Secretion I: Salival, Gastric & Intestinal
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
95 Terms
What type of epithelium lines the oral mucosa and esophagus?
Stratified squamous non-keratinized epithelium
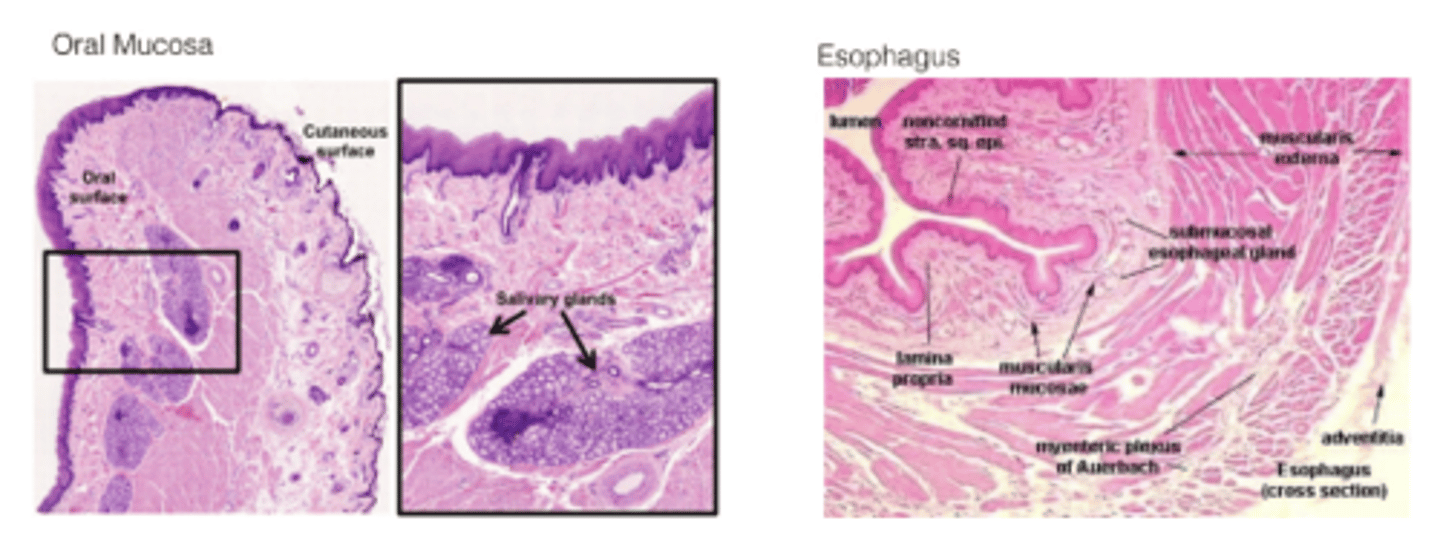
What is found in the submucosa of the mouth?
Salivary glands
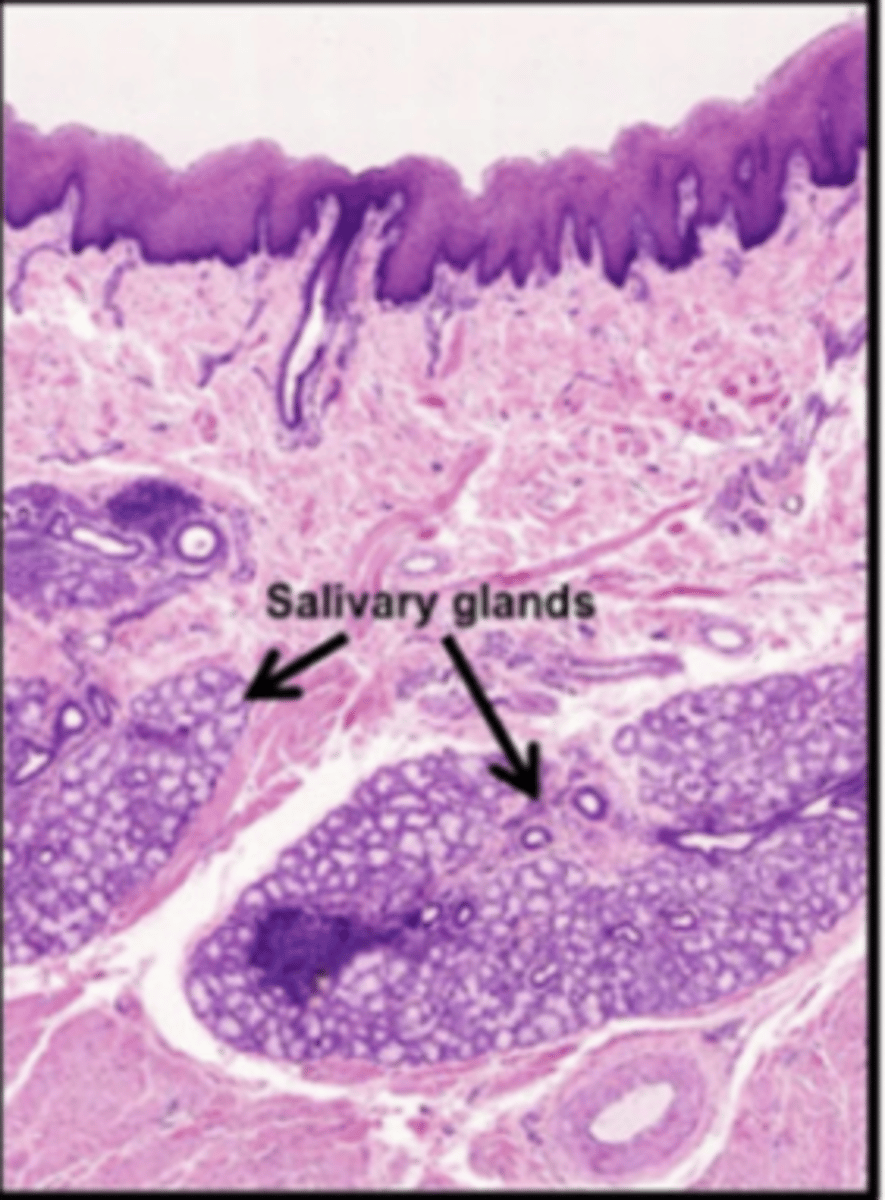
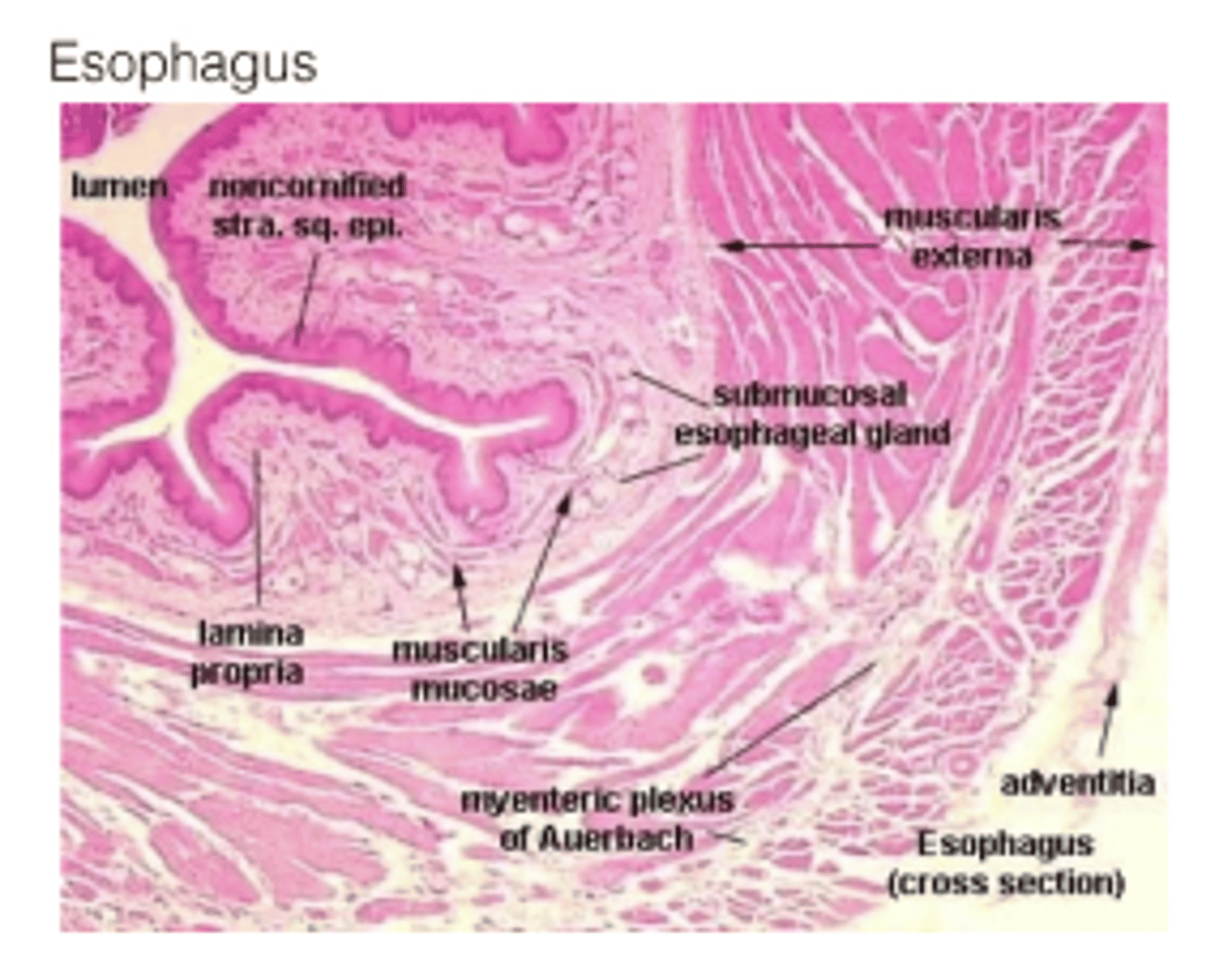
What additional muscular layer is found in the esophagus' submucosa?
Muscularis mucosae
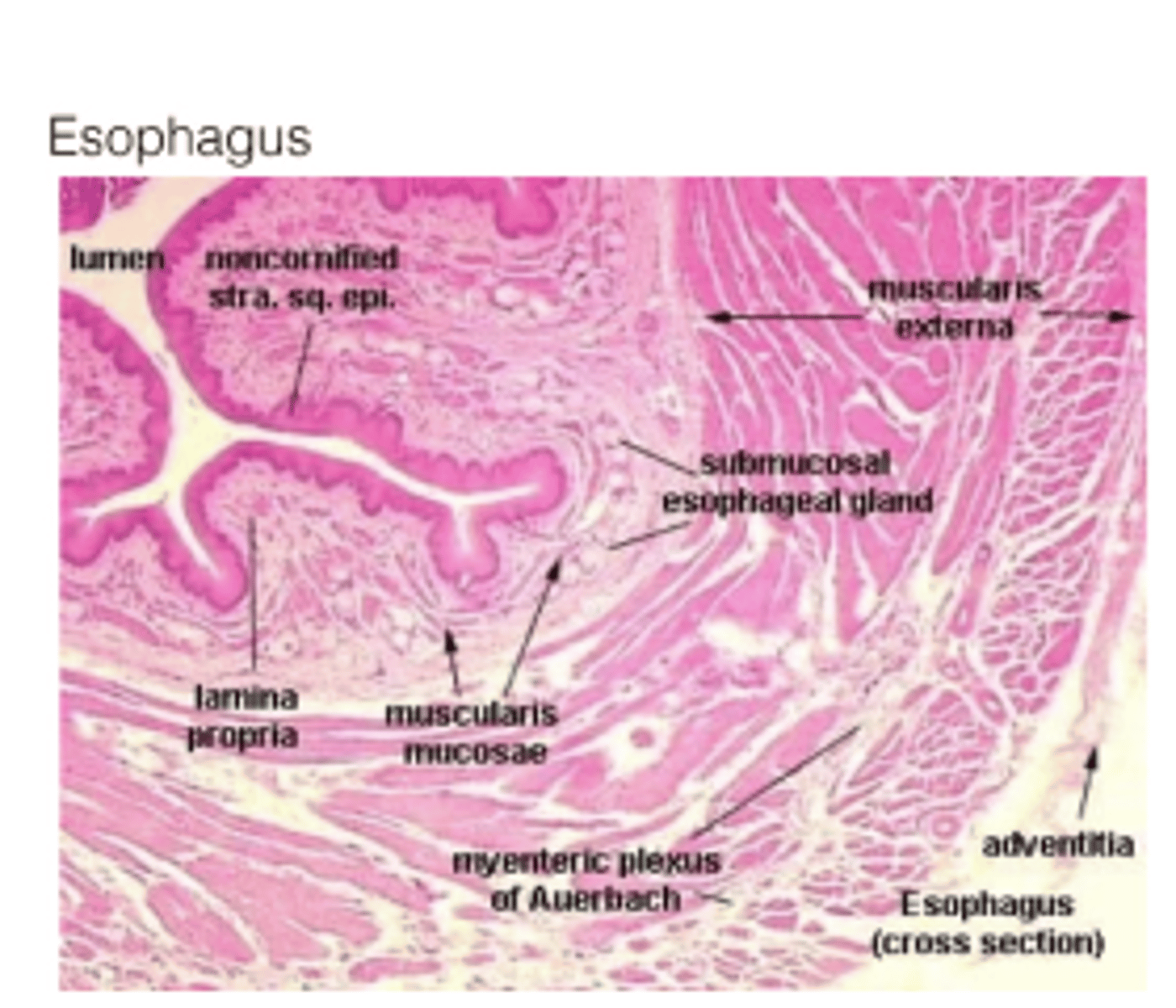
What special feature does the muscularis mucosae have?
Its own neural plexus
A neural plexus is a network of interconnected nerve fibers (axons) and sometimes neuronal cell bodies. It’s like a web or mesh of nerves that work together to coordinate signals to and from organs.
What type of epithelium lines the stomach, small intestine, and colon?
Simple columnar epithelium
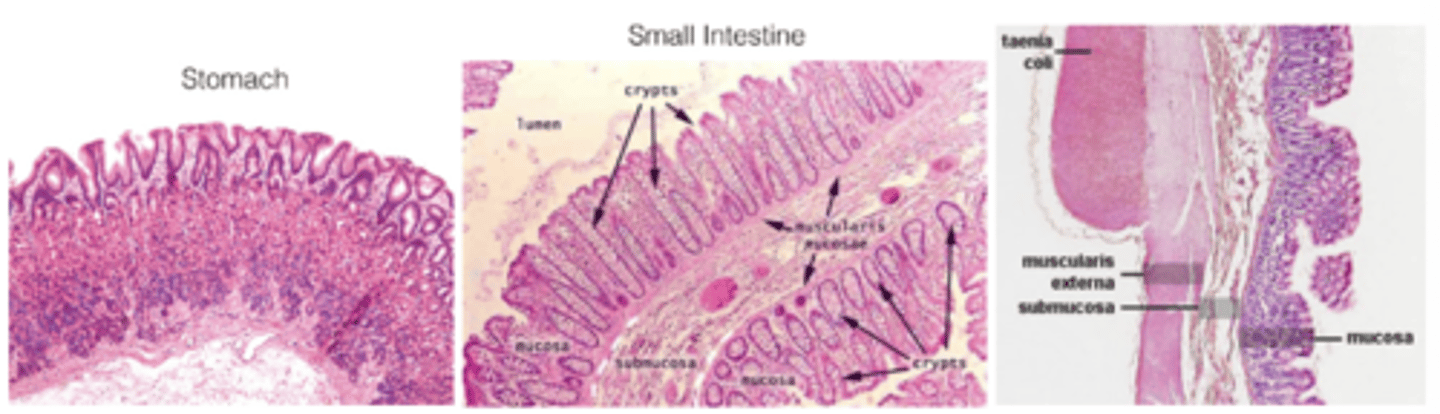
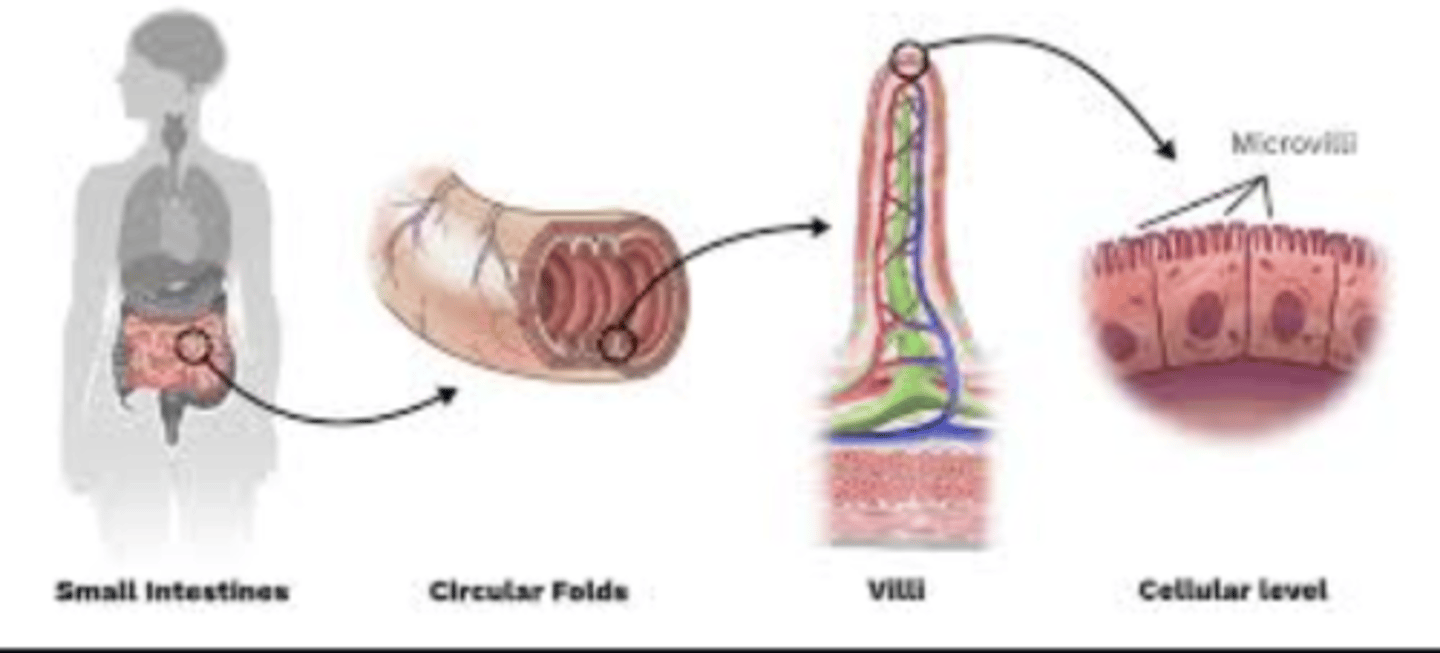
What structures increase the absorptive surface in the small intestine?
