Kinesiology Unit 3 Exam
1/264
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
265 Terms
Early in life, child needs _-_ months to learn to stand and walk
11-15
Age _-_ resembles adult walking
4-5
Visual gait analysis
easy, doesn't require any tools or equipment, but eyes can't detect high-speed movements. Joint kinematics and forces not measured. Difficult to track improvements without measurements; requires proficient clinical skills.
Video-based analysis
Requires recording device, allows slowing down and replaying of footage to assess motion. Kinematics may be assessed (accuracy depends on camera placement), but doesn't provide force or muscle activity information. Can be used for patient education and pre-post comparisons.
Gait cycle
Beginning of a walking event by one limb and continuing until the event is repeated with the same limb
(i.e. time from heel strike to next ISPILATERAL heel strike)
Stride
one complete gait cycle (right step + left step)
Step
beginning of an event of one limb until the beginning of same event of contralateral limb
Stride length
distance between successive heel contacts of same foot
Step length
distance between successive heel contacts of the two different feet
Step width or BOS
lateral distance between the heel centers of two consecutive foot contacts
Step width decreases as _ increases
cadence
Foot angle
amount of toe-out (~5-7º)
Cadence/Step rate
number of steps per minute
(walking: 110-120 steps/min)
Speed
step rate * step length or distance / time
-usually described in m/sec or mph
For a given limb, stance is _% of gait cycle
60%
For a given limb, swing is _% of gait cycle
40%
Initial contact (heel strike):
when foot touches ground
Loading Response (foot flat)
between initial contact and beginning of other leg swing
Mid stance
when other foot off floor until body directly over stance limb
Terminal stance (heel off)
when heel of stance limb rises to other foot touching ground
Pre-swing (toe off)
when other foot touches ground and stance foot reaches toe off
Initial swing (acceleration)
when stance foot lifts from floor to maximal swing knee flexion
Mid swing (same)
from maximal knee flexion during swing to when tibia perpendicular to ground
Terminal swing (deceleration)
From when tibia perpendicular to floor to when foot touches ground
Functional tasks for each limb during the gait cycle
-Weight acceptance
-Single limb support
-Swing limb advancement
Speed can be increased by increasing
•Step length (A)
•Step rate (B)
•Or both
With faster walking speeds, a smaller percentage of gait cycle is spent in
double-limb support
Pelvis Sagittal Plane Kinematics
5º ant & post pelvic tilt
_ pelvic tilt during double limb support
Posterior
_ pelvic tilt during single-limb support
Anterior
Hip sagittal plane kinematics
30º flexion - 10º extension
Hip flexed ~__º at initial contact
30
As body moves over foot, hip extends to ~__º at toe off
10
Knee sagittal plane kinematics
60º flexion - 0º extension
Ankle sagittal plane kinematics
10º of DF - 20º of PF
At initial contact, knee is flexed _º and it flexes _-_º
5 degrees, 10-15 degrees
_º of knee flexion at toe off and maximal knee flexion (60º) at mid swing
35 degrees
Heel makes contact in slight
plantarflexion
After heel off, ankle PFs to
15-20º
During swing, the ankle
DFs to neutral to clear toes
Pelvis frontal plane kinematics
10-15º pelvis-on-femur hip adduction and abduction
During weight acceptance on Right, Left iliac crest initially _ before elevating (hip abduction)
drops (hip adduction)
STJ frontal plane kinematics at initial contact
Inverts 2-3º
STJ frontal plane kinematics at midstance
Everts to 2º
STJ frontal plane kinematics at toe-off
reverses direction to 6º inversion
Excessive frontal plane movement of the stance hip is
common
Possible reasons for excessive frontal plane movement at the hip
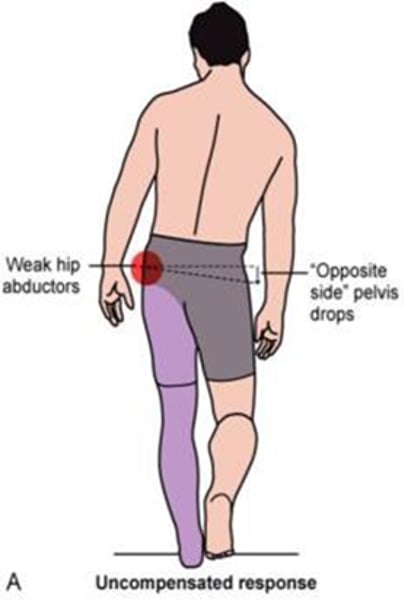
•Weakness of hip abductors --> contralateral hip drop
•Reduced "shortening" of the swing limb ---> contralateral hip hiking
•Limb length difference
During double-limb support, iliac crest of longer limb will be
higher
Initial 1/3 of stance phase generally characterized by
internal rotation of pelvis
Swing phase is primarily
internal rotation
Hip flexion needed for gait
0-30º
Hip extension need for gait
0-10º
Knee flexion needed for gait
0-60º
Knee extension needed for gait
0º
Ankle dorsiflexion needed for gait
0-10º
Ankle plantarflexion needed for gait
0-20º
CoM at lowest and most central position during
middle of double limb support (5 & 55% of gait cycle)
CoM at highest and most lateral position at
mid-stance of each limb (30 & 80% of gait cycle)
Energy expenditure during walking is lowest at
80 m/min (~1.3 m/s or 3 mph)
-which is normal walking speed.
