ryanef123: Complete Denture (Midterm Exam): Week 3
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
What is the purpose of boxing the final edentulous impressions?
to preserve the peripheral borders/rolls of the patient
What materials do we use for the matrix for boxing the final impressions?
dental plaster and pumice flour (50-50 mixture)
Place the maxillary tray/impression into the pumice/plaster mixture. Center it and push it all the way down. Work the mixture up toward the peripheral rolls. Work the mixture up toward the top of the rolls but only to the point where there will still be ____mm of the peripheral rolls above the crest of the mixture. Put it aside to set.
5mm
Place the mandibular final impression into the middle of the mix and push it all the way down. Please note that the M.F.P. of the mandibular impression should be __________ to the bench top. The bending of the handle has make this possible.
Parallel
What is the anterior point for the Mean Foundation Plane (MFP) of the mandibular final edentulous impression?
the midline of the crest of the edentulous mandibular ridge
What are the posterior point for the Mean Foundation Plane (MFP) of the mandibular final edentulous impression?
the areas of the left and right ascending rami of the mandible
T/F: the Mean Foundation Plane (MFP) of the mandibular final edentulous impression is from the anterior crest of the ridge to the retromolar pads
FALSE!!
How should the retromolar pads area of the boxing impression look?
Retromolar pad should be deeply imbedded into the mix but completely exposed (be sure that the retromolar pad areas have been cleared of all of the mix that is covering them)
On a model trimmer, after peeling off the paper bowl, reduce the excess outside walls of the matrix so that they are about ____ mm
10mm
Carefully trim the land area around the impression so that about ____mm of the impression’s peripheral roll is showing.
5mm
T/F: The matrix is very soft so you need to be super careful when trimming
True!
What should the final maxillary and mandibular matrices be like before boxing the impression?
- Sit flat on the bench top.
- Have their mean foundation planes parallel to the bench top.
- Have a matrix material land area, about 10 mm wide around the impression.
- Have the peripheral rolls of the impression extend up about 5 mm above the land area (don’t forget the lingual rolls).
- Pay special attention to the retromolar pads.
When pouring the impressions, think ahead! How thick should the final master cast be at the thinest area?
15 mm (usually the depth of the palatal vault on the maxillary cast and the depth of the lingual peripheral roll on the mandibular cast)
What type of stone is the following:
- Dental stone (microstone)
- Has 0.20% expansion Beta calcination, not refractory
- Processing of acrylic dentures
Type III
What material do we use use to pour the final casts?
dental stone type III
Why do we not use model/dental plaster to pour our master casts?
it is not strong enough
Why do we not use die stone when pouring our master casts?
Die stone is so hard that it will be very difficult to separate the final cast from the processed denture.
Why do we use dental stone to pour our master csats?
Dental stone is just right, strong enough to take the pressure yet not too difficult to separate from the processed dentures.
What is the proper mix for water and dental stone?
- 30 ml of water
- 100 g of powder
T/F: Powder is always added to liquid for mixing
True (instant wetability)
Are there bevels on the final casts?
No! The land areas are flat and square all the way around the final edentulous casts.
You will trim the final edentulous casts very carefully and precisely by making the land areas square, flat and about ____mm above the peripheral rolls.
5mm
The maxillary land area should be square and smooth, 3 to 5 mm above the peripheral rolls and about ____mm wide.
5mm
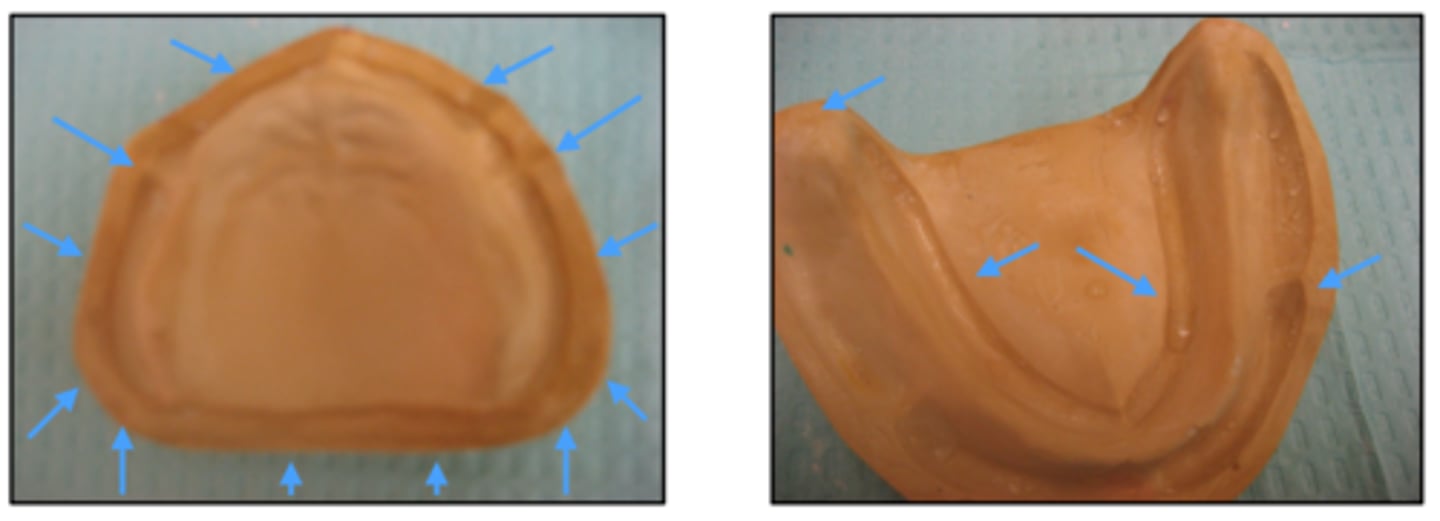
ID the area:
Land area
Assess the final casts for tissue detail and what three anatomical landmarks?
- Hamular notches
- Retromolar pads
- Full peripheral rolls
Mandibular facial land areas are square, smooth, and 3 to 5 mm above the depths of the facial peripheral rolls. Be sure to also maintain a lingual peripheral roll that is ___-___mm below the level of the lingual land area.
3-5 mm
Check the final casts and make sure that there are at least 15 mm thick at their thinnest portion which is between the base of the cast and the ___________ for the maxillary and the ___________ for the mandible
- Palatal vault (max)
- Lingual peripheral rolls (mand)
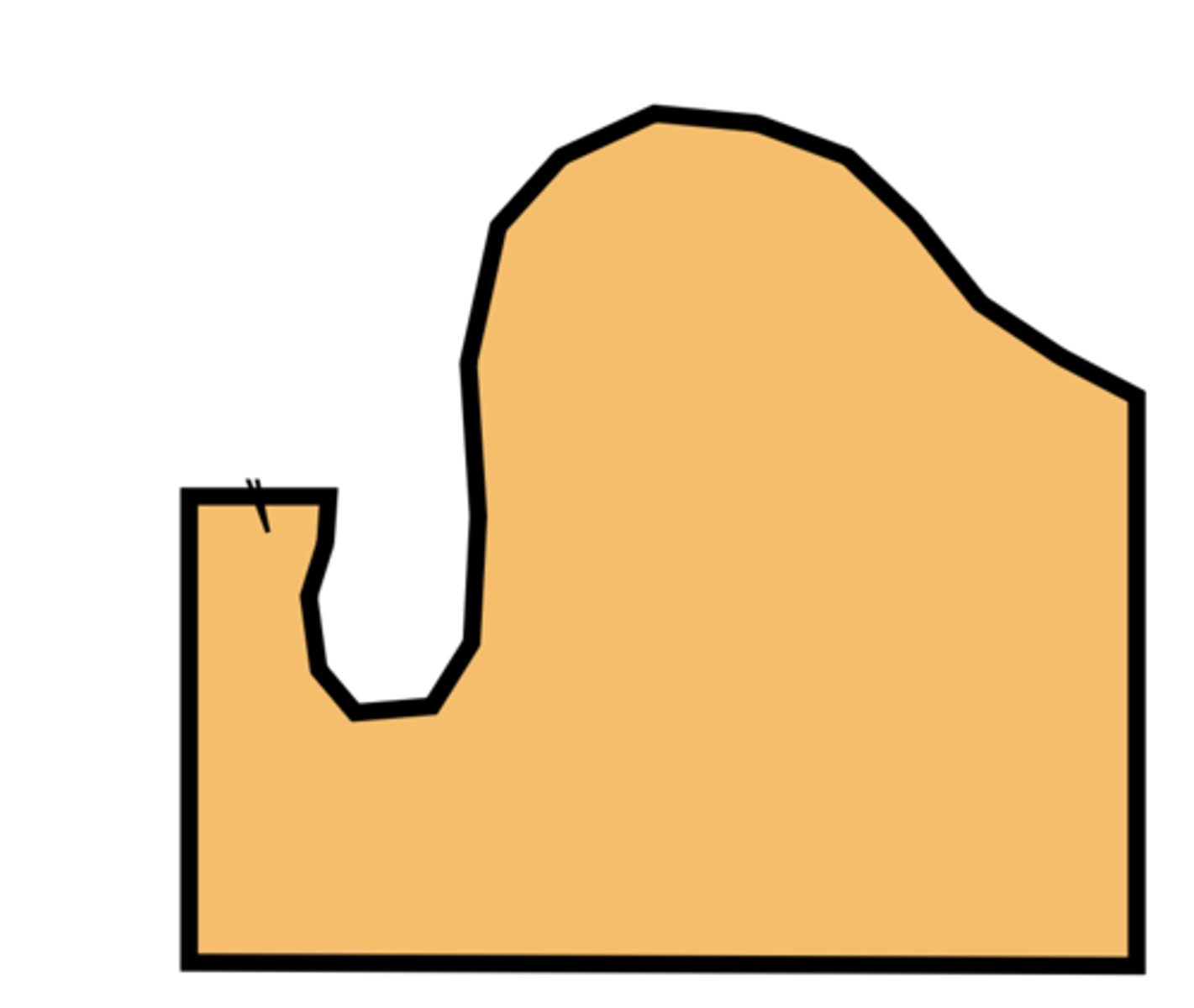
What do you think of this trimming cast?
