UNIT 6 URBAN VOCAB
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
rural
countryside
urban
in, relating to, or characteristic of a city or town.
suburbs
residential areas surrounding a city
site
The physical character of a place or absolute location
situation
the location of a place relative to other places
city-state
A sovereign state comprising a city and its surrounding territory
urban hearth
An area, like Mesopotamia or the Nile River Valley where large cities first existed.
metropolitan area
region that includes a central city and its surrounding suburbs
pedestrian city
car-free cities designed to be walkable
suburbanization
The process of population movement from within towns and cities to the residential areas on the outskirts of cities
urban sprawl
The process of urban areas expanding outwards, usually in the form of suburbs, and developing over fertile agricultural land.
boomburbs
Rapidly growing suburb cities that has the population of a city but is residential in nature
edge cities
A large node of office and retail activities on the edge of an urban area built along a beltway or major transportation route around the city
counter-urbanization (deurbanization)
the counter-flow of urban residents leaving cities
exurbs
communities that arise farther out than the suburbs and are typically populated by residents of high socioeconomic status
do not need to commute, work from home
megacities
cities with more than 10 million people
metacities
A new term used to describe cities that have 20 million or more people
megalopolis
a region in which several large cities and surrounding areas grow together
world cities (global cities)
Centers of economic, culture, and political activity that are strongly interconnected and together control the global systems of finance and commerce (examples include: New York City, London, Tokyo, Sydney, Shanghai
urban hierarchy
A ranking of settlements (hamlet, village, town, city) according to their size and economic functions.
rank-size rule
In a model urban hierarchy, the idea that the population of a city or town will be inversely proportional to its rank in the hierarchy.
higher-order services
usually expensive, need a large number of people to support it
luxury car dealerships; major sports teams, specialized hospitals
lower-order services
provided by small centers, a good or service, usually inexpensive items that people buy often a regular, often daily or weekly basis
grocery stores, gas stations, fast food
primate city
The largest settlement in a country, if it has more than twice as many people as the second-ranking settlement.
many developing countries but can be MDC's
London, Paris, Mexico City, Lagos
gravity model
A model that states that larger and closer places will have more interactions than places that are smaller and farther from each other
The model states there are numerous flows to bigger cities and between nearer cities
central place theory (Christaller)
A theory that explains the distribution of services, based on the fact that settlements serve as centers of market areas for services; larger settlements are fewer and farther apart than smaller settlements and provide services for a larger number of people who are willing to travel farther.
market area
The area surrounding a central place, from which people are attracted to use the place's goods and services.
threshold
The minimum number of people needed to support the service
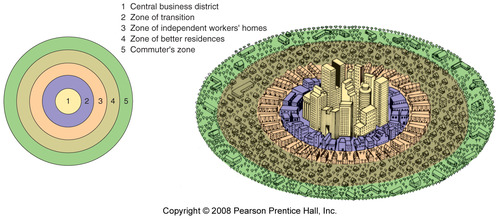
concentric zone model (burgess)
A model of the internal structure of cities in which social groups are spatially arranged in a series of rings.
hoyt sector model
A model of the internal structure of a city in which social groups are arranged around a series of sectors or wedges instead of rings radiating out from the CBD.

multiple nuclei model (Harris and Ullman)
Large cities develop by spreading from several nodes of growth; individual nodes have special functions which expand as the city grows

galactic city model (peripheral model)
1.People moved into the suburbs (Still worked in the CBD) - Bedroom Communities
*contains edge cities
2.Got tired of going into downtown so markets moved to the suburbs
3.Jobs followed into these areas built along a beltway

latin american city model
Griffin-Ford model. Blends traditional Latin American culture with the forces of globalization. The CBD is dominant; it is divided into a market sector and a modern high-rise sector. The elite residential sector is on the extension of the CBD in the "spine". The end of the spine of elite residency is the "mall" with high-priced residencies. The further out, less wealthy it gets. The poorest are on the outer edge.

southeast asian city model
McGee model. The focal point of the city is the colonial port zone combined with the large commercial district that surrounds it. McGee found no formal CBD but found separate clusters of elements of the CBD surrounding the port zone: the government zone, the Western commercial zone, the alien commercial zone, and the mixed land-use zone with misc. economic activities.

sub-saharan city model
Huge cities characterized by squatter settlements on the outskirts of cities
Residential homes based on ethnicity (tribalism)
Three CBDs: Colonial, open-air market, traditional CBD

residential area
an area where people live
commercial area
an area where businesses and stores are found
industrial area
an area where factories or large industries are located
zoning ordinance
Law that specifies how and for what purpose each parcel of private real estate may be used. Also called zoning code.
infrastructure
Fundamental facilities and systems serving a country, city, or area, as transportation and communication systems, power plants, and schools
municipal
refers to a local government of a city or town
bedroom communities
Commuter towns (suburbs) inhabited by people who drive or take public transport to another city for work.
smart growth policies
an urban planning theory that concentrates walkable city areas to prevent urban sprawl
mixed land use
land development that blends a combination of residential, commercial, cultural, institutional and/or industrial uses
transit-oriented development (TOD)
Development that attempts to focus dense residential and retail development around stops for public transportation, a component of smart growth.
livability
All the characteristics of a community that contribute to the quality of life of the people who live there
supports sustainable urban design
new urbanism
Outlined by a group of architects, urban planners, and developers from over 20 countries, an urban design that calls for development, urban revitalization, and suburban reforms that create walkable neighborhoods with a diversity of housing and jobs.
green belt
A ring of land maintained as parks, agriculture, or other types of open space to limit the sprawl of an urban area.
slow-growth cities
urban communities where the planners have put into place smart growth initiatives to decrease the rate at which the city grows horizontally to avoid the adverse affects of sprawl
urban infill
the process of building up underused lands within a city
redlining
A process by which banks draw lines on a map and refuse to lend money to purchase or improve property within the boundaries.
blockbusting
Illegal practice of inducing homeowners to sell their properties by telling them that a certain people of a certain race, national origin or religion are moving into the area
affordable housing
housing that people on low/limited income are able to afford to buy or rent
inclusionary zoning
zoning regulations that create incentives or requirements for affordable housing development
urban renewal
Program in which cities identify blighted inner-city neighborhoods, acquire the properties from private members, relocate the residents and businesses, clear the site, build new roads and utilities, and turn the land over to private developers.
gentrification
A process of converting an urban neighborhood from a predominantly low-income renter-occupied area to a predominantly middle-class or wealthier owner-occupied area.
disamenity zones
The very poorest parts of cities that in extreme cases are not connected to regular city services and are usually controlled by gangs and drug lords.
zones of abandonment
areas with lack of jobs, declining land values and falling demand that cause people to leave and businesses to close
range
The maximum distance people are willing to travel to use a service.
urban growth boundary
Geographical boundaries placed around a city to limit suburban growth within that city.