03 Material Characterization and Mechanical Properties
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Which kind of testing methods are there?
Destructive testing: characterization of material properties and validation of component parameters in test & design phases, control
Non-destructive testing: quality assurance, inspection
Examples of destructive testing (6)
Tension test
Compression test
Bending test
Hardness test
Creep test
Fatigue test
Examples of non-destructive testing (3)
Ultrasonic inspection
X-ray
Acoustic emission
Usual loads for material characterization (5)
Tensile
Compressive
Shear
Torsional
Bending
Are testing methods standarized?
Yes, normally by DIN or ISO
What are isotropic materials?
Materials with the same properties in every direction
Whar are orthotropic properties?
Properties that vary as a function of the direction
What is the setup for a tensile test? (6)
Electro-mechanical test frame with moveable traverse and gauge to determine position s
Material specimen
Gripper
Mechanical extensomenter/strain gauge/optical extensometer to measure ΔL
Load cell to determine F
Data acquisition device over time t
Which parameters can be read from the Stress-Strain-Diagram? (7)
Modulus of elasticity (E)
Proportional limt
Yield strength
Ultimate tensile strength
Elastic strain (strain in elastic (linear) region)
Plastic strain
Elongation to failure
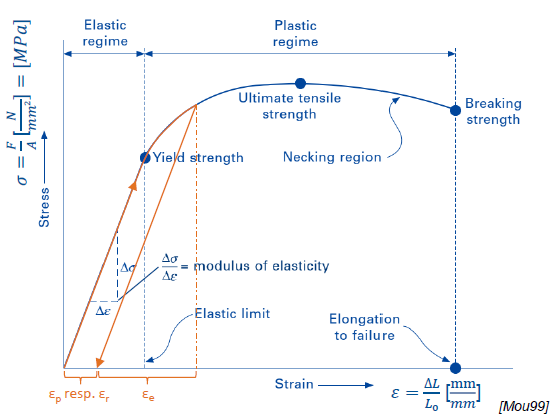
What is the elastic region?
Region in which deformation is reversible (no permanent deformation after loading)
What is the plastic region?
Region in which deformation is permanent
What is the ultimate tensile strength?
Point in which σ is max.
What is the breaking strength?
σ close to failure of specimen
What is the elongation to failure?
ε at breaking strength
What is the yield strength?
σ at the elastic limit (σ withstand by the material without undergoing plastic deformation)
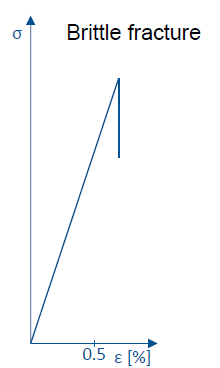
How does brittle fracture look like?
High E and abrupt break at (yield point, elastic limit)
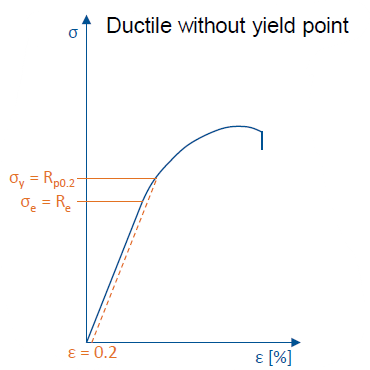
How does a ductile fracture without yield point look like?
Continuous graph without oscillations and eventual break in plastic region
How does a ductile fracture without yield point look like?