Microvilli and villi
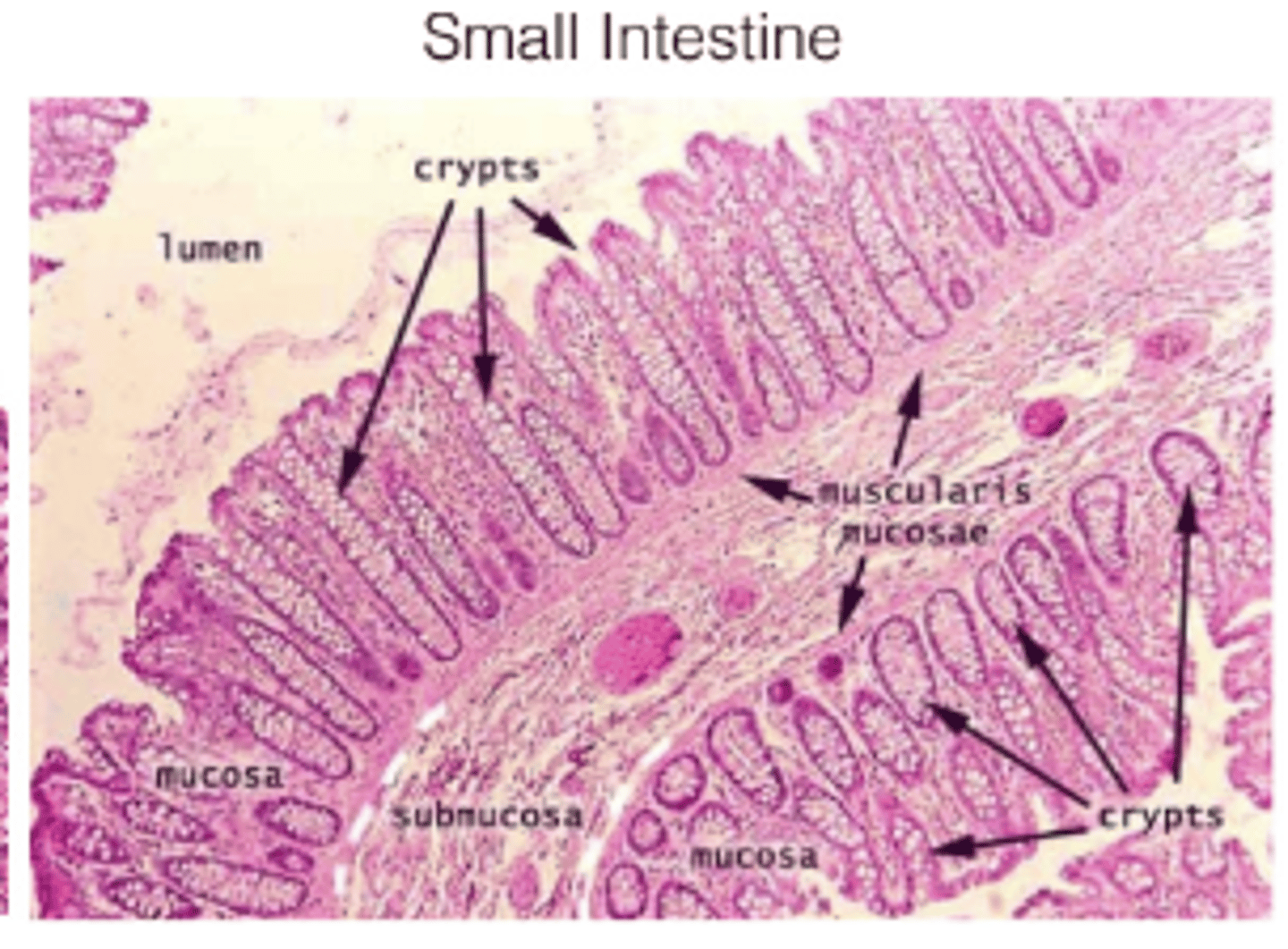
What are intestinal crypts?
Gland-like structures located at the base of villi
What are taenia coli?
Longitudinal muscle bands in the colon
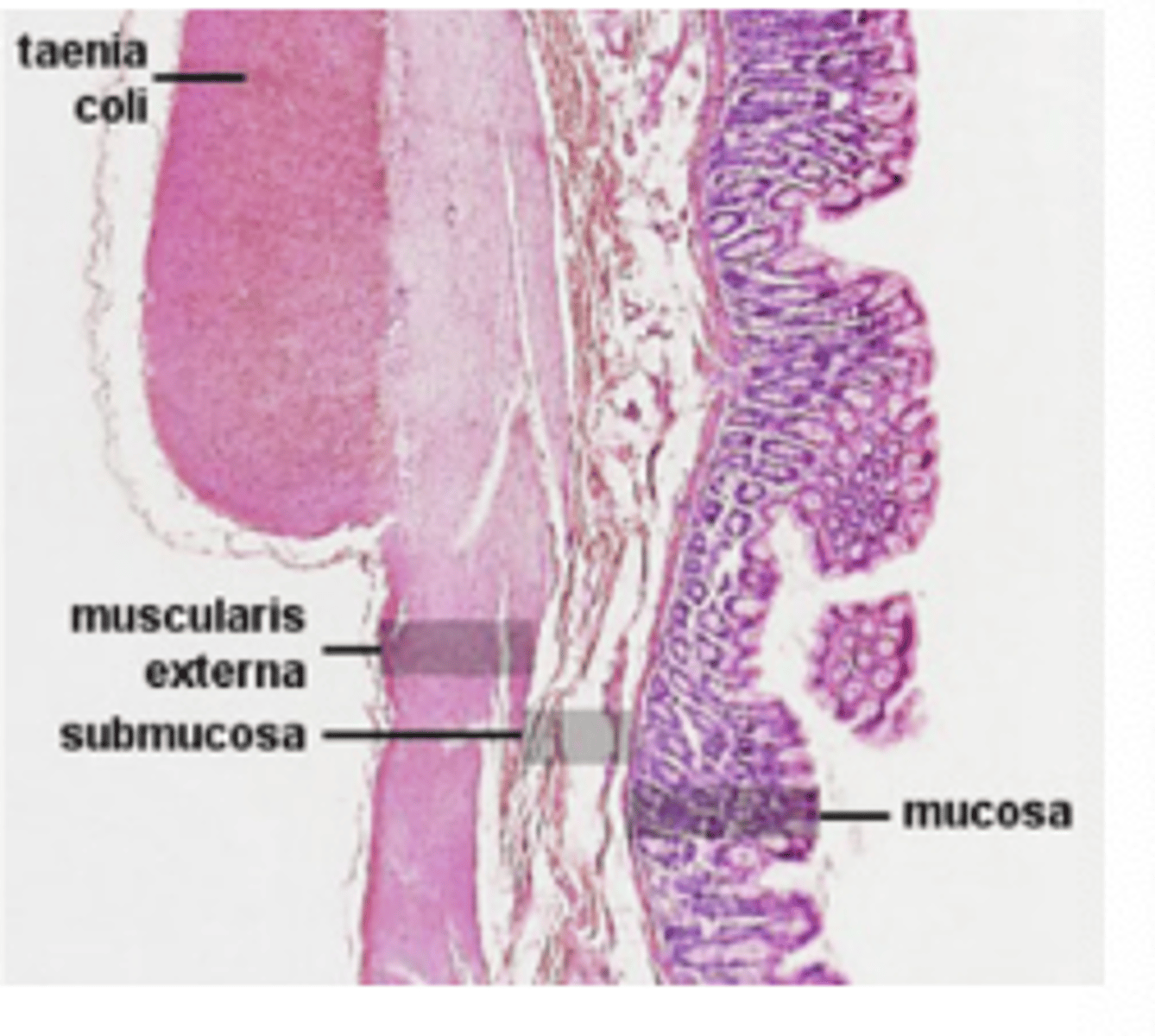
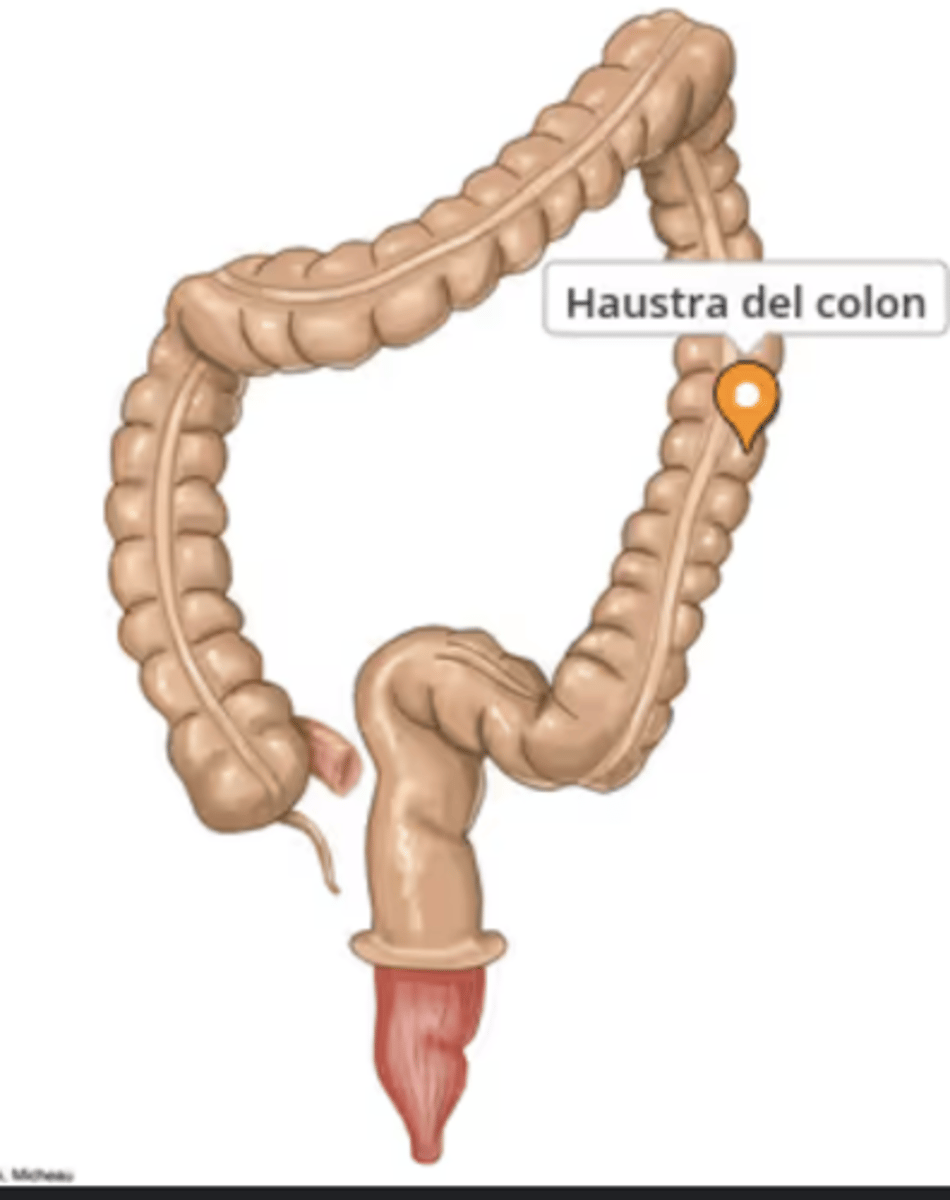
What are haustra?
Segments of the colon formed by taenia coli
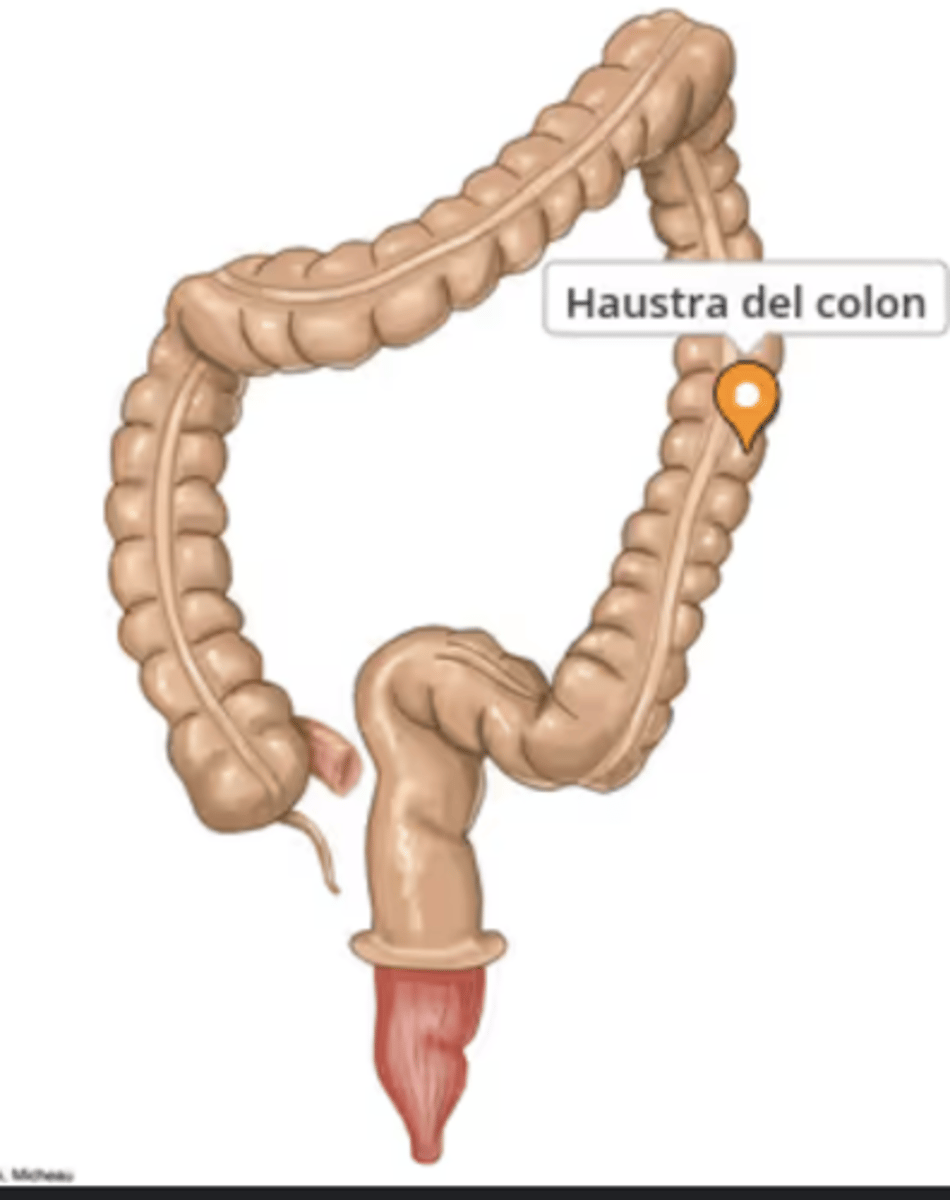
What is the purpose of haustra contraction?
To produce segmentation movements that mix intestinal contents
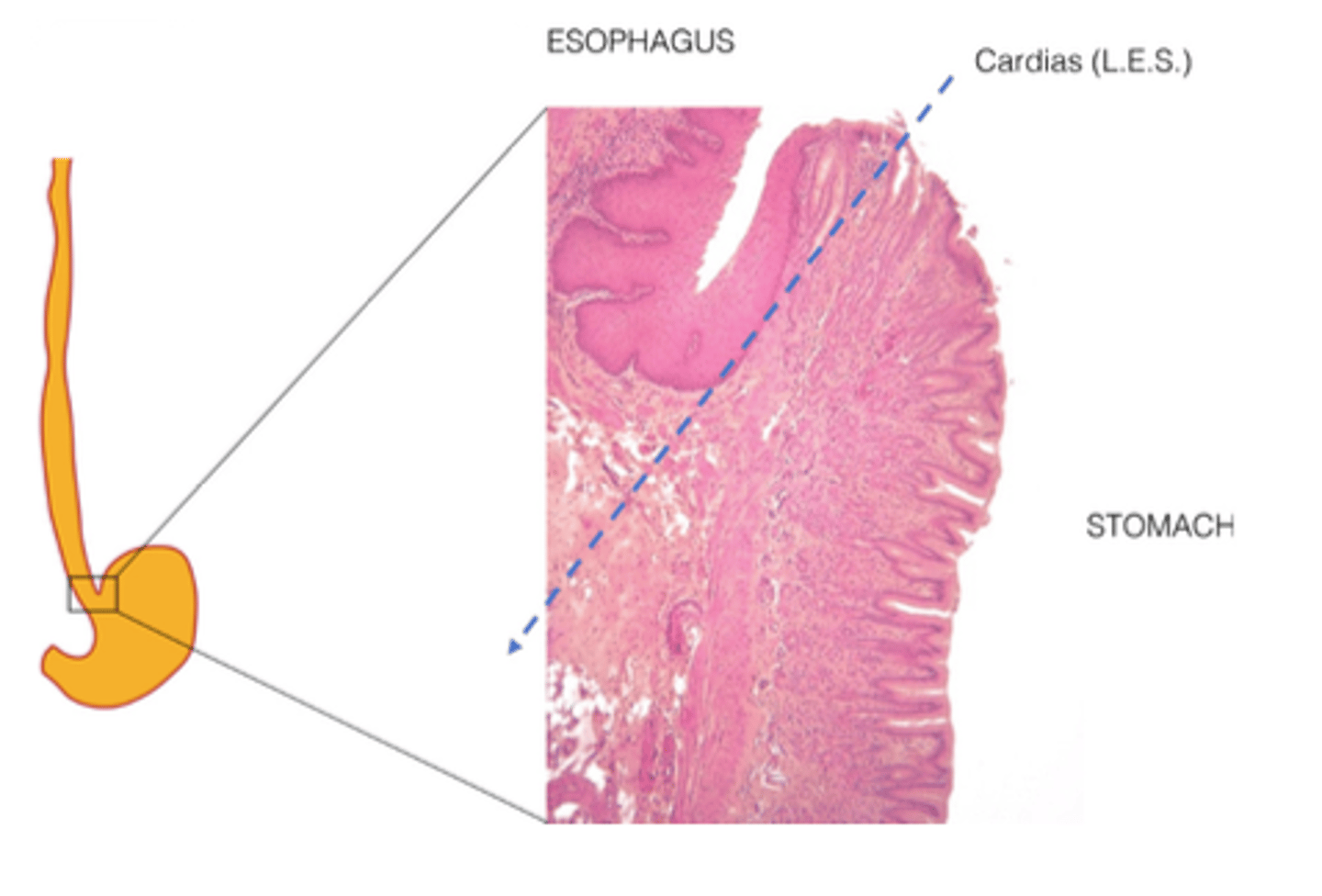
What is the epithelial transition point between esophagus and stomach?
The cardias (lower esophageal sphincter)
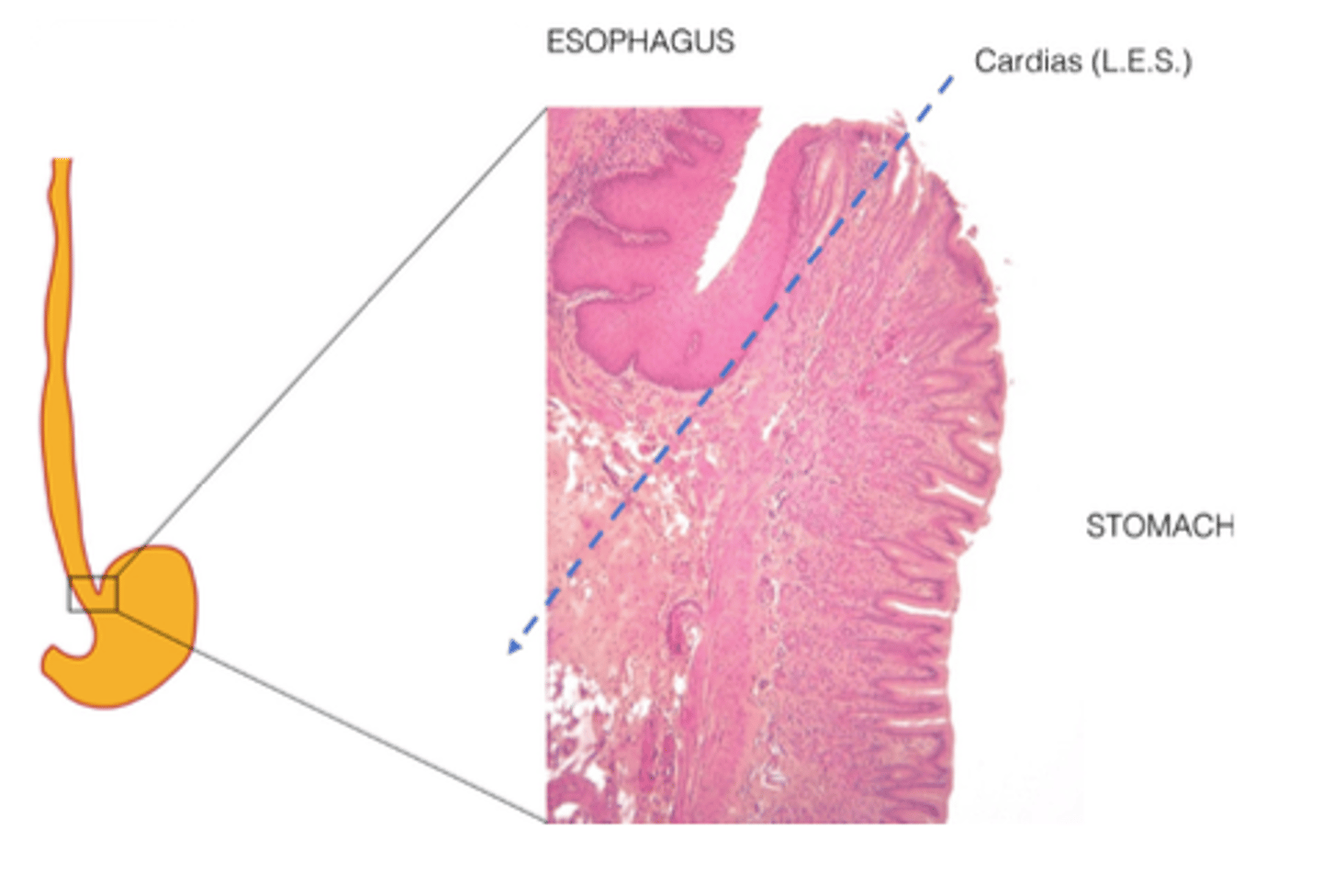
What epithelial change occurs at the cardias?
