South College AVL Clinical Anatomy 1: Special Senses - Lecture 18
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
110 Terms
vision, smell, taste, hearing, equilibrium
what are the special senses?
eyebrows, eyelids, conjunctiva, lacrimal apparatus, extrinsic eye muscles
What are the accessory structures of the eye?
Eyelashes, tarsal plate, sebaceous glands
What are three important aspects of the eyelid?
eyelashes
Richly innervated by nerve endings
Reflexive blinking
tarsal plate
Connective tissue
Supports eyelids internally
Anchor eyelid muscles
sebaceous glands
Produce oily secretions - lubricate eye (tarsal glands, and other small glands)
Protect the eyes, keep the eye moist
Function of the eyelids?
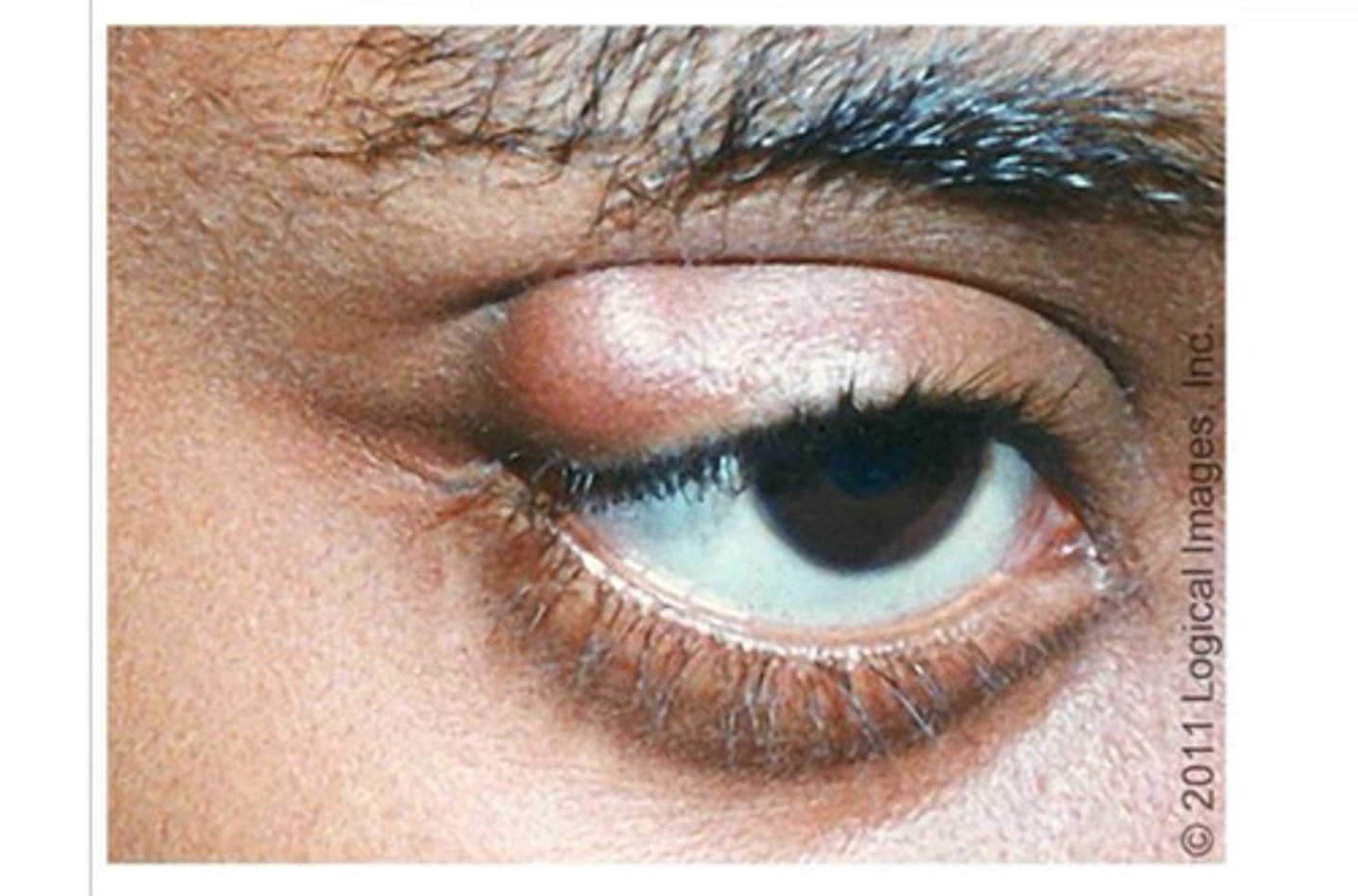
chalazion
Painless nodule caused by obstruction of the eyelid gland
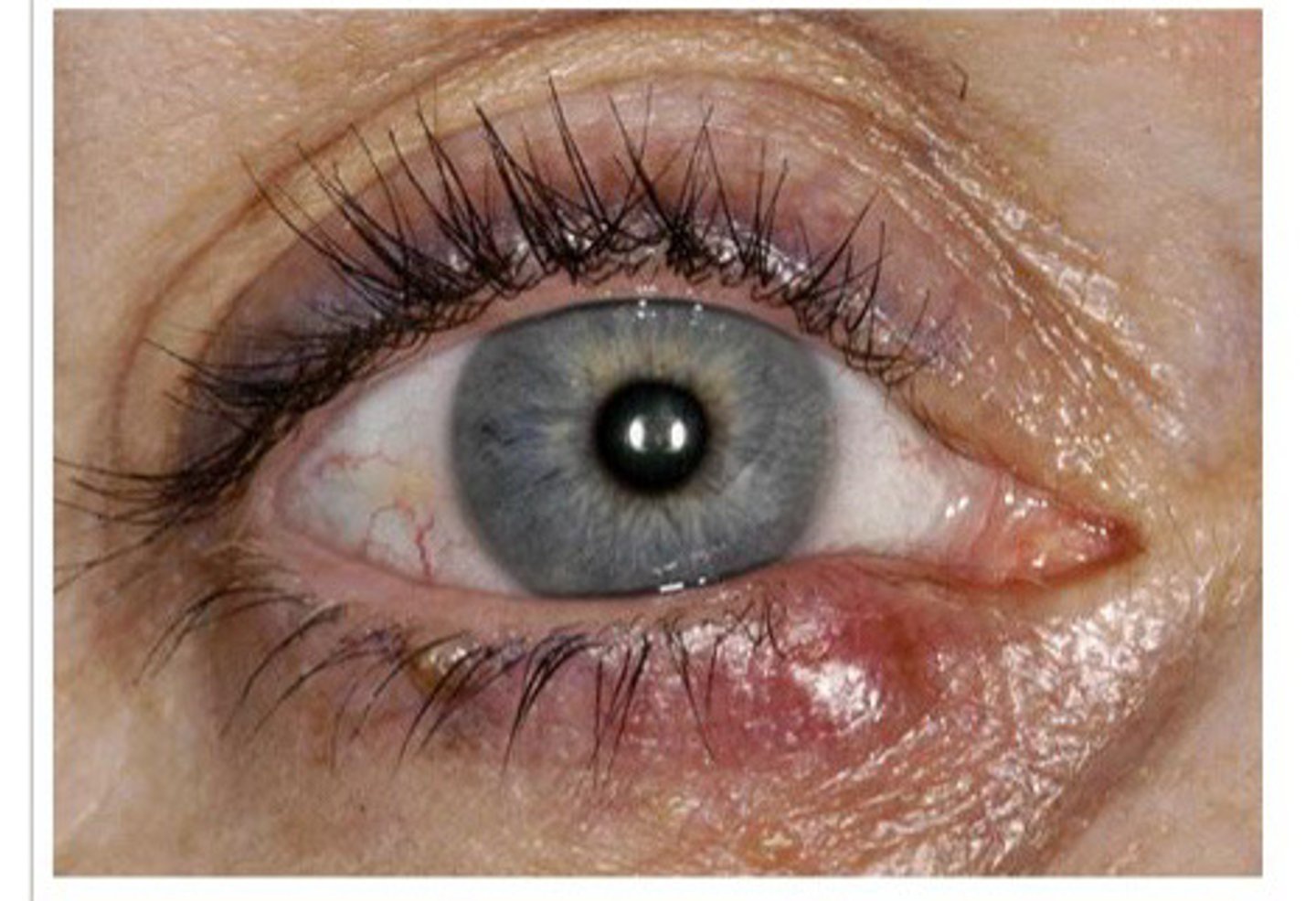
hordeolum (stye)
