Brain Basics
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
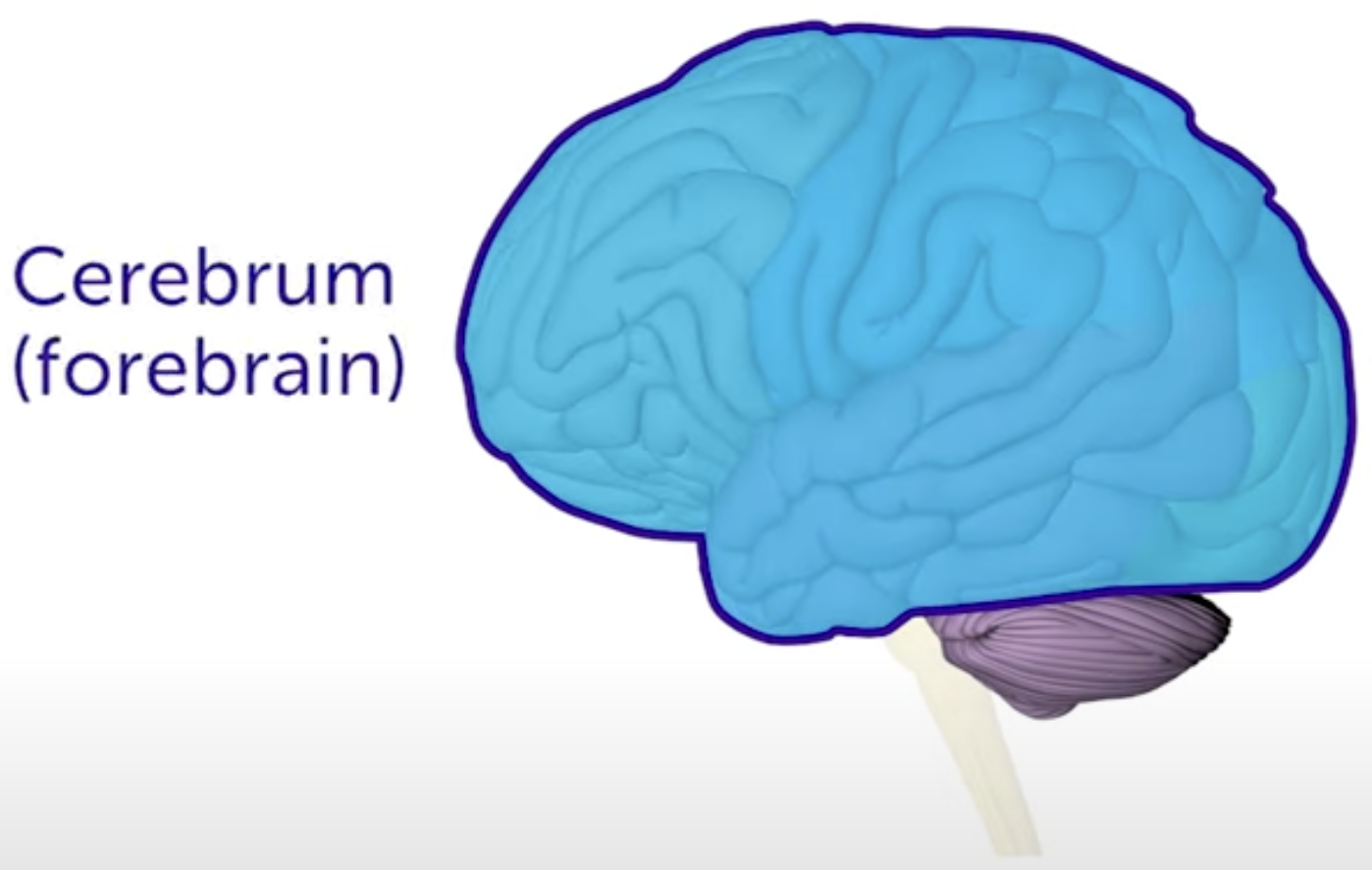
Cerebrum
It obtains information and sends it to a specific part of the cerebrum.
The largest part of the brain. It’s not a layer (that is the cerebral cortex).
It is divided into the left and right hemisphere by a deep groove known as the longitudinal fizzure.
