Marine Vert Lab Practical 1
1/89
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Labs 1-5 Content
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
90 Terms
Characteristics of Osteichthyes:
Bony skeleton (endoskeleton is completely bone)
Also called teleostomi
Fresh and marine water
~27,000 spp
Exoskeleton is made of bony plates called cycloids
Mouth is at anterior tip of the body
2 sets of jaws
4 pairs of gills, which are covered by an operculum
Have gas bladder
Homocercal tail tin
Carnivores, omnivores, herbivores, filter-feeders or detritivores
External fertilization
Excretes ammonia
Characteristics of Chondrichthyes:
Cartilaginous skeleton
Also called elasmobranchii
Exclusively marine water
~970 spp
Exoskeleton made up of small denticles coated with enamel (placoid scales)
Mouth is ventrally-located
Single set of jaws
5-7 gill pairs
No operculum- gill slits instead
Oil-filled liver buoyancy control instead of air bladder
Generally carnivores
Some internal fertilization
Main excretion is urea

Which body shape is this?
Fusiform. Examples: tuna, swordfish, shark, striped bass.
Streamlined, torpedo-shaped
Fast-swimming fish, predators, live in open water
Move tail side to side
What body shape is this?
Compressiform. Examples: Tautog, moonfish, angelfish.
Compressed from side to side
Quick bursts of speed over short distances
Live among plants and move in narrow spaces
Move tail side to side
What body shape is this?
Depressiform. Examples: Skate, flounder, skates, rays.
Flattened from top to bottom
Benthic and slow
Flap fins up and down to swim like a bird flies
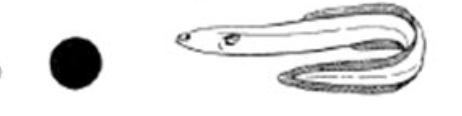
What body shape is this?
Anguilliform. Example: Eel fish.

What body shape is this?
Filiform. Example: pipe fish, eels, sand lance
Elongated shapes
Live in soft mud, sand, or under rocks
Slow
Slither like a snake

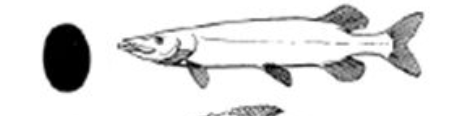
What body shape is this?
Taeniform. Example: Ribbon fish
What body shape is this?
Sagittiform. Example: snake head.
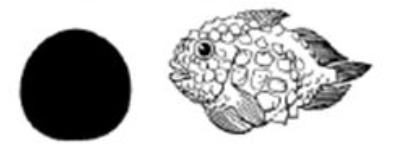
What body shape is this?
Globiform.
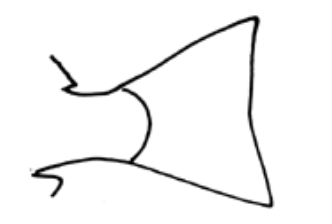
What fin shape is this?
Indented

What fin shape is this?
Rounded
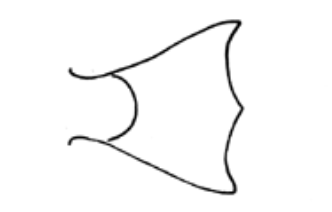
What fin shape is this?
Double truncate
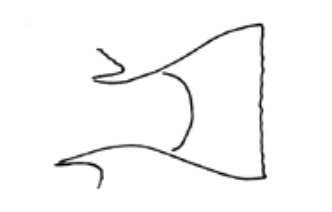
What fin shape is this?
Square, truncate, straight
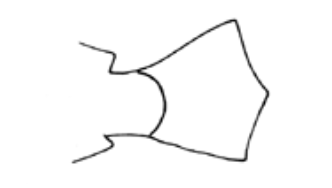
What fin shape is this?
Forked
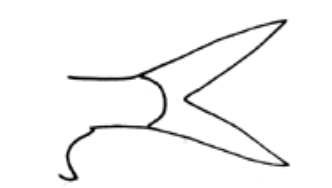
What fin shape is this?
Pointed (fin present)
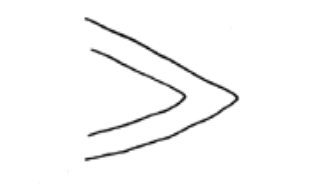
What fin shape is this?
Pointed (fin not differentiated)

What fin shape is this?
Naked (without rays on tip)
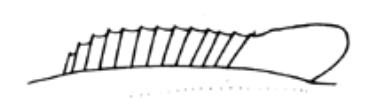
What type of dorsal fin is this?
Continuous dorsal fin

What dorsal fin type is this?
Contiguous dorsal fins (slightly joined to or adjacent to each other)
What bones do caudal rays extend over?
Hypural bones
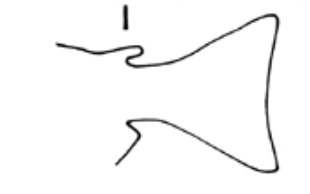
What fin is the line pointing to?
An adipose fin.
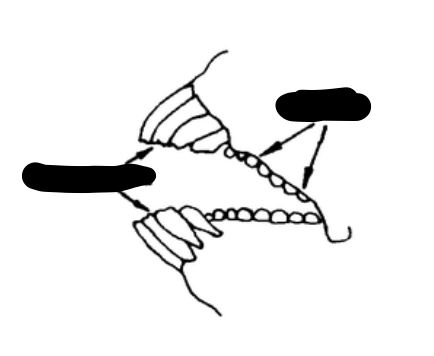
What kind of teeth are the arrows on the left pointing to? What about the arrows on the right?
Left: incisors
Right: molars
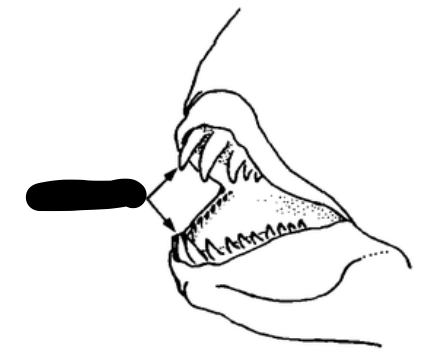
What type of teeth are the arrows pointed to?
Canines

What type of teeth are in the image?
Villiform
Homocercal tails are SYMMETRICAL/ASYMMETRICAL and heterocercal tails are SYMMETRICAL/ASYMMETRICAL.
Homocercal: symmetrical
Heterocercal: asymmetrical
What are the pros and cons of a homocercal rounded tail?
Pro: Large amount of surface area allows sharp turns and quick starts to avoid predators
Con: Creates drag- fish tires easily
What are the pros and cons of a homocercal truncate tail?
Pros:
Allows short bursts of speed to escape predators or constant slow swimming
Less drag than rounded
Characteristic in bottom-dwelling fish like flounder and killifish
What are the pros and cons of a homocercal forked tail?
Pros: constant swimming over long distances, reduces drag
Cons: not much speed for feeding or protection
Characteristic of open-water fish or schooling fish
Pros and cons of a homocercal lunate fin shape
Pros: Fast-moving, less drag, great acceleration
Cons: reduced maneuverability
Common in oceanic fish like tuna and swordfish
Pros and cons of a heterocercal tail
Pros: medium speed, provides lift in the absence of air bladder
Cons: reduced maneuverability

