Lecture 10
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
1
New cards
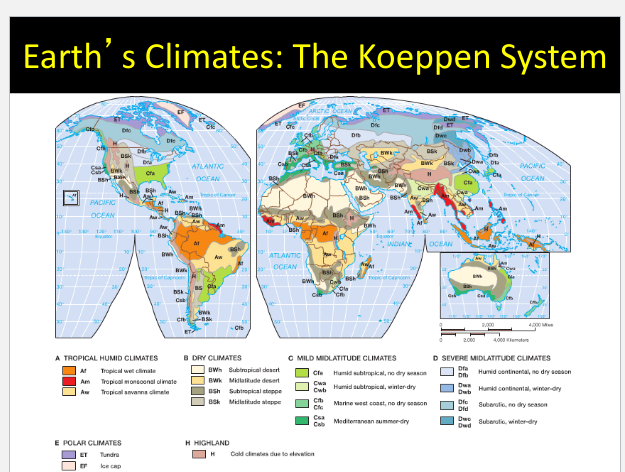
What's the Koeppen System?
Maps that specifically tell us the climate of different regions in the world
2
New cards
What are Prochlorococcus?
Smallest photosynthetic organism on the planet, responsible for 50% of atmospheric O2
large surface area: good at obtaining nutrients
there are high concentrations of it in the middle of the ocean (gyres)
large surface area: good at obtaining nutrients
there are high concentrations of it in the middle of the ocean (gyres)
3
New cards
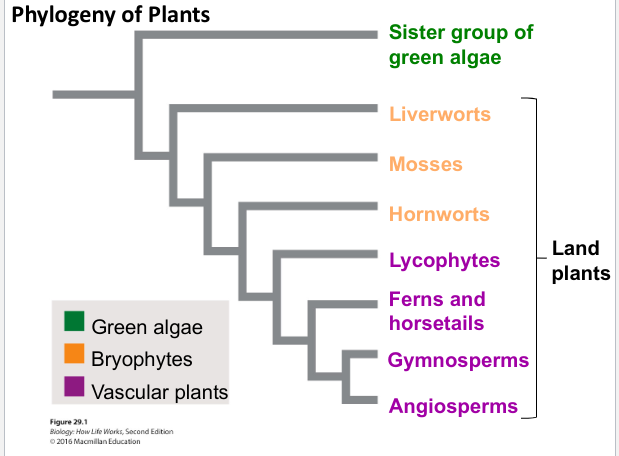
What is the phylogeny of plants?
1. Sister group of green algae
2. Bryophytes (LAND PLANTS)
* Liverworts
* Mosses
* Hornworrts
3. Vascular Plants (LAND PLANTS)
* Lycophytes
* Ferms and horsetails
* Gymnosperms
* Angiosperms
\
They’re all common ancestors
4
New cards
What are green algae?
\
* Range from the tiniest unicellular photosynthetic organisms to the giant kelp
* Live entirely in the water
* Range from the tiniest unicellular photosynthetic organisms to the giant kelp
* Live entirely in the water
5
New cards
What are phytoplankton?
Are phototrophic autotrophs of the oceans, mostly unicellular
its distribution by species are always dependent on nutrient supply
its distribution by species are always dependent on nutrient supply
6
New cards
What is the difference between plankton,
nekton, benthos?
nekton, benthos?
Plankton: at the mercy of the currents
Nekton: anything that moves independently of the currents
Benthos: anything on the sea floor
Nekton: anything that moves independently of the currents
Benthos: anything on the sea floor
7
New cards
\n
What are some types of phytoplankton that with low and high nutrients?
What are some types of phytoplankton that with low and high nutrients?
Low nutrients water:
* Cynaboacteria (mainly prochlorococcus)
High nutrient water:
* Dinoflagellates
* Diatoms
* Coccolithophores
* Cynaboacteria (mainly prochlorococcus)
High nutrient water:
* Dinoflagellates
* Diatoms
* Coccolithophores
8
New cards
What are diatoms: big and greedy?
20-200 microns
Use silica (sustains its) for protection
Regions w/high nutrient concentrations
Small surface area to volume ration:
need extra work at getting nutrients but need lots of them
Use silica (sustains its) for protection
Regions w/high nutrient concentrations
Small surface area to volume ration:
need extra work at getting nutrients but need lots of them

