Pulmonary Vascular Disease - Patho 1
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
What does this refer to
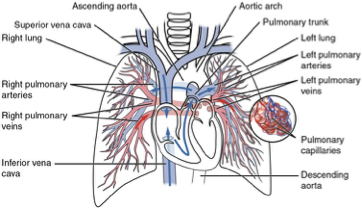
Low-resistance, high-compliance system
Pressure: 15 mmHg (mean); Flow: ~5L/min
Thin-walled vessels accommodate entire cardiac output
Normal Pulmonary Circulation
What does this refer to
: carry deoxygenated blood
Pulmonary arteries
What does this refer to
: site of gas exchange
Capillaries
What does this refer to
: return oxygenated blood to left atrium
Veins
What does this refer to
: regulates tone, permeability, inflammation
Endothelium
What does this refer to
Subjective sensation of uncomfortable breathing
Severe _______
Flaring of the nostrils
Use of accessory muscles of respiration
Retraction of the intercostal spaces
_______ on exertion
Shortness of breath with activity
Orthopnea
_______ when lying down
Dyspnea
What does this refer to
: Awaking at night and gasping for air; must sit up or stand up
Paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea
What does this refer to
Protective reflex that helps clear the airways by an explosive expiration
Acute ______
Resolves within 2–3 weeks
Chronic ______
Lasts longer than 3 weeks
Cough
What does this refer to
Changes in amount, consistency, color, and odor provide information about the progression of disease and the effectiveness of therapy.
Abnormal sputum
What does this refer to
Coughing up blood or bloody secretions
Hemoptysis
What does this refer to
Normal breathing pattern
Eupnea
What does this refer to
Adjustments made by the body to minimize the work of the respiratory muscles
Kussmaul respirations (hyperpnea)
Slightly increased ventilatory rate, very large tidal volume, and no expiratory pause
Labored breathing
Increased work of breathing
Restricted breathing
Disorders that stiffen the lungs or chest wall and decrease compliance.
Cheyne-Stokes respirations
Alternating periods of deep and shallow breathing; apnea lasting 15–60 seconds, followed by ventilations that increase in volume until a peak is reached, after which ventilation decreases again to apnea.
Abnormal breathing patterns
What does this refer to
Alveolar ventilation is inadequate in relationship to metabolic demands.
Leads to respiratory acidosis from hypercapnia.
Is caused by alterations in pulmonary mechanics or in neurologic control of breathing.
Hypoventilation
What does this refer to
Alveolar ventilation exceeds the metabolic demands.
Leads to respiratory alkalosis from hypocapnia.
Is caused by anxiety, head injury, or severe hypoxemia.
Hyperventilation
What does this refer to
Bluish discoloration of the skin and mucous membranes
Develops when having five grams of desaturated hemoglobin, regardless of concentration
Peripheral ______
Most often caused by poor circulation.
Best observed in the nail beds
Central _______
Caused by decreased arterial oxygenation (low partial pressure of oxygen [PaO2]).
Best observed in buccal mucous membranes and lips
Cyanosis
What does this refer to
Is the most common pain caused by pulmonary diseases.
Is usually sharp or stabbing in character.
Infection and inflammation of the parietal pleura (pleuritis or pleurisy) can cause pain when the pleurae stretch during inspiration and are accompanied by a pleural friction rub
Pleural pain
What does this refer to
May be from the airways.
May be from muscle or rib pain.
Chest wall pain
What does this refer to
Increased carbon dioxide (CO2) in the arterial blood
Occurs from decreased drive to breathe or an inadequate ability to respond to ventilatory stimulation
Hypercapnia (Conditions Caused by Pulmonary Disease or Injury)
What does this refer to
Hypoxemia vs. hypoxia
Ventilation-perfusion abnormalities: Most common cause
Shunting
Alveolar dead space: Area where alveoli are ventilated but not perfused
Hypoxemia (Conditions Caused by Pulmonary Disease or Injury)
What does this refer to
Gas exchange is inadequate (hypoxemia).
PaO2 is ≤50 mmHg.
Hypercapnia occurs, during which partial pressure of carbon dioxide (PaCO2) is ≥50 mmHg.
pH is ≤7.25.
