ID Lecture 20: Intro to Virology & Viral Pathogens | Quizlet
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
How do viruses contradict the central dogma?
RNA --> DNA or RNA --> protein
What are the different components of a virus?
Nucleic acid genome
Capsid
Envelope
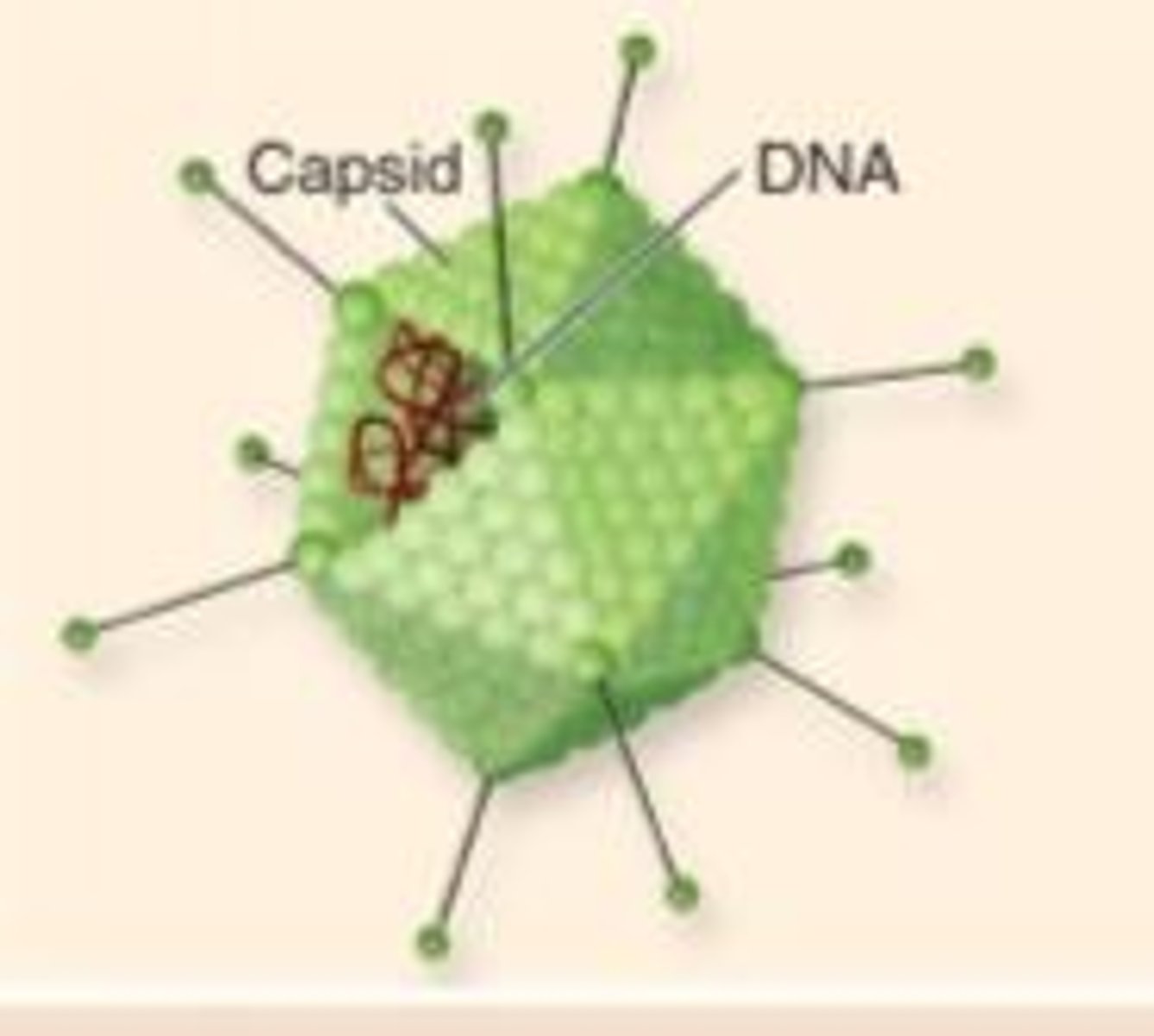
Capsid
protein shell that encloses the viral genome
can be helical or icosahedral