From stratified squamous to simple columnar epithelium
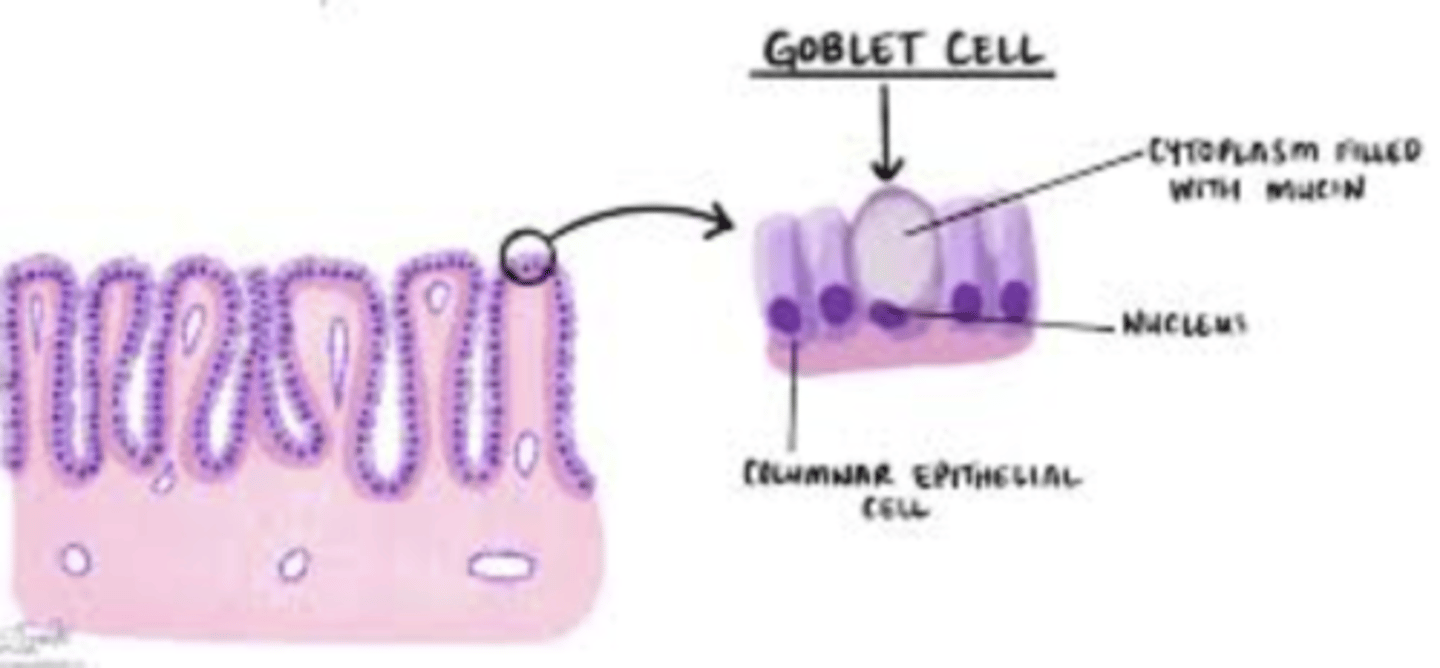
What is an example of a unicellular secretory gland?
Goblet cell.
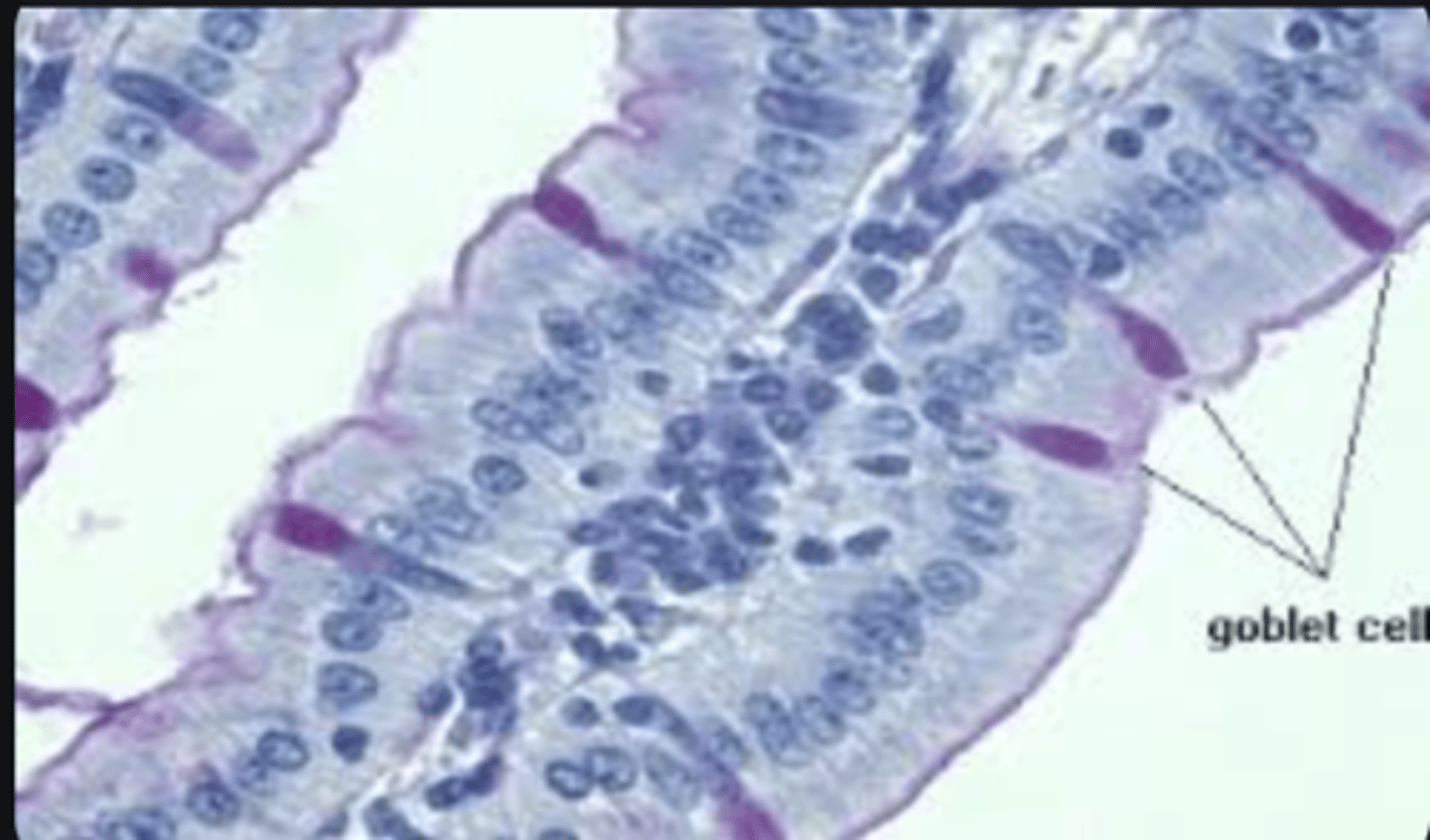
What do goblet cells secrete?
Mucus
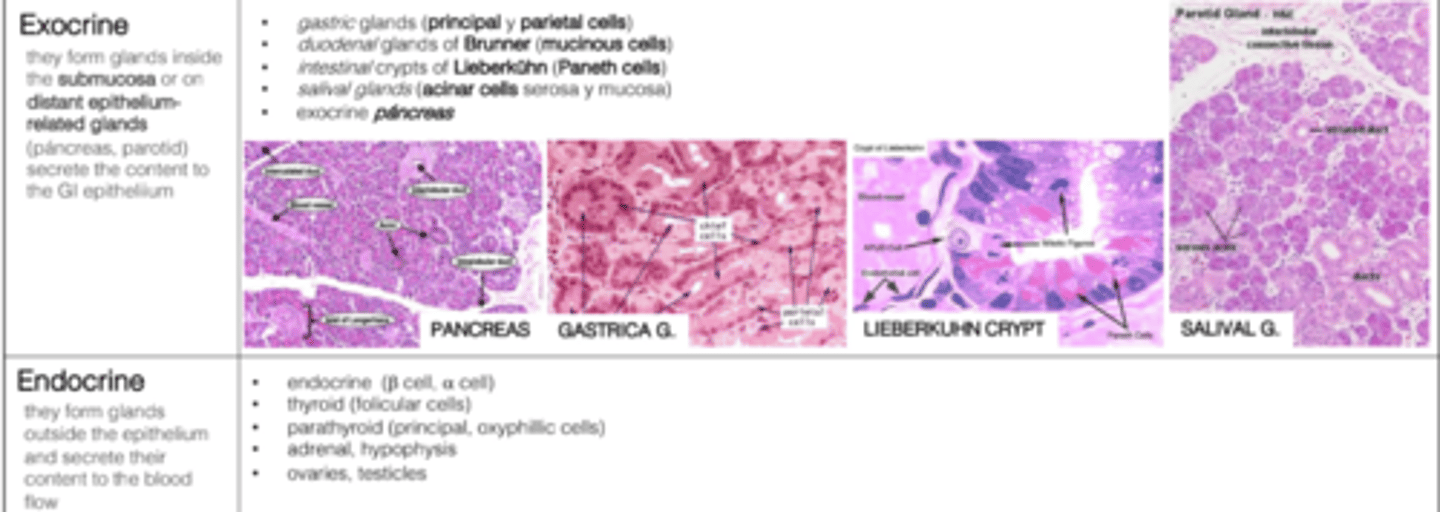
What is the difference between exocrine and endocrine glands?
Exocrine glands secrete via ducts (to the GI epithelium); endocrine glands release into the bloodstream.
Are goblet cells endocrine or exocrine?
Exocrine (unicellular, mucous-secreting)
How do nutrients enter epithelial gland cells?
Through the basal membrane from capillaries
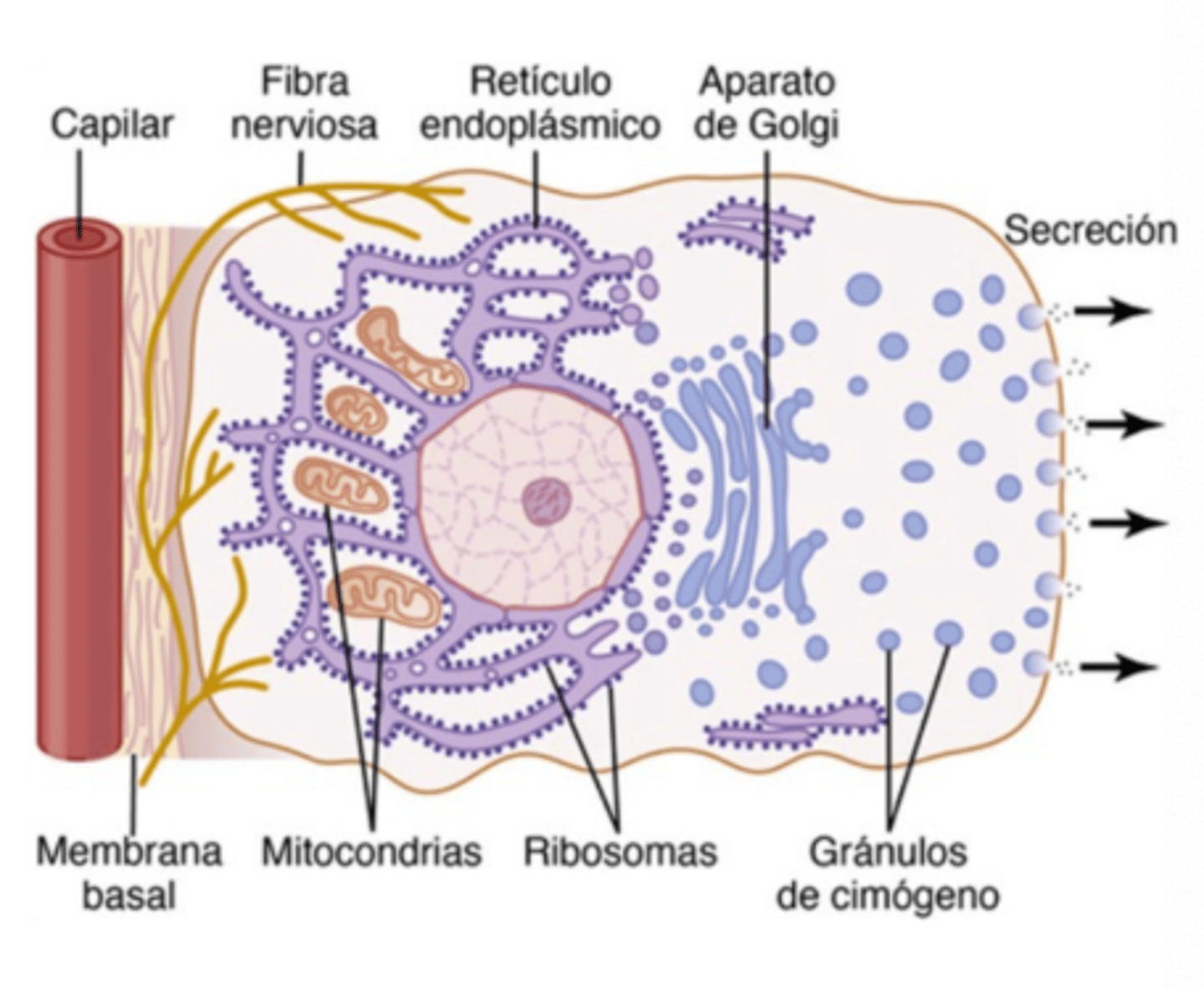
Where are proteins synthesized and folded in gland cells?
In the endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
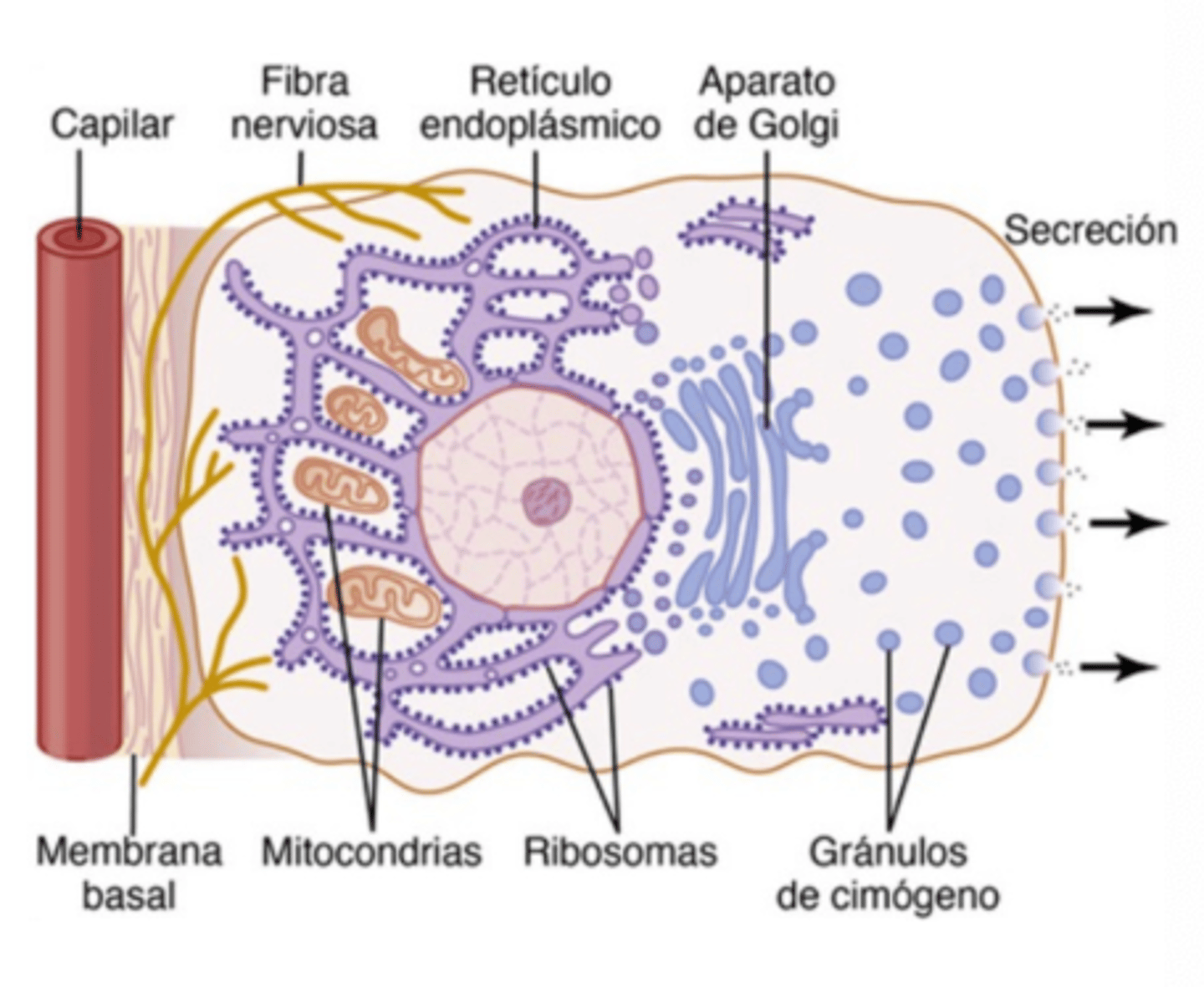
What organelle modifies proteins before secretion?
The Golgi apparatus
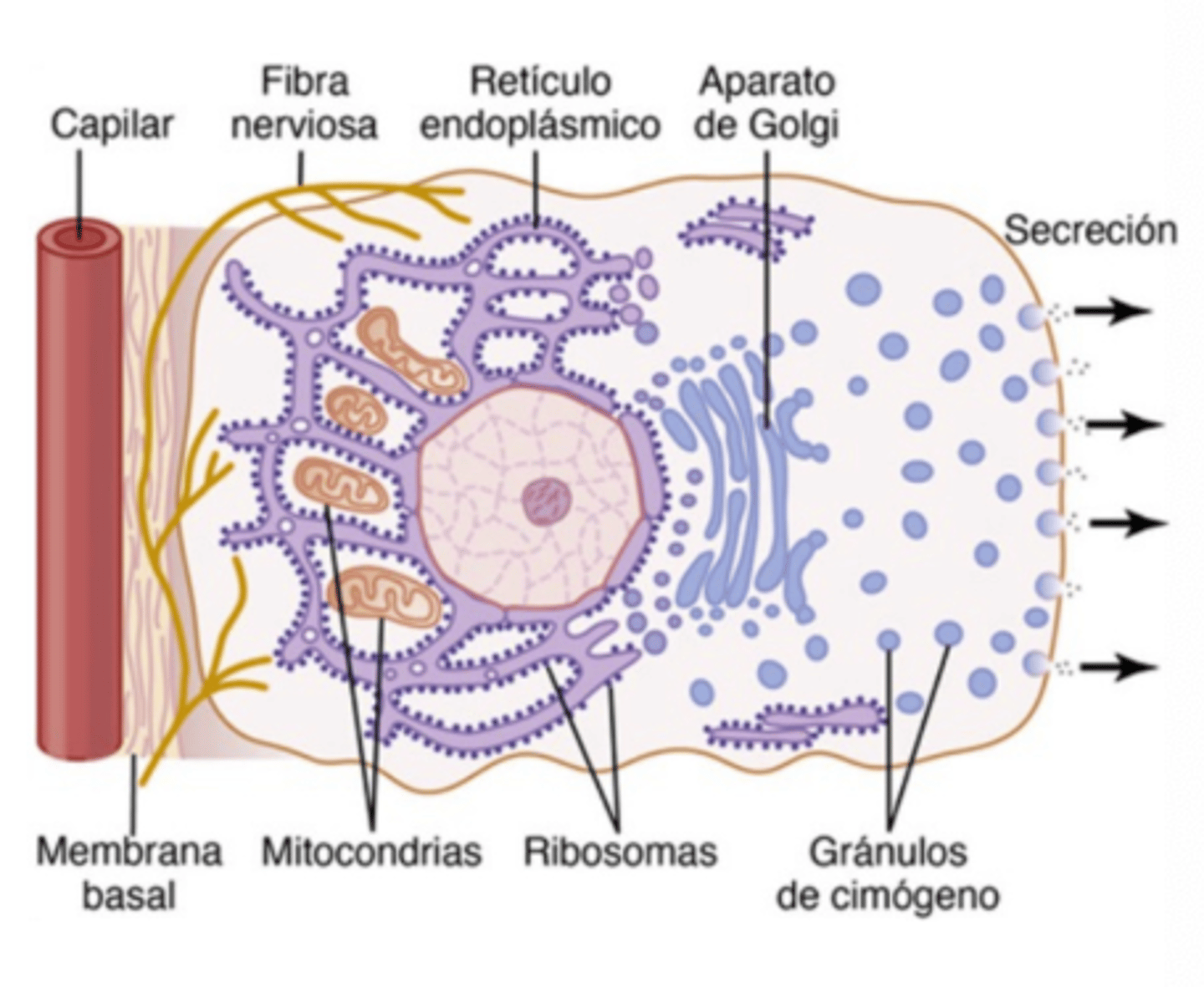
How are secretory vesicles released from the cell?