Acute eyelid inflammation that presents with localized pain, erythema, edema
conjunctiva
Transparent mucous membrane
Two types: (palpebral and bulbar)
Function: produced lubricating mucus that prevent prevents dry eye
palpebral conjunctiva
Lines the inner eyelid
bulbar conjunctiva
Covers the sclera on the anterior eye
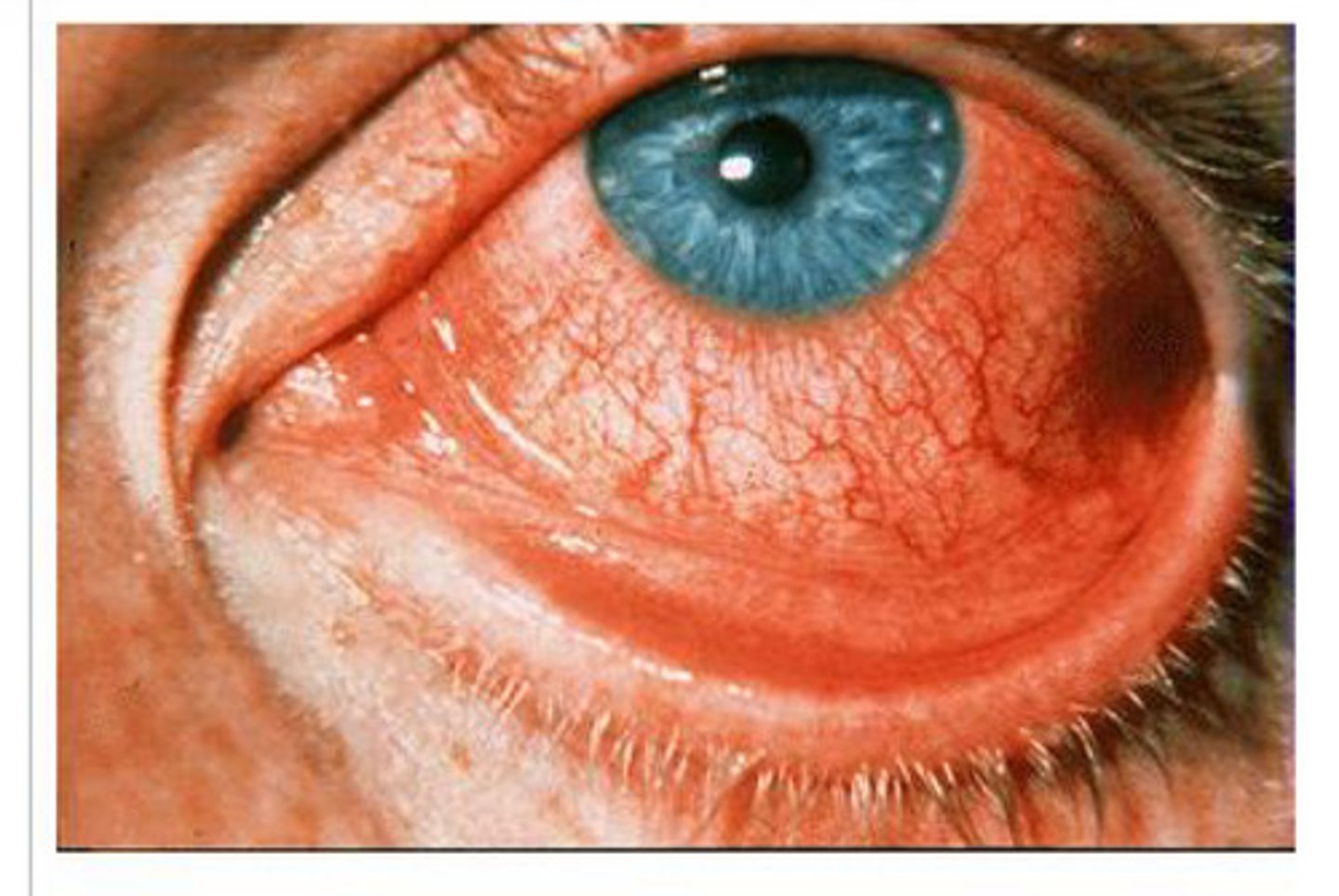
viral conjuctivitis
most common etiology
Presents as injection, watery, or mucous discharge and burning, sandy, gritty feeling in one eye
lacrimal apparatus
Contains lacrimal glands - produced tears
Ducts - tears empty into the nasal cavity
Function: moisten/lubricate eye, cleanse/protect eye
Mucus, antibodies, and lysozymes
What does lacrimal fluid contain?
extrinsic eye muscles
Six muscles
Origin - walls of orbit
Insertion - outer surface of eyeball (sclera)