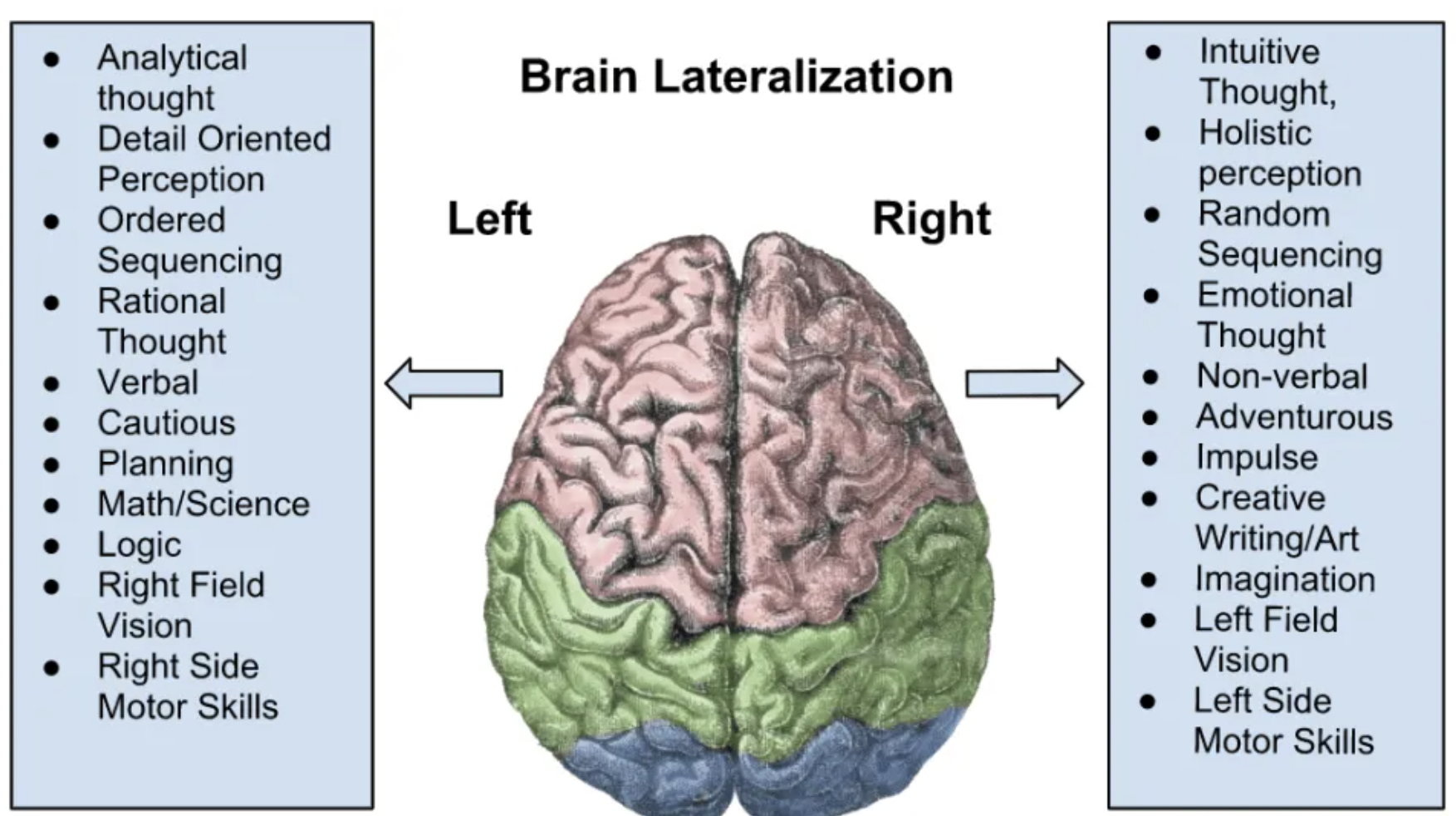
Right Hemisphere
Controls the left half of our body.
Nonverbal, creative, emotional, artistic, imaginative, impulsive.
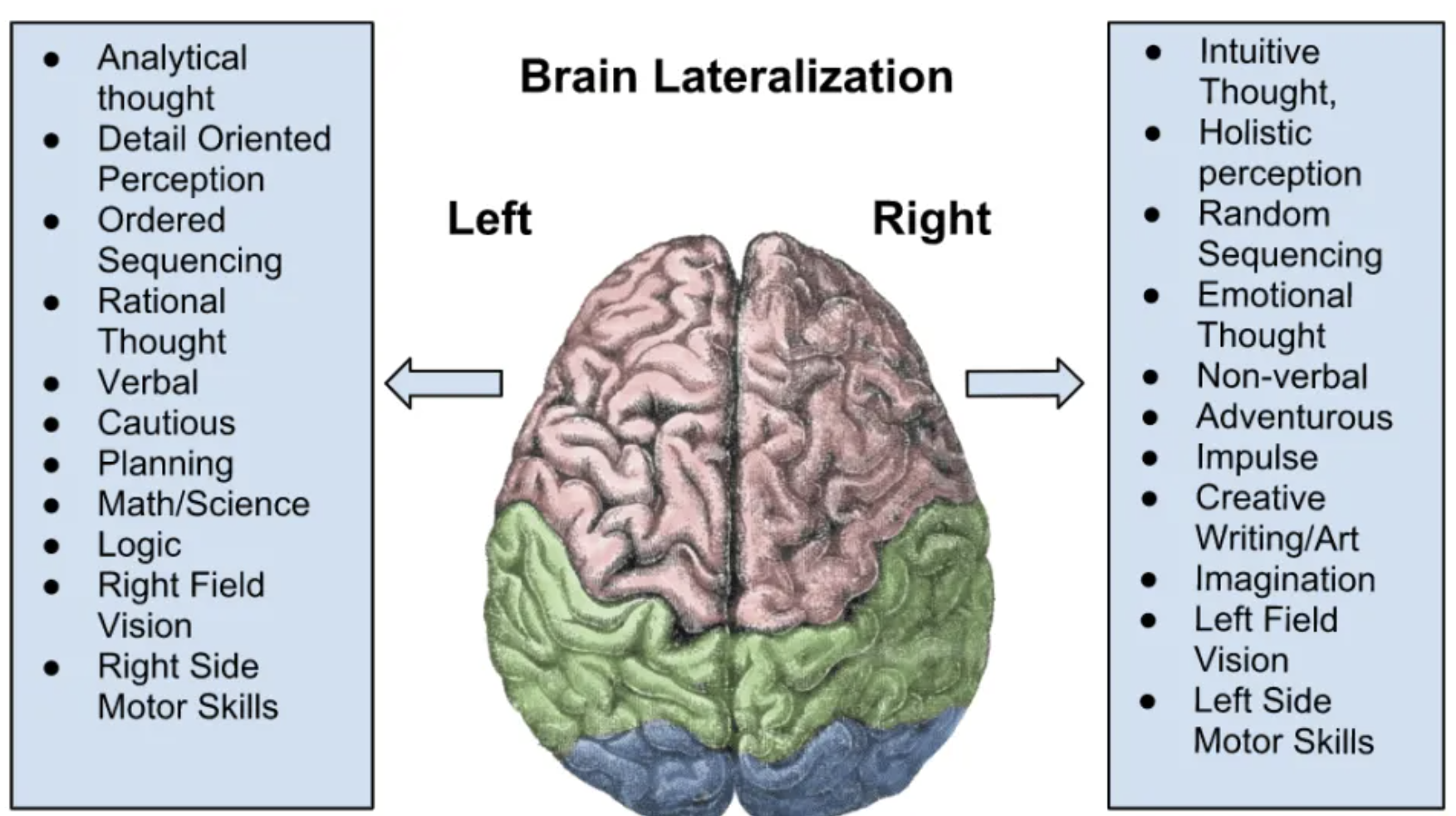
Left Hemisphere
Controls the right half of our body.
Verbal, logical, mathematical, ordered sequencing, planning, motor skills, rational thought.
Corpus Callosum
A bundle of nerual fibers that link the left and right hemispheres of the brain.
