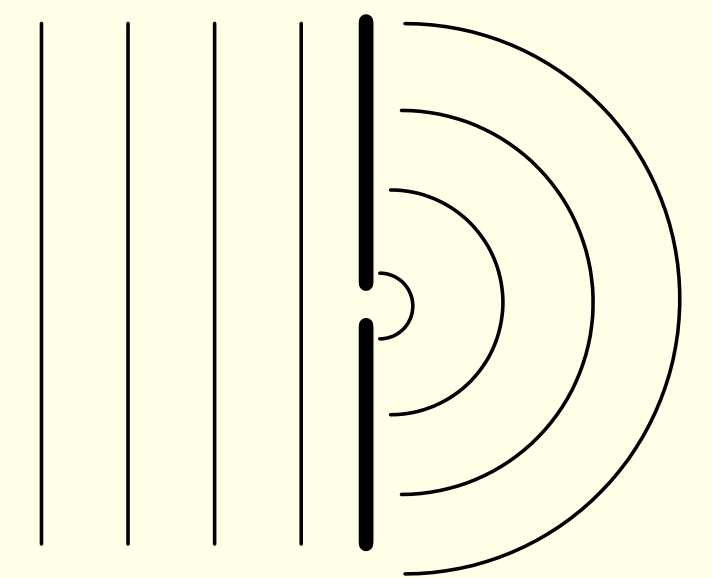
what happens when you use 2 slits in X-ray diffraction?
how are x-rays scattered?
broad lines as waves constructively interfere
scattered in all directions from both slits
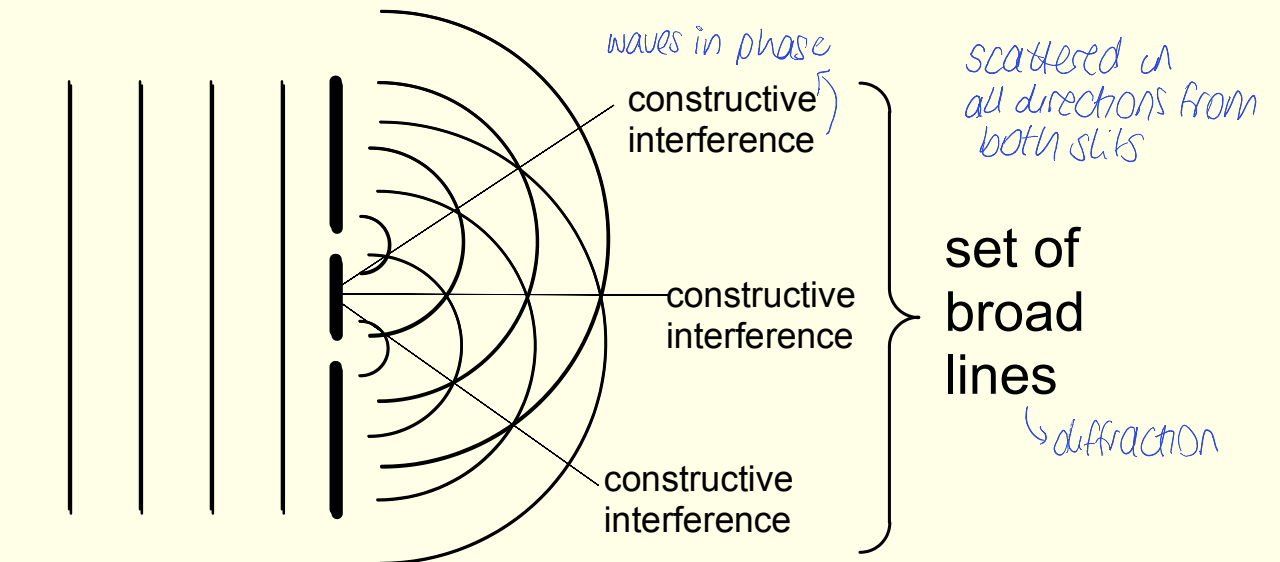
what happens when you have many slits in X-ray diffraction vs 2?
narrower lines, more detailed patterns
what is wavelength in slit experiment?
