AP Euro - Time Period 1: Unit 1 - 2
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

62 Terms
Great Famine
1. A terrible famine in 1315-1322 that hit much of Europe after a period of climate change
2. An effect of the Little Ice Age, cooling that happened at the beginning of the 14th century
3. Led to lower grain production, higher prices, and ant-Semitism
Black Death
1. A deadly plague that swept through Europe between 1347 and 1351
2. Ultimately lead a loss of 1/3 of the European population, significantly decreasing the supply of labor
3. People's view of religion became more personal and anti-Semitism continued
Flagellants
1. People who believed that the plague was God's punishment for sin and sought to do penance by flagellating (whipping) themselves.
2. They thought they were simulating the suffering of Jesus and would therefore help ease the punishment, but in reality their actions helped spread the plague
3. They are an example of religious extremism developing during tough times, to these day we still see extreme political and religious movements pop up when there are tough times
Hundred Years War (1337-1453)
1. Series of campaigns over control of the throne of France, involving English and French royal families and French noble families.
2. Resulted in England and France gaining little and settling for the idea that a unified Europe (Like the Roman Empire) may not be attainable
Joan of Arc (1412-1431)
1. Grew up in peasant family; very religious. Claimed that God told her that she was to free France and ensure coronation of dauphin Charles VII; gets army form him
