Untitled
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/70
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:52 PM on 9/16/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
1
New cards
economics
study of how society manages its scare resources
2
New cards
society
individuals, firms, government
3
New cards
scarcity
limited nature of society's resources, individuals face time and income scarcity
4
New cards
behavior of the economy
reflects the behavior of the individuals who make up the economy
5
New cards
opportunity cost
what you give up
- value of certain resources could have produced had they been used in the best alternative way, not always cost related, could be time
- implicit+explicit cost
- living expenses are not opp cost, since you're going to spend that anyway
- value of certain resources could have produced had they been used in the best alternative way, not always cost related, could be time
- implicit+explicit cost
- living expenses are not opp cost, since you're going to spend that anyway
6
New cards
marginal change
small incremental adjustments around the edges of what you're doing
- ex: marginal benefits, marginal costs
- ex: $40 a month for a movie streaming service and you watch 8 movies a month, the marginal cost: the extra you would have incurred by streaming another film (would be 0) because you pay the same $40 for the service
- ex: marginal benefits, marginal costs
- ex: $40 a month for a movie streaming service and you watch 8 movies a month, the marginal cost: the extra you would have incurred by streaming another film (would be 0) because you pay the same $40 for the service
7
New cards
marginal benefit
depends on how much the person already has
- water vs diamonds, water is essential but the marginal benefit of having it is small because water is plentiful
- water vs diamonds, water is essential but the marginal benefit of having it is small because water is plentiful
8
New cards
a rational decision maker
takes an action if the action benefits exceed its cost
9
New cards
incentive
something that induces a person to act
- ex: when the price of apples rises, people decide to eat fewer apples, and tax on gas encourages different transportation
- ex: when the price of apples rises, people decide to eat fewer apples, and tax on gas encourages different transportation
10
New cards
trade
allows each person to specialize in the activities she does best
11
New cards
market economies
the decisions of the central planner are replaced by the decisions of millions of firms and households
- firms decide who to hire, households decide which firms to work for
- these all interact in the marketplace where prices and self interest guide decisions
- firms decide who to hire, households decide which firms to work for
- these all interact in the marketplace where prices and self interest guide decisions
12
New cards
free markets
contain many buyers and sellers, and goods and servies
-
free market, an unregulated system of economic exchange, in which taxes, quality controls, quotas, tariffs, and other forms of centralized economic interventions by government either do not exist or are minimal.
-
free market, an unregulated system of economic exchange, in which taxes, quality controls, quotas, tariffs, and other forms of centralized economic interventions by government either do not exist or are minimal.
13
New cards
market failure
to refer to a situation in which the market on its own fails to produce an efficient allocation of resources, caused by externalities and market power
- the individual incentives for rational behavior do not lead to rational outcomes for the group, known as negative externalities: traffic, litter, obesity, pollution
- the individual incentives for rational behavior do not lead to rational outcomes for the group, known as negative externalities: traffic, litter, obesity, pollution
14
New cards
externality
can be harmful or beneficial, the impact of one person's actions on the well-being of a bystander
- in a negative externality such as pollution the market may fail to take this cost into account
- positive externality=getting an education
- in a negative externality such as pollution the market may fail to take this cost into account
- positive externality=getting an education
15
New cards
market power
ability of a firm to unduly influence the market prices-> having only one well for water, the person who owns it has lots of power and takes advantage
- causes externalities
- causes externalities
16
New cards
a country standard of living depends on...