λ≈slit separation
what does a diffraction grating give and what is it caused by?
what is needed for constructive interference to occur?2
diffraction pattern from incident waves
pattern caused by constructive interference between scattered waves
sources of secondary scattering (e.g. slit) must be in ordered array, and separated by approximately the wavelength of the wave
what are x-rays scattered by? separation?
regions of high electron density e.g. atoms
0.8-4Å
why are x-rays diffracted from crystals?
atoms/ions are in regular pattern
areas of high electron density as atoms with close separation
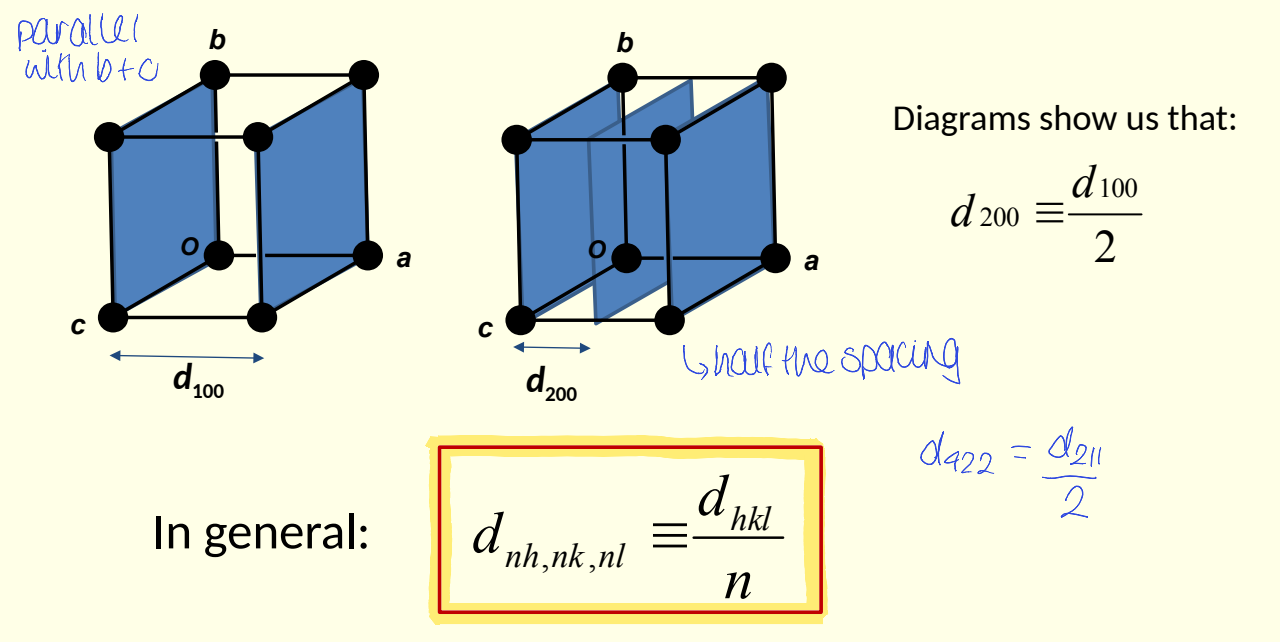
what is equation for dnh,nk,nl? e.g. show d200 vs d100
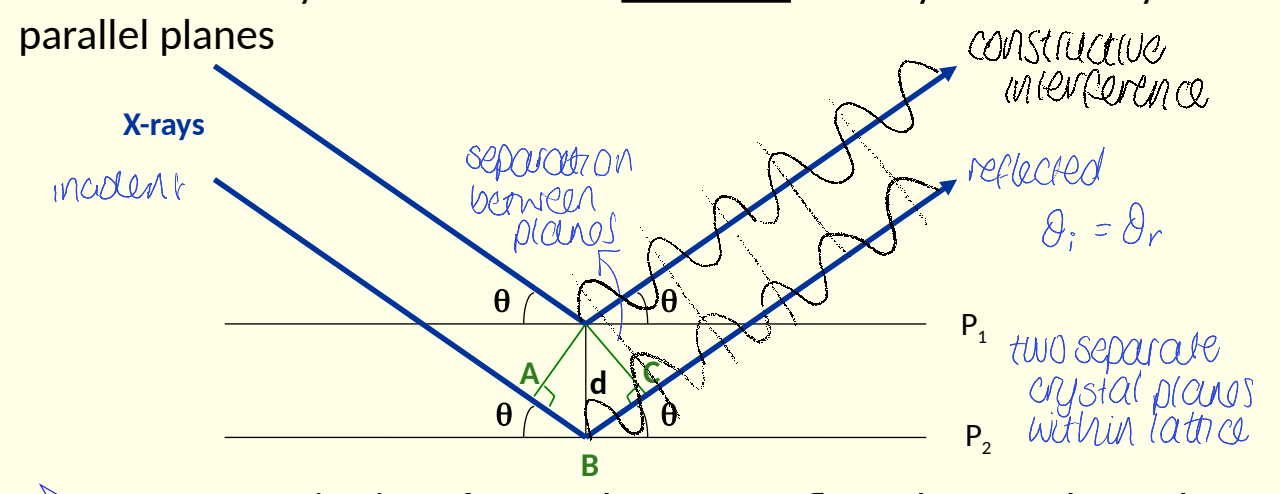
what did Bragg consider X-ray diffraction to be, instead of secondary scattering?