It passes messages between the two halves so they can communicate.
Occipital Lobe
Processes visual information.
“Striate Cortex” - means the cells here are striated
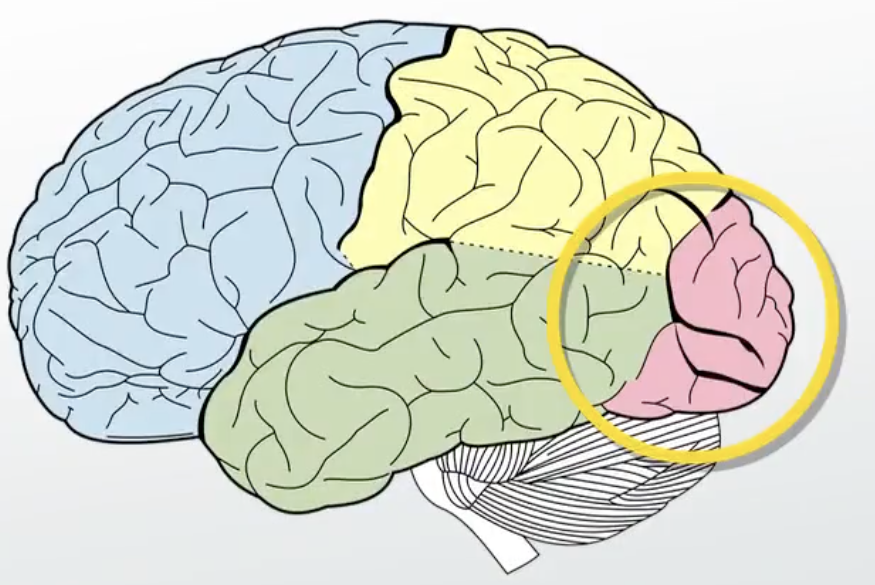
Temporal Lobe
There are two, one in each hemisphere.
It primarily functions in auditory processing.
It also can also be involved in emotion, learning, and pronunciation/learning a new language.
Wernike’s Area - Language reception and comprehension.
