Breast/Lymphatics
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
What is physiologic (normal) nipple discharge?
physiologic hypersecretion is seen in pregnancy, lactation, chest wall stimulation, sleep, and stress
What is pathologic (abnormal) nipple discharge?
when discharge is blood or serous, unilateral, spontaneous, associated with a mass, and occurring in women ages > 40 yo
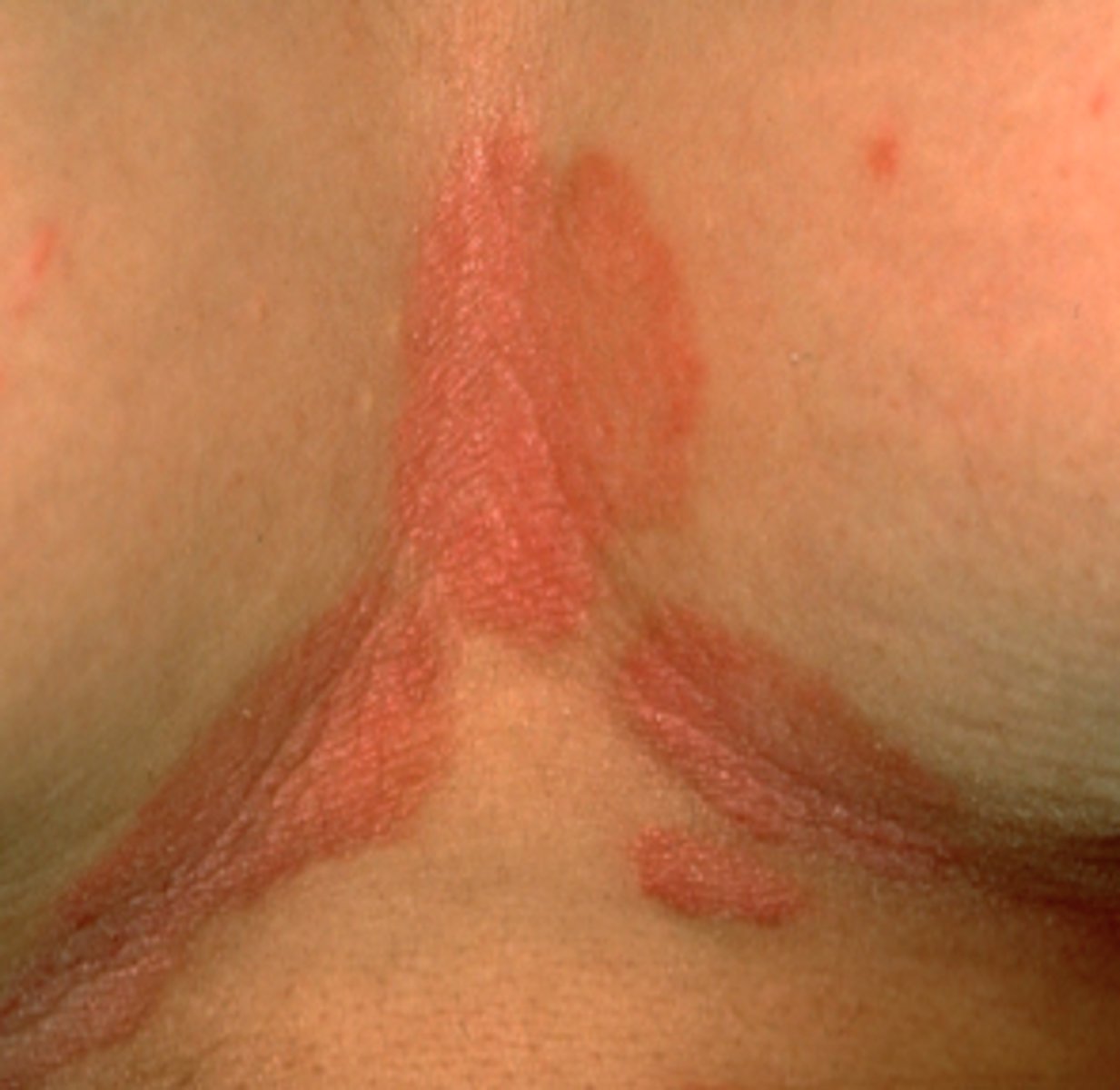
What is monilial intertrigo?