Requires ventilatory support, oxygen, or both
Acute respiratory failure (Conditions Caused by Pulmonary Disease or Injury)
What does this refer to
Mean Pulmonary Artery Pressure (mPAP) < 20 mmHg
Pulmonary Vascular Resistance (PVR) < 3 Wood units
Wood unit - a unit of measurement for pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR). Specifically, one Wood unit (WU) is equal to 1 mmHg·min/L. This unit is derived from the relationship between pressure (measured in mmHg) and blood flow (measured in L/min) through the pulmonary circulation.
mPAP ≥ 25 mmHg = Pulmonary Hypertension (PH)
Hemodynamic Parameters
What does this refer to
Group of disorders affecting pulmonary arteries, veins, capillaries
Characterized by elevated pressure, vascular remodeling, or obstruction
Overview of Pulmonary Vascular Disease
What does this refer to
: triggered by hypoxia, endothelin-1
Vasoconstriction
What does this refer to
: smooth muscle proliferation, fibrosis
Vascular remodeling
What does this refer to
: localized coagulation in pulmonary vessels
In situ thrombosis
What does this refer to
Loss of vasodilators (NO, prostacyclin)
Excess vasoconstrictors (endothelin-1, thromboxane)
Increased permeability and inflammation
Endothelial Dysfunction
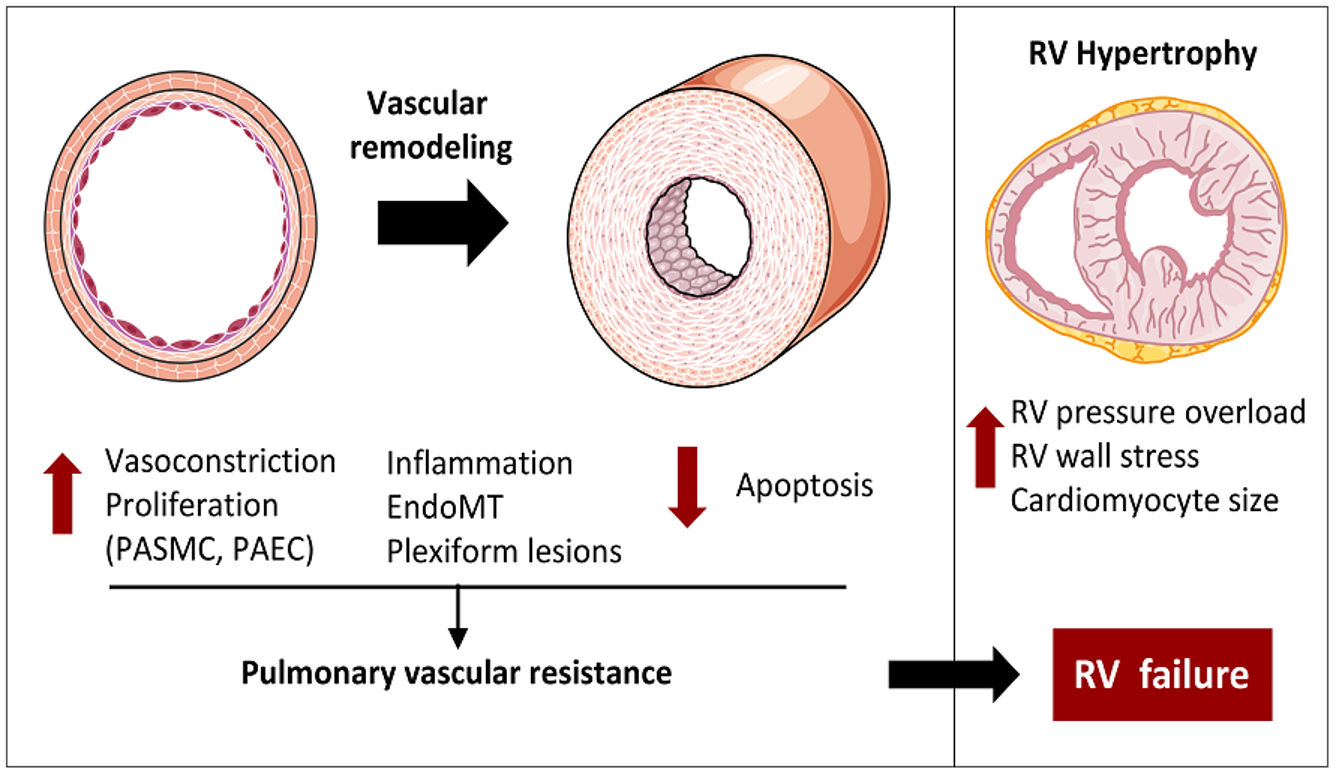
What does this refer to
Medial hypertrophy and intimal fibrosis
Formation of plexiform lesions (in PAH)
Reduced lumen diameter → ↑ resistance
Vascular remodeling
What does this refer to
Infiltration by T cells, macrophages
Cytokines (IL-6, TNF-α) contribute to vascular changes
Autoimmune diseases may initiate injury (e.g., SLE, scleroderma)
Inflammation & Immunity
What does this refer to
Chronic alveolar hypoxia → persistent vasoconstriction
Common in COPD, ILD, high altitude exposure
Reversible early, later leads to fixed changes
Hypoxic Vasoconstriction
What does this refer to
Increased afterload → RV hypertrophy
Chronic strain leads to RV dilation and failure
Septal flattening on echo is an early sign
Right Ventricular Response
What does this refer to
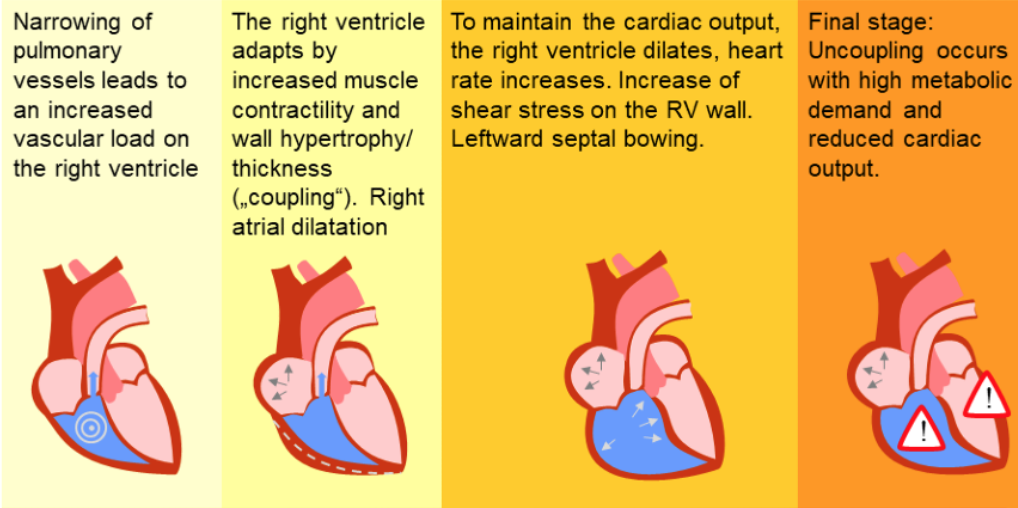
