Intro to Functions and Function Behavior
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Domain
How far left or right a graph goes
Range
How far up or down the graph goes
X-intercepts
Where the graph crosses the x-axis (#,0)
Y-intercepts
Where the graph crosses the y-axis (0,#)
Horizontal Asymptote
Where horizontal line graph approaches but does not touch
Vertical Asymptote
Vertical line graph that approaches but does not touch
Refelectional Symmetry
Object can reflect (flip) onto itself
Rotational Symmetry
Object can rotate onto itself
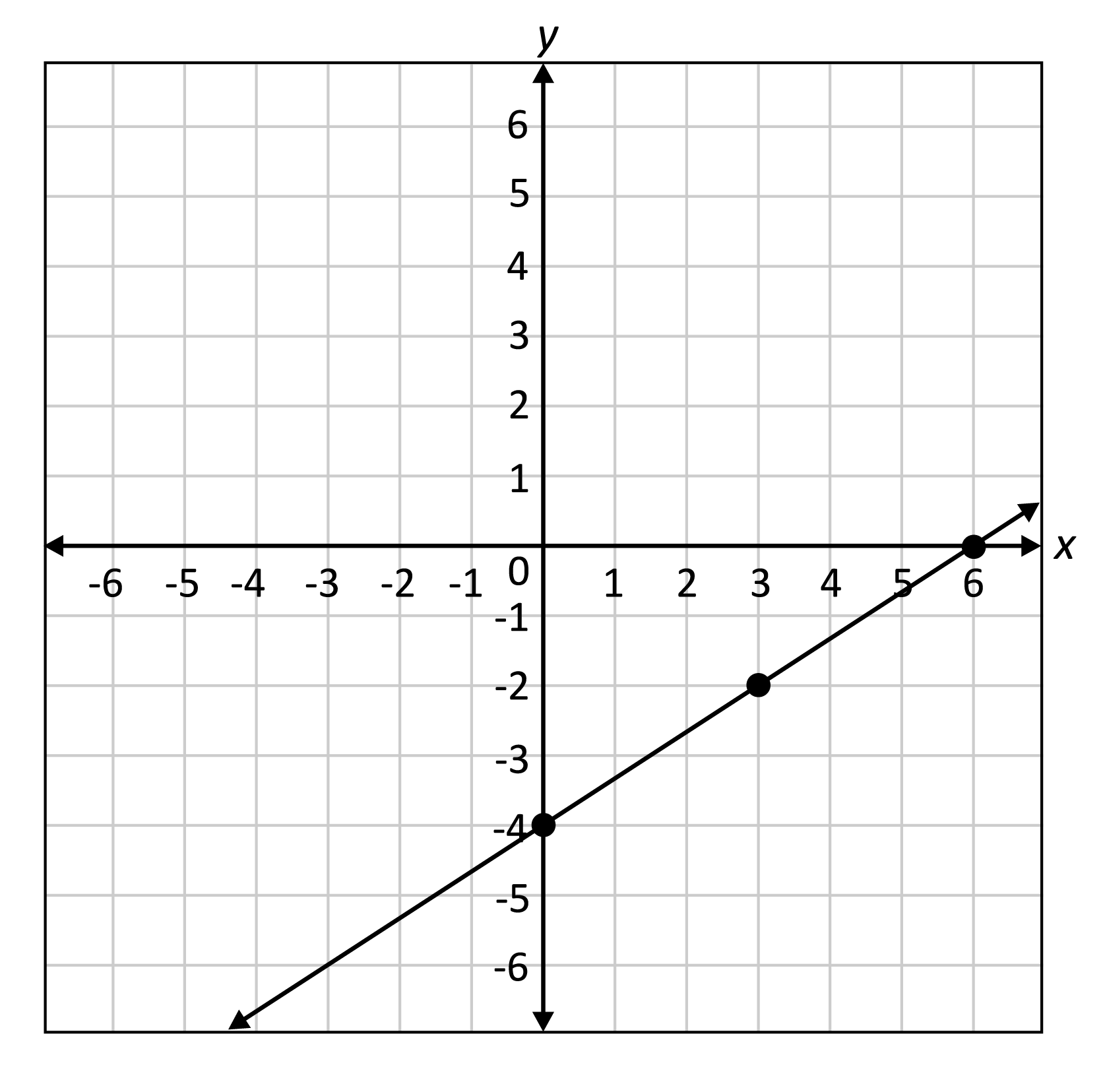
Linear Family** Parent Function**
y = x
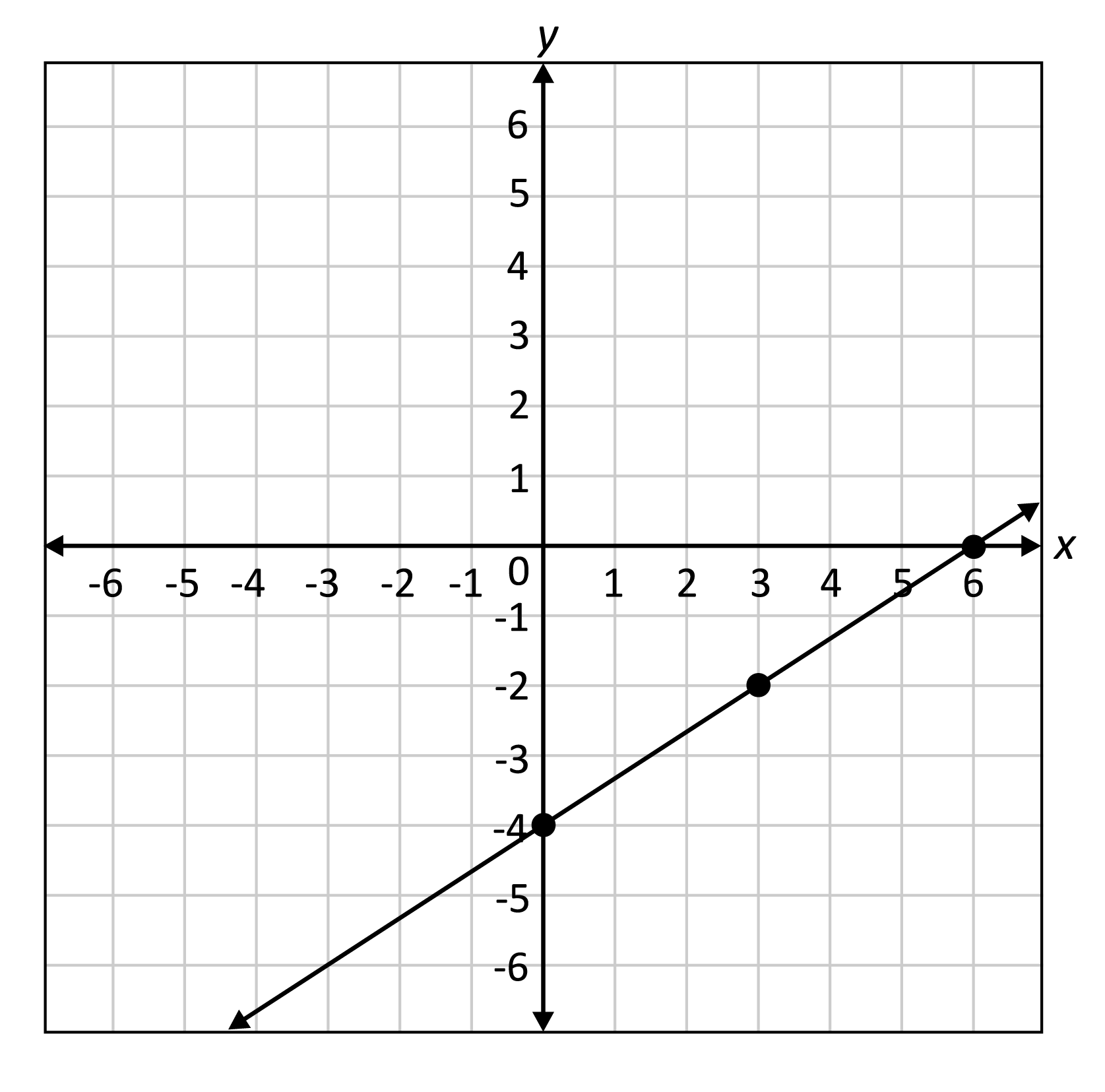
Linear Family** General Form**
y = mx+b
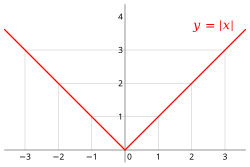
Absolute Value Parent Function
y = |x|
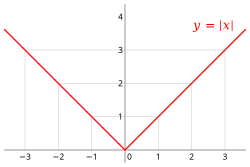
Absolute Value General Form
y = a|x-h| + k
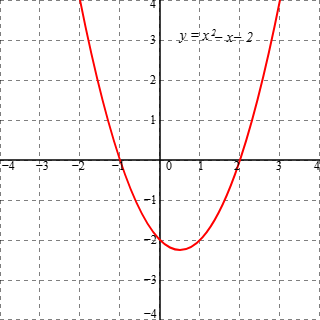
Quadratic Family Parent Function
y = x^2
