Topic 8 -Exchange and Transport in Animals
1/103
Earn XP
Description and Tags
1 Core Practical: 8.11 Investigating the rate of respiration in living organisms
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
8.1 What is the need for transport in animals?
In order for an organism to function properly, it needs to exchange substances between itself and the environment
8.1 What are some examples of substances which organisms exchange?
oxygen, carbon dioxide, water, dissolved food molecules,, mineral ions and urea
8.1 Where does the exchange of substances take place?
across the cell membrane
8.1 What are the 3 transport processes that living organisms use for exchange?
diffusion. osmosis and active transport
8.1 How does surface area affect transport of molecules?
Give an example
Organisms with a larger surface area to volume ratio will transport molecules at a faster rate.
E.g Unicellular (single-celled) organisms like amoeba have very larger surface areas in comparison to their volumes.
8.1 What is needed to aid transport in animals with smaller surface area to volume ratios?
They need specialised exchange surfaces or transport systems
8.1 Do unicellular organisms have specialised exchange surfaces/ transport system?
No, unicellular organisms such as amoeba do not require transport systems due to their large surface area to volume ratio
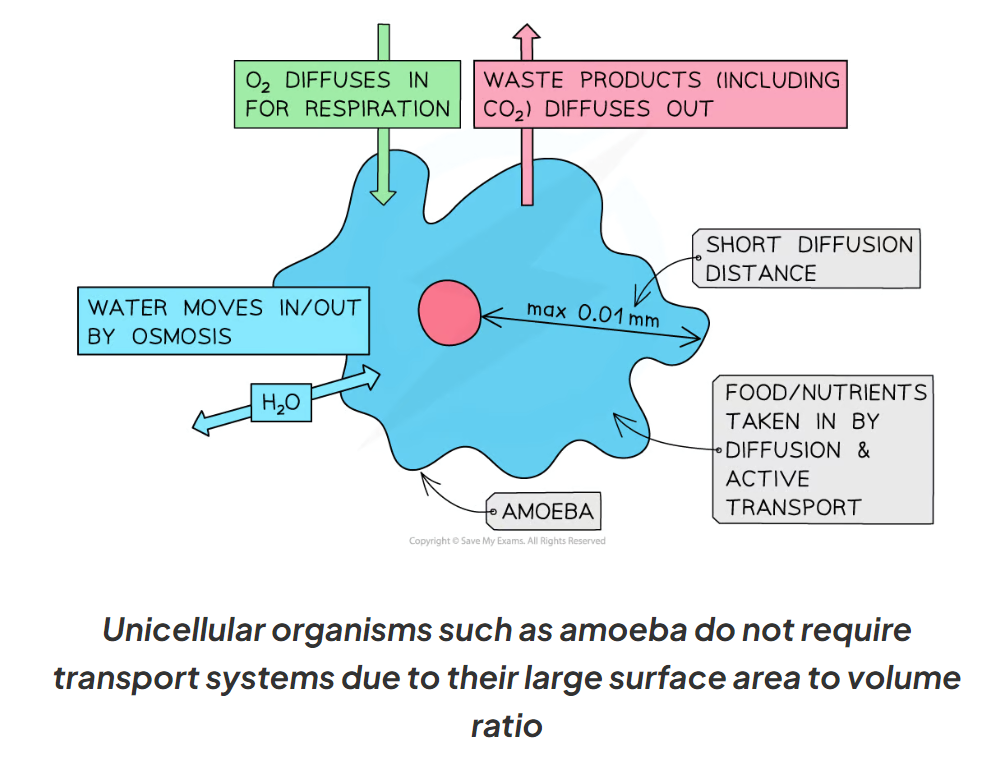
8.1 Do multicellular organisms have specialised exchange surfaces/ transport systems? Why?
Yes. For larger multicellular organisms the distance between the surface of the organisms to its centre is relatively long
This is why larger organisms usually have exchange surfaces and transport systems; as diffusion, osmosis and active transport cannot happen sufficiently to meet a larger organism’s need otherwise
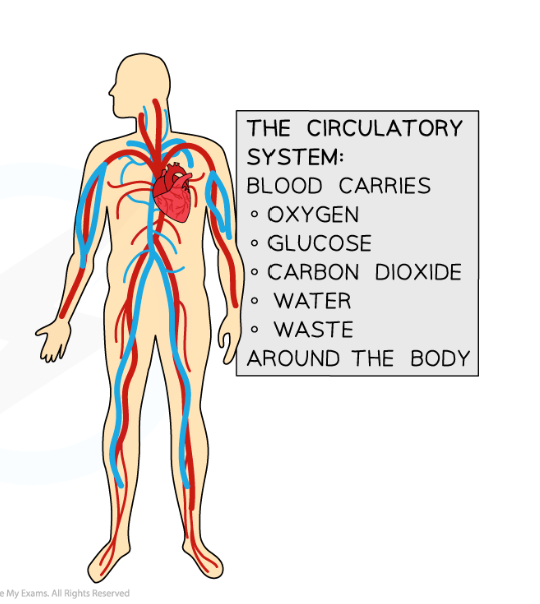
8.1 What is the main transport systems in animals? What do they do
blood and circulatory system - carries the necessary substances around the body
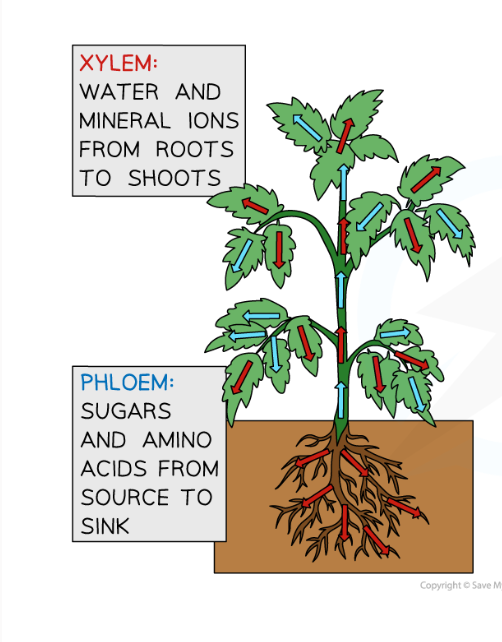
8.1 What are the 2 transport systems in plants? What is their purpose?
-Xylem: moves water and mineral ions from roots to shoot
-Phloem: moves sugar and amino acids to where they are needed in the plant
8.1 Define diffusion
the movement of particles high concentration to low concentration
8.1 Name the factors which affect the rate of diffusion
-temp
-concentration gradient
-surface area
-diffusion distance
8.1 Why can't multicellular organism just rely on diffusion?
Because diffusion is too slow to transport materials from the outside, to cells on the inside
8.1 Finish off the sentence:
The larger the organism the smaller ….”
… the surface area to volume ratio
8.2 What is the need for exchange surfaces?
Large organisms need exchange surfaces within their transport system to carry out diffusion, osmosis and active transport at a sufficient rate.
This is because they have a relatively small surface area to volume ratio.