show diagram with two planes, P1 and P2, ABCd and θ
show constructive interference
considered it to be a reflection of x-rays off a family of parallel lines
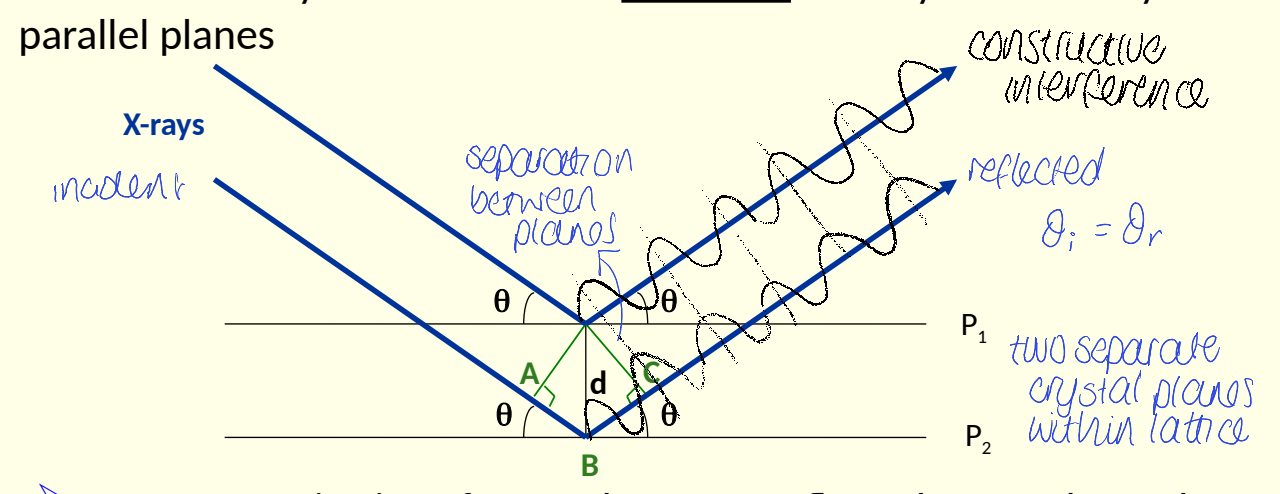
how can constructive interference occur (what is the condition?) for Bragg’s law?
path difference must be a whole number of wavelengths
AB + BC = nλ
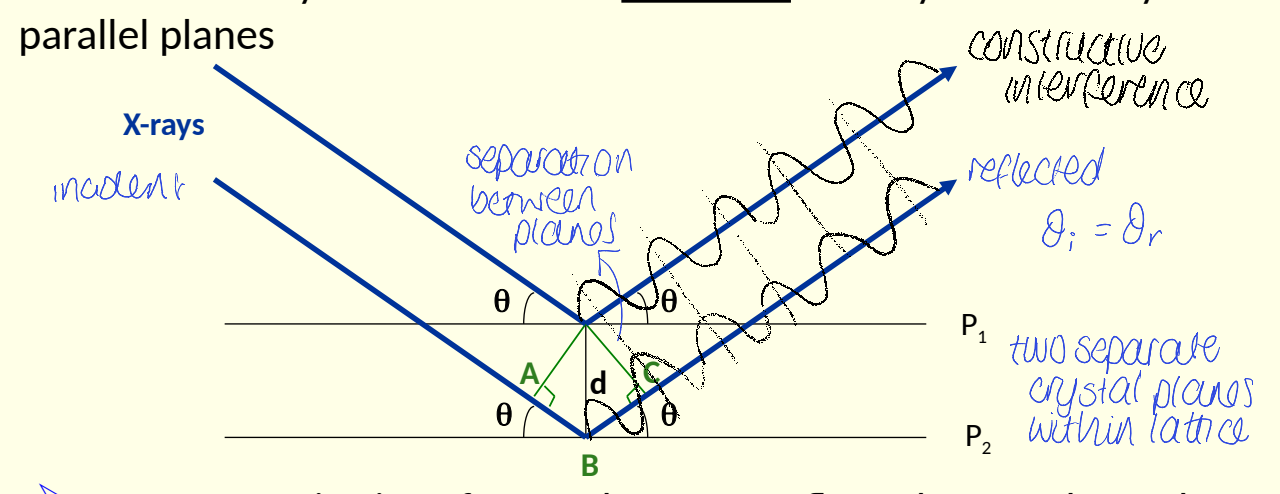
have the X-rays travelled the same distance?