Function: control movement of eyeball (follow moving object), maintain shape, hold eye in orbit (it doesn't pop out of eye socket)
Strabismus (misaligned eyes)
Vision disorder in which both eyes do not look at the same point in the visual field
Congenital weakness of the external eye muscles
Three layers (fibers, vascular, inner layer), internal chambers, lens
What are the components of the eyeball?
fibrous layer of eye
Avascular - outermost layer
Sclera: white of eye, tough and tendon-like
Cornea: transparent, outer covering, many nerve endings, regenerate/repair repairs quickly
Function: protection, cornea bends light
corneal abrasion
scratch on the cornea, painful and photophobia
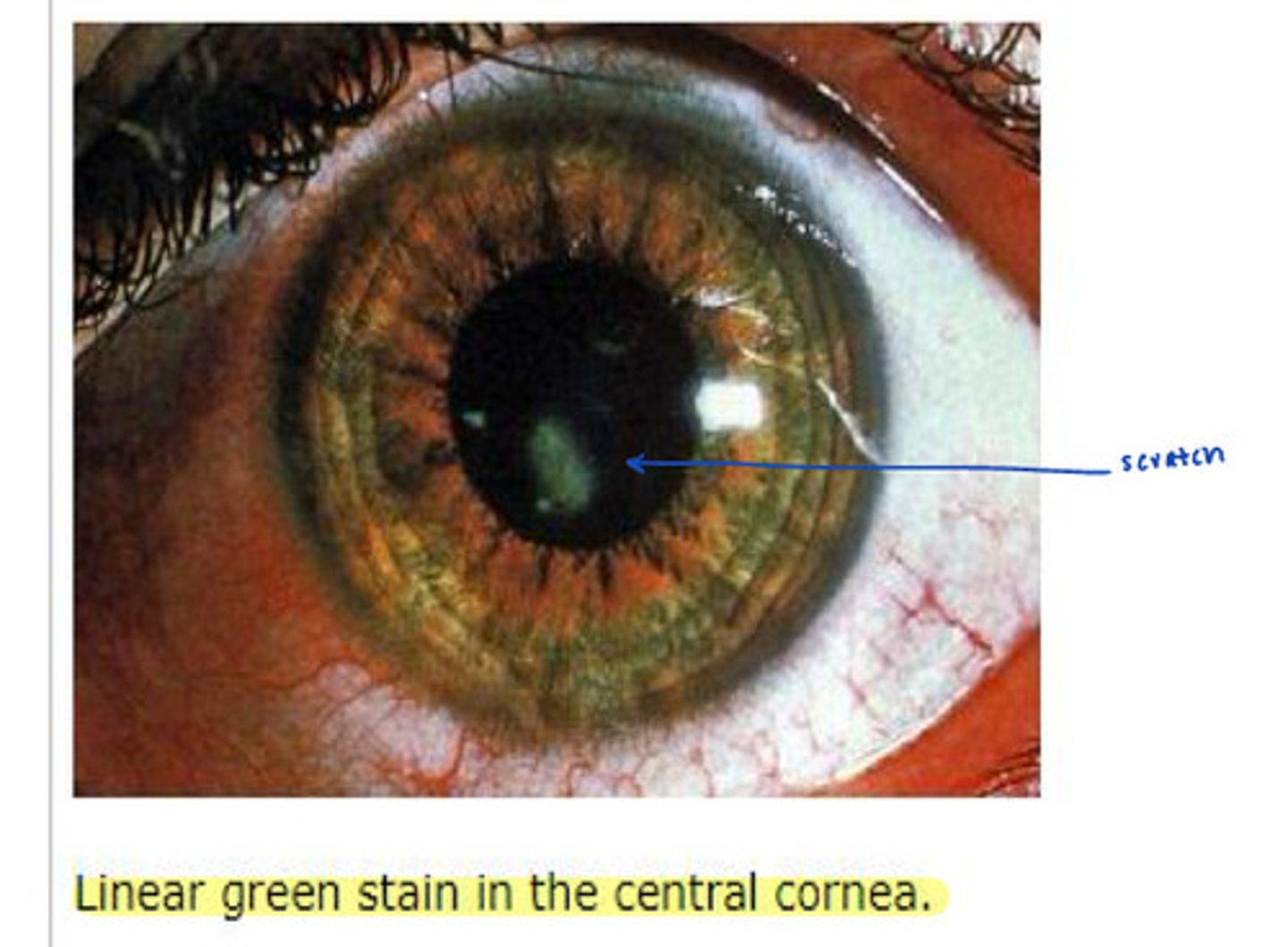
linear corneal abrasion
Commonly caused by a foreign body
vascular layer of eye
contains the choroid, ciliary body, and iris
choroid
Highly vascular, dark brown membrane - melanocytes