8.2 Name some exchange surfaces in animals + their function
-the alveoli and lungs for gas exchange
-the small intestine and villi for absorption of digested food
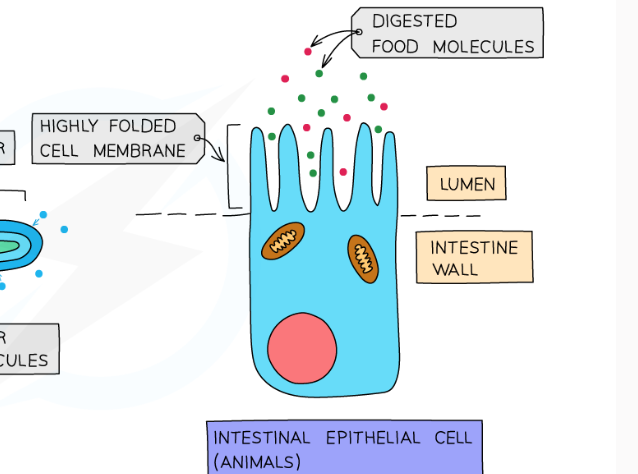
8.2 Name some of the exchange surfaces in plants + their function
-roots and foot hairs where mineral ions and water are absorbed
-the leaves for gas exchange
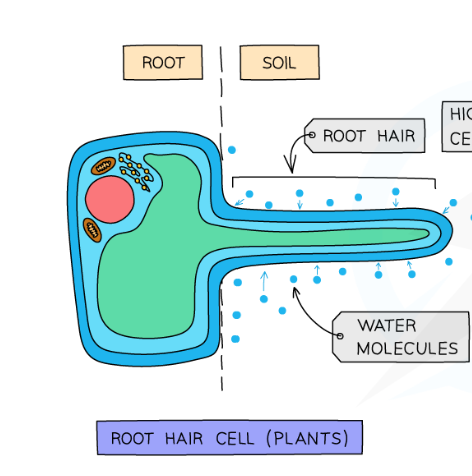
8.2 What are the properties of exchange surfaces in multicellular organisms?
-having a large surface area to increase the rate of transport
-a barrier that is as thin as possible to separate two regions, to provide as short a diffusion path as possible for substances to move across.
-a large network of blood vessels throughout the body:
to reduce the distance of exchange of materials between cells and the bloodstream
To move substances towards and away from exchange surfaces to maintain concentration gradients
-gas exchange surfaces that are well ventilated to maintain concentration gradients.
8.2 How do you calculate surface area to volume ratio?
1) calculate the surface area (SA): Area of 1 side x number of sides
2) calculate the volume (V): length x width x height
3) then put it in a ratio: SA:V
4) Divide the surface area by the volume to see how many times larger the SA is to the V
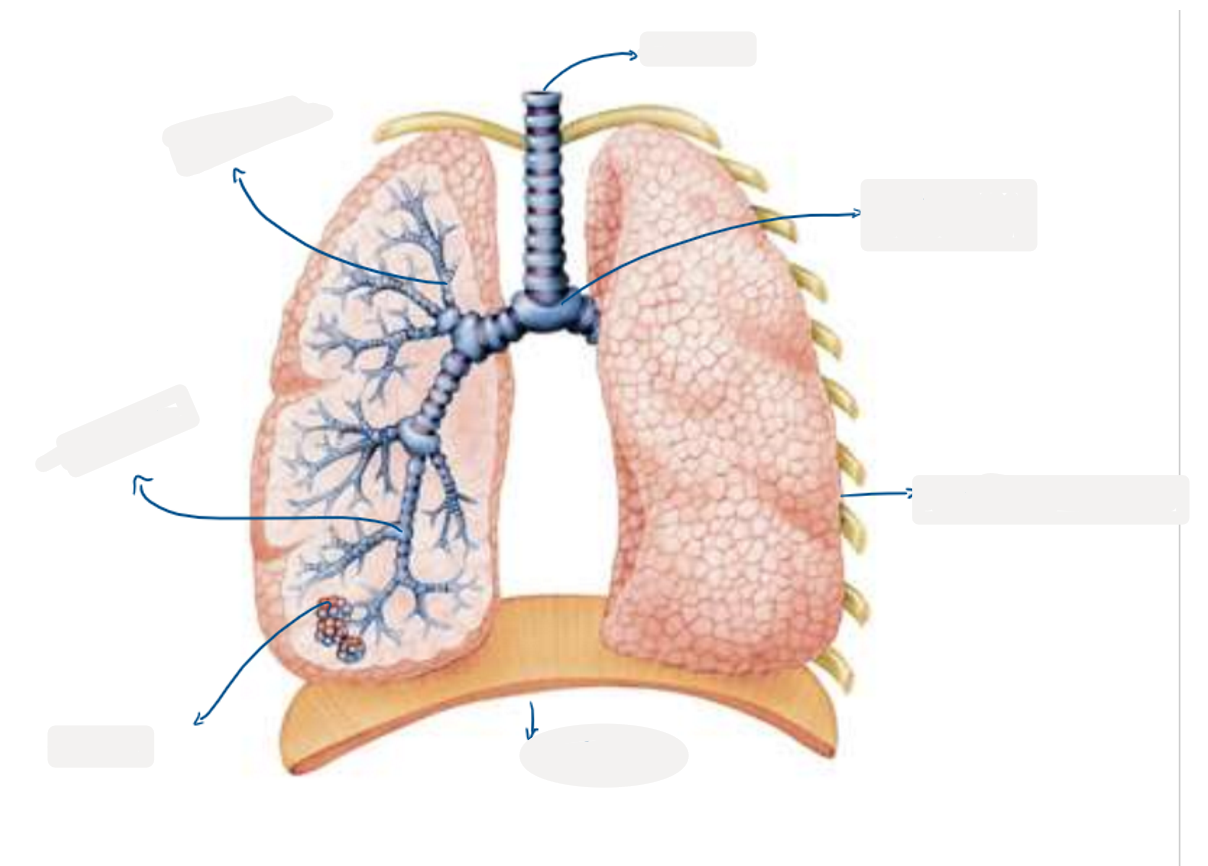
8.3 Label this diagram of the lungs
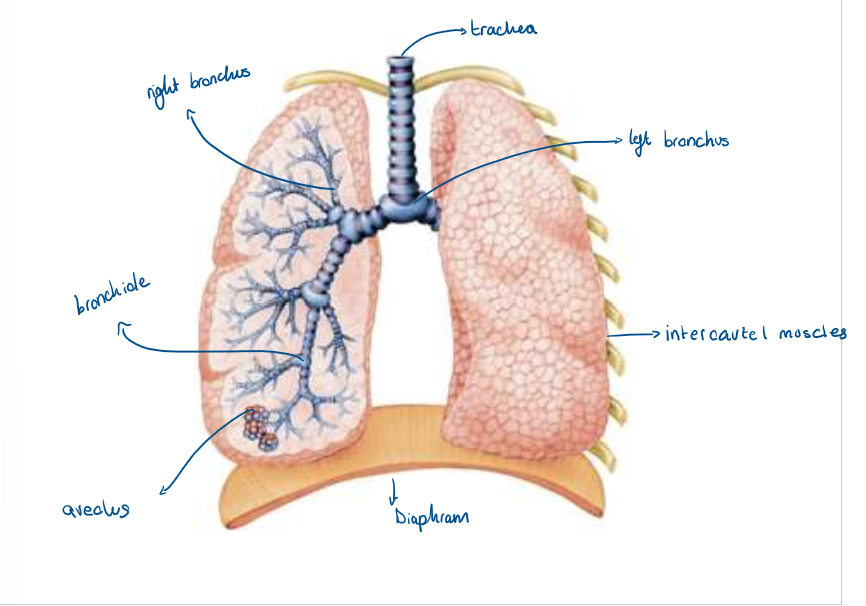
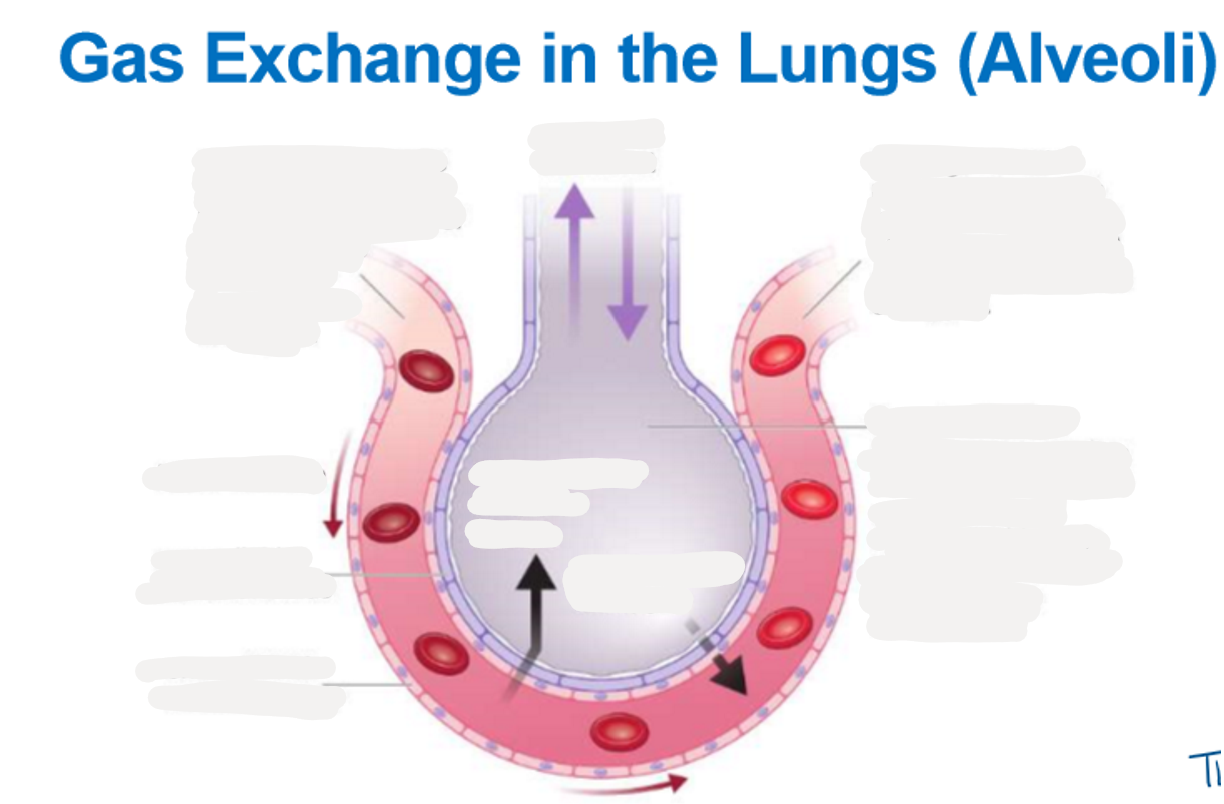
8.3 Explain the process of gas exchange in the lungs (alveoli) using this diagram
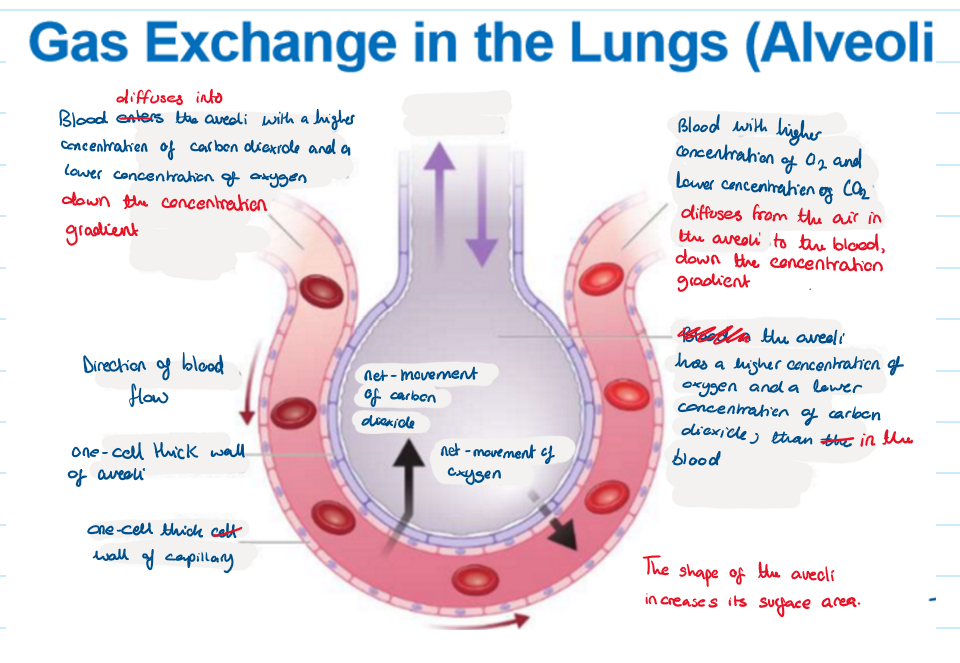
8.3 Explain the process of gas exchange at the alveoli (4marks)
The carbon dioxide diffuses from the blood into the air of the alveolus down the concentration gradient.