Continuous graph with oscillations aroud yield point (between lower and upper yield strength) and eventual break in plastic region
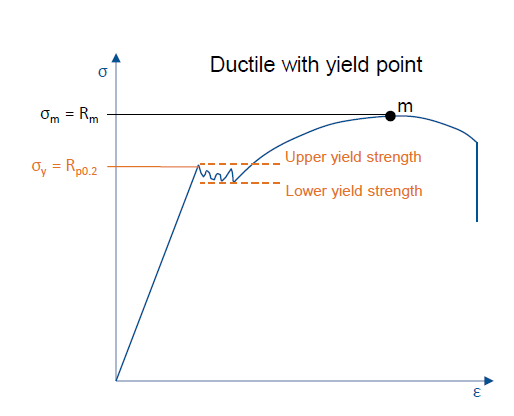
Ductile vs. Brittle fracture
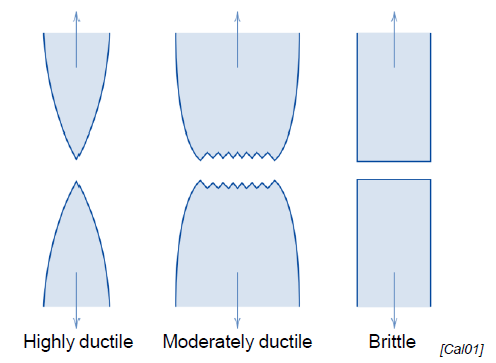
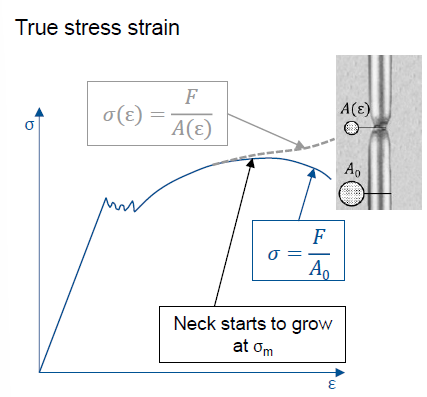
Where does the neck appear in the σ-ε-Diagram?
After the ultimate strength
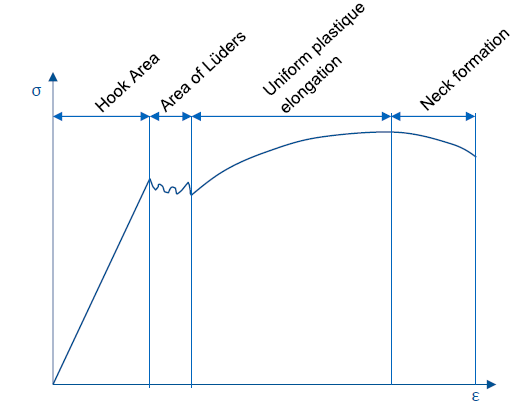
What are the regions of the σ-ε-Diagram?
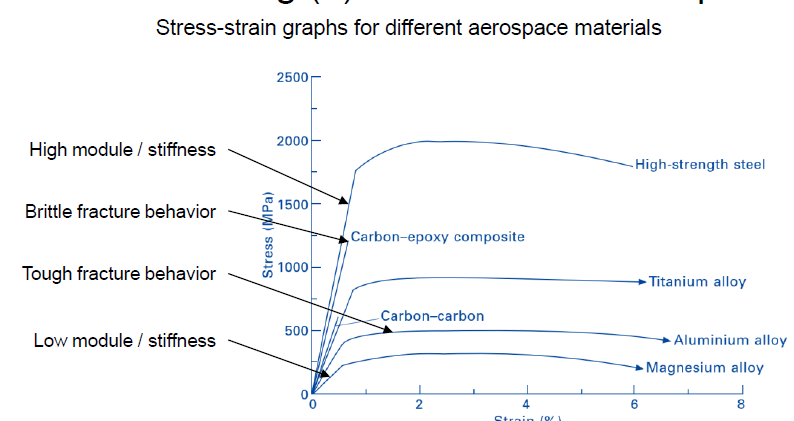
How are aerospace materials ordered in a σ-ε-Diagram? (4 by E)
Magnesium Alloy < Aluminium Alloy < Titanium Alloy < Carbon-Carbon (brittle) < Carbon-epoxy composite (brittle) < High-strength Steel
What is the relation between temperature and σ-ε-Diagram?