Function: nourish all layers, absorb light - prevent scattering
ciliary body
Ciliary muscles and ciliary processes
Function: control, lens shape, secrete fluid - fills anterior eyeball
Iris
"Colored part of the eye"
Two smooth muscles
Sphincter pupillae - constricts (parasympathetic)
Dilator pupillae - dilates (sympathetic)
Function: adjust to control the amount of light entering eye
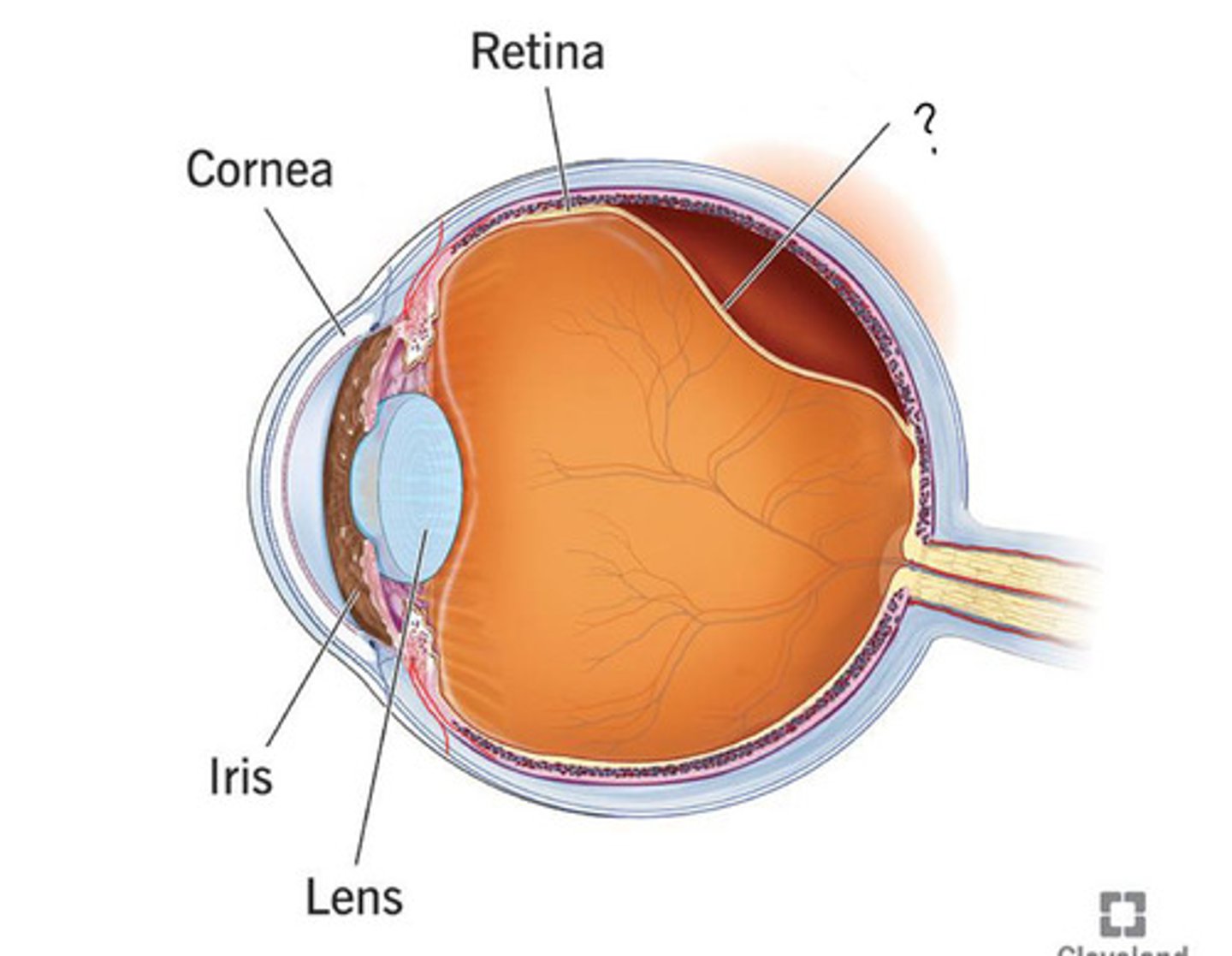
Rentina
Contains pigmented and neural layer, optic disc (where optic nerve exits eye - "blind spot"), central artery and vein
Function: vision
pigmented layer of retina
Pigmented cells
Function: absorbs light - prevent light from scattering, store, vitamin A, act as phagocytes (photo receptor cell renewal)
neural layer of retina
Signals are produced in response to lay and spread from:
Photoreceptors - bipolar cells - ganglion cells - optic nerve - visual pathway
Photoreceptors