occurs in the folds of the breasts
type of dermatitis
inflammatory skin condition
itchiness, tenderness
occurs with large, pendulous breasts
tx: shower and change bra after exercising
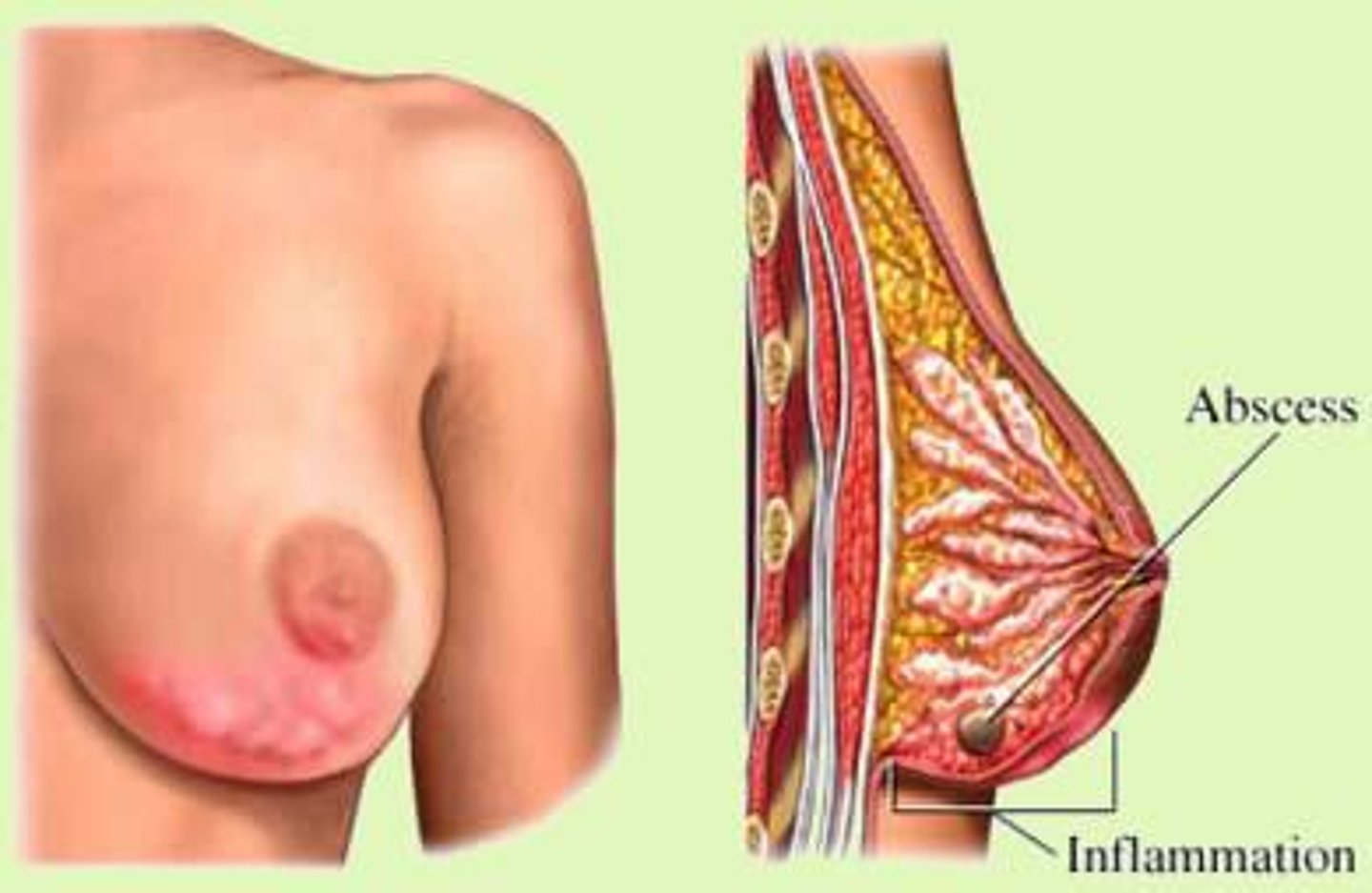
What is mastitis?