The higher the temperature, the more ductile the material
The lower the temperature, the more brittle the material
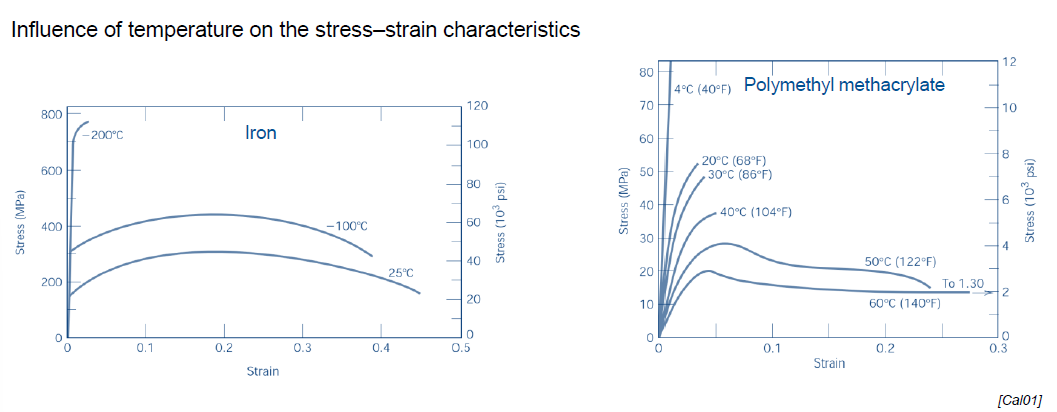
How is hardness defined?
Resistance of a material to penetration by another materials
Which methods are used to test hardness? (5)
Brinell (HB)
Vickers (HV)
Rockwell
Knoop (HK)
Shore
What are general characteristics of hardness tests?
Only slightly destructive (small indentation)
Inexpensive
Used for quality assurance in production lines (deviations in composition/production is detectable in the grade of hardness)
What is the indenter of every main hardness test?
Brinell: sphere
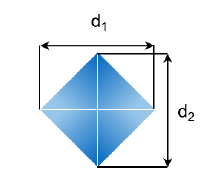
Vickers: pyramid
Knoop: pyramid
Rockwell: cone (double sphere)
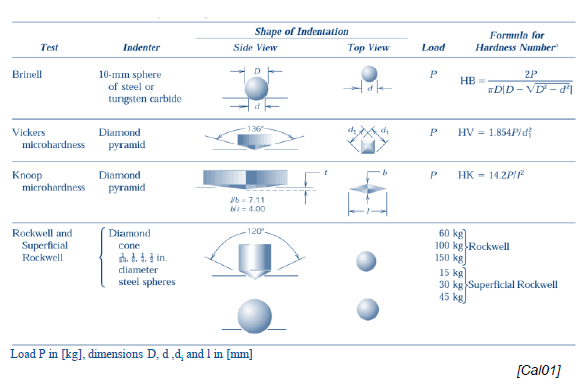
Pros and cons of Brinell:
Pros:
Measure medium hardness for heterogenous materials
Cons:
Not for thin layer materials
For hard materials the load is too large
Pros and cons of Vickers:
Pros:
Wide range of materials
Thin plates
More precise than Brinell
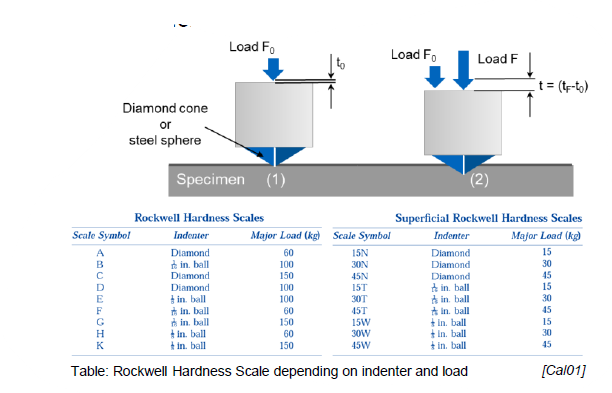
Pros and cons of Rockwell:
Pros:
Quick and automatable
Cons:
Small indenter, sensitive local effects
Reduced accuracy at high hardness
Various scales
What is creep?
Tendency of a solid material to slowly and permanently deform under the influence of constant mechanical stresses over extended periods, often at elevated temperatures.