Under-trimmed
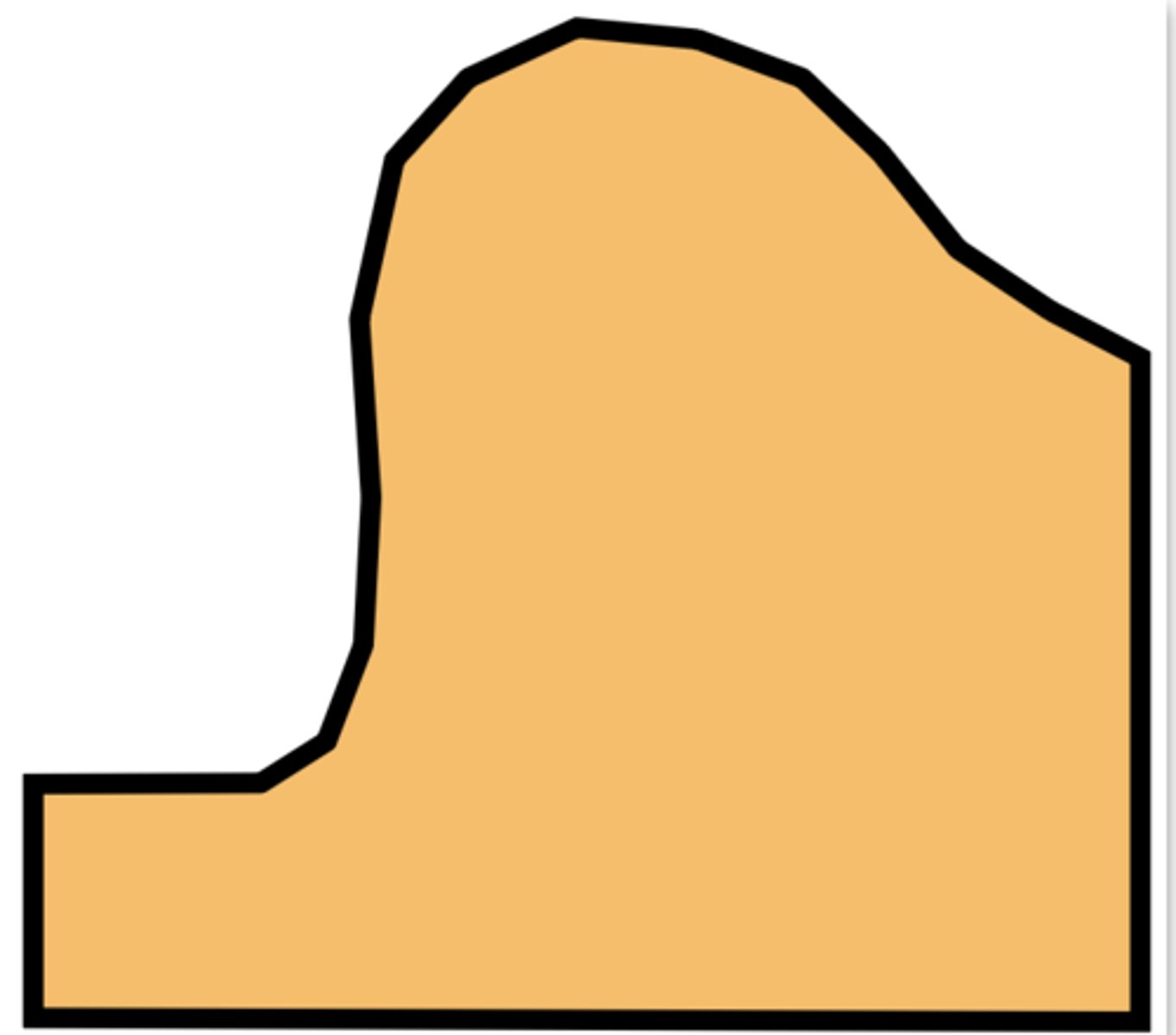
What do you think of this trimming cast?
Over-trimmed
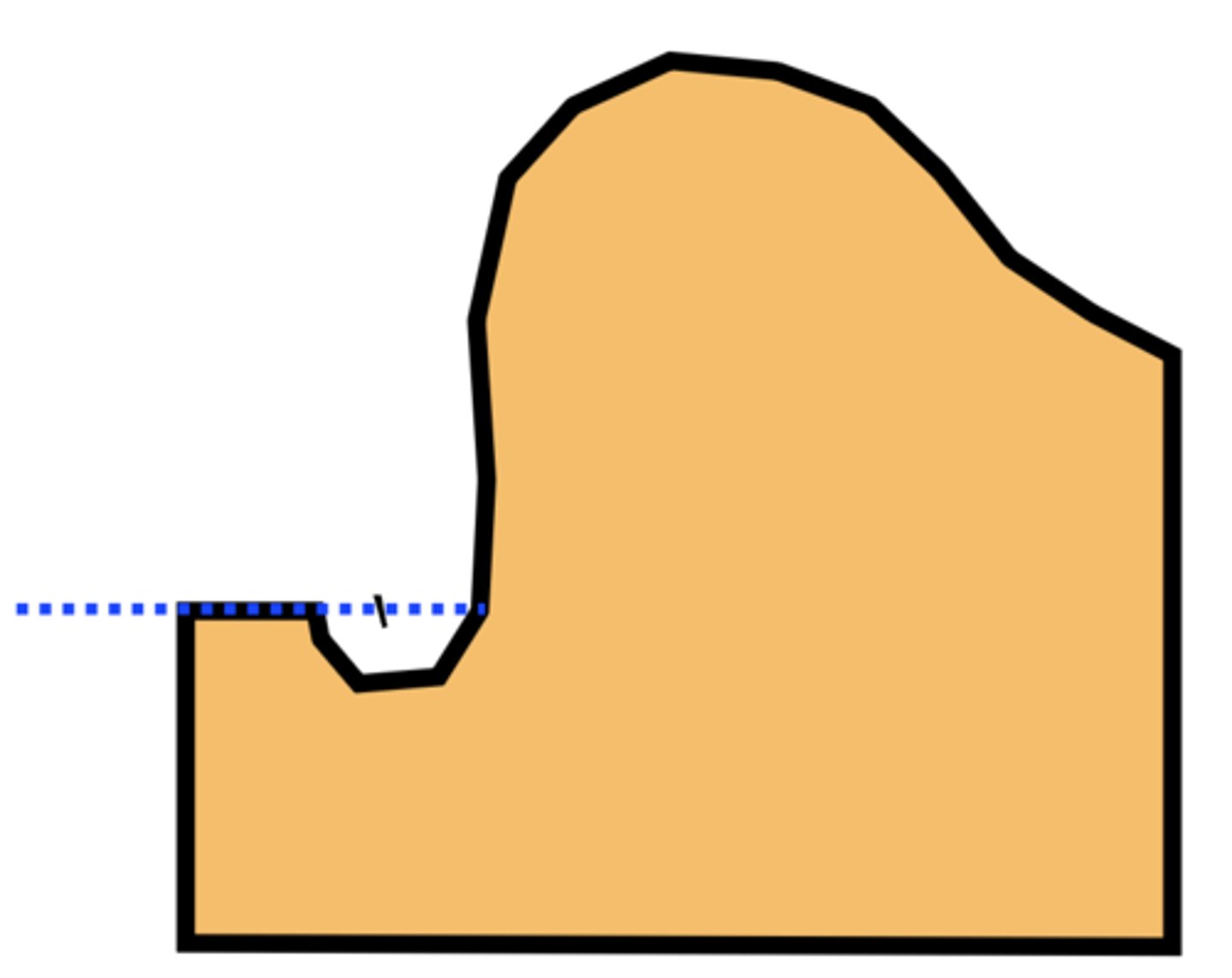
What do you think of this trimming cast?
