ECE Unit 6: General Purpose Input/Output
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Whats usually on each on-chip peripheral device?
It usually has a few registers, like control registers, status registers, data input registers and data output registers
What are the 2 approaches to exchange data between the processor core and a peripheral device?
Port mapped I/O: uses special CPU instructions
Memory mapped I/O:
most CPUs today use this for I/O
its simpler and more convenient to interface I/O
each device is assigned to a memory address in the address space of the microprocessor
uses native load/store instructions to input or output data: LDR/STR Reg, [Register, #immediate value]
What type of microprocessors use memory mapped I/O
ARM microprocessors
Explain parallel ports and components of them:
There are many parallel ports implemented in the FPGA that support input, output, and bidirectional transfers of data between the ARM A9 processor and I/) periphery
Each parallel port is assigned a base address and contains up to 4 32-nit registers.
ports that have output capability include a writable data register
ports with input capability have a readable data register
Bidirectional parallel ports also include a direction register
Each bit in the data register can be configured as
an input by setting the bit in the direction register to 0 or
an output by setting this bit position to 1
What is 3 state pipelining and what does it allow?
Pipelining includes fetching instruction, decoding it and executing it, and it allows hardware resources to be fully utilized.
What happens when a push button is pressed?
The program waits in a loop until the key is released.
How many pins does a typical joystick hardware have?
It usually has 6 pins.
one to connect to the power supply
4 switches oriented in the up, down, left and right directions
and a 5th switch connected to a button on the shaft (called the centre)
These joysticks are called 4-way directional with center select
What does reading from the GPIO pins do?
It informs the microcontroller which in which direction the user is pushing the joystick shaft, allowing the program to adjust accordingly
What are the hardware components of a JS 5208 joystick?
pin 1 connects to power supply
pin 2 connects to the left button
pin 3 connects to the center button
pin 4 connects to the up button
pin 5 connects to the right button
pin 6 connects to the down button
NOTE different joystick models have different pin assignments
How many GPIO ports are there and how many pins in each port?
There are 8 GPIO Ports: A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, and there’s up to 16 pins in each port
What do the protection diodes do in a I/O Port Bit Input and Output
The protection diodes limit the input voltage to not be above Vdd or below Vss
Whats Debouncing?
When a switch or button is pressed, the switch/button may bounce back and forth a few times before settling down.
Example signal when a switch is pressed (without debouncing)
To solve: the bounces usually settle within 20 ms to 30ms:
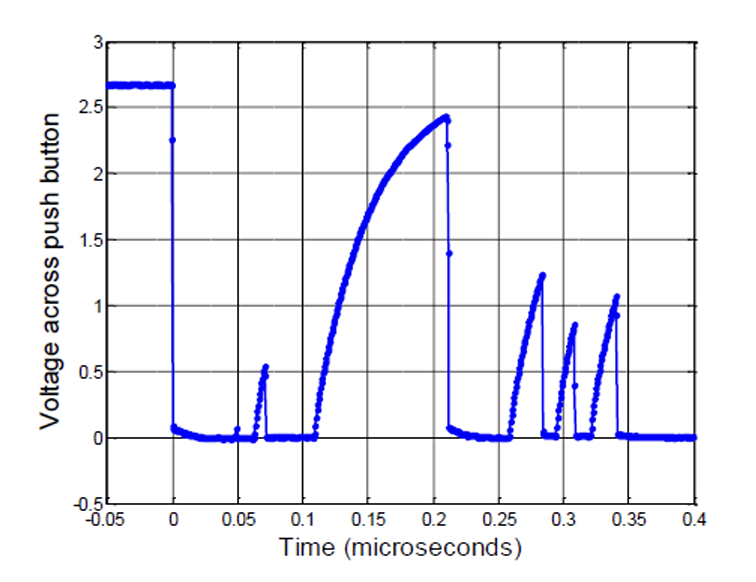
Whats bouncing?
Its an electromechanical noise in the system that could be interpreted as a meaningful signal if the CPU is acting too quickly
What are the solutions to eliminate debouncing effects?