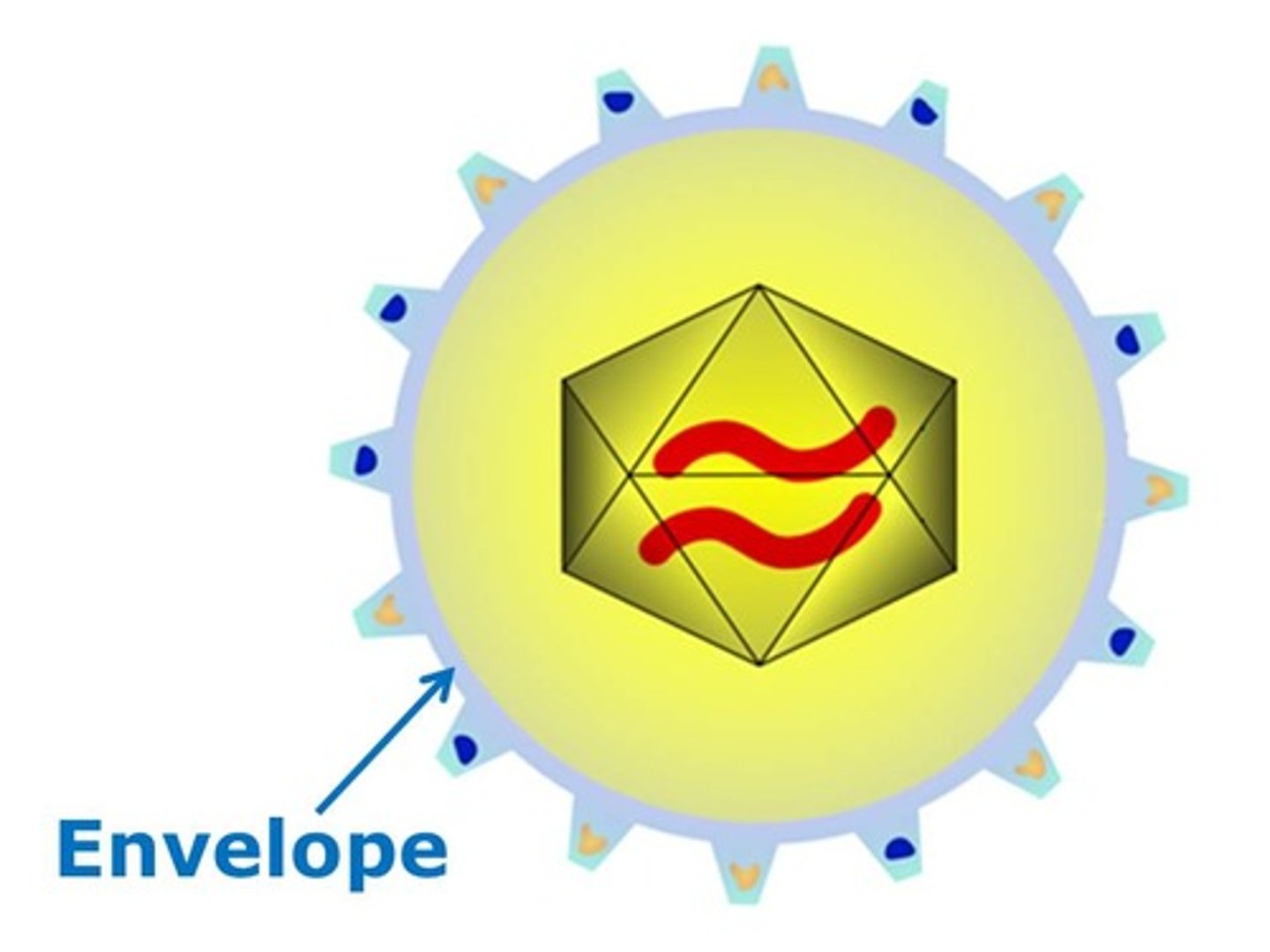
Envelope
lipid-containing membrane that surrounds some viruses
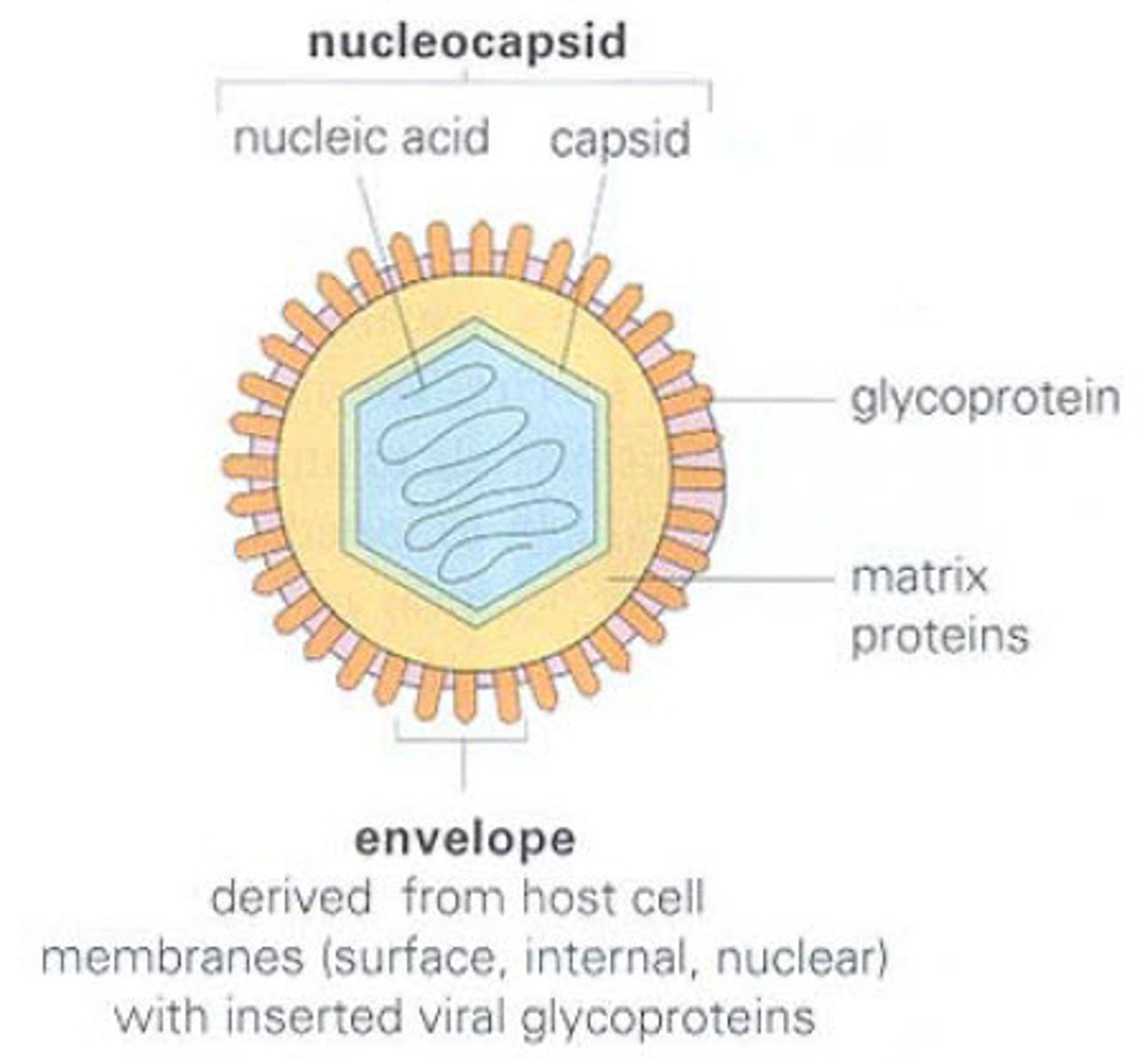
Nucleocapsid
capsid and nucleic acid together
Zoonotic viruses