Ideal (180 degrees)
Between the second and third appointment, a record base is made on each cast and a wax rim is made on each record base. These are occlusal rims that will allow you to what?
Articulate your master casts
Why do we mark the final impression casts?
To create guidelines for the proper placement of the denture teeth in a complete denture set-up
What set of marks do we make as a guideline for positioning the facial surfaces of the maxillary central incisors?
- Circle the incisive papilla
- Make the front edge of the ruler perpendicular to the mid-palatal suture. Draw lines on the left and right land areas, directly beneath the front edge of your ruler
Why do we mark the retromolar pads on the mandibular cast?
to determine the height of the posterior occlusal plane in a complete denture set-up
Where do you place a dot on each retromolar pad?
Place a dot anterior 2/3 of the height of each retromolar pad (make dots/reference points while holding cast at eye level and look at it from the facial aspect)
After marking the retromolar pads, what are the second markings on the mandibular casts?
- Crest of the residual ridge
- Determine the bucco-lingual placement of posterior teeth
- The central fossae of the premolar and molar denture teeth are placed directly over the crests of the mandibular residual ridges
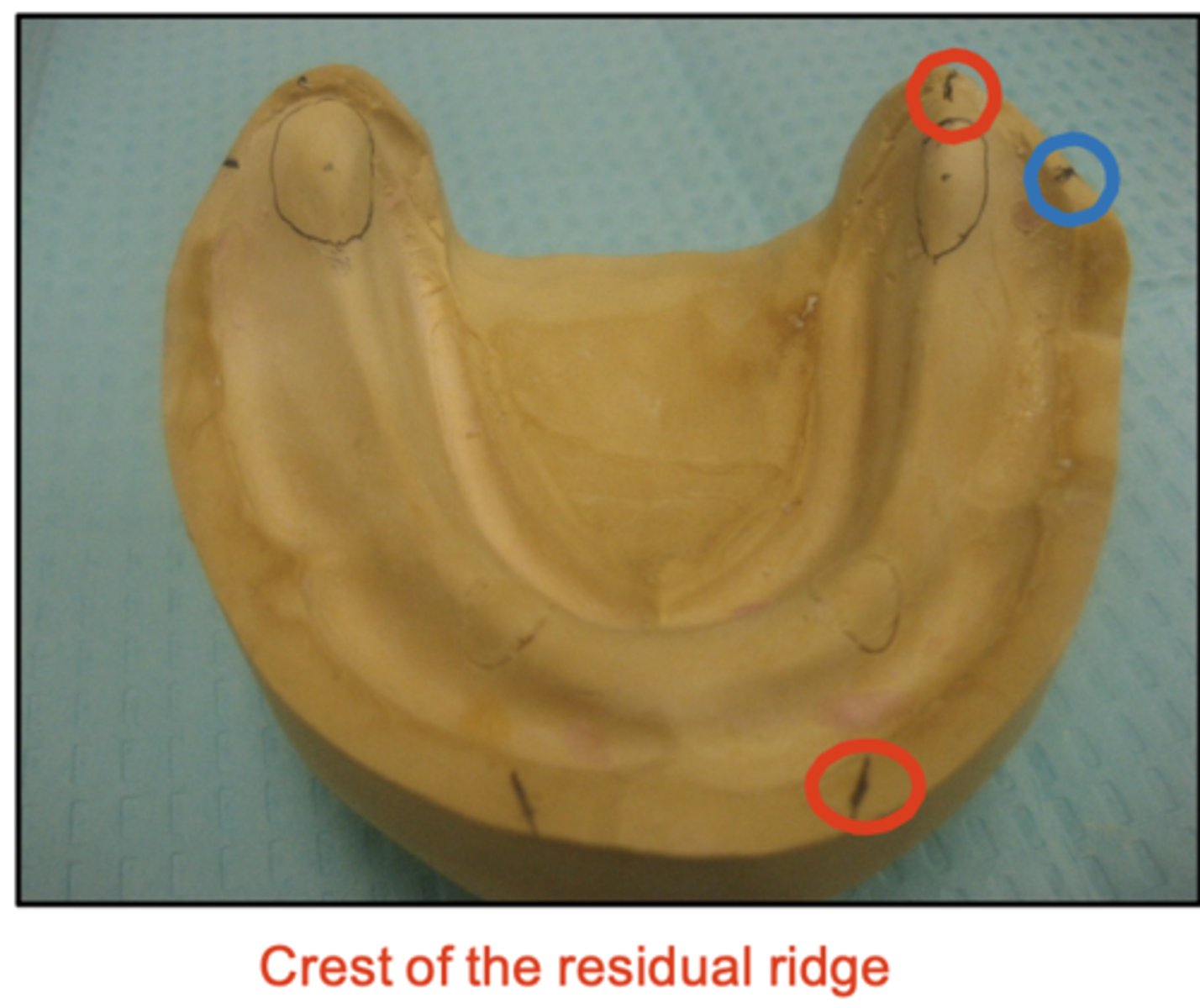
It is important that we mark the crest of the mandibular ridge correctly because, if we set teeth too buccally, what would happen?