Right heart insufficiency in pulmonary hypertension ——→
What does this refer to
Mean pulmonary artery pressure above 25 mmHg at rest
Idiopathic, familial, or associated
Pathophysiology
Overproduction of vasoconstrictors and decreased production of vasodilators
Remodeling
Resistance to pulmonary artery blood flow, thus increasing the pressure in the pulmonary arteries
Workload of the right ventricle increases and subsequent right ventricular hypertrophy, may be followed by failure and eventually death
Pulmonary Hypertension
What does this refer to
Group 1 PH: pre-capillary, idiopathic or associated
Proliferation of endothelial and smooth muscle cells
Often involves genetic mutation (e.g., BMPR2)
Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH)
What does this refer to
Masked by primary pulmonary or cardiovascular disease
First indication: Chest radiograph (enlarged pulmonary arteries and right heart border) or an electrocardiogram that shows right ventricular hypertrophy
Clinical manifestations of pulmonary hypertension
What does this refer to
Loss of vascular tone regulation
Smooth muscle proliferation and fibrosis
Increased PVR → RV failure and hypoxia
Pathophysiology of pulmonary hypertension
What does this refer to
↓ Prostacyclin, ↓ NO → vasoconstriction
↑ Endothelin-1 → proliferation and fibrosis
BMPR2 mutation → unchecked cellular growth
Molecular pathway of pulmonary hypertension
What does this refer to
Oxygen, diuretics, anticoagulants
Avoidance of contributing factors such as air travel, decongestant medications, nonsteroidal antiinflammatory medications, pregnancy, and tobacco use
Prostacyclin analogs (epoprostenol, beraprost, iloprost)
Endothelin receptor antagonists (bosentan, ambrisentan)
Phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors
Calcium channel blockers
Lung transplantation
Secondary pulmonary artery hypertension
Treat the primary disorder.
Once pulmonary hypertension has persisted long enough for hypertrophy to develop, it is no longer reversible.
Supplemental oxygen reverses hypoxic vasoconstriction.
Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension
What does this refer to
Persistent obstruction after PE
Fibrotic webs and bands in arteries
Secondary arteriopathy develops over time
Chronic Thromboembolic PH (CTEPH)
What does this refer to
Initial emboli cause mechanical obstruction
Non-resolving thrombi stimulate remodeling
↓ perfusion → mismatch, RV overload
Pathogenesis Chronic Thromboembolic PH (CTEPH)
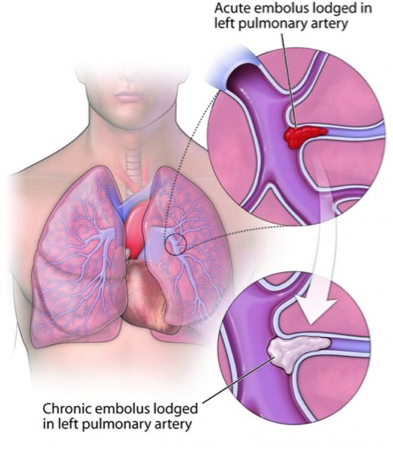
What does this refer to
Persistent obstruction after PE
Fibrotic webs and bands in arteries
Secondary arteriopathy develops over time
Chronic Thromboembolic PH (CTEPH)
What does this refer to
Back-pressure from LA → ↑ venous pressures
Capillary stress → remodeling, rarefaction
RV dysfunction due to chronic afterload
Pulmonary Hypertension (PH) Due to Left Heart Disease
What does this refer to
Destruction of capillaries (e.g., emphysema)
Alveolar hypoxia → vasoconstriction
ILD and fibrosis cause obliteration of vessels
Pulmonary hypertension (PH) due to lung diseases
What does this refer to
Chronic hypoxia → pulmonary vasoconstriction
Loss of vessels in emphysema
Low grade PH worsens prognosis
COPD & PH
What does this refer to
Secondary to pulmonary hypertension
Right ventricular enlargement
Pulmonary hypertension, creating chronic pressure overload in the right ventricle
Cor Pulmonale
What does this refer to
Heart appears normal at rest.
With exercise: Decreased cardiac output, chest pain
Clinical manifestations of Cor Pulmonale
What does this refer to
Decrease workload of the right ventricle by lowering pulmonary artery pressure.
Same as for PAH
Reversal of the underlying lung disease
Treatment of Cor Pulmonale
What does this refer to
Is the occlusion of a portion of the pulmonary vascular bed by a thrombus, embolus, tissue fragment, lipids, foreign body, amniotic fluid, or air bubble.
Commonly arise from the deep veins in the thigh.
Virchow triad
Venous stasis, hypercoagulability, and injuries to the endothelial cells that line the vessels
Pulmonary Embolism
What does this refer to
Release of neurohumoral substances
Widespread vasoconstriction
Atelectasis of the affected lung segments, further contributing to hypoxemia
Pulmonary edema, pulmonary hypertension, shock, and even death
Pathophysiology of Pulmonary Embolism
What does this refer to
Sudden onset of pleuritic chest pain, dyspnea, tachypnea, tachycardia, and unexplained anxiety
Clinical Manifestations of Pulmonary Embolism
What does this refer to
Bed exercises, frequent position changes, early ambulation, and pneumatic calf compression
Prophylactic anticoagulation with low–molecular-weight heparin, warfarin, or fondaparinux
Filter in the inferior vena cava: To prevent emboli from reaching the lung
Prevention of venous stasis
What does this refer to
Oxygen and hemodynamic stabilization with fluids
Anticoagulation and/or fibrinolytic agent (streptokinase)
Percutaneous or surgical embolectomy
Treatment of pulmonary embolism
What does this refer to
Occlusion of post-capillary venules
Leads to pulmonary edema, capillary congestion
May mimic PAH but worsens with vasodilators
Pulmonary Veno-Occlusive Disease
What does this refer to
Thickened venules, capillary proliferation
Lymphatic dilation due to congestion
Associated with EIF2AK4 gene mutation
PVOD Pathology
What does this refer to
Inflammation of vessel wall (e.g., GPA, EGPA)
Granulomatous changes and necrosis
May cause aneurysms or hemorrhage
Pulmonary Arteritis
What does this refer to
↑ PVR → RV hypertrophy and failure
Reduced cardiac output, increased venous pressure
Systemic hypotension and exercise intolerance
Hemodynamic Consequences
What does this refer to
Volume overload: tricuspid regurgitation
Forward failure: hypotension, fatigue
Backward failure: hepatomegaly, edema
RV Failure in Pulmonary Vascular Disease
What does this refer to
: ventilation with poor perfusion
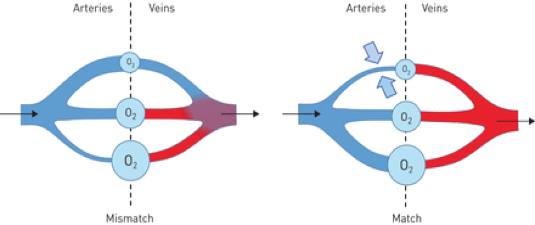
V/Q mismatch
What does this refer to
V/Q mismatch: ventilation with poor perfusion
Impaired diffusion due to thickened capillary membrane
Right-to-left shunting in extreme cases
Gas Exchange Abnormalities
What does this refer to
Hypoxemia leads to polycythemia
Reduced oxygen delivery to organs
Neurohormonal activation (RAAS, SNS)
Systemic Effects
What does this refer to
Pathophysiology varies by disease but involves vascular remodeling, increased resistance, and RV strain
Understanding mechanisms helps guide diagnosis and treatment
Summary (kind of silly but why not)