By exocytosis through the apical membrane, in response to a hormonal or neural signal
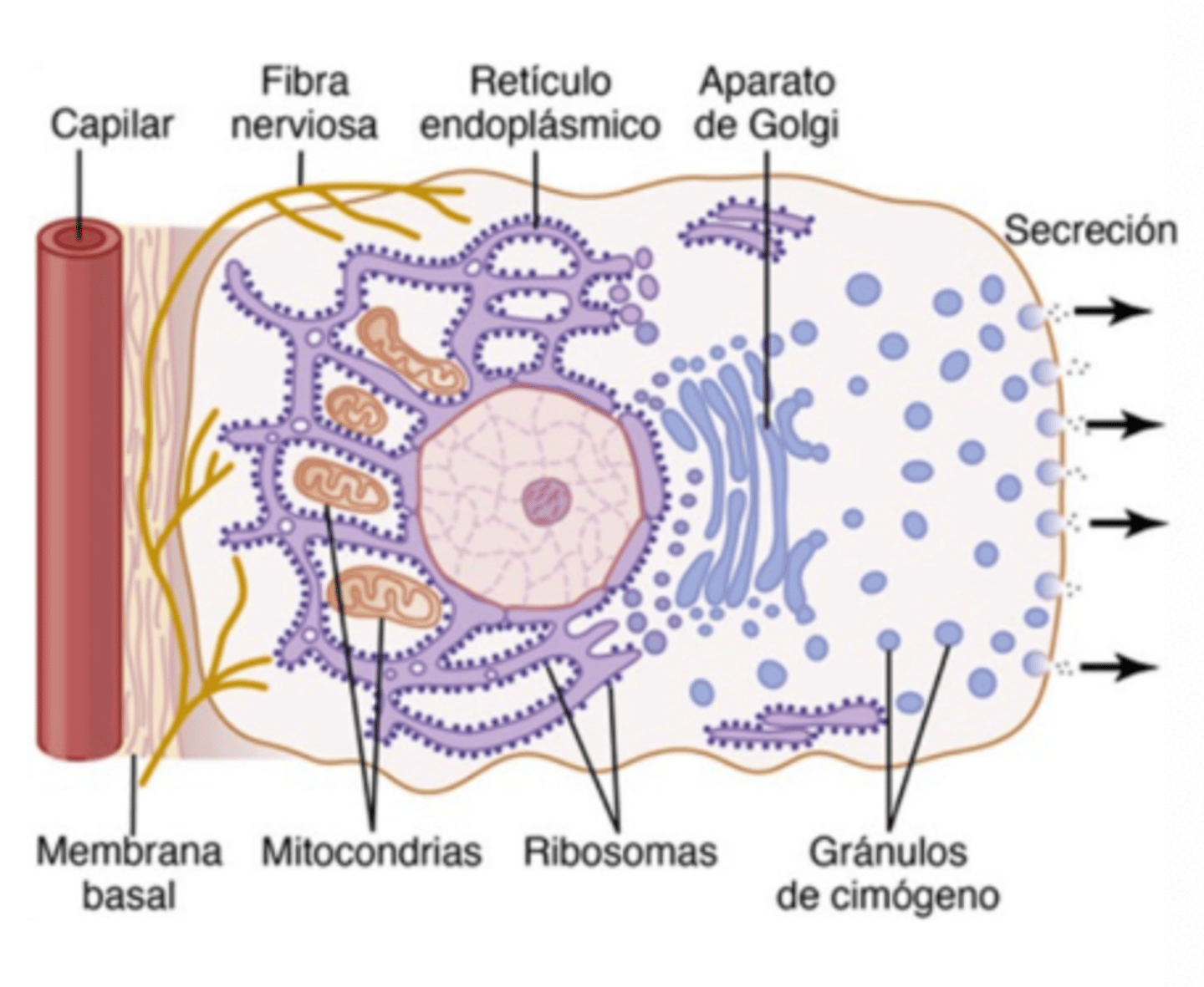
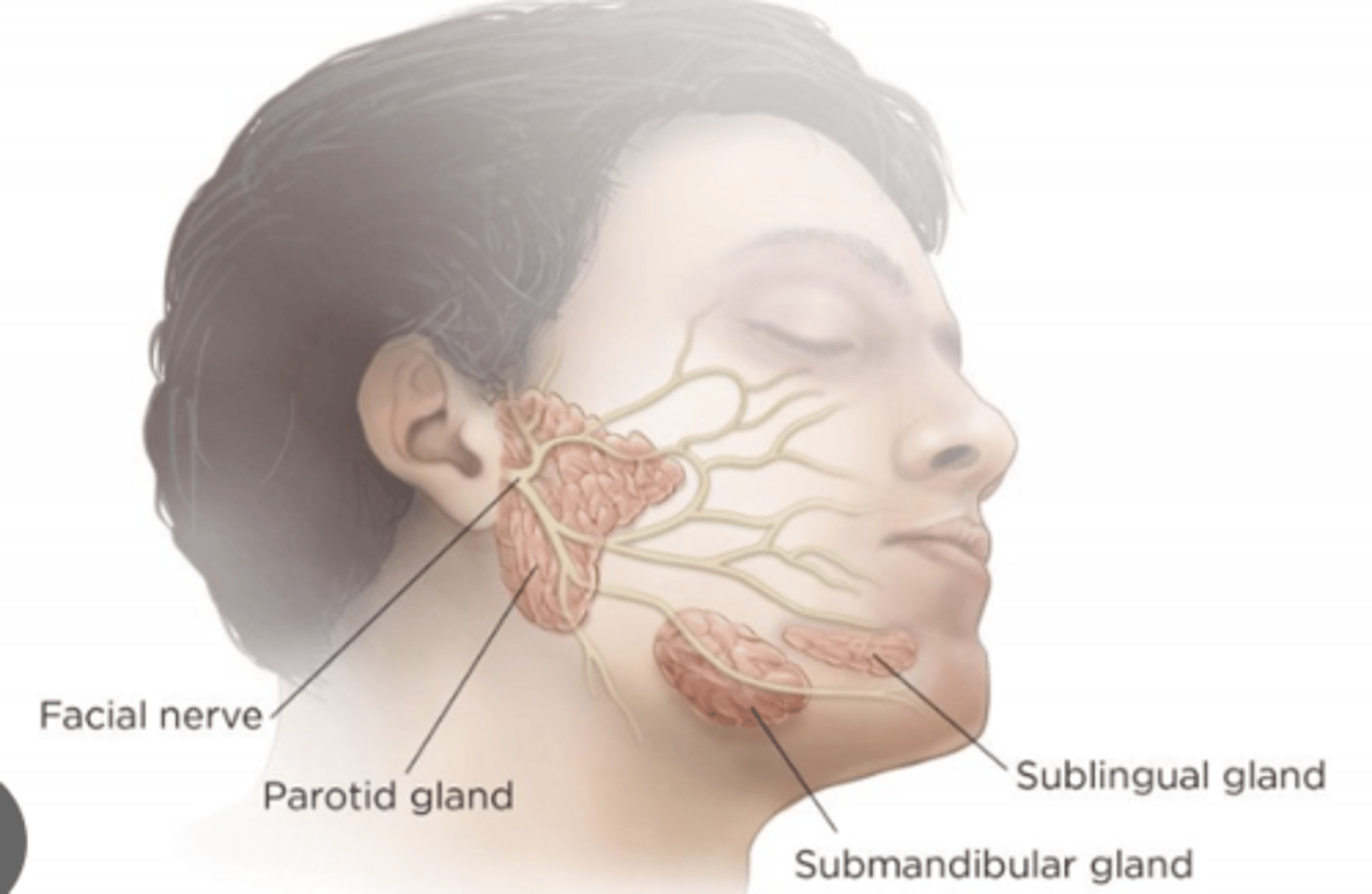
Which salivary glands produce serous secretion?
Parotid and Submaxillary (submandillar) glands
What is the serosa?
ptialine (amylase) found in saliva and lingual lipase
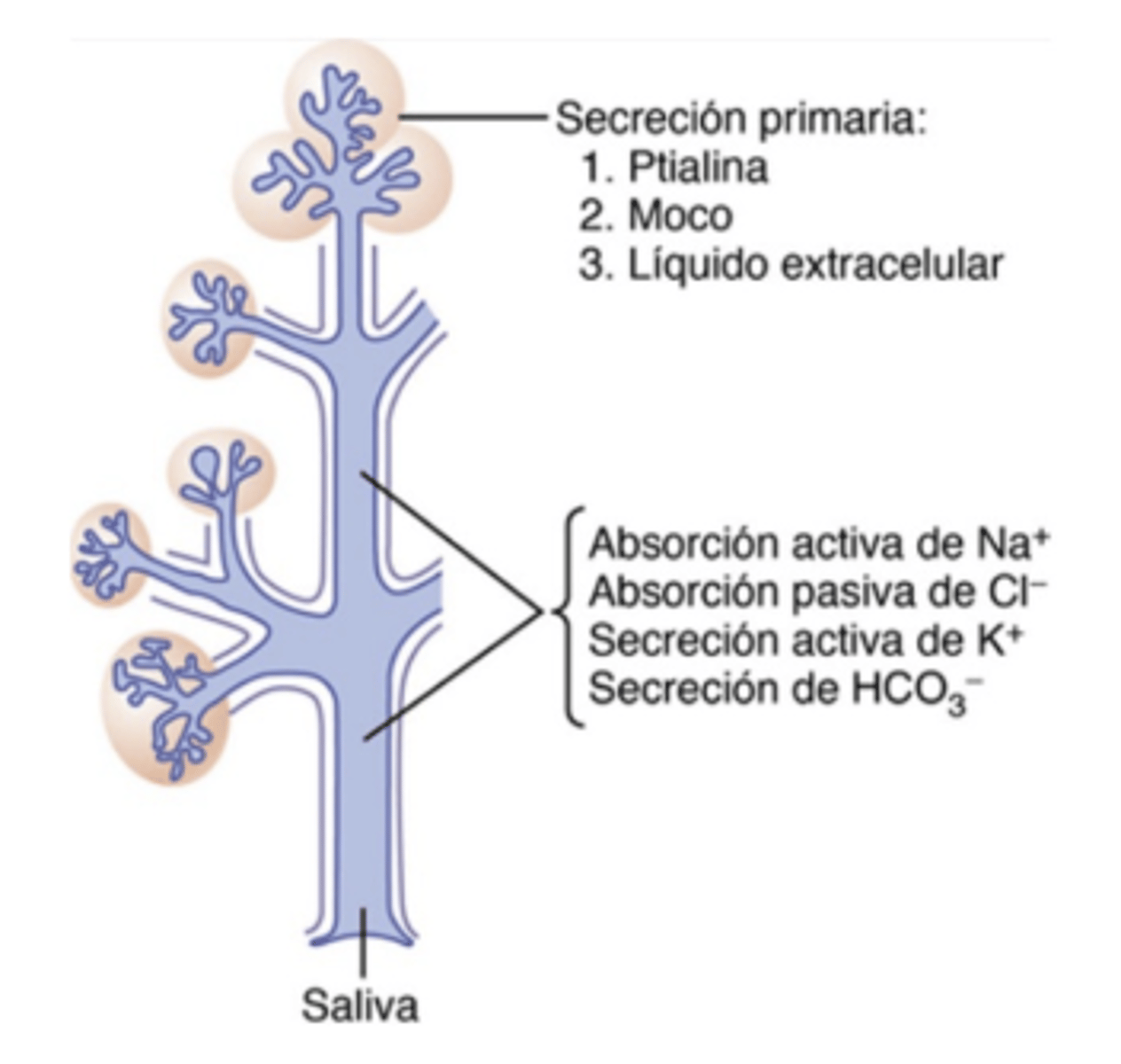
What enzyme in saliva breaks down starch?
Ptyalin (salivary amylase)
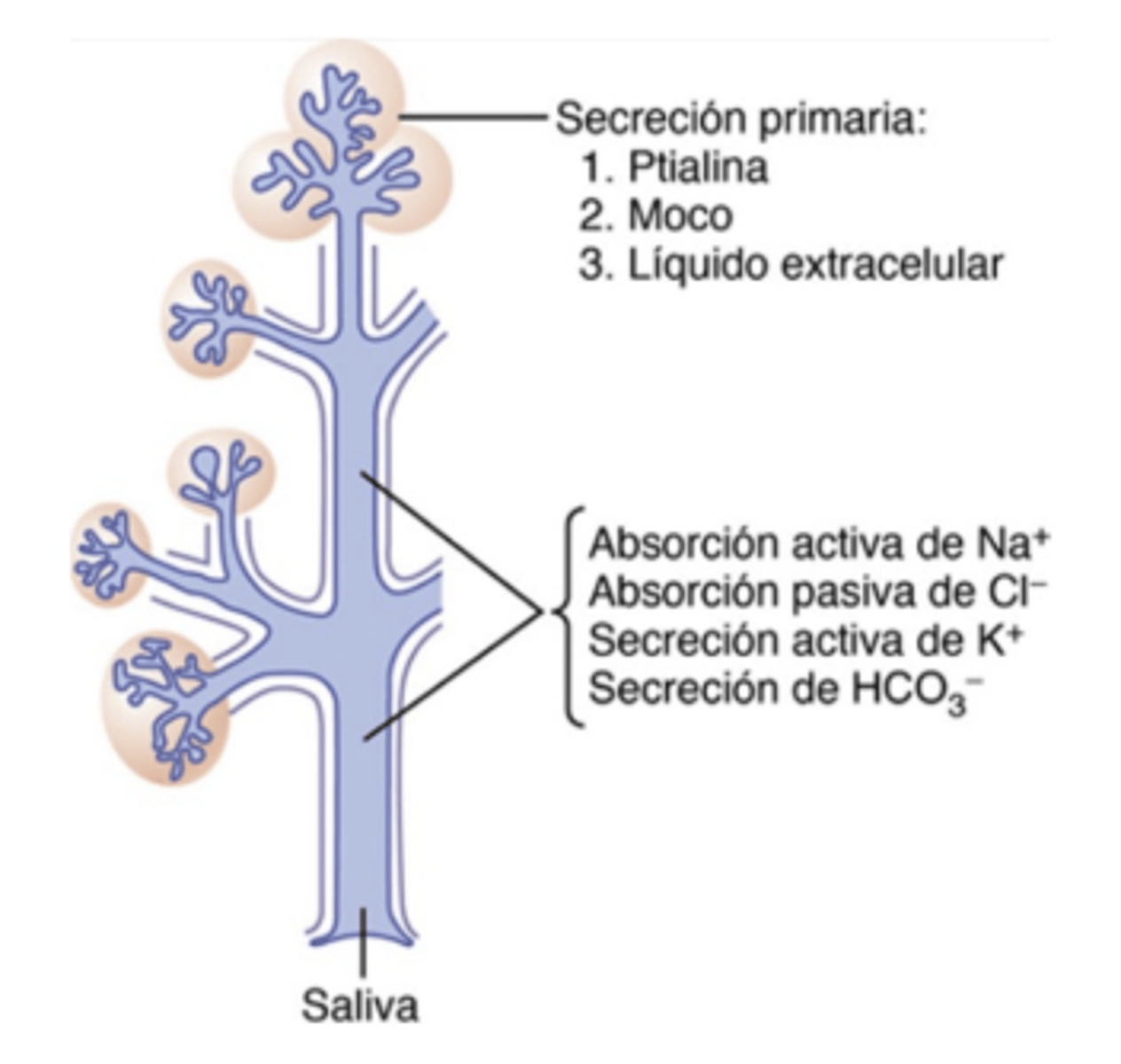
What enzyme in saliva begins fat digestion?
Lingual lipase
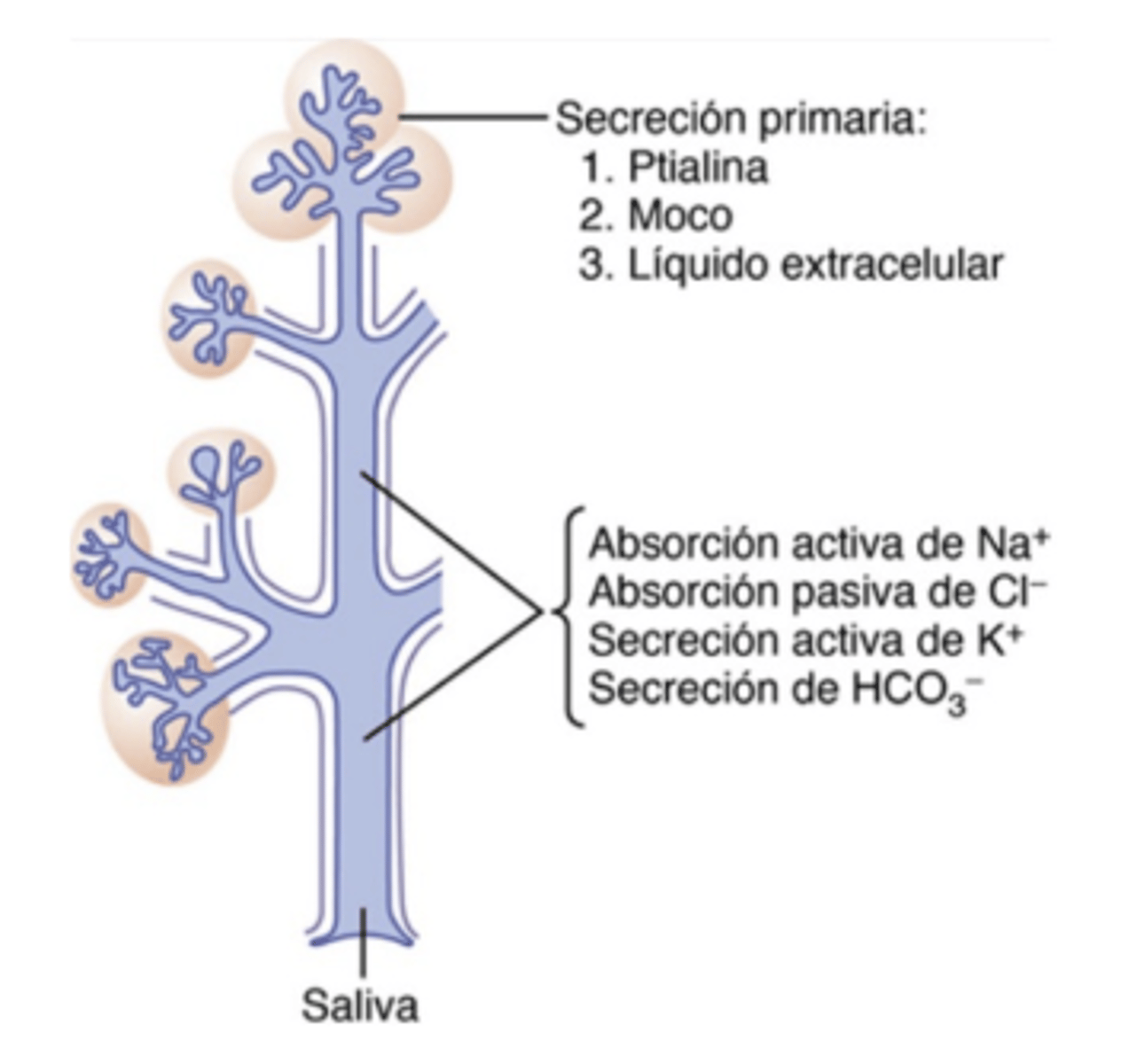
Which glands produce mucous secretion?