Rods and cones
rods, cones
1) Receptors for dim light, peripheral vision receptors
2) receptors for bright light, provide high-res color vision
macula lutea
Yellowish oval region of the retina
Contains mostly cones (sharp vision)
Located lateral to the optic disc
Function: provides detailed, central colored vision
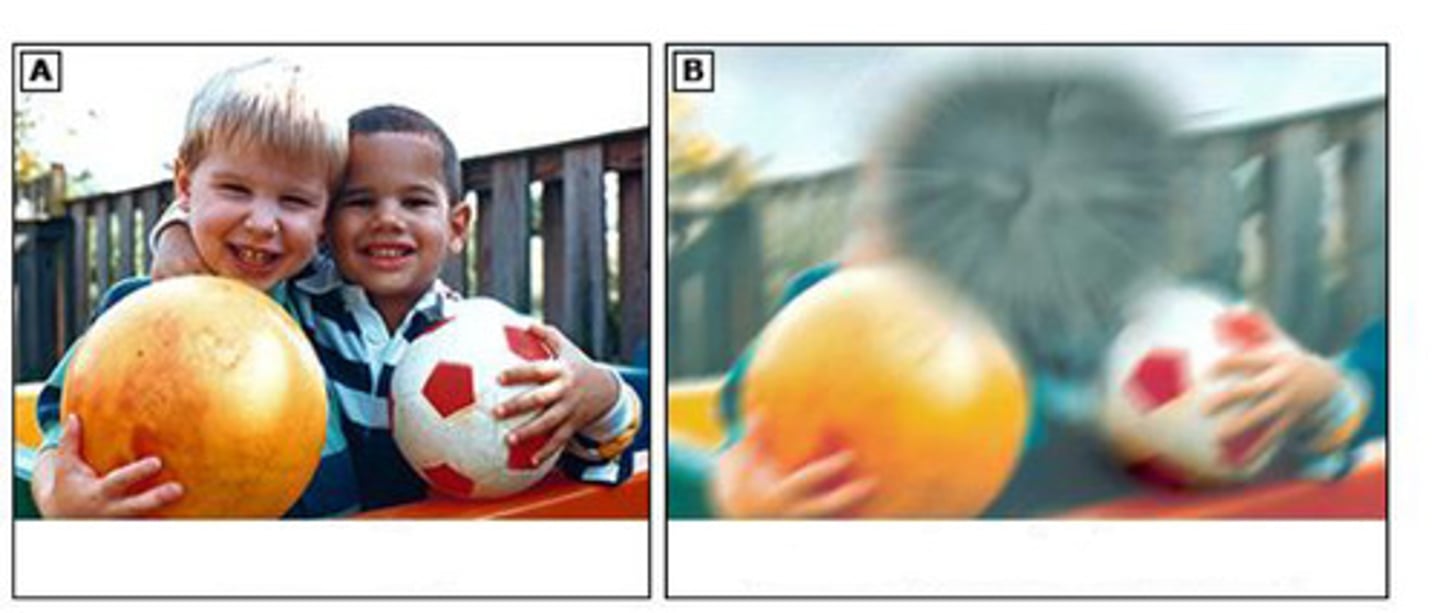
macular degeneration
Common age related eye condition
Degeneration of the macular lutea
Loss of central vision -certain spots look blurry, especially in the center

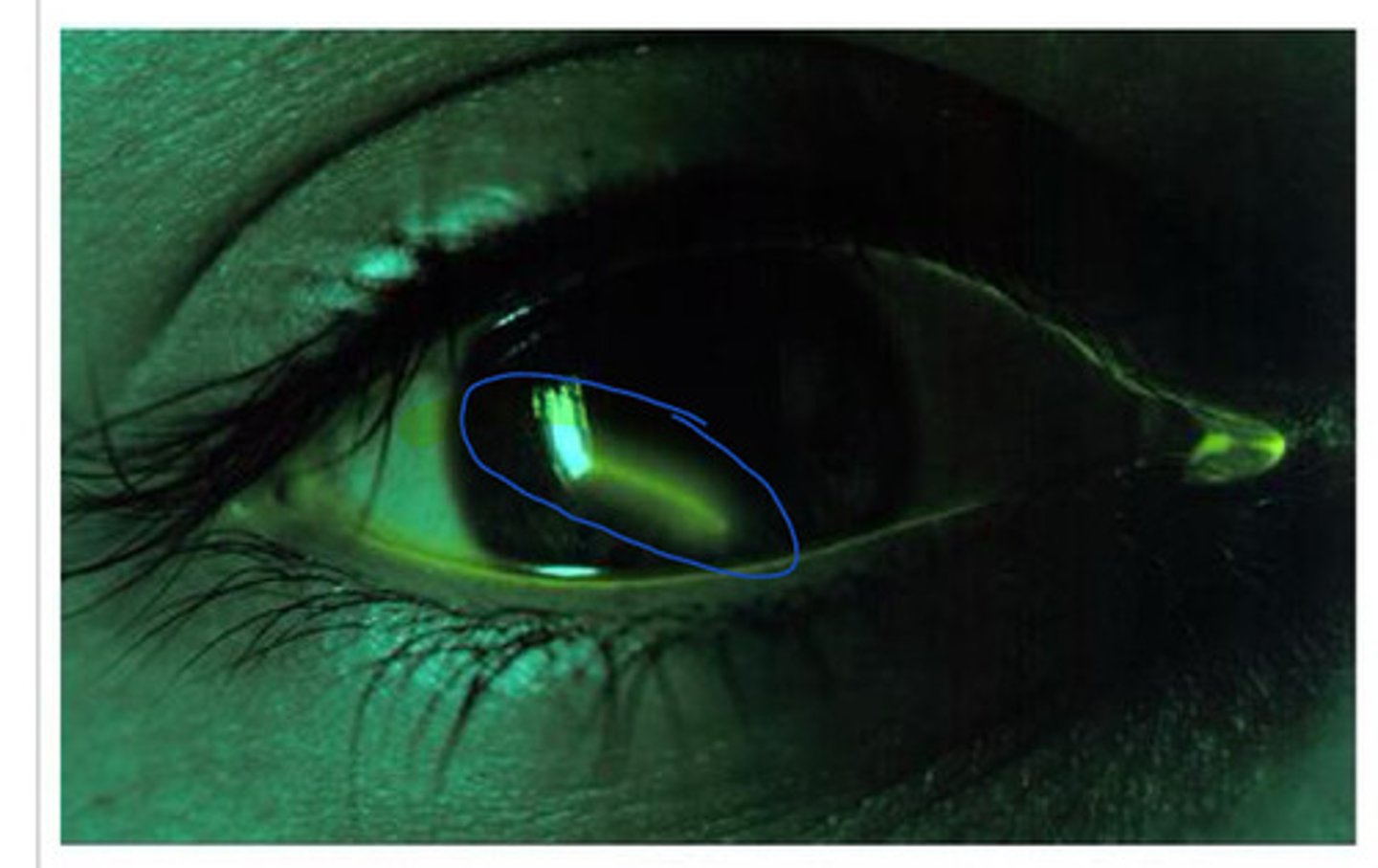
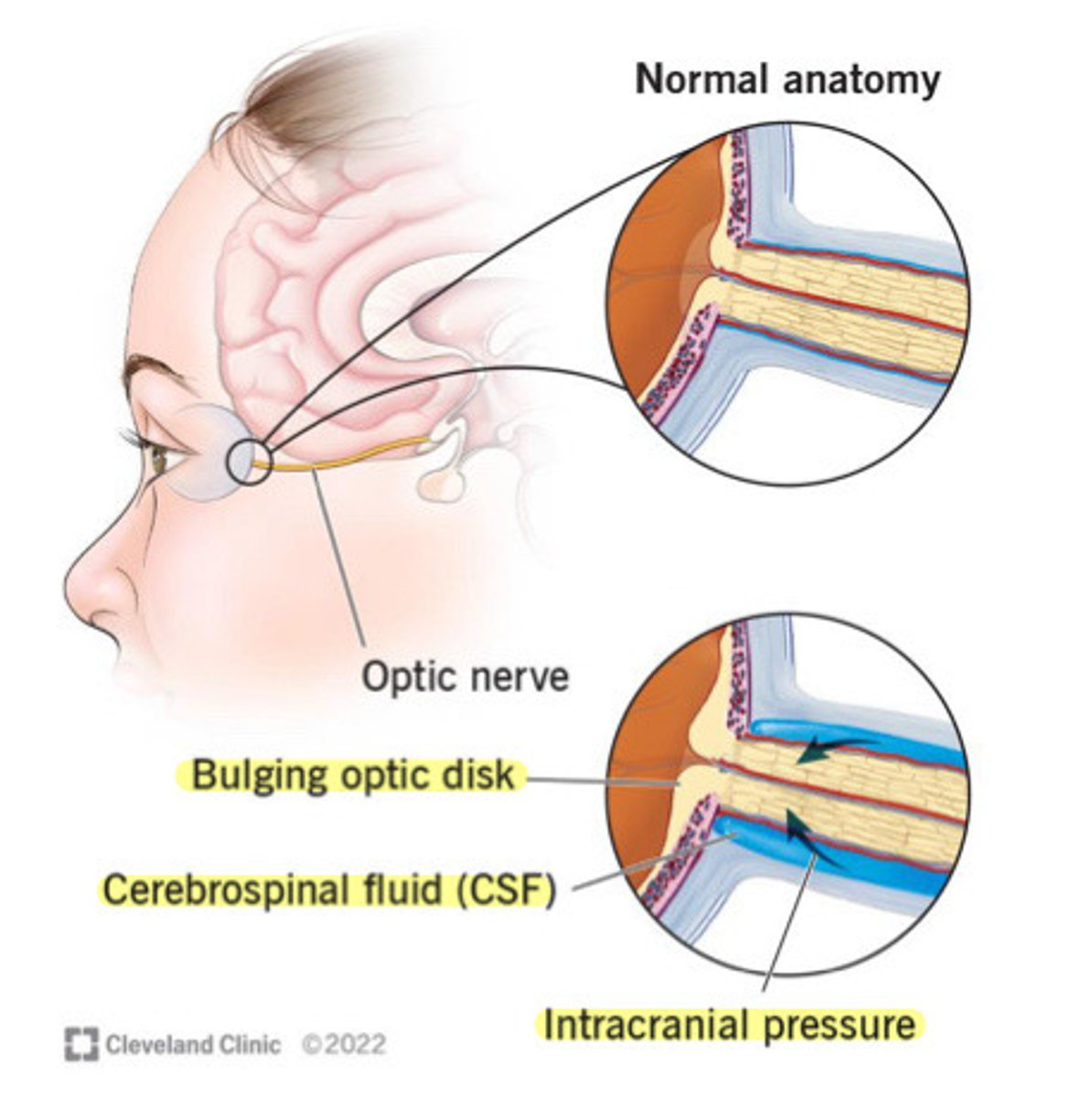
Papilladema
Optic disc swelling due to raise cranial pressure
Many causes
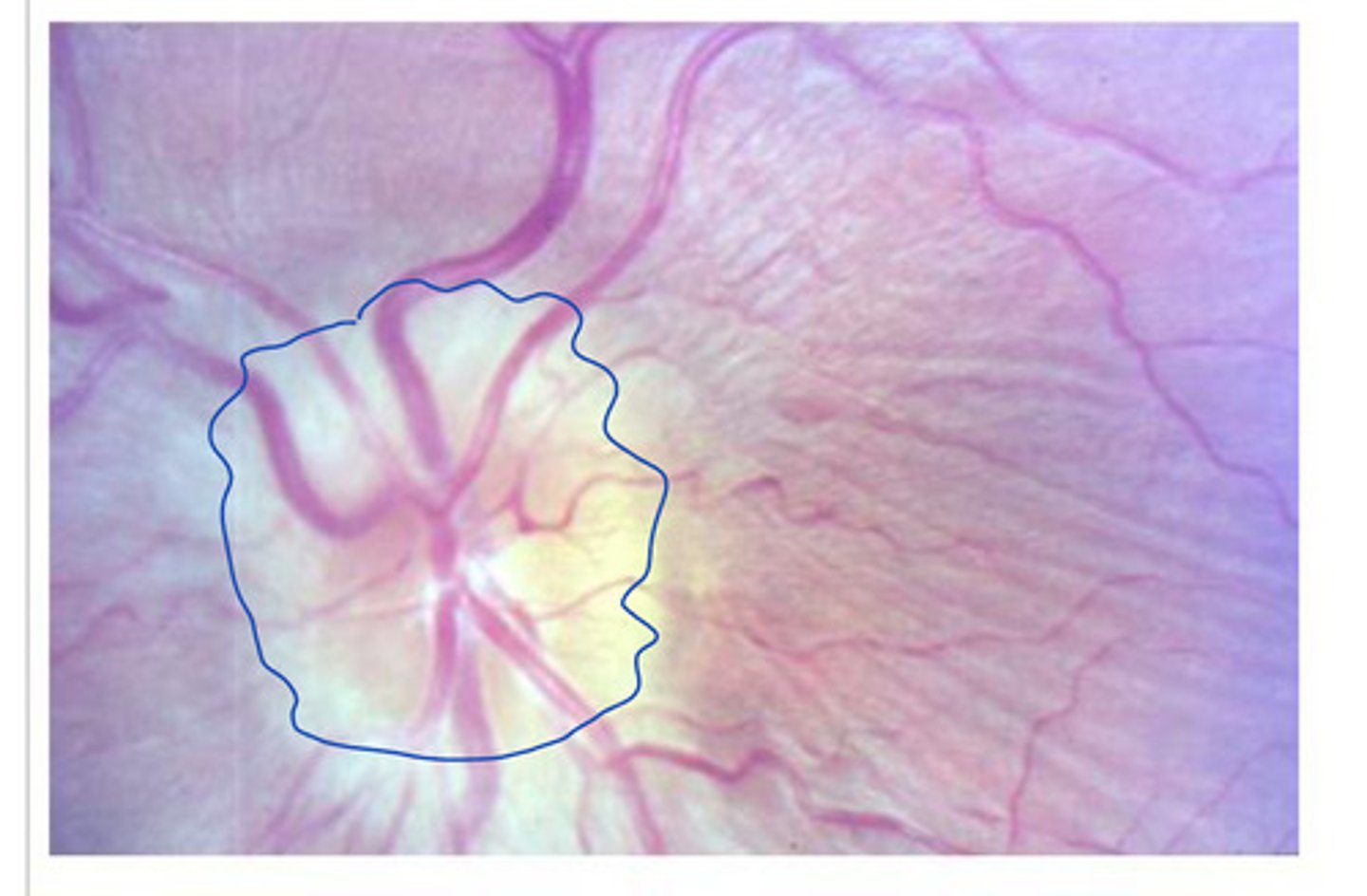
early papilledema (no clear borders, not circular)
What does this show?
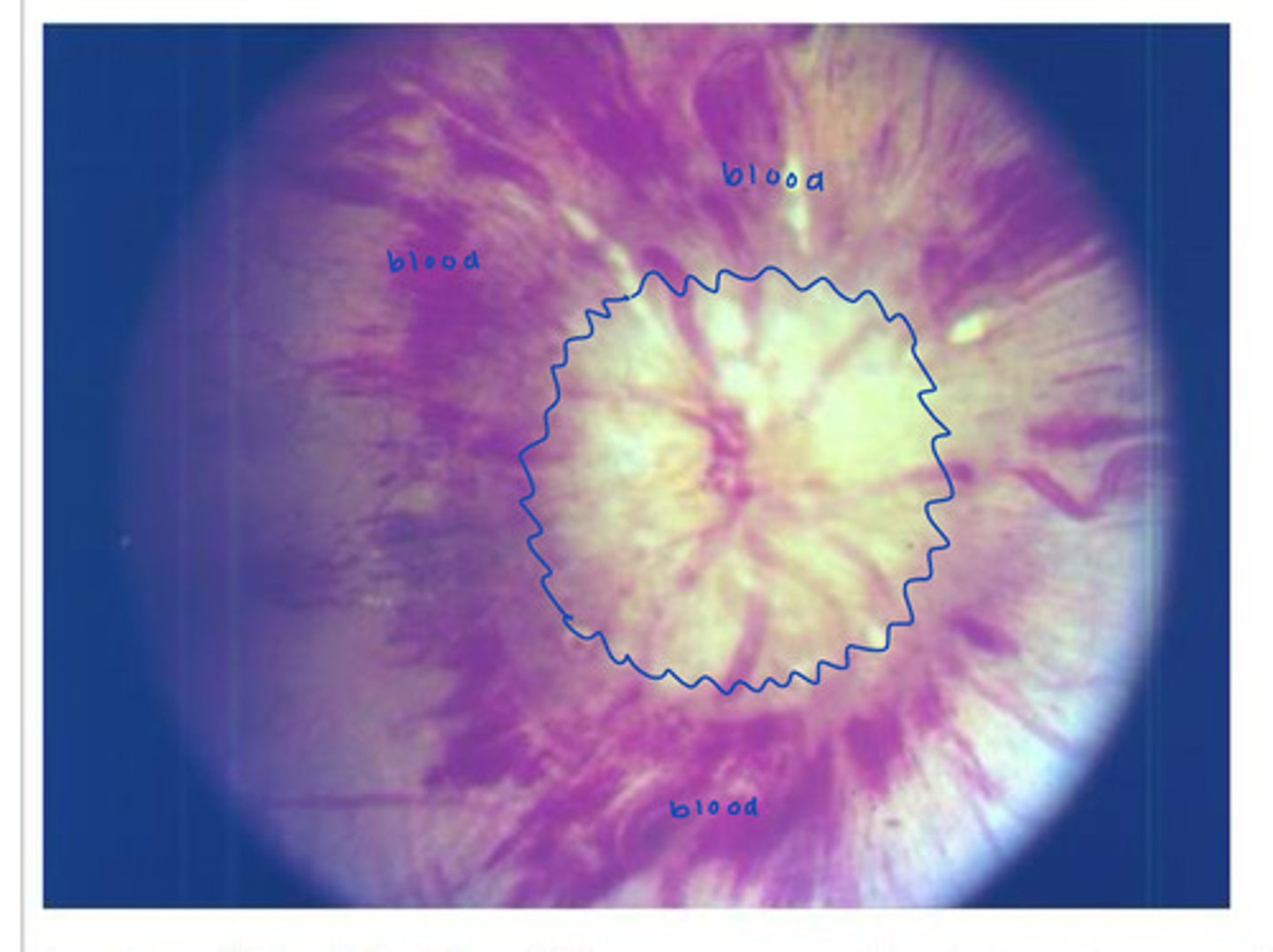
Fully developed papilledema
What does this show?