The oxygen diffuses from the air in the alveoli to the blood, down the concentration gradient
8.3 give 3 properties that enable efficient gas exchange + the adaptation
-large surface area: Millions of alveoli
-steep diffusion gradient: A higher concentration of oxygen and lower concentration of carbon dioxide
-short diffusion distance: Walks if alveoli are one cell thick
8.4 What are the factors which affect the rate of diffusion?
-Surface area
-Diffusion distance
-Concentration gradient
-Temperature
8.4 How does surface area affect the rate of diffusion?
The larger the surface area the faster the rate of diffusion
The bigger a cell or structure is the smaller it's surface area to volume ratio (slower rate at which substances can across its surface).
Many cells which are adapted for diffusion have increased surface areas (eg root hair cells)
8.4 How does diffusion distance affect the rate if diffusion?
The smaller the distance the molecules have to travel the faster the rate of diffusion
This is why blood capillaries and alveoli have cell walks that are one cell thick, so the rate of diffusion can be as fast as possible
8.4 Explain how the concentration gradient affects the rate of diffusion
The greater the difference in concentration on either side of the membrane, the faster the movement across it will occur - the faster the rate of diffusion
This is because on the side with the higher concentration gradient, more random collisions against the membrane will occur.
8.4 Explain how temperature affects the rate of diffusion
The higher the temperature the more energy the molecules have therefore the faster they will move around.
