Medicine Part 1: Kidney Disease
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
which organ is the major determinant of average blood pressure?
kidney
t/f: high blood pressure & kidney disease cause each other
true
t/f: high blood pressure & kidney disease are clinically silent over most of their progression
true
Saying the product of the kidneys is urine is like saying the product of a factory is pollution...”
“Urine is a by-product. The product is
homeostasis
normal kidney functions to clean blood of waste products and regulate…?
water balance
acid-base status
volume status (BP)
BP (hormonally)
bone health (get rid of phosphorus, activate vitamin D)
RBC production (by producing erythropoetin)
kidney failure occurs at % function
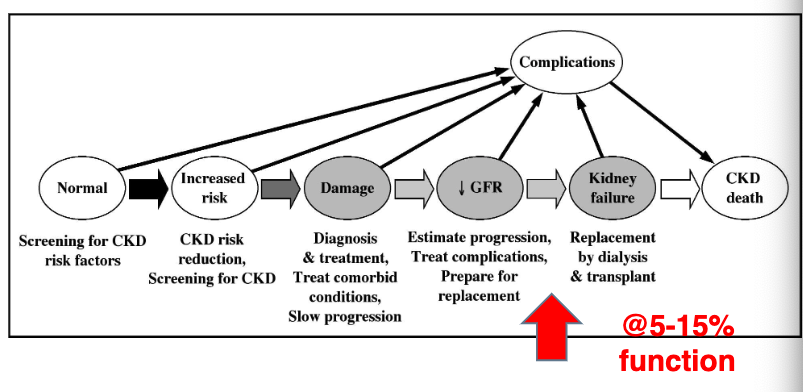
5-15%
2 kidneys together weight about __ g
280
2 kidneys receive about % of cardiac output at rest. this is __x the blood flow/g vs the body on average.
20%
50x
the kidneys are viscerally innervated which means they are almost never painful EXCEPT FOR…?
kidney stones (in ureters)
what does it mean that there are about 1 million individual nephrons, in which glomerular capillary is uniquely leaky (and fragile)?
Entire plasma volume drips out of these about twice an hour, departing body and heading to bladder
glomerular capillary
what does the high filtering capacity of the renal system allow for?
rapid recovery of homeostasis after dietary or physiologic events
clears any new toxins even the unknown
t/f: Because most is reabsorbed, urine volume represents the distillate of 100x or more of filtrate. Therefore can have vastly reduced kidney function without perceptible changes in urine volume
true
t/f: the purpose of the kidney is to make urine, and urine production guarantees kidney function
false. can have vastly reduced kidney function without perceptible changes in urine volume
t/f: Loss of renal capacity does mean slower recovery from changes
true
what are some causes of acute kidney injury?
Obstruction of urine flow (“post-renal”)
Nephrotoxins (e.g. aminoglycosides, radiocontrast) (“intrinsic”)
Hypoperfusion (low blood pressure) (“pre-renal”)
combination (e.g. sepsis)
what are the categories of acute kidney injury causes?
post renal
intrinsic
pre renal
combination
what are some causes of chronic kidney injury?
Diabetes- often with proteinuria
Hypertension
Heart or liver failure
Structural kidney disease (e.g. polycystic kidney disease)
Glomerular disease, either systemic or kidney-limited
Tubulointerstitial disease from drugs, toxins, paraproteins
Obstruction
can kidneys regrow?
Kidneys can bounce back, but never regrow. Therefore long term goal is defense– to reduce ongoing injury from chronic causes
what is the single best summary of kidney function?
glomerular filtration rate (GFR)
what does low GFR mean?
reduced speed & effectiveness in establishing chemical homeostasis
worsening endocrine/anemia/BP
high blood pressure
what is the range for normal GFR?
120-130 ml/min/1.73 m^2
what can affect GFR?
body size, sex, diet
Biochemical abnormalities develop below about (GFR value), but most prominently below
60
30
Below __ (GFR value) approaches inability to keep up with fundamental metabolic needs. What are possible treatment options?