Teeth/denture will lean outward and cause cheek biting
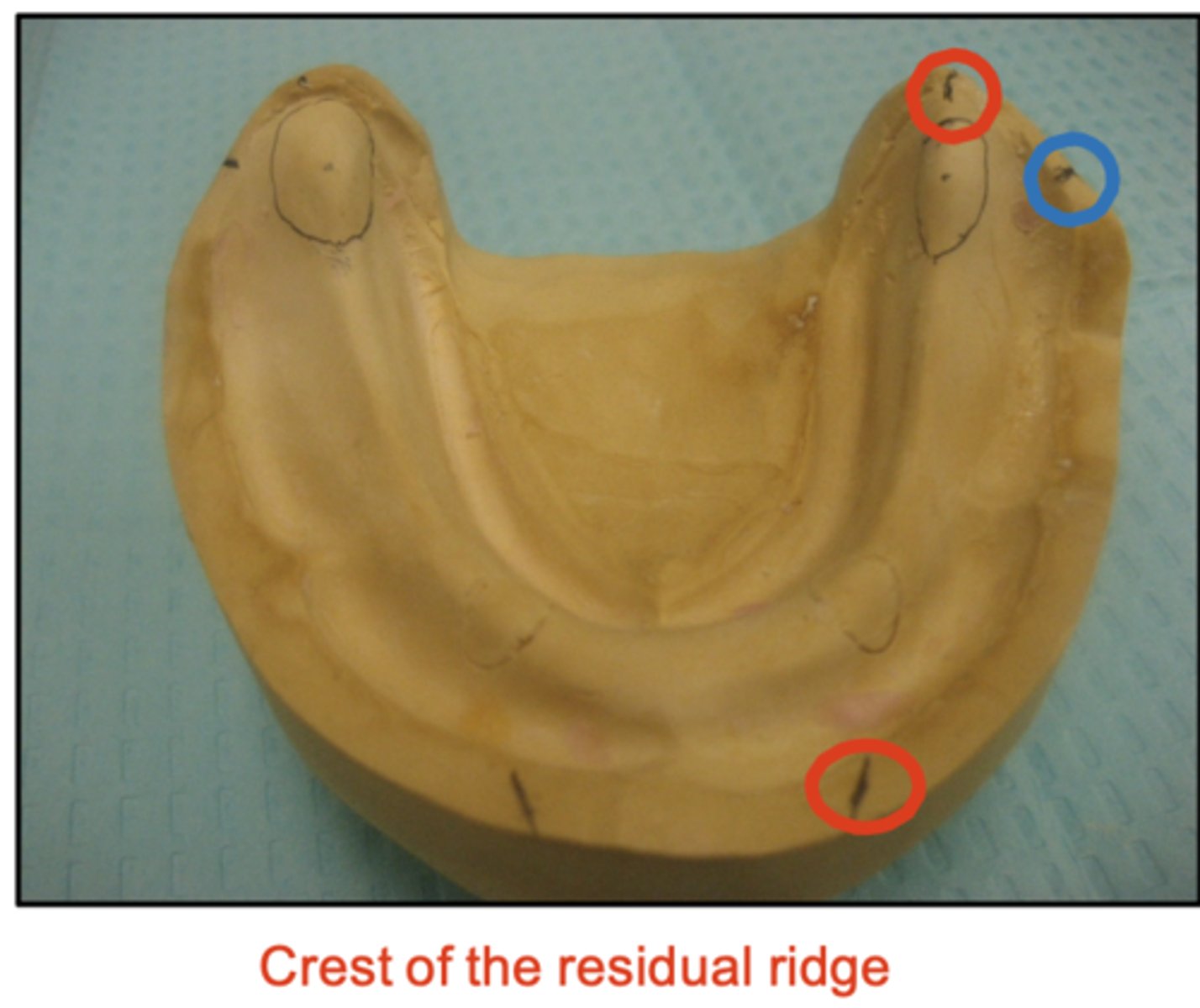
It is important that we mark the crest of the mandibular ridge correctly because, if we set teeth too lingually, what would happen?
Teeth/denture will tip too lingual and reduce space for tongue
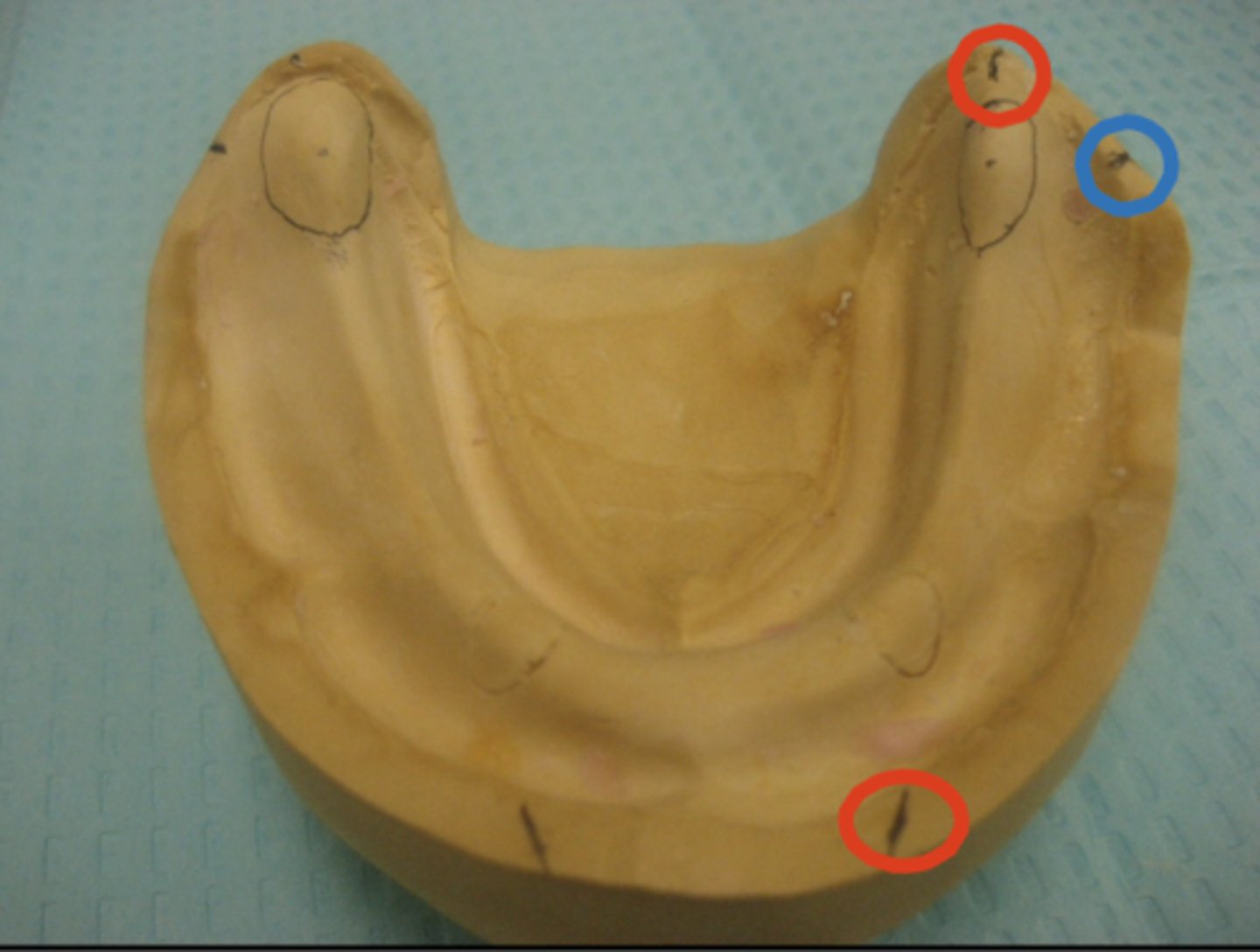
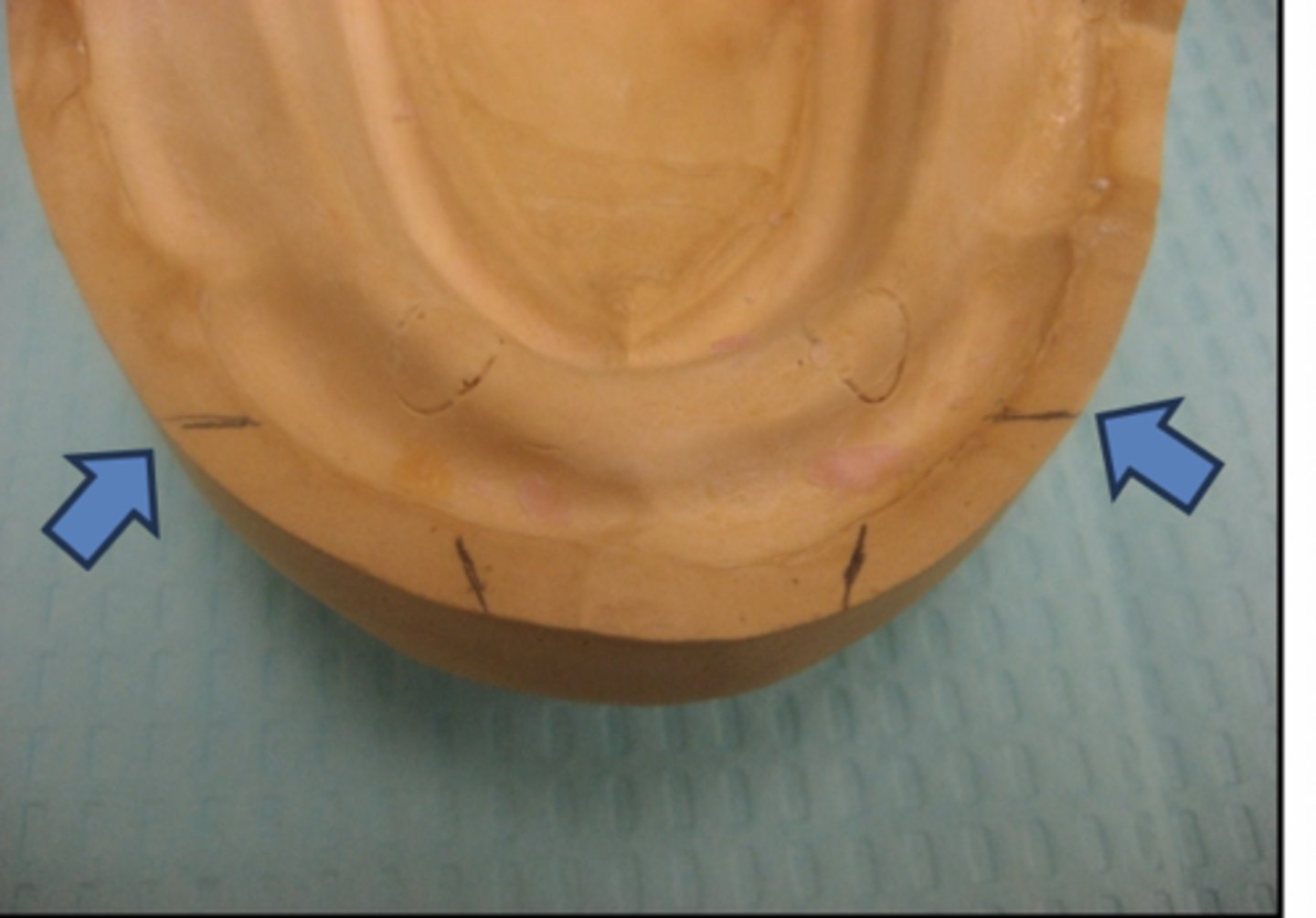
What do the red dots represent?
