L2 Lids & Lashes Anatomy
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Jessica
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
what muscle of the eyelid is the main protractor of the eyelid originating from canthal tendons
orbicularis oculi
what muscle of the eyelid is responsible for the eyelid closure, blink, drainage of tears and MG secretion
orbicularis oculi
what are the 3 portions of the orbicularis oculi muscle
orbital, preseptal, pretarsal
orbicularis oculi- orbital portion
orbicularis oculi- preseptal portion
orbicularis oculi- pretarsal portion
orbicularis oculi- riolan muscle
what are the two roles of riolans muscle
-position the puncta
-contract the MG for secretion
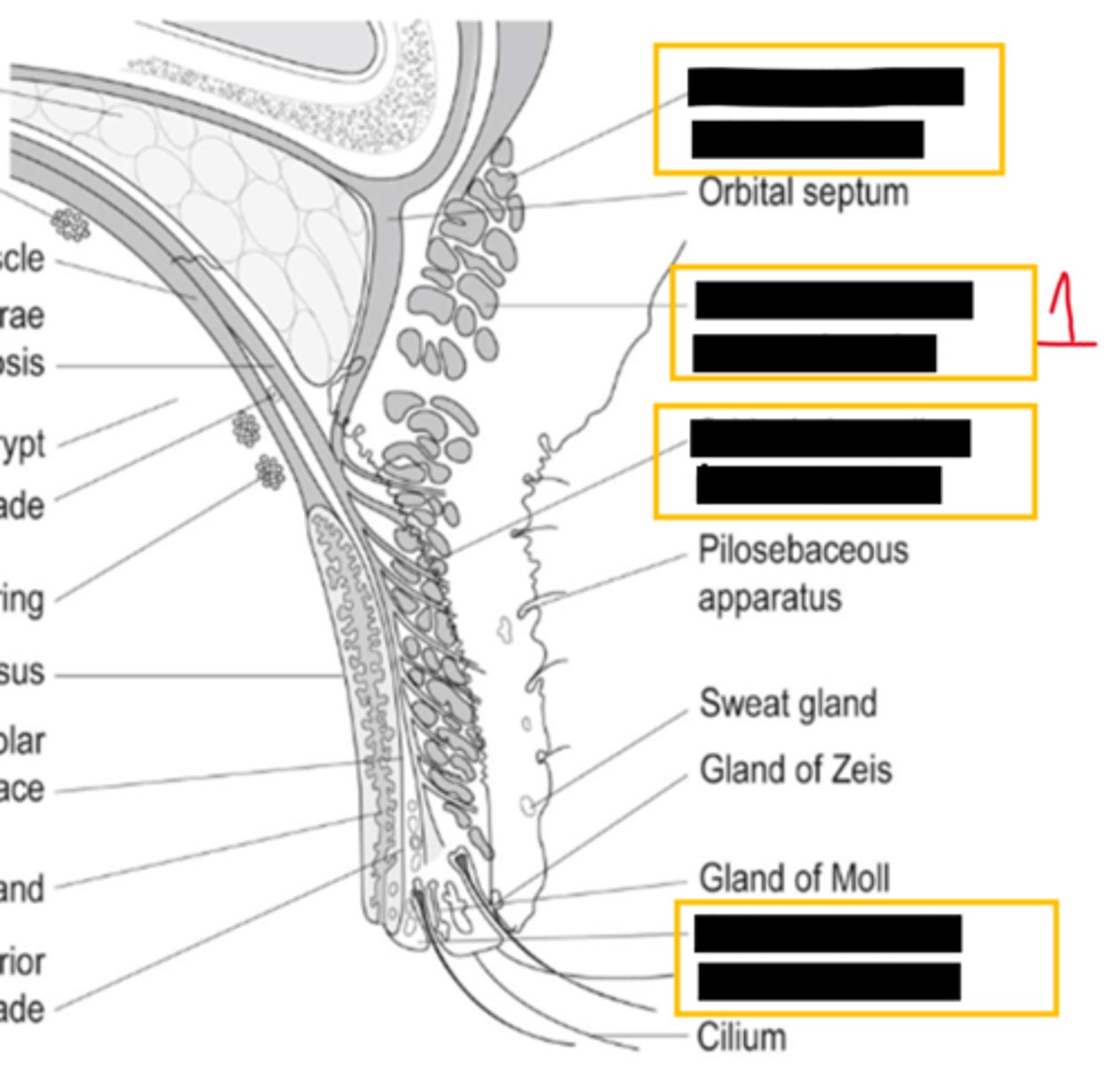
what is located between the preseptal tissue and the orbit
orbital septum
what kind of tissue is the orbital septum made of
thin fibrous
the orbital septum begins in ___ ___ and fuses with eye lid retractors
arcus marginalis
orbital is anterior to
orbital fat
cellulitis is classified based on location relative to the orbital septum so
preseptal =
anterior to the orbital septum