Hip extensors control hip _ (via eccentric or isometric activity) and initiate hip _
flexion, extension
Hip _ control frontal plane pelvis movement
abductors
Hip flexors control hip _ at terminal stance and initiate hip _ in swing
extension, flexion
Knee extensors control knee _ and initiate knee _
flexion, extension.
Ankle dorsiflexors control ankle _ & initiate ankle _
plantarflexion, dorsiflexion
Ankle plantarflexors control ankle _ and initiate ankle _
dorsiflexion, plantarflexion
Ankle supinators (PF/Inv) control ankle _
pronation (especially when excessive pronation occurs)
Ankle pronators (DF/Ev) control ankle _
supination
Key muscle activity during initial contact
-ankle DF
-quads/hamstrings
-hip extensors
-abductors
Key muscle activity during loading response
-ankle DF
-quads
-hip extensors
-ankle PF to control DF
-posterior tibialis to control pronation
key muscle activity during midstance
-ankle PF (ecc)
-quads
-hip extensors
-hip abductors
Key muscle activity during terminal stance
-ankle PF (con)
-hip abductors
-hip flexors to control rate of hip extension
Key muscle activity during pre-swing
-peak ankle PF (con)
-hip flexors
Key muscle activity during initial swing
-ankle DF
-hamstrings to flex knee
-hip flexors
Key muscle activity during midswing
ankle DF
Key muscle activity during terminal swing
-ankle DF
-ankle invertors
-quads/hamstrings
-hip extensors
Peak vertical GRF
120% BW
Peak ant-post GRF
20% BW
Peak med-lat GRF
5% BW
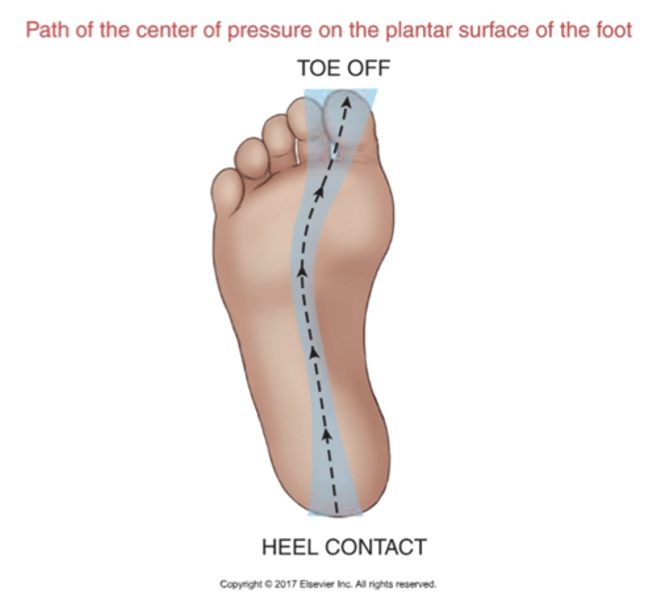
Path of the center of pressure (COP)
-Typically initial contact is on lateral heel so CoP just lateral to midpoint of heel
-moves toward lateral midfoot at midstance
-moves towards medial forefoot under 1st or 2nd MT head during heel-off to toe-off
External torques are resisted by
internal torques
Joint power formula
Net Internal Joint Torque (Nm) * Joint angular velocity (º/s)
Positive power
Energy generation = Concentric muscle activation and release of energy from stretched tissues
Negative power
Energy absorption = Eccentric muscle activation and stretching of passive tissues
During the early part of stance, line of action of GRF is
posterior to ankle and knee and anterior to hip.