Crest of the residual ridge
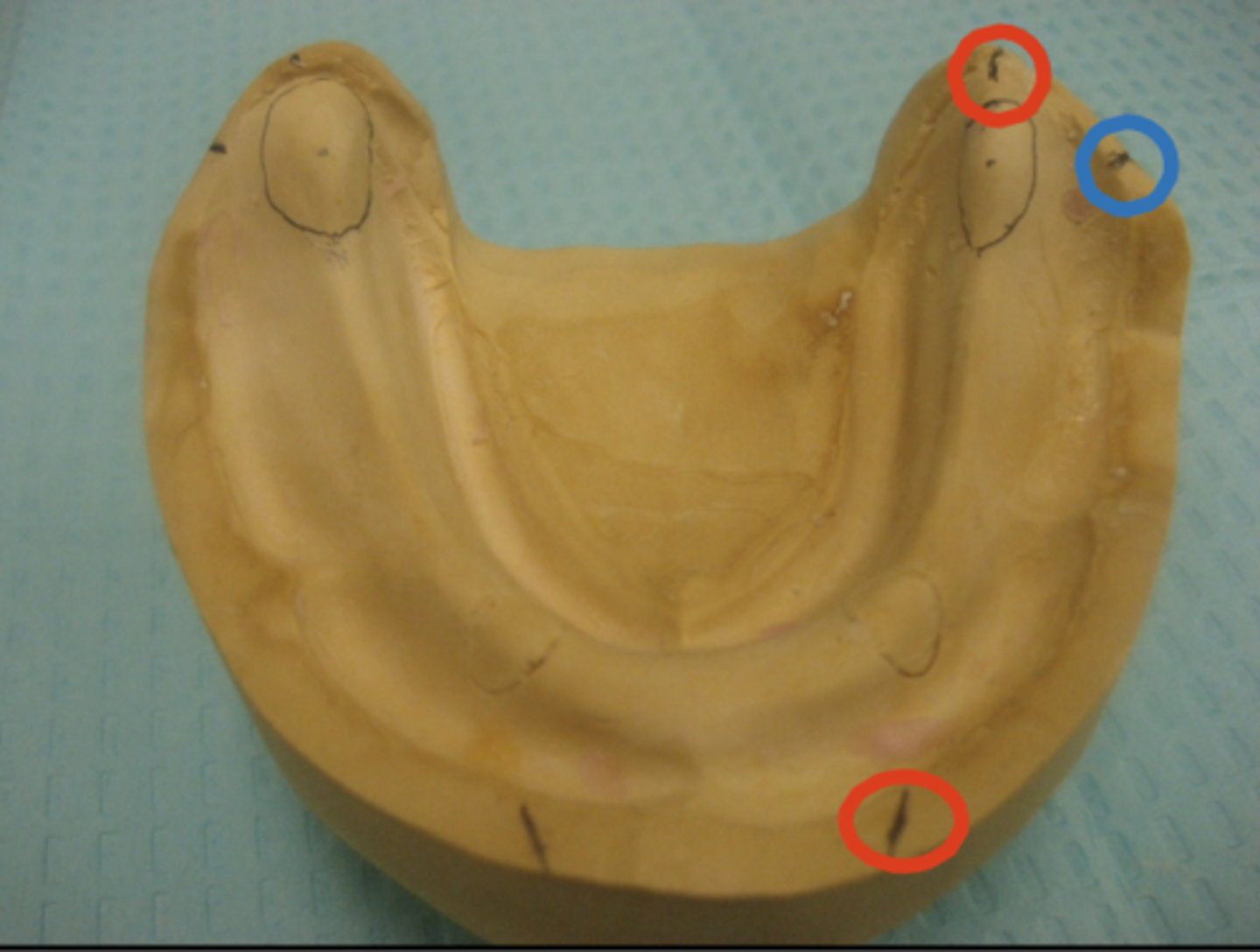
What does the blue dot represent?
Height of the occlusal plane
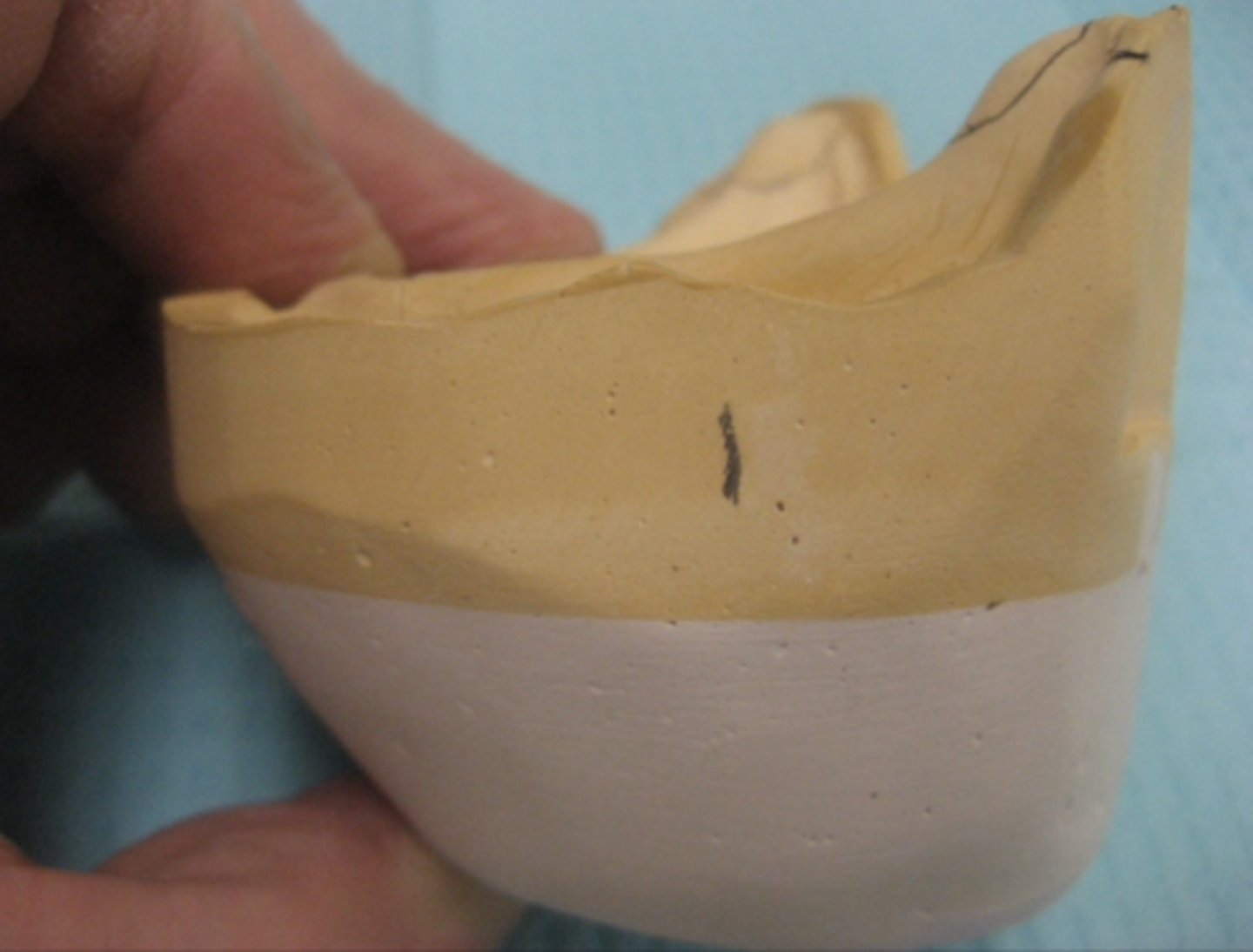
What does this marking represent?