retinal detachment
separation of the retina from the underlying epithelium, disrupting vision and resulting in blindness if not repaired surgically
"Curtain vision"
Ocular emergency
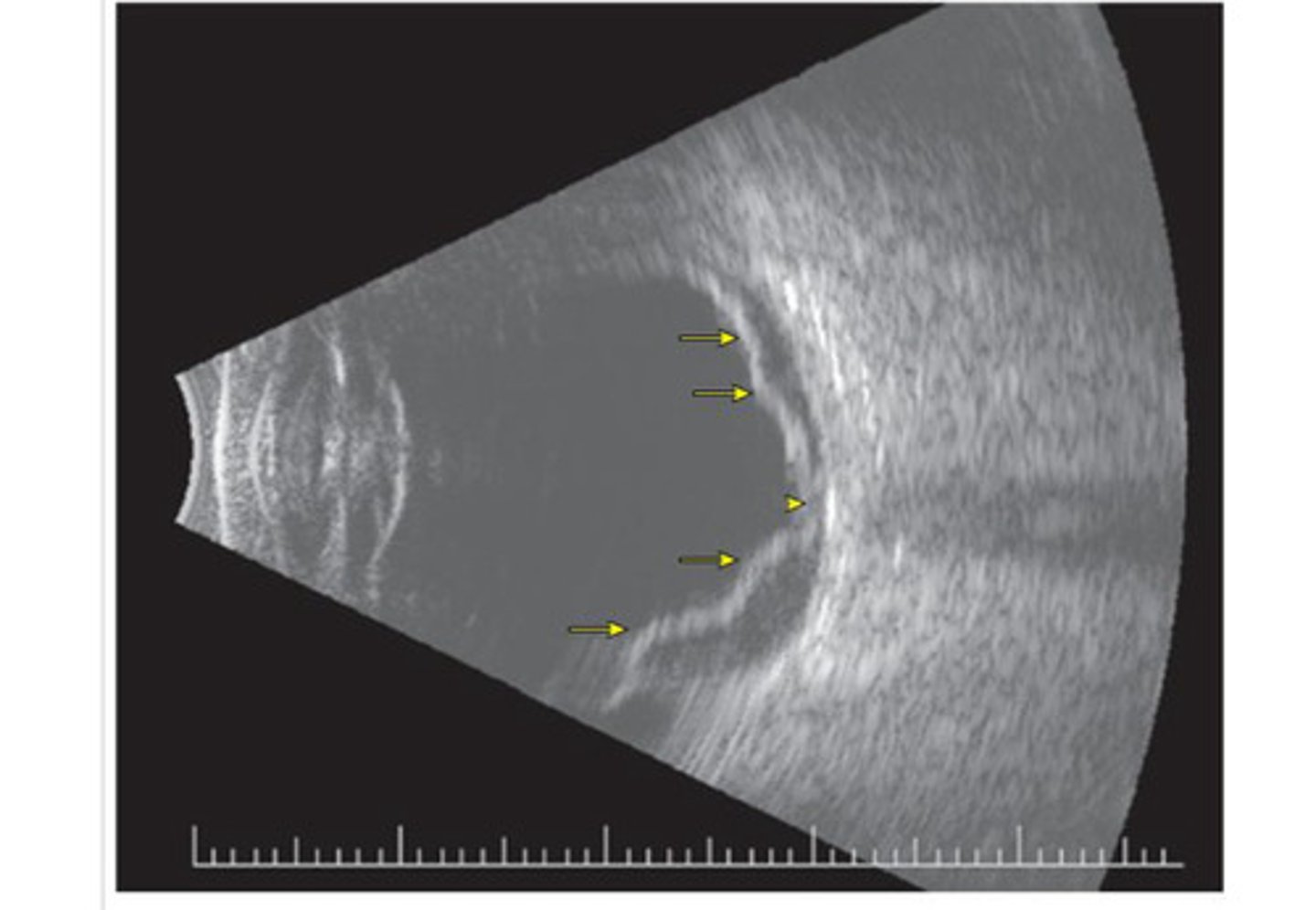
Retinal detachment - retina is floating in the vitreous (tethering at the optic nerve -yellow arrows)
What does this ultrasound show?
Anterior and posterior segments
What are the segments of the internal chambers that are divided by the lens and ciliary zonule?
Anterior and posterior chamber (aqueous humor)
What does the anterior segment contain?
Everything from lens - retina (vitreous humor)
What does the posterior segment contain?
aqueous humor
Fills the anterior segment
Continuously forms and drains
Maintains a constant intraocular pressure of about 16 mmHg
Eyeball support internally, supplies nutrients/oxygen to lens and cornea, carries away metabolic waste
What is the function of acqueous humor?
vitreous humor
Fills the posterior segment
Forms in the embryo and lasts for a lifetime
Transmit light, support posterior surface of lens + holds neural layer of retina against pigmented layer, contributes to intraocular pressure (counteracts pulling force of extrinsic eye muscles)
What are the functions of vitreous humor?
acqueous humor - formed by ciliary processes - flow from posterior chamber through pupil to anterior chamber - aqueous humor is reabsorbed into venous blood by scleral venous sinus
What is the process of how aqueous humor is formed and how it flows?
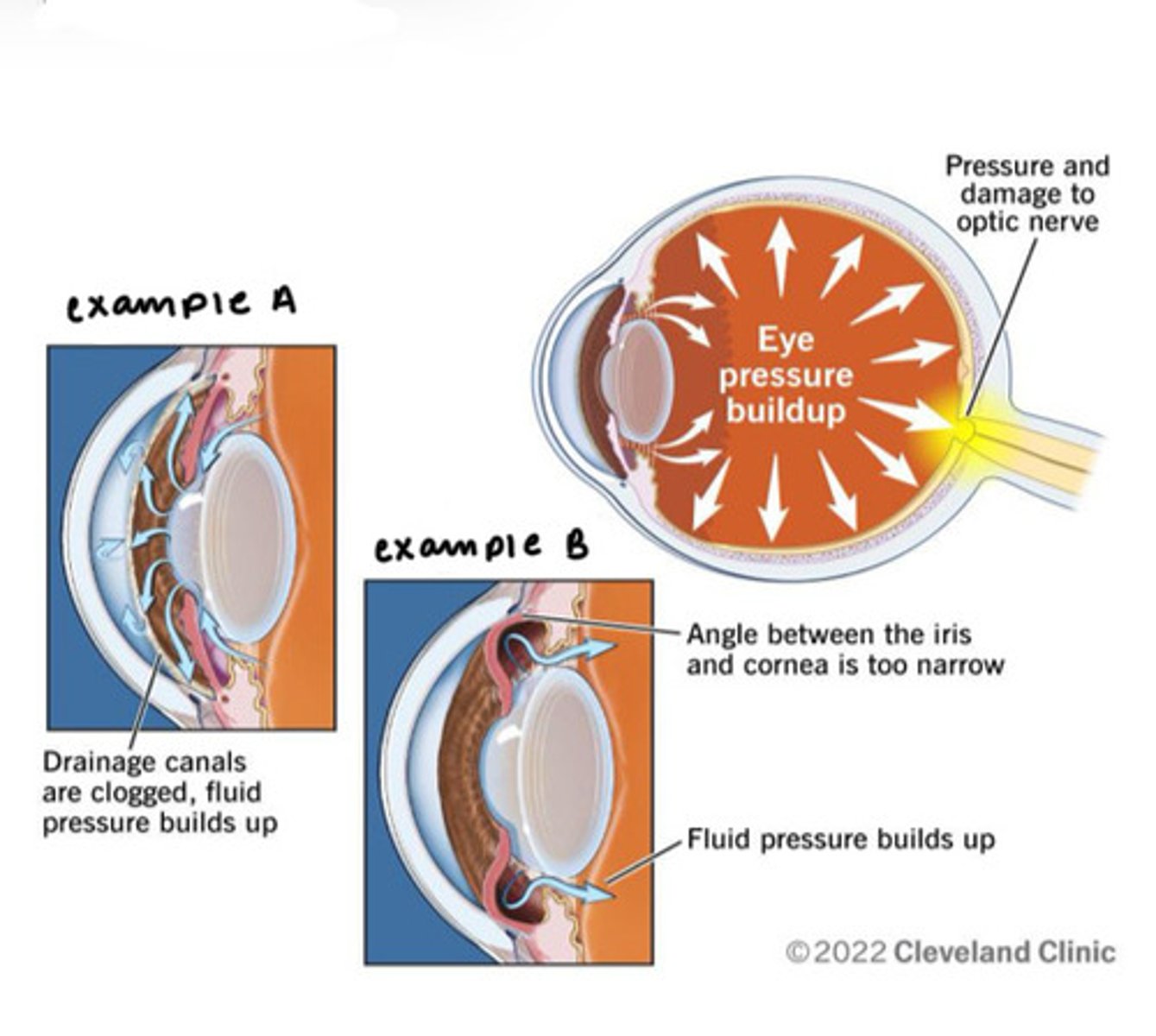
Glaucoma
Drainage of aqueous humor is blocked
Pressure within the eye may increase to dangerous level
Compressed retina and optic nerve
Blindness
lens
Transparent, flexible, biconcave disc
Function: changes shape to focus light on retina
