Science Exam Review - Grade 9
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Physical properties
a characteristic of a substance that can be observed or measured without changing the composition of that substance.
Physical change
a change to a substance in which the composition of the substance stays the same and no new substances are produced.
Chemical properties
a characteristic of a substance that is determined when the composition of the substance changes or one or more new substances are produced.
Chemical change
a change in the composition of the substance and one or more substances are created.
Groups and Periods
Groups- horizontal
Period- vertical
Metals, Non-Metals, Metalloids
Metals- left of the staircase
Non-metals- right of the staircase
Metalloids- staircase
Determine the number of protons, electrons, and neutrons in an atom
Number of protons= atomic number
Number of electrons= atomic number
Number of neutrons= mass number - atomic number
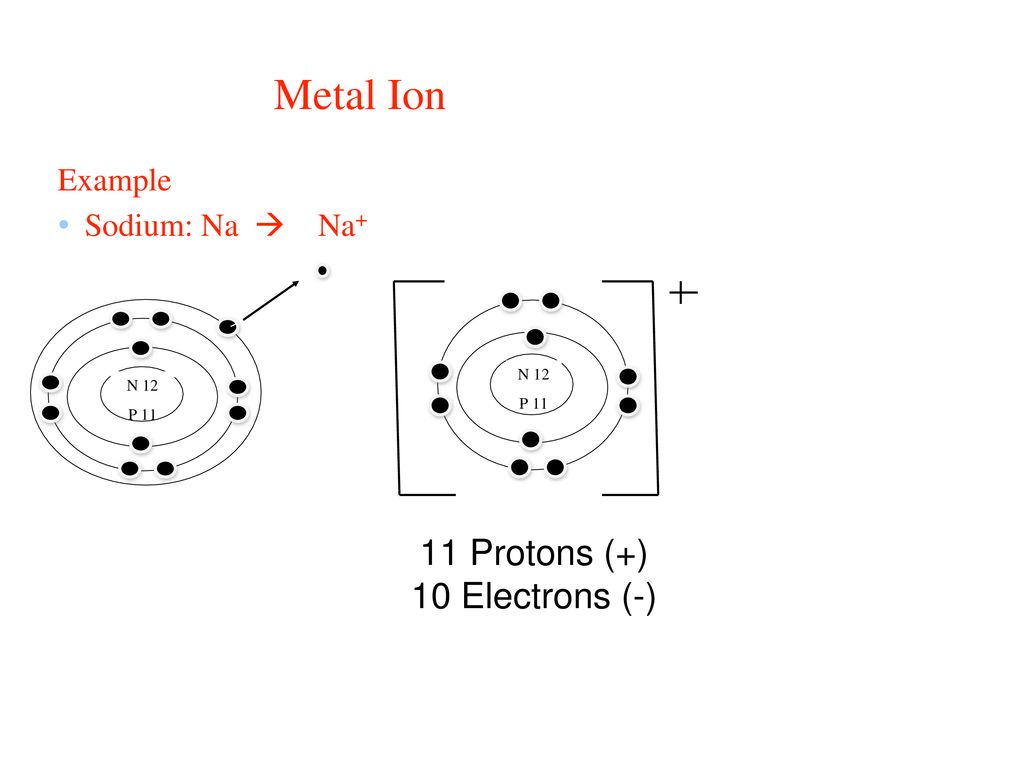
Determine the number of protons, electrons, and neutrons in an ion
Protons= atomic number
Electrons= atomic number - the charge
Neutrons= atomic number - mass number
Draw Bohr-Rutherford Diagrams for atoms
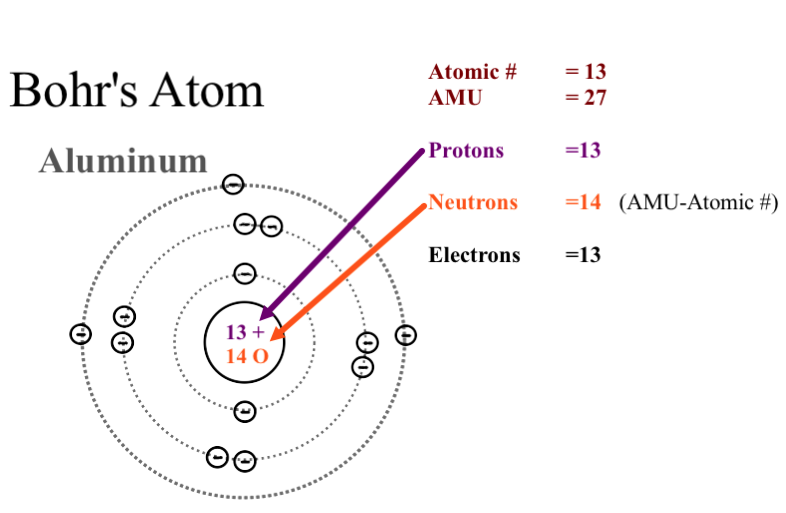
Draw Bohr-Rutherford Diagrams for ions
Use Bohr-Rutherford Diagrams to draw Ionic Compounds and Molecular Compounds
Draw it yourself
Law of Electric Charges
A charged object and a neutral object will attract each other.
