Large Animal Clinical Practice - Ruminant Nutrition and Poisonous Plants
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards for Large Animal Clinical Practice lecture notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Ruminants
Animals with one true stomach and three forestomachs that regurgitate food to chew it more before swallowing again.
Six Categories of Nutrients
•Protein
•Fats
•Carbohydrates
•Minerals
•Vitamins
•Water
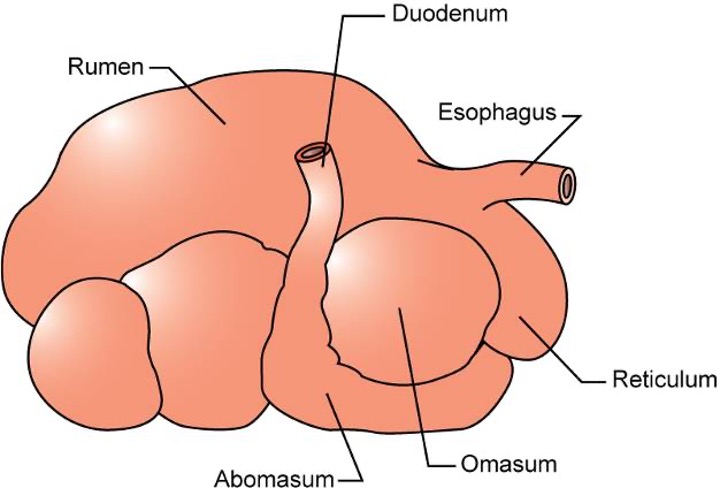
Abomasum
The true stomach in ruminants, similar in function to a monogastric stomach.
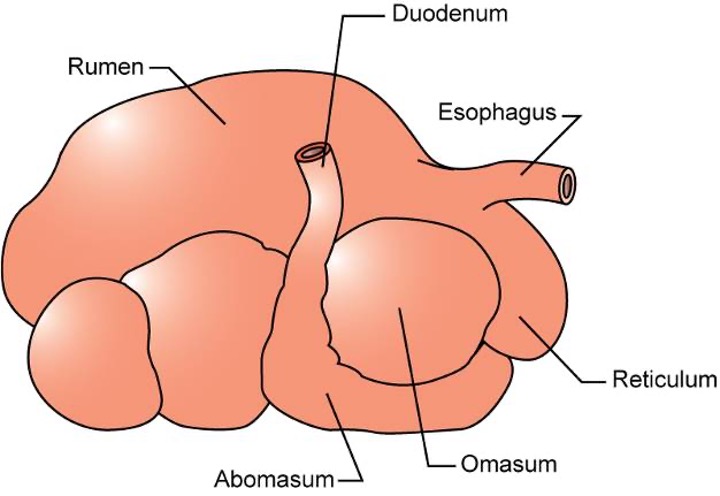
Reticulum
The smallest, most cranial compartment of the forestomach, with a honeycomb arrangement of folds.
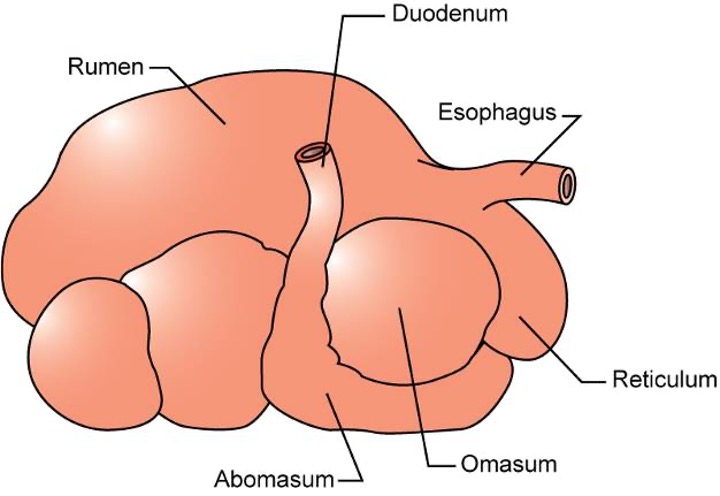
Rumen
fermentation vat