10-15
dialysis, kidney transplant, conversative management
how is GFR clinically determined?
creatiinine (produced continuously by muscle, builds up in blood as filtration drops)
high blood creatinine = low filtration
what are potential problems with using creatinine as a clinical determination of GFR?
blood Cr. is also affected by production, which is a function of muscle mass, sex, age, diet, genetics, and other factors
Cr in “normal range” does NOT equal normal kidney function
cognitive problem hyperbolic relationship
increase from 4.0 Cr to 5.0 is not as concerning as 0.5 to 1.0
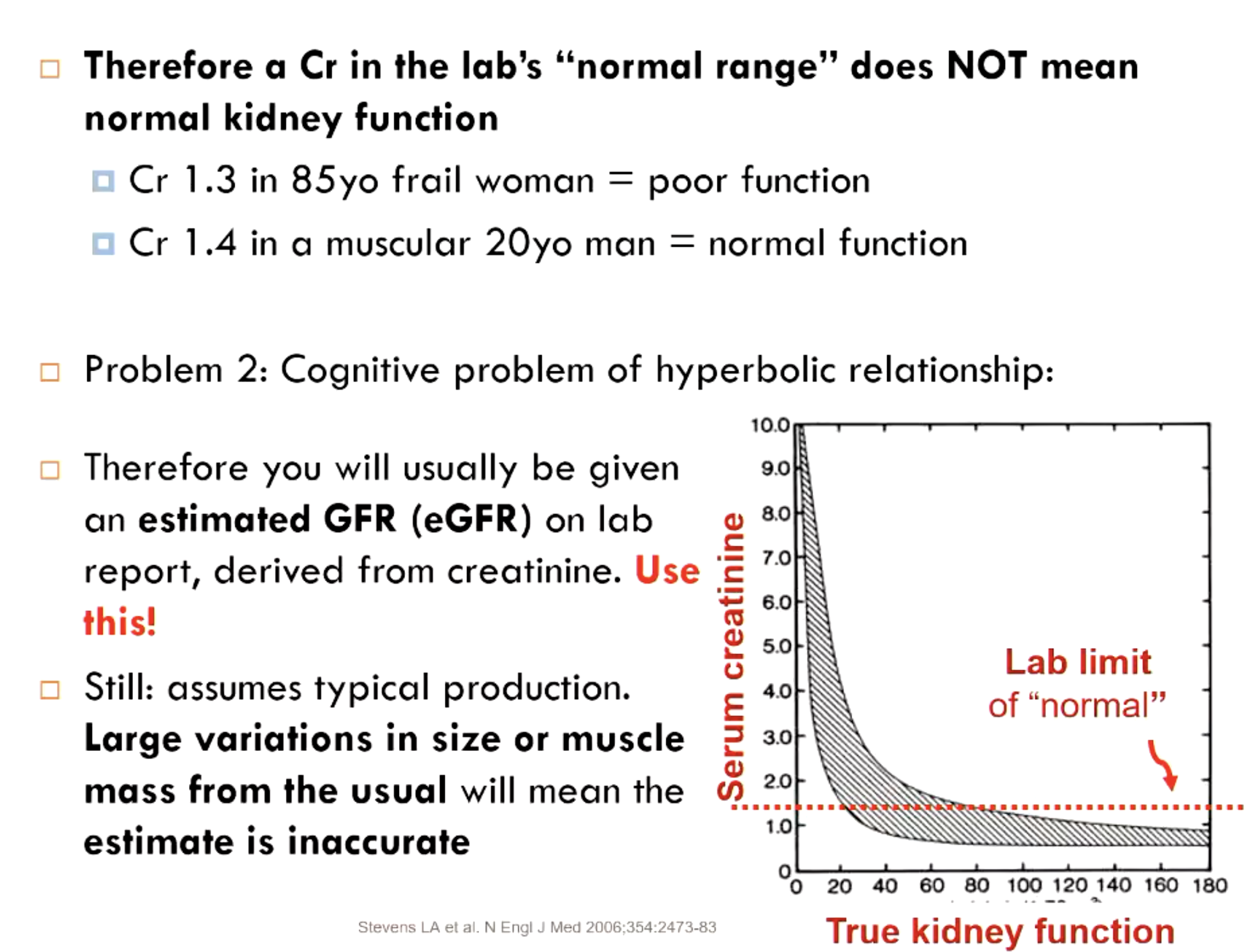
why is it important to use an estimated GFR (eGFR)?
accounts for production differences in creatinine based on demographic data BUT be careful because Large variations in size or muscle mass from the usual will mean the estimate is inaccurate
what is the current best equation for estimated GFR?
