2.3.1- algorithms
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
2 considerations when developing an algorithm
time complexity
space complexity
what is time complexity and what notation does it use
time taken to solve a particular problem, shown using big-O notation
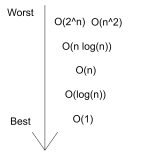
types of time complexities
constant time complexity 0(1)
linear time complexity 0(n)
polynomial 0(n²)
exponential 0(2^n)
logarithmic 0(logn)
worst to best time complexities
what is depth first traversal for trees?
Go to the furthest node, and then backtrack (outputting the left/right child node first before outputting the current node) using a stack
-same as post order traversal
what is breadth first traversal?
visits current node before going to children (left first) that are directly connected to the current node using a queue
-traverses in layers
process of insertion sort
iterates over the length of the list times and sorts the first n items based on the nth iteration the program is on
-each item in the list is compared to the current items in the list (on left) and inserted into correct position
insertion sort code

process of merge sort
mergeSort divides the input recursively until each sublist has length 1
merge sorts each sublist together until a final whole sorted list is produced
merge sort code

process of quick sort
selecting a pivot of the list recursively and sorting smaller/larger elements on the left/right side of the pivot to form 2 new sublists
-re-repeats until all elements are old pivots (already sorted) or form lists of length 1 (nothing left to sort)
binary search code

time complexity of binary search
O(log n)
2 pathfinding algorithms
dijkstra’s
A* algorithm
purpose and process of dijkstra’s algorithm
-finds the shortest path between 2 nodes in a weighted graph
-implemented using a priority queue (smallest distances from initial node moved to the front)
process of A* algorithm
Has two cost functions:
1) The first cost function is the actual cost between two nodes. This is the same cost as is measured in Dijkstra’s algorithm.
2) The second cost function is an approximate cost from node x to the final node. This is called a heuristic, and aims to make the shortest path finding process more efficient. The approximate cost might be an estimate of the length between x and the final node, calculated using trigonometry
process of finding an unbalanced tree and result on time complexity
from root node, calculate number of left nodes - number of right nodes
-any result that’s not +1, 0 , or -1 is unbalanced and is treated as a linear search
time complexity of DFS/BFS
O(n)