viruses that jump from animal to human
Arbovirus
viruses spread by arthropods (mosquitos and ticks)
Central dogma
DNA -> RNA -> Protein
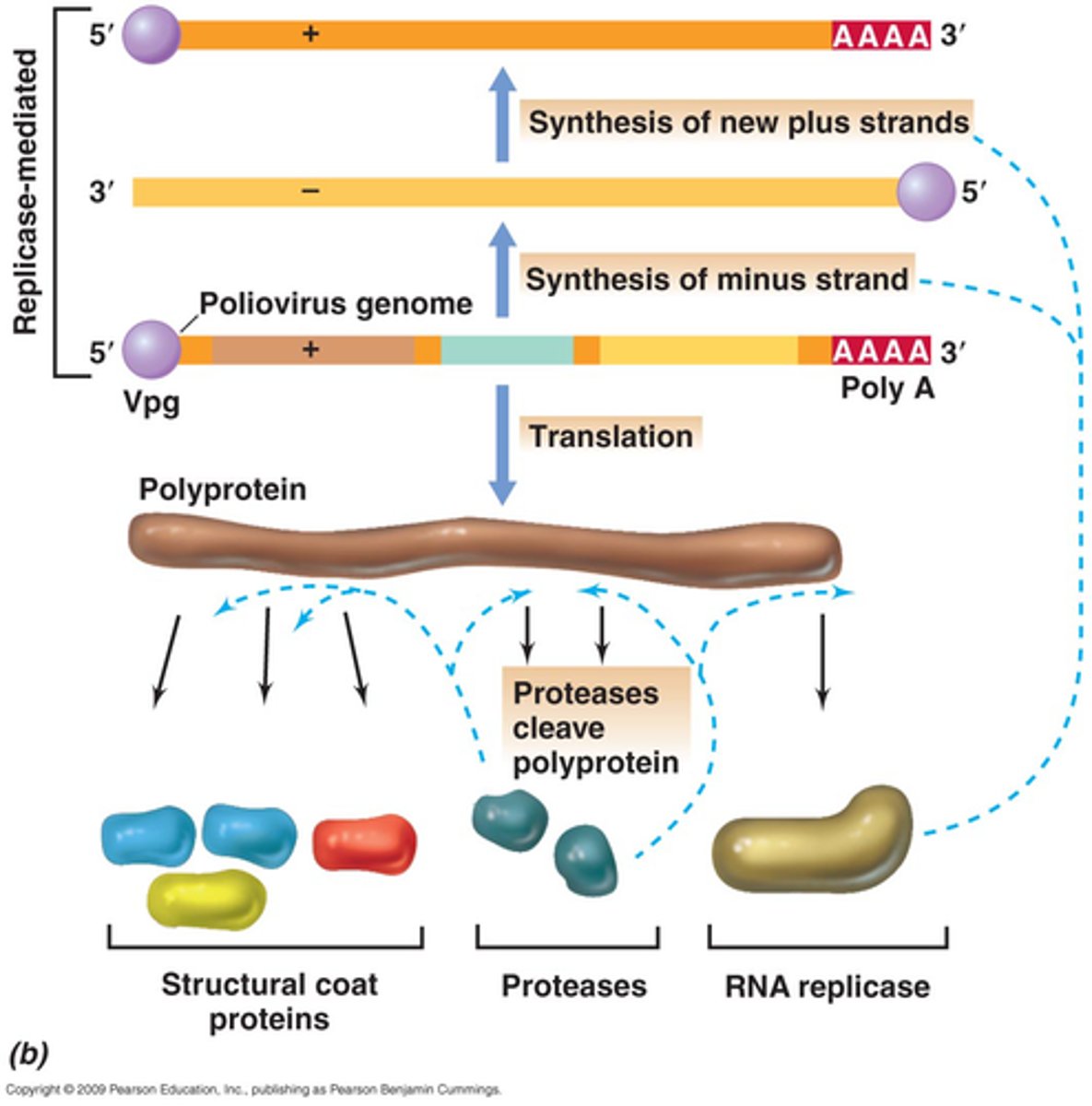
How is a + sense ss RNA virus replicated?