Sublingual and Submaxillary glands
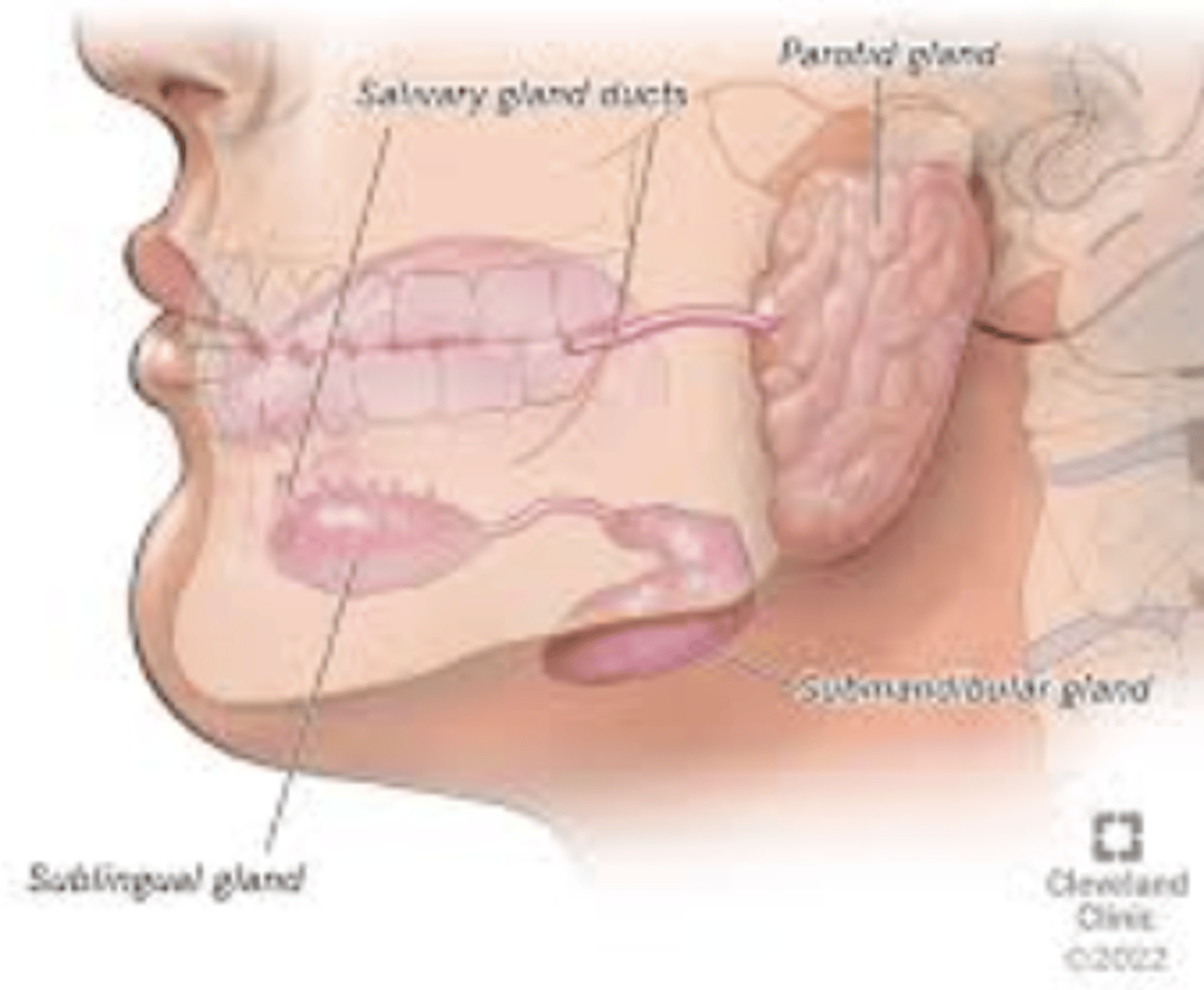
What does mucinous secretion provide?
Protection and lubrication
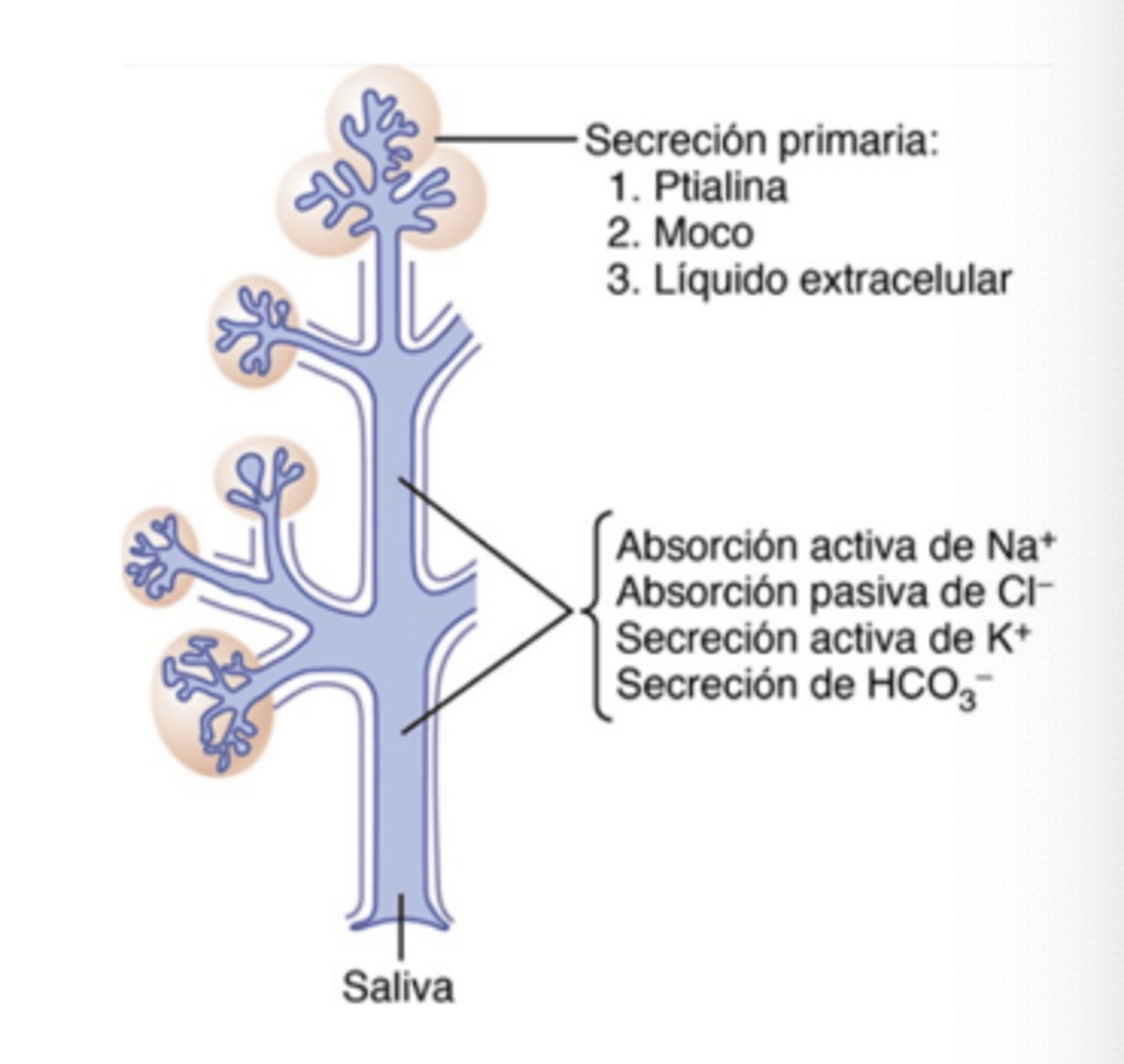
What ions are increased in the final (secondary) saliva?
Potassium and Bicarbonate
What antimicrobial ions are found in saliva?
Thiocyanate ions
What enzyme in saliva attacks bacterial walls?
Lysozyme
Which immunoglobulin is found in saliva?
IgA
What is the difference between primary and secondary saliva secretion?
Primary is produced by acini; secondary is modified in the ducts
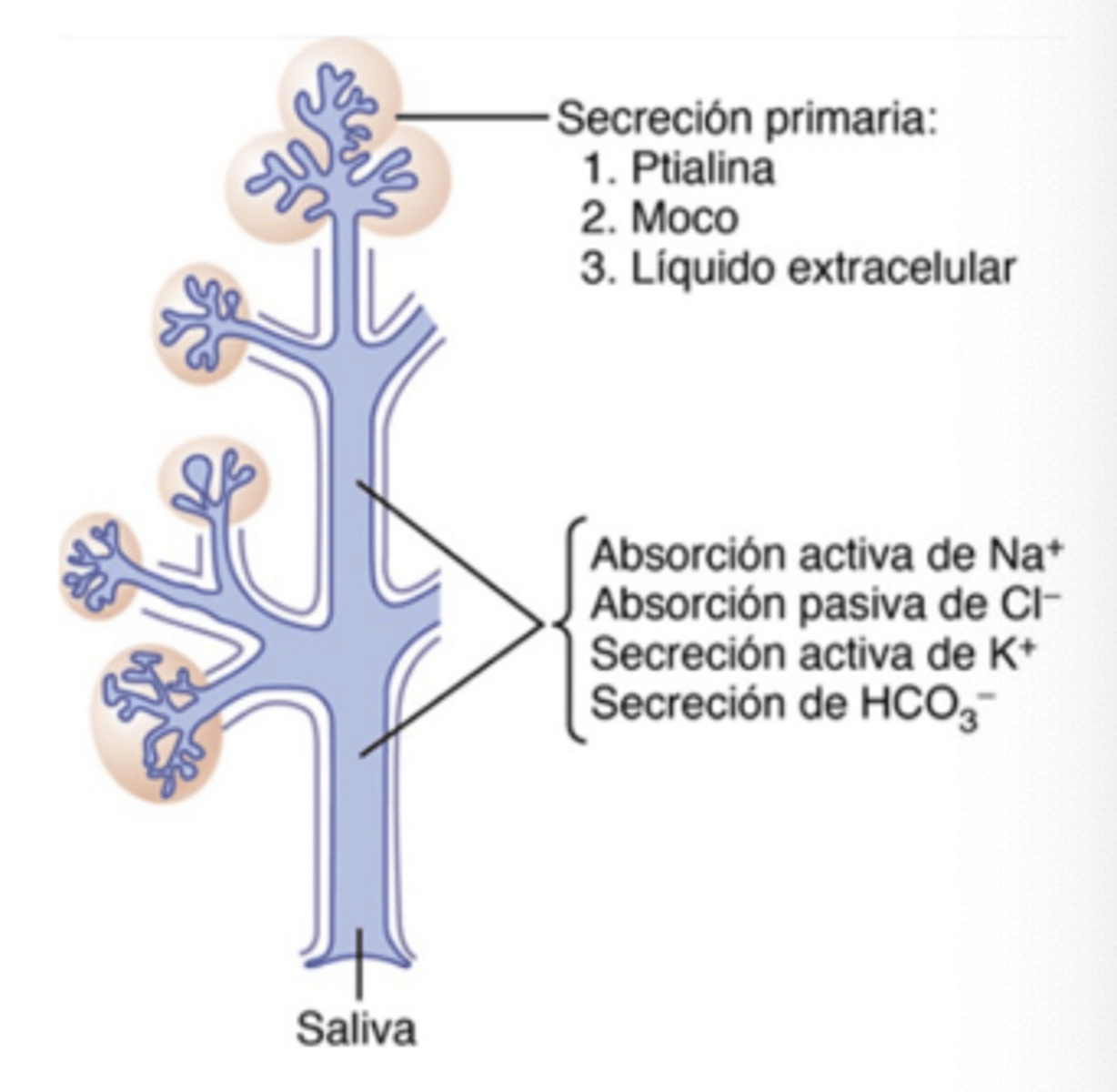
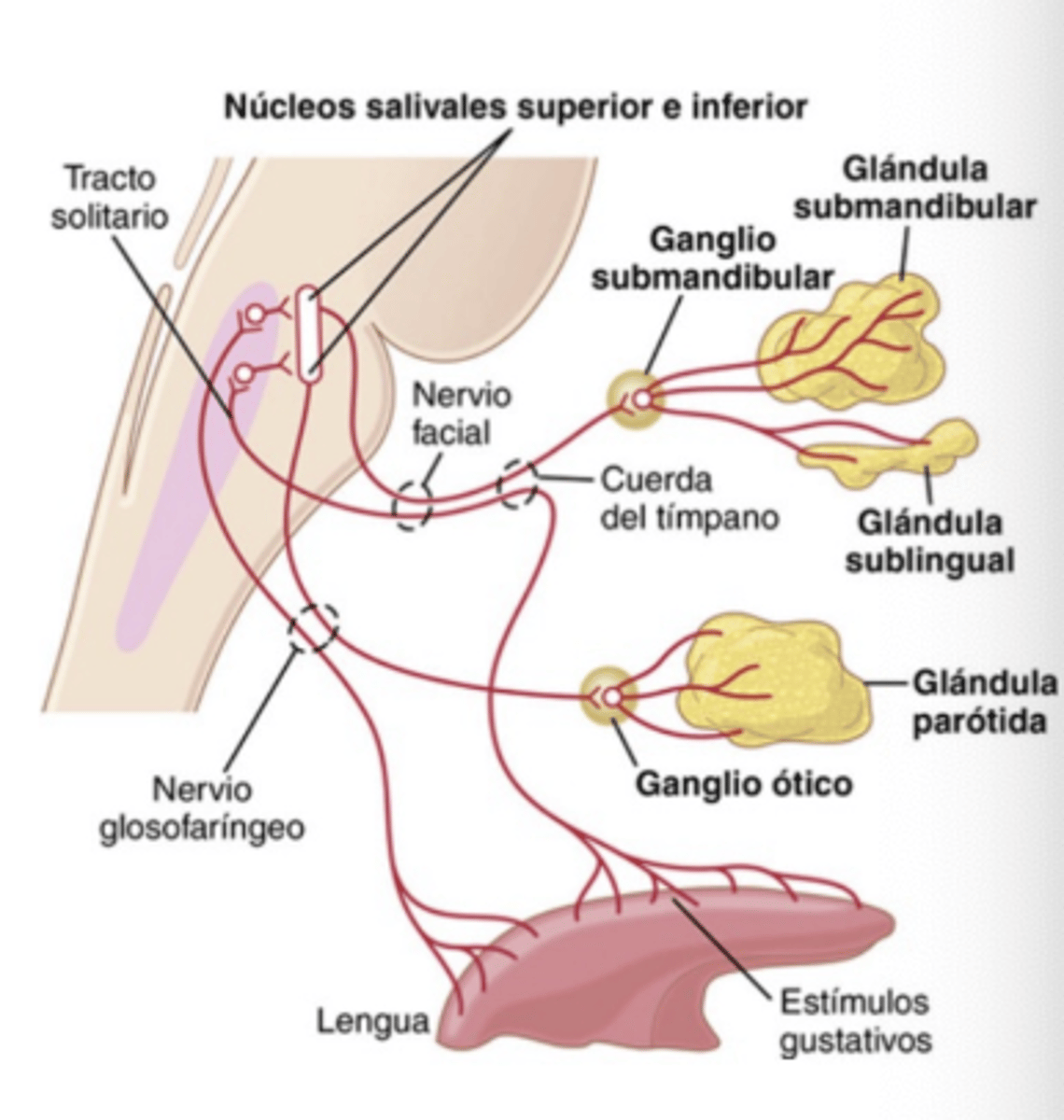
Which cranial nerves carry salivary afferent signals?
Facial (VII) and Glossopharyngeal (IX)
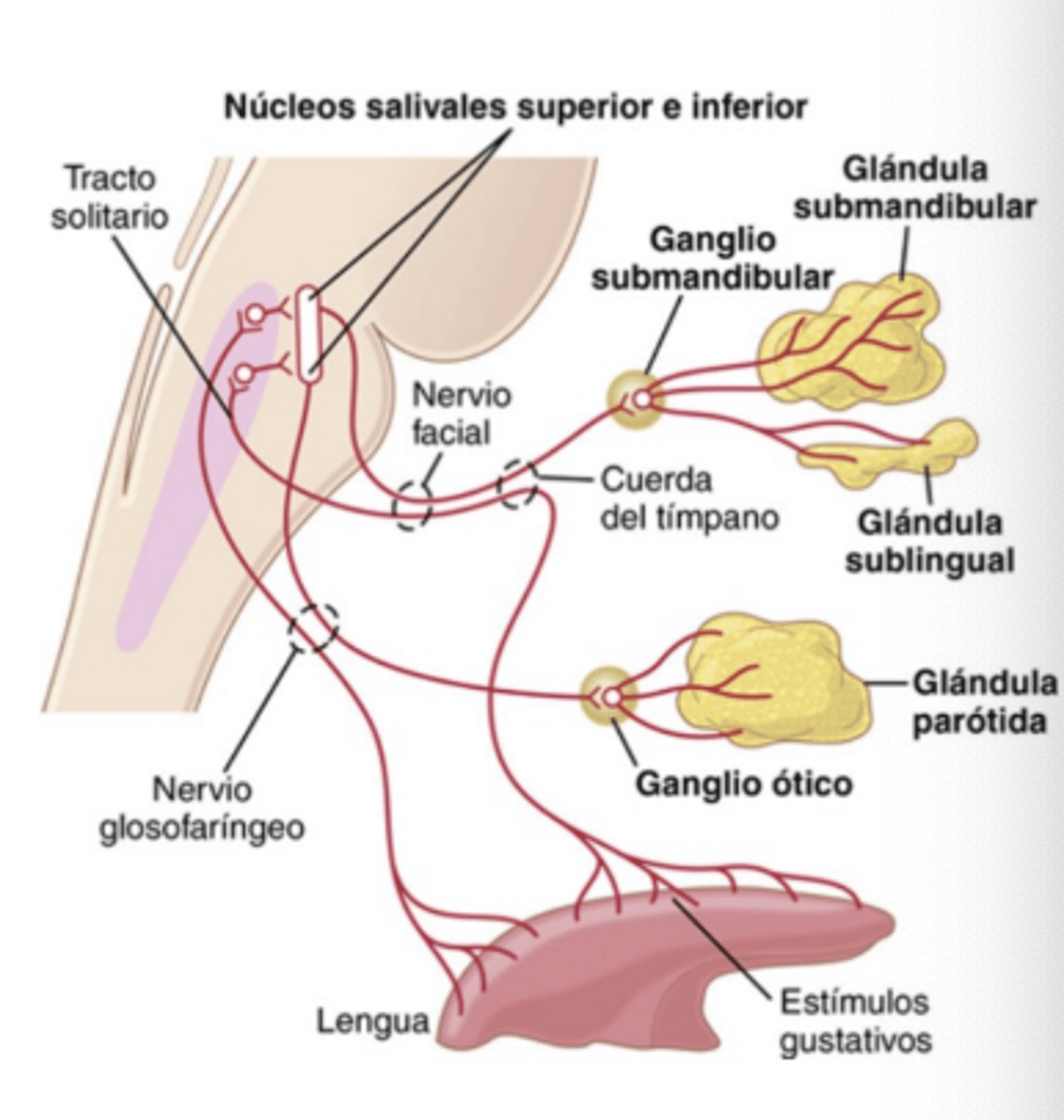
Where do these signals first synapse in the brain?