2. At age 17 she inspired rescue of the city of Orleans from siege in 1429 (turning point of war) and restored French sprit and confidence, a significant turning point in the Hundred Years War
3. Captured by Burgundians (ENG allies); tried as witch and burned at stake but slowly France reclaimed land and war finally ended in 1453
Great Schism (1378-1417)
1. A conflict in the European Church where there were 2 popes all fighting for power, one in Avignon, France and another in Vatican City in Rome.
2. The split brought the church into major conflict and weakened the religious faith in the church
Jan Hus
1. The leader of the Czech Hussite movement, and the spiritual founder of the Protestant reformation in the 1500's
2. Argued the supremacy of the Bible over clergy
3. He was convicted for heresy and burned at the stake
English Peasant Revolt (1381)
1. A prominent uprising in 1381 against monarchy's imposed taxes upon the peasant population
2. Richard II (boy-king) made false promises to pacify the peasants
3. While the revolution doesn't change much it does make the aristocracy more careful of taxation and forces them to recognize the influence of the peasants
Divine Comedy
1. Book by Dante Alighieri, describes soul's progression into heaven
The Decameron, Boccaccio
1. A collection of 100 stories told by 10 friends who are trying to hide from the Black Death. 2. Very modern, very scandalous stories.
Canterbury Tales