Compartment that contains microbes that produce Volatile Fatty Acids (VFAs) used by the body for glucose and fat storage and is lined by papillae for nutrient absorption
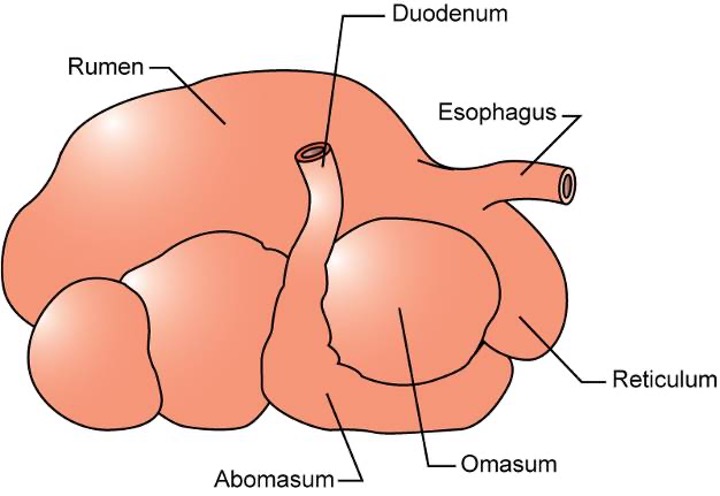
Omasum
Muscular organ with many muscular folds that breaks down food particles further, absorbs VFAs, removes bicarbonate ions, and absorbs water.
Roughages/Forages
Feed sources fed for fiber and bulk.
Concentrates
Feed sources fed for energy and/or protein.
Life Stage Nutrition
Based on the use of animal (dairy vs. beef), body condition scoring (BCS), growth/maintenance, lactation/pregnancy
Feed costs are the largest portion of dairy or beef operation
Feedstuff availability, cost, and quality play a large role in cattle feeding management
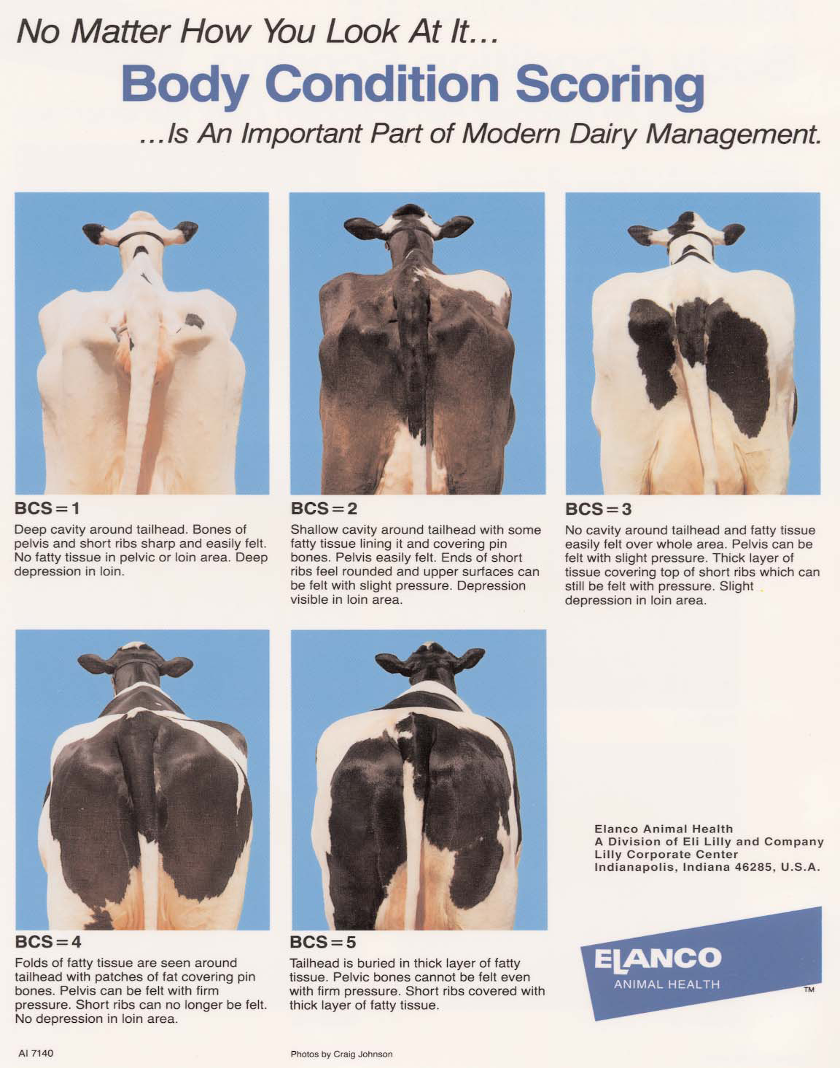
Body Condition Scoring
A method used to assess an animal's fat reserves and overall health, critical to dairy cow management.