Nucleus Tractus Solitarius (NTS)
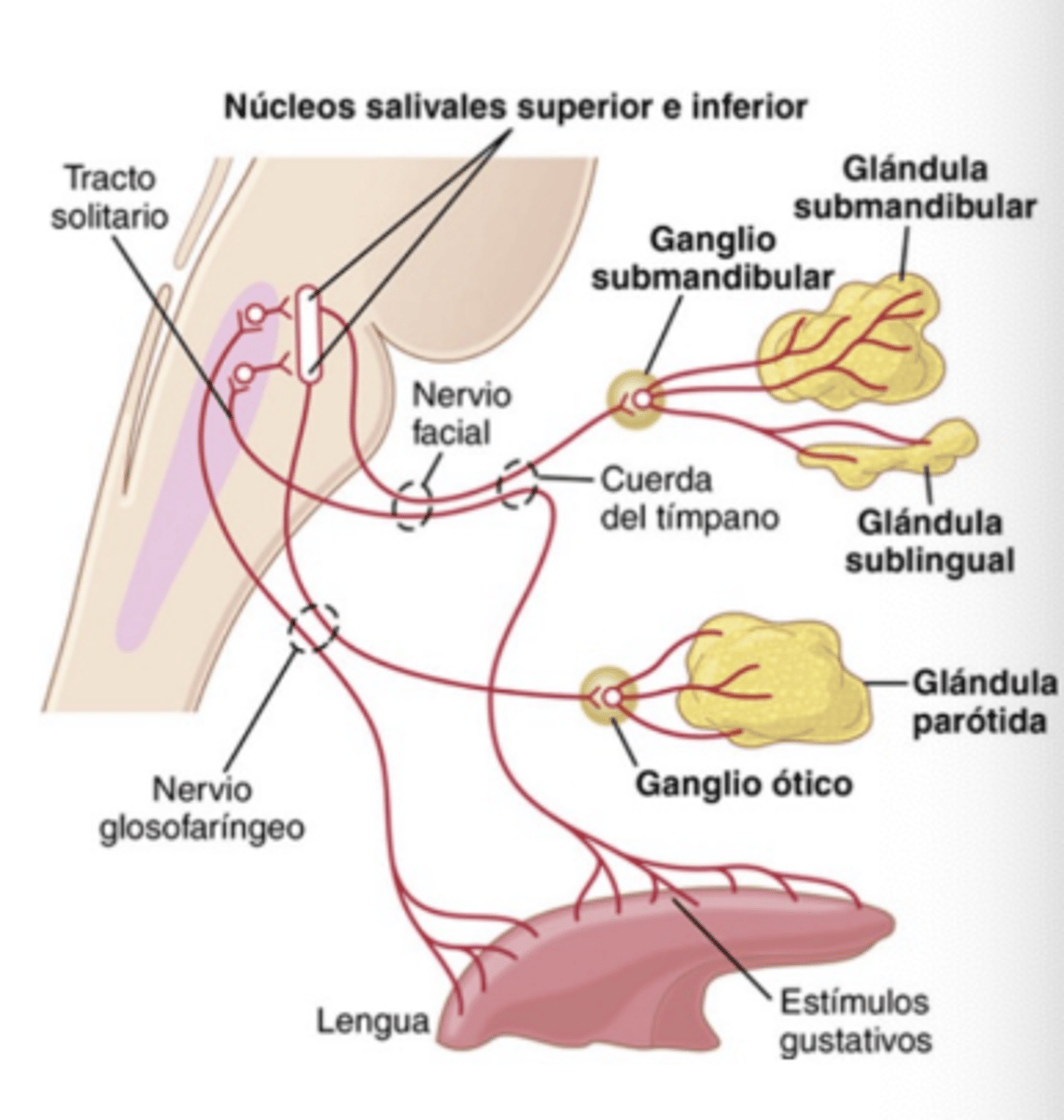
From NTS goes to
Cortex (to a region related to taste)
Amygdala
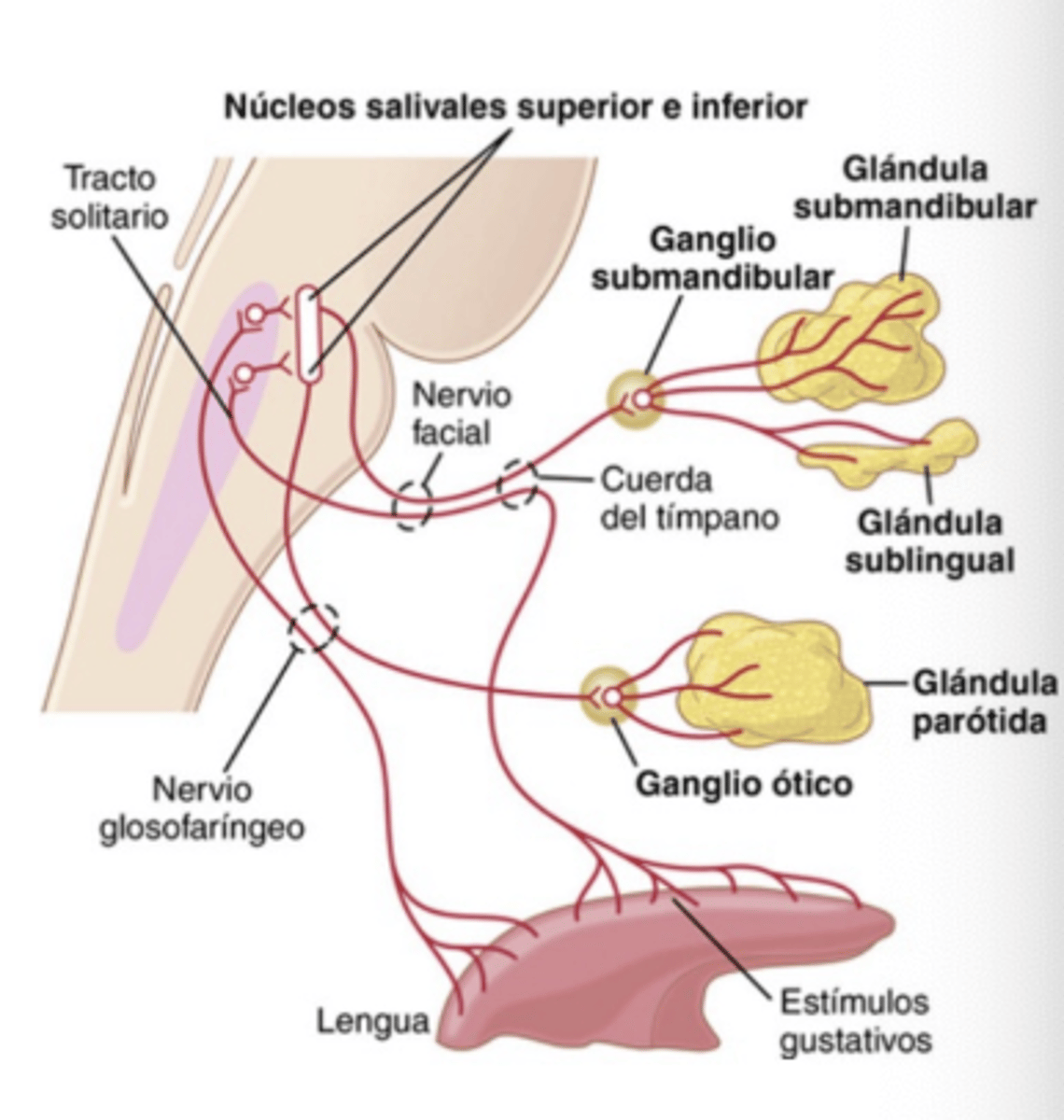
From Cortex and amygdala to
Hypothalamus, connects superior and inferior salivary nuclei
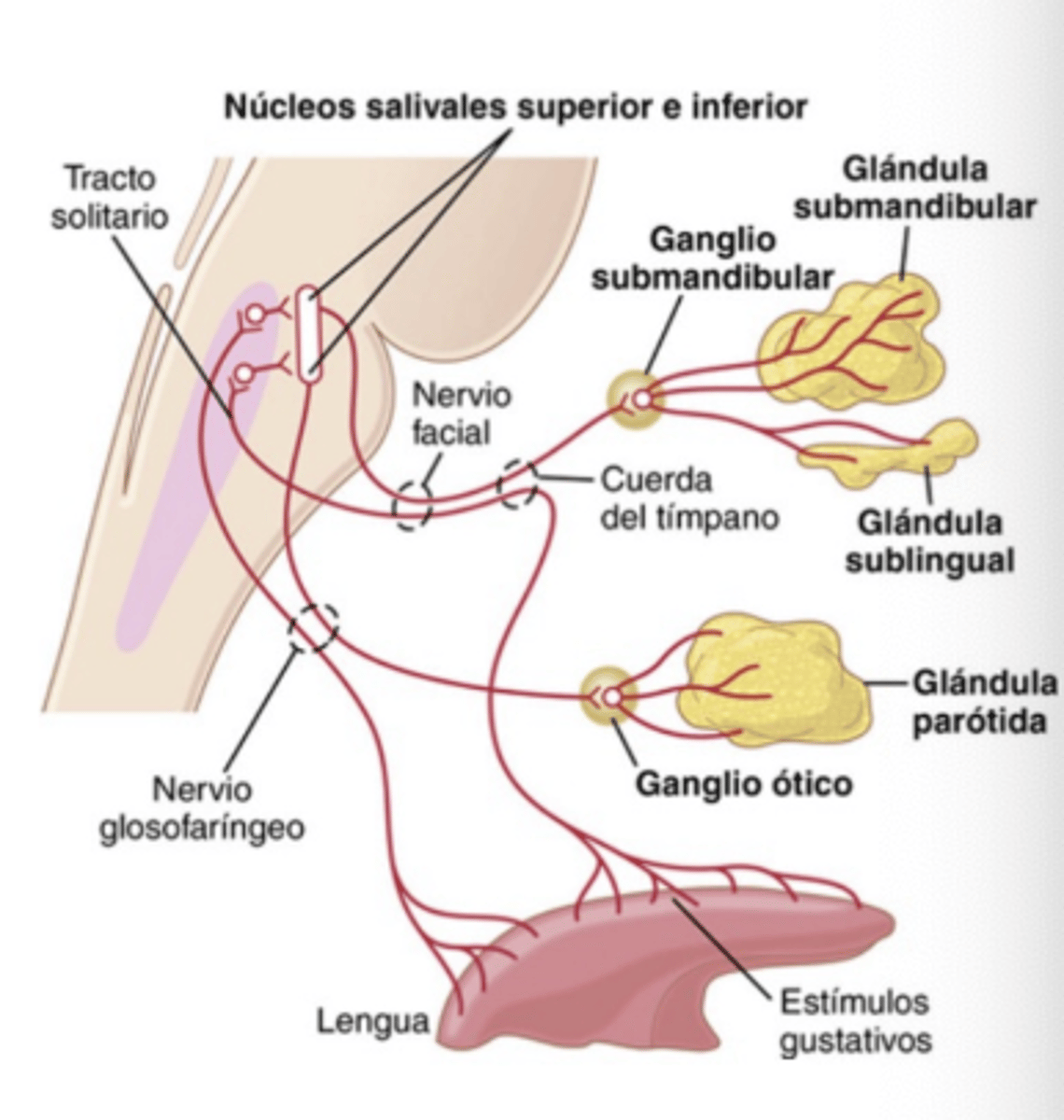
Describe stimuli (afferent pathway to salivary nuclei)
. Tongue -> nerves IX and VII -> NTS -> Cortex and Amygdala -> Hypothalamus
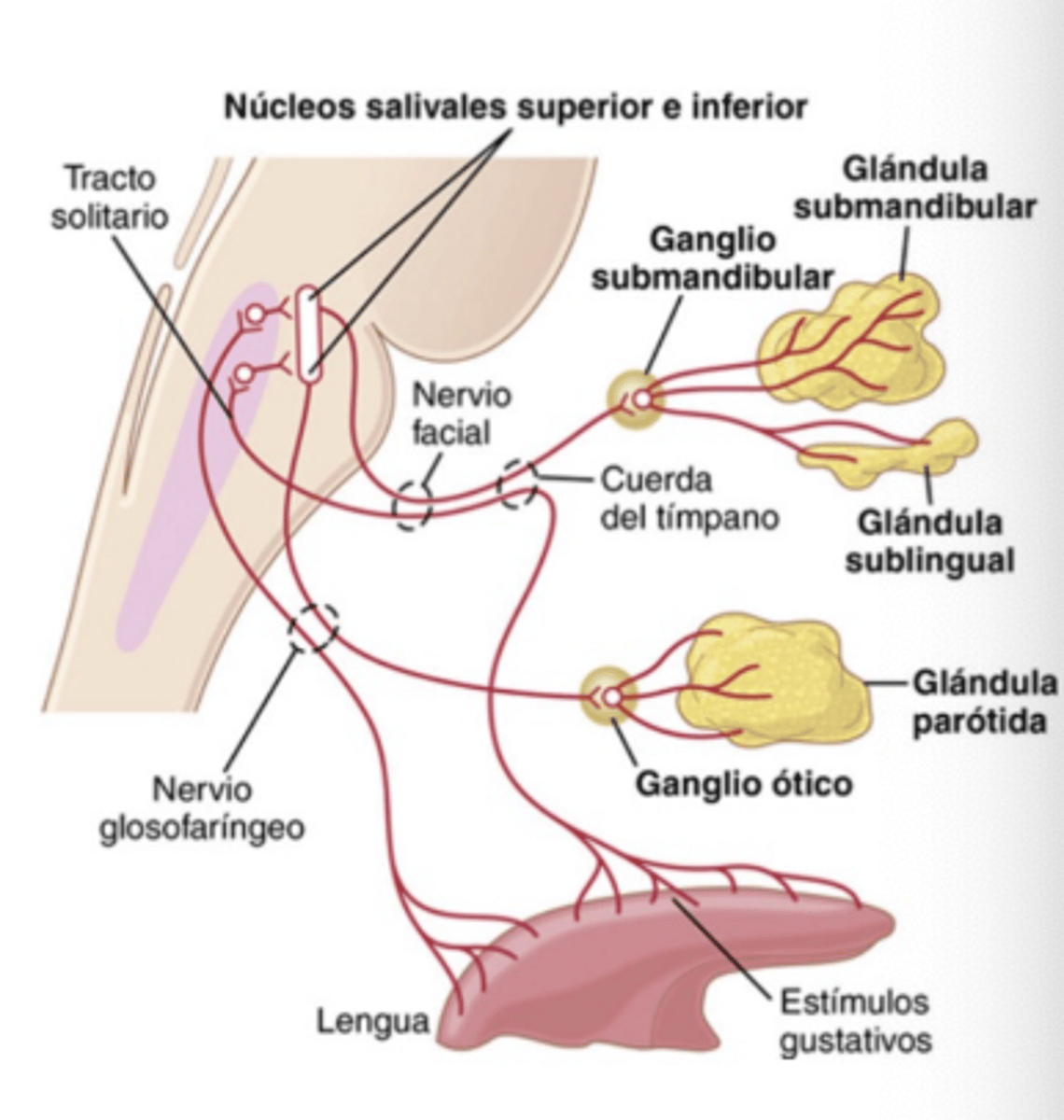
Which gland is innervated by CN VII via the submandibular ganglion?
Submaxillary and Sublingual glands
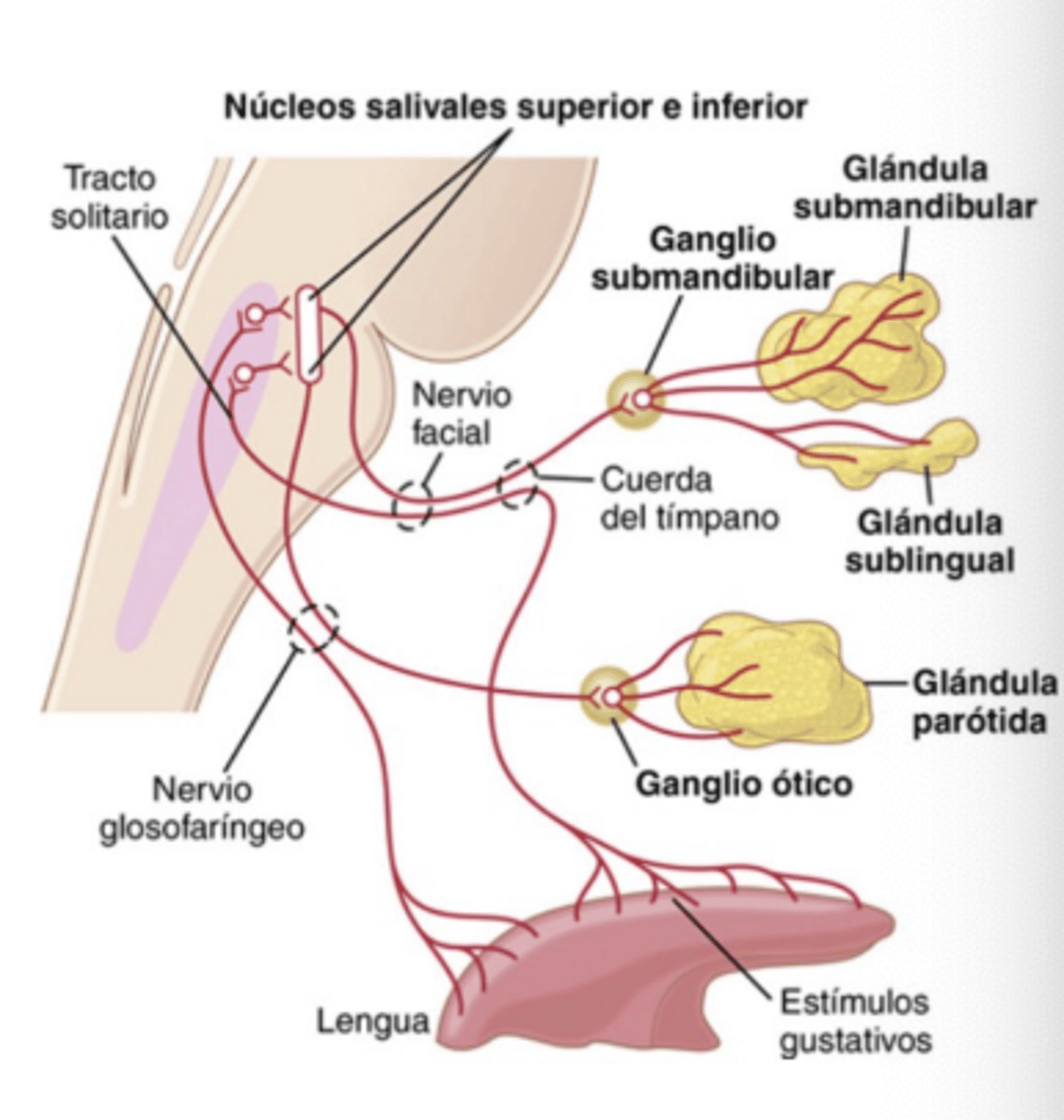
Which gland is innervated by CN IX via the otic ganglion?
Parotid gland
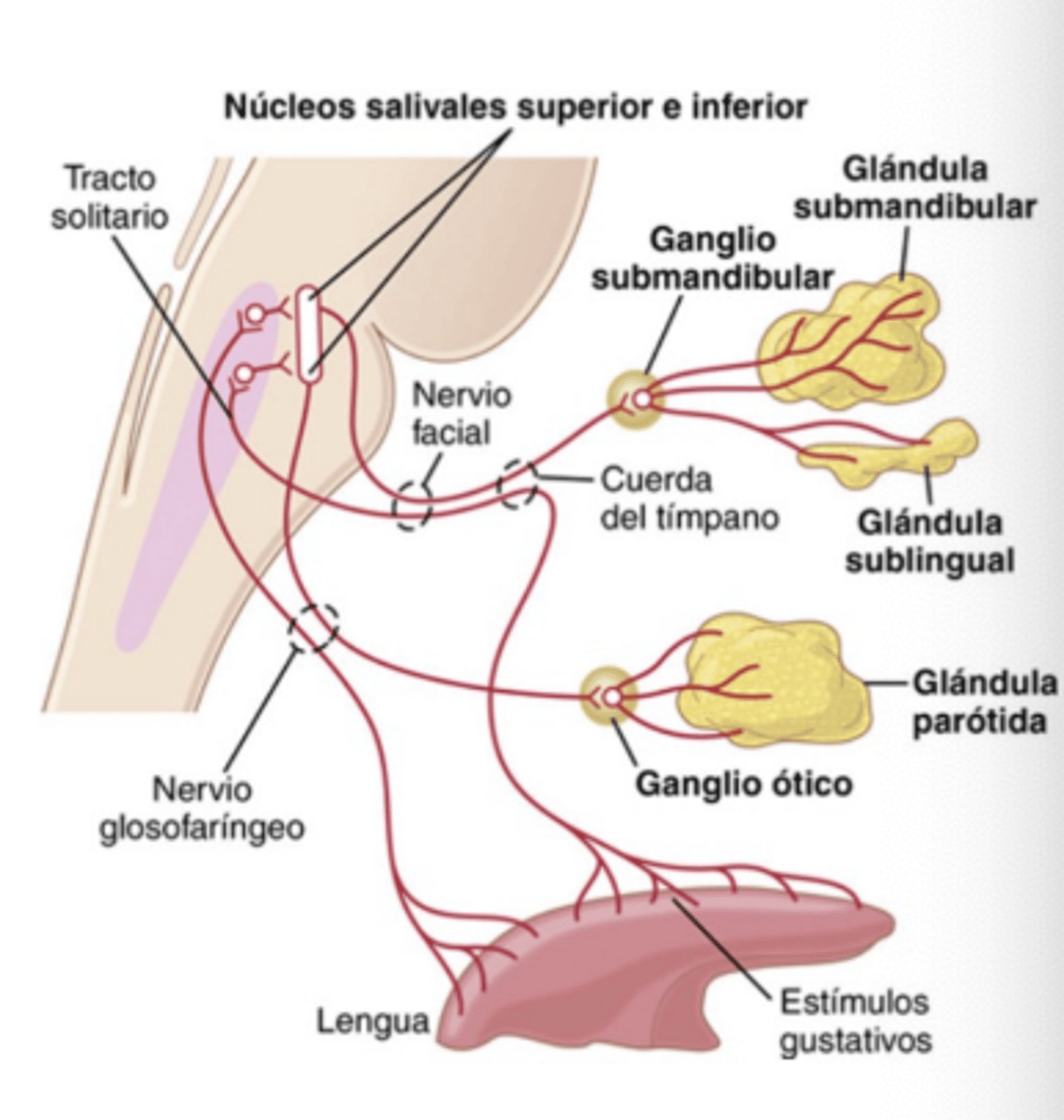
Describe the efferent pathway (from salivary nuclei)?