2021 CKD-EPI eGFR
There are many medications cleared by the kidney. Appropriate dosing is therefore not based just on the condition treated, but kidney function. What do we as prescribed need to know of every patient for whom medications are prescribed?
eGFR or CrCI (adjustments may start when eGFR<60)
advanced kidney disease? (because some meds not safe to use)
clinical kidney disease diagnostic criteria:
eGFR <60 ml/min/1.73 m²
abnormal structure (image/biopsy)
functional evidence of kidney damage
proteinuria or hematuria (failure to maintain blood/urine barrier)
which 2 features of clinical kidney disease diagnosis allow for classification as “disease” before filtration starts to fall?
abnormal structure
functional evidence of kidney damage
t/f: kidney function worsens with age (hatural history)
true
what are the 5 stages of kdiney disease?
Stage 1: GFR > 90 but something abnormal
Stage 2: GFR 60-90 but something abnormal
Stage 3: GFR 30-60 : affects med dose adjustment
Stage 4: GFR 15-30 : above, + chem/heme abnl
Stage 5: GFR <15 : above, + symptoms/dialysis
at which stage of kidney disease does dialysis/transplant occur
stage 5
__ in 7 has some kidney disease
1
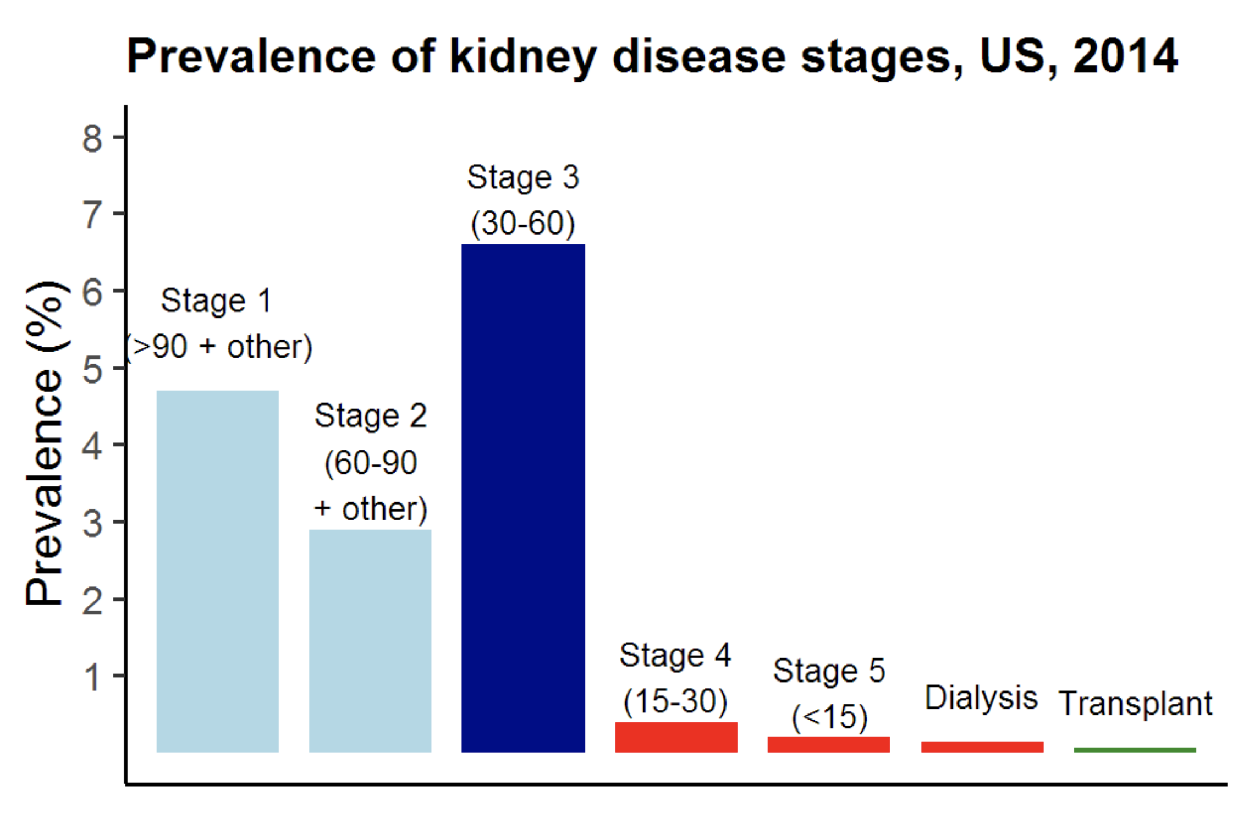
what is the most common stage of kidney disease?