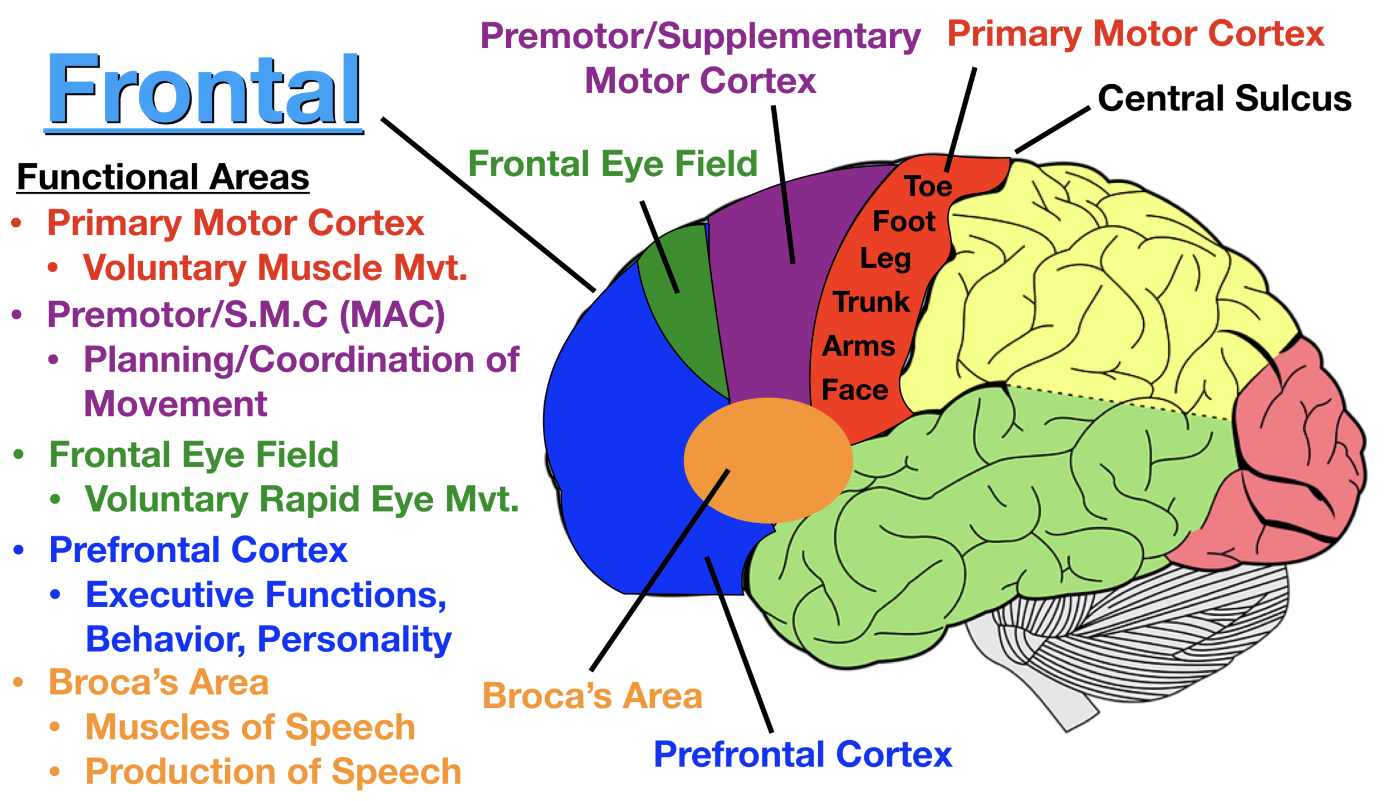
Frontal Lobe
Voluntary movement, planning, personality, thinking and problem solving, supervises and directs other parts of the brain
Broca’s area is here - speech production
Motor Cortex is here - Body movements
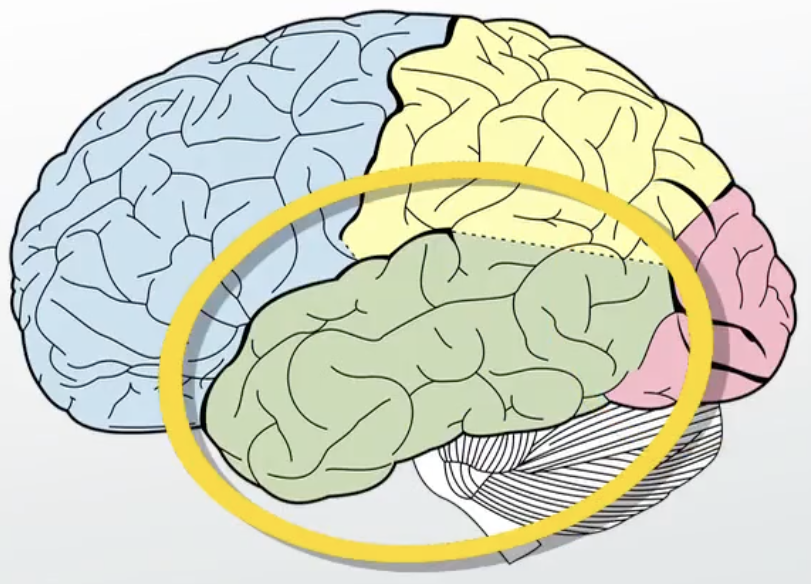
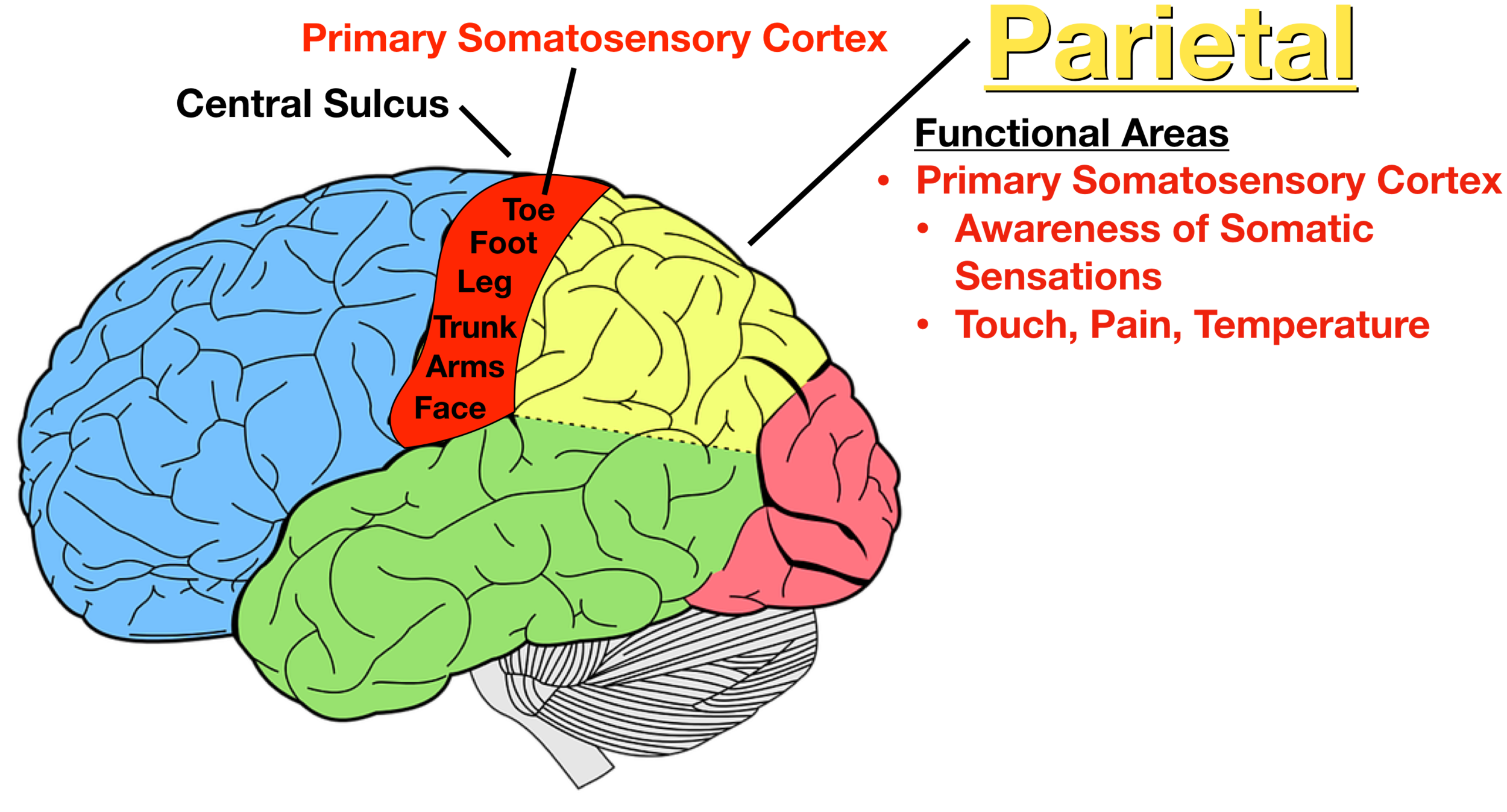
Parietal Lobe
Somatosensory Cortex (aka Sensorimotor Cortex) is here - sensory feeling like pain, ex: feeling pressure of a cup in our hand or the heat