firm erythematous in lighter skin
darker area on darker skin
tender, swollen area
occurs in breastfeeding
caused by engorgement and obstruction of milk drainage of a lactating person
presents with flu-like symptoms associated
Tx for mastitis
Abx, warm compress, encouragement of further breastfeeding
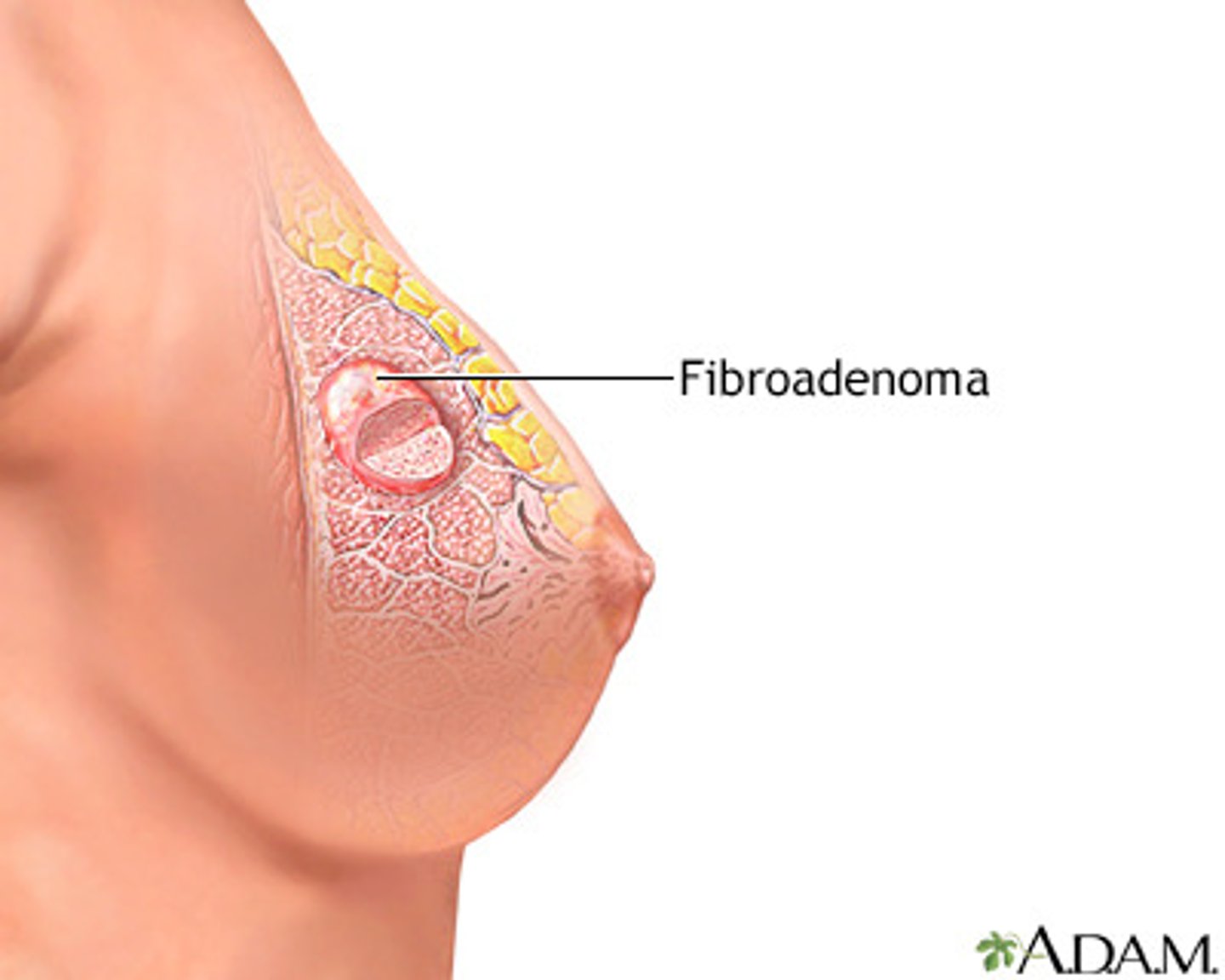
What is fibroadenomas?