second has travelled further as it has gone through crystal before being reflected by P2

show how rule of constructive interference leads to Bragg’s law
use dhkl/n to give law

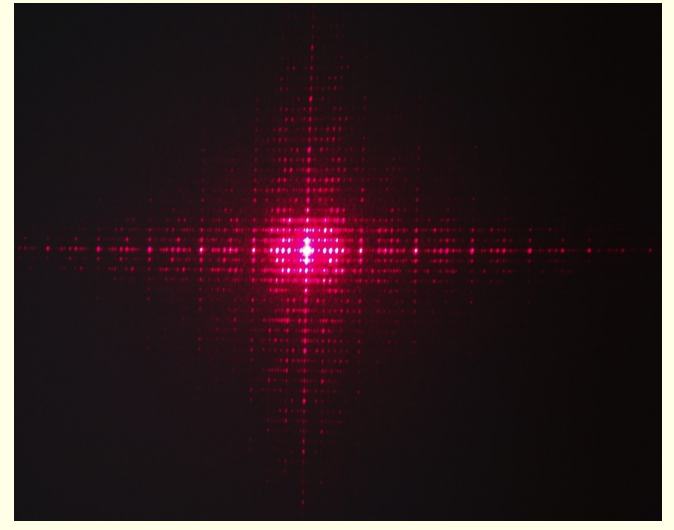
what does each diffraction spot in a pattern correspond to?
corresponds to set of crystal planes defined by miller indices hkl
why are many diffraction patterns superimposed on each other for crystalline powders?
many many small crystallites - each has its own diffraction pattern
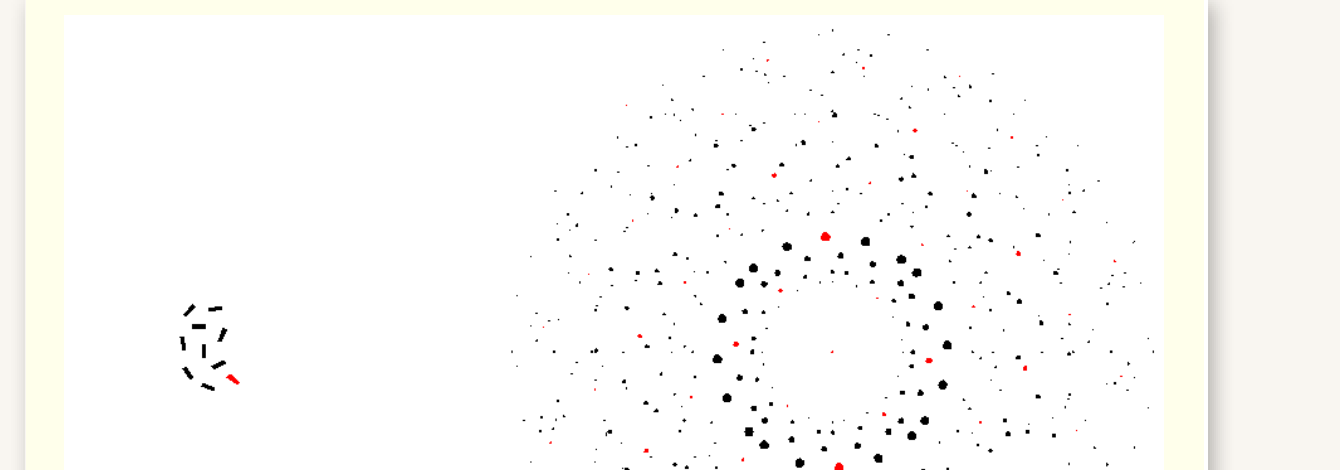
how does changing the orientation of crystallites give rings?
superimposed at a different orientation
change orientation of crystal changes the orientation of the diffraction pattern
pattern is being rotated as crystal is rotated leading to rings
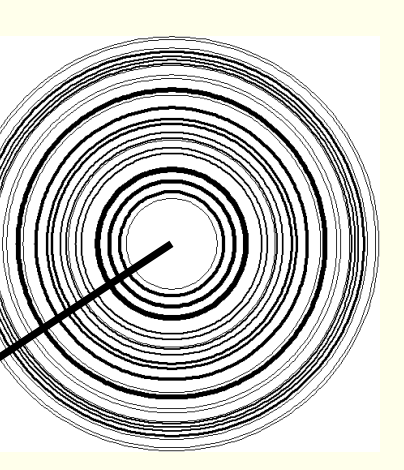
where is 2θ?
what is each ring/line?
