Atmosphere Chemistry
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Atmosphere
helps protect living organisms from genetic damage by solar ultraviolet radiation, solar wind and cosmic rays
Composition of Atmosphere
78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, 0.9% argon, 0.1% carbon dioxide and other gases
Significant Atmospheric Gases
Nitrogen, Oxygen, Argon, Carbon Dioxide, Water Vapor
Nitrogen
a gas which is fixed by bacteria and lightning to produce ammonia, which is used in the building of nucleotides and amino acids
Oxygen
a gas used by most organism for respirations
Argon
a noble gas obtained from the air as a byproduct of the production of oxygen and nitrogen
Carbon Dioxide
one of the trace gases used for photosynthesis by photosynthetic algae, plants and cyanobacteria
Water Vapor
a gas found in the lower layer or altitude of the atmosphere, accounting for 0.25% of it by mass
Carbon
main component of biological compounds and mineral deposits
Carbon Cycle
exchange of carbon among four reservoirs: atmosphere, ocean, land, fossil fuels
Importance of Carbon Cycle
carbon cycle approximates the flows of energy around the Earth, and the metabolism of every system
50% of the dry weight
carbon forms the structure of all life on earth as it makes up about _ of all life forms
-33 degrees celsius
Earth’s average temperature without greenhouse gases
carbon dioxide CO2 and methane CH4
contributes to the natural greenhouse effect that keeps the planet warm to sustain life
Carbon Cycle Diagram
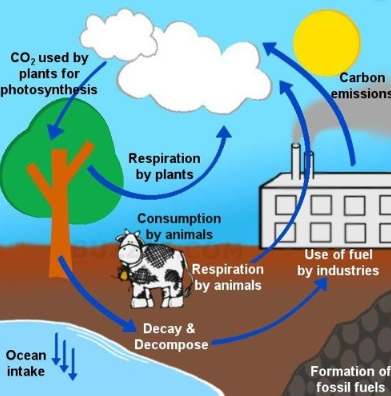
when carbon is stored in different reservoirs other than the ocean, land, or air, it tends to
be released into the atmosphere as greenhouse gases
increased use of fossil fuels
causes imbalance in the release and consumption of carbon dioxide in nature
Air Pollutants
can be released directly into the atmosphere or can form as a result of chemical interaction involving precursor substances
Sources of Emissions
Man-made and Natural
Man-made Sources
burning of fossil fuels; industrial processes or solvent use; agriculture; waste treatment
burning of fossils fuels
coming from households, industry, electricity generation and transport
industrial processes and solvent use
exemplified by the chemical and mining industries
agriculture
methane (CH4) from cattle belching and nitrous oxide (N2O) from fertilizers
waste treatment
treatment plants produce direct emissions of greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4) and nitrous oxide (N2O)
Natural Resources
volcanic eruptions; windblown dust or soil dust; sea-salt spray; volatile organic compounds
volcanic eruptions
emit water vapor and toxic gases into the atmosphere, such as carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide, hydrogen sulfide, hydrochloric acid, and carbon monoxide
windblown dust or soil dust
emitted through wind erosion and wildfires
sea-salt spray
contribute to global gas emissions; are a dominant contributor to the direct scattering of solar radiation; and are an important source of cloud droplets.
volatile organic compounds
chemical substances produced by plants and other organisms composed of carbon
depletion of the ozone layer
Influential greenhouse gases in the form of air pollutants cause __ in the atmosphere.
Ozone Layer
This layer covers the entire planet and protects life by absorbing harmful UV-B radiation from the Sun.