stage 3
what are some causes of end-stage kidney disease?
diabetes (#1 cause of dialysis dependence)
hypertension
glomerulonephritis
cystic kidney
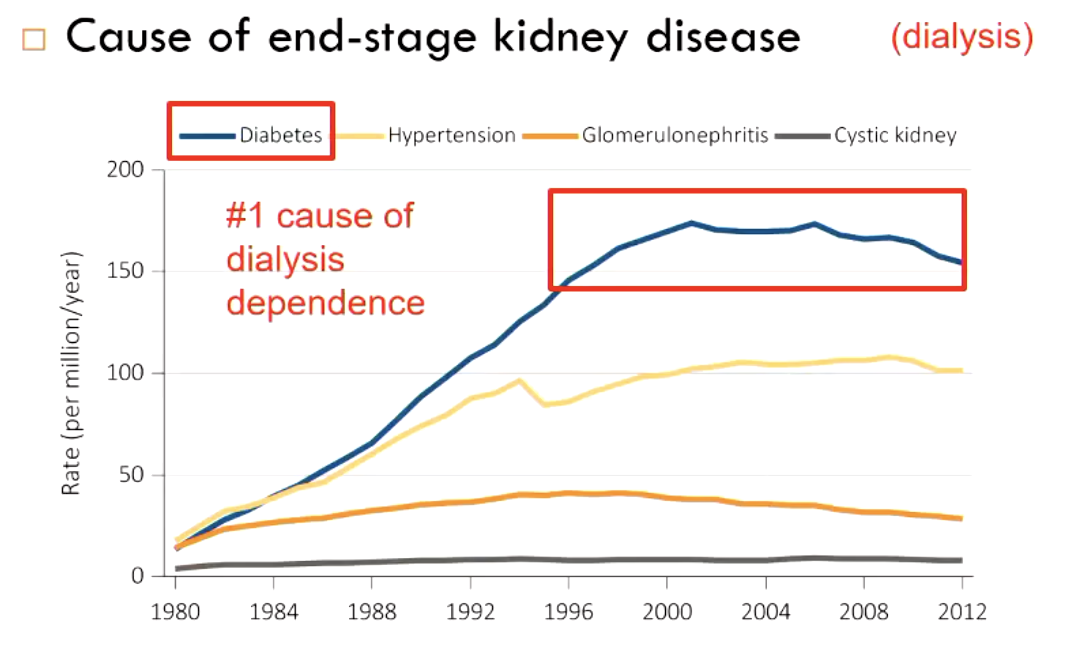
what is the #1 cause of dialysis dependence?
diabetes
what are some conequences of progressive kidney failure?