can be immediately translated into protein in the cytoplasm by host machinery upon entry because it is practically already mRNA
How is a - sense ss RNA virus replicated?
has to be copied into ds RNA so the + sense strand can serve as template before it can be translated into a protein through its own machinery
How is a ds RNA virus replicated?
has both + and - sense strands so it is able to follow the central dogma
How is a + ds DNA virus replicated?
Follows the central dogma
Transcription and replication happens in the nucleus
Translation occurs in the cytoplasm
How is a - ss RNA retrovirus replicated?
must go through a ds DNA intermediate first, then it follows the central dogma
How is a ss DNA virus replicated?
Gets copied to ds DNA in the nucleus first, then it goes to the cytoplasm for translation
What are the general steps of viral replication?
1. Attachment/Entry
2. Replication
3. Release
Describe the steps of viral entry.
Attachment
Endocytosis/Fusion
Uncoating/Penetration
Viral attachment
ALL VIRUSES bind to cell surface receptors
What happens during Endocytosis of viral entry?
cell-mediates the uptake of the virus
What happens during fusion of viral entry?
virus fuses with the host's cell membrane before, during, or after endocytosis
What happens during uncoating/penetration of viral entry?
removal of the viral genome from its capsid
Which types of viruses undergo fusion when entering a cell?
enveloped viruses