No ideal body condition score- just range of desirable scores depending on individual animal and stage of lactation
Feeding Cattle for Growth
Adequate colostrum intake in the first 18 hours of life is vital
Beef calves are “creep-fed” concentrates to aid in weaning
Dairy calves are pail-fed or bottle-fed until >1 month of age
Fed almost an entirely concentrate diet by the time/age/weight for slaughter
Cattle Diseases Related to Improper Nutrition DAIRY
Bloat
Grass Tetany
Milk Fever (Hypocalcemia)
Displaced Abomasum
Ketosis
Rumen Acidosis
Cattle Diseases Related to Improper Nutrition BEEF
Bloat
Polioencephalomalacia
Rickets
Water Belly
White Muscle Disease
Rumen Acidosis
Bloat
History of diet change- lush pasture or high concentrate diet
Frothy bloat or free gas bloat
"Downer Cow"
A nutritional disease in dairy cattle caused by mineral deficiencies in diet such as grass tetany or milk fever (or calving trauma or neurologic diseases), leading to recumbency.
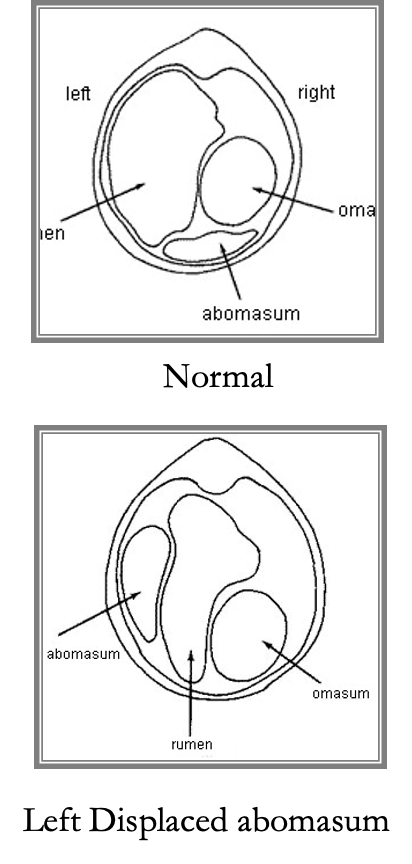
Displaced Abomasum (DA)
A condition in high-producing dairy cows fed high concentrate diets, where the abomasum can displace to the left or right.
Diagnosed by “pinging” the abdomen
Ketosis
A negative energy balance (peak lactation) causes fat catabolism
Ketones are formed as a byproduct which are passed in urine and milk
Causes anorexia and decreased milk production
Treat with 50% dextrose IV- must be given IV- if given outside of the vein it will cause tissue necrosis
Polioencephalomalacia
A disease caused by thiamine deficiency, leading to neurologic deficits.
Rickets
A condition caused by calcium and/or phosphorus imbalance.
White Muscle Disease
A condition caused by vitamin E and/or selenium deficiency.
Nitrate Toxicity
A condition where excessive nitrite production occurs due to high nitrate consumption, leading to inadequate oxygen to tissues and chocolate brown blood.
Fescue Toxicosis
A toxicity caused by fescue grass infected with a fungal endophyte, leading to various clinical signs in cattle, horses, and small ruminants.
Heinz body
Hemoglobin within RBC's clumps together due to oxidative damage. commonly a sign of Red Maple Toxicosis.
Treatments for Plant Toxicity
Usually supportive care (IV fluids, nutritional support, injury prevention, etc.)
Oral binding agents (universal antidote gel, activated charcoal) require large amounts to administer to large animals (effective in small ruminants).