This results in more collisions against the membrane and therefore a faster rate of movement across the membrane -faster rate of diffusion
8.5 What is Fick’s law?
The rate of diffusion is directly proportional to the (surface area x concentration gradient)/ diffusion distance
According the the law, if:
-the surface area doubles or
-then concentration gradient doubles or
-the diffusion distance halves
the rate of diffusion double
8.6 What does the blood consist of?
-red blood cells
-white blood cells
-platelets
-plasma
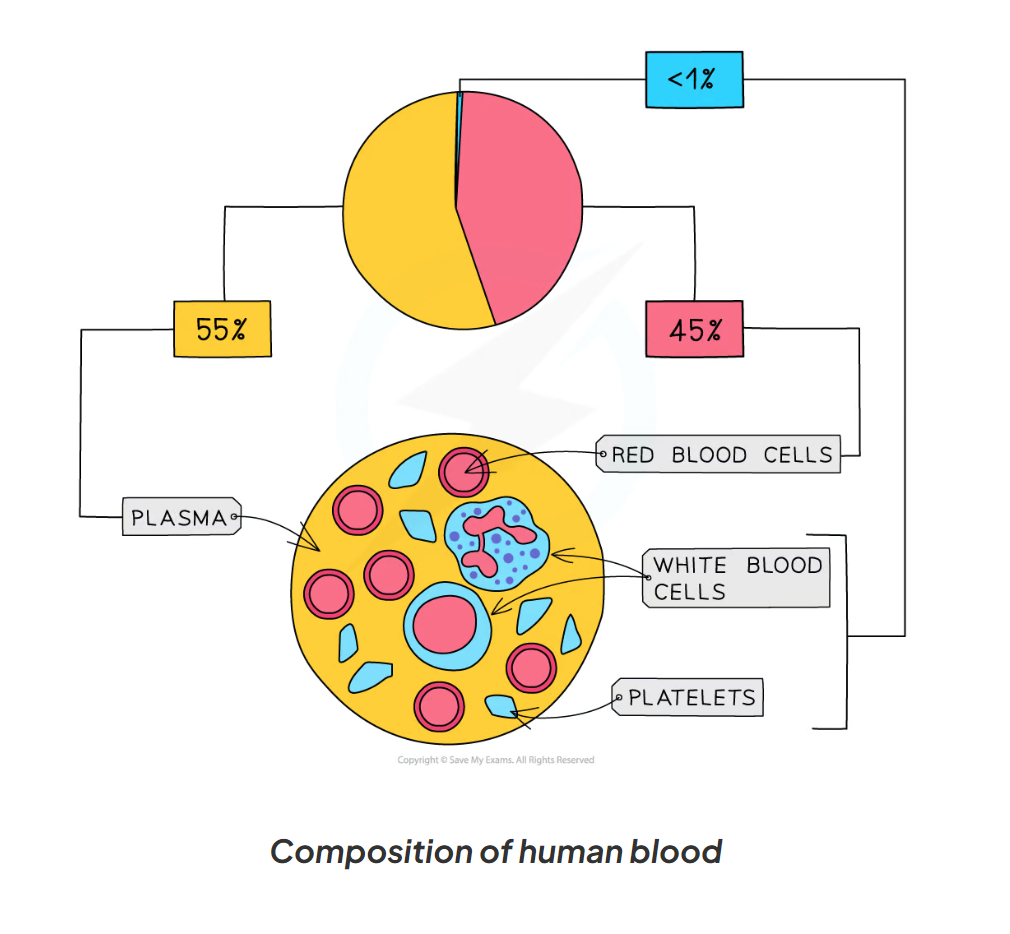
8.6 Describe red blood cell
-Biconcave shape to increase their surface are
-With no nucleus so that plenty of haemoglobin can be stored
-they pick up oxygen from the lungs and transport it to cells
-the oxygen binds to a red pigment called haemoglobin
8.6 Describe white blood cells
-large cells containing a big nucleus
-part of the body’s immune system
-some form y-shaped antibodies which bind to organisms
-others engulf and digest pathogens
8.6 Describe platelets
-small fragments of cells
-no nucleus
-they are important for making blood clots and forming scabs
8.6 Describe plasma
-is a yellow coloured liquid which carries blood cells
-carries the waste gas product, carbon dioxide, from cells to the lungs
-it transports urea from the kidney and moves it to the bladder
8.6 Where are red blood cells made? What is its main function ?
bone marrow
To carry oxygen from the blood to cells
8.6 Where are white blood cells made? What are their main functions?
bone marrow
Phagocytes engulf pathogens
Lymphocytes products antibodies, which results in an immune response
8.6 Where are platelet cells made? What is their main function?
Bone marrow
To initiate blood clots
8.7 What are the three main blood vessels?
Arteries, Veins and Capillaries
8.7 What are arterioles?
Small arteries: smaller vessels that branch off from the arteries
The narrow vessels that connect arteries to capillaries are called arterioles
8.7 What are venules?
Small veins: small vessels that branch into veins
The narrow vessels that connect capillaries to veins are called venules
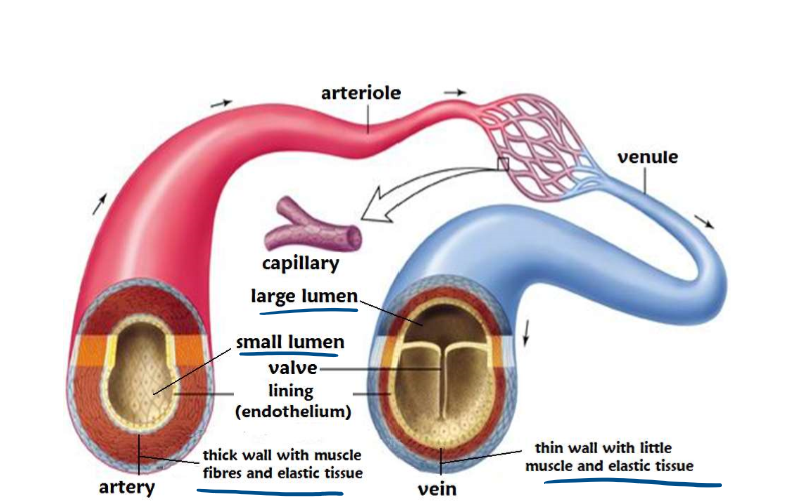
8.7 Function of arteries
-carry blood at high pressure away from the heart
-carry oxygenated blood (except the pulmonary artery)