9
New cards
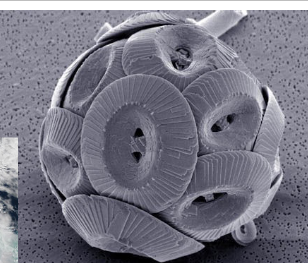
What are coccolithophores?
* Armored but fragile beauties
* 5-100 microns size smaller than diatoms
* CaCO3 tests (deposit chalk)
* They prefer water with high nutrient concentrations
* 5-100 microns size smaller than diatoms
* CaCO3 tests (deposit chalk)
* They prefer water with high nutrient concentrations
10
New cards
\n
What are dinoflagellates?
What are dinoflagellates?
Pesky (annoying) but important
* Have flagella
* Very diverse
* Common endosymbionts
* Can have toxins, be bioluminescent
* Common in “red-tide” events
* Produce toxins, ingested by shellfish in large quantities
* Have flagella
* Very diverse
* Common endosymbionts
* Can have toxins, be bioluminescent
* Common in “red-tide” events
* Produce toxins, ingested by shellfish in large quantities

11
New cards
What are red-tides?
contain
* high concentrations of phytoplankton, often dinoflagellates
* have toxin-producing algae (harmful algal blooms)
Examples of toxins include:
* Saxitoxin causes paralytic shellfish poisoning
* Brevetoxin can be aerosolized, causing respiratory problems
* high concentrations of phytoplankton, often dinoflagellates
* have toxin-producing algae (harmful algal blooms)
Examples of toxins include:
* Saxitoxin causes paralytic shellfish poisoning
* Brevetoxin can be aerosolized, causing respiratory problems
12
New cards
Climate regulation
1. Marine Phytoplankton produce DMS gas
which is Oxidized in the atmosphere to sulfur-base aerosols
* Phytoplankton to gas (positive more cloud condensation)
* DMS gas to CNNs postive
Aeroles become cloud condensation nuclei (CCNs) responsible for cloud seeding
* CCN to albedo positive
Albedo to phytoplankton negative
Clouds impact albeldo which has a cooling effect (negative)
13
New cards

What are bryophytes? (THE AMPHIBIANS OF THE PLANT WORLD)
First Land Plants aka mosses do not have roots which they requires lots of water
Rely on other structures to be sustained
Limited by water loss (desiccation)
Low-growing
Can withstand long periods w/out water, but eventually DIE
Rely on other structures to be sustained
Limited by water loss (desiccation)
Low-growing
Can withstand long periods w/out water, but eventually DIE
14
New cards
What are vascular plants?
\\n
1. Contains vascular tissues (xylem and phloem) distrubute resources (water nutrients, sugar) through the plant
2. “Alternation of generation reproduction
1. Contains vascular tissues (xylem and phloem) distrubute resources (water nutrients, sugar) through the plant
2. “Alternation of generation reproduction
15
New cards

What were the first to evolve of vascular plants?
1. Lycophytes (single vein)
16
New cards