Conductors
Conductor are materials that let electrons easily move through.
Insulator
Insulator are materials that don’t easily let electrons move through them.
Generating Current Electricity
Current electricity- the controlled flow of electrons through a conductor.
Coal
Burns in an engine to produce steam that is made into electricity.
Natural gas
Burns gas creating heat and electricity.
Solar energy
Energy created from the sun
Wind energy
Energy made from wind.
Hydroelectric energy
Energy produced with moving water.
Geothermal energy
Heat energy from the earth.
Nuclear energy
the energy in the nucleus, or core, of an atom.
Series Circuits
Series Circuit are a circuit in which there is only one path for electrons to flow.
Parallel Circuits
Parallel circuit are a circuit in which the load(s) are connected so there are two or more paths for electrons to flow.
Define and Calculate Voltage, Current, and Resistance using Ohm’s Law (GRASS Method)
GRASS= given, required, analysis, solution, statement
v= i x r
i= v/r
r= v/i
Calculate electrical quantities in a circuit using Ohm’s Law and Kirchhoff's Laws for Current and Voltage
Current:
Series: I source = I1 =I2 = I3 - current is equal across the circuit
Parallel : I source = I1 + I2 + I3 - the current at the source is the sum of the loads
Voltage
Series: V source = V1 + V2 + V3 - the voltage at the source is the sum at the loads
Parallel: V source= V1 = V2 = V3 - voltage is equal across the circuit.
Draw Circuit Symbols: battery (1, 2, and 3-cell), wire, open switch, closed switch, light bulb, voltmeter, ammeter
Draw Circuit Diagrams: Series and parallel
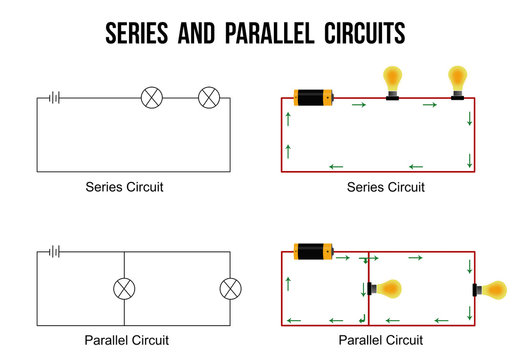
Define Biodiversity
Biodiversity is the variety of life in a particular ecosystem.
Atmosphere
the layer of gasses that surrounds the Earth. 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, 1% argon, carbon dioxide, etc.
Lithosphere
Earth’s solid outer layer. rocks and minerals.
Biosphere
the zone in, on and around the Earth where life can exist. layer of ground, water and lower atmosphere.
Hydrosphere
Earth’s water in solid, liquid, and gas forms. oceans, lakes, groundwater, clouds.
Biotic Factors
all the living things, their remains, features, and waste associated with their activities. ( animals, plants, fungi, bacteria)
Abiotic Factors
all non-living things that are found in an ecosystem. ( sunlight, water, air, soil, minerals)
Organism
a living thing
Population
all individuals of the same species that can be found in the same area
Community
members of different species from all of the populations that can be found in the same area
Ecosystem
An ecosystem consists of all the biotic (living) and abiotic (non-living) components in an area.
Food Webs
a representation of the feeding relationships within a community. It shows a series of interconnecting food chains.
Food chain
a sequence of organisms, each feeding on the next, showing how energy is transferred from one organism to another.
producer
A producer is an organism that creates its own food or energy
consumer
A consumer is an organism that gets its energy by eating plants or animals.
decomposer
An organism that feeds on and breaks down dead plant or animal matter, making organic nutrients available to the ecosystem
Scavenger
A scavenger is an organism that mostly consumes decaying biomass, such as meat or rotting plant material
Photosynthesis
the process by which the Sun's energy is converted into chemical energy
Formula:
6CO2 + 6H2O → C6 H12 O6 + 6O2
carbon dioxide + water → glucose + oxygen
Cellular Respiration
the process by which sugar and oxygen are converted into carbon dioxide, water, and energy to provide energy for the organism
Formula: C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP
glucose + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water + sunlight
Sustainability and Actions that Reduce Carbon Footprints
bring your own bags to the grocery store
turn flights when not in use
walk places when you can
plant a garden to reduce transportation of goods, pollution, waste, etc
Impacts of climate change on Indigenous communities and solutions
IMPACTS
Loss of land
Rapid water decline; less availability of food
Hotter summers meaning more destructive fires
Homes in Northwest Territories are disappearing from ice melting
SOLUTIONS
Canadian is government putting aside 340 million dollars to contribute in helping the fight against climate change on First Nations land.
Develop a plan with fellow communities to let the Indedinous communities have a voice against their fight