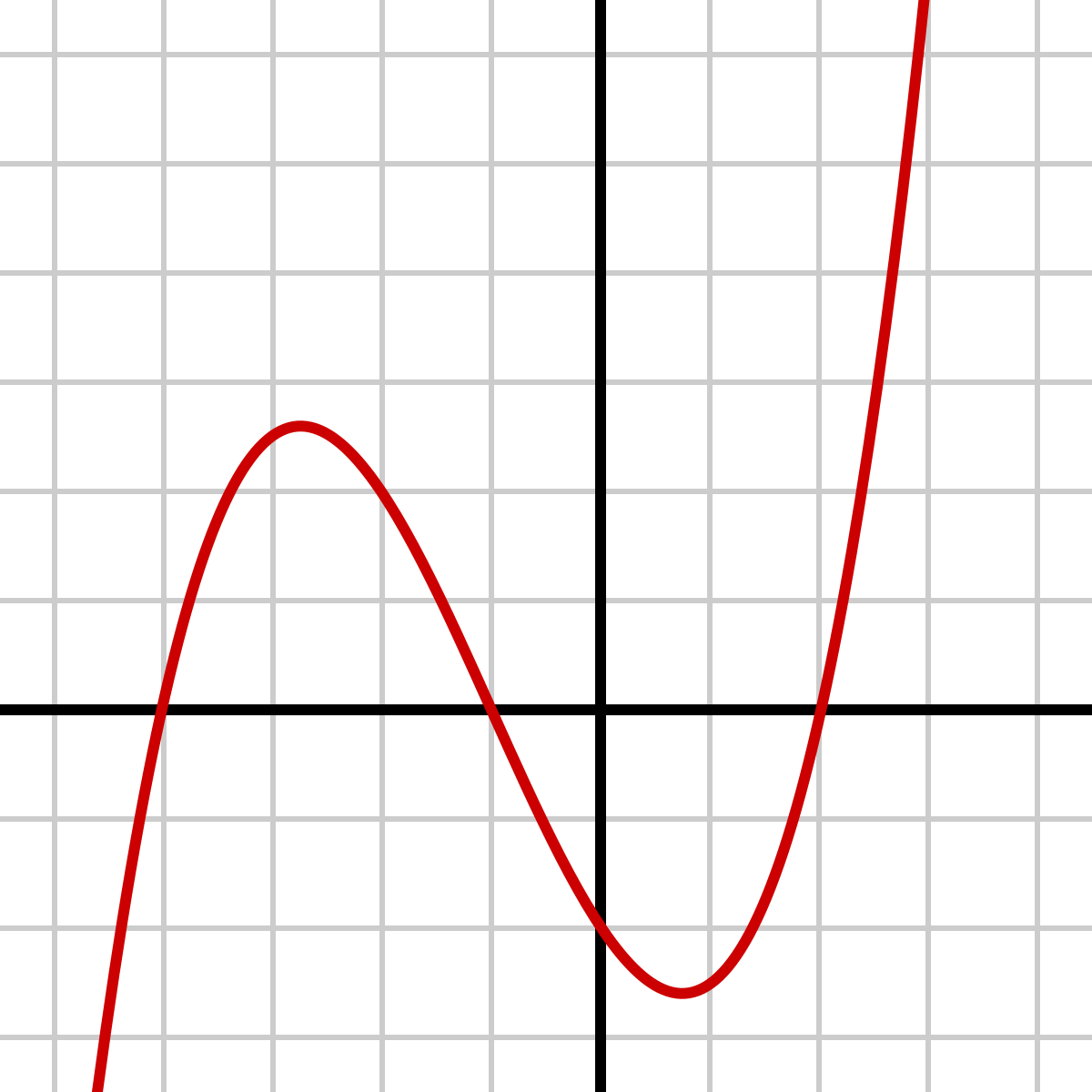
Cubic Family** Parent Function**
y = x^3
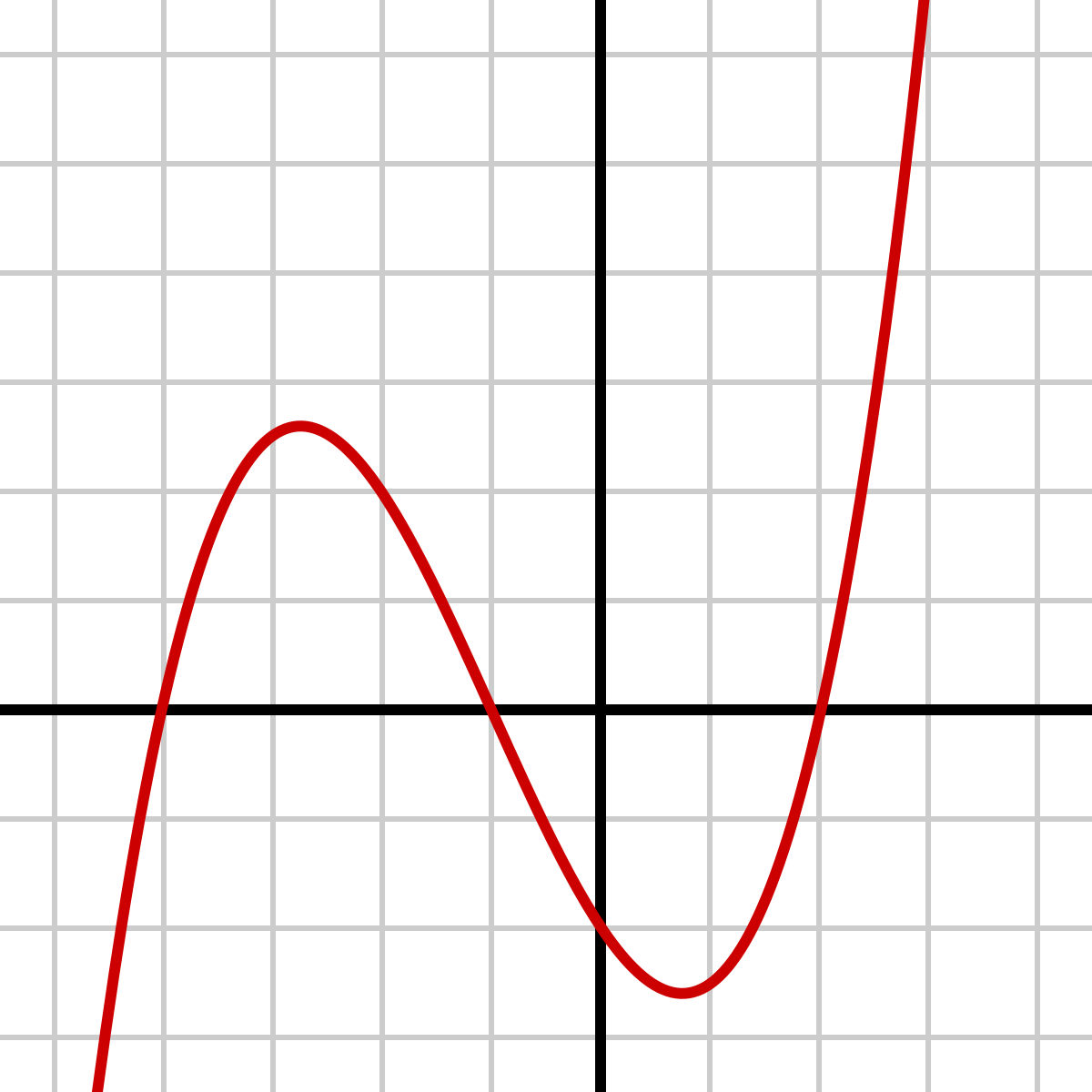
Cubic Family** General Form**
y = a(x-h)^3 + k
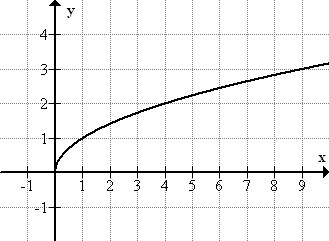
Square Root Family** Parent Function**
y = \sqrt{x}
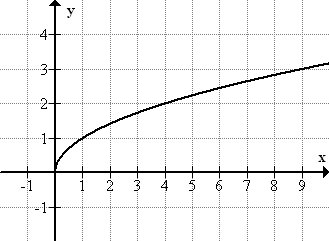
Square Root Family** General Form**
y = a\sqrt{x-h} + k
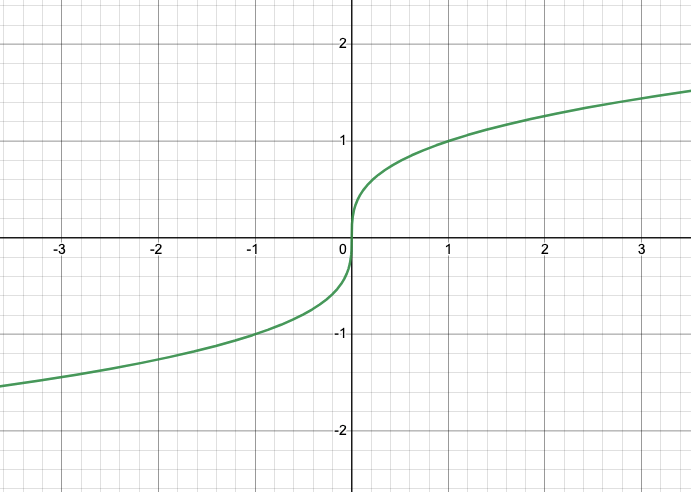
Cube Root Family** Parent Function**
y = \sqrt[3]{x}
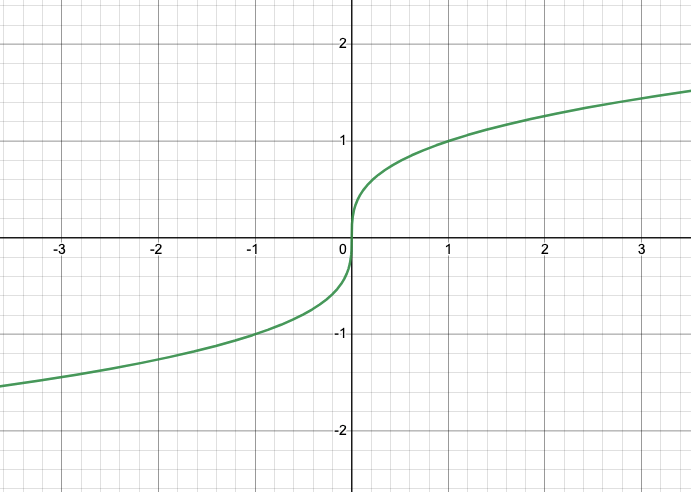
