Membrane and Action Potentials
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
Membrane Potential
• Voltage measured across the plasma membrane (-50mV - 100mV)
• Difference in electrical charge between inside and outside of a cell
Membrane Structure
• Phospholipid bilayer, proteins
• Lipids – phospholipids, glycosphingolipids, sterols
• Proteins - pumps, channels, receptors, enzymes, markers, structural components
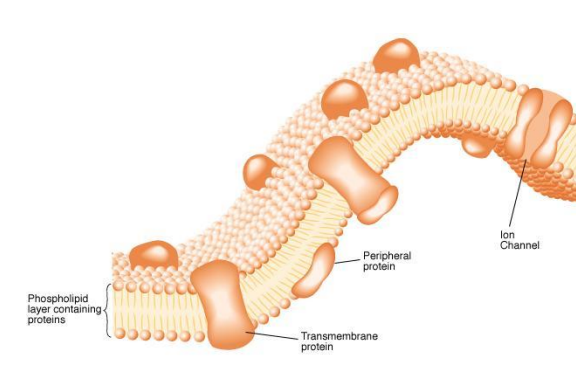
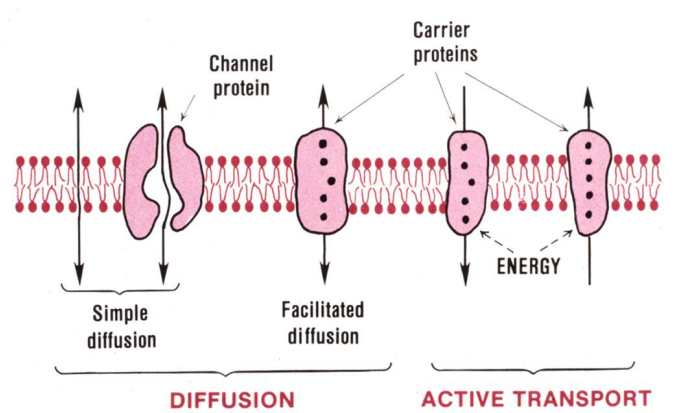
Types of transport
Active transport: needs energy
Diffusion/passive transport
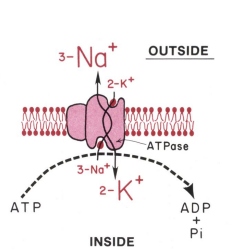
Sodium-Potassium Pump
• Creates membrane potential by unequal movement of charge
• Uses ATP to move 3 Na+ out for every 2 K+ ions in
Resting Membrane Potential
• Typical membrane potential -70mV
• Balance of intracellular and extracellular ions dictate membrane potentials
Ions important in neural signals
– Na+ , Cl- , and Ca2+ have inward gradient » greater concentration outside cell
– K+ has outward gradient » greater concentration inside cell
Nernst Equation
• Calculates equilibrium potential for each ion based on its concentration gradient
• Difference between equilibrium potential and membrane potential is net gradient for that ion
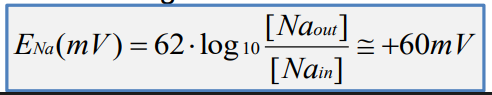
Goldman Equation
• Goldman constant field equation gives predicted membrane potential based on concentration gradients for principal permanent ions
• p = relative permeability for each ion (other ions e.g. Calcium are essential impermeable in an unstimulated neuron)
• Position of positive and negative ions due to opposite effects on membrane potential
• At rest, K most permeable (pK=1.00), with pCl=0.45 and pNa=0.04.