2θ is arrow - take 1D trace through rings
each ring corresponds to a different set of lattice planes (hkl)
how does translational symmetry change reflections?
results in destructive interference between diffracted X-rays
causes certain sets of reflections to be missing = systematic absences
what are translational symmetry examples? 3
cell centring
screw axes
glide planes
what are the reflections absent for primate, body and face centring?
primitive = none absent
body = h+k+l = odd number
face = h,k,l not all even or all odd
what is a diffractometer?
for powder diffractometer, what its measured? how are different values accessed?
instrument that measures diffraction pattern
sample ground to fine powder, 2θ vs intensity measured
sample and or detector rotated to access different 2θ measurements
diagram of powder diffractometer and detector and graph

why do different atoms have different scattering power?
ability to scatter X-rays depends on number of electrons which changes with element
what is fj?
scattering factor of an element type j
why do non crystalline contaminants not matter for pXRD?
only crystalline material produces powder patterns
how can different polymorphs be obtained?
how can these be detected and identified? limitation?
obtained through phase change where one phase transformed to another through heat or pressure
powder diffraction experiments can detect and identify through fingerprinting
need a more sensitive technique if only trace amounts
what does structure factor Fhkl describe?
describe amplitude (size) and phase (directionality) of diffracted wave
what is structure factor (resultant wave)
resultant wave from linear superposition of wave vectors from all atoms in the unit cell
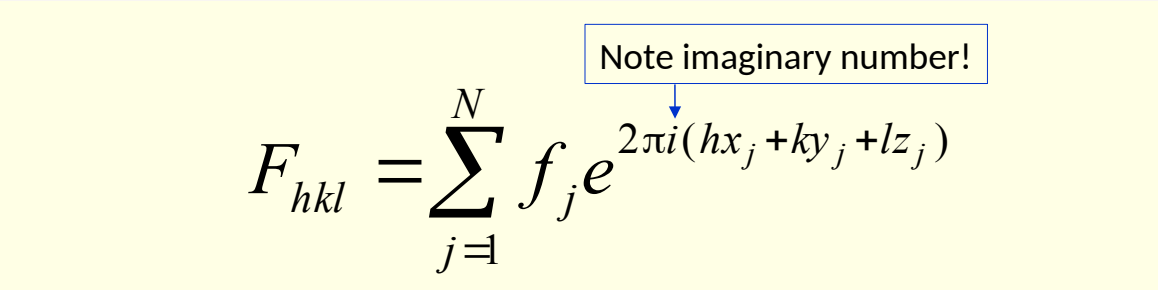
what is each term?
N = number of atoms in unit cell
fj scattering factor of atom j
xj,yj,zj = atomic coordinates of atom j

show diagram of Fhkl for 4 atoms - consider each scattered wave as vector (length f and phase angle ϕ)
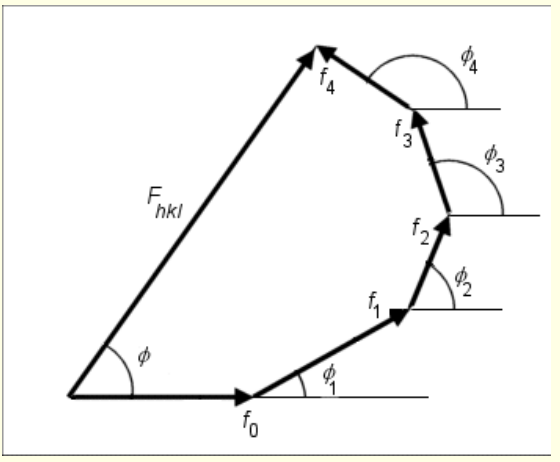
which atoms contribute to Fhkl?