A collection of stories written in Middle-English by Geoffrey Chaucer at the end of the 14th century. The tales are told as part of a story-telling contest by a group of pilgrims as they travel together on a journey .
Vernacular
Everyday language of ordinary people
Renaissance
1. "rebirth"; following the Middle Ages, a movement that centered on the revival of interest in the classical learning of Greece and Rome
2. Influenced by the Crusades and Christians interacting with Muslims in the middle east and bringing back classical (Rome and Greece) ideas
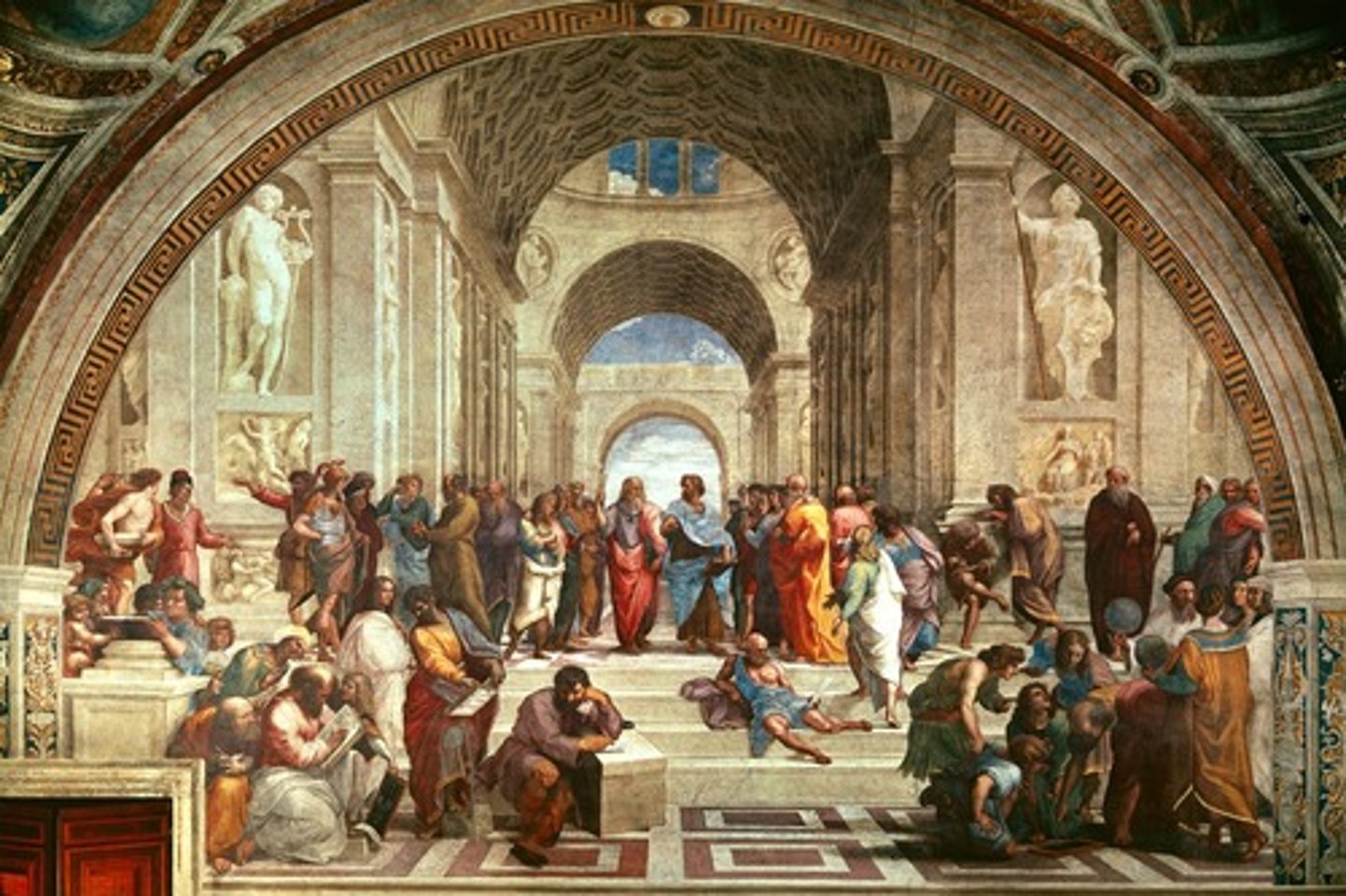

Humanists
1. A Renaissance movement focused on human dignity
2. broke from scholasticism, which focused on religion and focused on God
3. focused on secular (non-religious) pursuits
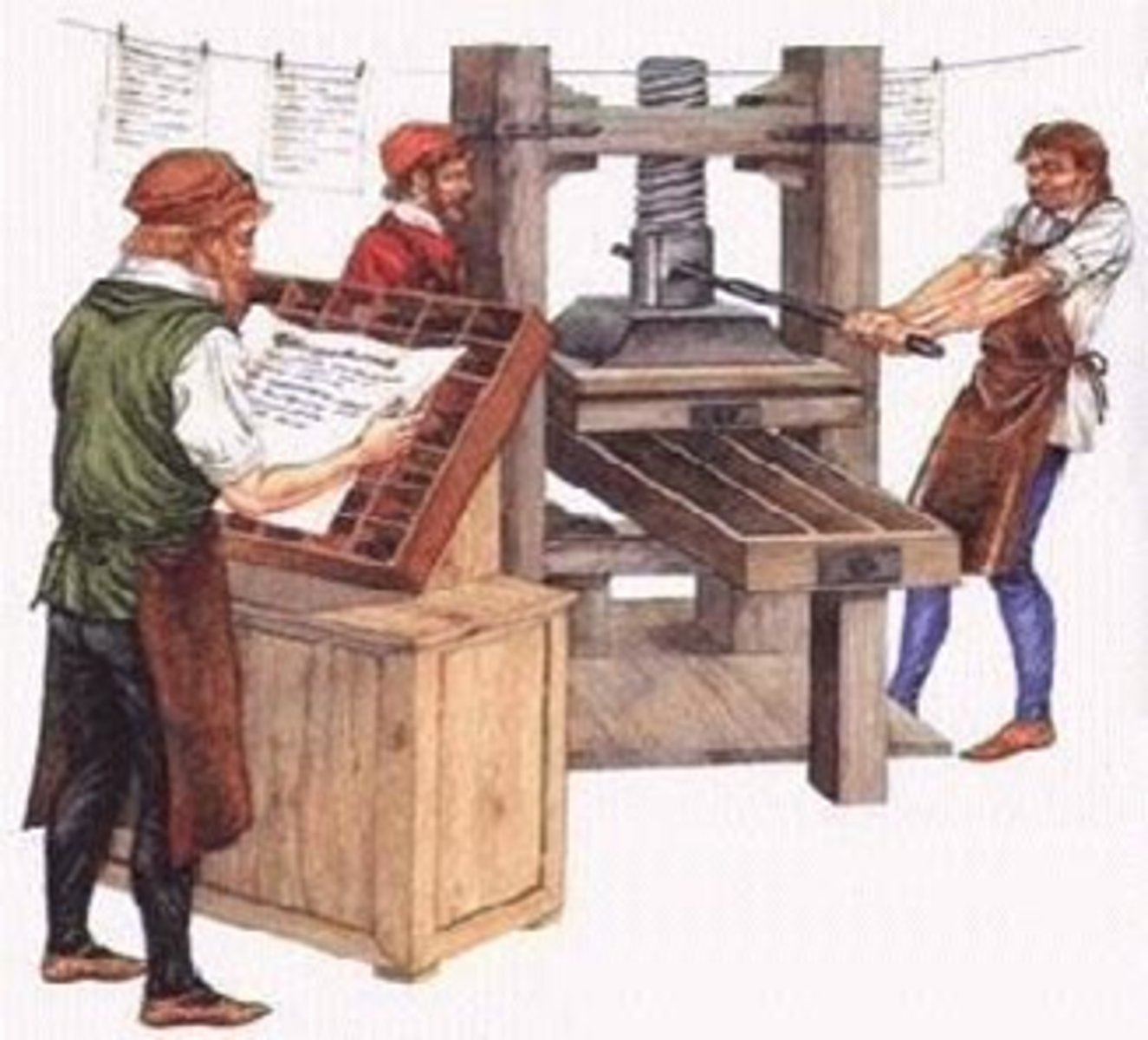
Printing Press
1. 15th century invention, using moveable type, which revolutionized the ability to print information which in turn affected the speed of the spread of information itself.
2. Invented by, German, Johannes Gutenberg
3. One of the first books printed using the printing press and moveable type was the Gutenberg Bible, allowing for more people to own a Bible and giving direct access to the Christian Holy Book
Commercial Revolution
1. A dramatic change in the economy of Europe at the end of the Middle Ages. It is characterized by an increase in towns and trade, the use of banks and credit, and the establishment of guilds to regulate quality and price.
2. Largely driven by Northern Italian city-states of Venice and Florence. Overseas trade lead to an increased demand for foreign goods.