its ability to produce, more productive, then high standard of living
17
New cards
prices rise when
too much money is printed
18
New cards
inflation
increases in overall prices in the economy, value of money decrease so prices rise
19
New cards
a short run trade-off between inflation and unemployment
increasing the amount of money in the economy stimulates overall level of spending thus higher demand for goods and services, more demand may overtime cause firms to raise their prices but also encourages them to higher more workers
- over a period of a year or two, many economic policies push inflation and unemployment in opposite directions
- over a period of a year or two, many economic policies push inflation and unemployment in opposite directions
20
New cards
explicit cost
monetary cost $$$
21
New cards
implicit cost
time, things you could've done instead, a student who gives up income of a job when he stays in college for 4 years
22
New cards
marginal analysis
every decision you make you have to determine that the marginal benefit is at least as great as the marginal cost
23
New cards
total benefit
revenue generated by all customers for all advertising hours
24
New cards
total cost
total amount of time spend for all hours of advertising
-change in total cost, margins of total cost
-change in total cost, margins of total cost
25
New cards
net benefit
total benefit-total cost
26
New cards
marginal benefit
revenue generated by additional customers gained from the last hour of advertising- the margins of total benefit
27
New cards
you are going to keep advertising
as long as marginal benefits exceeds or equals marginal cost, advertising is MB is at least as great as MC
28
New cards
circular flow diagram
model how the economy is organized and how participants interact
- outer arrow is the flow of dollars, inner arrows, flow of inputs and outputs
- two markets: goods and services and factors of production
- two groups of people: households and firms
- outer arrow is the flow of dollars, inner arrows, flow of inputs and outputs
- two markets: goods and services and factors of production
- two groups of people: households and firms
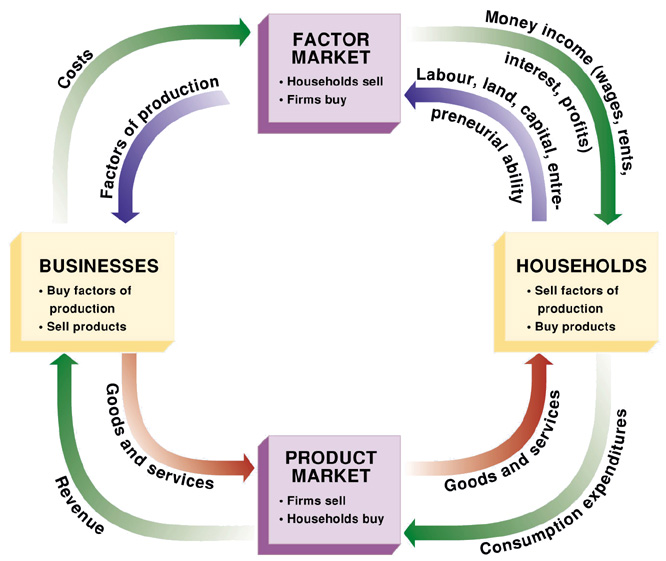
29
New cards
two types of decision makers
firms and households (in a circular flow diagram)
30
New cards
firms
produce goods and services using inputs, labor, land, capital,
- inputs are called factors of production
- inputs are called factors of production
31
New cards
factors of production
labor, land, capital
32
New cards
households
own the factors of production and consume the goods/services the firms produce
- sell factors
- buy products
- sell factors
- buy products
33
New cards
households and firms in the market
households are buyers, firms are sellers, and in the market for factors of production, firms are buyers and households are sellers
34
New cards
factor market
households sell, firms buy (top of diagram)
35
New cards
businesses
(left side of diagram)
- buy factors of production
- sell products
- buy factors of production
- sell products
36
New cards
product market
firms sell, households buy (bottom of diagram)
37
New cards
inner loop
flows of inputs and outputs
- households sell labor, land, and capital, to firms for factors of production
- firms use these factors to produce goods and services, which in turn are sold to households
- households sell labor, land, and capital, to firms for factors of production
- firms use these factors to produce goods and services, which in turn are sold to households
38
New cards
outer loop
the corresponding flow of money
- households spend money to buy goods and services from firms
- the firms use the revenue from sales for payments to the factors of production such as wages
- whats left is the re-profit for the firm owners who are themselves, members of households,
- households spend money to buy goods and services from firms
- the firms use the revenue from sales for payments to the factors of production such as wages
- whats left is the re-profit for the firm owners who are themselves, members of households,
39
New cards
economists
develop models to explain behavior and/or events
- model is a relationship between variables
- model is a relationship between variables
40
New cards
law of demand
all else the same, an increase in the price of a good will reduce the quantity demanded of the good
41
New cards
ppf
an economy that only produces two goods--> cars and computers
- the ppf shows the various combinations of output that the economy can possibly produce given the available resources
- slope measures the opp cost of a car in terms of computers
- the ppf shows the various combinations of output that the economy can possibly produce given the available resources
- slope measures the opp cost of a car in terms of computers
42
New cards
less steep parts of the curve
less opportunity cost, bowed out because the opp costs isn't consistent
43
New cards
what determines the price that trade takes place