These fishes are examples of ____ mouths:
Superior

These fishes are examples of ______ mouths:
Inferior
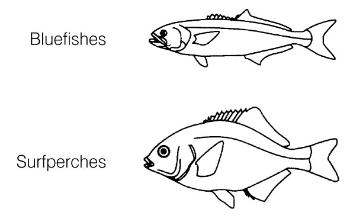
These fishes are examples of _______ mouths:
Terminal
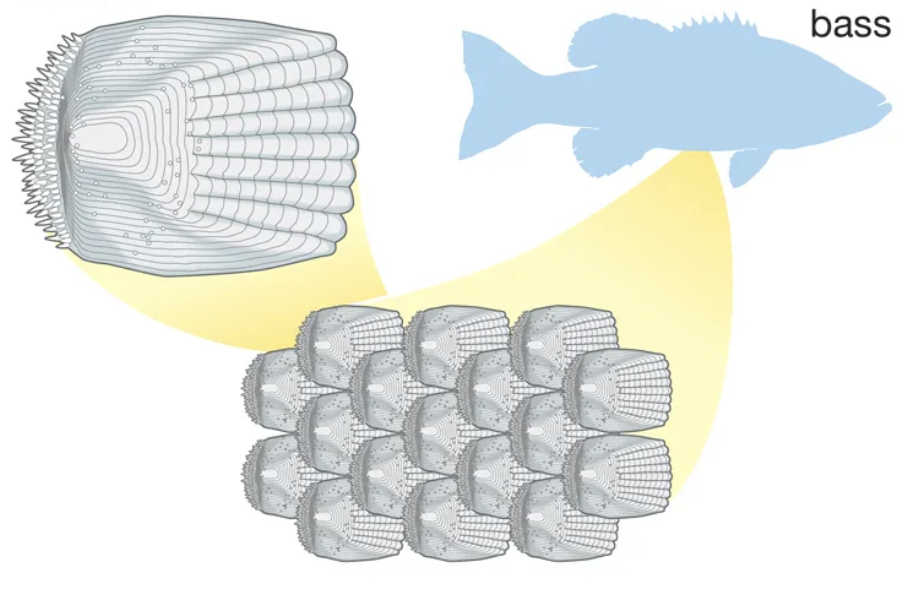
This is a ______ scale.
Ctenoid
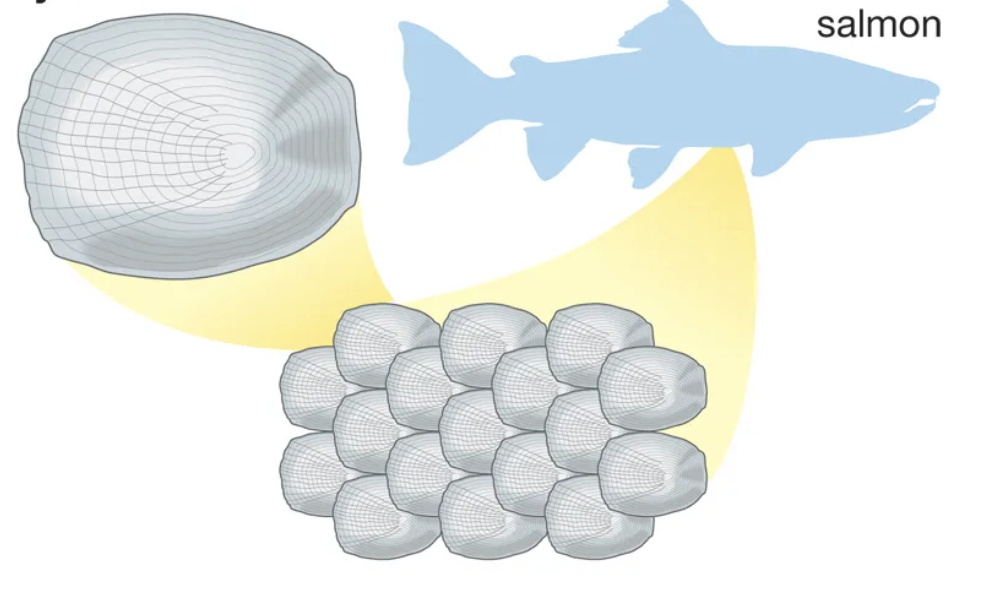
This is a _____ scale.
Cycloid
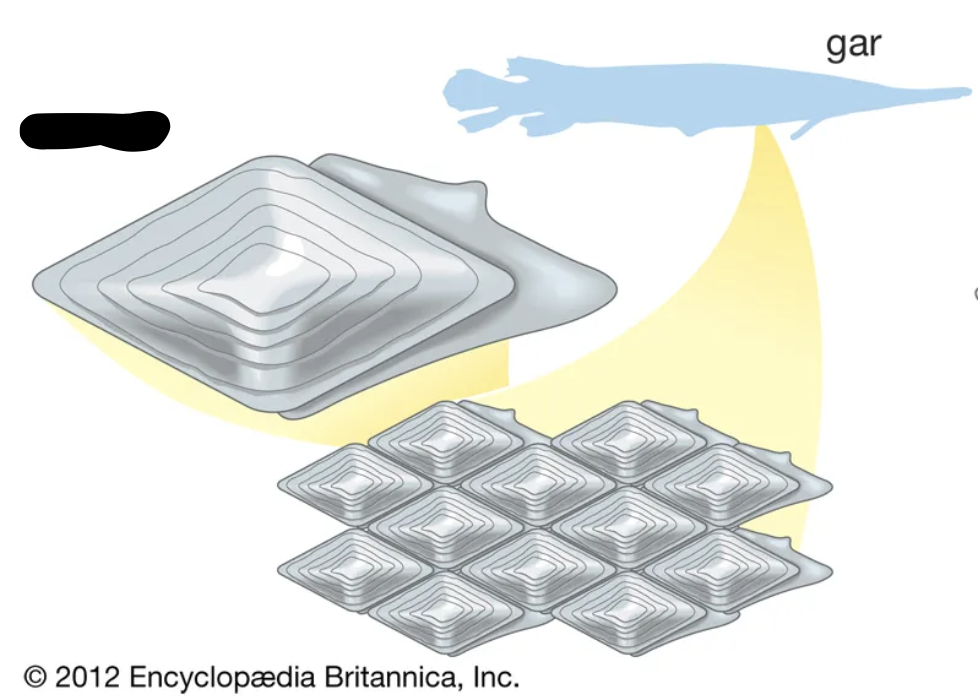
This is a ______ scale.
Ganoid
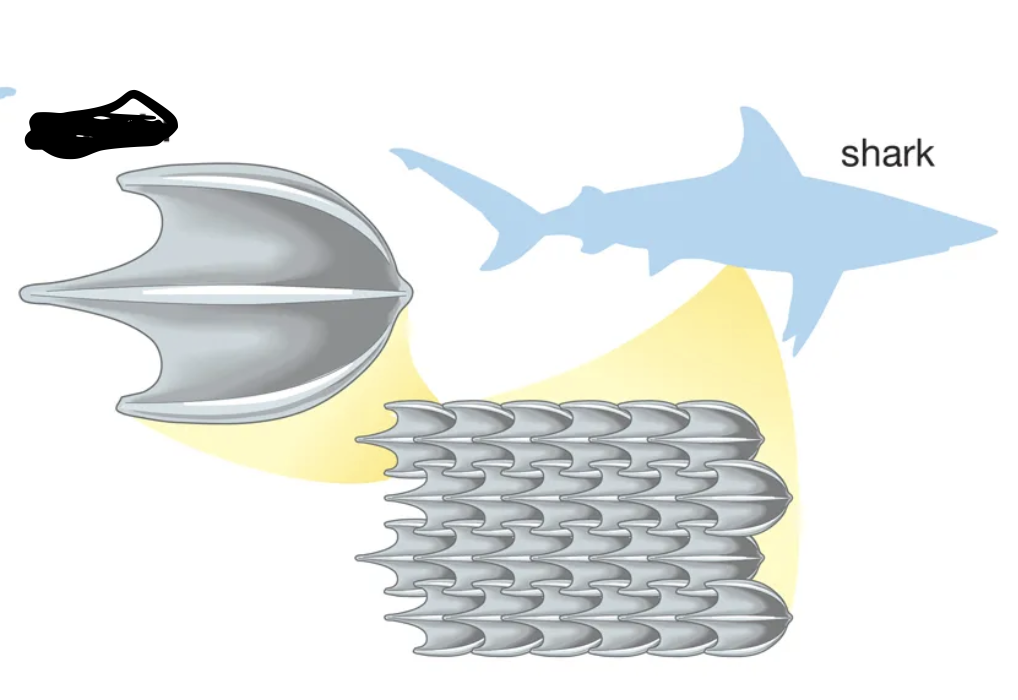
This is a _______ scale.
Placoid
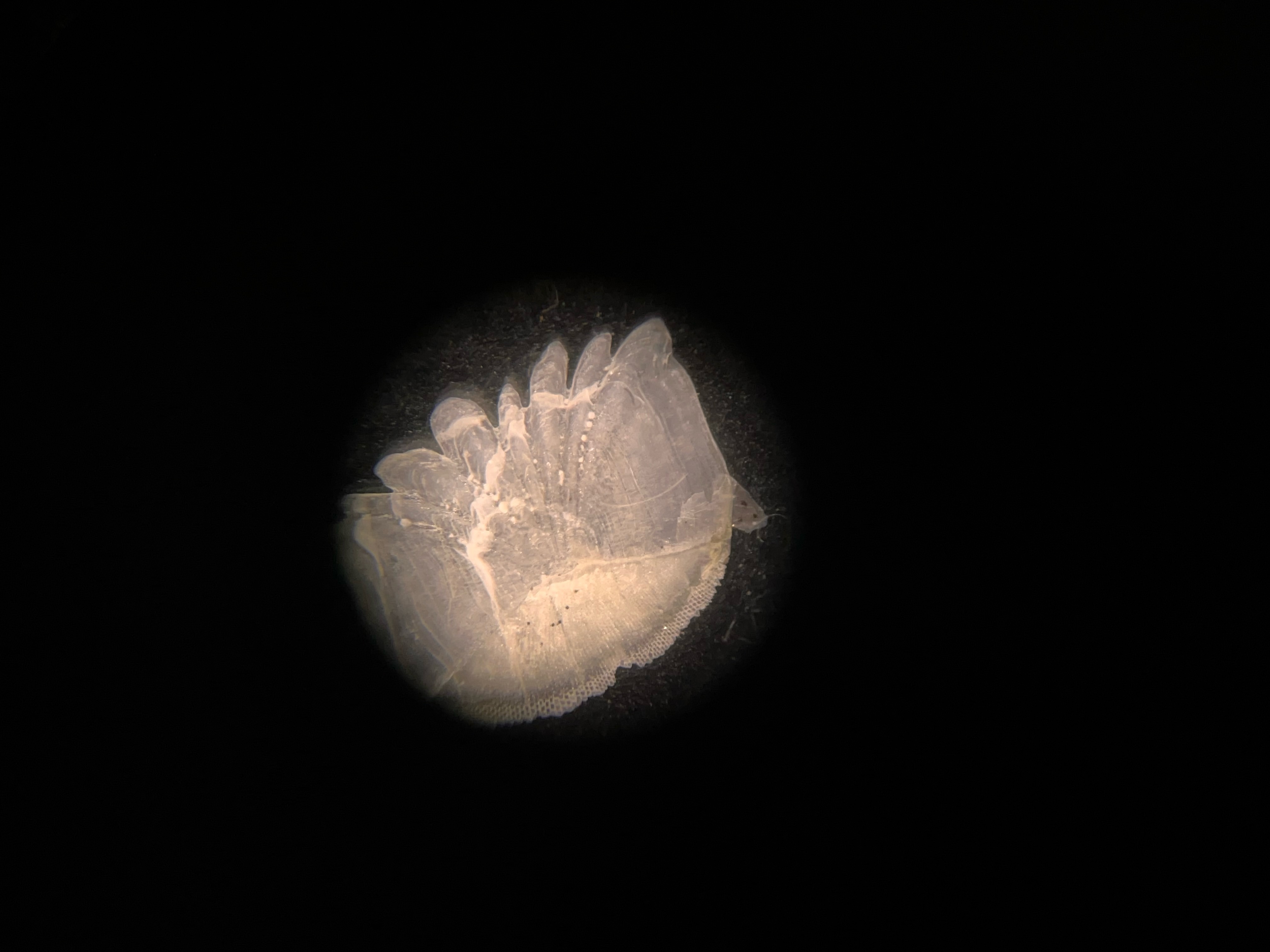
This is a ________ scale.
Ctenoid (image)
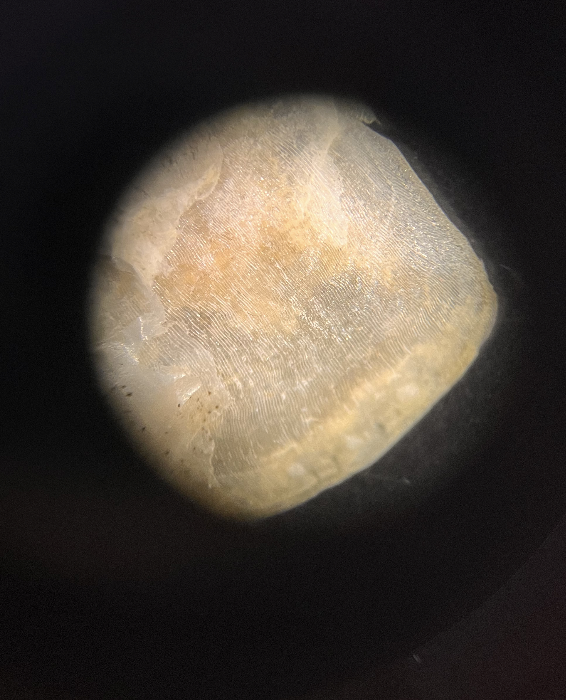
This is a ______ scale.
Cycloid (image)
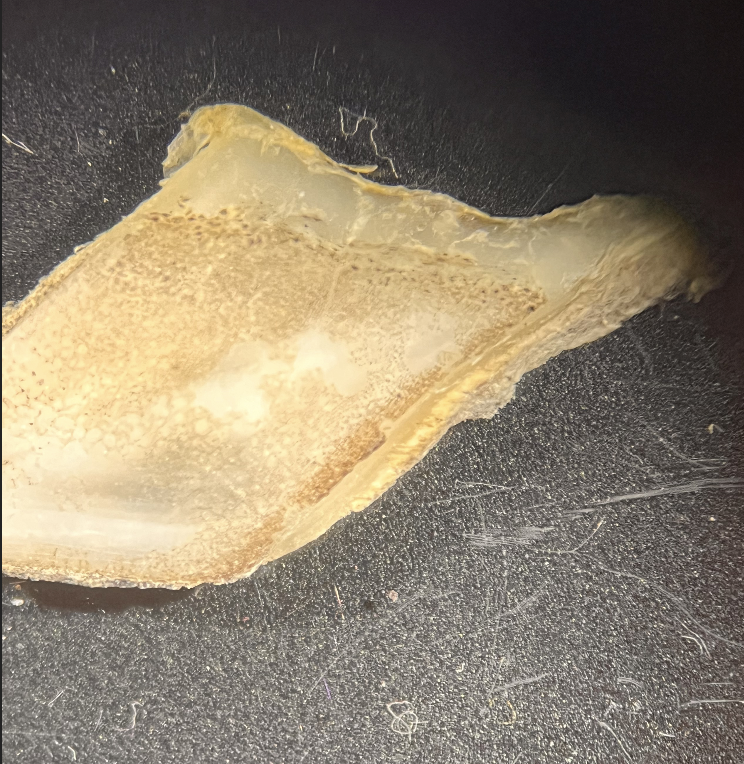

This is a _______ scale.
Ganoid (image)
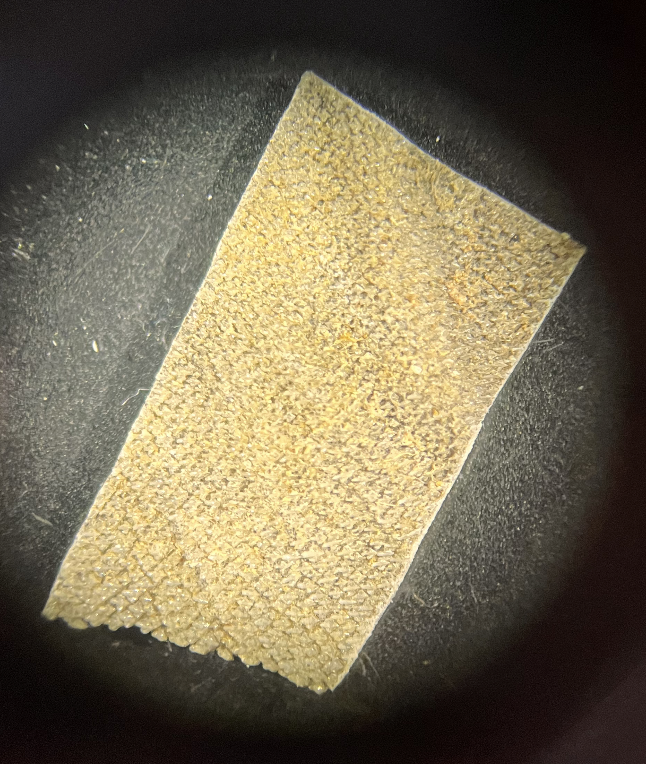
This is a ______ scale.
Placoid (image)
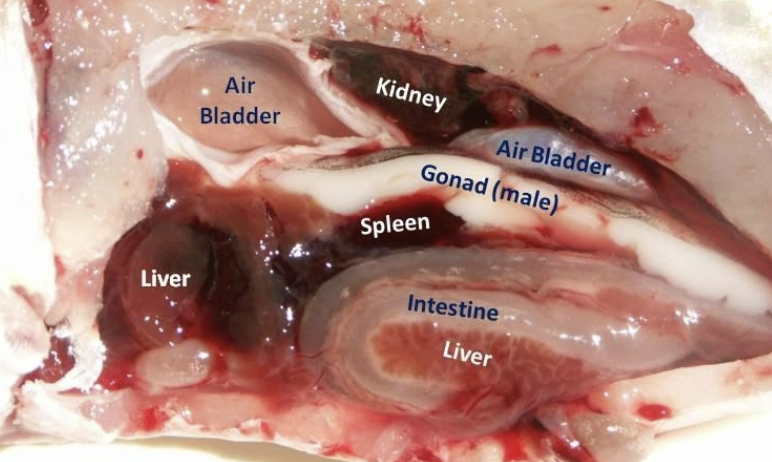
Fish guts- yum! (couldn’t think of a question)
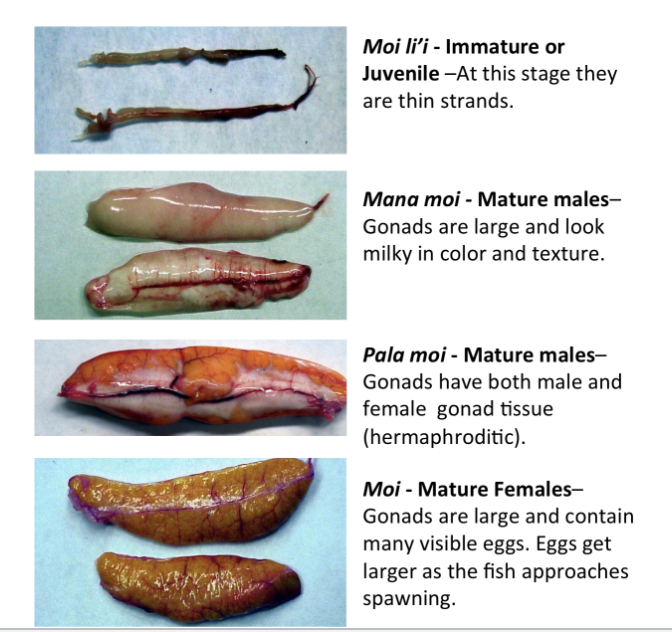
What “moi” term is used for mature males?
Mana moi. This is determined from the gonads being large and milky in color and texture.
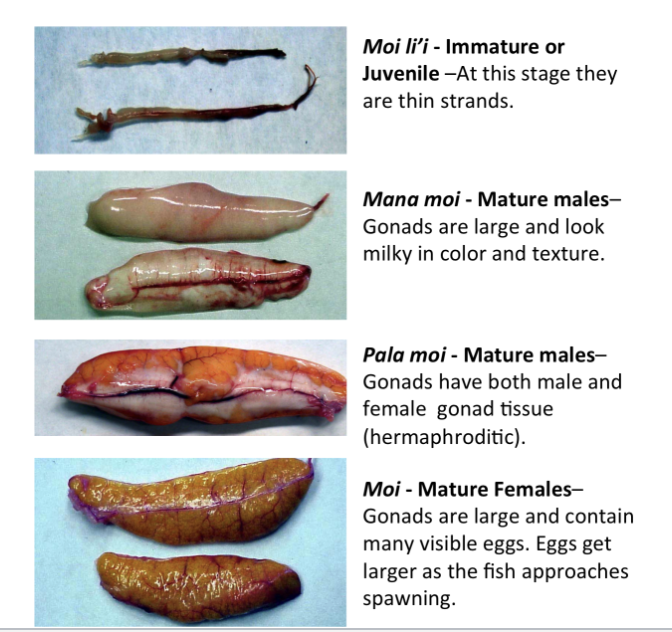
What is the “moi” term for mature hermaphrodites?
Pala moi. This is determined from the gonads containing both male and female gonad tissue.
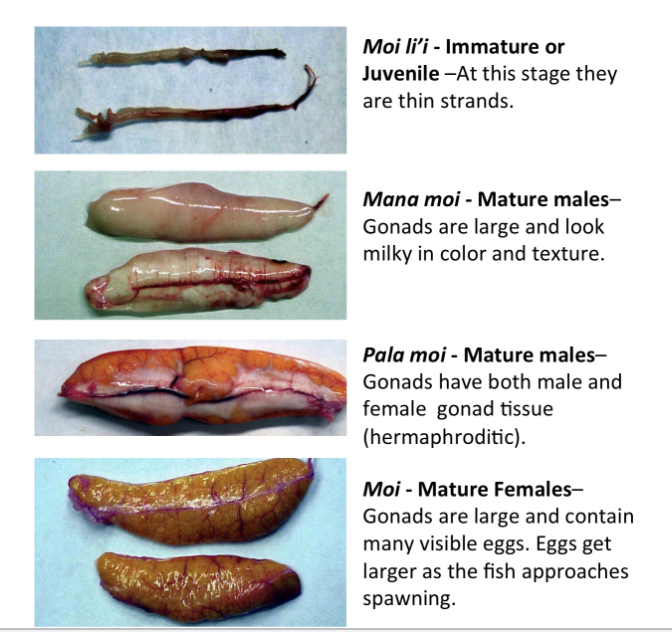
What is the “moi” term for a sexually immature specimen?
Moi li’i. At this stage the gonads are small strands.
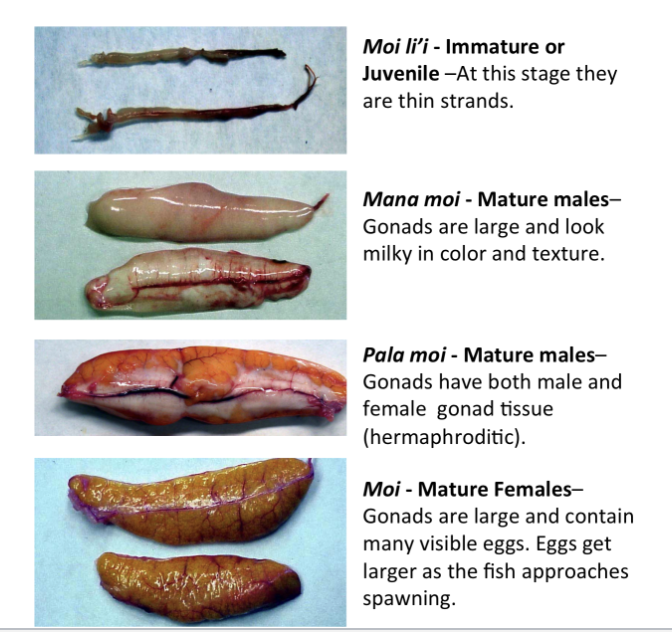
What is the “moi” term for a sexually mature female?
Moi. This is determined by the gonads being large and containing visible eggs.
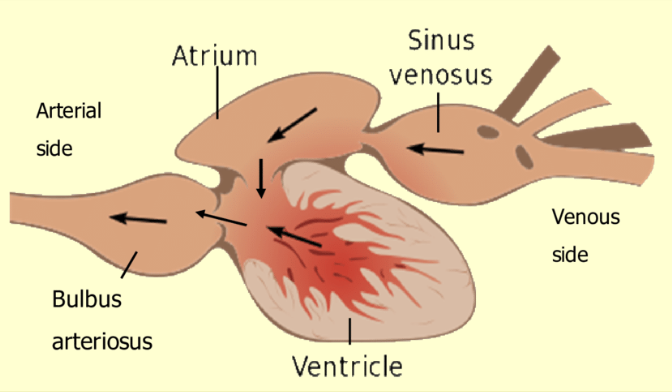
What are the four chambers of a fish heart?
Atrium
Ventricle
Sinus venosus
Bulbus arteriosus (bony fish) / conus arteriosus (shark)
As the water flows across the gill’s ______ oxygen diffuses into the capillaries.
Lamellae. Blood flows through the lamellae in the opposite direction of the water flow.
If a fish’s pelvic fins are underneath the head/pectoral fins it is in the ______ position.
Thoracic
If a fish’s pelvic fins are at a mid-ventral placement they are in the _____ position.
Abdominal
What is the function of an anal fin?
Provides stability
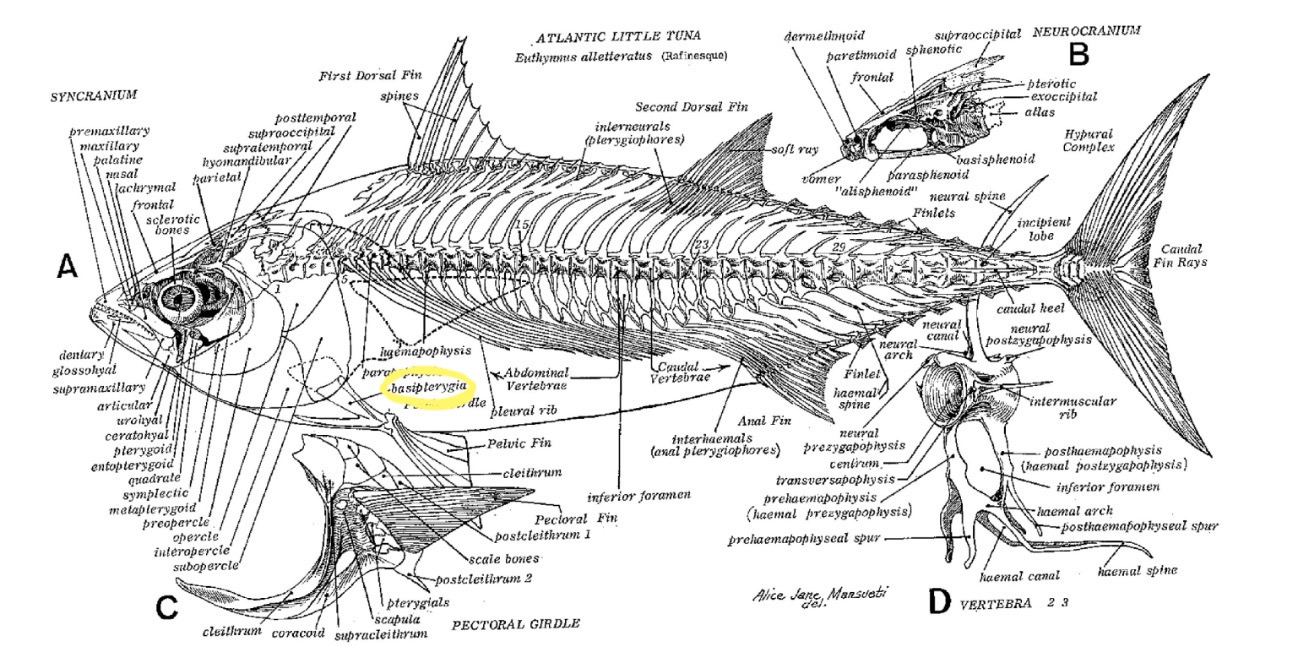
What is the function of the basipterygia?
Supports pelvic fin
Allows fish to extend pelvic fins for increased maneuverability and facilitates fin movement
Specific paired element within the pelvic girdle of bony fishes
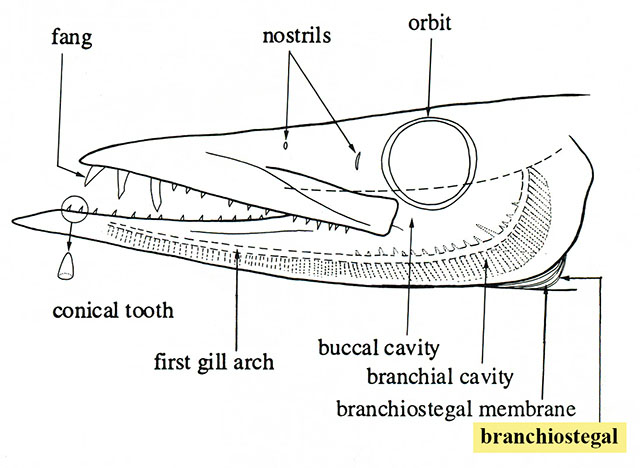
What’s the function of the branchiostegals/gill rays?
Provide gill ventilation
Number of gill rays helps differentiate amongst taxa
Forms the floor of the branchial chamber
What is the function of the dentary?
Serves as a lower jaw for feeding
Houses/holds teeth
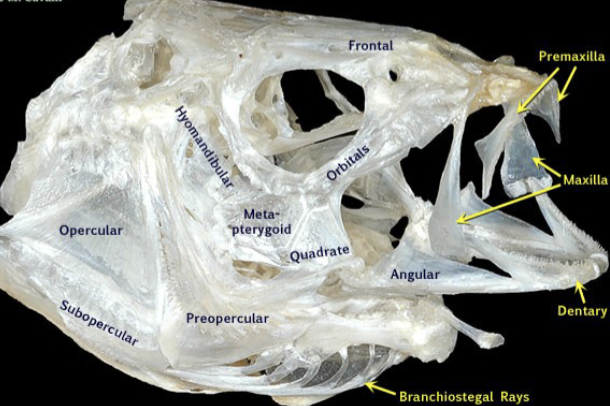
What is the function of the frontal?
Supports fish and eyes
Provides framework for face
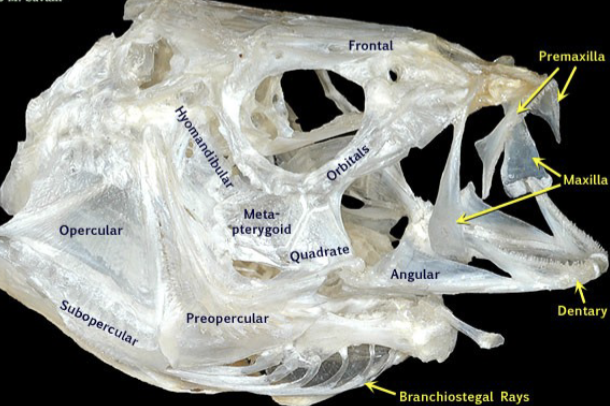
What is the function of the maxilla?
Enables jaws to open and protrude
Pushes premaxilla forward
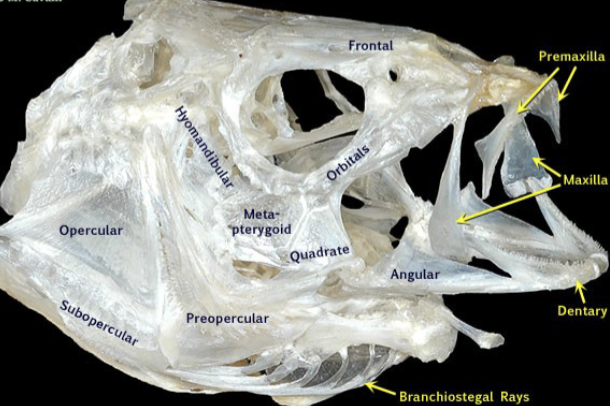
What is the function of operculum?
Prevent backflow of water over gills
Protects gills
Allows fish to push water over gills
What is the function of a pectoral fin?
Allows fish to turn and steer
Helps maintain position in the water column
What is the function of the pectoral girdle?
Aids in support for pelvic fins by acting as an anchor for them
Provides structural support but is not connected to axial skeleton
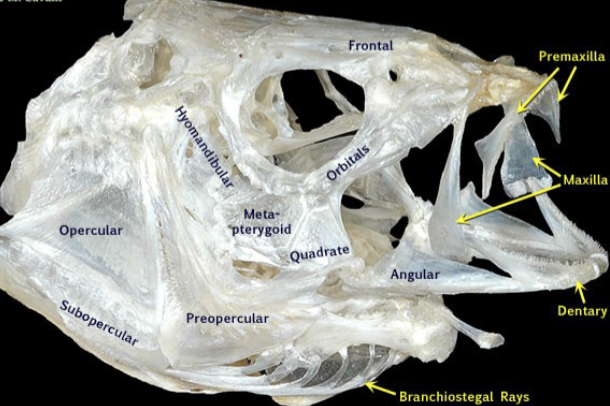
What is the function of premaxilla?
Pushed forward by the maxilla to protrude mouth
Enhances suction generation
What is the function of the supraoccipital crest?
Attachment point for epaxial muscles to generate force during suction feeding
(Image is rear view of skull)
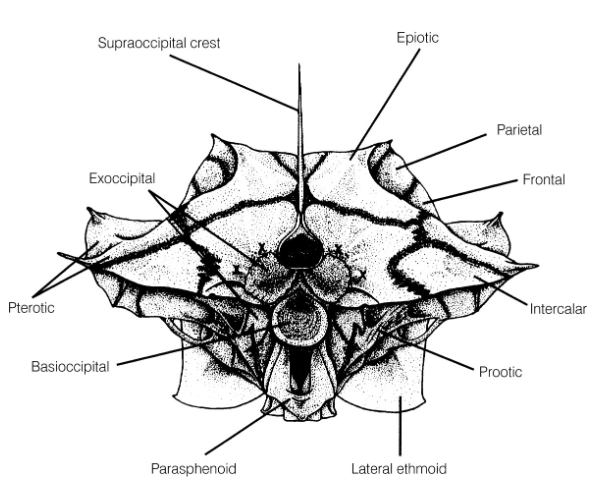
What is the function of vertebrae?
Structural support
Attachment point for other bones
Supporting structure for muscles, which enhances functions like swimming

The neural spine is on the DORSAL/VENTRAL side of a vertebrae and the hemal spine is on the DORSAL/VENTRAL side of a vertebrae.
Neural = dorsal
Hemal = ventral
What is the function of hemal arches in vertebrae? What about the neural spine?
Hemal arches protect blood vessels and the neural spine protects the spinal cord. As vertebrate components, they also provide structural support to the fish.
Otoliths are composed of ______ while bone is made of ______
Otoliths: Calcium carbonate
Bone: Calcium phosphate
What are annual growth rings seen in otoliths called?
Annuli
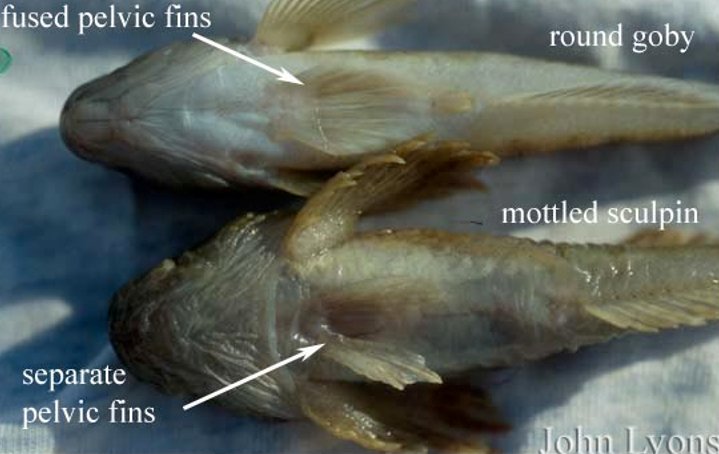
What specialized adaptation do goby pelvic fins have?
Their pelvic fins are fused together into a suction cup-like structure.
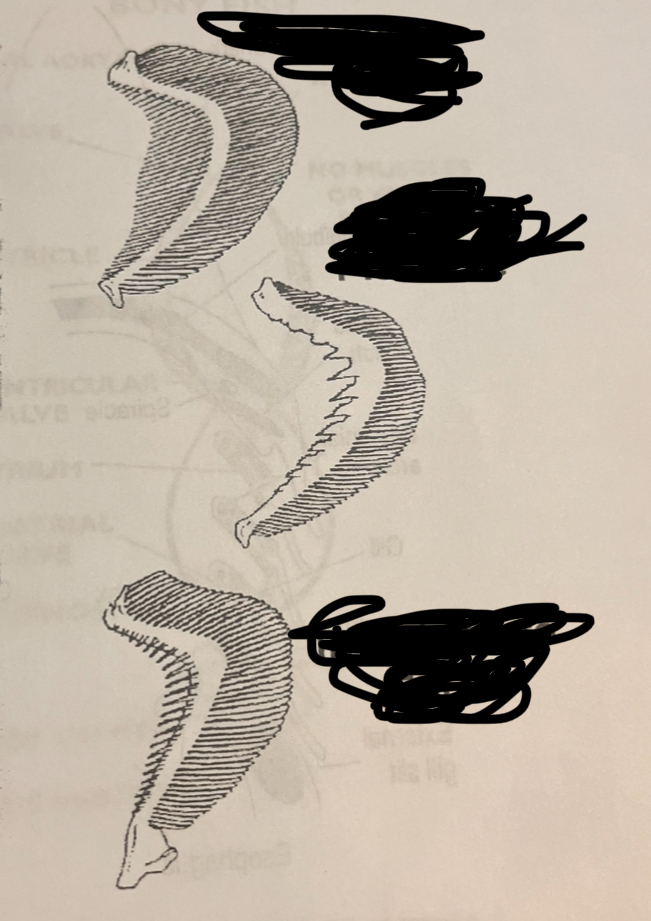

From top to bottom, name these gill arch types.
Top: Planktivore
Middle: Piscivore
Bottom: Invertebrate eater
What group contains conus arteriosus in their circulatory system? What group has bulbus arteriosus?
Chondrichthyes/sharks have conus arteriosus. Osteichthyes/Bony fish have bulbus arteriosus.
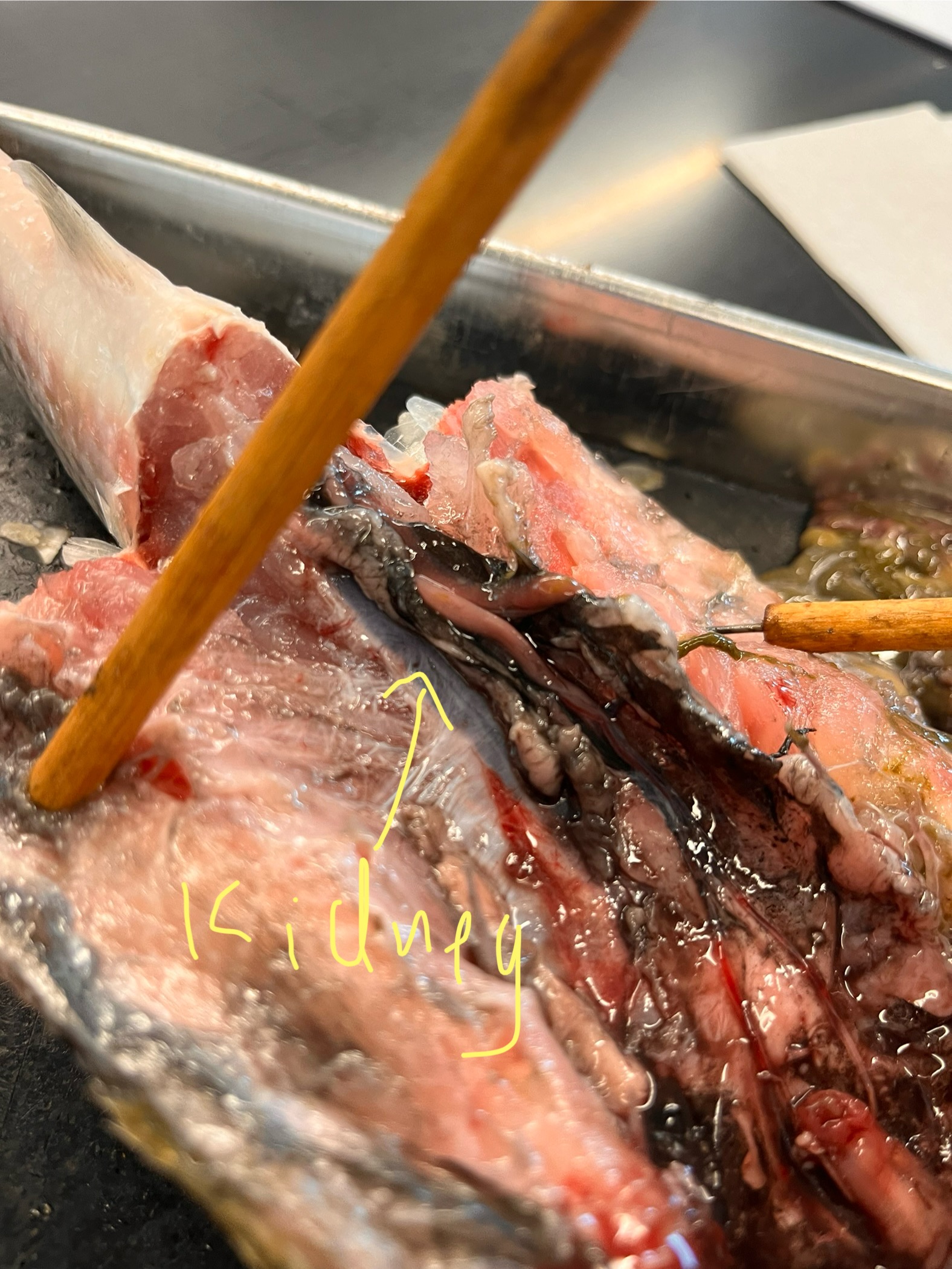
What does a kidney look like in a mullet?
Long dark thing towards dorsal side.

Where is the heart in a mullet?
Basically the head- far anterior of fish.
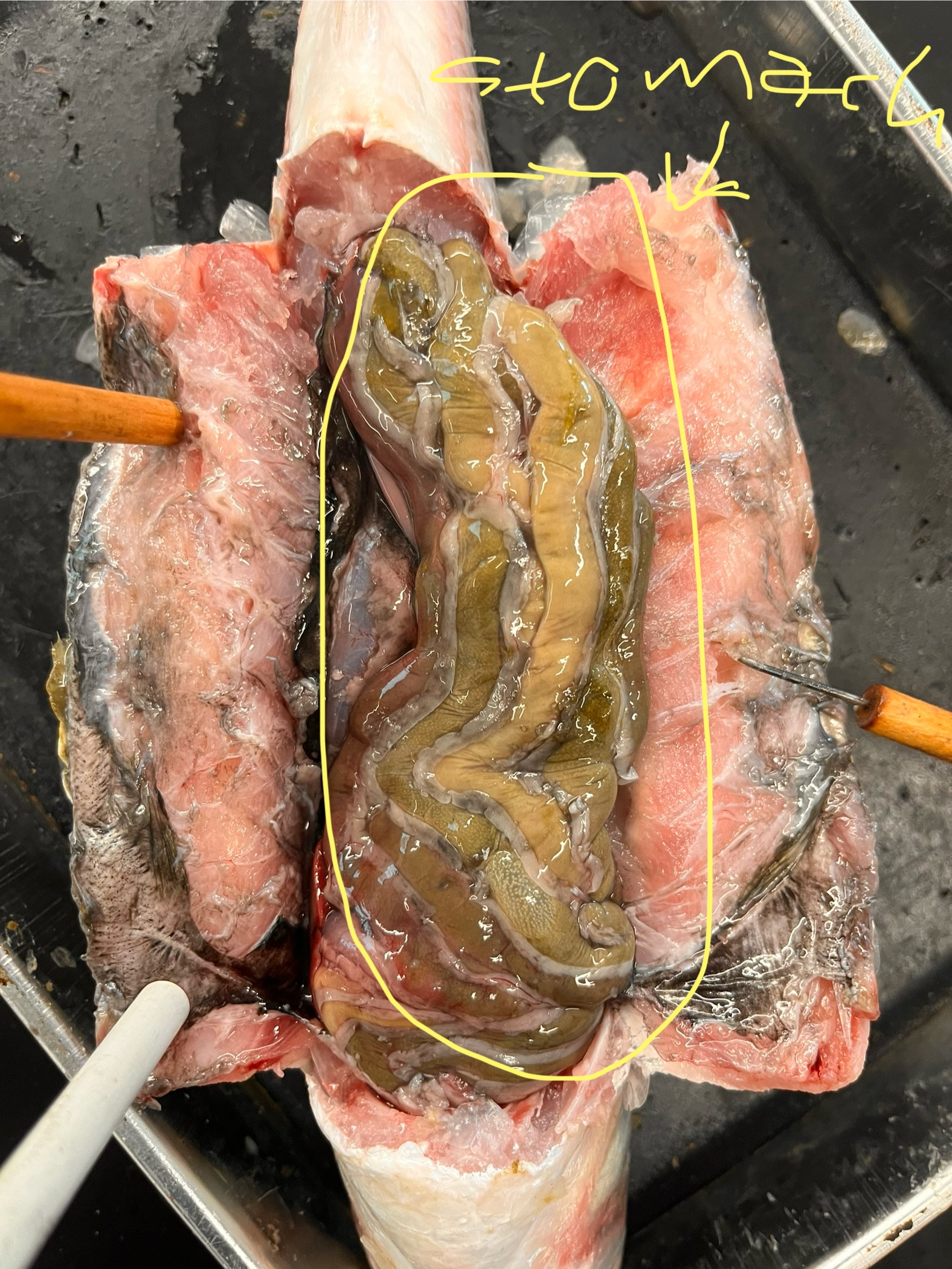
Where is the stomach/intestines of a mullet? What does it look like?
It is at the far ventral side of the belly.
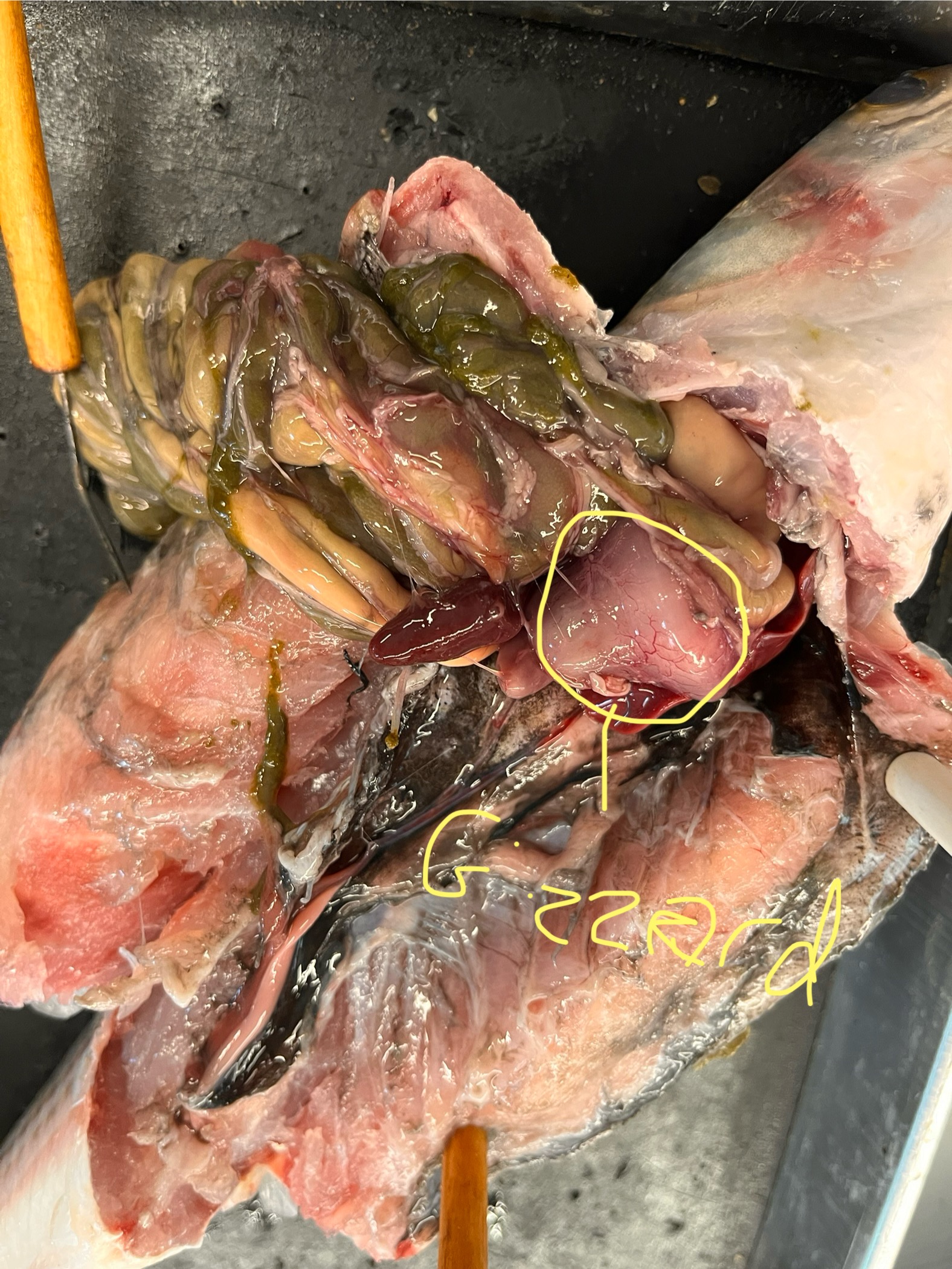
Where is the gizzard of a mullet? What does it look like? What does it do?
It is a rubbery and rigid pink/tan bell-shaped organ that aids in digesting complex foods.
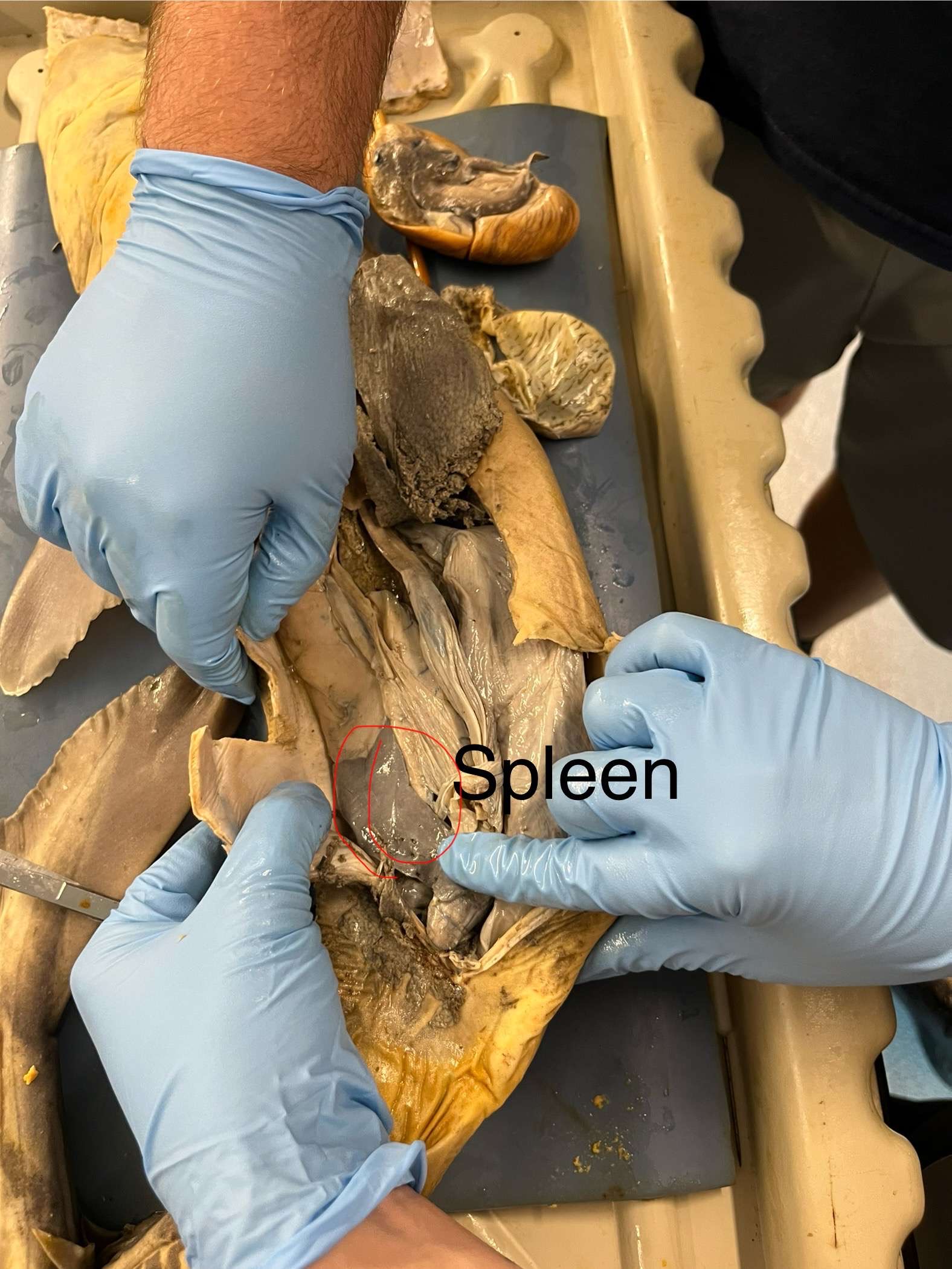
Where is the spleen of a mullet? What does it look like?
It is dorsal to the stomach/intestines and about as anterior as the gizzard. It is a dark red kidney bean shaped organ.
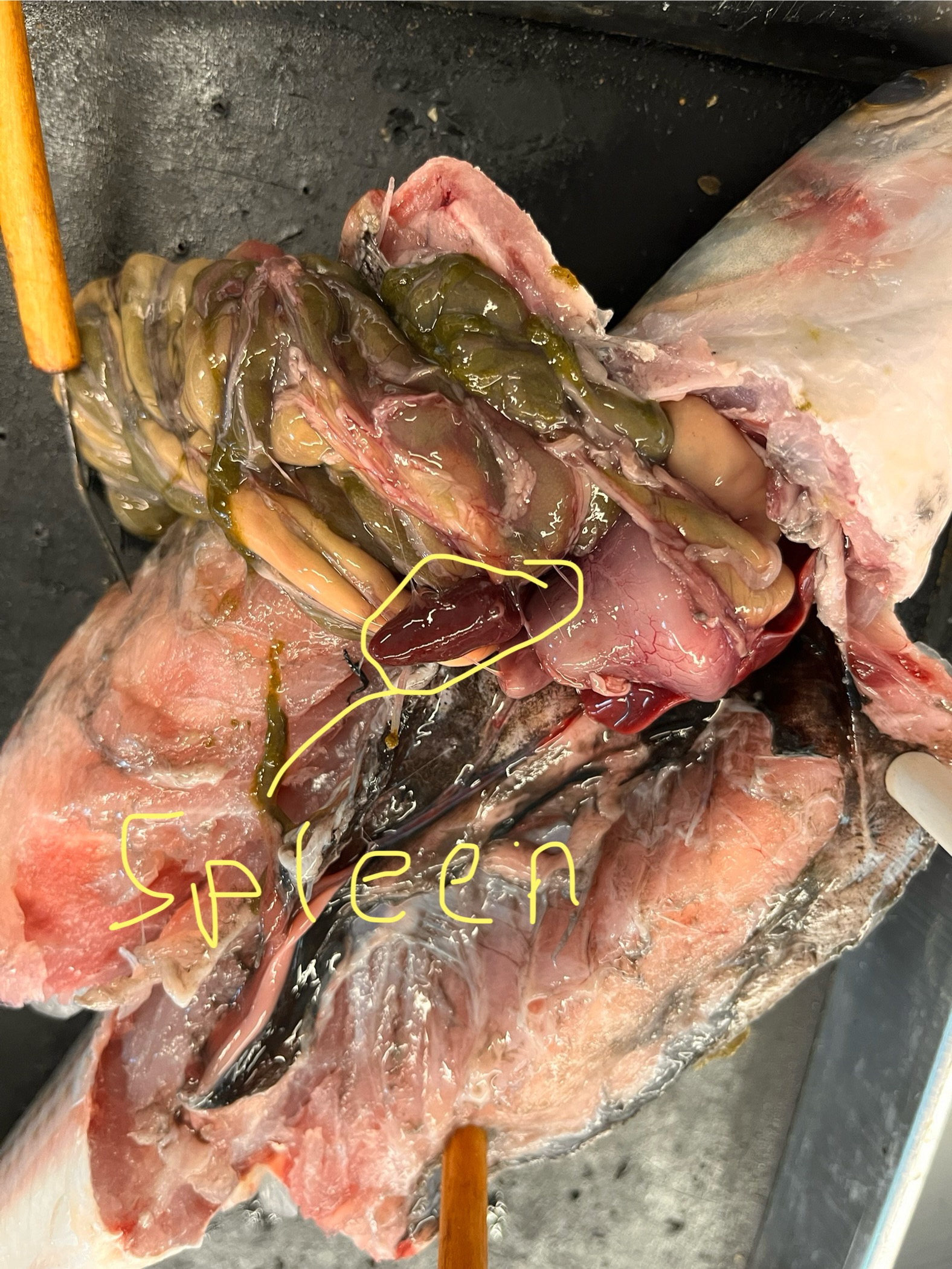
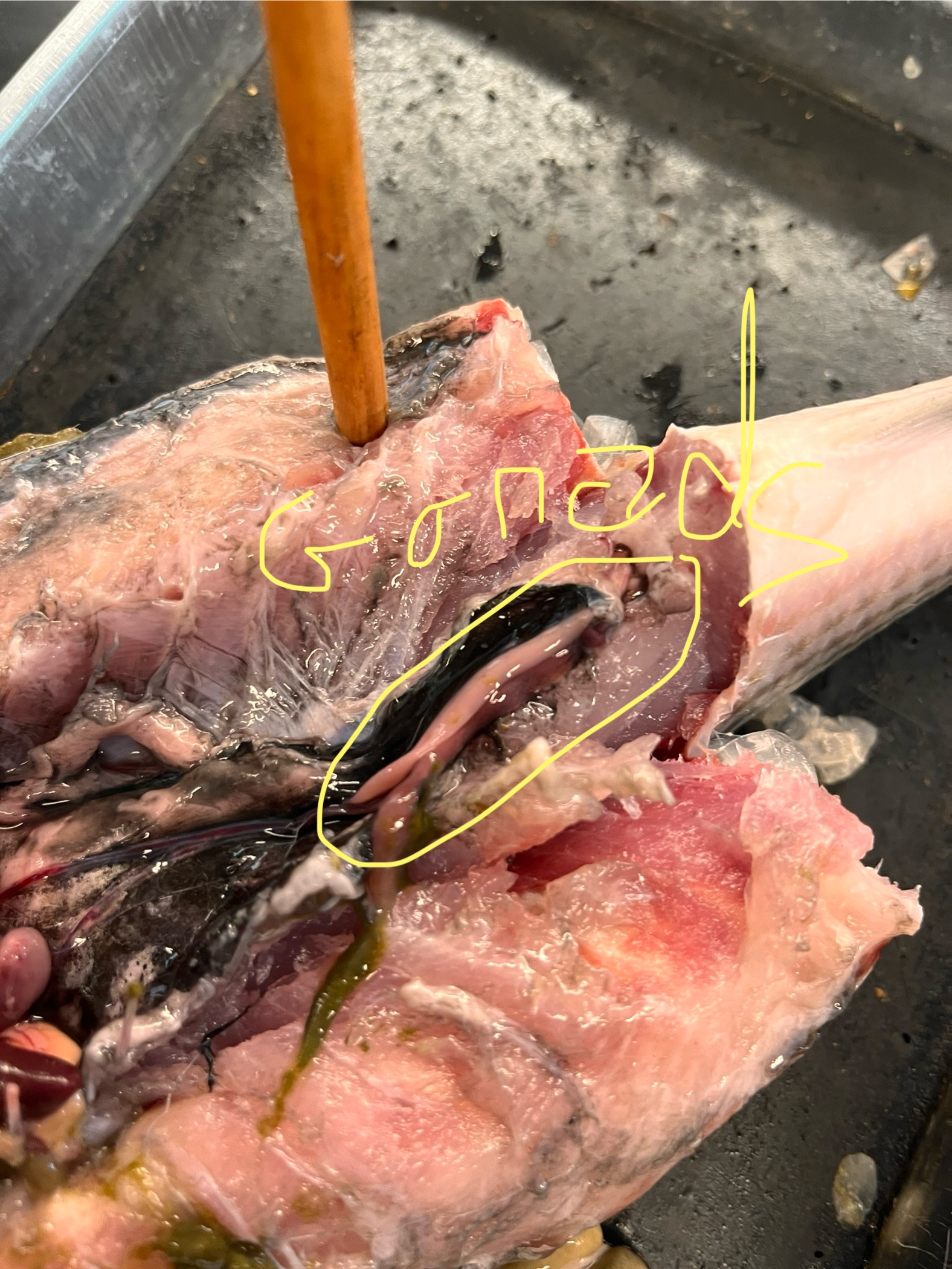
Where are the gonads of a mullet? What do they look like?
They are thin lines extending from the posterior region of the fish several inches long. One was a dark color, and one was a pink fleshy color. Our dissected specimens were sexually immature.

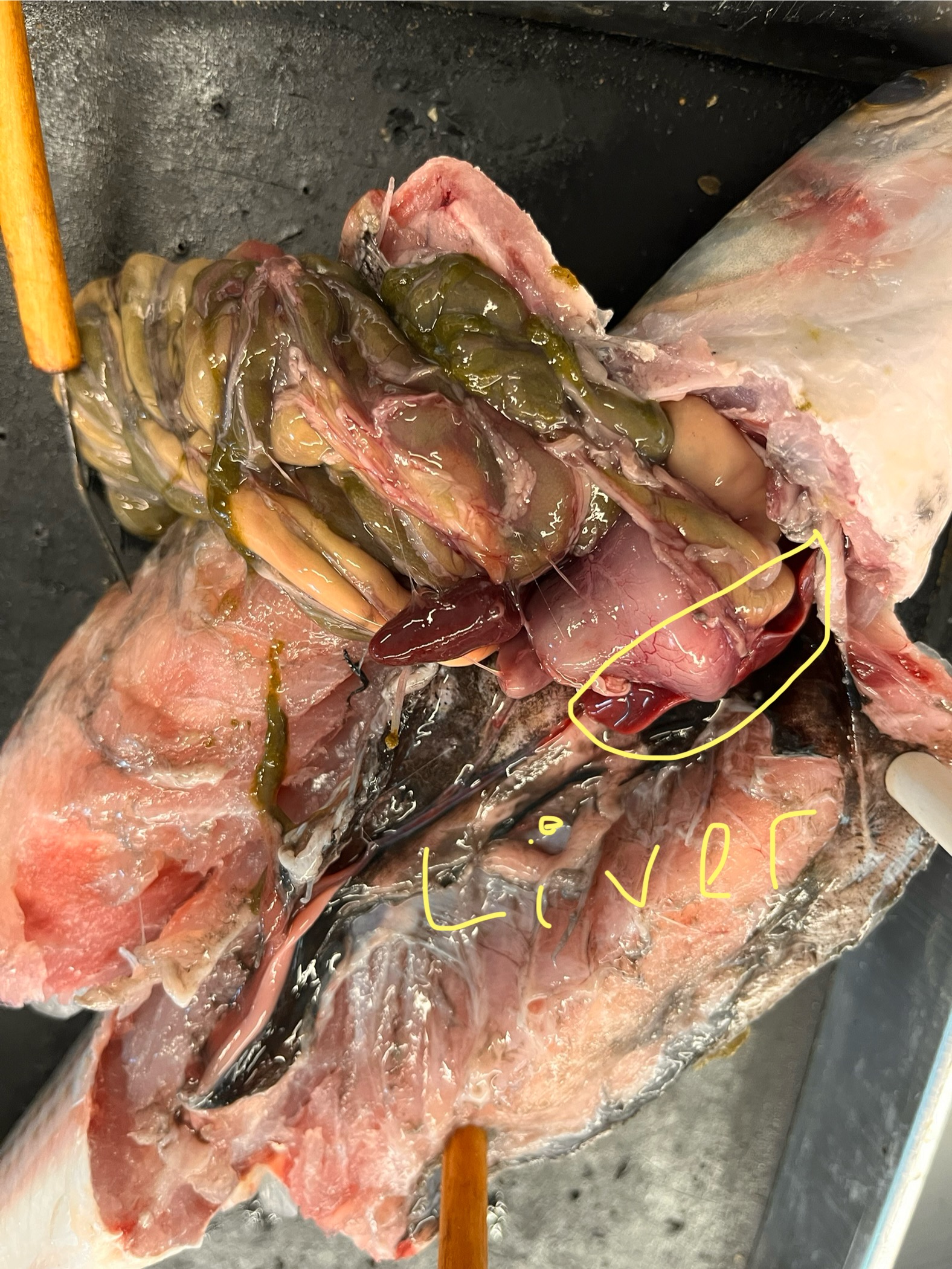
Where is the liver in a mullet? What does it look like?
The liver wraps around the other organs and is bright red
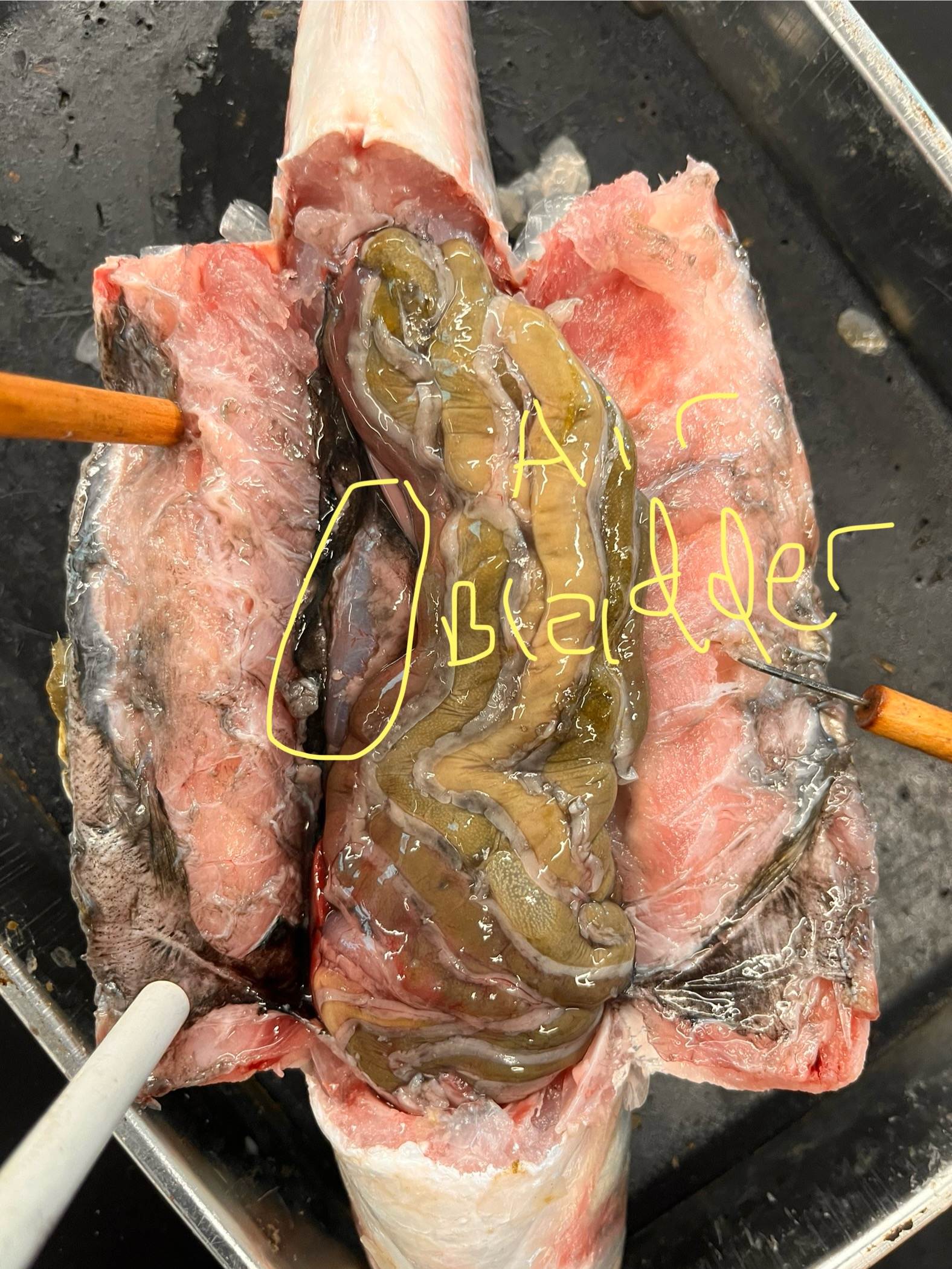
Where is a mullet’s air bladder? What does it look like?
It is dorsal to the stomach/intestines and is a pearly colored sack.
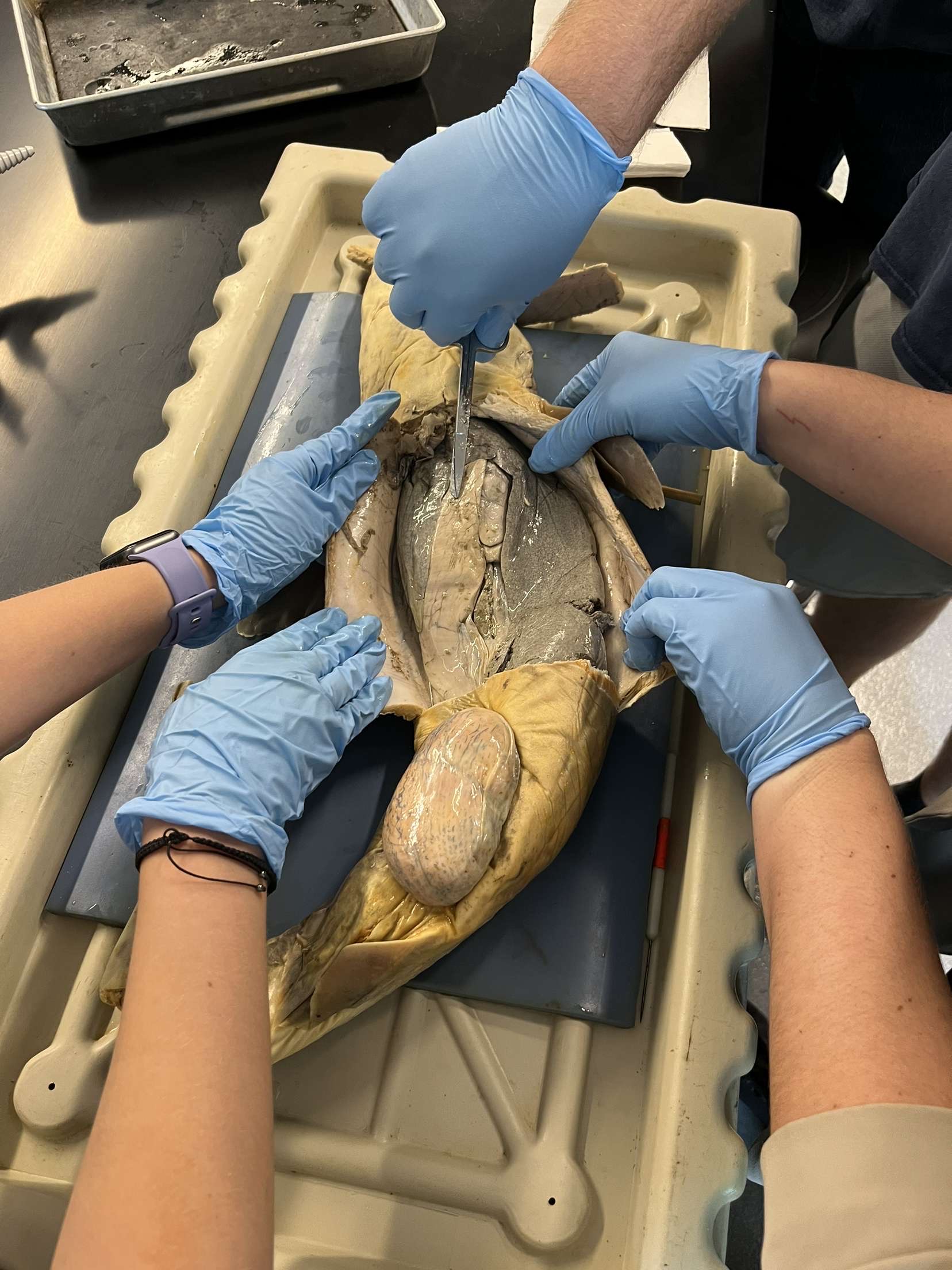
Where is a shark’s liver? What does it look like?
It is a large greyish fatty organ that wraps around the other organs.
Where is a shark’s spleen? What does it look like?
The spleen is a dark grey lump attached to the squiggly part of the stomach.
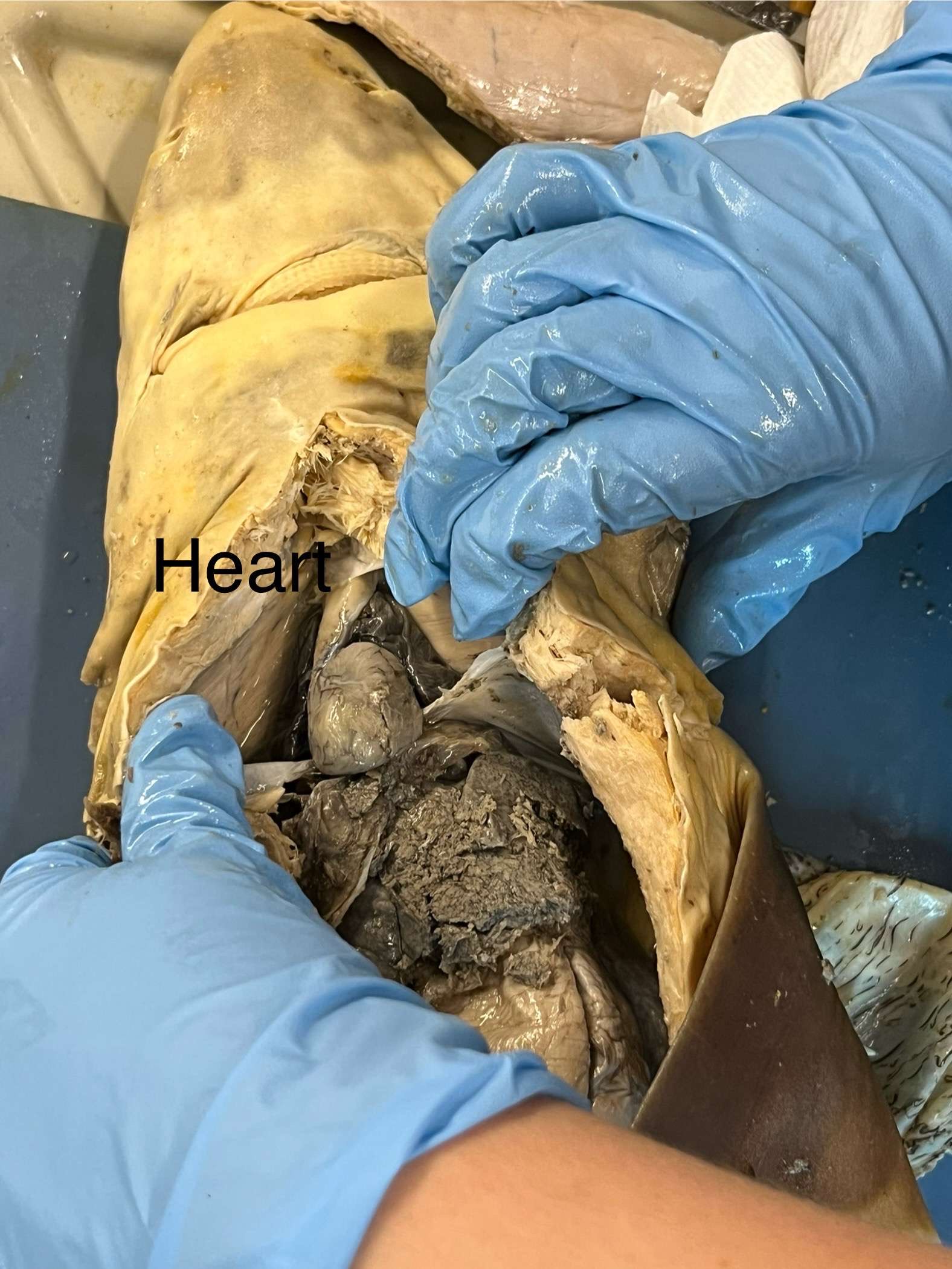