3. Many of the wealthiest families from this period financed the art of the Renaissance at patrons, like the Medici Family of Florence
Vernacular Literature
1. Literature written in the everyday language spoken by common people
2. During the Renaissance there was a move away from the writing of books in the formal language of the church, Latin, to local vernacular
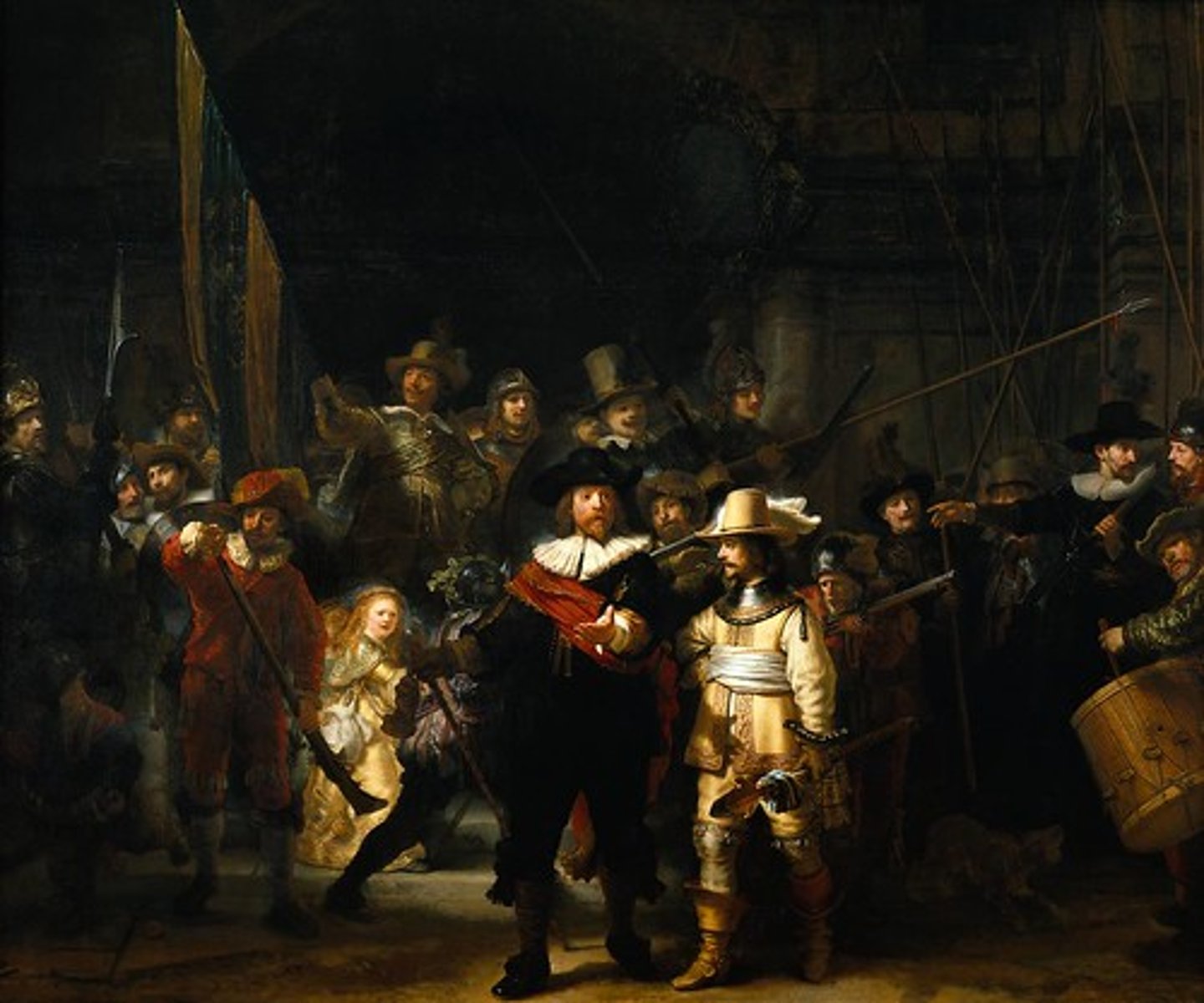
Baroque
1. An artistic style that created Bold, dramatic, and complex. It leaves realism and has a more exaggerated look.
2. Rembrandt's Night Watch is a popular example of Baroque Art

The Prince
1. A book wrote by Niccolò Machiavelli in 1513 about the imperfect conduct of humans and says how a ruler is able to keep power and manage to keep it disregarding enemies.