Where the ascending rami begin
Where the __________ begin, draw vertical lines on the left and right sides of the cast. No tooth will be set completely distal to this line
ascending rami
What line marks where no tooth will be set completely distal to the line?
Where the ascending rami begin

What do these markings represent?
Crest of the anterior aspect of the ridge
How many total markings are there between the maxillary and mandibular casts?
18
Ideal border molder determines the proper ________, ________, and ________ of the final complete denture
- Height
- Width
- Contour
For this project, we will assume that our impression are perfect. The triad material should completely fill the entire __________ of your final edentulous casts.
Peripheral rolls
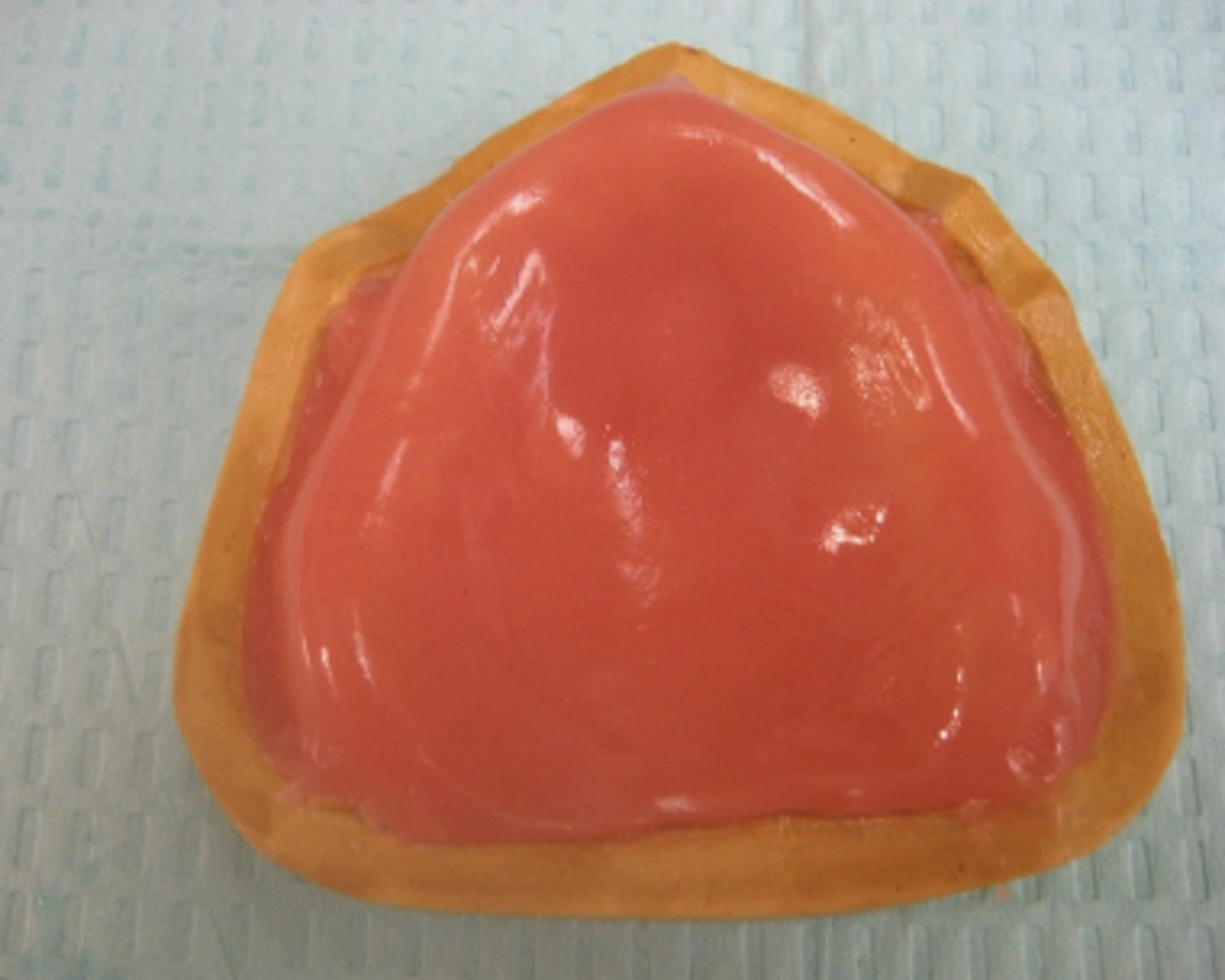
When fabricating the maxillary record paces, be sure that the material completely fills the ___________ areas and is straight across the posterior aspect of the cast.
Hamular notch
When making the record bases, why do we thin down the posterior hard palate?