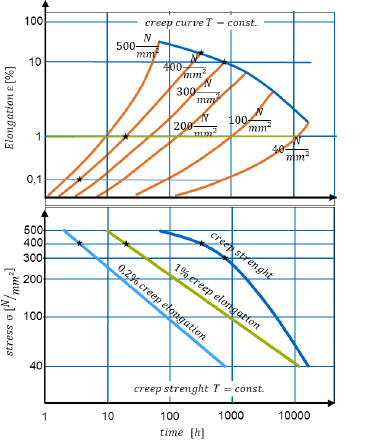
How is creep displayed normally?
With a creep curve (elongation as a function of time (logarithmic) for a given temperature)
With the creep strength (withstood stress as a function of time (log) for a given temperature)
What is fatigue?
Progressive and localized structural damage that occurs when a material is subjected to cyclic or fluctuating stresses or strains
Like creep but due to cyclic loads and not to constant loads
Ex: bending repeatedly a plastic fork until it breaks
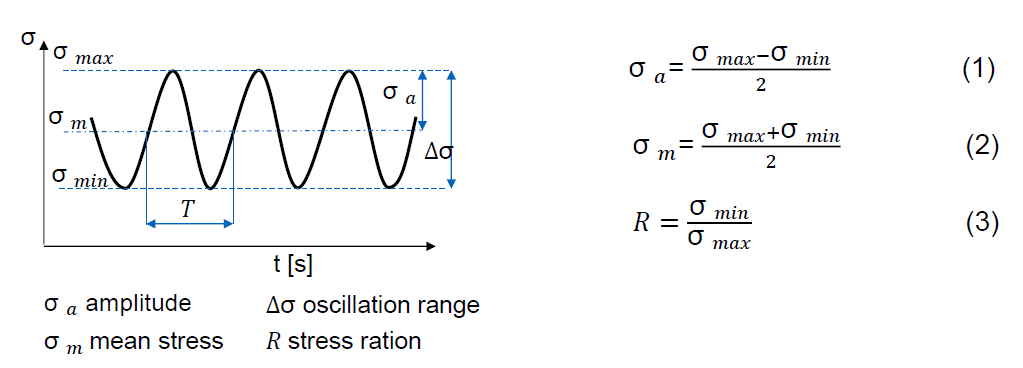
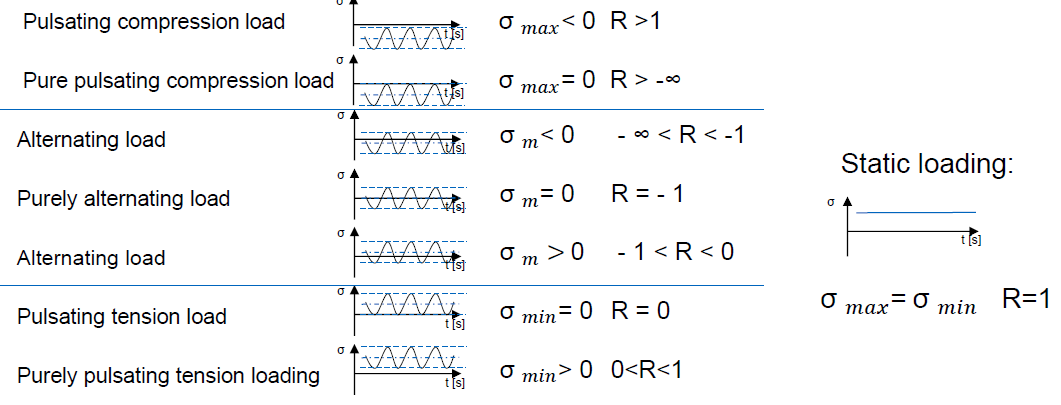
Through which load cases is fatigue tested? (7)
Pulsating compression load (σmax < 0; R > 1)
Pure pulsating compression load (σmax = 0; R > -infinite)
Alternating load (σm < 0; -infinite < R < -1)
Pure alternating load (σm = 0; R = -1)
Alternating load (σm > 0; -1 < R < 0)
Pulsating tension load (σmin = 0; R = 0)
Pure pulsating tension load (σmin > 0; 0 < R < 1)
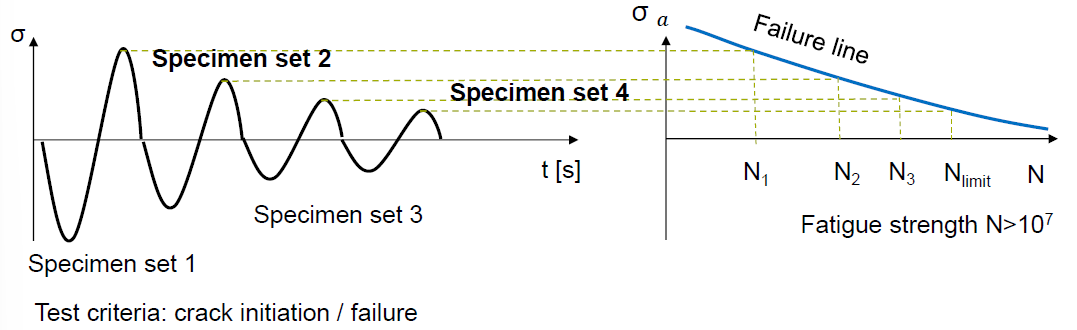
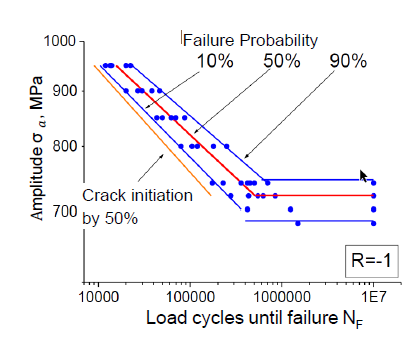
What is described by the Wöhler Curve?