2. The book is a clear move away from religious morals and the basis for tyrannical leadership in the centuries to come
Leonardo DaVinci (1452-1519)
1. Scientist, inventor, mathematician, engineer, artist - considered the ideal Renaissance Man
2.An artistic master with two of the most famous paintings ever, Mona Lisa and The Last Supper
3. His many fields of study lead to greater depth in his art, he was one of the first Europeans to keep record of cadaver dissections - using the knowledge to create more realistic images in his art
Italian Masters (Artists)
1. The famous painters of the Italian Renaissance including Donatello, Raphael, Leonardo di Vinci, and Michelangelo
2. They create many of the most famous artwork of the Renaissance
3. They are heavily financed by major patrons of the Renaissance like the Medici and the Church
Northern Renaissance
1. An extension of the Italian Renaissance to the nations Germany, Flanders (Belgium/Netherlands), France, and England
2. Two of the most famous artist of the Northern Renaissance are Jan van Eyck and Rembrandt
3. They are known for leaning in even more to humanism than Italian painters and focusing on more daily / domestic life
Erasmus
1. A leading figure in the Christian Humanist movement along with Thomas More
2. His work, "In Praise of Folly," satirized (criticized) the corruption in the Church
3. His work will heavily influence the Reformation (the protest against the Church)
New Monarchies
1. Monarchies that emerged that differed from their medieval predecessors in having greater centralization of power
2. Defined political boundaries that are more similar to the England, France, and Spain of today than in the Middle Ages
English Reformation
1. Henry VIII breaks from the Catholic Church and creates the Anglican Church as part of his attempt to separate from Catharine of Aragon and marry Anne Boleyn
2. Act of Supremacy - King taking control of the church in England assuming its wealth but kept much of the norms of the Catholic Church and some reform like an English Bible
3. The top down approach different than the reformation in the rest of Europe, led to less social upheaval, but more political change
Ferdinand and Isabella of Spain
1. During the late 15th century, they became King and Queen of a united Spain
2. Complete the Reconquista to expand their power by eliminating Islamic Granada and use the Spanish Inquisition to consolidate Christian influence in Spain
3. Patrons of Columbus, benefit from the discovery and colonization of New Spain
Mercantilism
1. An economic policy under which nations sought to increase their wealth and power by obtaining large amounts of gold and silver and by selling more goods than they bought
2. System used by Portugal and Spain to obtain wealth from colonies in the Age of Exploration
Gold, God, Glory
1. Motivations for European Exploration
2. Driven by trade developed after the Crusades and the desire for goods from Southern and Eastern Asia
3. Caused by mercantilism and result in increased wealth in Europe and the spread of Christianity
Treaty of Tordesillas (1494)
1. Signed by Spain and Portugal, dividing the territories of the New World.
2. Spain received the bulk of territory in the Americas, compensating Portugal with titles to lands in Africa and Asia.
Columbian Exchange
1. The widespread transfer of plants, animals, culture, human populations, technology, and diseases between the Americas and the Old World following Columbus's voyages.
2. Lead to the plantation system, slavery, and European colonial expansion
3. Lifestyles of Europeans were transformed due to increased nutrition and an influx of wealth
Portuguese Exploration
1. First European power to explore the Atlantic and helped establish the shift of power from the Mediterranean to the Atlantic.
2. Henry the Navigator, was a Portuguese royal who significantly advanced maritime exploration and established a school for navigators in the 15th century.
3. They establish forts on the West Coast of Africa, the Gold Coast, that become significant to slavery and establish a trade route around Africa,
Plantation System
1. Large agricultural estates established in the Americas, used to produce cash crops, used enslaved labor, and benefitted the Mercantile System
2. Through the Treaty of Tordesillas Portugal established lucrative sugar plantations in Brasil
Vasco da Gama
1. A Portuguese explorer who was the first to sail directly from Europe to India
2. This significantly impacts the spice trade and leads to Portugal establishing a port in Malacca in the Spice Islands
Triangle Trade
1. A transatlantic trading system that involved the exchange of goods and enslaved people between Europe, Africa, and the Americas.
