Personal Health Ch 4: Sleep
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
sleep biology
Sleep affects all systems in the body, including consciousness, which is profoundly altered during sleep.
sleep architecture
the structure of the various elements involved in the sleep cycle, including normal and abnormal patterns of sleep
eeg
An amplified recording of the waves of electrical activity that sweep across the brain's surface. These waves are measured by electrodes placed on the scalp.
NREM sleep
non-rapid eye movement sleep; encompasses all 3 sleep stages except for REM sleep
stage 1: alpha rhythm
a brief translational period from wakefulness to sleep. the eyes move slowly back and forth, respiration grows more regular than during wakefulness; muscles relax, and may twitch.
stage 2: theta rhythm
This stage comprises about half of time spent sleeping. Eye movement and muscular activity are minimal. has a frequency of 4 to 7 cycles per second.
Stage 3: Delta Rhythm
This is a period of deep and restful sleep. Muscles are relaxed, heart rate and blood pressure fall, and breathing slows. No eye movement occurs. has a frequency of 1.5 to 3 cycles per second.
slow-wave sleep
Characteristic patterns of electrical brain activity measured by the electroencephalogram (EEG) during the deepest stage of sleep, Stage III.
stage 4: rapid eye movement (REM) sleep
One of two main phases of sleep; the final phase of a sleep cycle, when most dreaming occurs and eyes rapidly move under closed eyelids. Brain activity increases to levels equal to or greater than those during waking hours, and blood pressure, respiration, and heart rates rise.
circadian rhythm
The body's sleep-and-wake pattern coordinated by the brain's master internal clock, the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN).
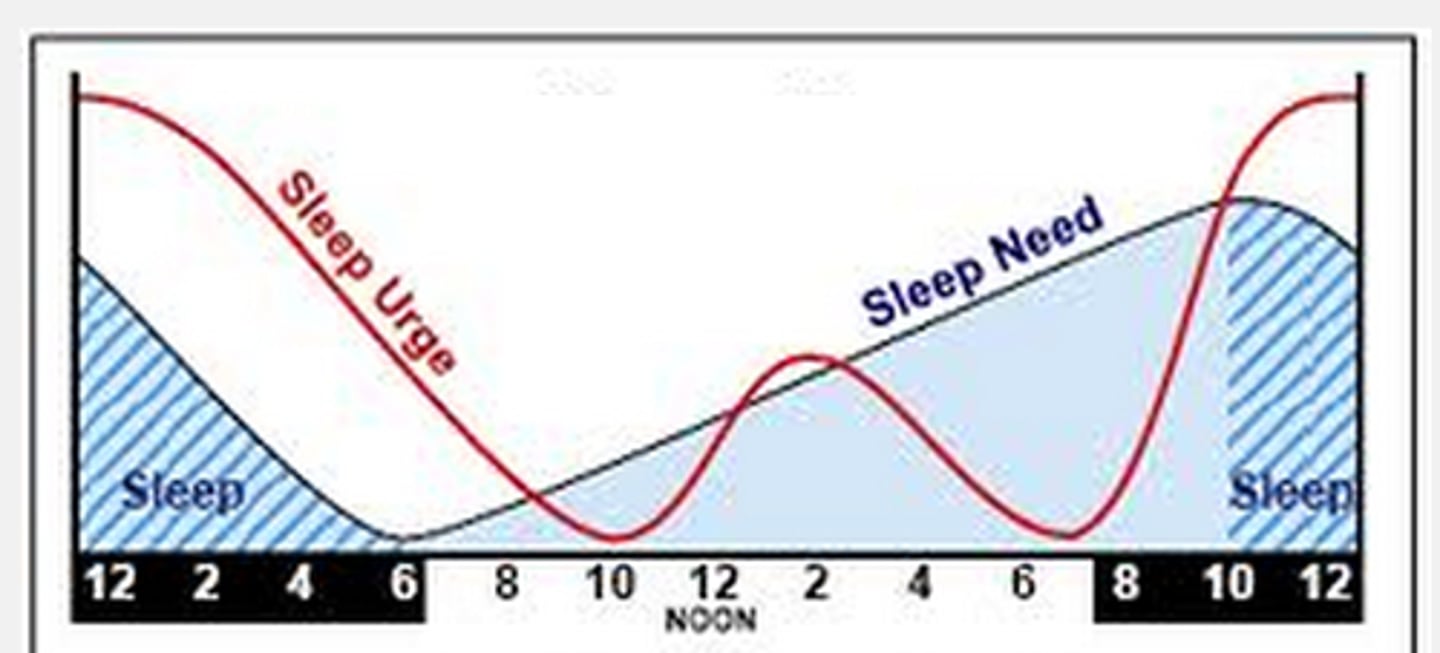
zeitgebers
Phenomena that can influence and reset the body's master clock, such as light, activity, exercise, and eating. Light directly affects cells in the eye to send signals directly to the SCN to measure outside light.
melatonin
A hormone secreted by the pineal gland, especially in response to darkness and in inverse proportion to the amount of light received by the retina. It helps control sleep-and-wake cycles and circadian rhythms.
light and sleep
consistent light appearances at the beginning of our days signal when we should get up
homeostatic sleep drive
Pressure to sleep that builds the longer one is awake, mainly driven by adenosine, a neurochemical that accumulates in the brain. Sleep clears the adenosine, thereby reducing the pressure to sleep.
adenosine
An important neurochemical that accumulates during wakefulness, and after a prolonged period will mediate sleepiness.
how much sleep do babies need
16 hours
how much sleep do teens need
8-10 hours
how much sleep do adults need?