High blood pressure
Cardiovascular risk increase
Need for dietary restriction/medication to avoid:
Salt and water retention (edema, pulmonary edema)
Hyperkalemia
Severe bone disease from hyperphosphatemia
Altered medication metabolism
Dysfunctional bone (overactive OR underactive)
Anemia
Acidosis
Cachexia, inflammatory state
Platelet dysfunction
Neurologic changes (an indication for dialysis)
of all possible consequences of kidney disease, what is the #1 major cause of death?
cardiovascular disease (CV events are accelerated in kidney disease)
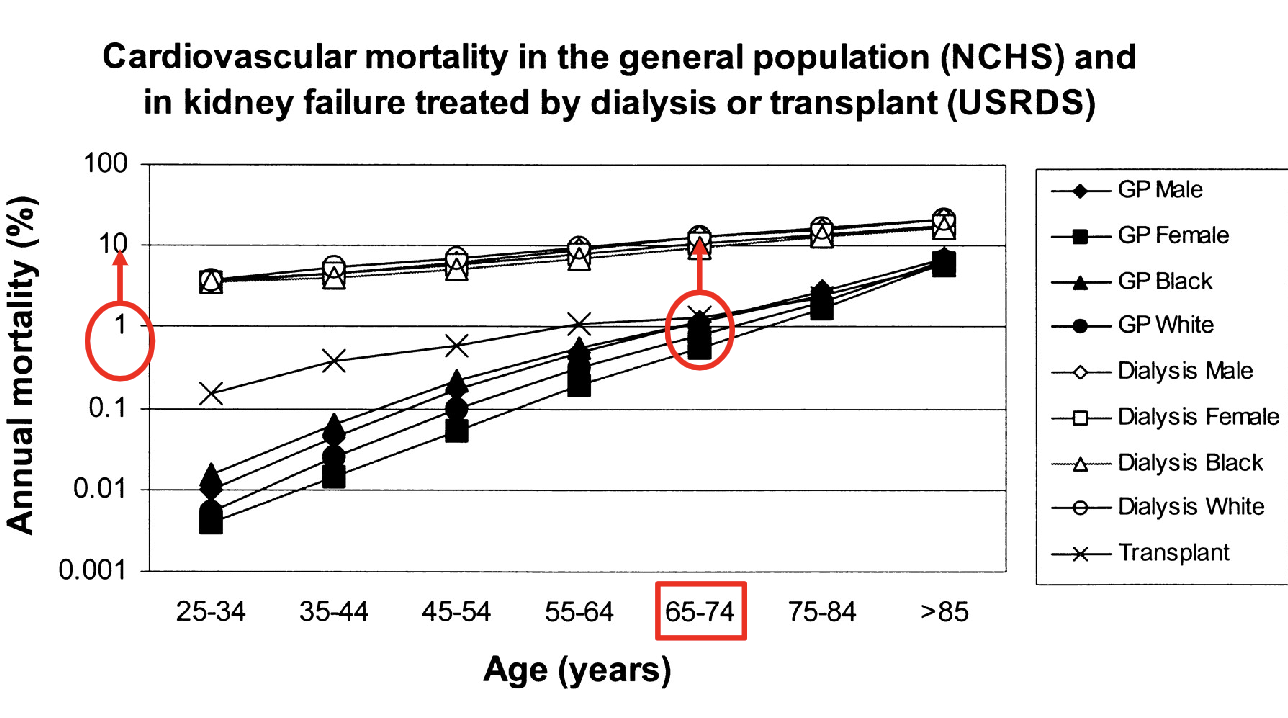
risk of hospitalization increases how many fold with chronic kidney disease?
death?
cardiac events?