-have thick muscular walks containing elastic fibres
-have a narrow lumen
-no valves
-blood flows through at fast speed
8.7 What are the adaptations of arteries?
-thick muscular walls containing elastic fibres withstand the high pressure of blood and maintain the blood pressure as it recoils after the blood has passed
-narrow lumen also helps to maintain high pressure
8.7 Functions and characteristics of veins
-carry blood at low pressure towards the heart
-carry deoxygenated blood (other than the pulmonary vein)
-have thin walls
-have a large lumen
-contain valves
-blood flows through at low speed
8.7 What are the adaptations of veins
-They have a large lumen which reduces resistance to blood as it is under low pressure
-valves prevent the backflow of blood ad it is under low pressure
8.7 Compare the structure of veins and arteries
Arteries have thick cell wall vs veins have a thin cell wall
Aeries have a narrow lumen vs veins have a wider lumen
Arteries have a thick layer of smooth muscle +elastic fibres vs veins have a thin layer of smooth muscle + elastic fibres
Veins have one way valves to prevent backflow of blood vs arteries do not
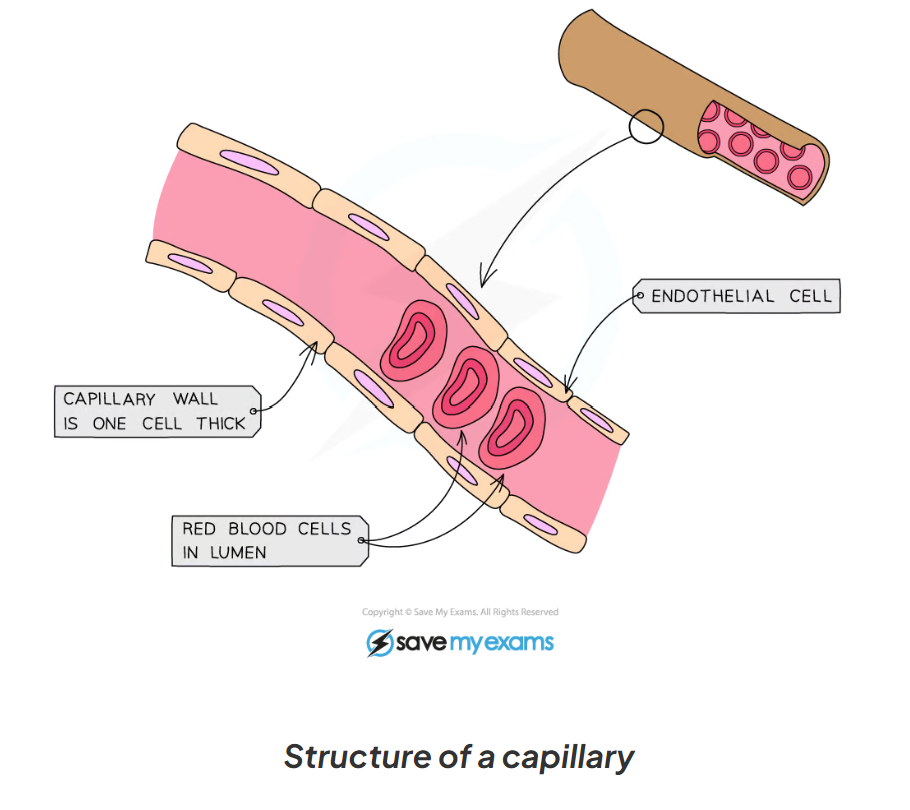
8.7 Capillary functions
-carry blood at low pressure within tissue
-carry both oxygenated and deoxygenated blood
-have walls that are one cell thick
-speed of blood flow is slow
-leafy cell wall
8.7 What are the adaptations of capillaries?
-have walls that are one cell thick to decrease the diffusion distance so substances can diffuse in and out efficiently - faster rate of diffusion
-have leaky walls to allow blood plasma to leak out and form tissue fluid surrounding cells
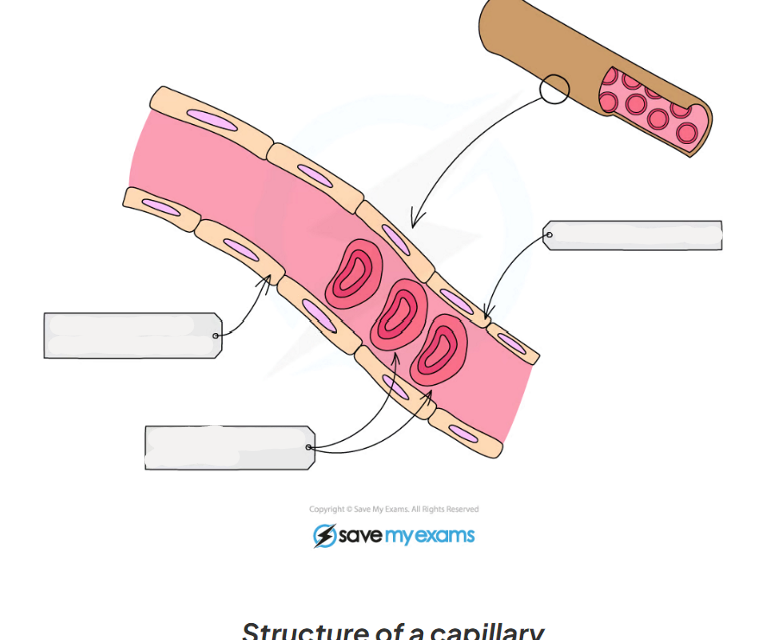
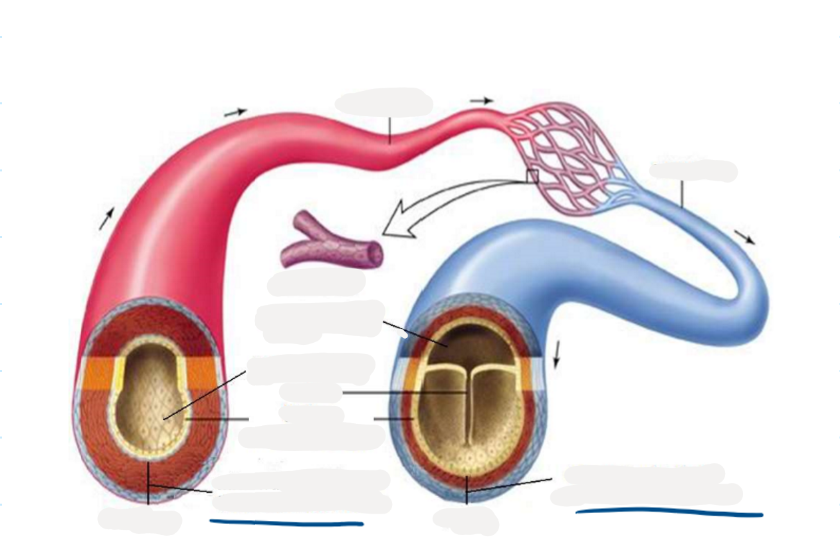
8.7 label this diagram of a capillary
8.7 label this diagram of an artery and vein
8.8 What is the heart? What takes place in the heart?
It is a double pump organ
-oxygenated blood from the lungs enters the left side of the heart and is pumped to the rest of the body (the system circuit)
The left ventricle has a thicker cell wall then the right ventricle as it has to pump blood at a high pressure around the body.
-deoxygenated blood from the body enters the right side of the heart and is pumped to the lungs (the pulmonary circuit)
The right ventricle is pumping blood at lower pressure to lungs
8.8 What separated the two sides of the heart?
a muscle wall called the septum
8.8 What pumps blood away and towards the heart?
Arteries pump blood away from the heart and veins pump deoxygenated blood from the heart
8.8 What is the role of the coronary arteries?
they supply the cardiac muscle tissue of the heart with oxygenated blood
8.8 why does the heart need a constant supply of oxygen?
