W16: ACID CHLORIDE, ACID ANHYDRIDES, AND ESTERS
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
An _________________ is a carboxylic acid derivative in
which the —OH portion of the carboxyl group, has been replaced with a —Cl atom.
acid chloride
Draw the general formula of acid chloride
answer:
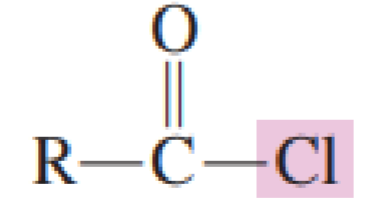
Naming acid chlorides:
Replace the -ic acid ending of the common name of the parent carboxylic
acid with _____________.
-yl chloride
Naming acid chlorides:
Replace the -oic acid ending of the IUPAC name of the parent carboxylic acid with _______________.
-oyl chloride
Preparation of an acid chloride from its parent carboxylic acid involves reacting the acid with one of several ____________
inorganic chlorides
Give the three inorganic chloride:
1.) PCI3
2.) PCI5
3.) SOCI2
Acid chlorides react rapidly with water, in a _________________, to regenerate the parent carboxylic acid.
hydrolysis reaction
______________ are useful starting materials for the synthesis of other carboxylic acid derivatives, particularly _______ and __________.
1.) Acid chlorides
2.) esters
3.) amides
Synthesis of esters and amides using acid chlorides is a ________________ process than ester and amide synthesis using a carboxylic acid.
more efficient
An ____________ is a carboxylic acid derivative in which the -OH portion of the carboxyl group has been replaced with carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom (C=O) and single-bonded to another oxygen atom (C-O).
acid anhydride
Draw the general formula of acid anhydride:
Answer:

Structurally, acid anhydrides can be visualized as two carboxylic acid molecules bonded together after ________________ from the acid molecules.
removal of a water molecule
____________________ both R groups are the same) are named by replacing the acid ending of the parent carboxylic acid name with the word anhydride.
Symmetrical acid anhydrides
_______________ (different R groups present) are named by using the names of the individual parent carboxylic acids (in alphabetic order) followed by the word anhydride.
Mixed acid anhydrides
In general, acid anhydrides _________________ by directly reacting the parent carboxylic acids together.
cannot be formed
Instead, an _____________ is reacted with a _______________ to produce the acid anhydride.
1.) acid chloride
2.) carboxylate ion
Like acid chlorides, acid anhydride cannot exist in biological systems, as they undergo __________ to regenerate the parent carboxylic acids.
hydrolysis
Reaction of an ________ with an acid anhydride is a useful method for synthesizing esters.
alcohol
Inorganic acid such as ____________, _____________, and ___________ react with alcohols to form esters in a manner similar to that for carboxylic acids.
1.) sulfuric acid
2.) phosphoric acid
3.) nitric acids
A ____________ is an organic compound formed by reaction of an alcohol with phosphoric acid.
phosphate ester
What are the three biologically important phosphoric acid that exist?
1.) phosphoric acid
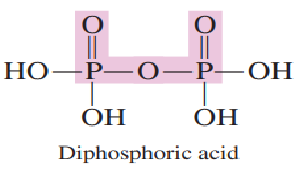
2.) diphosphoric acid
3.) triphosphoric acid
_________________, the simplest of the three acids, undergoes intermolecular dehydration to produce diphosphoric acid.
Phosphoric acid
Phosphoric acid, the simplest of the three acids, undergoes ______________ to produce diphosphoric acid.
intermolecular dehydration
Another intermolecular dehydration, involving diphosphoric acid and phosphoric acid produces ________________.
triphosphoric acid
All three phosphoric acids undergo esterification reactions with alcohols, producing species such as:
1.) Diphosphate monoester
2.) Triphosphate monoester
Draw carboxylic acid anhydride
answer:
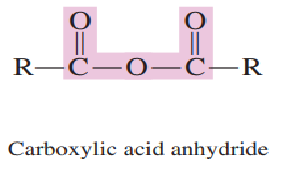
Draw diphosphoric acid:
Answer: