Pompeii and Roman Urban Structures
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
What happened to Pompeii
After the volcanic eruption the entire city became covered in a layer of concrete by the volcanic ash
Most escaped but left everything behind
Pompeii city walls
High, strong
Had houses and shelter
Had graffiti
Pompeii walls and graffiti
Acted as a sort of message board almost
Latin was universal so high literary rate
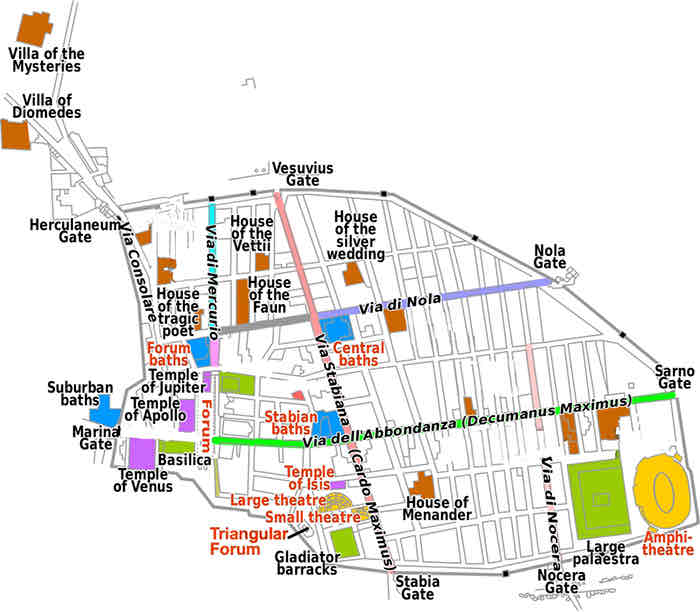
Pompeii city layout
Grid layout based on four main streets
Roman stepping stones
Used to avoid gross street, used to cross as a crosswalk, makes person more visible as well, controls traffic
Pompeii streets and traffic stones
High levels of traffic present, created groves into the stone street between the stepping stones
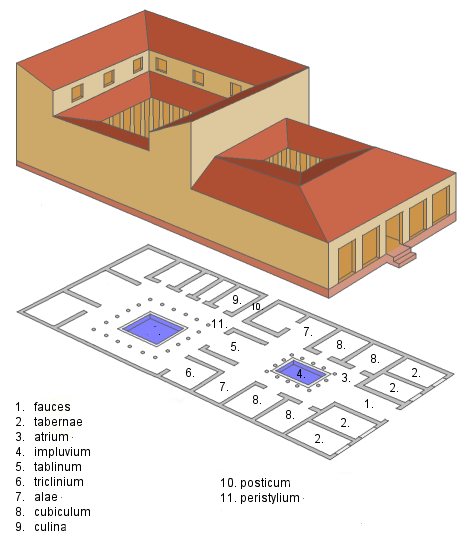
Typical Roman Domus
Yuh
Atrium
Living room/lobby space for guests, has a small shallow pool to collect rainwater from an opening above to cool the house.
Colorful fresco paintings on walls
Family shield would be present and cult statues
Domus
private family residence of
modest to palatial proportions,
found primarily in ancient Rome
and Pompeii.
Typical Roman house windows
Not very open to the street, few windows and opening facing it, second inner sector of home houses the family and has more windows
Insula
(Latin: “island”), in
architecture, block of grouped but
separate buildings or a single
structure in ancient Rome.
High rise apartment building
Middle/lower class
Sometime shops at lower level
Typical Roman bathhouse
Separated by gender and temperature of water, and by whether for bathing or sport activities.
Was for socializing, workout/sports as well
Outside areas may be separate shops attached to the same building
Frigidarium
Fold room cold water house
Many had painted fresco walls
Arches, vaulted dome ceiling w/ oculus at top
Oculus
a round or eye-like opening
or design, such as a circular
window or an opening at the apex
of a dome-
Pompei forum
large open space in city
Sanctuary space, courtyard
Separated from urban
Pompeii forum plan
Has multiple temples, one to the emperor (temple of vespasian)
Voting,government building
Very organized
Important center for civic life
Often two stories (Pompeii was)
Doric order post and lintel system of colonnades
Pompeii basilica
Separated from rest of city
Peripteral design
Business purpose + meetings + trade negotiations + economic hub = civic hub