7-9 hours
sleep apnea
a sleep disorder characterized by temporary cessations of breathing during sleep and repeated momentary awakenings
women are more likely to be diagnosed with
insomnia
pregnancy and sleep
More sleep needed during 1st trimester related to progesterone levels
Hormone fluctuations can disrupt sleep through night sweats (esp dip in estrogen)
Change in body shape can cause discomfort
sleep and menopause
Sleep patter can change, need for sleep decreases with age, may only need 6-7 hours
the older we get
the more easily we wake
Risk for depression rises with
insomnia
neurochemical changes from sleep deprivation can make people more prone to
depression
sleep and dementia
Recent research has found a link between sleep and dementia; less sleep you get, more risk of dementia
glymphatic system
a lymphatic system in the brain that participates in removal of wastes and the movement of nutrients and signaling compounds. Without sleep, it can't work as efficiently.
Sleep and Athletic Performance
well-rested athletes have faster reaction times, more energy, and greater endurance
- do not do any heavy workouts right before bed
10 hours is ideal for them
musculoskeletal pain
often presents after exercise, trauma, or prolonged coughing episodes. symptoms can be improved with good sleep
Sleep and weight gain
Less sleep is associated with weight gain in young adults. People are more susceptible to eating disorders when they feel too fatigued
people with mild sleep apnea are significantly more likely to
develop hypertension
people who sleep less are at high risk for
cardiovascular disease
microsleep
a momentary lapse in which some parts of the brain lose consciousness. loss of perception of outside world
sleep disrupters
Factors that interfere with falling or staying asleep; they can usually be corrected if targeted specifically.
reflux
when a small amount of fluid from the acidic contents of the stomach rises into the esophagus, irritating the upper airway. Disrupts sleep
sleep disrupter examples
reflux, nasal congestion and cough, urination, anxiety and stress, pain, poor environment, too much caffine
sleep log
A diary of an individual's time in bed, estimated total sleep time, lights out time, lights on time, and daily activities. can help clinicians determine circadian rhythm disorders and causes of insomnia.
insomnia
A sleep problem involving the inability to fall or stay asleep.
insomnia symptoms
difficulty falling sleep, waking up frequently during the night, difficulty returning to sleep, waking up too early in the AM, unrefreshing sleep, daytime sleepiness, difficulty concentrating, irritability
insomnia treatment
sleep hygiene, stimulus control, relaxation, sleep restriction, and cognitive behavioral therapy. Stimulus control focuses on eliminating stimulating bedroom activities and getting into bed only when sleepy.
restless leg syndrome (RLS)
A sleep disrupter characterized by a feeling of discomfort or body tension, often affecting the legs. Symptoms are determined by the time of day they appear. Can be helped by moving around and made worse by sitting still for too long
restless leg syndrome treatment
more exercise, less caffeine, stretching legs and muscles, ensuring iron levels are mid-ranged
the most common sleep disruptor
sleep apnea
sleep apnea treatment
- Weight loss is encouraged.
- Tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy (T&A).
- Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UPP).
- CPAP apparatus or dental appliances to keep airway open in adults; home apnea monitor for infants.
narcolepsy
A rare neurological disorder characterized by excessive daytime sleepiness, sleep paralysis, and sudden loss of muscle control.
Narcolepsy treatment
Provigil to help them stay awake and antidepressants to suppress REM sleep
What happens when humans fall asleep?
- body temperature declines
- blood pressure drops
It is difficult for us to wake up quickly during, and if we do, we might become confused.
slow-wave sleep
We enter into deep sleep less as we age. By what stage of life is it possible that deep sleep may be completely absent?
mid- 70s
Studies conducted during the Covid-19 pandemic highlighted the link among:
depression
insomnia
anxiety
When is melatonin usually produced?
when the sun sets
What issues may increase the risk of developing dementia or cause an earlier onset of dementia?
poor quality sleep
sleep disruptions during the night
ghrelin
increases appetite
leptin
decreases appetite
Which system helps remove proteins, such as amyloids, during sleep and is protective against dementia?
glymphatic system
Which sleep-related phenomena can contribute to diabetes?
sleep apnea
difficulty falling or staying asleep
sleep and pain
Poor sleep can create a lower pain threshold.
Poor sleep can increase the risk of developing pain.
By which percentage do leptin levels decrease in individuals who are sleep deprived?
20-30%
According to research findings, people with moderate to severe sleep apnea are ______ more likely to develop hypertension within four years.
three times
Reflux is worsened by
chocolate
caffeine
mint
What are treatments for the physical disrupters of anxiety and stress?
a "wind-down" time before bedtime
meditation and other relaxation strategies
a warm room
is good for sleep
To treat nasal congestion that disrupts sleep, it is best to avoid medications that have ______ on a long-term basis since they can actually worsen congestion.
ephedrine
Which would be the best activity to try to reduce stress and worry that interrupt sleep?
daytime planning sessions
What is the primary cause of the physiological tendency to sleep?
the homeostatic sleep drive
Who is most likely to have chronic insomnia?
a person with a high arousal tendency
Which factors can help improve the symptoms of restless leg syndrome (RLS)
stretching the legs before bedtime
avoiding caffeine
engaging in daily exercise
Which groups are most at risk of developing sleep apnea
people with a family history of sleep disorders
people who are overweight
people who snore
the supratympanic nucleus is located in
the brain
Getting enough sleep is important in minimizing the risk for dementia by
allowing sufficient time for the glymphatic system to do its work.
Alcohol and opioids can affect sleep similarly in that they
affect breathing during sleep.
Which could lengthen the time a person stays in Stage III sleep?
exercising