(Ciliary muscle and the ciliary zonule focus on an image by changing the shape of this)
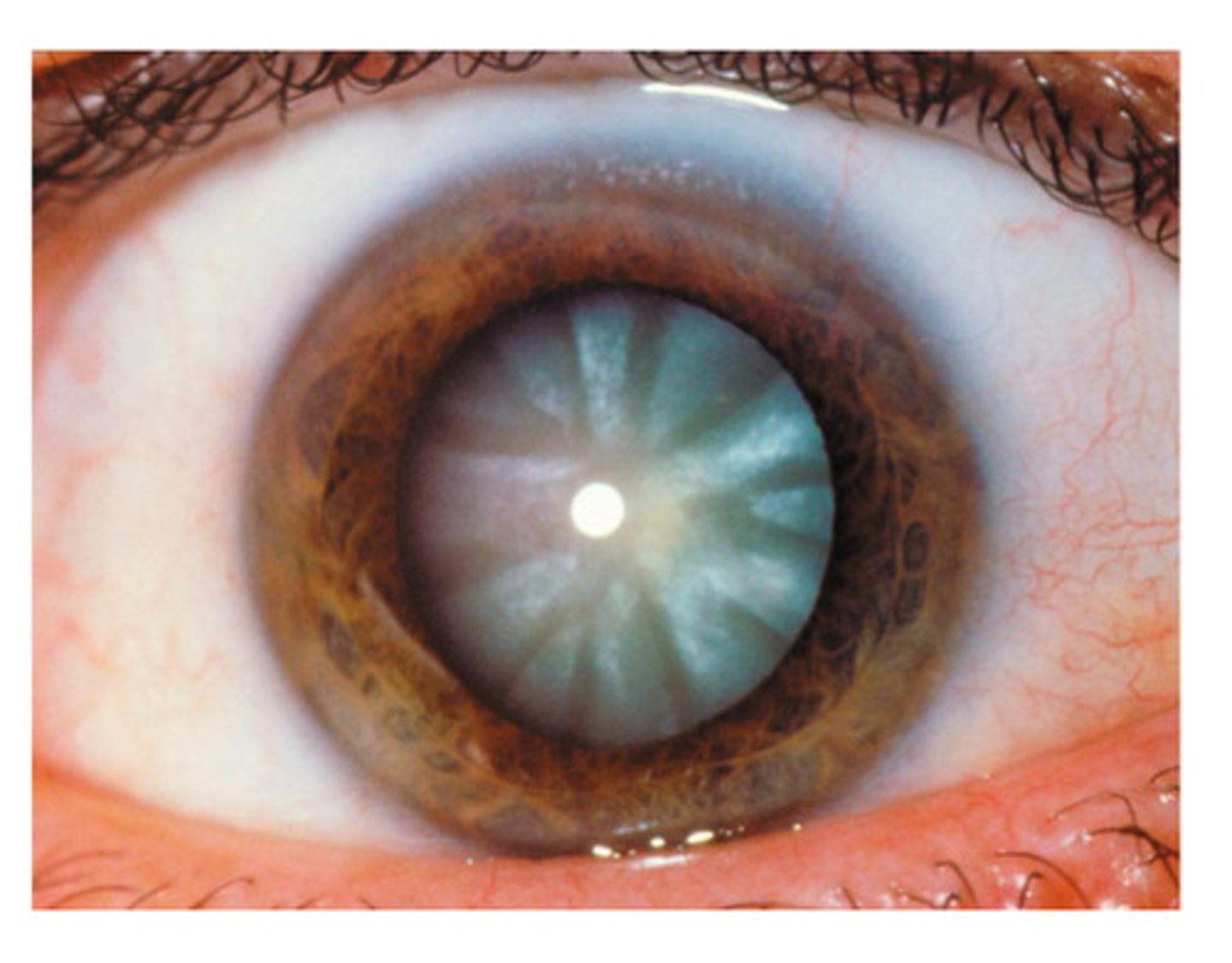
Cataracts
Hardening, thickening, clouding of the lens
Causes vision to be distorted, as of seeing it through frosted glass
Cornea (outer layer, light is bent) - aqueous humor (front part of eye) - lens (refracts light - see close or far) - vitreous humor - retina: neural layer - photoreceptors (rods and cones)
What is the direction of light (from the sun) throughout the eye up to photoreceptors?
lens
Bends or refracts light rays so they converge to a point (inversion of an image)
Lens flattens, ciliary muscles completely relax, low refractory power (not bending a lot of light)
What happens during distant vision?
Lens bulges, ciliary muscles contract, high refractory power
(Constriction of pupils - accommodation, convergence of eyeballs - medial rotation of the eye to focus on an object)
What happens during close vision?
Myopia (nearsightedness)
"Short vision"
Can see up close objects
Distant objects are blurry
Hyperopia (farsightedness)
"far vision"
Can see distant objects
Close-up objects are blurry
astigmatism
Unequal curvatures in different parts of the cornea or lens of the eye - leads to blurry vision
Cornea - aqueous humor - lens (refracts light - see close or far) - vitreous humor - retina: neural layer - photoreceptors (rods and cones) - optic nerve (partial crossing over at the optic chasm) optic tracts - lateral geniculate nuclei (thalamus - "gatekeeper") - primary visual cortex
(The optic tract can veer off to other stops in the mid brain)
What is the direction of light (from the sun) throughout the eye all the way until primary visual cortex?
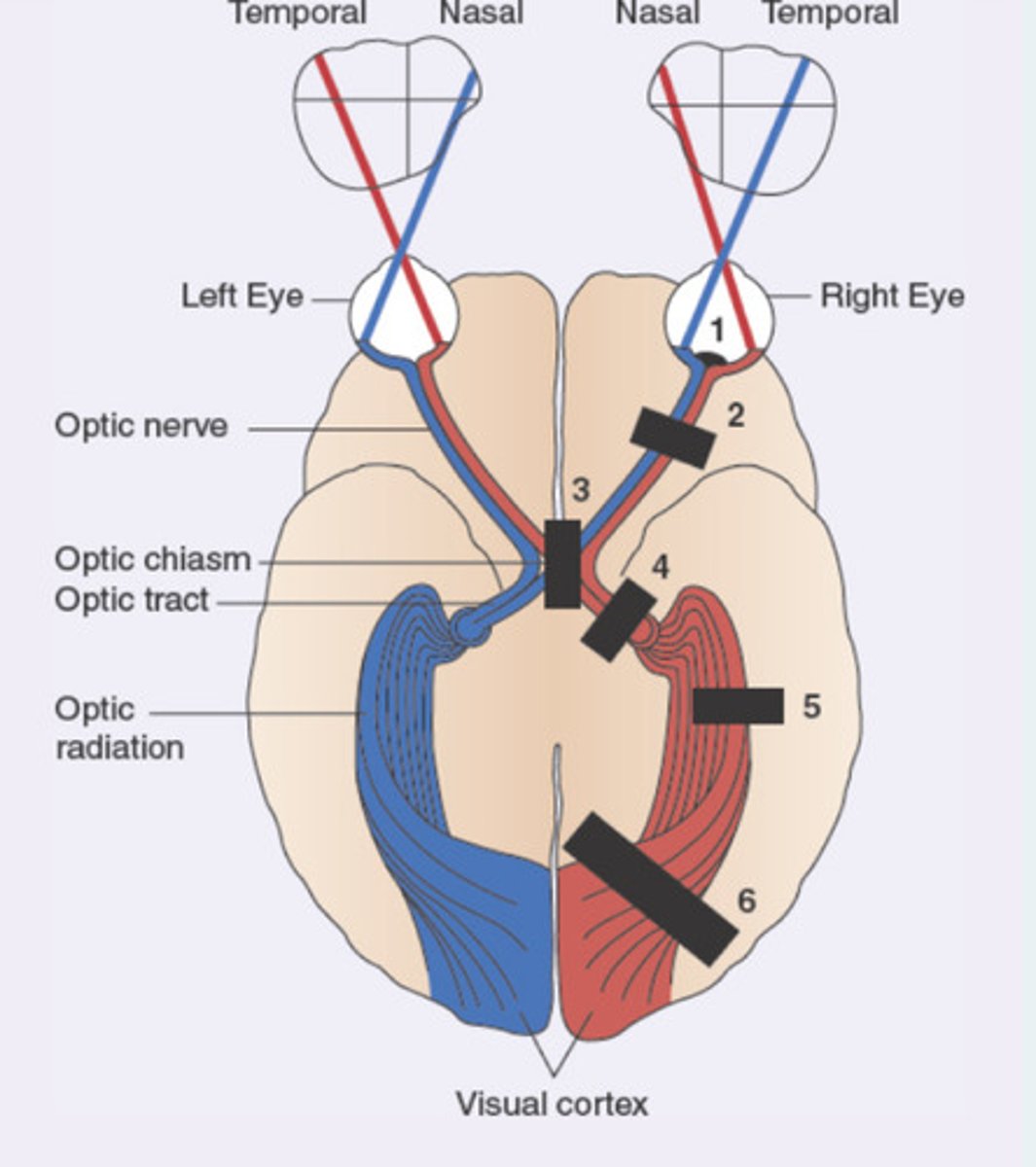
Vision, optic nerve, optic chasm, optic tract, primary visual cortex
What are the components of the visual fields?