Hb the second ones?
1. Ferns and Horsetails (spores)
17
New cards

The third one?
1. Gymnosperms “naked seed” first-seeded plants
* Rely on animals and wind for seed dispersal
Examples: Cycads, Ginkgos (fossils) trees, Conifers(trees that bear their seeds in cones)
18
New cards
What about the 4th one?
Angiosperms = “Protected Seeds”
* 90% of the species of land plants present today
1. Contain Flowers!
2. Encase seeds in
protective coat (i.e. a
fruit)
3. Co-evolved w/insects
4. Flowers attract a pollinator, rewards plants & animals seed/pollen dispersal
* 90% of the species of land plants present today
1. Contain Flowers!
2. Encase seeds in
protective coat (i.e. a
fruit)
3. Co-evolved w/insects
4. Flowers attract a pollinator, rewards plants & animals seed/pollen dispersal
19
New cards
Why are angiosperms successful?
Efficient at building their bodies & completing their life cycle
Reproduce quickly & with minimum of resources
Reproduce quickly & with minimum of resources
20
New cards
What contributes to angiosperm diversity?
the interaction of flowers and animal pollinators
21
New cards
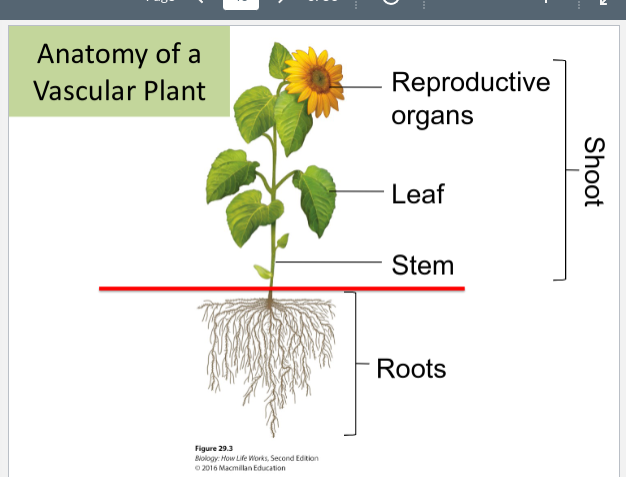
What is the anatomy of a vascular plant?
Shoot
* Very Top: Reproductive organs
* Leaf
* End: Stem
Roots very bottom
* Very Top: Reproductive organs
* Leaf
* End: Stem
Roots very bottom
22
New cards
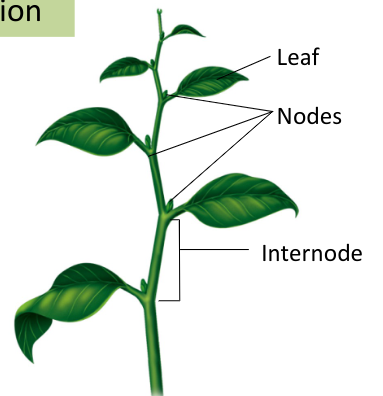
What are shoots made of?
Repeating units of nodes and internodes; one or more leaves attached at each node
23
New cards
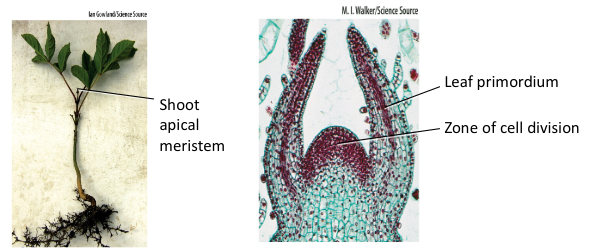
What is shoot apical meristem & where is it?
Site of new cell division
tip of shoots
tip of shoots
24
New cards
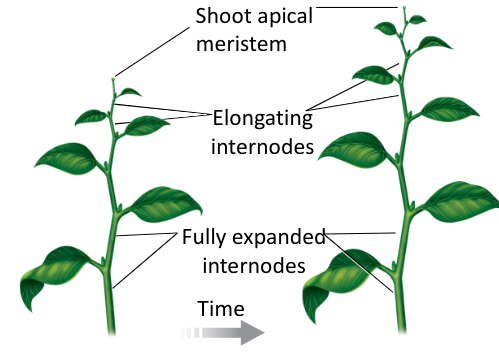
What is primary growth?
Plants grow up, then out
25
New cards
What do all vascular plants have?
LEAVES which are:
* Sites of photosynthesis
* Serve as a way for plants to climb/reach sunlight
* Protection
* Trap nutrients
* Sites of photosynthesis
* Serve as a way for plants to climb/reach sunlight
* Protection
* Trap nutrients