Hip extensors are most active in which phases?
the 1st half of stance phase and terminal swing phase
Hip flexors are most active in which phases?
2nd half of stance phase and initial swing phase
Antalgic gait
-limp to avoid pain
-shorter step length and shorter stance phase on involved leg
Ataxic gait
Unsteady, uncoordinated, with wide base of support
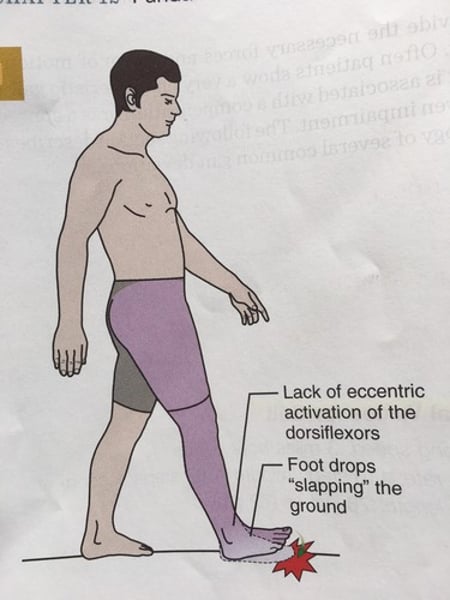
Foot slap
weak dorsiflexors, dorsiflexor paralysis
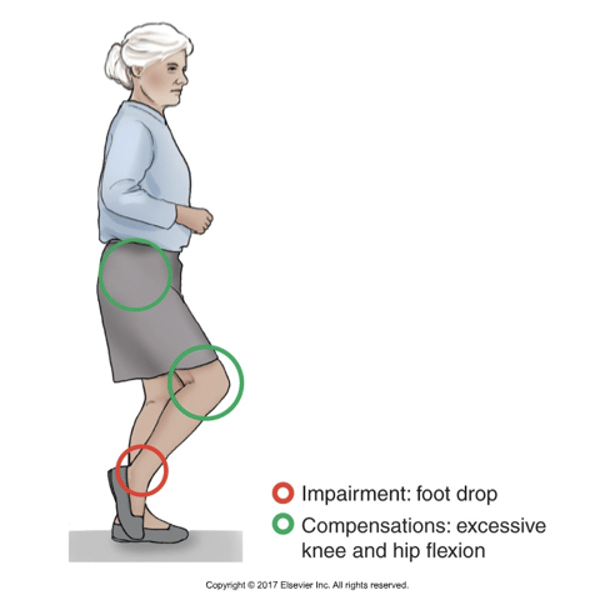
Steppage gait
-Excessive Hip and Knee Flexion to Compensate for Foot Drop
-Weak ankle dorsiflexion may result in foot drop during swing phase requiring excessive knee and hip flexion for the toes to clear the ground as the limb is advanced
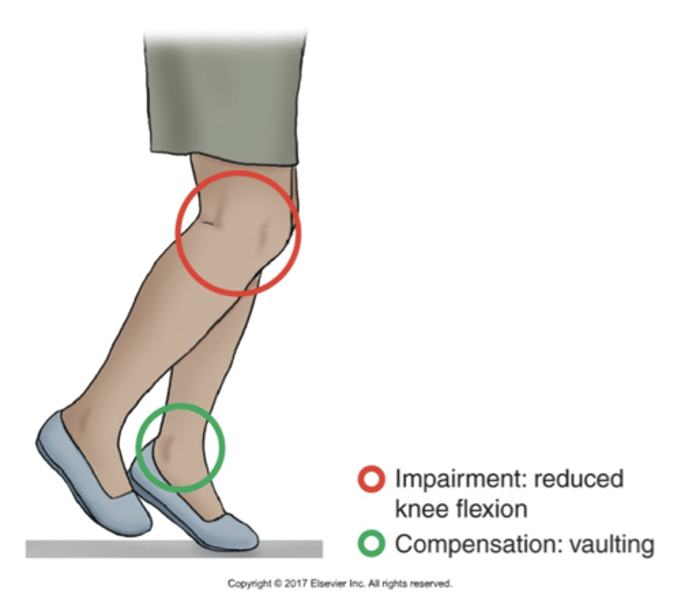
Vaulting gait