Hence: E (mV)=-67.4 mV
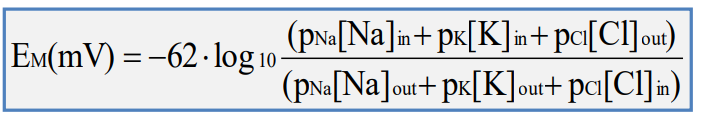
Resting Membrane Potential Summary
• Changes in [K+ ] cause most changes in EM because it is most permeable
• Since K+ is actively transported and is most permeable, its concentration is most important in determining EM at rest
• If an ion becomes more permeable, EM will change towards that ion’s equilibrium potential
– high permeability of one ion reduces equation to Nernst equation for that ion
Action Potential
• Needs a stimulus
• Short-lasting event, all-or-none, travels in one direction
• Occurs in excitable cells
• Neurons summate synaptic inputs to a threshold
– Threshold may be 10-25 mV depolarization above the resting potential
Voltage-gated Channels
• Voltage-sensitive Na+ and K+ channels alter the membrane potential
– Depolarization (inside of cell becomes less negative)
– Na+ channels open but do not stay open very long
• Na+ influx depolarizes the membrane even more
– K+ channels open slowly and remain open until EM returns to normal, then slowly close
• K+ efflux causes hyperpolarization
– Number of open channels can be measured as membrane conductance for each ion
• Larger stimulus will open more channels and result in larger change in membrane potential
Phases of an Action Potential
• Rise and fall of action potential due to Na+ and K+
– Na+ channels rapidly open, increasing pNa and changing EM towards ENa
– Membrane potential depolarizes
– Membrane potential reverses (overshoot)
– Na+ channels rapidly close (inactivate) at same time as K+ channels open
– EM changes towards EK , hyperpolarized relative to membrane potential at rest
• At rest, membrane is most permeable to K+ , least to Na+
• At peak, Na+ permeability rises
• Na+ channels open and close rapidly
• K+ channels take longer to open and close
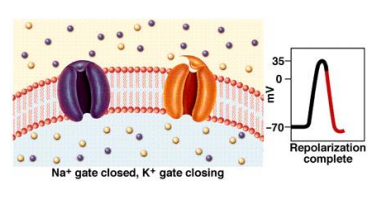
Refractory Period