Age 15-25
Usually puberty and young adulthood, but up to age 55
Usually single, may be multiple
Round, disc-like, or lobular
May be soft, usually firm
Well delineated
Very mobile***
Usually nontender
no retraction signs
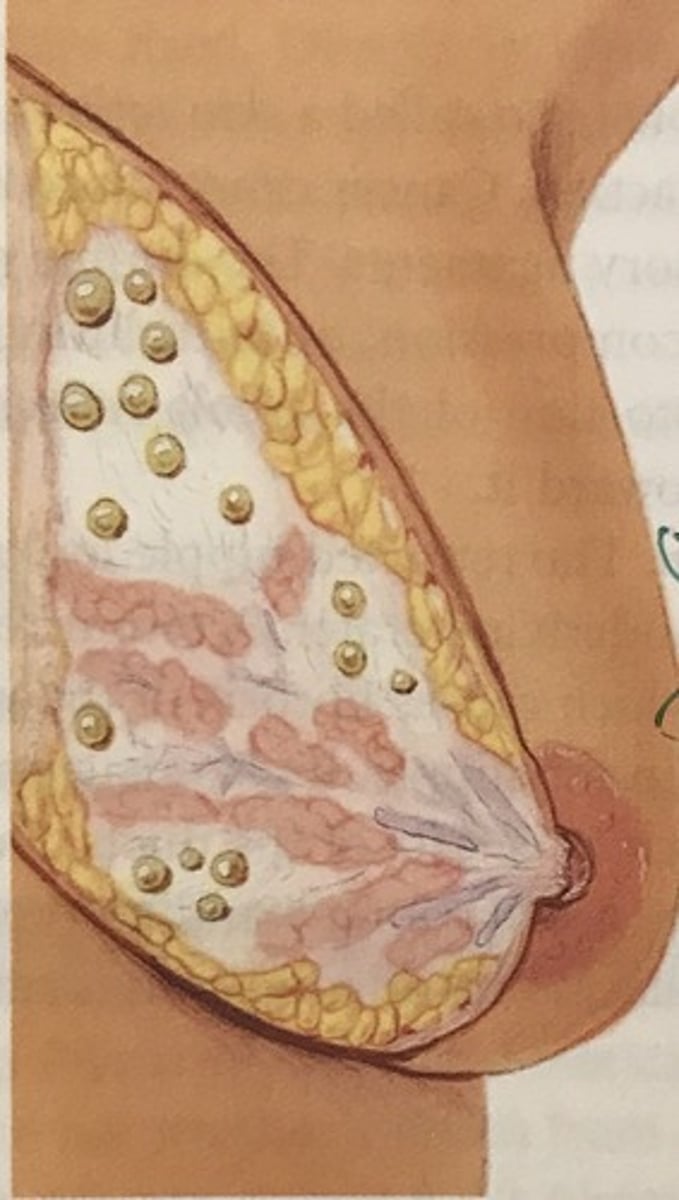
What is fibrocystic breast disease?
age 30-50
regress after menopause except with estrogen therapy
may fluctuate with menstrual cycle
single or multiple
round
soft to firm, usually elastic
well-delineated
mobile
often tender
no retraction of the nipple
What is breast cancer?
age 30-90, most common over 50
usually single, although may coexist with other nodules
irregular or stellate
firm or hard
not clearly delineated from surrounding tissues
may be fixed to skin or underlying tissues
usually non-tender
retraction signs possible
changes in contour of the breast
What are non-modifiable risk factors of breast cancer?
female gender > 50
personal hx of breast cancer
mutation BRCA1/BRCA2
first-degree relative with breast cancer
previous breast irradiation
menarche < 12; menopause > 50
What are lifestyle related risk factors for breast cancer?
nulliparity or first child after 30
long-term use combined HRT
alcohol intake of 2-5 drinks daily
obesity and high-fat diet
physical inactivity
not breast-feeding
What are retraction signs?
sign of breast cancer
as breast cancer advances, it causes fibrosis (scar tissue)
shortening of this tissue produces dimpling, changes in contour, and retraction or deviation of the nipple
other causes of retraction include fat necrosis and mammary duct ectasia
Nipple retraction and deviation
nipple is flattened or pulled inward
nipple may be broadened and feel thickened
when involvement is radially asymmetric, the nipple may deviate or point in a different direction
typically points toward underlying cancer
What is edema (Peau d'orange)?
edema of the skin is produced by lymphatic blockade
appears as thickened skin with enlarged pores "orange peel"
often seen first in the lower portion of the breast or areola
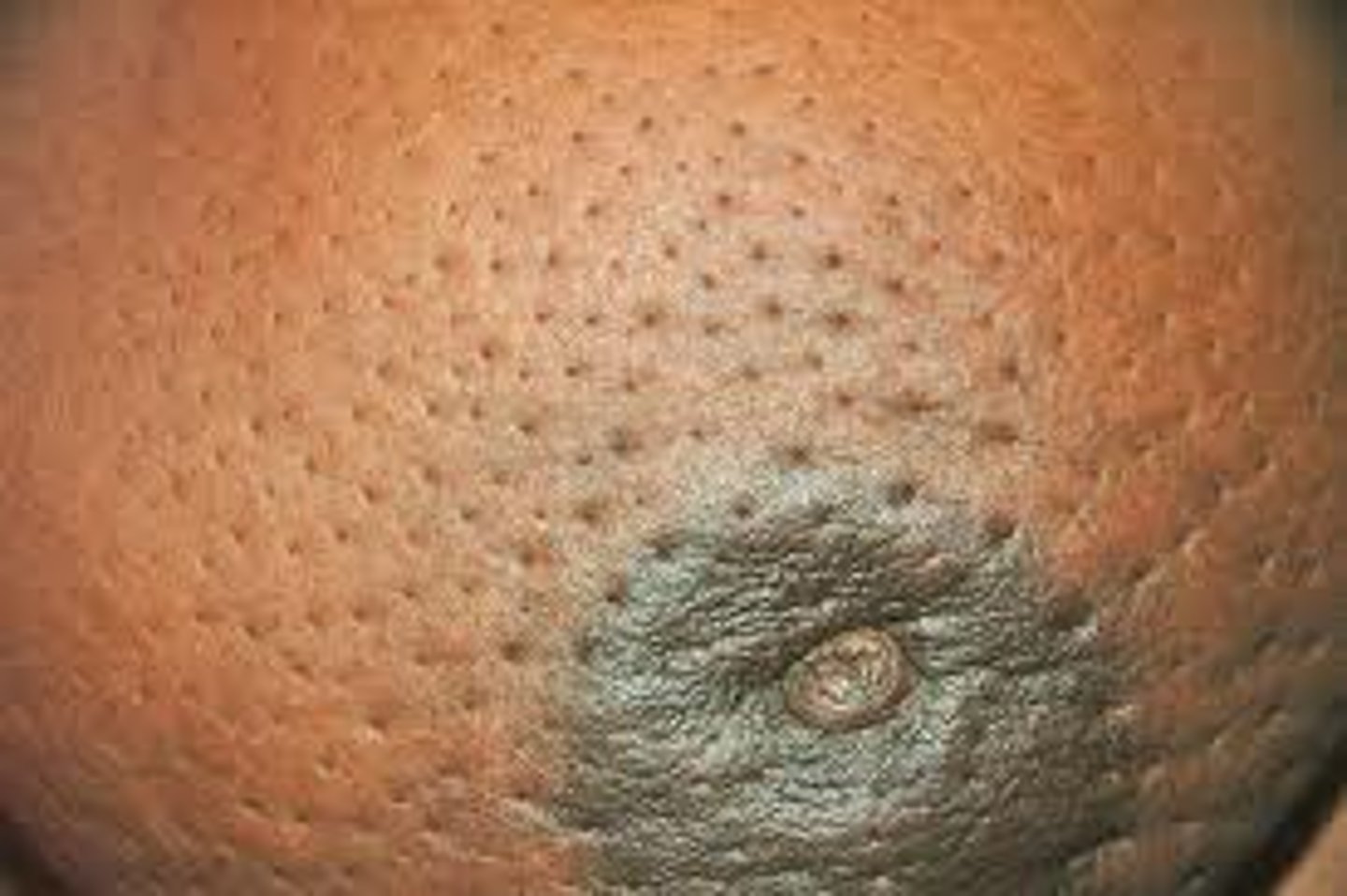
What are signs of cancer?