Software
Hardware
How to use hardware vs software to eliminate debouncing effects:
A simple low pass RC filter can remove most electrical noise, bounces and glitches from an input signal and a Schmitt trigger can clean up the resulting analog signal.
Sometimes a combo of hardware and software filtering is also necessary, depending on the peripheral and how important it is for the microcontroller to receive accurate input.
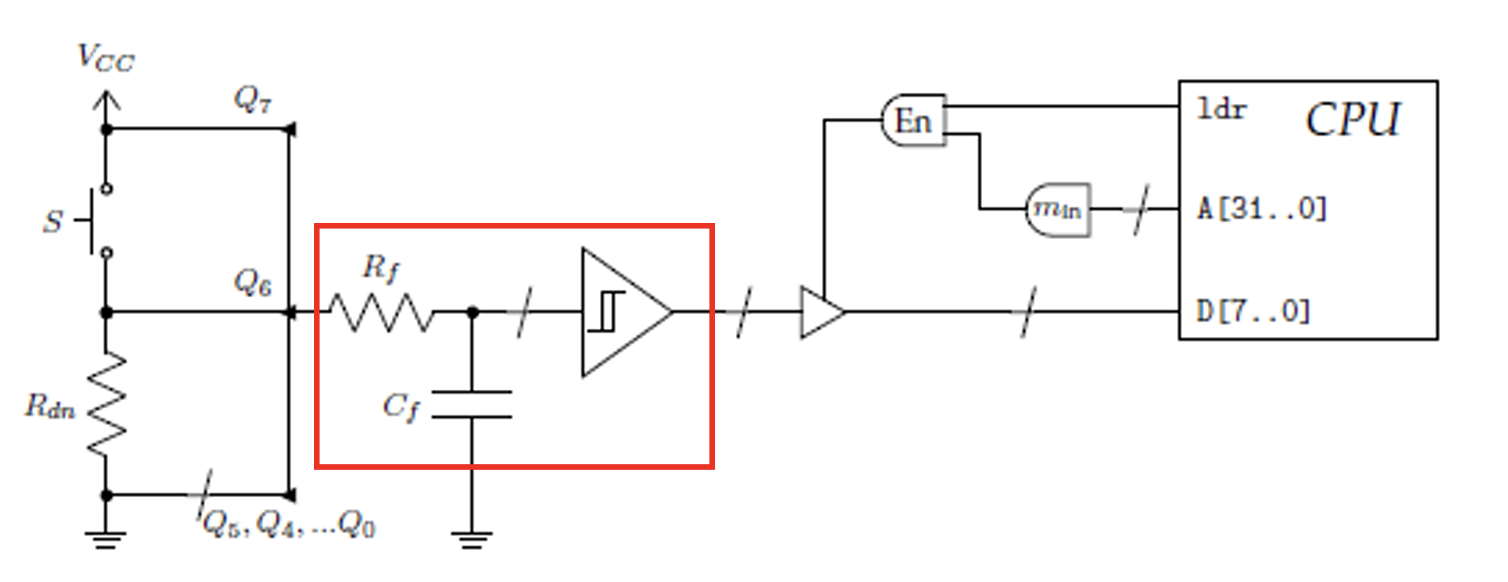
What are software debouncing solutions?
Read the switch after a sufficient delay to allow the bounces to settle down
Read periodically, and use a counter as a filter
reset the counter when the signal is “unpressed”
counts up if “pressed”
If counter>threshold, the contacts has stopped bouncing
What is the Schmidt trigger used for?
To reduce noise and increase slew rate.
Problem with active keypad: When software scans that there are 2 buttons clicked at the same time, the short circuit causes hardware damage. There are 2 solutions to this problem:
Hardware: configure all output pins as open drain instead of push-pull.
Software: switch all the row pins to input except the one that’s currently used as output.
Whats a passive keypad?
It doesn’t have a power supply
What does the microcontroller typically do with row pins and column pins?
The microcontroller typically writes outputs to the row pins and reads inputs from the column pins. Its assumed that the input pins have pull down resistors, or otherwise interpret a floating value as zero.
this kind of GPIO keypad therefore requires some of the port pins to be set to input, and others set to output