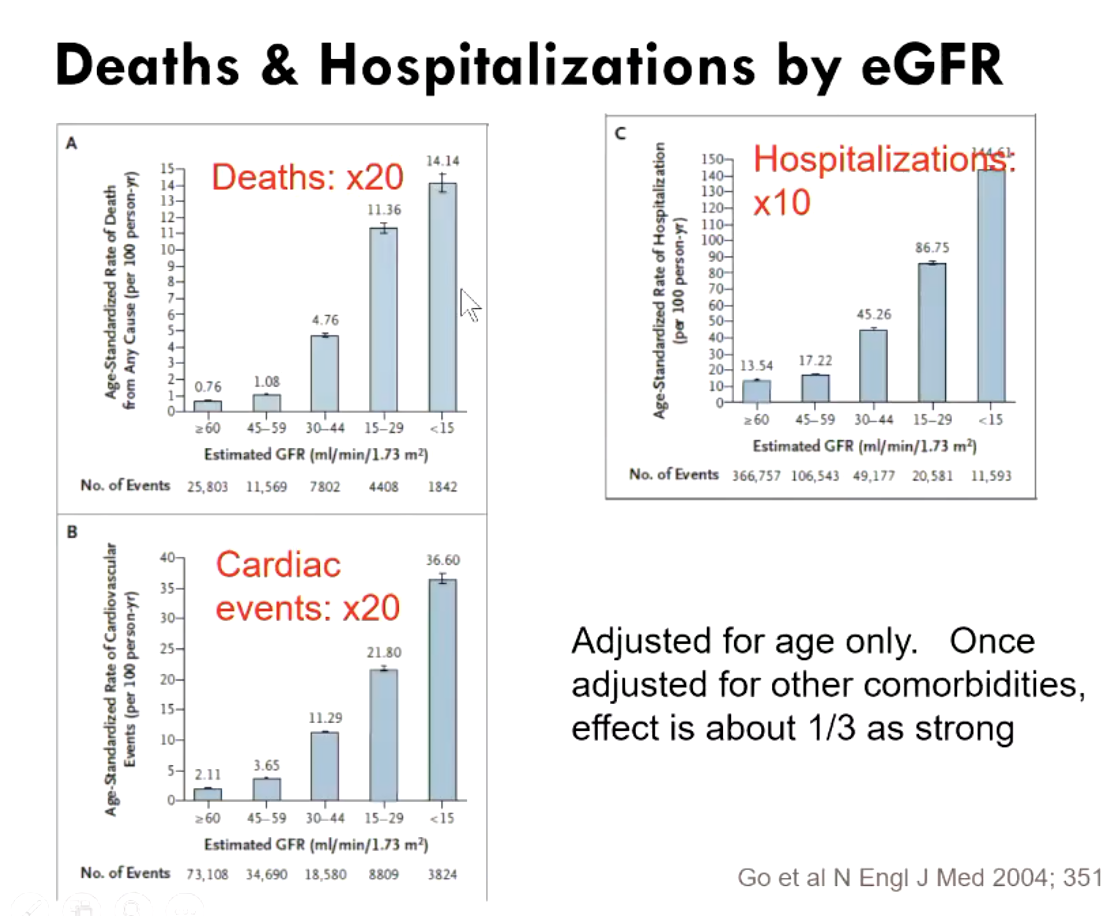
what are treatment strategies for kidney disease?
keep BP <130/80 mmHg
treat diabetes + other risk factors
ACE inhibitors (lisinopril) and angiotensin receptor blockers (losartan)
to reduce proeinuria
SGLT2 inhibitors
what medications are often prescribed to treat kidney disease?
ACE inhibitors (lisinopril) and angiotensin receptor blockers (losartan)
to reduce proeinuria
SGLT2 inhibitors
what are some more aggressive treatment options when kidney disease is advanced?
transplantation
dialysis
conservative treatment (esp. elderly)
what are the types of dialysis options?
peritoneal at home/nursing facility
hemodialysis in-center vs at home
t/f: on average, outcomes from transplantation and dialysis lengthen life and improve functional scores
false. outcomes from above do not lengthen life much or improve functional scores
how to improve chances of successful kdiney transplantation?
living > deceased donor
pre-emptive living donor transplant (BEST)
exchange programs
what are some pros and cons with kidney transplants?
Pros | Cons |
|
|
what are some absolute indications a pt needs dialysis?
Encephalopathy
Pericarditis or pleuritis
Uremic bleeding
Intractable hyperkalemia
Intractable metabolic acidosis
ntractable volume overload
what are some relative indications a pt needs dialysis?