Also functions for spatial processing and manipulation
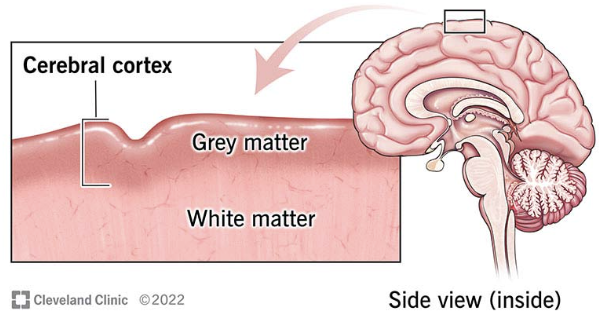
Cerebral Cortex
Outermost layer of the brain composed of tightly packed neurons. Aka “grey matter”
Thinking, learning, memory, personality, crucial for these higher order thinking capabilities.
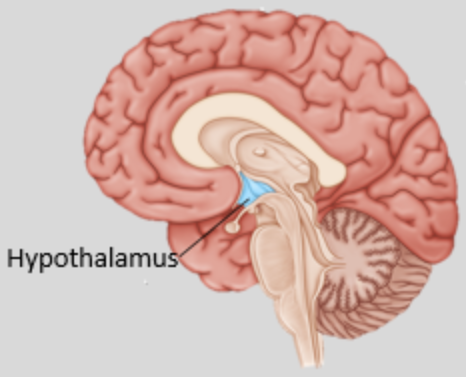
Hypothalamus
Maintains homeostasis for the body so like heart rate, temperature, blood pressure, sleep-wake cycle
Appetite, endocrine system,
Releases hormones that control the pituitary gland.