Where are DNA viruses replicated?
Nucleus for transcription and cytoplasm for translation
Where are RNA viruses replicated?
everything occurs in the cytoplasm
How does a ss RNA retrovirus replicate?
Could translate immediately in the cytoplasm or nucleus and code for its own DNA-dependent RNA polymerase
Describe the process of viral replication once it enters the host cell.
capsid releases genes, which typically gene for structural proteins to make more capsids via polyprotein processing
What is polyprotein processing?
virus mRNA is translated into a single giant polypeptide that is post-translationally cleaved by proteases into several smaller mature polypeptides
How are enveloped viruses released from a host cell?
the nucleocapsid will "bud" through the host membrane where virus-specific proteins have been placed during replication
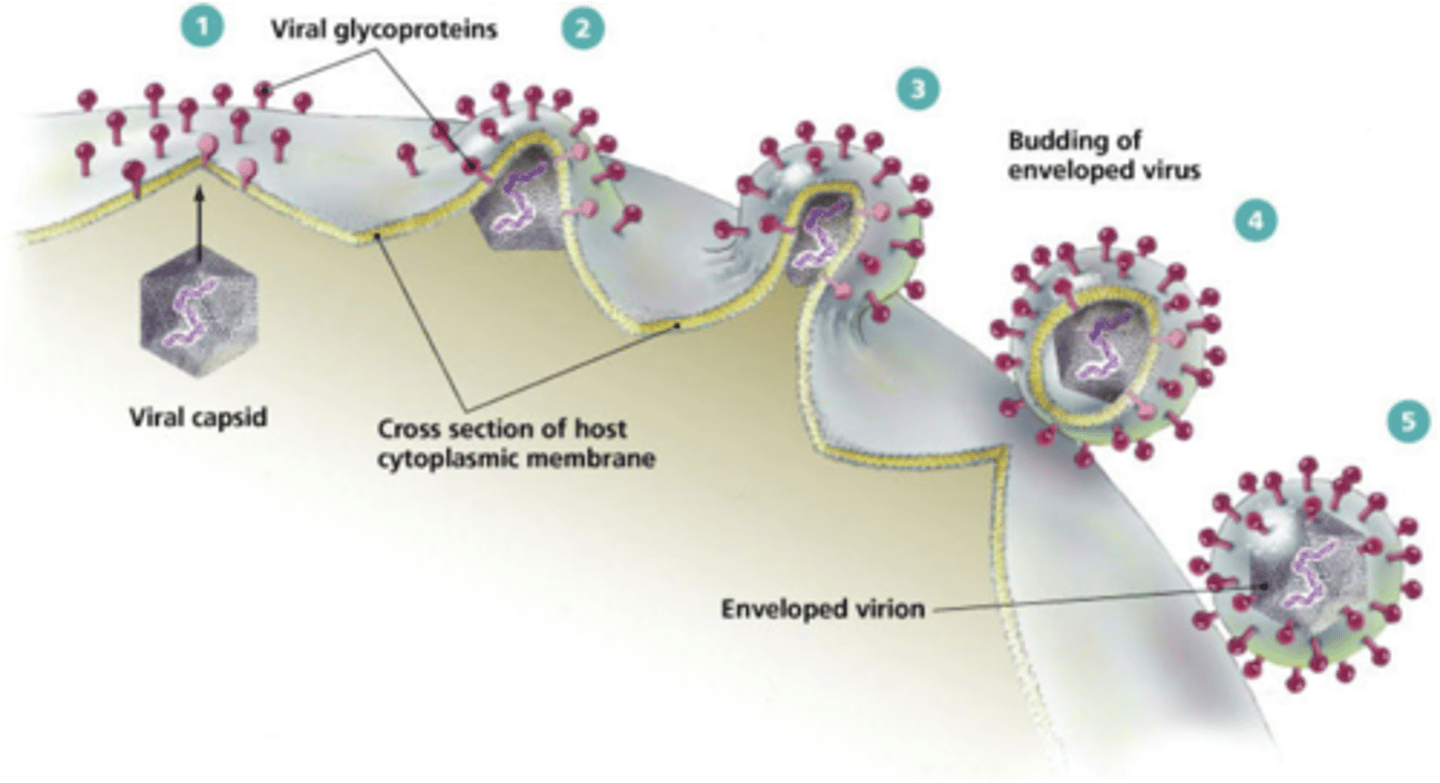
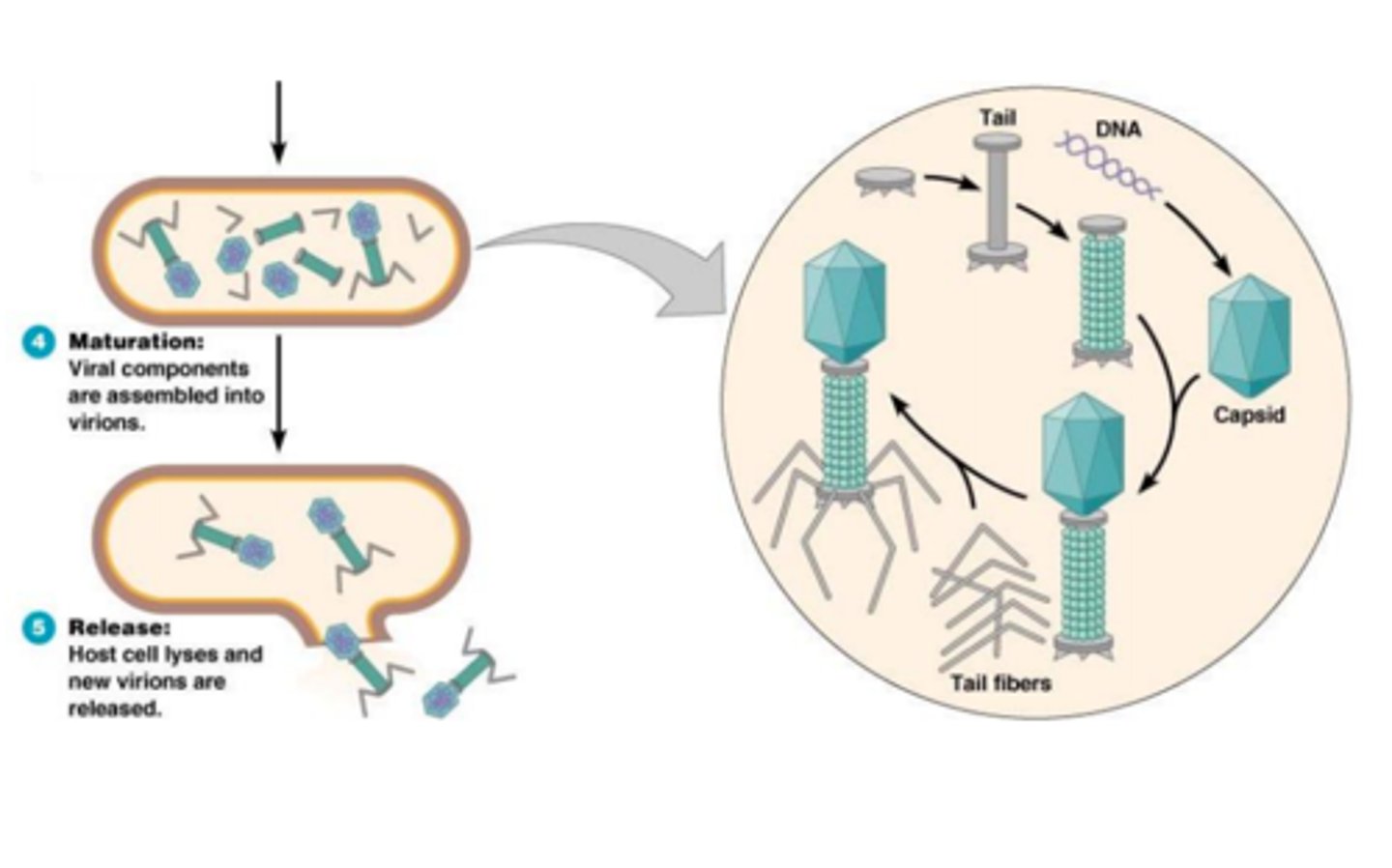
How are naked viruses released from a host cell?
lysis
Viral load
how much virus an infected individual produces
low load = low transmission
What are the general steps of viral pathogenesis?
1. Infection
2. Virus travels to lymph nodes
3. Virus goes into the bloodstream to travel to bone marrow, liver, spleen, or blood vessles (primary viremia)
4. Virus returns to the blood stream to an area it is able to be shed (mucous membranes, skin, lungs, etc) (secondary viremia)

How do viruses evade the host immune response?
Mutations