Cube Root Family** General Form**
y = a\sqrt[3]{x-h} + k
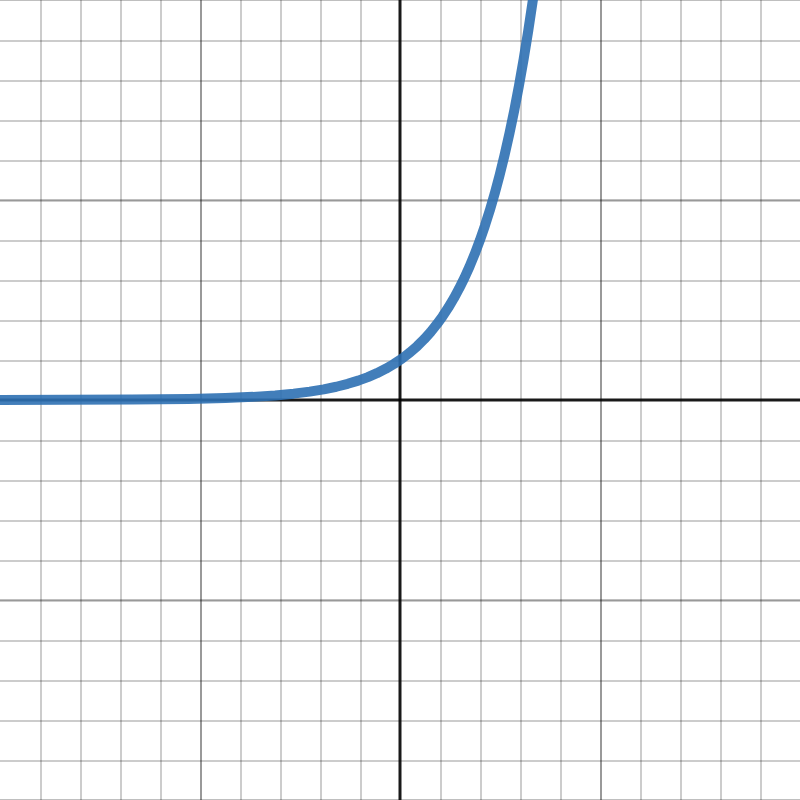
Exponential Family** Parent Function**
y = b^x
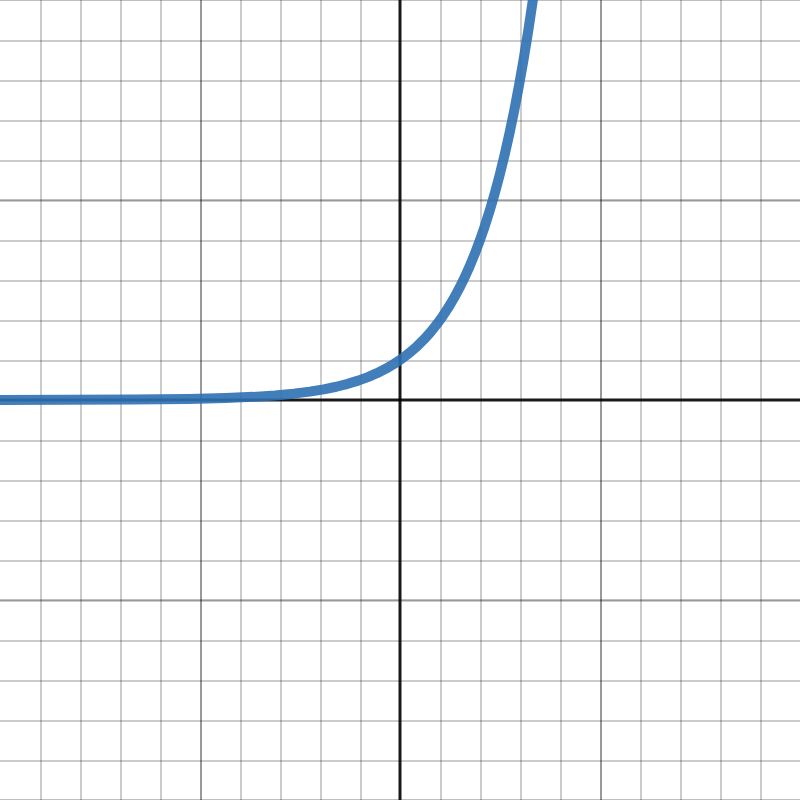
Exponential Family** General Form**
y = ab^{x-h} + k
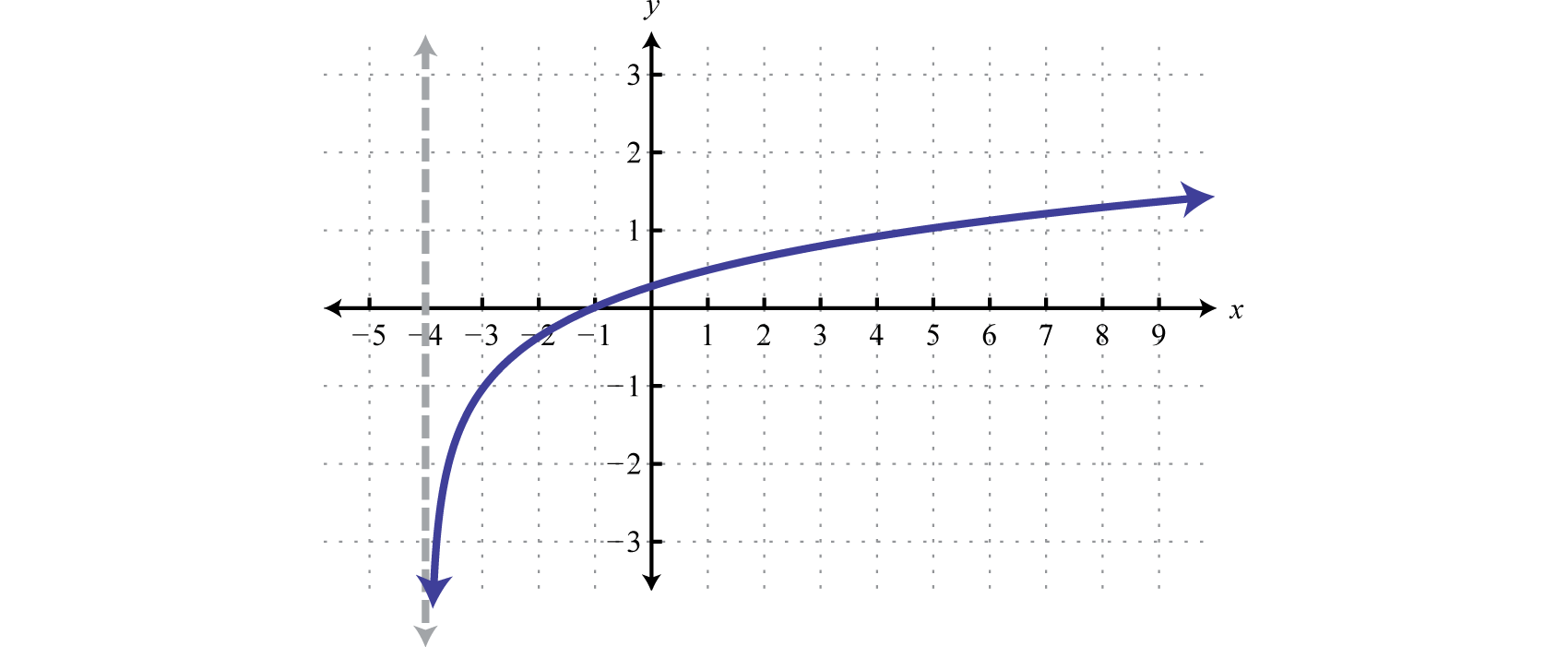
Logarithmic Family** Parent Function**
y = \log_b(x)
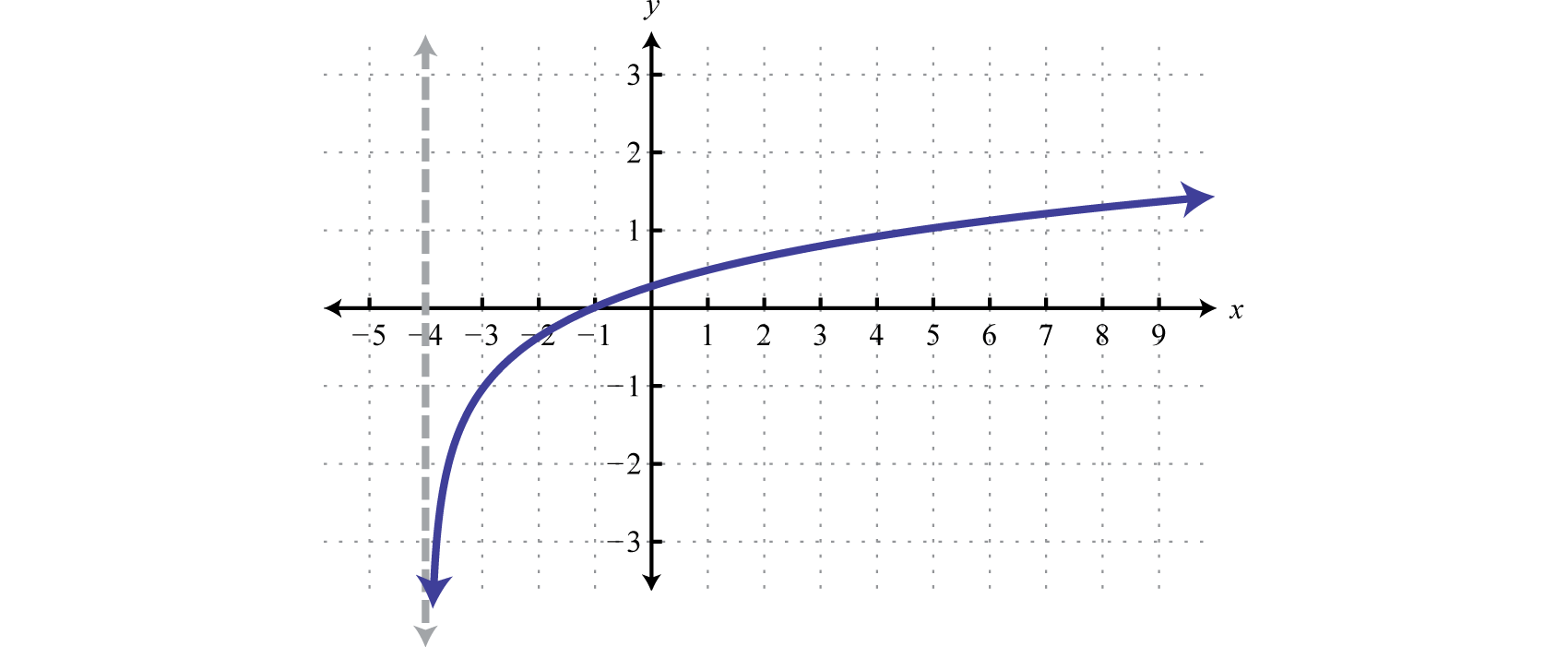
Logarithmic Family** General Form**
y = a\log_b(x-h) + k
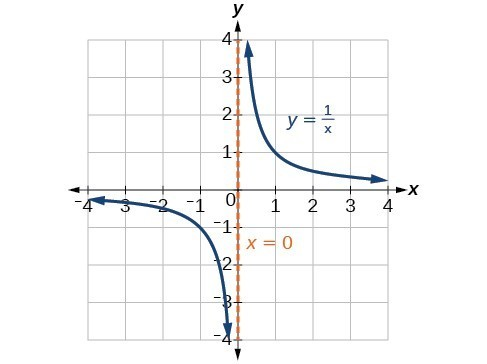