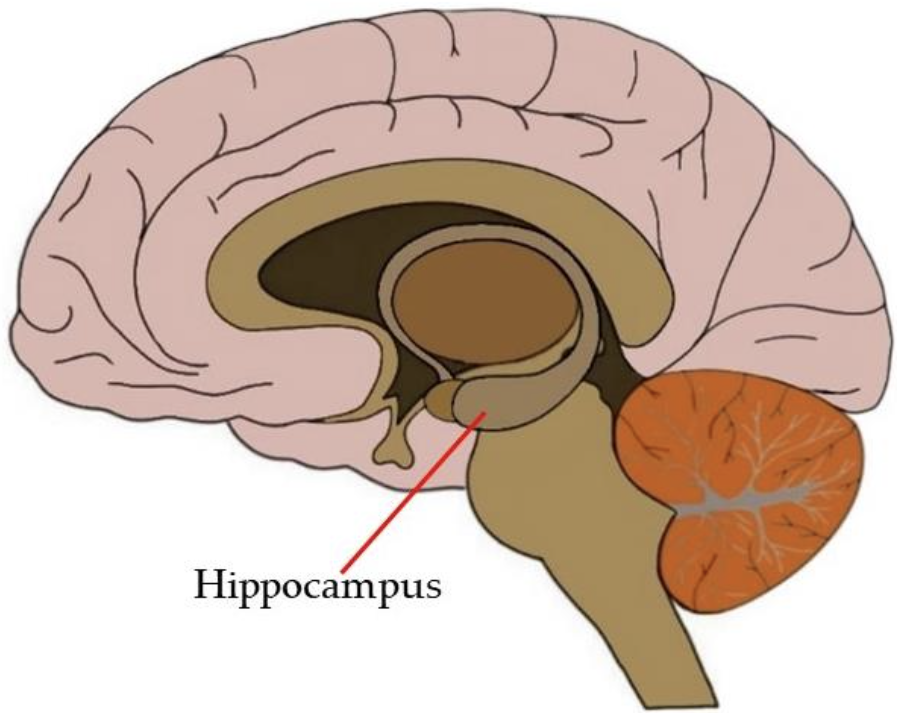
Hippocampus
Memory. Converts short-term memory to long-term memory and retrieval of memories. Also with episodic memory (like personal experiences like time and place of first lottery ticket win)
Also spatial memory (mind maps of places).
Physically connected to the amygdala so also has some emotional and stress functions.
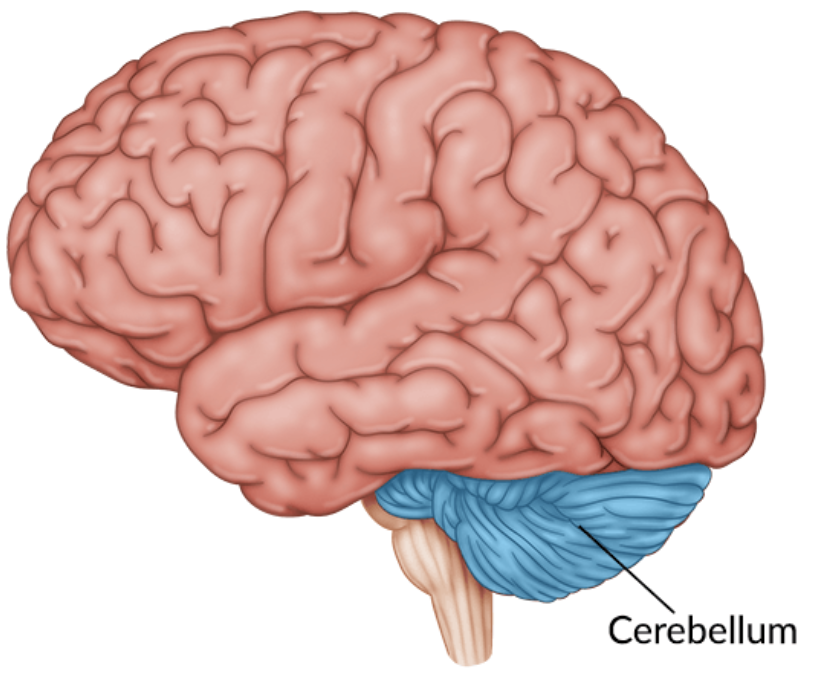
Cerebellum
Balance control in movement.
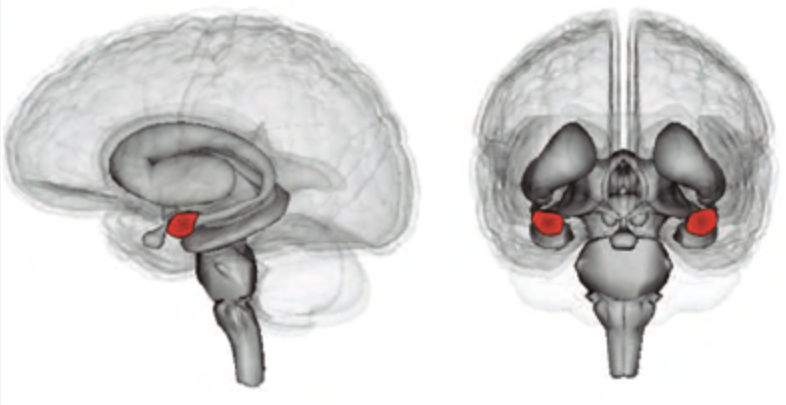
Amygdala
Processing emotions.
There are two, one in each hemisphere.
Identifying threats to initiate fight/flight/freeze, processing positive stimuli, links emotions to memories and learning and senses.