Recombination
Latent infections
Target the host's cytokines
What is the general approach to viral chemotherapy?
Target processes in the virus that are NOT present in the host cell
OR
Target a mechanism that is significantly increased by viral infection
What are the different antiviral drug targets?
Viral polymerase inhibitors
Reverse transcriptase inhibitors
Protease inhibitors
Integrase inhibitors
Fusion inhibitors
Inhibitors or viral uncoating
Inhibitors of viral relase
True or false: A (+) ssRNA virus must enter the nucleus to initiate viral replication.
False
True or false: A dsDNA virus must enter the nucleus to initiate viral replication.
True
All the following are ways the viruses evade the immune system EXCEPT:
A. Interfere with the host's ability to secrete IFNs
B. Antigenic shift
C. By integrating their viral genomes into host RNA
D. By mutating proteins that are part of the nucleocapsid
C. By integrating their viral genomes into host RNA
Which part of the viral infection life cycle would most likely be affected by an inhibitor that targets V-ATPses involved in endosome fusion?
Viral entry (attachment and uncoating)
Picornavirus
Polio virus
Flavivirdae
Zika virus
Rhabdoviridae
Rabies virus
Filoviridae
Ebola virus
Paramyxoviridae
Measles and mumps virus
Orthomyxoviridae
Influenza virus
Retroviridae
HIV
Papillomaviridae
HPV
Hepadnaviridae
Hepatitis B virus
Herpesviridae
Chicken pox virus
Poxviridae
small pox virus