Vaulting through excessive plantarflexion of the unaffected stance limb is used to compensate for limited functional shortening of affective swing limb like when having a knee braced in full extension
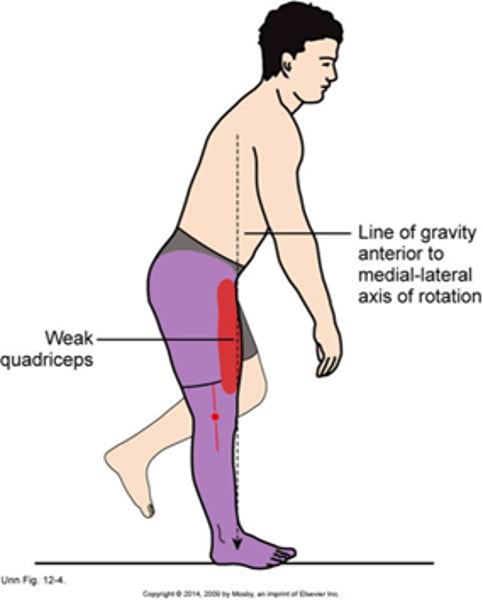
Weak quadriceps gait
•Excessive Anterior Trunk Bending to Compensate for Weak Quadriceps
•Weak quadriceps leading to anterior trunk lean to move the CoM of the body anterior to the axis of rotation of the knee
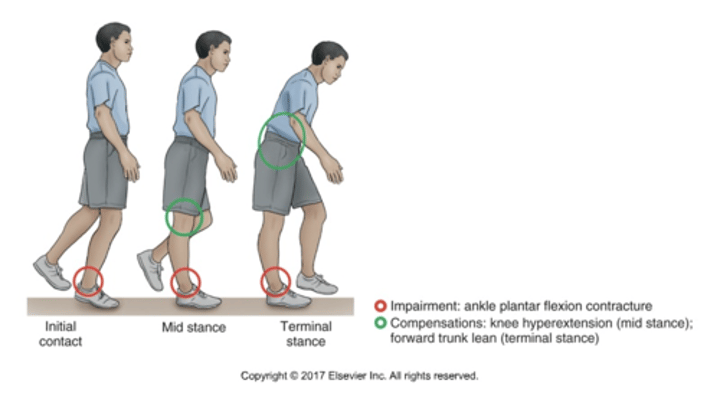
Genu recurvatum gait
•Knee Hyperextension and Forward Trunk Lean to Compensate for an Ankle Plantar Flexion Contracture (Pes Equinus Deformity)
Weak abductor gait
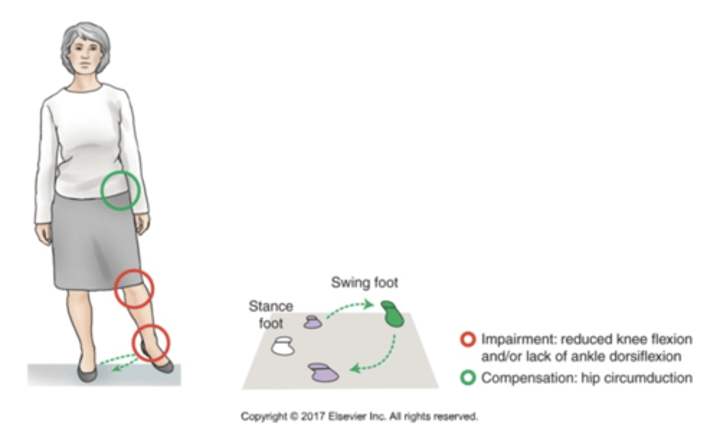
Hip circumduction gait
•Hip Circumduction During Swing Due to Inadequate Hip, Knee Flexion, Ankle Dorsiflexion
•Swinging leg out to the side compensates for inability to shorten the swing leg