. Facial nerve (VII CN) through submandibular ganclion to reach submaxillary and sublingual glands
. Glossopharyngeal nerve (IX CN) through otic ganglion to reach Parotid gland
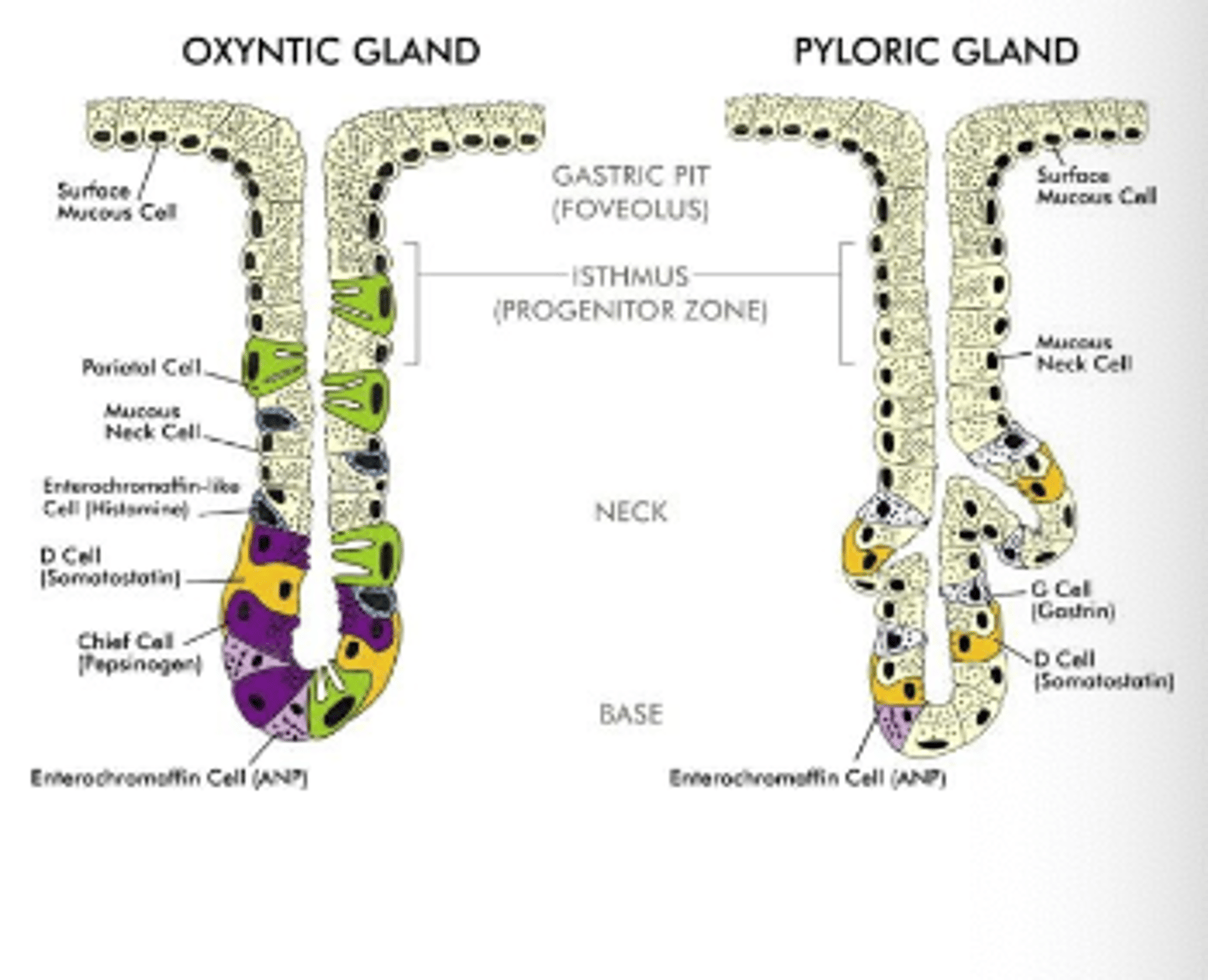
What are the 3 types of gastric/oxyntic glands?
. Mucous or principal cells
. Parietal cells
. Chief cells
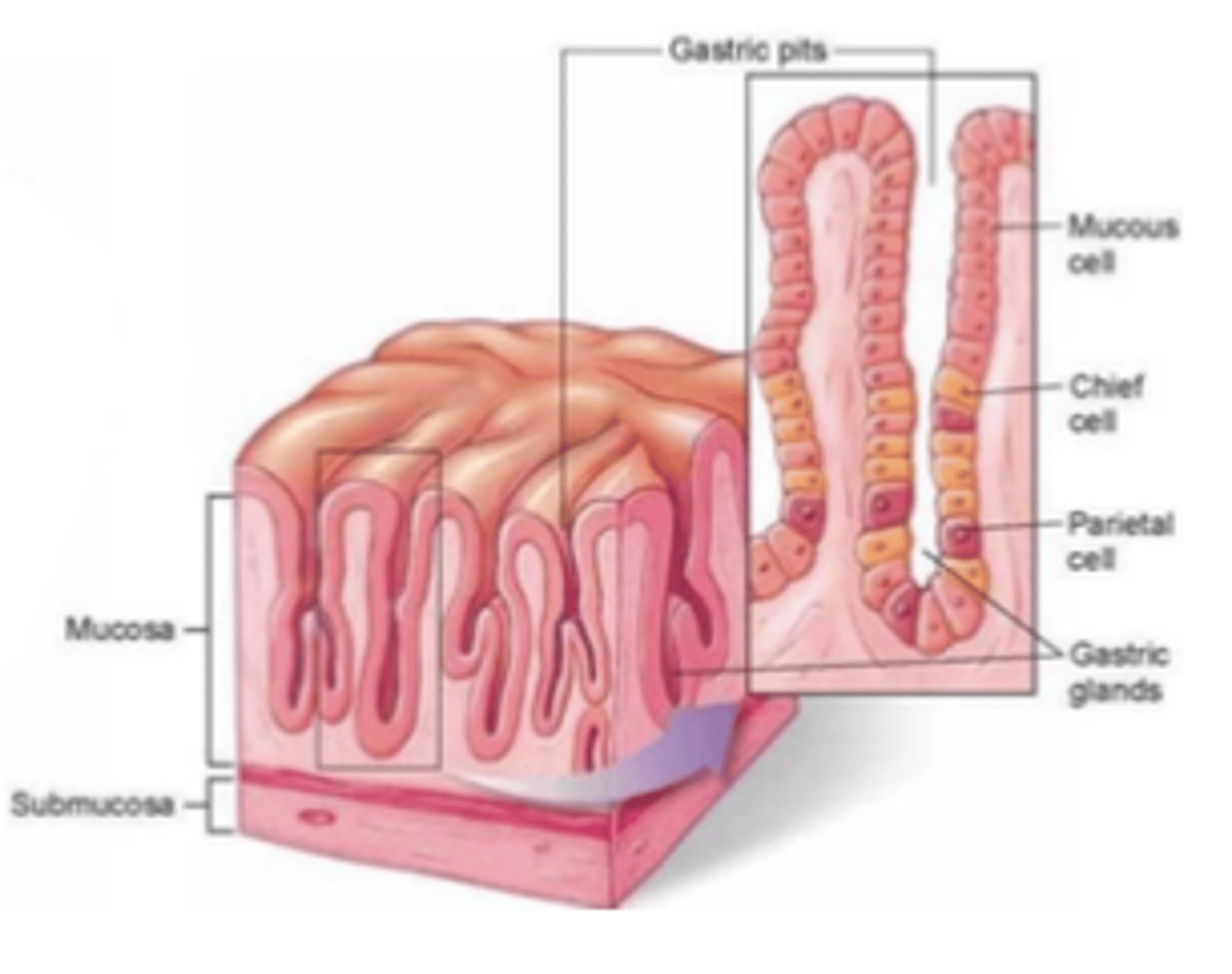
What do mucous or principal cells secrete?
Mucus (bicarbonate)
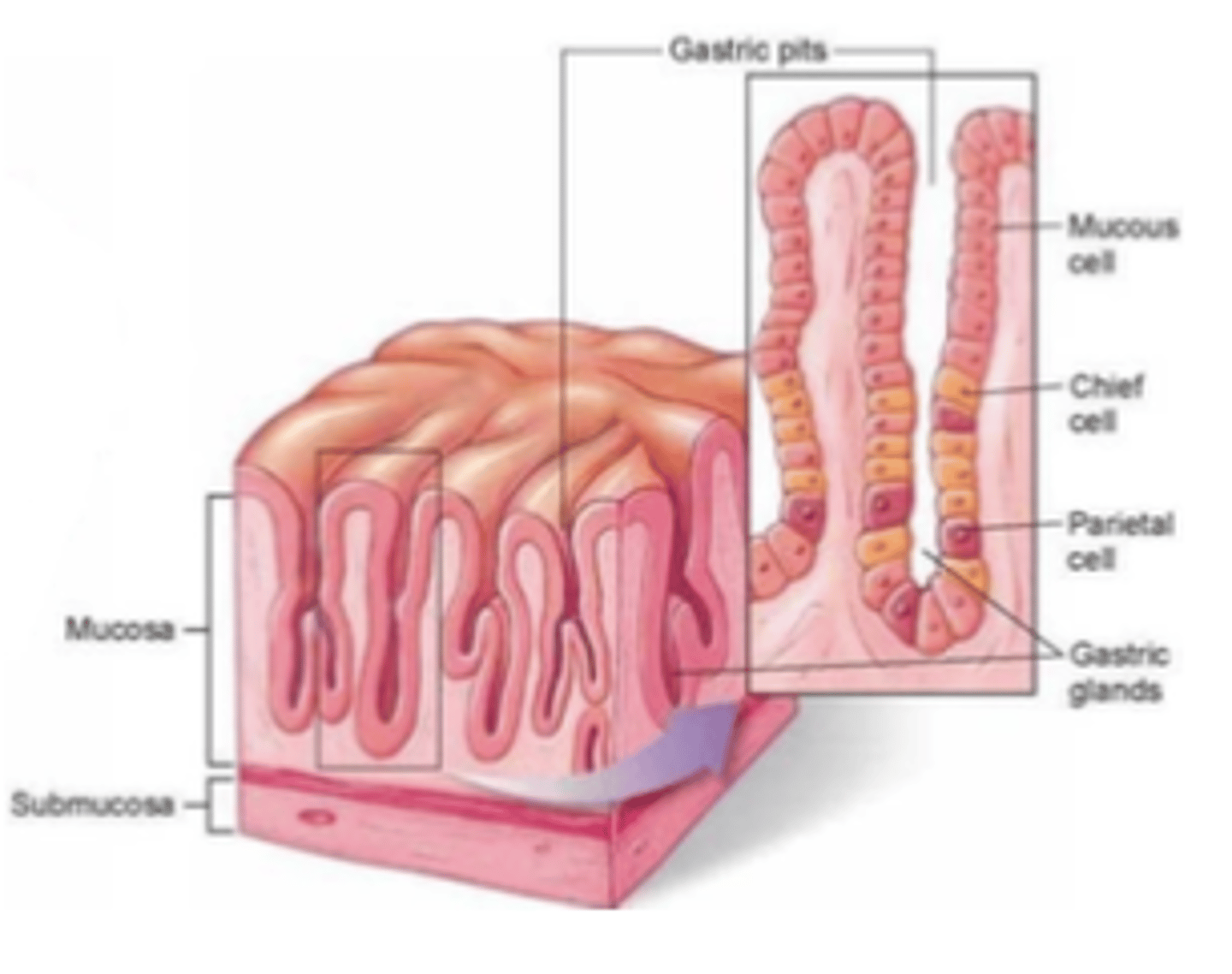
What is the function of intrinsic factor
It helps absorb vitamin B12
What's the purpose of HCl?
Sets a pH between 1 and 3 which allows digestive enzymes, such as
pepsin, to become active
What do parietal cells secrete?
HCl and intrinsic factor (for VitB12)
What activates pepsinogen into pepsin
HCl
What does pepsin do
Digests proteins
What secrete chief cells?
Persinogen -> Pepsin
What cells do we have in the pyloric or tubular glands?
. G cells
. D cells
. Enterochromaffin-lie cells (ECL)
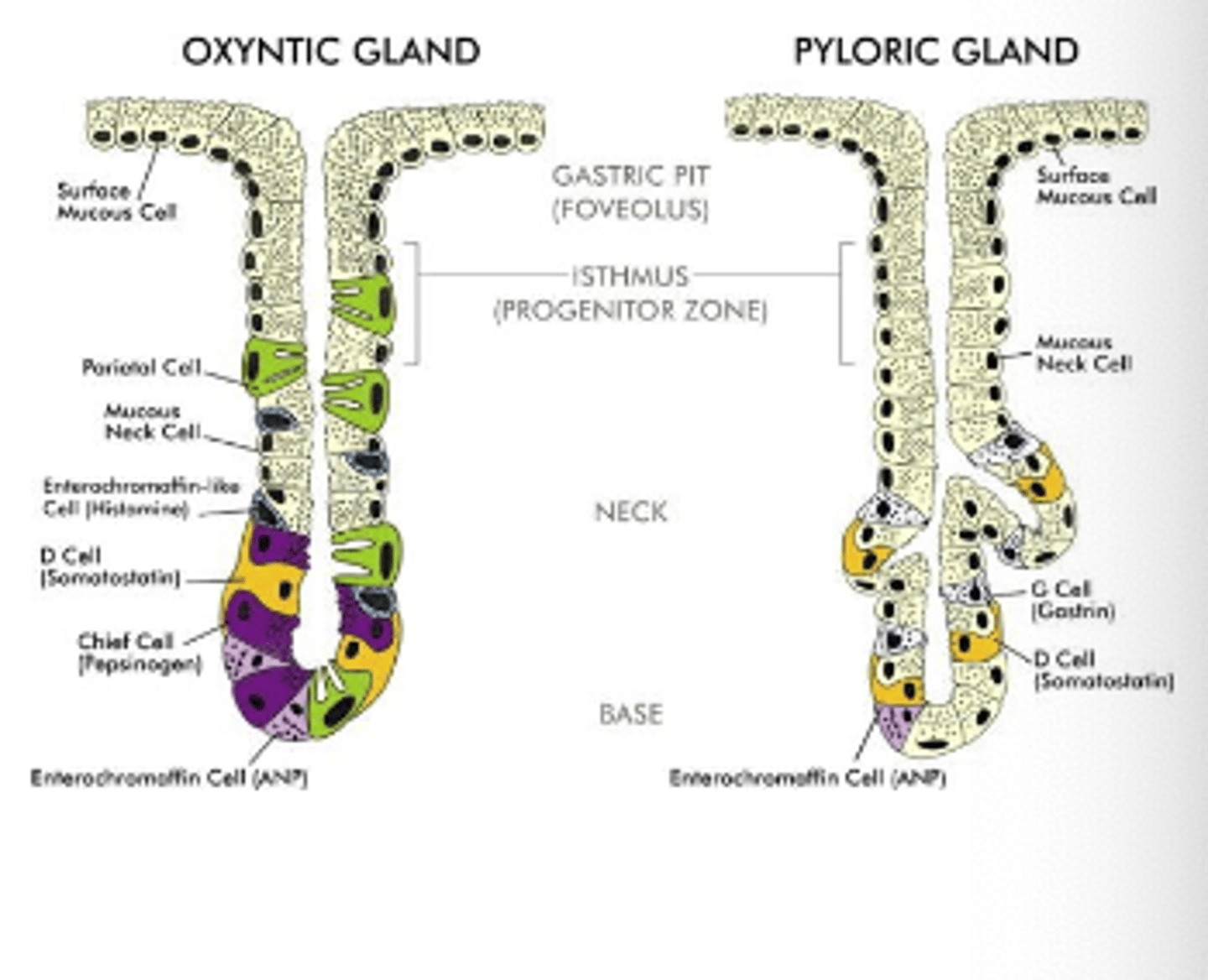
What do G cells secrete and what is the effect?
Gastrin; it stimulates HCl secretion
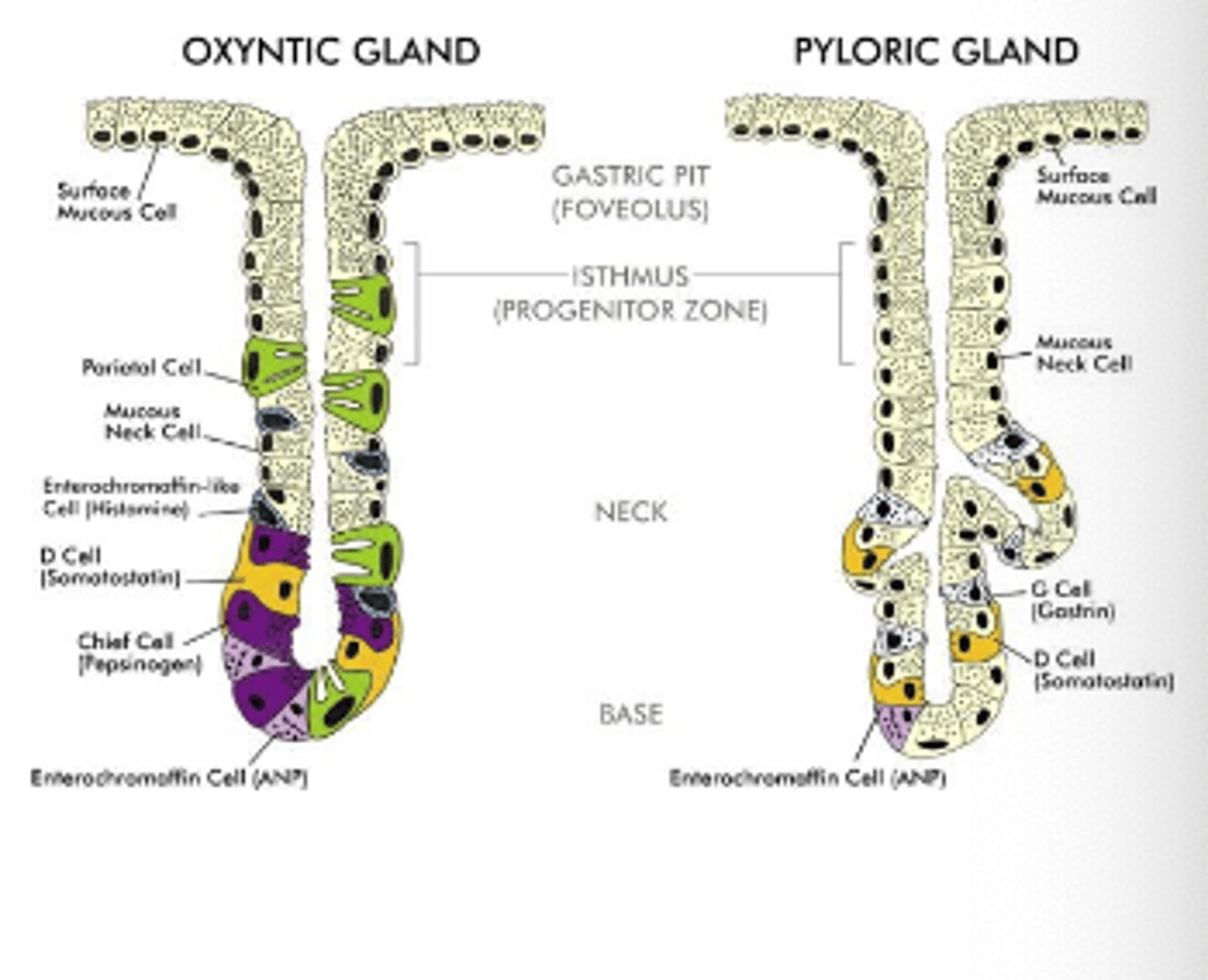
What inhibits gastrin and HCl secretion?