How the stress withstood by an specimen decreases as a function of the number of cycles of the applied load for a given load case
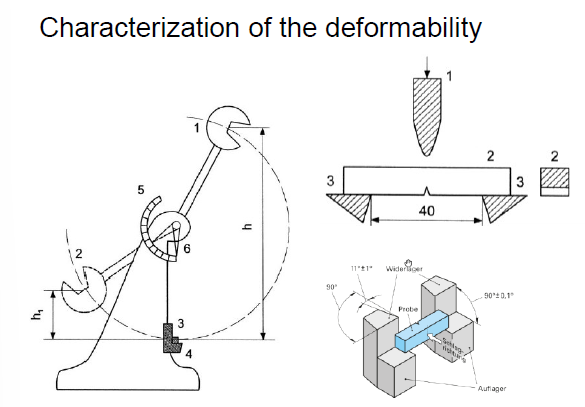
How does an impact bending test works?
A standarized specimen is stricken with a pendulum hammer
Suitable for comparative assessment only
High impact → ductile fracture
Low impact energy → brittle fracture
SQ: What information do you get out of the uniform plastic elongation zone which you get out of a tension test?
Yield point (initial point)
Ultimate strength (final point)
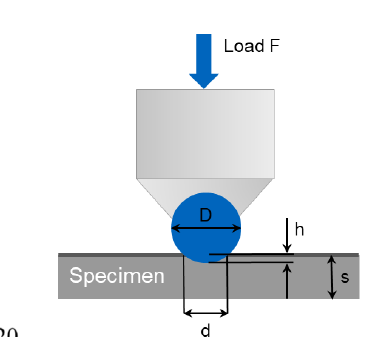
SQ: Is it possible to use the Brinell hardness with thin sheet metals? If yes, under which circumstances?
In general, no. Only if s >= 8h (thickness of sheet bigger or equal to 8 times the indentation depth)
SQ: How does a yield strength behave with temperature?
Is lower for higher temperatures
SQ: Which types of test methods are available?
Destructive
Non-destructive
SQ: How does a typical test method work?
Setup
Initial, standarized, known conditions
Physical relations
Measurements
Calculations
Output