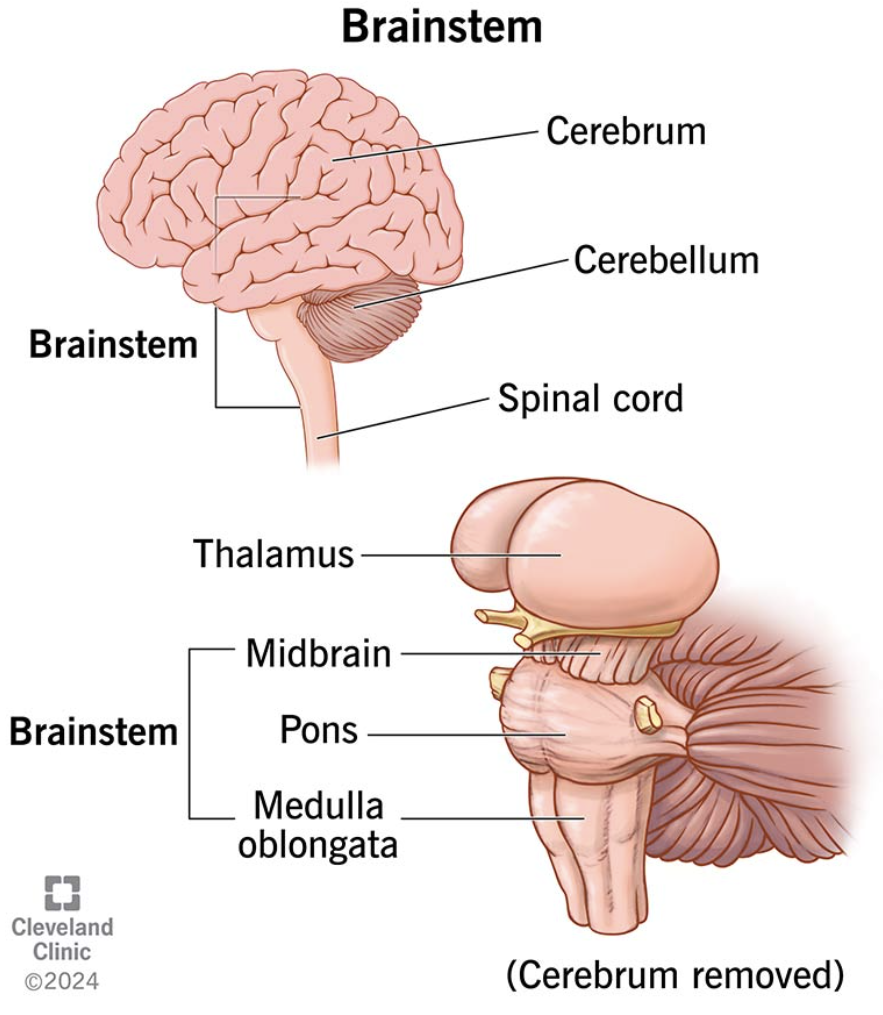
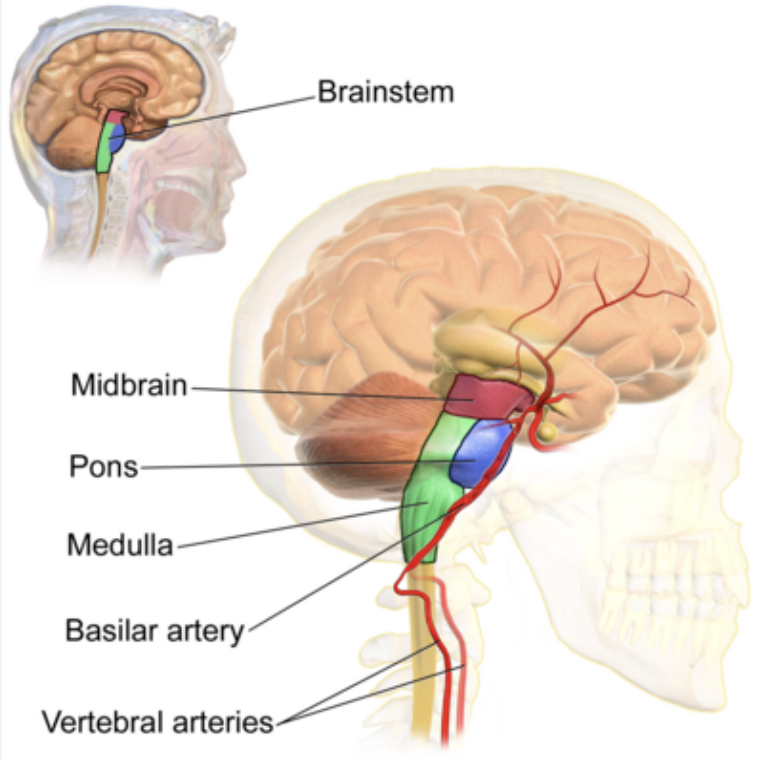
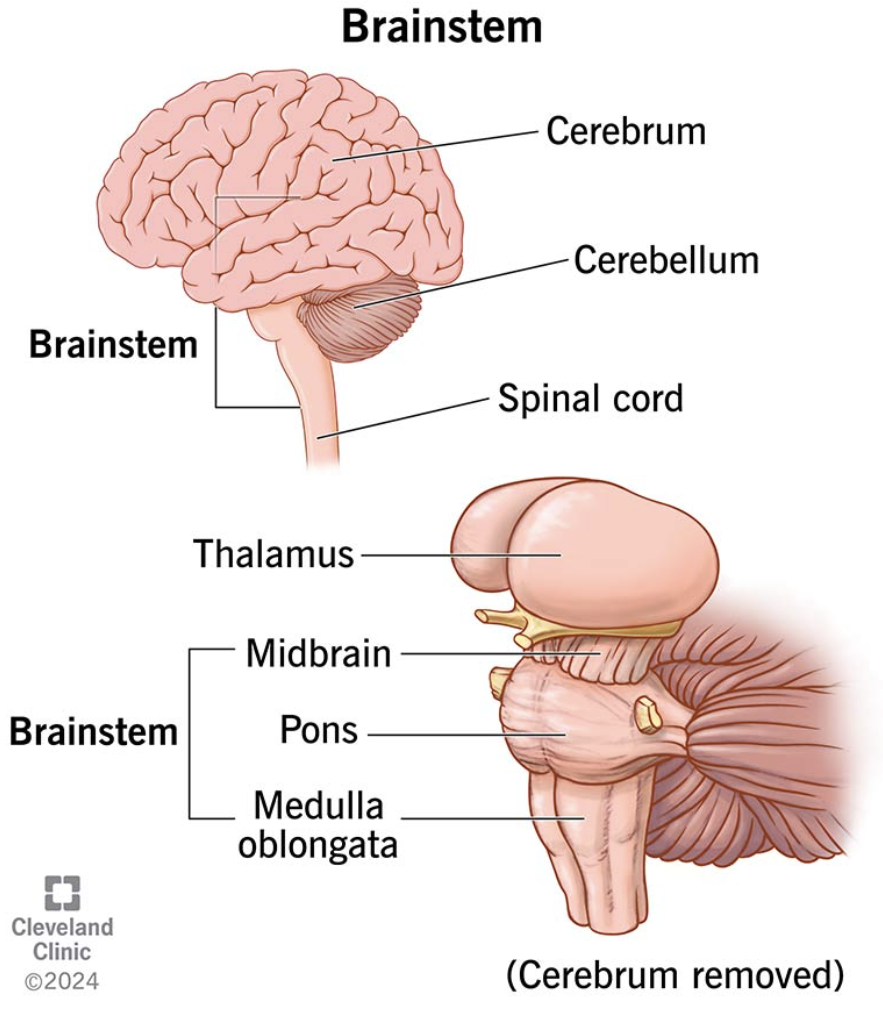
Brain Stem
Made up of the midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata.
Basic life-sustaining needs like breathing, heart beating, blood pressure, sleep, consciousness, involuntary actions like swallowing and eye movements, hunger and thirst.
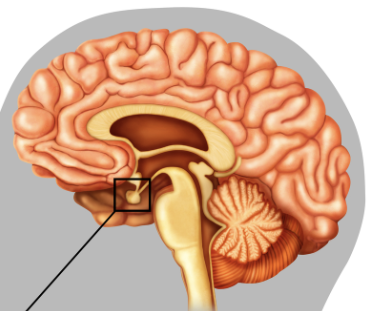
Pituitary Gland
Growth, metabolism, reproduction, lactation, etc.
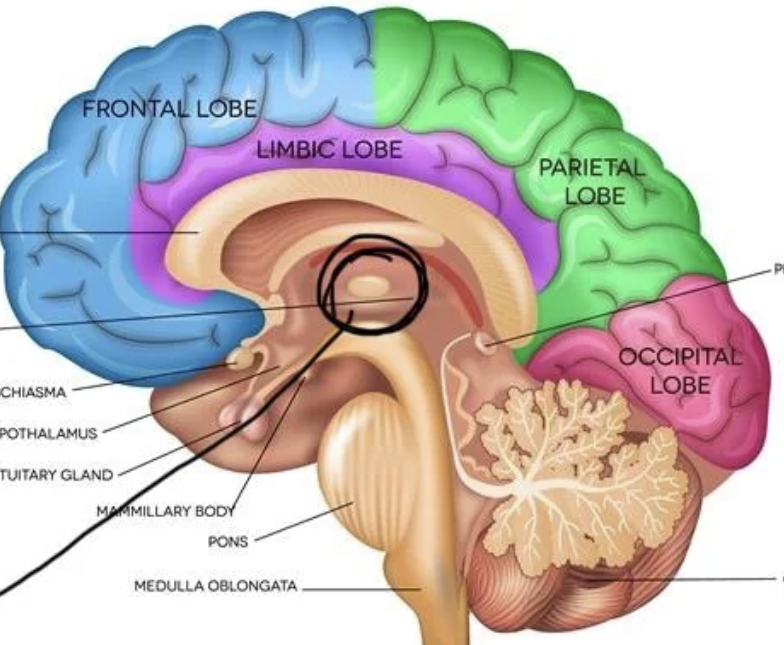
Thalamus
Relay station (processing sensory signals and sending them), Attention (deciding what to focus on), Alertness, Filtering information to decide what is important, Consciousness, and Sleep
Pons
Links the brain to the spinal cord.
Handles unconscious processes like sleeping and breathing, eye and facial movements, REM sleep.
Transmits signals between the forebrain (like the lobes), cerebellum, midbrain, spinal cord, and other parts.
Medulla
Balance.
Bodily functions like breathing, heart rate, blood pressure, coughing, sneezing, swallowing, vomiting.