cellulitis is classified based on location relative to the orbital septum so
orbital=
posterior to the orbital septum
what is the purpose of orbital fat
serves as barrier between eyelid and orbit by limiting spread of infection & bleeding
what is blepharoplasty surgery for
removal of excess fat, muscle and skin from eyelids
what complication can occur from blepharoplasty on the removal of medial fat pad
its close proximity to the trochlea can lead to superior oblique palsy and brown syndrome
which muscle is the primary retractor of upper eyelid
LPS
muller muscle is under parasympathetic or sympathetic innervation
sympathetic
muller muscles is responsible for ____ mm of vertical elevation of upper eyelid
1-2
_____ _____ affects sympathetic output, resulting in mild ptosis of the upper lid and reverse ptosis of the lower lid
horners syndrome
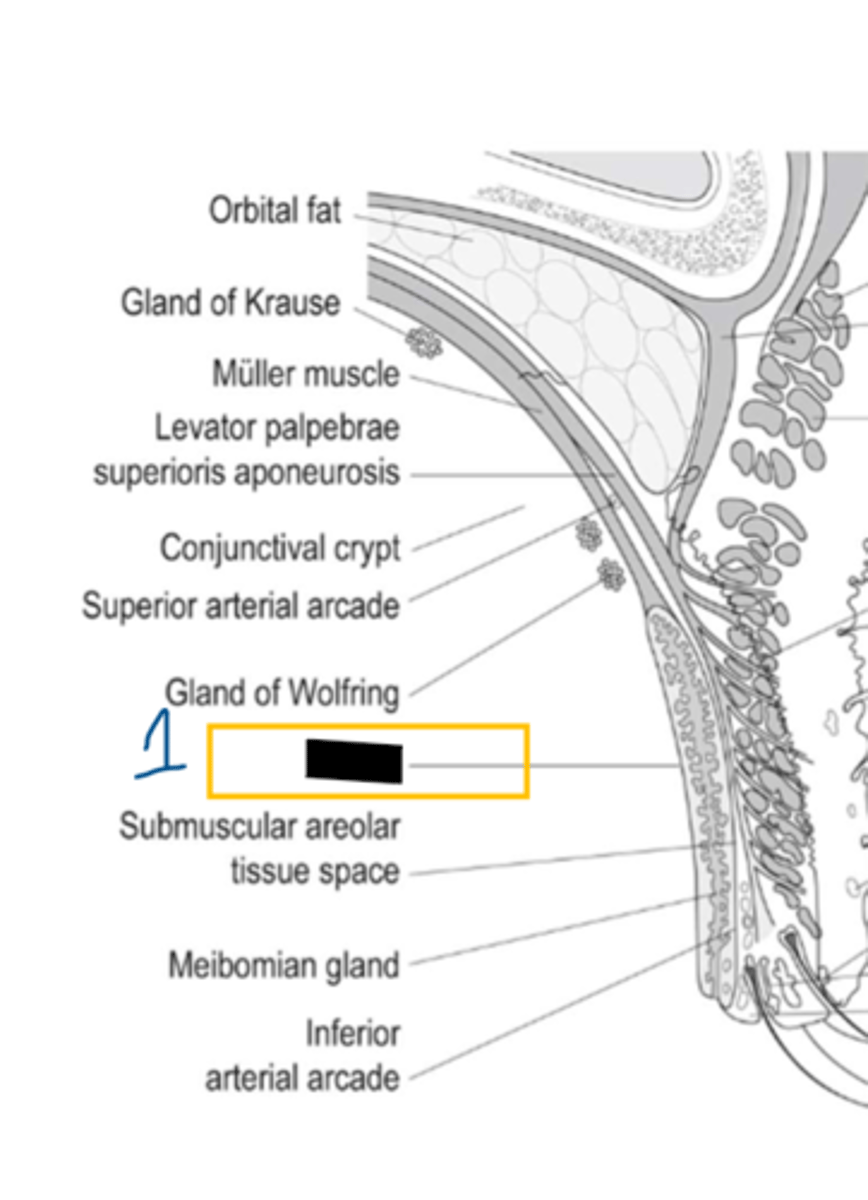
tarsus/ tarsal plate
function of tarsal plate
provide structure and contain MG
Meibomian glands are the site for inflammation leading to (2)
chalazion & internal hordeolum
what does MG dysfunction lead to
dry eye syndrome
what is the mucous membrane lining the inner surface of the eyelid