Rational Family** Parent Function**
y = \frac{1}{x}
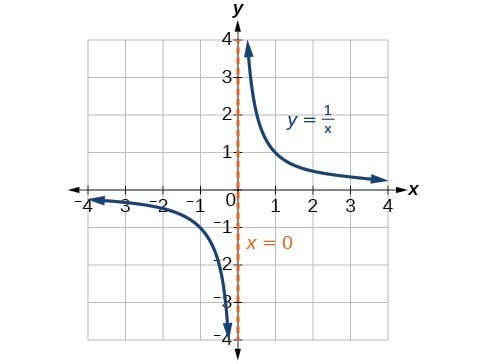
Rational Family** General Form**
y = \frac{a}{x-h} + k
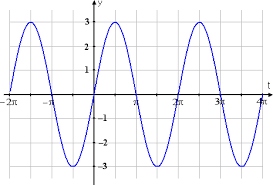
Trigonometric Family (Sine)** Parent Function**
y = \sin(x)
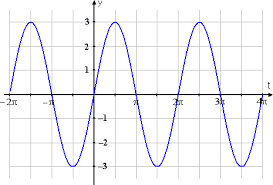
Trigonometric Family (Sine)** General Form**
y = a\sin(b(x-h)) + k
Vertex
point where graph changes directions
Max/Min
Highest/lowest points of a graph
Axis of symmetry