skin dimpling
edema
retraction
abnormal contours
nipple retraction and deviation
What is intraductal papilloma?
small, noncancerous (benign) tumor that grows in a milk duct of the breast
occurs most often in women ages 35-55
causes/risk factors are unknown
What may spontaneous unilateral blood discharge indicate?
intraductal papilloma
ductal carcinoma in situ
Paget disease
What is Paget's disease?
uncommon form of breast cancer usually starts as a scaly, eczema-like lesion on the nipple that may weep, crust, or erode
breast mass may be present
suspect if there is persisting dermatitis of the nipple and area
often presents with an underlying in situ or invasive ductal or lobular carcinoma
What are signs of cancer in the lymph system?
nodes that are large ( >1 or 2 cm) and firm or hard, matted together or fixed to the skin or underlying tissues suggest malignancy
What are breast cancers in AMAB?
occur under the nipple most commonly
What is mammogram?
low-powered x-ray technique that captures a picture of the internal structure of the breast
may help in the dx of breast problems, including cancer
recommended a woman have a baseline mammogram at age 40, followed by every couple of years until age 50, then annually
Who should get MRI?
BRCA 1 or BRCA2 mutation
1st degree relative (parent, sibling, child) with ^^^
lifetime risk of breast cancer has been scored at 20-25% +
radiation to chest between ages 10-30
Li-Frauemeni syndrome, Cowden syndrome, or Bannayan-Riley-Ruvalcaba syndrome
What is needle biopsy?
performed under local anesthesia
attempt to draw fluid from lumps that are thought to be cysts
withdrawn fluid and tissue is further evaluated to determine if there are cancerous cells present
Lumectomy (open biopsy)
surgical procedure
all or part of lump is removed → tested for malignancy
done under general anesthesia
hidradenitis supurativa
infected sweat glands from follicular occlusion
may be present when inspecting axillae
what can pigmented velvety axillary skin suggest?
acanthosis nigricans — associated with
diabetes
obesity
PCOS
rarely a neoplastic disorder