vision
Lateral visual field - medial retina
Medial visual field - lateral retina
optic nerve
Carries info from right or left eye
optic chiasm
Medial optic nerve fibers crossover
optic tract
Carries all information from the same half of the visual field (example: left optic tract carries a complete representation of the right half of the visual field)
Contains fibers from the lateral (temporal) aspect of eye on same side and medial (nasal) aspect of the opposite eye
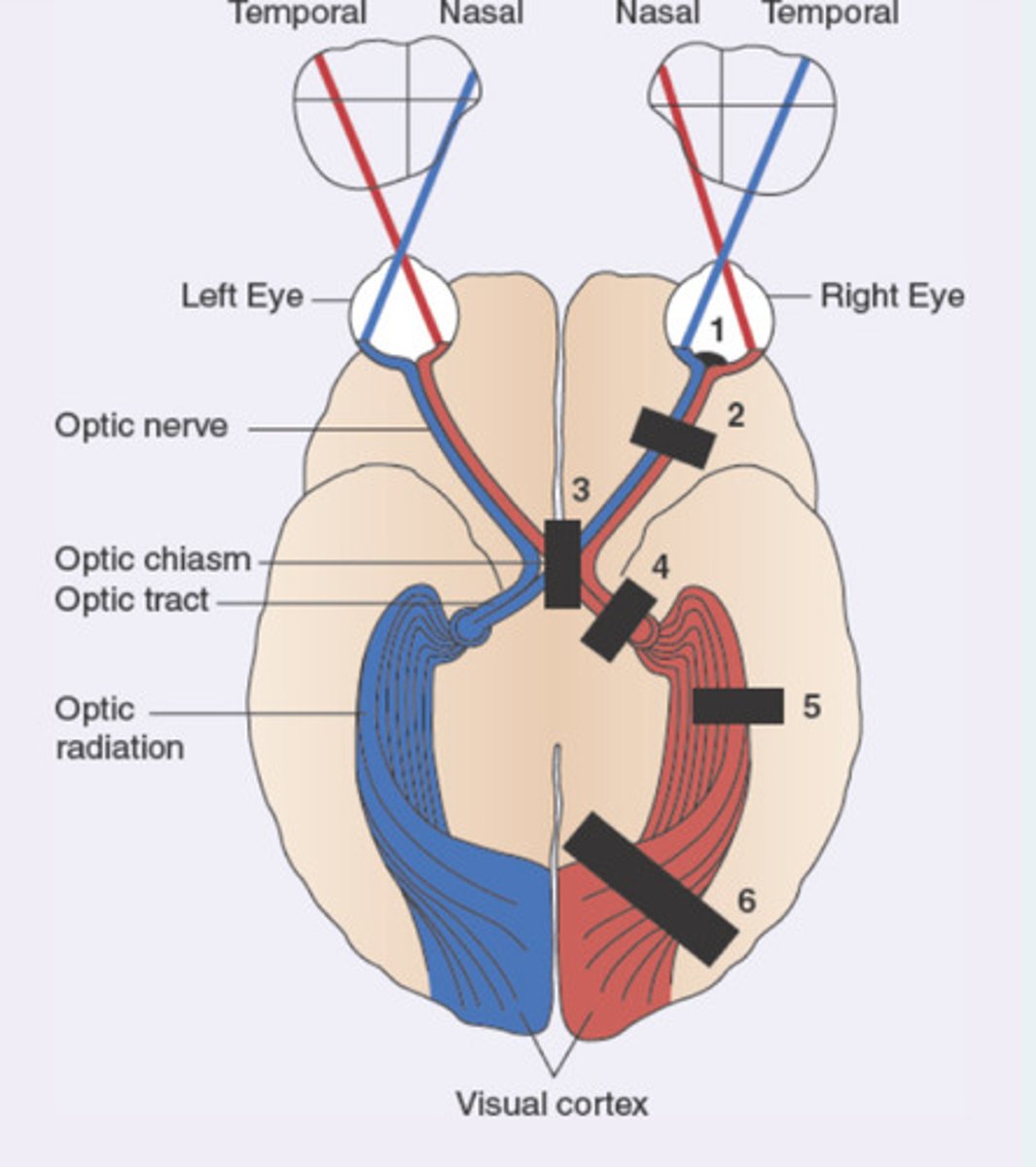
primary visual cortex
Left visual cortex receives input from the right visual field
Optic chiasm (both lateral visual fields lost)
A 42-year-old female patient presents to the primary care office with progressive loss of vision. She feels like she has "tunnel vision" . On physical examination, she has lost the lateral visual field in the right eye and loss of lateral visual field in the left eye. Which of the following anatomical locations is likely affected?
Left optic nerve
Left optic tract
Optic chiasm
Right optic nerve
Right optic tract
vitreous humor
Which of the following both supports the posterior surface of the lens and hold the retina against the back of the eye?
Lacrimal apparatus
Vitreous humor
Conjunctiva
Ciliary body
Sclera
Which of the following is visible on the exposed anterior surface of the eyeball?
Pigmented layer
Choroid
Sclera
Fovea
Chemoreceptors (smell and taste), smell receptors (excited by airborne chemicals - dissolve in fluid coating nasal membrane), taste receptors (excited by food chemicals dissolved in saliva)
What are the three things involved in smell and taste?
Tell us whether things are to be savored or avoided
What is the function of smell and taste?
CN I Olfactory Nerve
smell
olfactory receptors
Superior nasal cavity, poorly positioned for smell, olfactory epithelium
olfactory epithelium
Mucus -captures and dissolves airborne odorants
Olfactory sensory neurons:
- bipolar neurons
- olfactory cilia - extend from the dendrite (increase surface area)
Collectively, the axons form the CN 1
Stimulus (a.k.a. the smell of pizza) - travel to superior nasal cavity (mucus captures/dissolves airborne odorant) - olfactory sensory cells detect odor (AP to glomeruli in olfactory bulb for synapse) - mitral cells in olfactory bulbs (via olfactory tract) - primary olfactory cortex -
Frontal lobe (assist with conscious interpretation and identification)
Hypothalamus, amygdaloid body, limbic system (emotional response to odors)
What is the olfactory pathway?
sweet, sour, salty, bitter, umami
What are the basic taste sensations?
taste buds
Found in papillae
Gustatory epithelial cells (receptors for taste)
Basal epithelial cells (stem cells - differentiate into new gustatory epithelial cells)
Every 7 to 10 days
How often are taste buds replaced?
facial nerve (CN VII), glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX), vagus nerve (CN X)
Which nerves receive impulses from taste receptors?
Facial Nerve (VII)
Anterior 2/3 of the tongue
Glossopharyngeal nerve (IX)
Posterior 1/3 of the tongue and pharynx
Vagus nerve (X)
Few taste buds in the epiglottis and the lower pharynx
Facial, glossopharyngeal, vagus nerve - solitary nucleus in medulla oblongata - Pons - thalamic nucleus (ventral posteromedial nucleus) — gustatory cortex (in insula)
What is the gustatory pathway?
hearing apparatus
Allows us to hear extraordinary range of sounds
Equilibrium (balance) receptors
Continually informed the nervous system of head movements and position
internal ear
Controls both hearing apparatus and equilibrium independently
External, middle, internal ear
What are the three parts of the ear?
Auricle (pinna), external acoustic meatus, tympanic membrane
What is the external ear composed of?
auricle (pinna)
Elastic cartilage
Function: funnels sound waves
external acoustic meatus
Gland secrete cerumen
tympanic membrane
Thin, translucent
Boundary of outer and middle ear
Function: transfer sound waves to the bones of the middle ear
middle ear
The small air-filled space between the auditory canal and the cochlea that contains the ossicles
Mastoid antrum, auditory ossicles, oval window, round window, pharyngotympanic tube (eustachian tube)
What are some of the components of the middle ear?
mastoid antrum
Communicates with mastoid air cells
Entrance - where air cells get infected
oval window
Stapes creates pressure waves in the fluid of the inner ear - transfer signal
Round window
Absorbs pressure wave vibrations from inner ear
pharyngotympanic tube (eustachian tube)
Links the middle ear with the posterior oropharynx
Opens with yawning or swallowing
(equalize pressure in the middle ear with external pressure)
(TM only vibrates normally with equal pressure)
malleus (hammer - secured to TM), incus (anvil), stapes (stirrup - base fits into oval window)
What are the auditory ossicles?
Transmit vibrations from TM to oval window
What is the function of the auditory ossicles?
otitis media (ear infection)
Inflammation of the middle ear
Eustachian tube often not working properly
Fluid not draining (bacteria/viruses can grow in the fluid, pressure buildup behind the TM)
Common among children
Bony labyrinth, membranous labyrinth, perilymph/endolymph
What are the four main components of the internal ear?
bony labyrinth
System of torturous channels worming through temporal bone
Contains perilymph - similar to CSF
(Vestibule, semicircular canal, cochlea)
membranous labyrinth
Continuous series of membranous and ducts contained within the bony labyrinth
Contains endolymph
perilymph and endolymph
Conduct sound vibrations
Shipped with body position and acceleration