Fatigue
Anorexia, dysgeusia, early satiety, nausea, vomiting, weight loss
Itching,
Neuropathy
is there a benefit to an “early start” with dialysis?
no
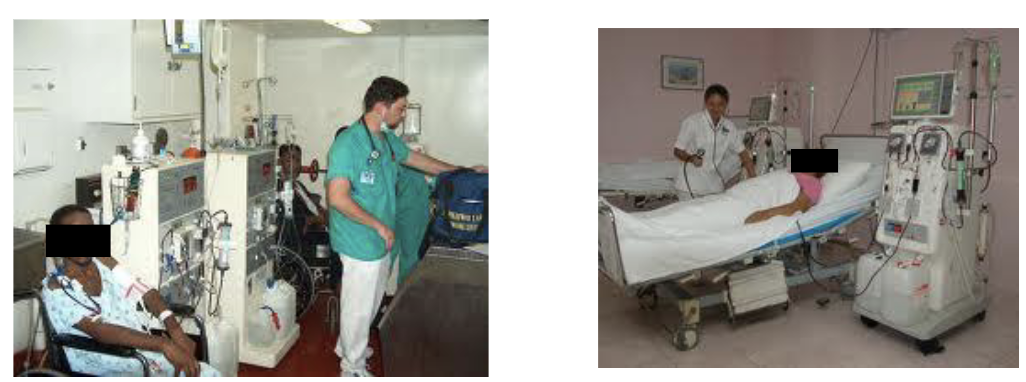
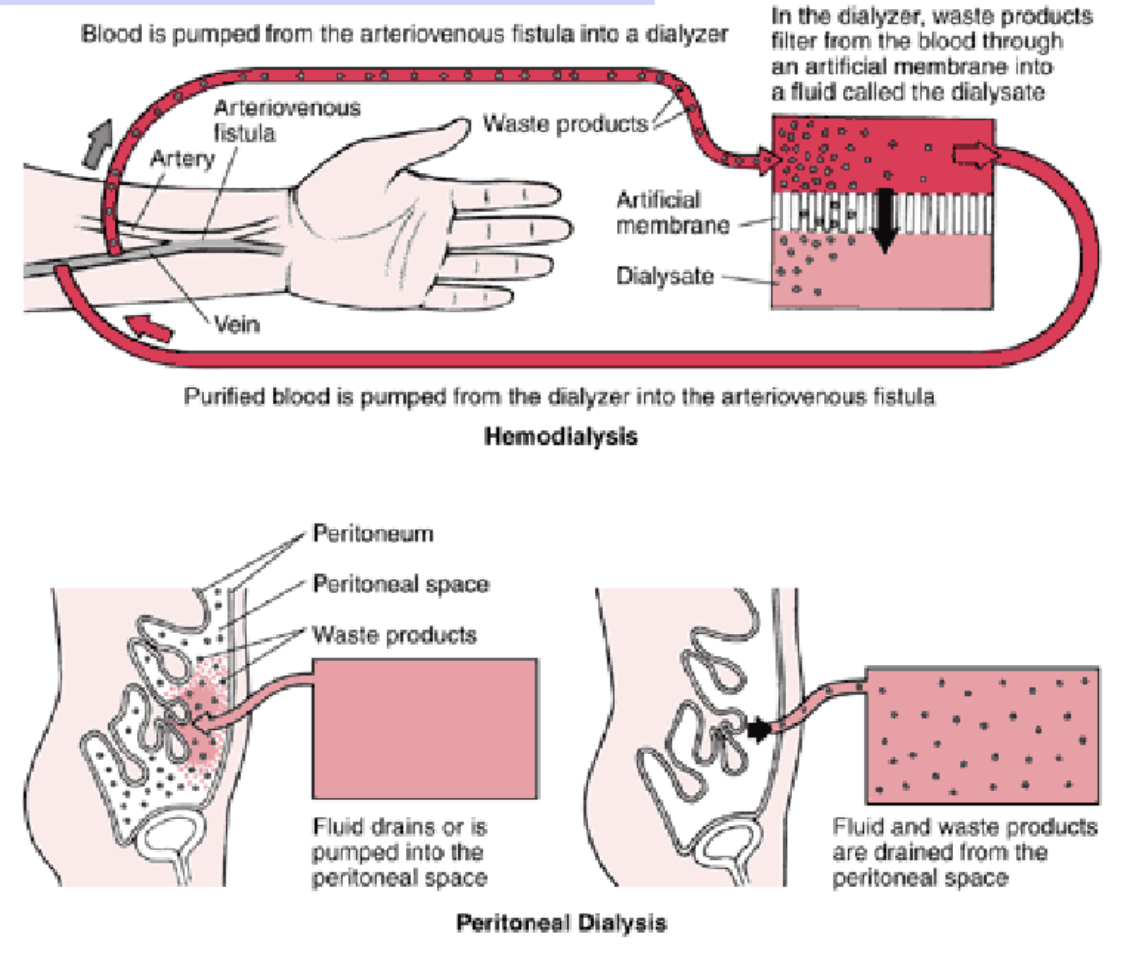
how does dialysis work?
