Lecture 23-24: Elastic Collisions and Momentum
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Types of Collisions
Elastic Collisions and Inelastic Collisions
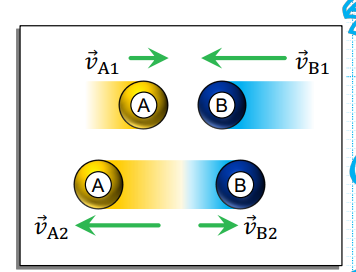
Elastic Collision
No kinetic energy is lost for this type of collision.
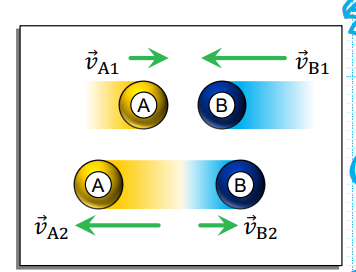
Inelastic Collision
Some kinetic energy is lost for this type of collision.
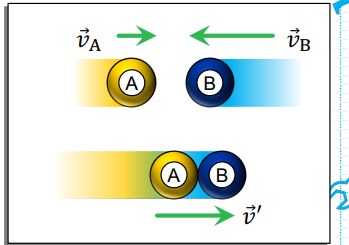
Perfectly Inelastic Collision
Objects stick together and Final velocity is common for this type of Collision.
Conservation of Kinetic Energy (State 1 and State 2) & Conservation of Momentum.
Important concepts for solving collisions: _________
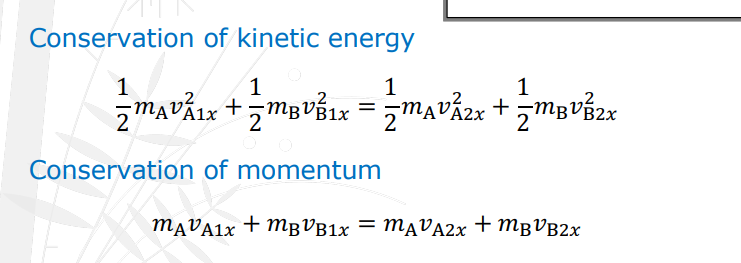
Formula for ________ when body B is initially at rest.
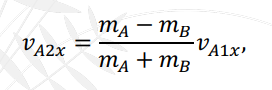
Final Velocity of VB2X or the Final Velocity of Body B along the horizontal axis.
Elastic Collision: Formula for ________ when body B is initially at rest.
Reflected, Boosted, Transferred Kinetic Energies.
Elastic Collision: 3 Cases affected by mass of bodies.
Ma<Mb
Ma>Mb
Ma=Mb
Va2x = -Va1x Where body A is reflected back, velocity remains almost the same, and VB2x = 0 as Body B is almost stationary.
Elastic Collision: 3 Cases affected by mass of bodies.
Ma<Mb
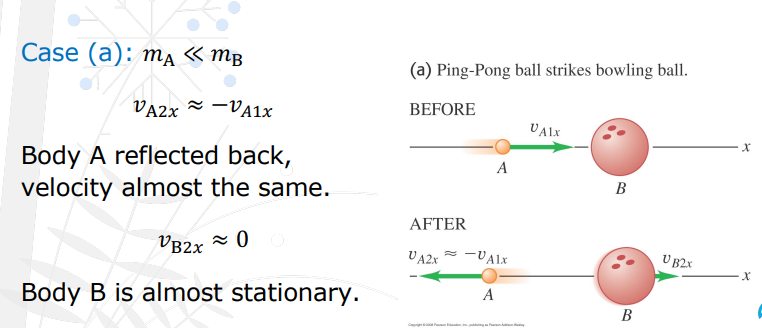
Va2x = Va1x Where body A is almost unchanged in the same direction, velocity remains almost the same, and VB2x = 2Va1x as Body B moves faster.
Elastic Collision: 3 Cases affected by mass of bodies.
Ma>Mb
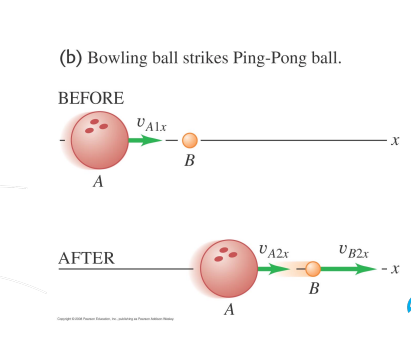
Va2x = 0 Where body A stops after collision, and VB2x = Va1x as Body B moves same as A before collision.
Elastic Collision: 3 Cases affected by mass of bodies.
Ma=Mb
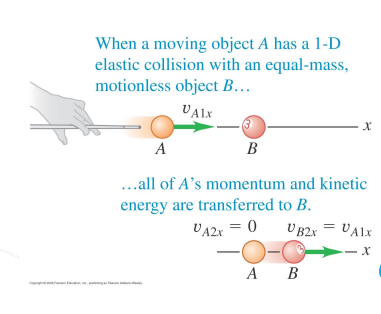
same magnitude but opposite sign
In 1D elastic collision between two bodies, the relative velocities before and after the collision have the ____________.
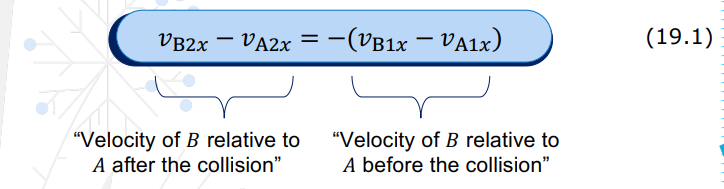
Relative velocity has the same magnitude before and after the collision.
Whenever this condition is satisfied, kinetic energy is conserved.
Product of (Mass x Position or Velocity) / Total Mass
Center of Mass Calculations for Position and Velocity is ________.

Conservation of Momentum
If the vector sum of the external forces on a system is zero, the total momentum of the system is constant.