all atoms - whether or not in set of crystal planes
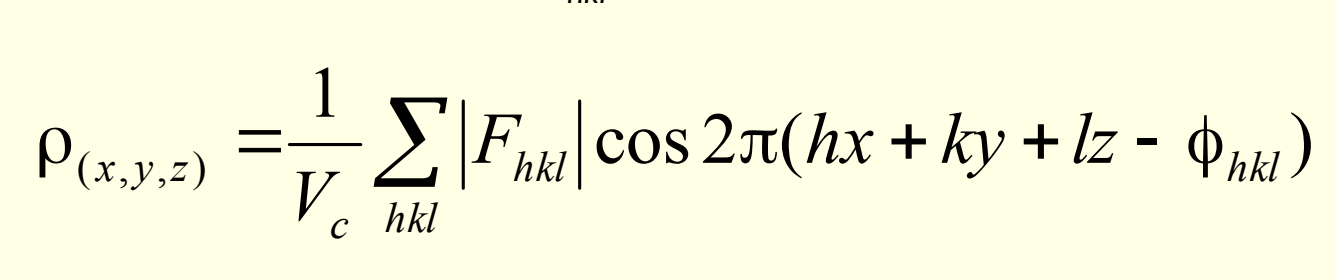
what is ρ(xyz) and Vc?
what is the phase problem?
what does this stop from being calculated?
inability to measure phase angles
what is solving a structure? what can be calculated?
what does solved structure give
need phases assigned to reflections to calculate Fhkl and hence ρ(xyz)
solved structure gives peaks of electron density that can be assigned as atoms
what is a beam stop?
stops x-ray beams otherwise most x-rays hit detector and damage it
why is measurement of good intensity data for pXRD hard?3
weak diffraction (smaller the crystal, the weaker the diffraction)
overlap of peaks
preferred orientation
what is preferred orientation? how can it be alleviated?
when crystallites not randomly orientated
line up or lie flat against surface of sample holder
alleviated by grinding sample into finer powder
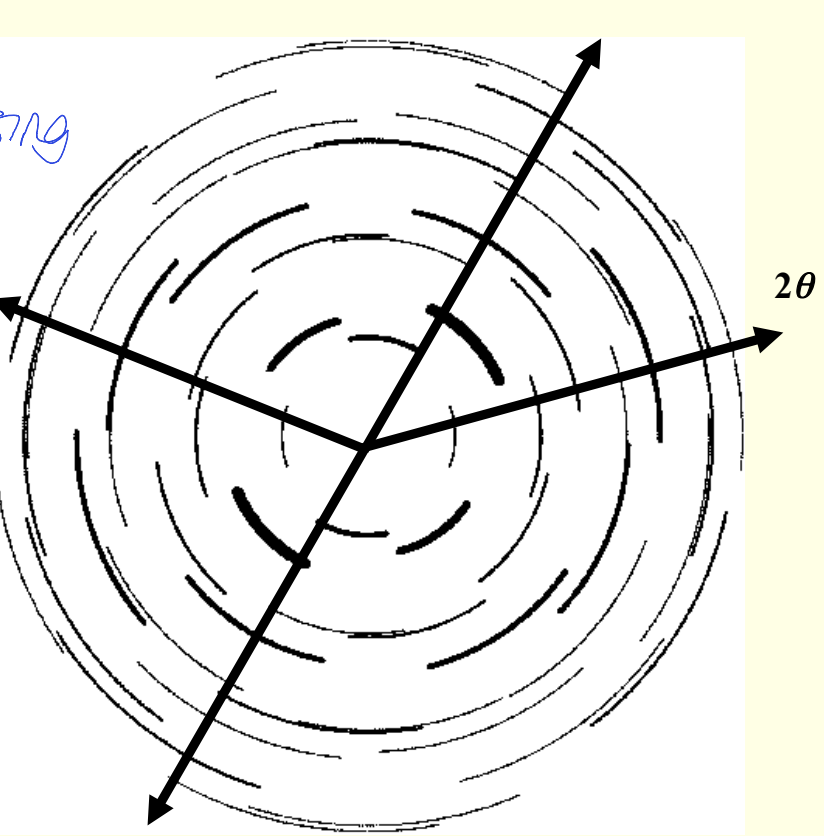
how does preferred orientation affect diffraction rings and measurement of intensity?
powder rings are incomplete - slicing means some peaks missing
wrong intensity
why is solving not needed for inorganic solid state chemistry? how can data be used?
material is of known structural type
structure of a similar material can be used as a starting material
can be refined against the data
how are differences between calculated and measured pattern minimised?
least squares refinement - Rietveld refinement
fits line profiles for powder pattern to account for overlap of peaks