occurs due to inactivated Na+ channels and hyperpolarization
Cells will not be stimulated → all Na+ channels closed after reaching peak positive potential
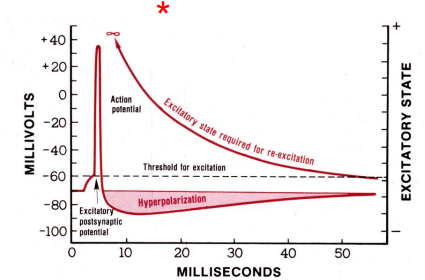
Refractory period (Relative and Absolute)
– Absolute refractory period – no amount of stimulation can trigger another action potential
• action potentials unidirectional (forced to go in the forward direction)
• axon before AP in refractory state
• axon ahead of AP has not been stimulated yet
– Relative refractory period – stronger than normal stimulus is required to stimulate an action potential
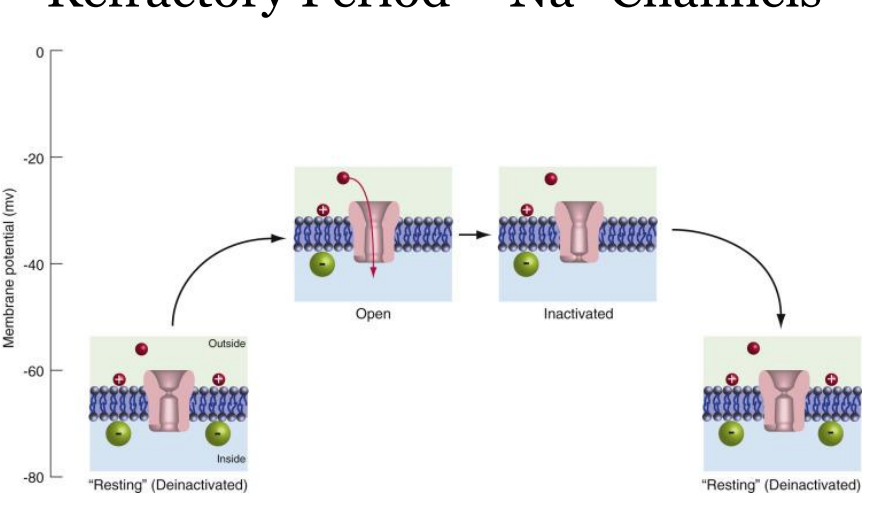
Action Potential Propagation - Passive conduction
a) Distance related to axon diameter and membrane resistance
b) To enhance speed, axon is covered in myelin except at Nodes of Ranvier
c) An action potential at one of the nodes will increase the membrane potential resulting in other action potentials upstream and downstream. (saltatory conduction)
d) The upstream node will not depolarize because it is in its refractory phase
e) The downstream node will reach threshold and an action potential will occur
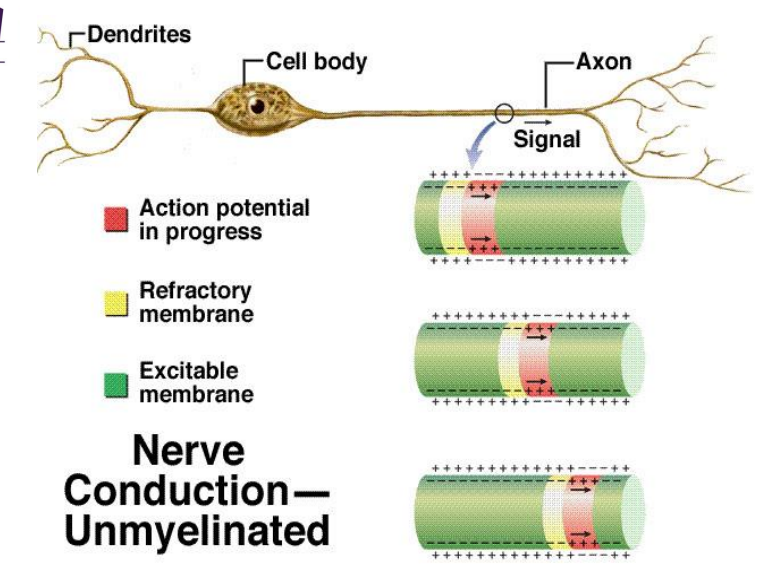
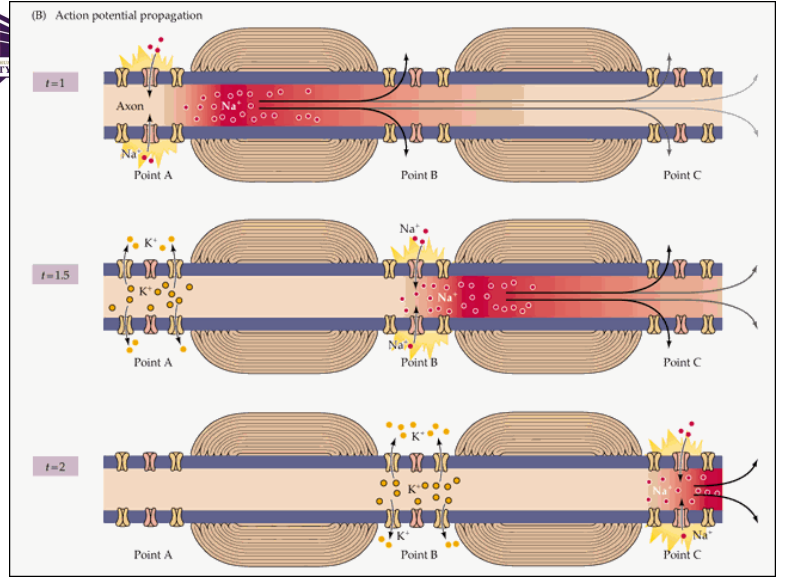
Saltatory conduction
Action potentials ‘jumps’ from one node to the next
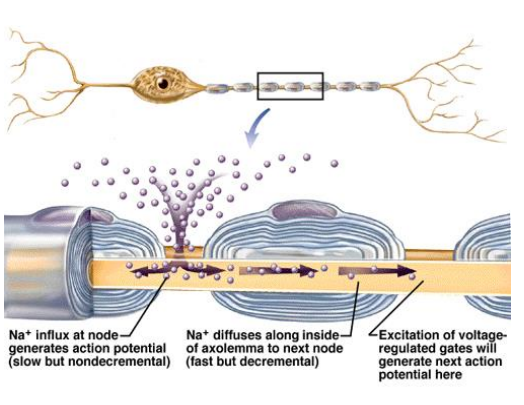
Clinical Example of Action Potential Propagation- Multiple Sclerosis
Autoimmune disease that affects CNS oligodendrocytes (glial cells that form myelin sheath)
In initial phases, see reversal of symptoms then get worse with each attack
– Caused by demyelination of axons
• Compromises action potential propagation
– Symptoms: neurological deficits
• Monocular blindness (lesions in the optic nerve) → myelinated, so affected
• Motor weakness or paralysis
• Double vision (lesions of medial longitudinal fasciculus) cranial nerves (oculomotor, abducens. trochlear)