CM ZS9
1/9
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapters 15&16 Voedsel → Energie en de Glycolyse
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
energy is required to meet which 3 fundamental needs?
1) mechanical work of movement
2) active transport of molecules across membranes
3) synthesis of biomolecules (and new cells)
hoe komt het dat ATP zo’n centrale rol vervult in metabolisme?
ATP is the universal currency of energy in bio systems
ATP hydrolysis is exergonic and the energy released can be used to power cellular reactions
ATP hydrolysis shifts equilibrium of a coupled reaction by a factor of 10^8!
wat is het belang van het koppelen van een thermodynamisch ongunstige reactie koppelen aan een thermodynamisch gunstige?
omdat als je de reacties koppelt, je de ΔG op mag tellen waardoor je een ΔG=-ve krijgt. dit betekend dan een reactie die zelf niet spontaan kon verlopen nu wel kan.
belangrijk want bepaalde reacties hebben ΔG=+ve maar zijn toch noodzakelijk voor cel.
anabolisme
the set of metabolic reactions that require energy to synthesize molecules from simpler precursors (energy in to build)
katabolisme
the set of metabolic reactions that transforms fuels into cellular energy (energy released by breaking)
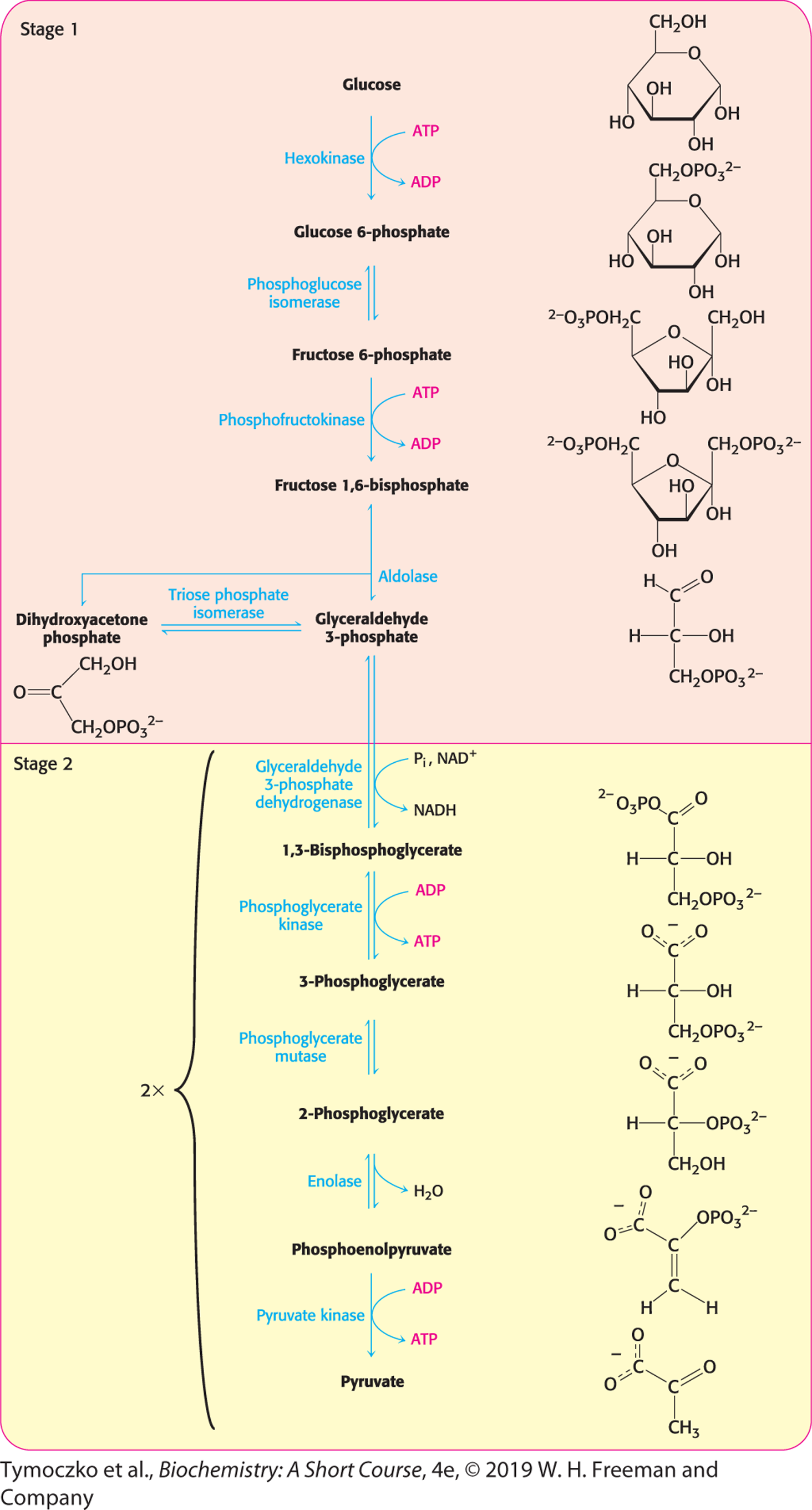
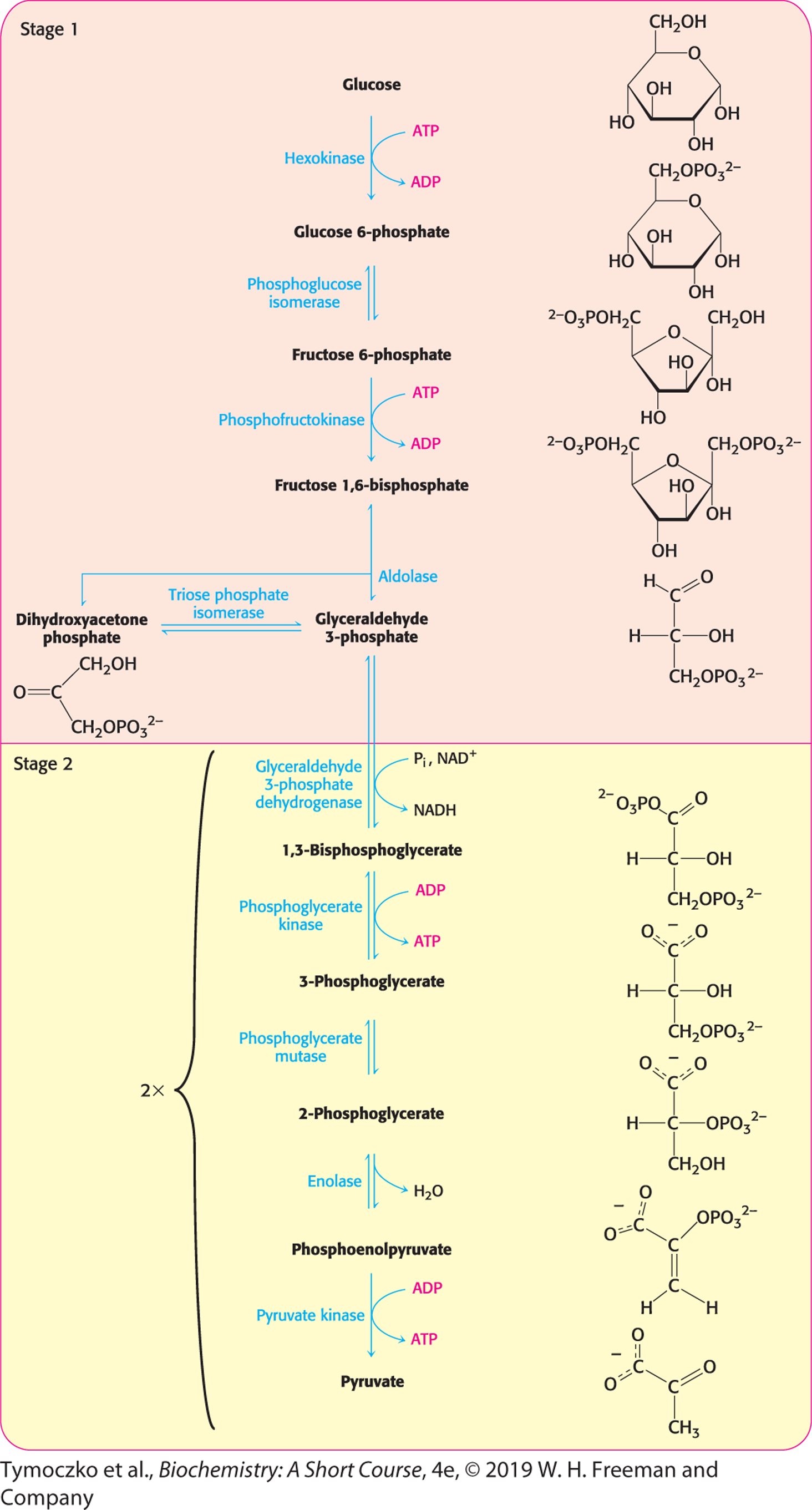
essentie van glycolyse
glycolyse is de conversie van glucose tot pyruvaat (via intermediates). tijdens deze omzetting komen 2x ATP en 2x NADH vrij
functie van glycolyse
provide energy for cellular activities, particularly in anaerobic conditions.
also produces intermediates that can be used for other metabolic pathways.
het proces van glycolyse
stage 1: glucose phosphorylated → fructose 1,6-bisphosphate → glyceraldehyde-3-P (inconvertible)
stage 2: glyceraldehyde-3-P oxidized & phosphorylated → 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate (which adds phosphoryl group to ADP → ATP +) 3-phosphoglycerate → phosphoenolpyruvate → pyruvate (+ another ATP)
hoe gebruiken anaeroob-functionerende cellen/organismen glycolyse voor ATP-productie?
hoe wordt de energie in glyceraldehyde-3-fosfaat gebruikt voor ATP en NADH productie?
when glyceraldehyde-3-fosfaat is oxidized, NAD+ is reduced to NADH