Module 6 - Nursing Assisting - Asepsis
1/45
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
bacteria
protozoa
fungi
viruses
1)one cell organism
2)classified by their pill shape
3)usually have long names
What do bacteria use to aid reproduction? What else does it do?
Bacteria use spores; spores help make bacteria more resistant to harsh environments.
1) simplest organism in the animal kingdom
2) need moisture to survive (puddles, watery environments)
What do protozoa need to transport them?
Vectors—commonly known as animals
What are some possible diseases from protozoa?
Malaria, Dysentery, and African Sleeping Sickness
What are some facts on fungi?
1) plant-like microorganisms that can be found in the air, dirt, soil, plants, or water
2) thousands of types (mushrooms, yeasts, mold)
3) only half of these are pathogenic
What are some possible fungal diseases?
Athlete’s foot, ringworm, yeast infections, and thrush
What are some facts on viruses?
1) neither dead or alive
2) smallest type of microorganism
How do viruses make more viruses?
they infect cells, converting them into hosts [in order to make more viruses]
What are some common viral infections
common cold, chicken pox, measles, herpes, COVID-19, hepatitis B and C, HIV, and AIDs
What do vaccines do?
they trigger the antibody response
Who first discovered the importance of handwashing? What are some facts about them?
Ignaz Semmelweis - He was a doctor in Hungary during the 1800s. He noticed that when students did not wash their hands, the death rate would go up (determined that matter from corpses were being carried on their hands). The medical community did not believe him.
Who is Louis Pasteur?
Pasteur is a man who used Semmelweis’s theory on handwashing—making the medical community accept hand washing as an accepted practice. He proved germ theory and was the inventor of the pasteurization process. (also made vaccines for anthrax/rabies).
How does living in the global society impact infection control?
People and goods can travel easier than before, which means infection can also travel easier then before.
What does the chain of infection look like?
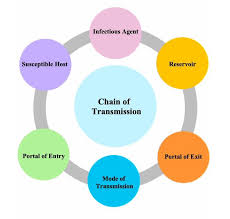
What is the infectious disease in the chain of infection?
Very self explanatory; literally the infectious disease (COVID, TB, etc)
What is a way to break the chain on infectious disease?
Handwashing/Hand sanitizer/Disinfectants
What is the reservoir in the chain of infection?
This is where the infectious grows. For example, mold (disease) can grow in the walls (reservoir) because they can be damp/moist.
What is the portal of exit in the chain of infection?
This is how the disease leaves. An example would be someone that sneezes while sick.
What is the mode of transmission in the chain of infection?
This would be how the disease travels. Some examples are: airborne, bloodborne, or by contact.
What is the portal of entry in the chain of infection?
This is how a disease can enter. For example, a cut on a finger.
What is a way to break the chain on portal of entry?
MAintaing an intact skin barrier/cover any open sores
What is a susceptible host in the chain of infection?
Also self explanatory. This is someone who can easily get sick. An example is someone who is immunocompromised/has AIDs.