•Elevating the pelvis (hip hiking) is a similar compensation
Crouched gait
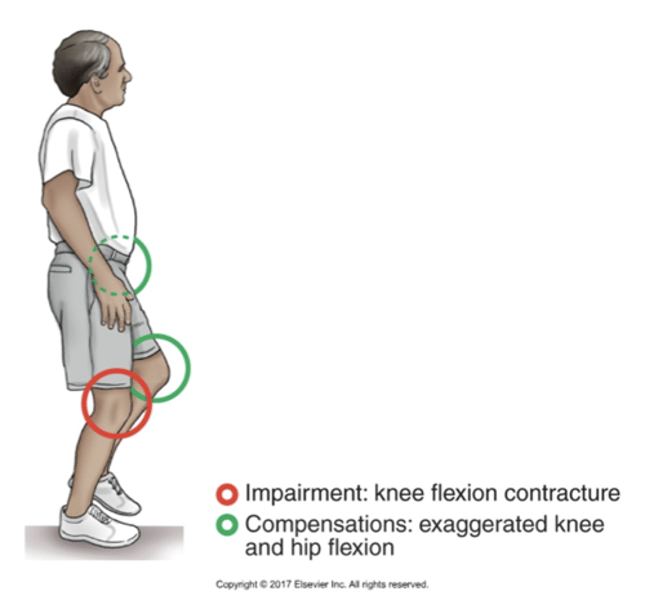
•Knee Flexor Contracture Causing a Crouched Gait of the Stance Leg
•To clear the toes during swing, the unaffected contralateral limb must compensate with exaggerated knee and hip flexion
Function of the vertebrae
•Provide stability
•Protects the spinal cord, ventral and dorsal n roots along with exiting spinal n roots.
Costocorporeal joint
head of a rib to pair of costal demifacets
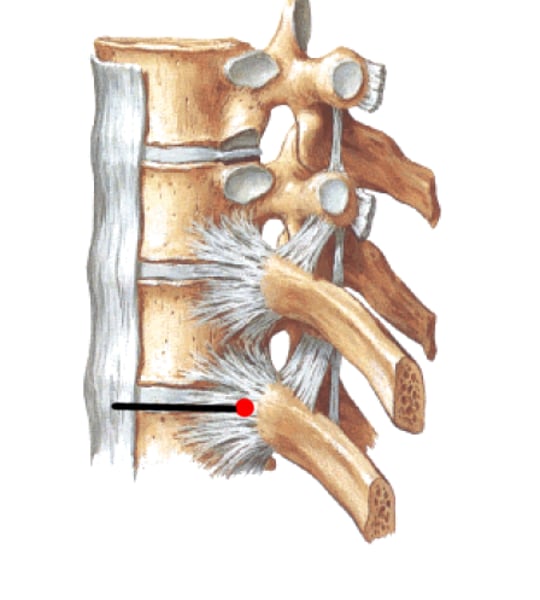
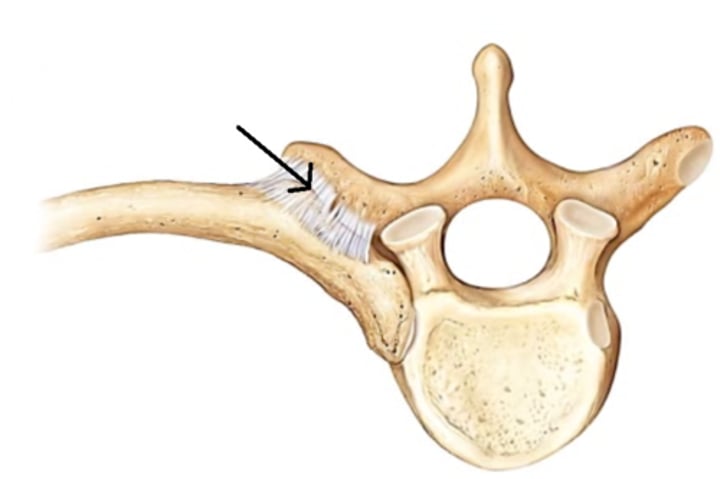
Costotransverse joint
tubercle of rib with costal facet on transverse process of corresponding vertebrae
How many vertebra are there?
33 vertebrae:
•7 cervical
•12 thoracic
•5 lumbar
•5 sacral
•4 coccygeal