Where is the shark’s heart? What does it look like?
It is at the anterior part of the body, and has four chambers: the sinus venosus, atrium, ventricle, and conus arteriosis.
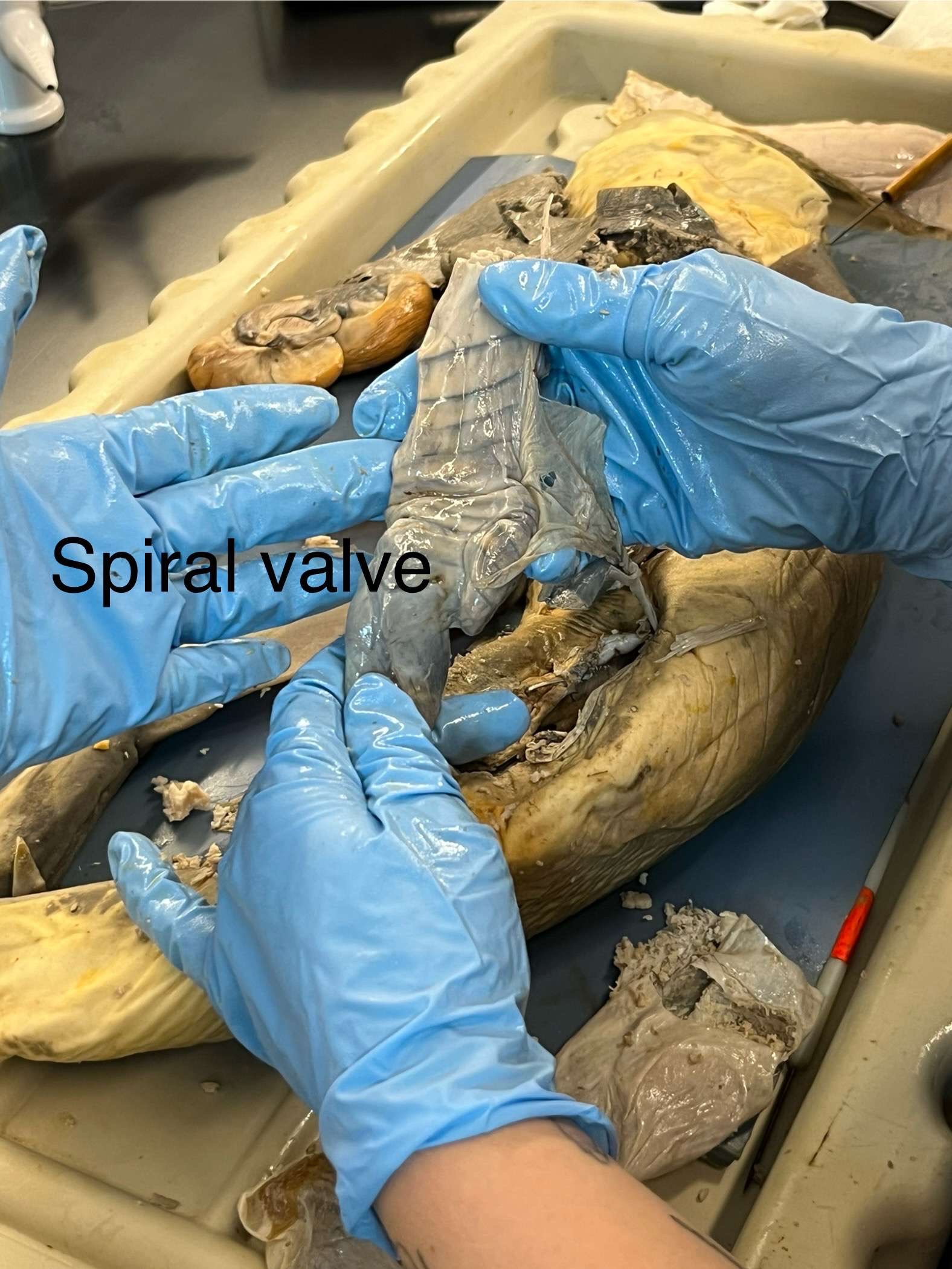
What is a shark’s spiral valve? Where is it in the body, and what does it look like?
It is a modified intestine with layered membranes to allow food to cover more digestive area within a smaller space. It is connected to the intestine and towards the posterior end of the body.
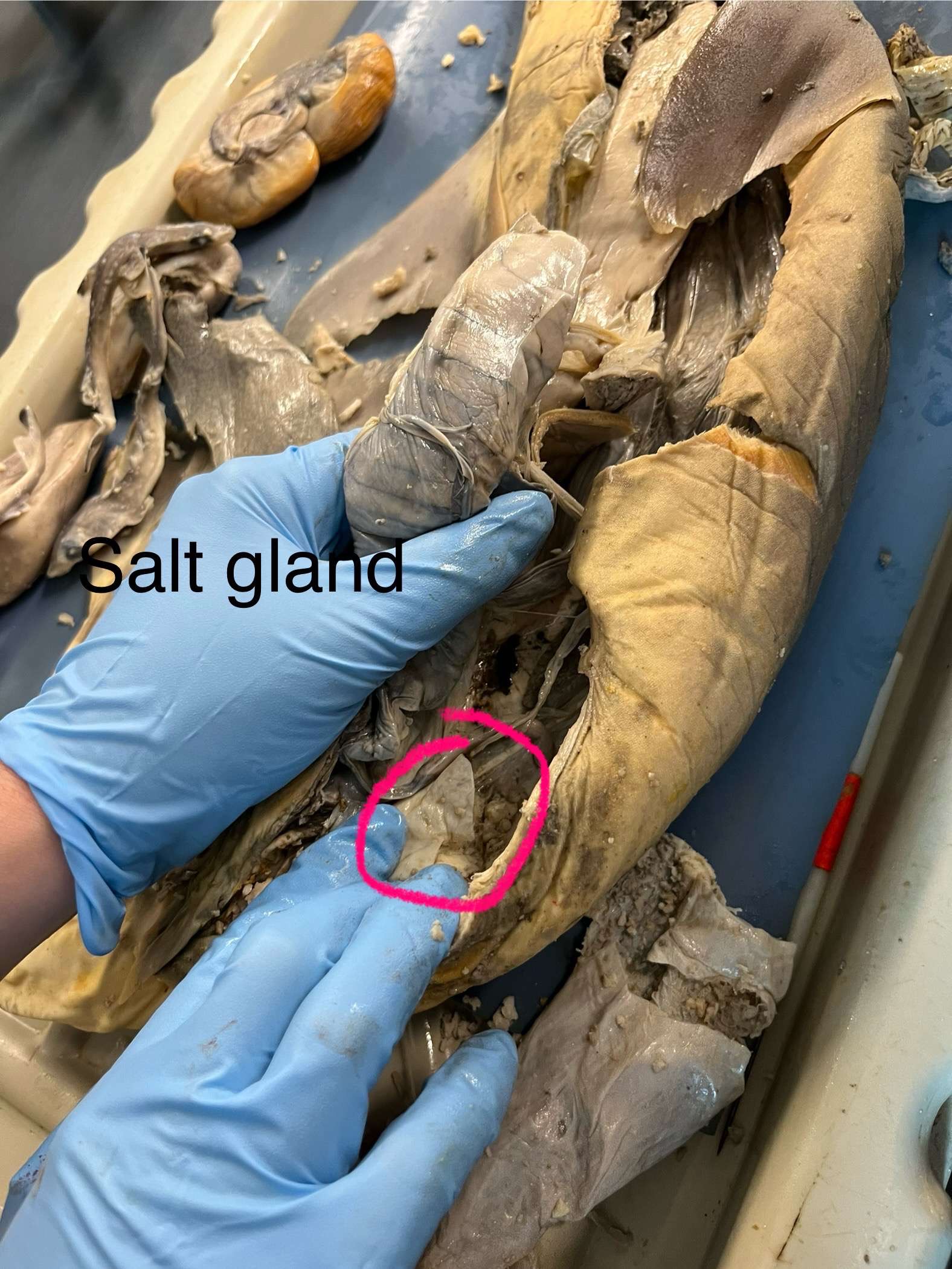
Where is the salt gland in the shark? What does it do?
It is near the anal fin/anus, and it is used for salt excretion.