Expose “dirty” blood to clean dialysate across a semi-permeable membrane (hemodialysis vs peritoneal dialysis)
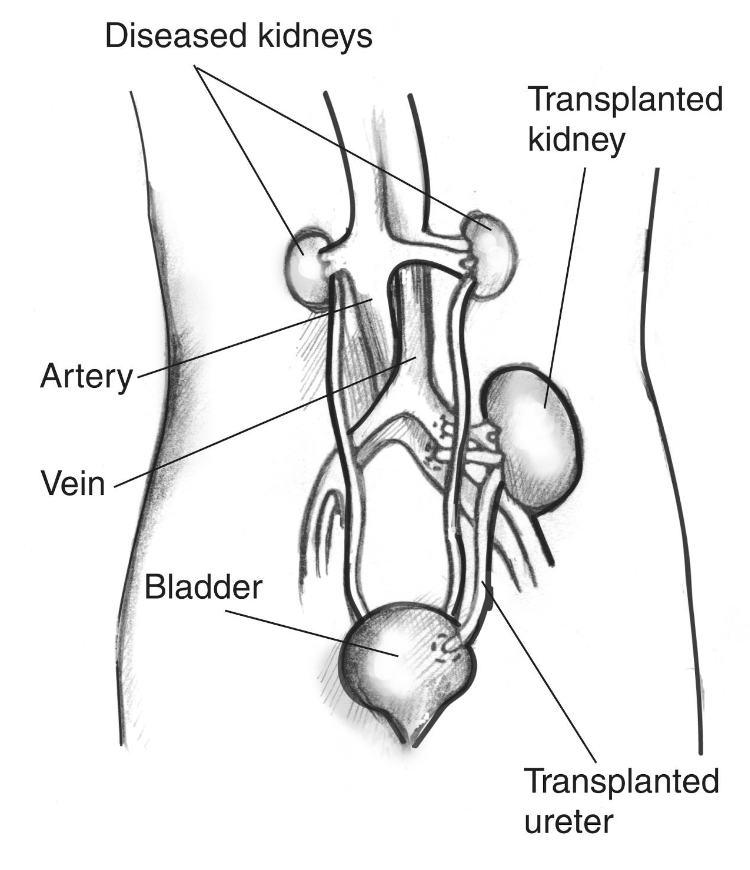
how does transplantation work?
is antibiotic prophylaxis required for kidney transplant/disease pts during dental procedures ?
no UNLESS there is a foreign body (bovine/synthetic graft, hemodialysis catheter, peritoneal dialysis catheter, high-grade bacteremia)
kidney transplant pts don’t need generally
what class of drugs can cause loss of remaining kidney function in CKD
NSAIDS
No clear cutoff (depends on risk/benefit, duration, dose) but generally avoid in CKD 4, usually lower end of CKD 3
what are some pain control drugs to be cautious of with CKD/dialysis pts?
morphine (can accumulate so hydromorphone is safer)
narcotics like codein/oxycodone (elderly/fragile pts very sensitive)
NSAIDs can cause loss of remaining kidney function in CKD
chronic kidney disease pts are prone to_______-
bleeding (+ uremic platelet defects)
what drugs may pts with CKD be taking that dentists must be aware of?
warfarin (Coumadin) and aspirin → for cardiovascular issues
heparin → during hemodialysis treatment (coordinate dental appts w non-HD days)
antibiotic doses may need to be adjusted for decreased GFR/CKD. what are some things to remember?
no adjustment:
most 1x doses (renal failure changes frequency needed)
Clindamycin, azithromycin, doxycycline
interval adjustment (dramatic)
Amoxicillin, cephalexin
t/f: You will need to know the dose adjustments for every patient for whom you prescribe abx.
true