Because it is a muscle it needs a constant supply of oxygen (and glucose) for aerobic respiration to release energy to allow continued muscle contractions
8.8 Label this diagram of a heart
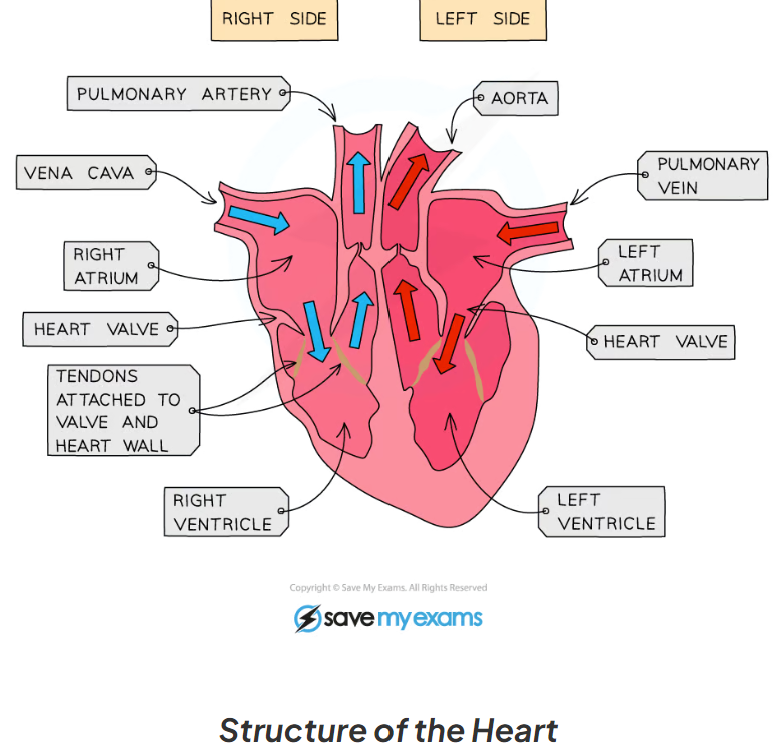
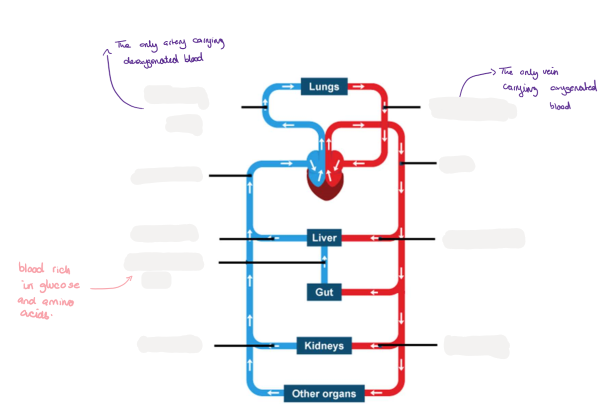
8.8 Label this diagram
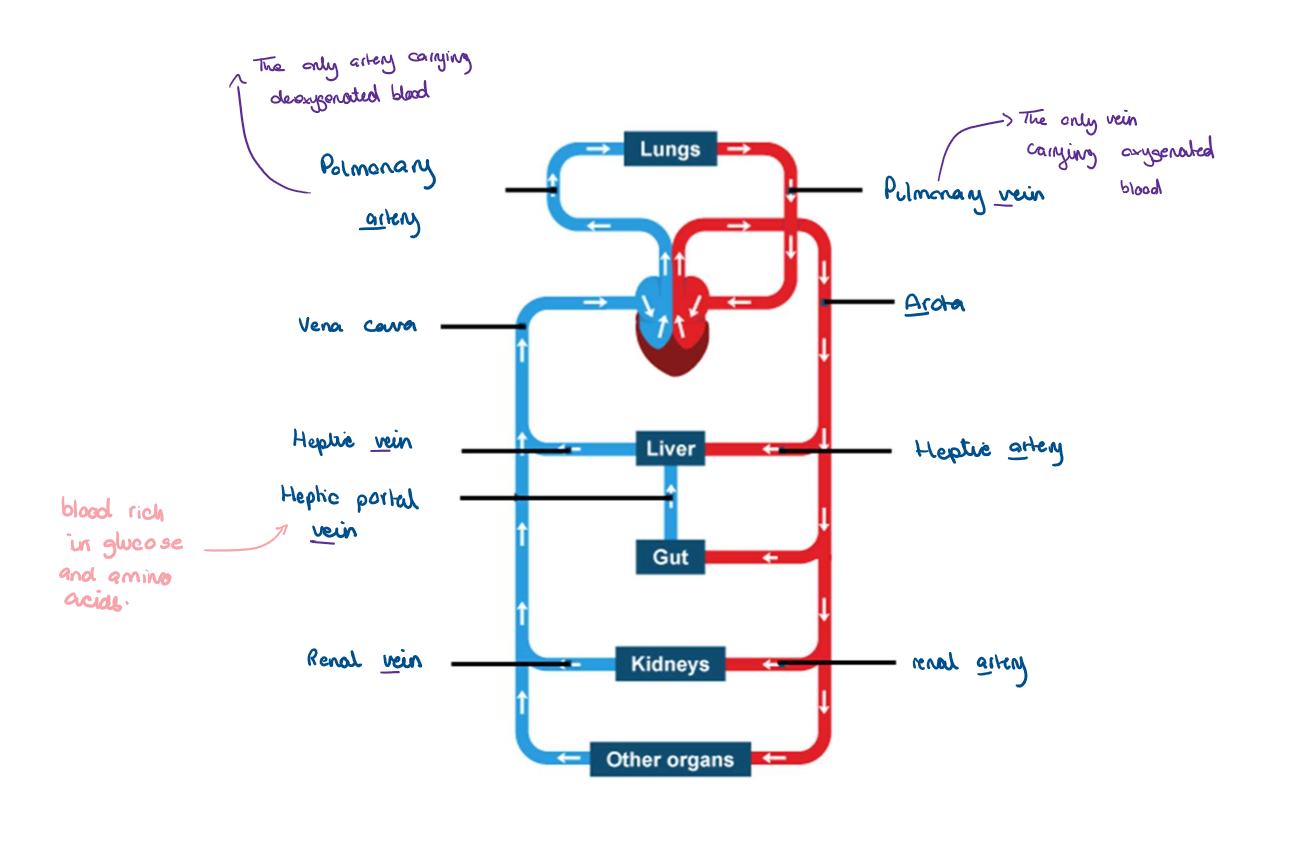
8.8 What is the purpose of the vena cava?
It is the major artery which takes blood from the heart to the rest of the body
8.8 What is the purpose of the arota?
the major vein which carries oxygenated blood around the body
8.8 What dose the pulmonary artery and pulmonary vein do?
The pulmonary artery carries deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs
The pulmonary vein collects oxygenated from lungs and takes it to the heart
8.8 What are the walls of the heart made of, give 2 key facts about this structure?
cardiac muscle (myogenic), which can never tire.
But cannot tolerate the lack of oxygen (risk of heart attack/ cramp of the heart)
8.8 What do atria do?
collect blood that enters the heart
8.8 What do ventricles do?
pump blood out of the heart
8.8 What are the main organs in the circulatory system?
heart, lungs, kidney
8.8 which organs bring blood towards the heart ? Which bring blood away from the heart?