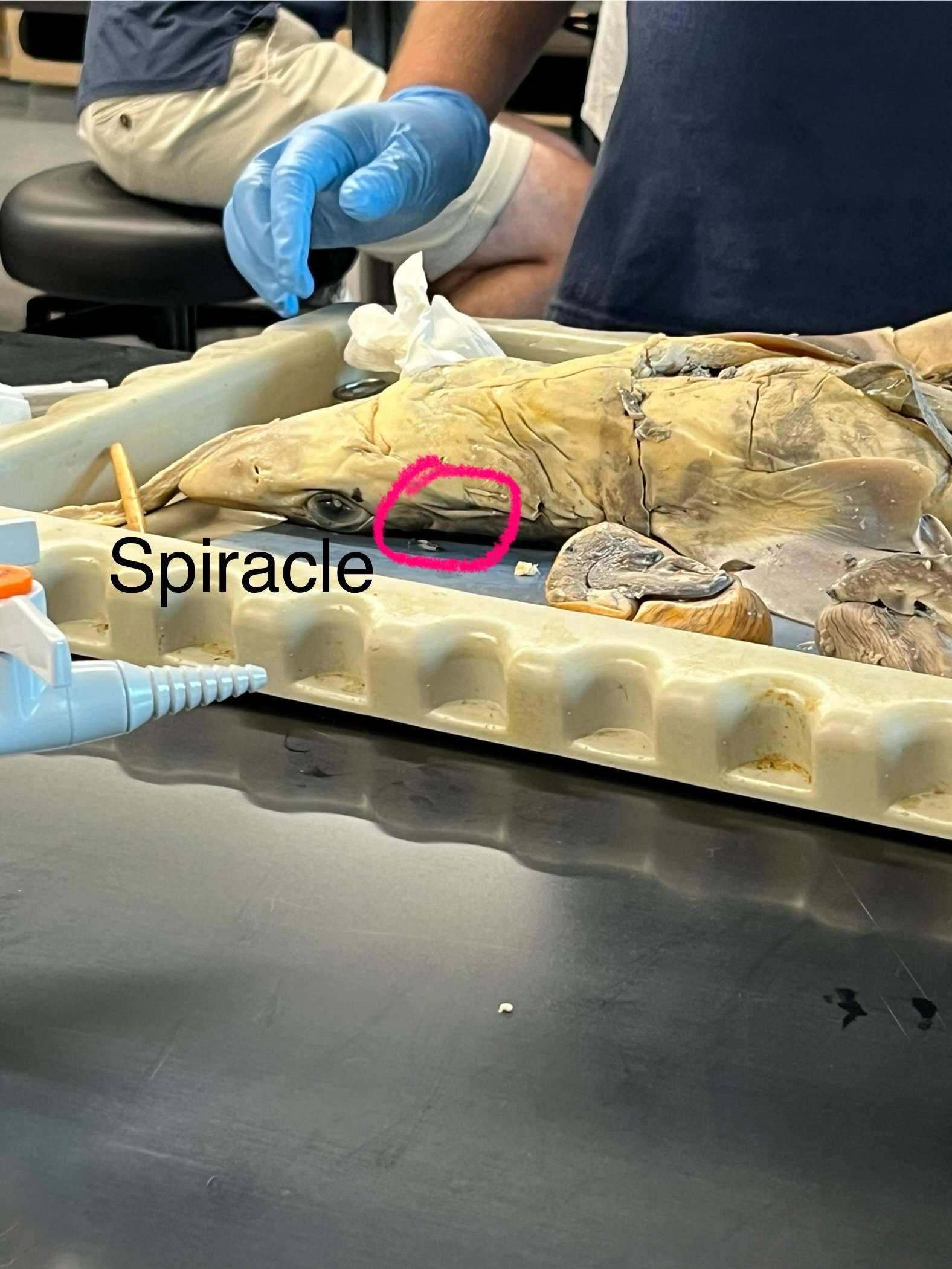
Where is the shark’s spiracle? What does it do?
It is behind the eye, and allows water to flow over the gills more easily.
How many generalized types of swimming are recognized among fishes?
12
What part of the body do subcarangliform body type fish (salmon, cods) use to power propulsion?
The posterior half
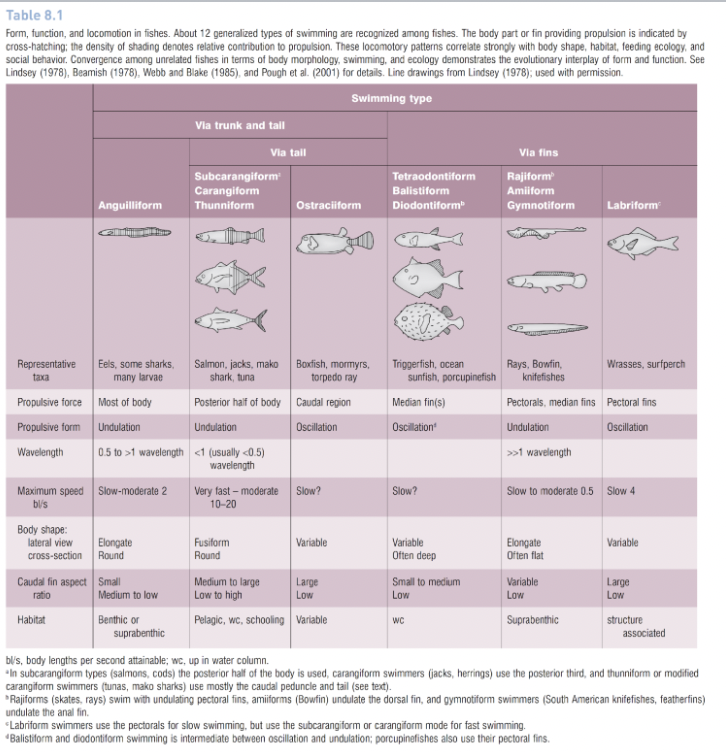
What part of the body do caringiform (jacks, herrings) swimmers use to power propulsion?
The posterior third of the body
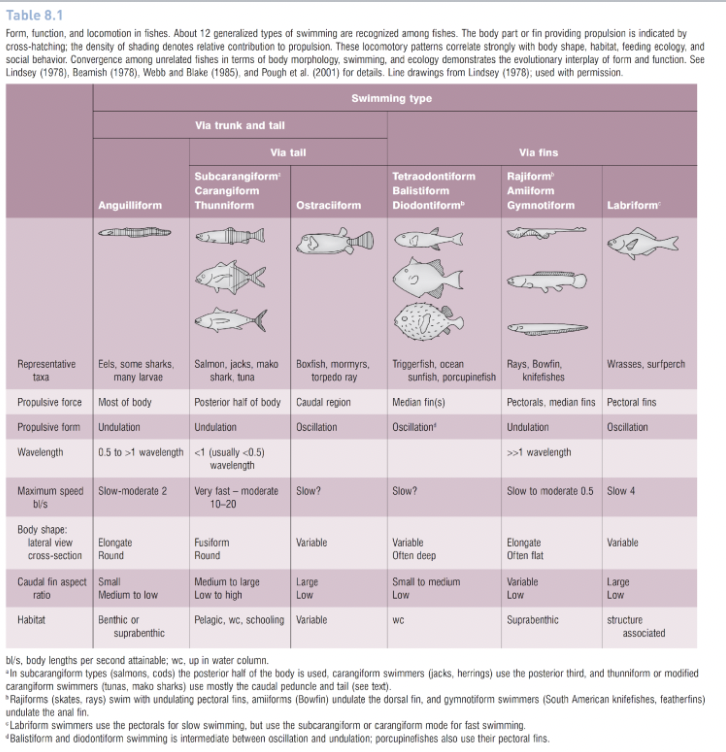
What part of the body do thunniform or carangiform modified swimmers (tunas, mako sharks) use to power propulsion?
The caudal peduncle and tail
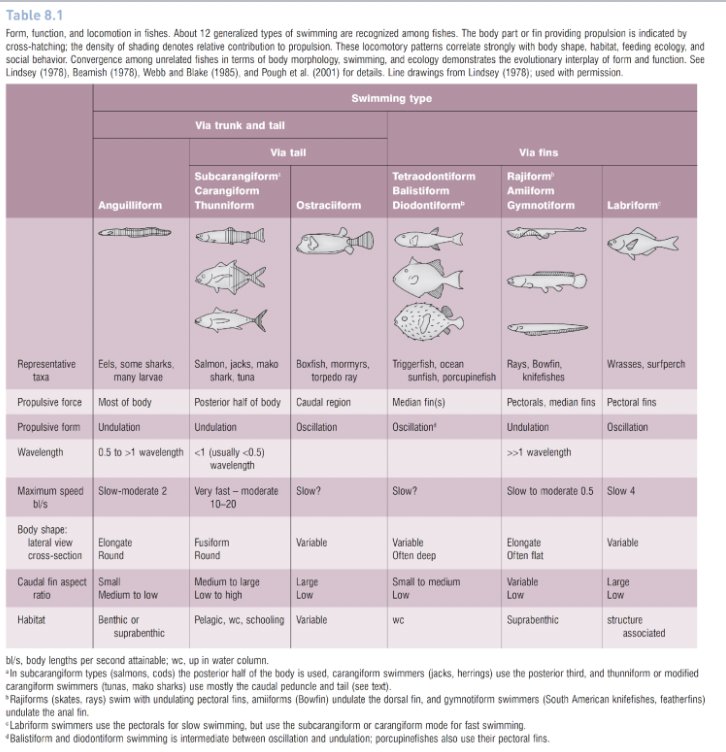
How to gymnotiform swimmers (south american knifefishes, featherfins) power their propulsion?
Undulation of the anal fin
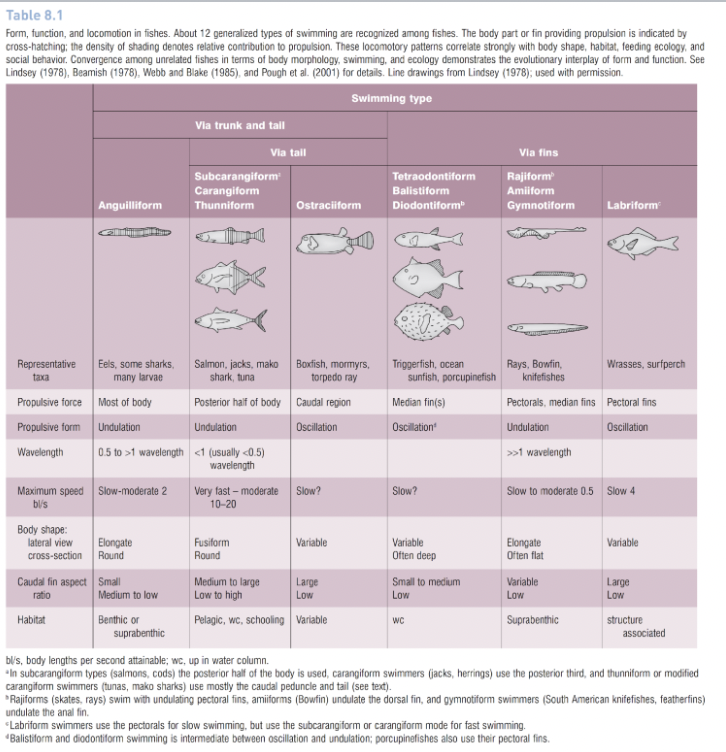
What part of the body do anguilliform (eels, some sharks, larvae) organisms use to power propulsion?
Most of the body.