The thinned down area at the posterior of the hard palate should be about 10 m, wide anterior posteriorly. This will minimize the acrylic shrinkage that will occur during the triad curing process
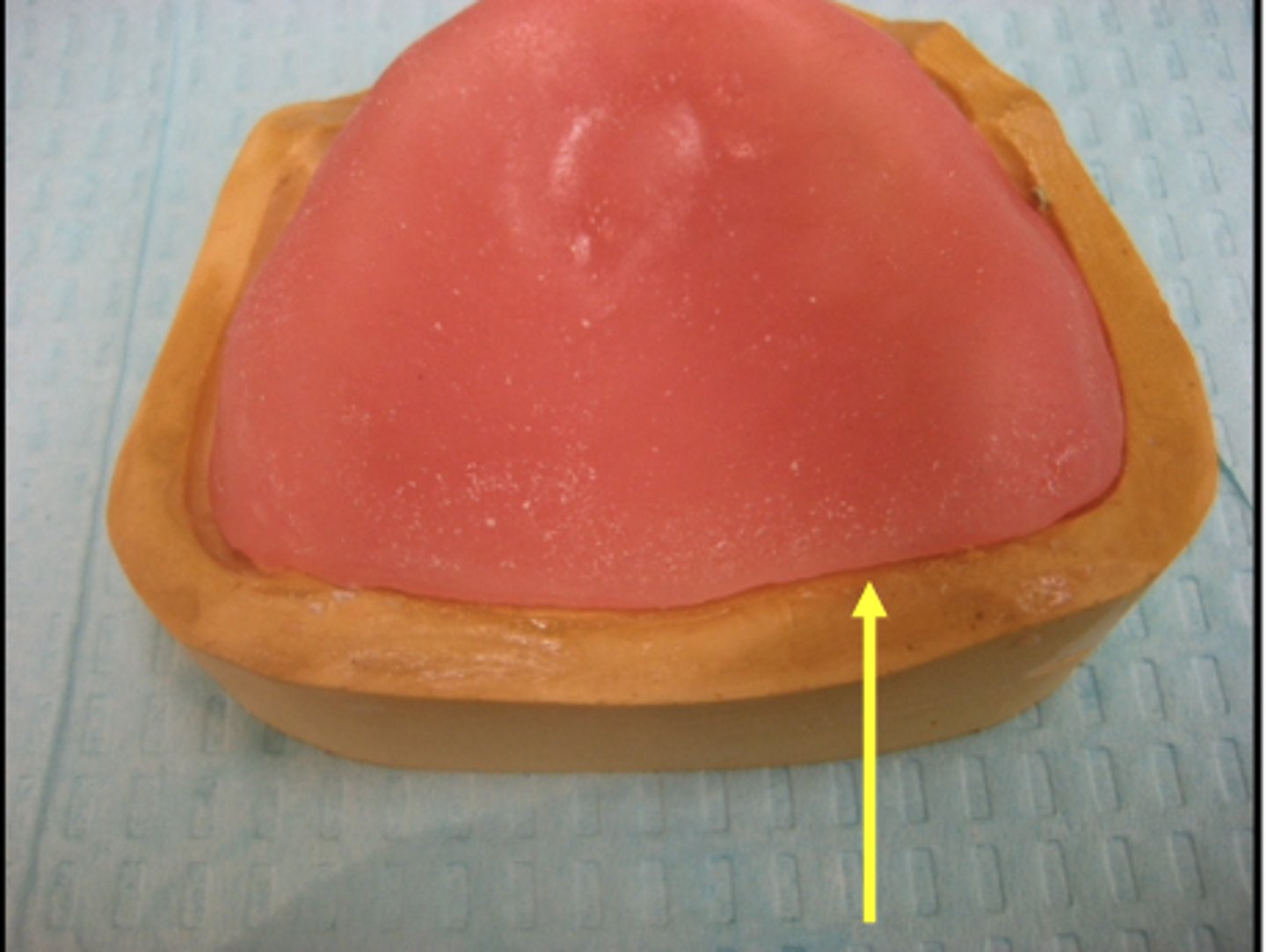
Check the posterior area of the maxillary rim and be sure that you do not have more than a 2 mm space. What happens if you have more than 2 mm space?
A new record base will be required
Why do we thin the anterior aspect of record bases?
Thinning makes the tooth arrangement easier as it provides a little more room for the denture teeth set-up - this should be done before adding wax
For the fabrication of the maxillary wax rim, there is a slight _______ inclination
anterior
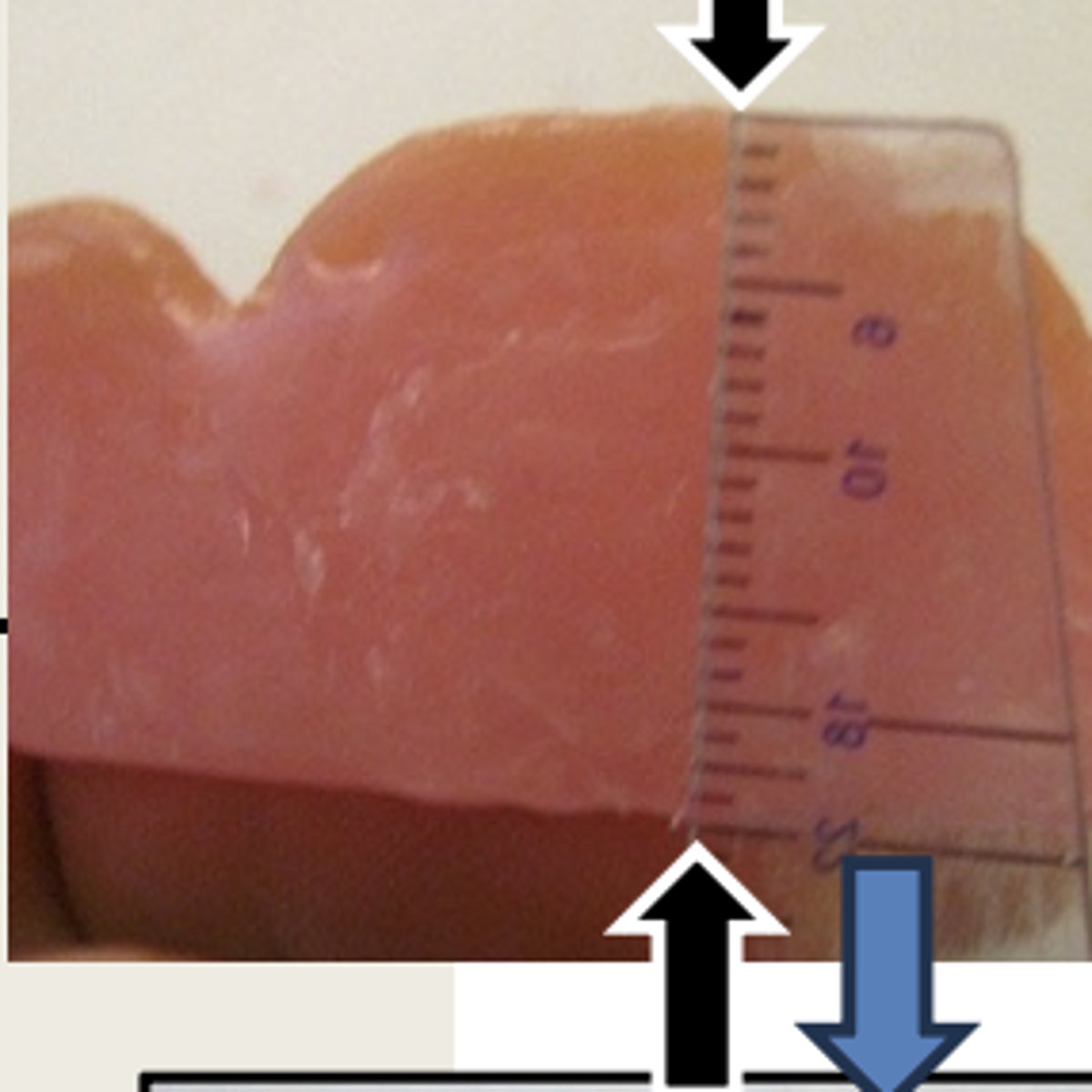
For the fabrication of the maxillary wax rim, it should have a smooth and flat facial surface which is _____ mm high at the lateral incisors (black arrows)
22mm
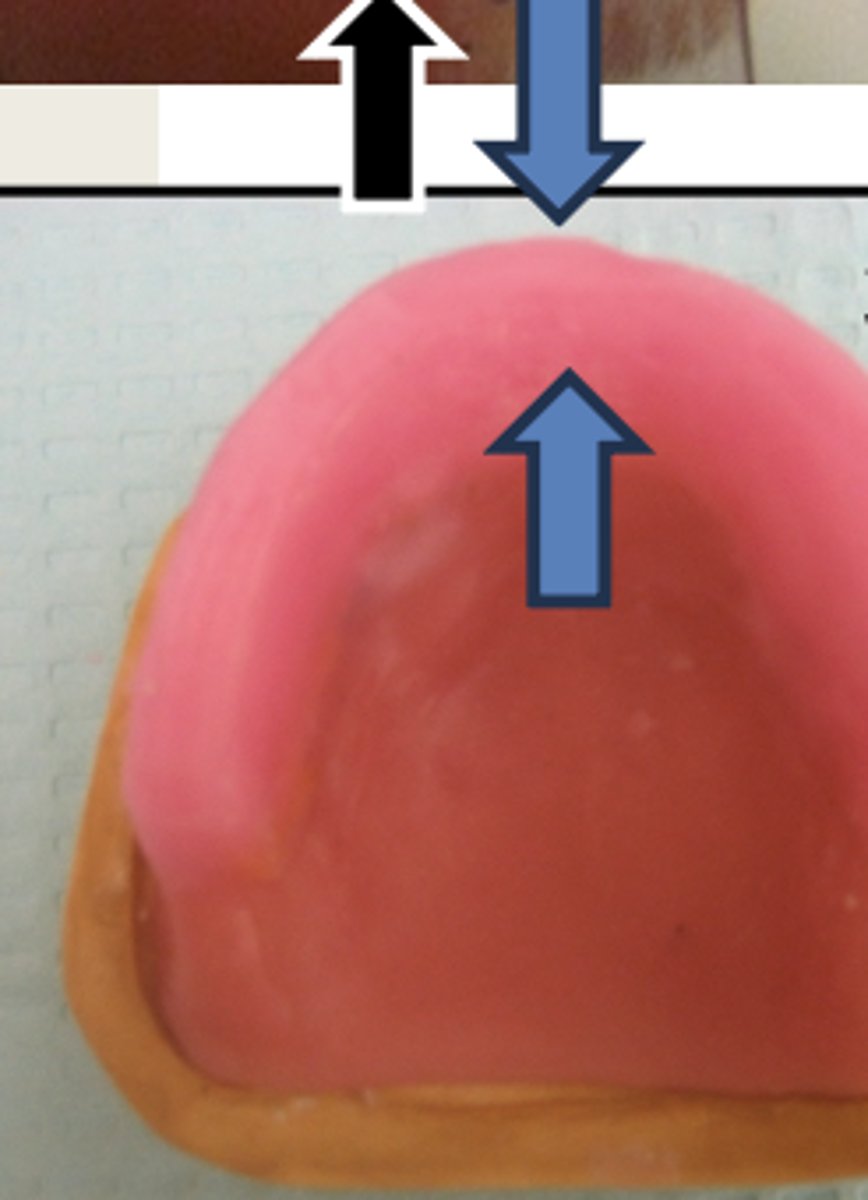
For the fabrication of the maxillary wax rim, it should have a flat and smooth incisal plane which is __ mm wide (blue arrows)
3mm
For the fabrication of the maxillary wax rim, the ________ surface is smooth and sloping towards the peripheral roll
Buccal
For the fabrication of the maxillary wax rim, the _________ surface is smooth and sloping towards the palate
Lingual
For the fabrication of the maxillary wax rim, it should have a lingual surface which is _________ and _________ toward the palate
smooth and sloping
Where should the posterior maxillary wax rim be located over?