2. The exchange from Africa to the Americas was the Middle Passage - The horrific sea journey undertaken by enslaved Africans
3. The trade strengthened the plantation system and benefitted European powers through the Mercantile System.
Commercial Revolution
1. A period of European economic expansion, colonialism, and mercantilism from the 11th to the 18th centuries, marked by the rise of capitalism.
2.
Capitalism
An economic system characterized by private ownership of the means of production and the creation of goods for profit.
Joint-Stock Companies
Business entities where multiple investors pooled resources to fund trade and colonization ventures, sharing profits and risks.
Double-Entry Bookkeeping
An accounting method that tracks both sides of a transaction, allowing for better financial management in growing businesses.
Enclosure Movement
The process in England of consolidating small landholdings into larger farms, leading to increased agricultural productivity but also rural poverty.
Subsistence Agriculture
A farming system where farmers grow enough food to feed themselves and their families, with little surplus for trade.
Martin Luther
1. A key figure in the Protestant Reformation who challenged the Catholic Church's practices, particularly the sale of indulgences, and emphasized salvation through faith alone.
2. His intent was to reform, not break away from the Church but he started a movement that would break away
95 Thesis
1. A document written by Martin Luther that criticized the Catholic Church's practices, particularly the sale of indulgences, and called for reform.
2. He was inspired by Pope Leo X trying to raise money for the building of St. Peter's Basilica through indulgences
3. He also felt the Church's teachings and practices were moving away from what was taught in the Bible
Indulgences
1. A practice in the Catholic Church where forgiveness for sins could be purchased
2. This practice started when the Church offered indulgences to soldiers for fighting in the Crusades
3. The abuse of selling indulgences, including sometimes fake indulgences is what inspired Martin Luther to act
Sola Scriptura (Scripture Alone)
1. The doctrine that the Bible alone is the ultimate authority in matters of faith and practice
2. One of Luther's main criticisms of the Church is that they had moved to far from the teachings of the Bible (scriptures)
3. One of the focuses of most protestant groups will be to bring followers closer to the Bible, often by printing it in common vernacular
Diet of Worms (1521)
1. An assembly where Martin Luther was asked to recant his writings but famously refused, stating, "Here I stand, I can do no other."
2. This along with a debate between Luther and Church scholars in 1519 starts to set a protestant break from the Catholic Church
3. Charles V declared Luther an 'outlaw of the empire' but allowed him to escape back to a castle under the protection of the Prince of Saxony - an elector of the Holy Roman Emperor
Calvinism
1. A branch of Protestantism founded by John Calvin that emphasized predestination and the sovereignty of God in salvation.
2. Predestination is the belief, particularly associated with John Calvin, that God has already determined who will be saved and who will be damned.
Anabaptists
1. A radical Protestant group that advocated for adult baptism and a separation from state affairs, often facing persecution from both Catholics and other Protestants.
2. The Amish are a modern example of this group
Peace of Augsburg (1555)
1. A treaty that allowed German princes to choose whether their territories would be Catholic or Lutheran, but did not recognize Calvinism or Anabaptism.
2. Prevented conflict between the Holy Roman Empire (Favored Catholicism)and the Schmalkaldic League (Protestant Alliance)
3. Caused by the Holy Roman Empire being ground zero for the Protestant Reformation and Charles V needing to keep his princes (electors) happy
French Wars of Religion
1. Wide spread killing of the Huguenots (French Calvinists) in events like the St. Bartholomew's Day Massacre driven by Queen Mother, Catherine de' Medici
2. Civil War lead to Henry IV, a Huguenot taking the throne
3. Edict of Nantes (1598) - A decree by Henry IV of France that granted religious toleration to Huguenots, allowing them to worship freely in certain areas, which is undone by Henry's assassination
Catholic Reformation (Counter Reformation)
1. a 16th century movement in which the Roman Catholic Church sought to make changes in response to the Protestant Reformation
2. Jesuits - A religious order founded by Ignatius Loyola in 1540, known for its missionary work and educational efforts, playing a significant role in reforming the Catholic Church
3. Council of Trent (1545-1563) - A series of meetings that addressed Church reforms and reaffirmed Catholic doctrines in response to the Protestant Reformation.