conjunctiva
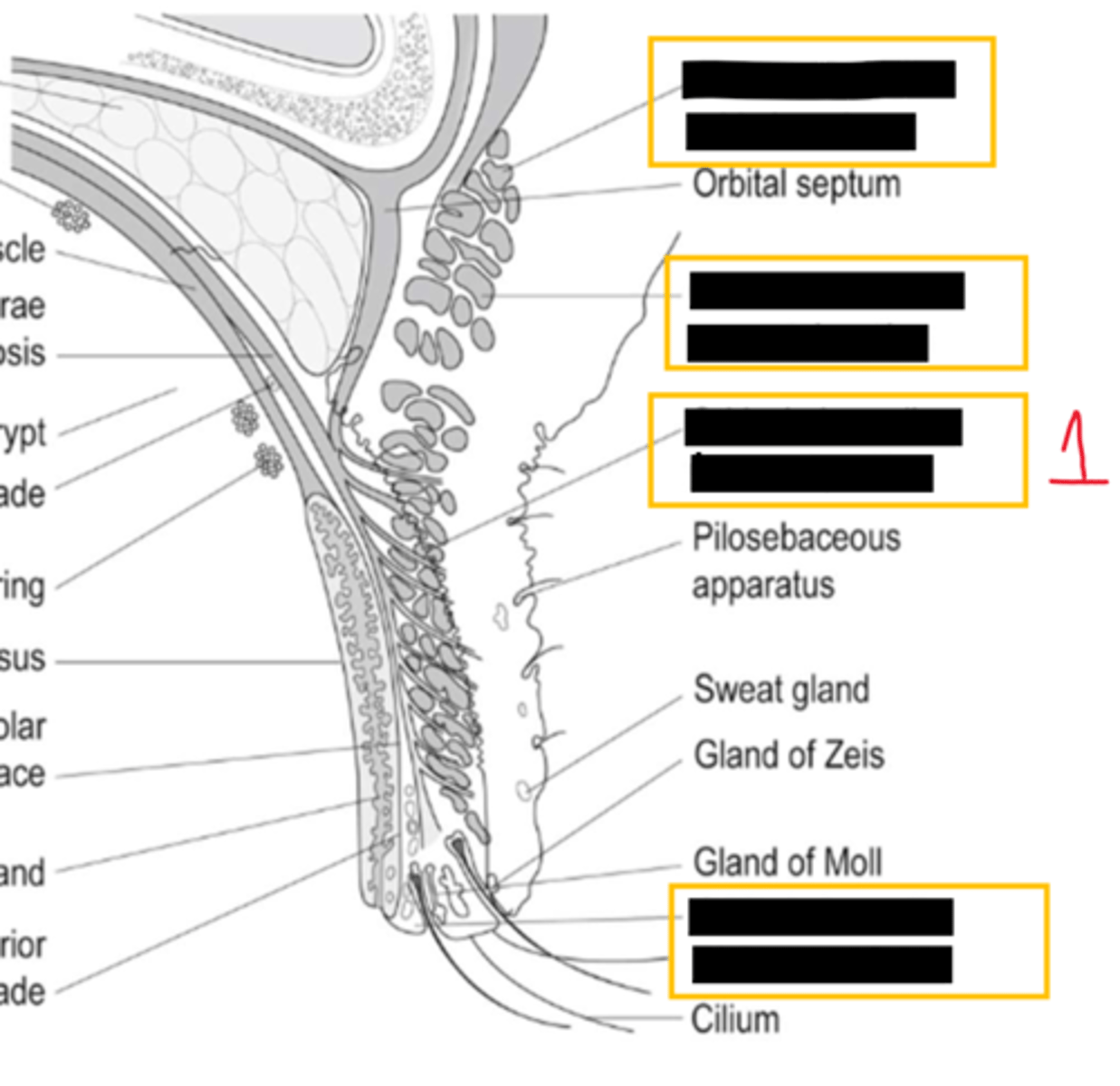
what are two lacrimal accessory glands
wolfring and krause
does the conjunctiva contain lacrimal accessory glands
yes as well as goblet cells
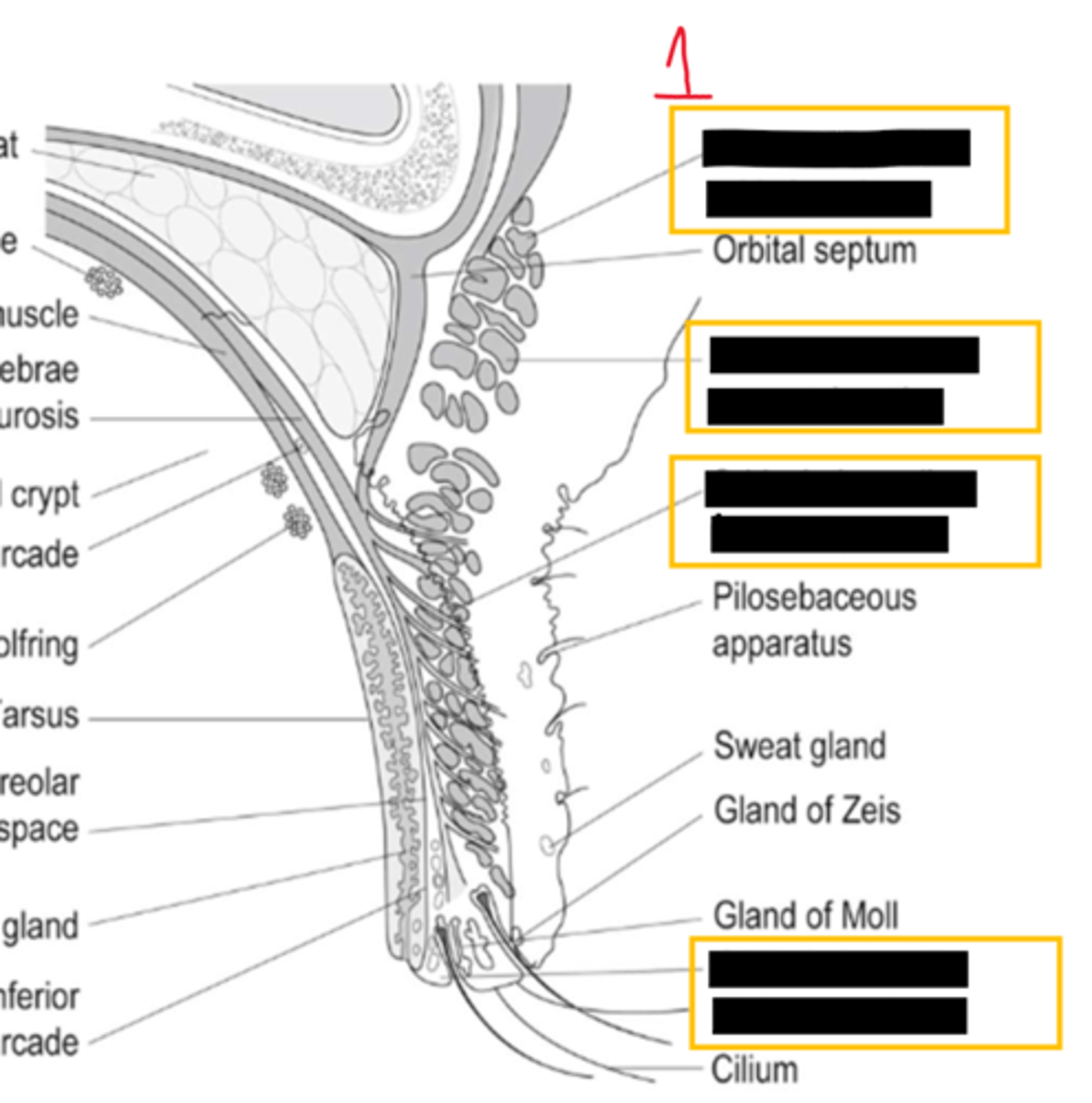
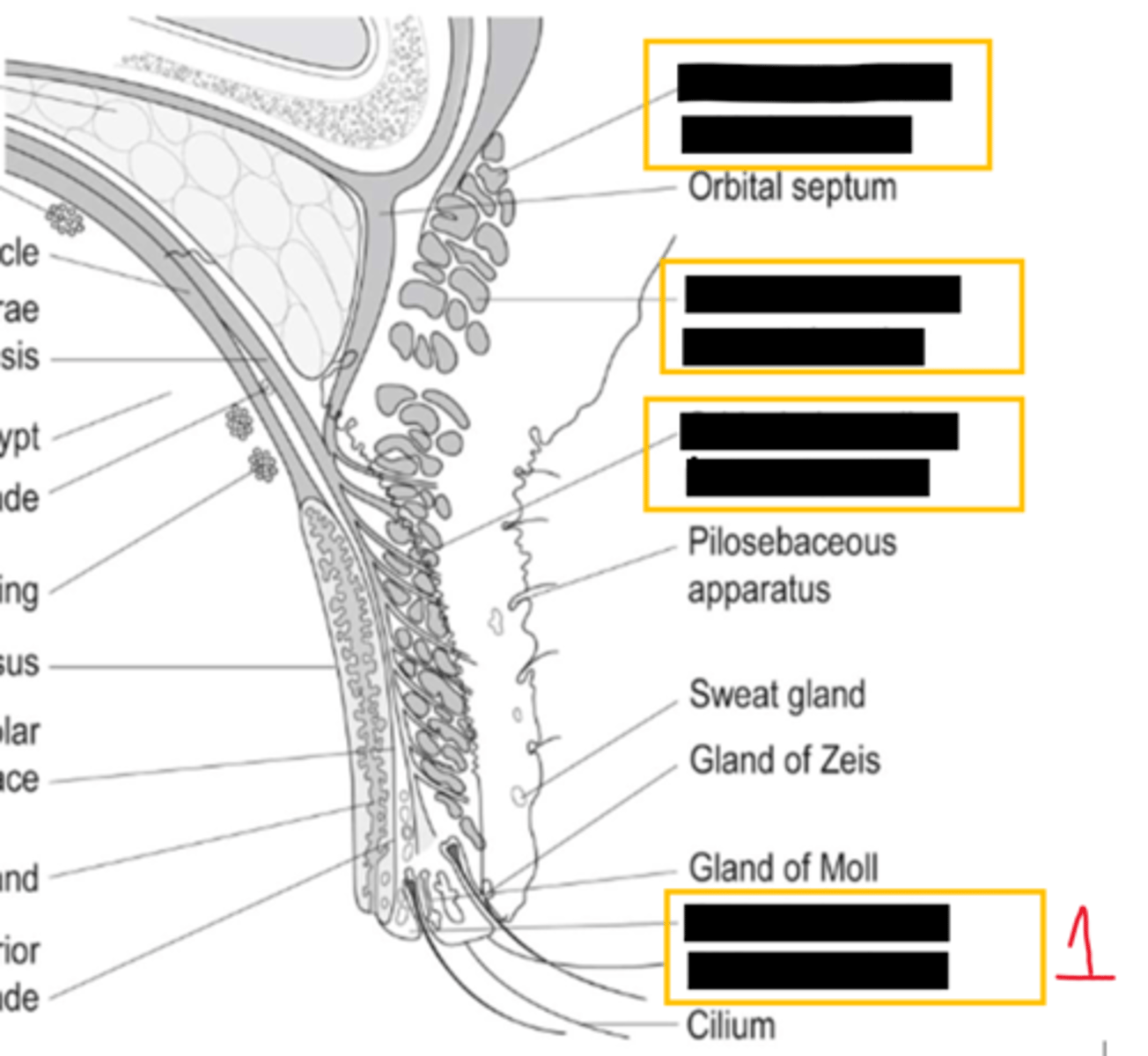
eyelid margin contains which 3 types of glands
zeis- sebaceous
moll- sweat
MG- sebaceous
inflammation of more external gland of zeis=
external hordeolum
inflammation of MG=
internal hordeolum
what is the normal flora of the eyelid margins
coagulase negative staph & s. aureus