Over the crest of the maxillary ridges
the posterior maxillary wax rim should be _______ to the maxillary mean foundation plane
parallel
the posterior maxillary wax rim should have a flat and smooth occlusal plane that is __ mm wide in the bicuspid areas and __ mm wide in the molar areas
5mm (bicuspids), 10mm (molar)
For the fabrication of the maxillary posterior wax rim, it should have a lingual wax smooth and sloping towards the ________
Midline
Where should you cut the posterior ends of the maxillary wax rim?
Where you expect the junction of the first and second molars to be - put about a 45 degree angle on this cut
For the mandibular wax rim, the anterior wax is __ mm high and __ mm wide
18mm (height), 3mm (width)
For the mandibular wax rim, the widths of the occlusal surfaces of the wax rim at __ mm in the bicuspid and __ mm in the molar areas. Keep all these features in mind as you are working
5mm (bicuspids), 10mm (molar)
The occlusal plane of the mandibular wax rim is _________ to the mandibular mean foundation plane
Parallel
The facial and lingual walls of the mandibular wax rim are flat with a slight flare as they feather toward the _________
Peripheral rolls
Is there a buccal inclination of the mandibular wax rim?
No
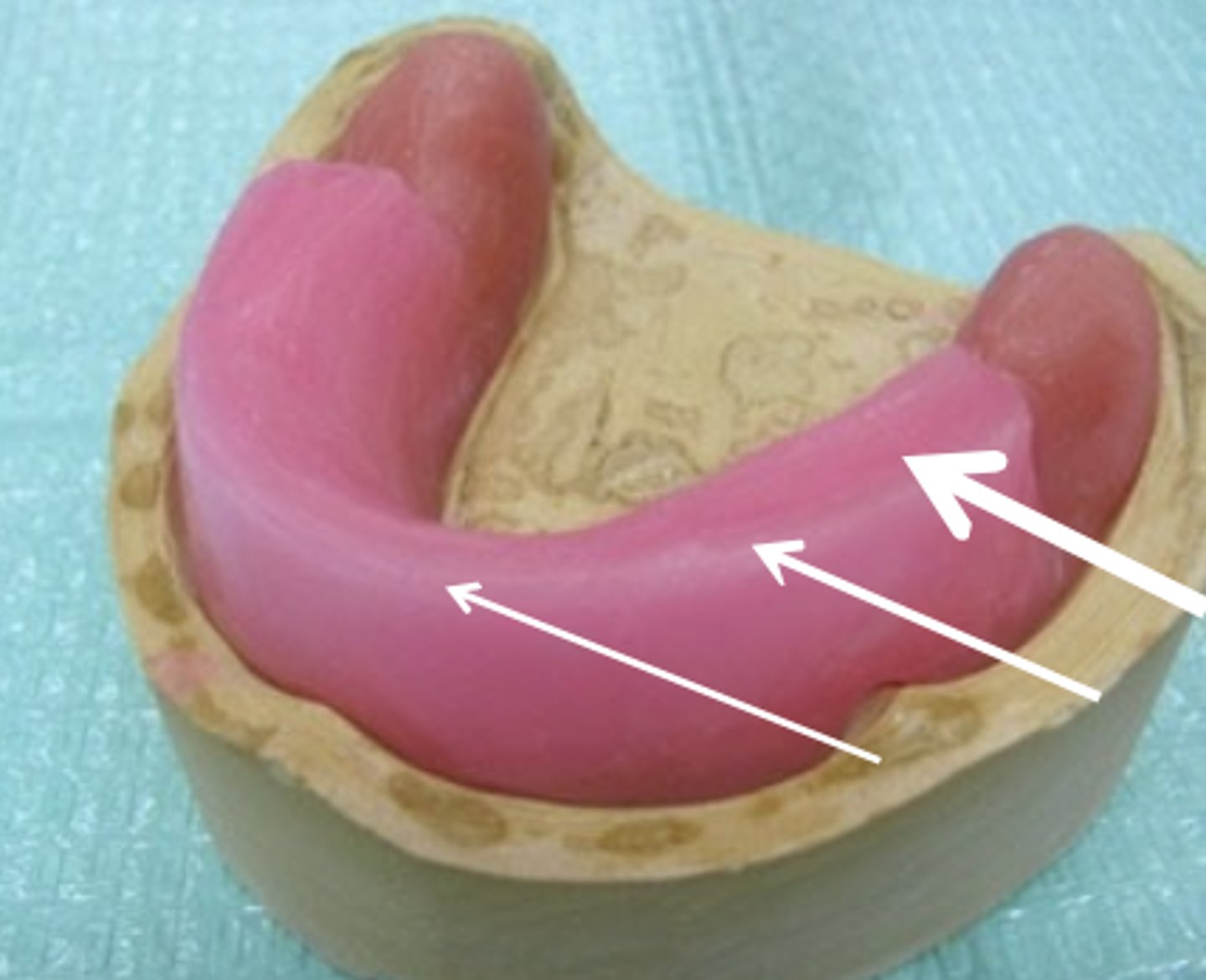
What are the varying widths of the mandibular wax rim?
3, 5, 10 mm
The rim former features a __mm hamular fence
5mm
Note that the incisal portion of wax rim is ________ to occlusal plane
perpendicular
Consider the sequence of treatment for making complete dentures:
When do you take preliminary impressions?
First vist
Consider the sequence of treatment for making complete dentures:
When do you do border molding and final impressions?
Second visit
Consider the sequence of treatment for making complete dentures:
When do you do the maxilla-mandibular relationships?
Third visit
Consider the sequence of treatment for making complete dentures:
When do you do the denture try in?
Fourth visit
Consider the sequence of treatment for making complete dentures:
When do you do insertion?
Fifth visit
Consider the sequence of treatment for making complete dentures:
When do you pour/trim preliminary casts and use those to fabricate the custom trays?
Between first and second visit
Consider the sequence of treatment for making complete dentures:
When do you pour/trim final casts and use those to fabricate the record bases and wax rims?
Between second and third visit
Consider the sequence of treatment for making complete dentures:
When do articulate the casts and set up the teeth?
Between the third and fourth visit