-vena cava and pulmonary vein bring blood towards the heart
-aorta and pulmonary artery take blood away from the heart
8.8 Which organs bring blood towards and the lungs and away from the lungs?
-pulmonary artery brings blood towards the lungs
-pulmonary vein takes blood away from the lungs
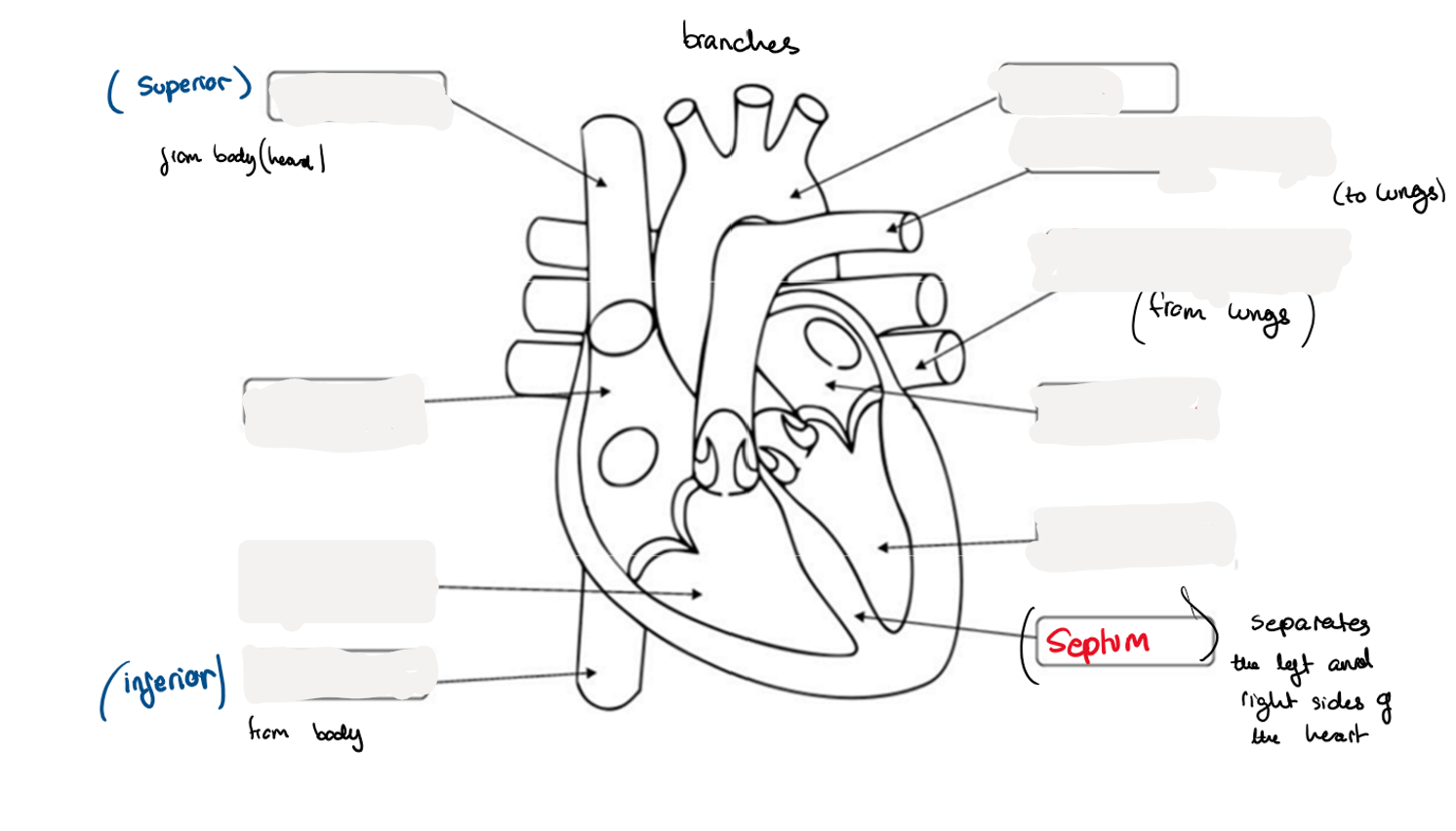
8.8 Label this diagram of a heart
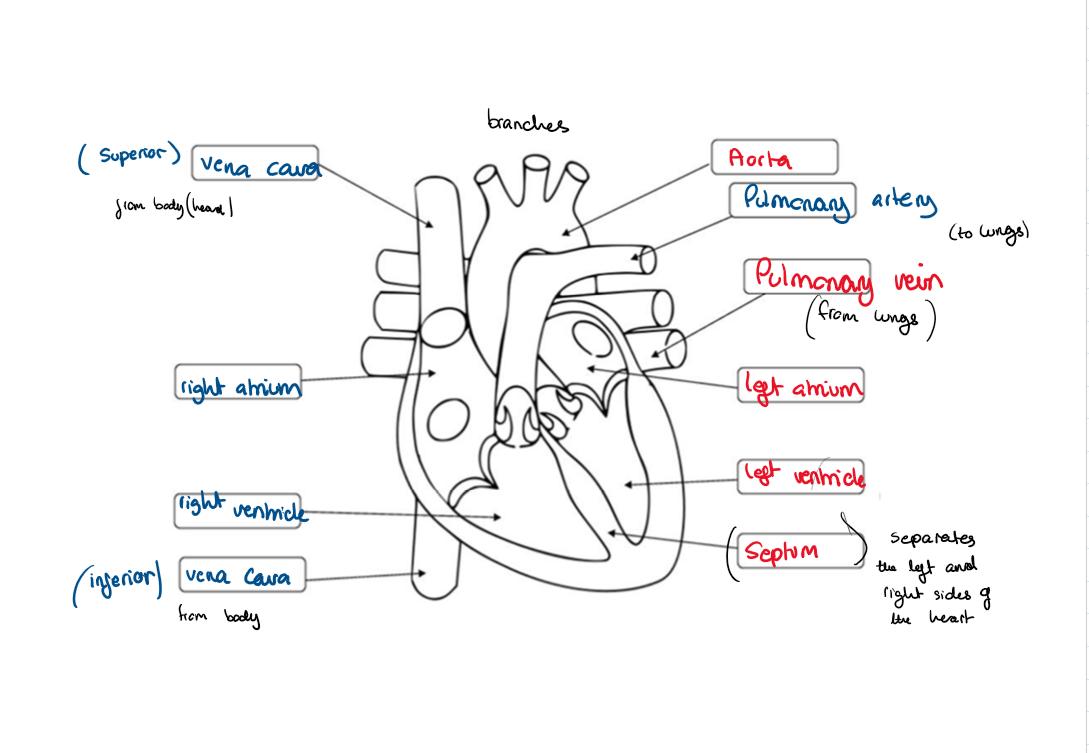
8.8 What is a chamber?
the upper parts of the heart: The left and right atria
8.8 What are the valves between the atria and ventricles called?
What are the functions of the valves?
left and right atrioventricular valves
These valves ensure a one way flow
8.8 What are the valves leading out of the left ventricle called?
Left and right semi-lunar valves
8.8 What are coronary arteries?
they branch off the aorta to supply the heart muscle with oxygen and glucose for respiration
8.8 List the correct sequence of the four marks blood vessels, four heart Chambers and valves taut a red blood cell passes through on it journey from the lungs through the heart and body, and back to the lungs
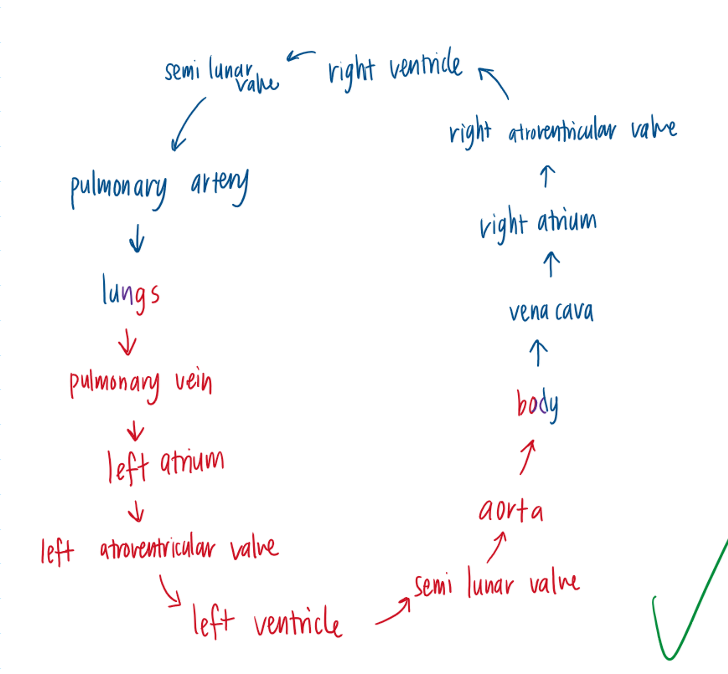
8.8 What is a cardiac output?
This describes the volume of blood that is pumped by the heart per unit of time.