Vertical line that splits parabola into two congruent halves
The axis of symmetry has the same value as
The x value for the vertex (h,k) (H)
Parabola
U Shape graph of a quadratic function
Zeroes of a function
X-ints of a function (roots or solutions)
Decreasing
Set of x values where the graph goes down left to right
Increasing
Set of x values where the graph goes up left to right
What situation best models a trigonometric function
When a value changes constantly (up and down and up and down in waves)
Quadratic Family General Form(s)
y = ax² + bx + c - Standard Form
y = a(x-h)² + k - Vertex Form
y = a (x-p)(x-q) - Intercept Form
Linear rate of change formula
y2 - y1/x2 - x1 OR rise/run
Nonlinear Rate of Change formula
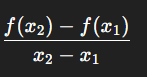
Example of nonlinear rate of change formula
(100 × 0.97^60) - (100 × 0.97^30) /60-30 (x2 = 60, x1 = 30)
Exponential Decay vs Growth
When exponential function either goes up or down
Vertical translation
Represented by the k or b value for a function (mx + b, y = a(x-h)² + k)
Horizontal Translation
Represented by the h or m value for a function (mx + b, y = a(x-h)² + k)
Dilations
represented by the a value, there two types: strech and compression
Stretch Dilation
when a graph gets bigger (looks narrow) (a >1)
Compress Dilatation
when a graph gets smaller (looks compressed) (a<1)
Reflections
Transformation over the line of reflection
Represented by negative a value. ( a = -)