Thirty Years War (1618-1648)
1. A series of conflicts in Europe primarily involving religious disputes between Catholics and Protestants, leading to significant political and social upheaval.
2. Peace of Westphalia - The 1648 treaties that ended the Thirty Years' War, recognizing the sovereignty of states and allowing for religious pluralism in Europe.
Baroque Art: Purpose & Context
1. during Catholic Counter Reformation
2. want to reenergize faithful and stop spread of Protestants and Council of Trent reaffirm works of art should stimulate piety
3. want dramatic works that involve worshippers
Baroque Art: Characteristics
1. dramatic use of light and dark and focus on dramatic moments
2. portrayal of everyday people not idealized
3. Baroque buildings feature grandiose scale and ornate decorations
Thirty Years War (1618-1648): Religious Divisions
1. Growing Calvinism
2. Peace of Augsburg didn't provide for recognition of Calvinists
3. Protestant Union formed = defend their interests
4. Catholic League formed = defend their interests
Thirty Years War (1618-1648): Political Divisions
1. Austrian Habsburgs = want reverse Protestants & build stronger monarchy
2. German princes and independent cities = want resist attempts Catholics centralize power
3. France (Richelieu) = oppose a Habsburgs/strong power in Germany = even though France Catholic--ally with Protestant princes
4. Lutheran kings in Denmark and Sweden = defend Protestant interests in HRE and spread power and influence
Thirty Years War (1618-1648): Peace of Westphalia
1. Rulers allow decide religious faith = Calvinism included
2. German States receive right to conduct diplomacy and make treaties
3. Independence of Dutch, Independence of Switzerland
4. France annex part of Alsace
5. Sweden gain territory around Baltic Sea
Thirty Years War (1618-1648): Effects
1. devastated German economy and population. Germany's long term commercial growth suffered
2. left Germany fragmented and delay German unification for two centuries
3. France = emerge as strongest power & weaken Habsburgs and keep HRE weak and divided
Cardinal Richelieu
1. (1585-1642) Minister to Louis XIII. Brought them into 30 Years War = political reasons, funded Sweden in the 3rd Phase of the war
2. Increased the power of France and reduce power of Habsburgs (Austria/Spain)
3. Break the power of the nobility, helped to send France on the road to absolute monarchy.
Military Revolution
during 30 years war,
--there was an increase in firearms & canons; greater mobility in tactics; better trained armies
--financed by heavier taxation and larger bureaucracy
--tip balance of power to states with sufficient resources for new military environment
Witch Trials
1. Accusations of witchcraft, peaked between 1580-1650, happening most often in places where the Reformation was most common
2. 75% of accusations occurred in the Holy Roman Empire (Germany) and 80% of the accused were women
3. Approximately 40,000 people were executed and 200,000 were arrested and tortured
Patriarchal Society
1. Male dominated government and private lives
2. Dowry - Property or gold given from a brides father to the groom as part of the marriage arrangement. During this period women gain more control over their dowry like the right to sue their husbands if it is misused or to retain the property if their husband dies
3. Primogeniture - The idea that everything that is left for the oldest son when the father dies. Because of a developing market and guild system younger sons now had more opportunities to succeed than ever before.
La Querelle des Femmes (The Woman Question)
1. Debate over the nature of women and their place in universities, often referring back to the story of Adam and Eve, and largely debated by men
2. One side debated that women were naturally inferior to men and could not learn while the other side cited the oppression of women by men and that freeing them of that oppression would help them contribute
3. This debate was caused by the Reformation and use of vernacular, opening up a greater opportunity and demand for education