has to lie between their opp costs
44
New cards
comparative advantage
ability to produce a good at a lower opp cost
45
New cards
market
place where buyers and sellers interact and determine the price of a good
- buyers determine the demand for a product and sellers determine supply
- buyers determine the demand for a product and sellers determine supply
46
New cards
supply and demand
supply-> sellers of a good or service
demand-> buyers of a good or service
they refer to the behavior of people as they interact with one another in competitive markets
demand-> buyers of a good or service
they refer to the behavior of people as they interact with one another in competitive markets
47
New cards
competitive markets
lots of buyers and many sellers that each has a negligible impact on the market price
- each seller of ice cream has limited control over the price because other sellers are offering similar products
- no buyer can influence the price because each buyer purchases only a small amount, raising prices too high means people will just buy elsewhere
- each seller of ice cream has limited control over the price because other sellers are offering similar products
- no buyer can influence the price because each buyer purchases only a small amount, raising prices too high means people will just buy elsewhere
48
New cards
perfectly competitive
the goods offered for sale are exactly the same
- the buyers and sellers are so numerous that no single buyer or seller has any influence over the market price
- buyers and sellers are price takers, they must accept the price the market determines, buyers can buy all they want, sellers can sell all they want
- the buyers and sellers are so numerous that no single buyer or seller has any influence over the market price
- buyers and sellers are price takers, they must accept the price the market determines, buyers can buy all they want, sellers can sell all they want
49
New cards
monopoly
a market in which there are many buyers but only one seller, and they set the price
50
New cards
demand curve
relationship between price and quantity demanded
51
New cards
quantity demanded
determined by the goods price
52
New cards
law of demand
as price increase quantity demanded goes down
53
New cards
market demand vs. individual demand
two peoples demand curve = market demand
- found by adding horizontally the individual demand curves
- found by adding horizontally the individual demand curves
54
New cards
variables that shift demand
income: lower income means less spending so less demand
- expectations:
-
- expectations:
-
55
New cards
normal good
if demand for a good falls, while income falls, its a normal good
56
New cards
inferior good
if demand falls while income increases
- if demand for a good rises when income falls
- bus rides: as income falls you are less likely to buy a car or take a cab
- if demand for a good rises when income falls
- bus rides: as income falls you are less likely to buy a car or take a cab
57
New cards
variables that influence buyers
price of good itself (movement along the demand curve)
- income, prices of related goods, tastes, expectations, number of buyers (all shift curve)
- income, prices of related goods, tastes, expectations, number of buyers (all shift curve)
58
New cards
quantity supplied
the amount that sellers are willing and able to sell
59
New cards
law of supply
relationship between price and quantity supplied (slopes upward)
60
New cards
market supply
some of all the supplies of all sellers
61
New cards
things that effect supply
- input prices
- technology
- expectations
- number of sellers
- technology
- expectations
- number of sellers
62
New cards
equilibrium
where supply and demand intersect, called equilibrium price and quantity
- at this point, the quantity that buyers are willing and able to sell balances the quantity that sellers are able to sell
- actions of buyers and sellers naturally moves markets towards equilibrium
- at this point, the quantity that buyers are willing and able to sell balances the quantity that sellers are able to sell
- actions of buyers and sellers naturally moves markets towards equilibrium
63
New cards
increase in demand no change in supply
P up
Q up
Q up
64
New cards
increase in demand, increase in supply
P ambiguous
Q up
Q up
65
New cards
increase in demand, decrease in supply
P up
Q ambiguous
Q ambiguous
66
New cards
no change in demand, increase in supply
P down
Q up
Q up
67
New cards
no change in demand, decrease in supply
P up, Q down
68
New cards
decrease in demand, no change in supply
P down, Q down
69
New cards
decrease in demand, increase in supply
P down, Q ambiguous
70
New cards
decrease in demand, decrease in supply
P ambiguous, Q down
71
New cards
invisible hand
in a free market economy, self-interested individuals operate through a system of mutual interdependence. This interdependence incentivizes producers to make what is socially necessary, even though they may care only about their own well-being.