8.8 What affect does exercising have of cardiac output and why
Cardiac output increases when an individual is exercising in order to supply oxygen and glucose for respiration
8.8 How do you calculate cardiac output?
Cardiac output (cm3m-1) = heart rate (bpm) x stroke volume (cm3)
8.9 What is respiration?
cellular respiration is an exothermic reaction which us continuously occurring in living cells
8.9 What is the purpose of respiration?
to release energy either in the presence of oxygen (aerobic respiration) or the absence of oxygen (anaerobic respiration).
The energy transferred supplies all the energy for metabolic processes to occur within cells and organisms.
8.8 Name 5 things organisms need energy for
-Chemical reactions to build larger molecules from small molecules
-Muscle contraction to allow movement
-Keeping warm (to maintain a constant temperature suitable for enzyme activity)
-Protein synthesis
-Cell division
8.8 What is aerobic respiration?
aerobic respiration requires energy
The breakdown of glucose to release large amounts of energy for use in cell processes and reactions
8.9 What is the word and symbol equation for aerobic respiration?
glucose + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water
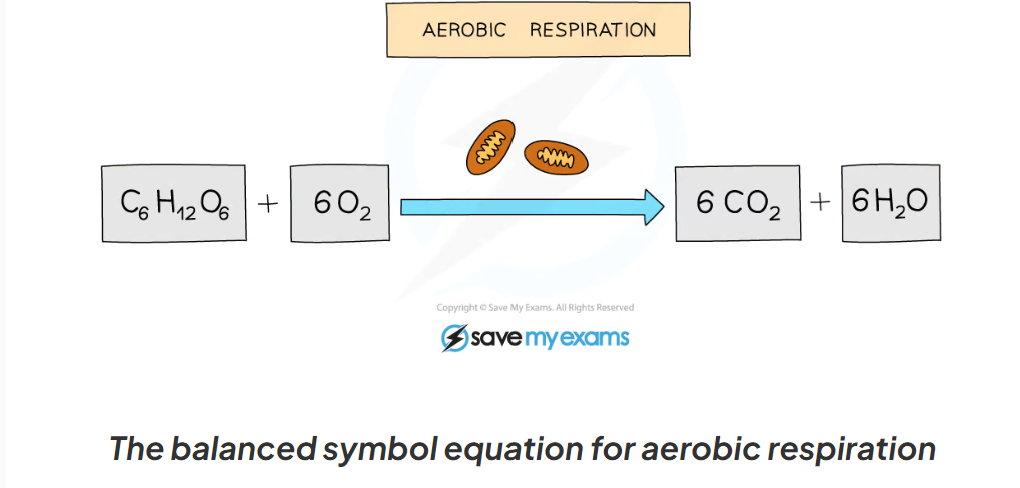
8.9 What is anaerobic respiration?
Respiration which doesn't require oxygen
It involves the incomplete breakdown of glucose, so releases a relatively small amount of energy to be used in cell processes
8.9 Explain anaerobic respiration in animals
-mainly takes place in muscles cells during vigorous exercise
-when exercising at high intensities the body has a higher demand for energy
-because the body can only deliver so much oxygen to muscles cells for aerobic respiration, when oxygen runs out, glycose is broken down without lactic
8.9 Which time of respiration releases the most energy?
aerobic respiration
8.9 What is the word and symbol equation for anaerobic respiration?
glucose → lactic acid

8.9 What is lactic acid?
It builds up in muscle cells and lowers the pH of the muscle tissue (making the conditions more acidic). Acidic conditions can denature enzymes.
Lactic acid will eventually be broken down using oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water as waste products
8.9 What is oxygen debt?
The amount of oxygen required to break down the lactic acid that has built up is called ‘oxygen debt’
8.9 Define the term ‘repaying oxygen debt’
The process of breaking down the lactic acid
8.9 Describe anaerobic respiration in plants and fungi
-pants and yeast can respire without oxygen
-they break down glucose in the absence of oxygen to produce ethanol and carbon dioxide
8.9 is Fermentation?
It is anaerobic respiration in yeast
8.9 Why is fermentation economically important?
it is important in:
-the manufacturing of bread (where the carbon dioxide produced helps the dough to rise)
-in brewing (where the thank produces makes beer)
8.9 What is the word equation for anaerobic respiration in yeast?
glucose → ethanol + carbon dioxide
C6 H12 O2 → 2C2 H5 OH + 2CO2
8.9 What type of reaction is cellular respiration?
An exothermic reaction (heat is given out to the surrounding)
8.10 Compare aerobic and anaerobic respiration considering the following factors:
-is oxygen needed?
-glucose breakdown
-products
-reactants
-energy release
Aerobic: Oxygen is needed , glucose is fully broken down, products are carbon dioxide +water, reactants are oxygen + glucose, a lot of energy is released
Anaerobic: Oxygen isn't needed, glucose isn't fully broken down, products are lactic acid in animals and carbon dioxide + alcohol in yeast, reactant is glucose, very little energy is released
8.11 What apparatus are needed in the investigate the production of carbon dioxide from respiration?
-water baths
-yeast and sugar mix
-50ml water
-conical flask
-gas syringe
-timer
8.11 What is the method for the investigation of the production of carbon dioxide in respiration
1) Place a beaker of water into the water bath to warm to correct temp
2) Add 50ml of this water into your yeast and glucose mix
3) Stir thoroughly
4) Syringe 15ml of this mixture into a conical flash
5) Put the bung, ensuring the gas syringe is pushed all the way in, then start timing
6) After 15mins read off the hoe much gas has been produced
8.11 Label this diagram of the apparatus needed for the investigation
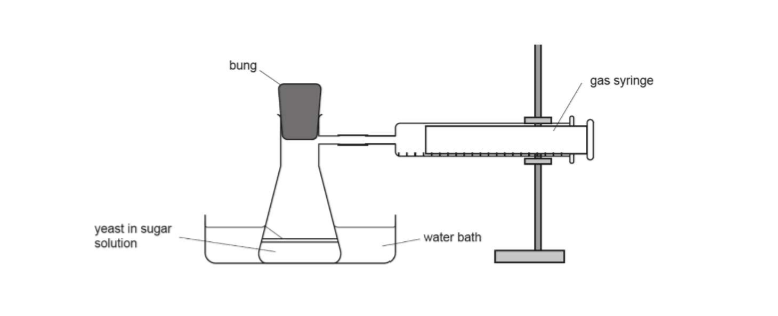
8.11 What is the independent variable in the experiment to investigate the production of carbon dioxide in respiration?
temperature
8.11 What is the dependent variable in the experiment to investigate the production of carbon dioxide in respiration?
time take
8.11 What is the controlled variable in the experiment to investigate the production of carbon dioxide in respiration ?
volume of water
8.11 Give a prediction for which temp will have the most gas produced
The optimum temperature (perhaps 40) will produce the most gas because the enzymes have the most kinetic energy therefore more successful collisions take place, resulting in a faster rate of reaction.
8.11 What chemical reaction is being investigated in this experiment to investigate the production of carbon dioxide in respiration?
fermentation: Glucose → carbon dioxide + ethanol