Somatostatin (from D cells)
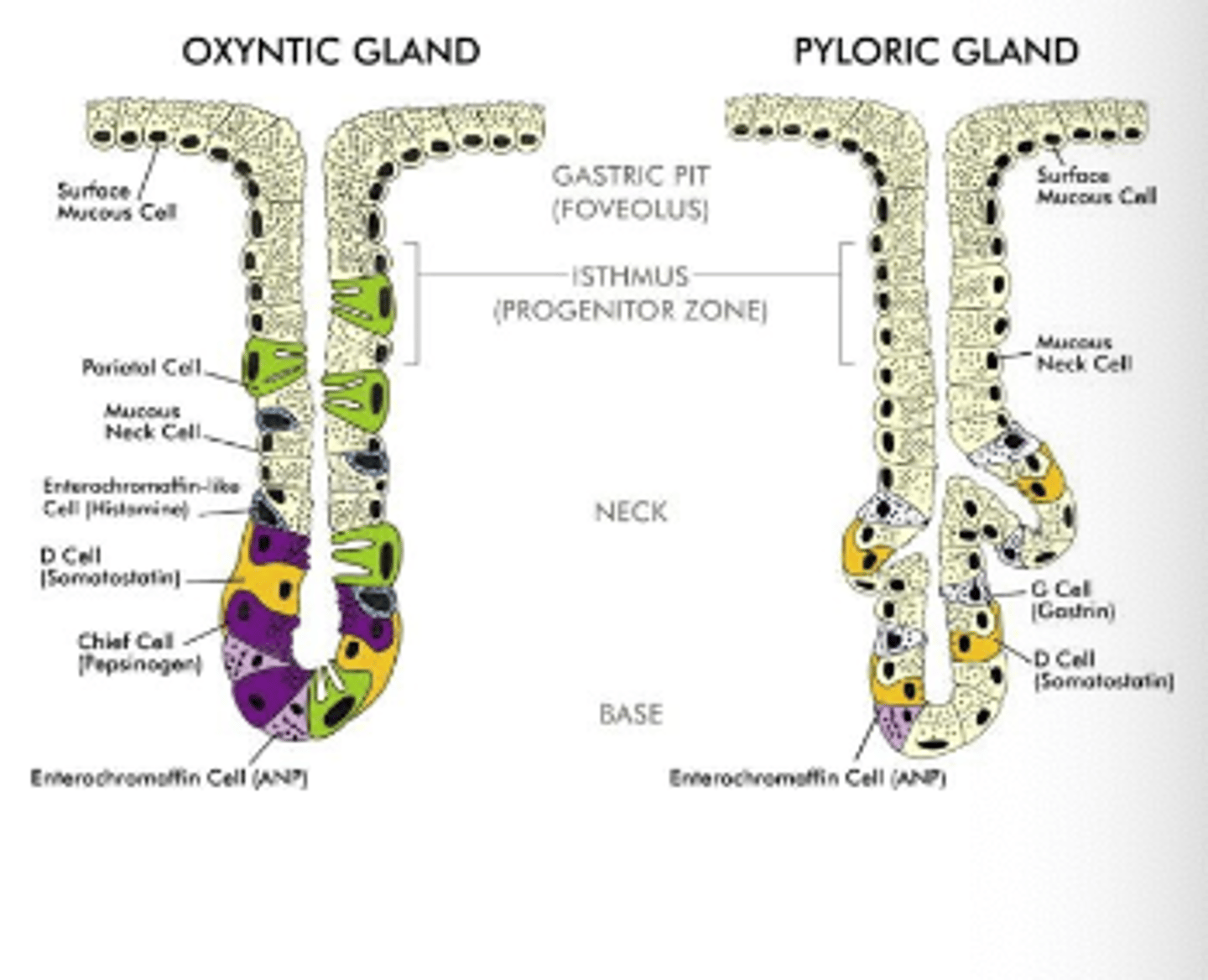
Which cells release histamine in the stomach?
Enterochromaffin-like (ECL) cells
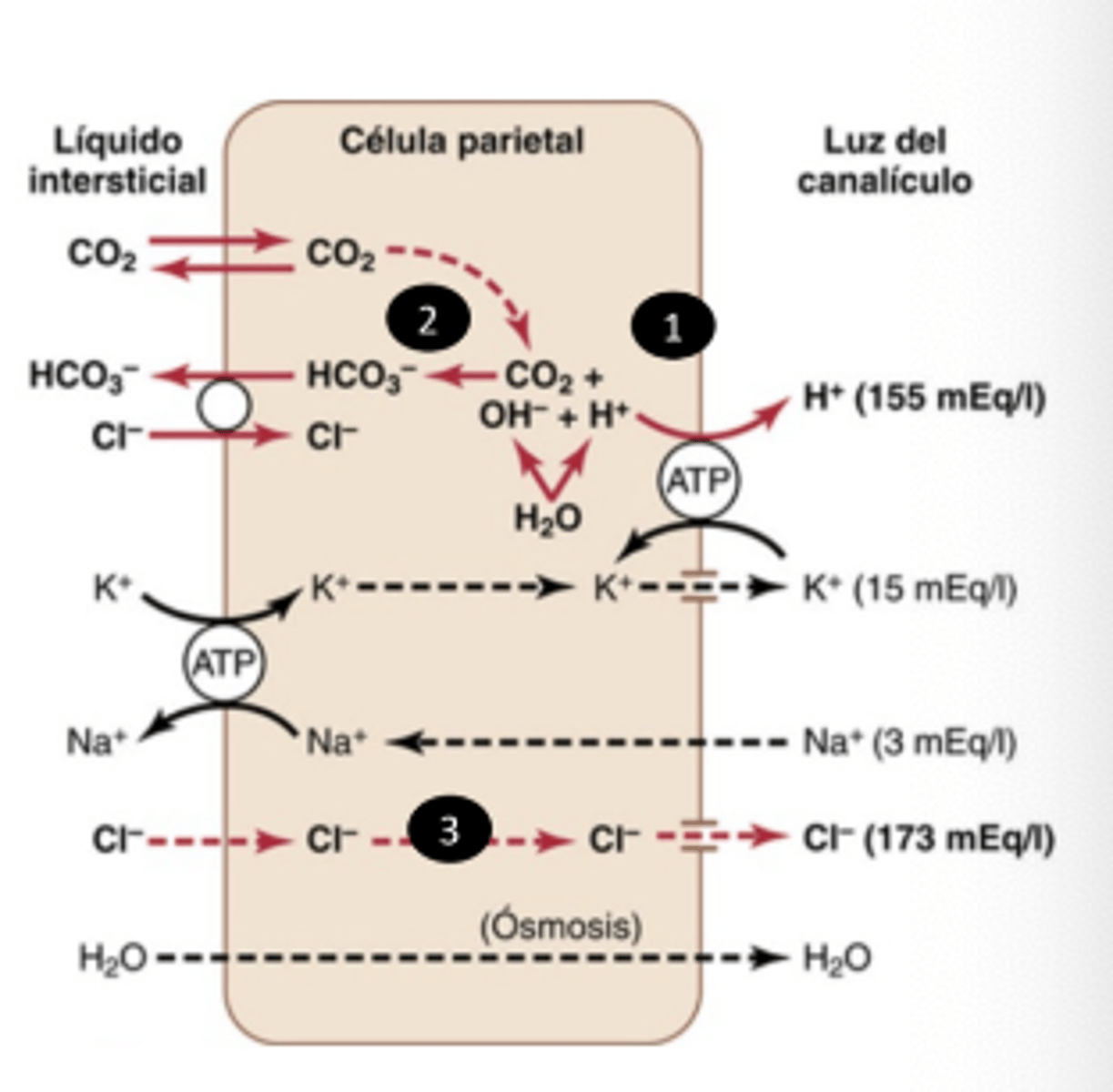
What's the mechanism of HCL secretion by parietal cells?
. Protons produced in H+/K+ ATPase
. C02 + OH -> HC03-
. Cl pass to lumen through passive gradient
. Cl- and H+ ->HCl
. Water diffuse by osmotic gradient to the lumen
What pump drives H⁺ secretion in parietal cells?
H⁺/K⁺ ATPase
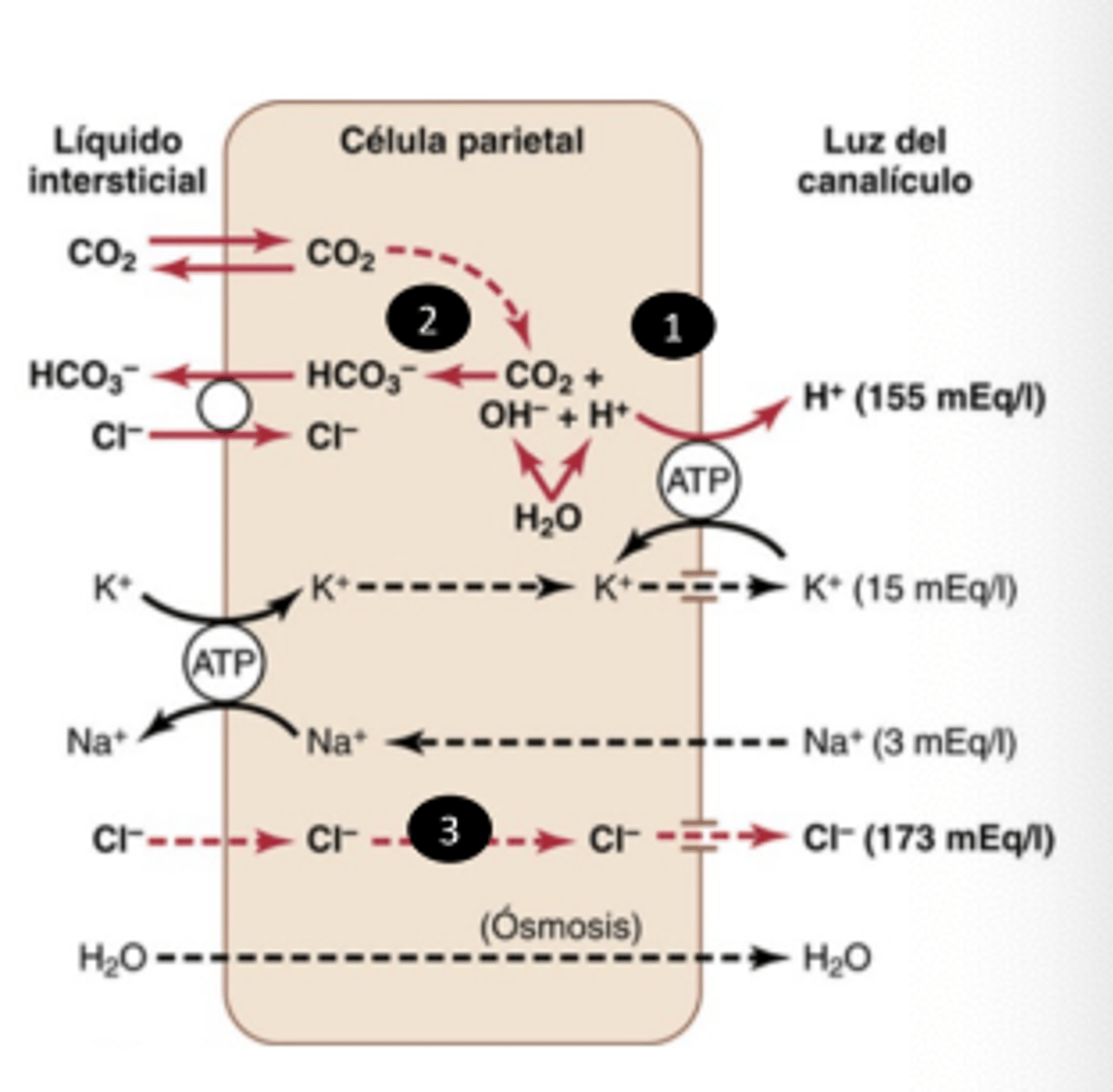
What enzyme generates bicarbonate in parietal cells?
Carbonic anhydrase
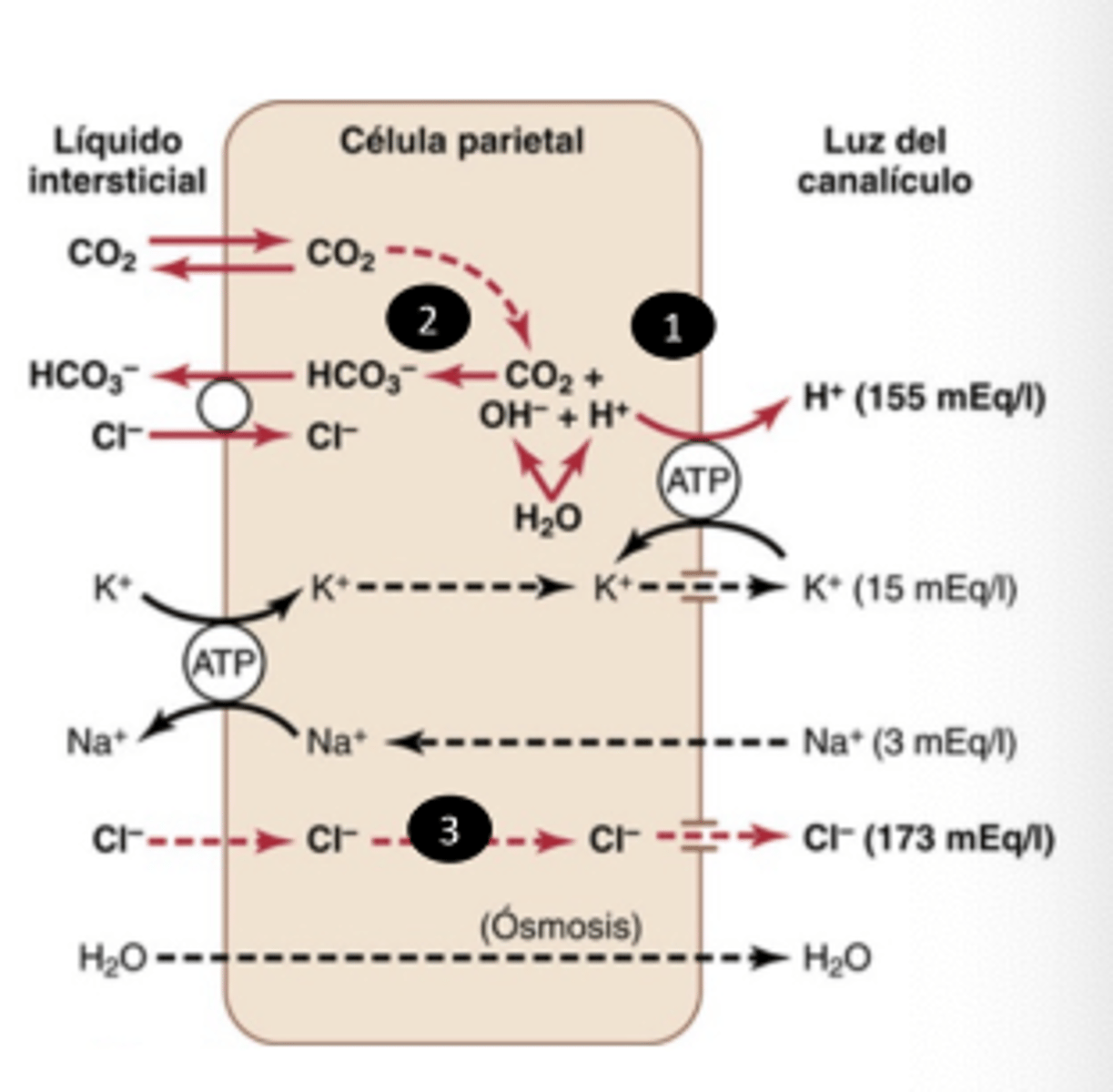
How does Cl⁻ reach the gastric lumen?
Passively, after entering via the Cl⁻/HCO₃⁻ exchanger
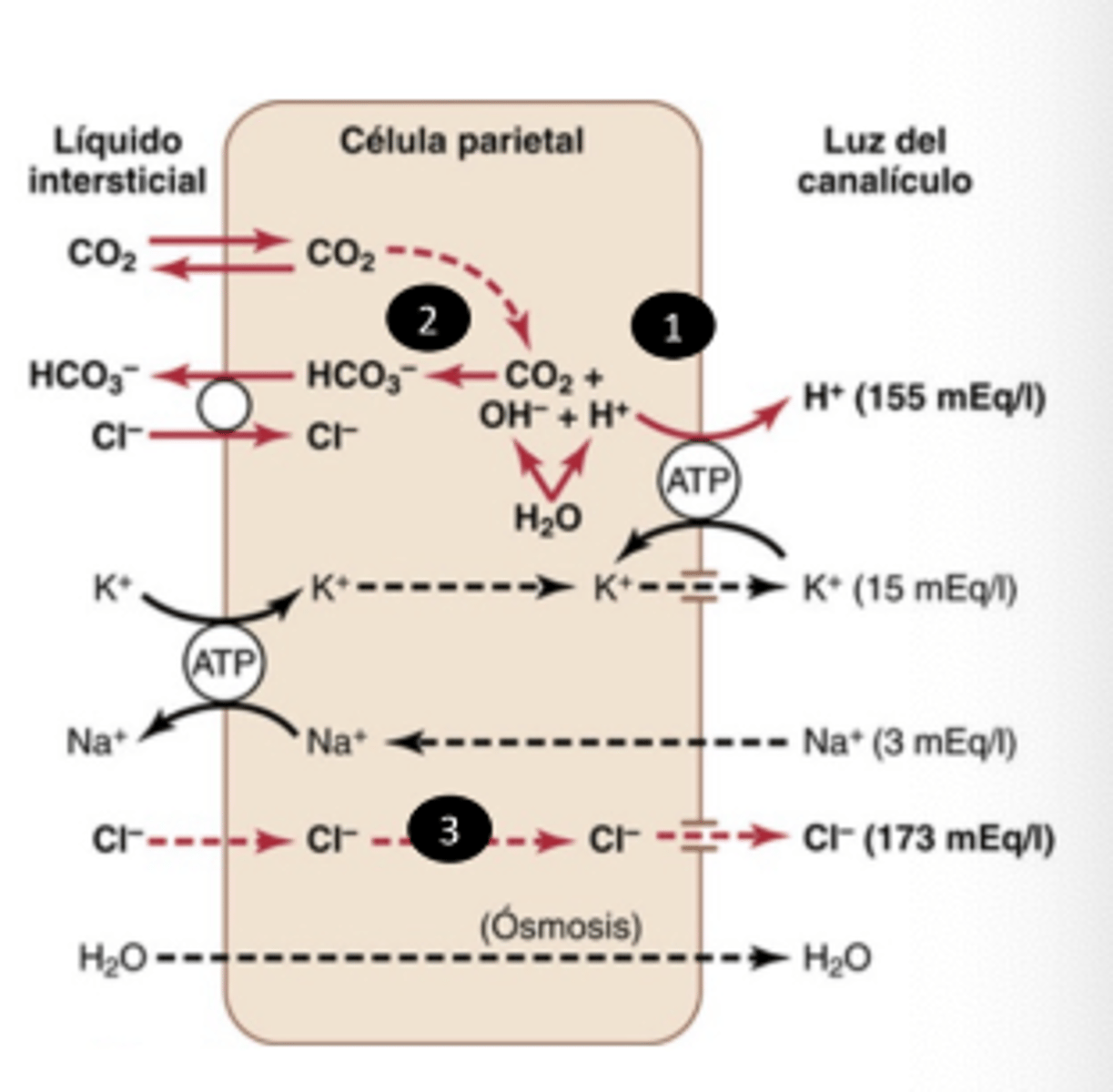
What combines to form HCl in the stomach lumen?
H⁺ and Cl⁻
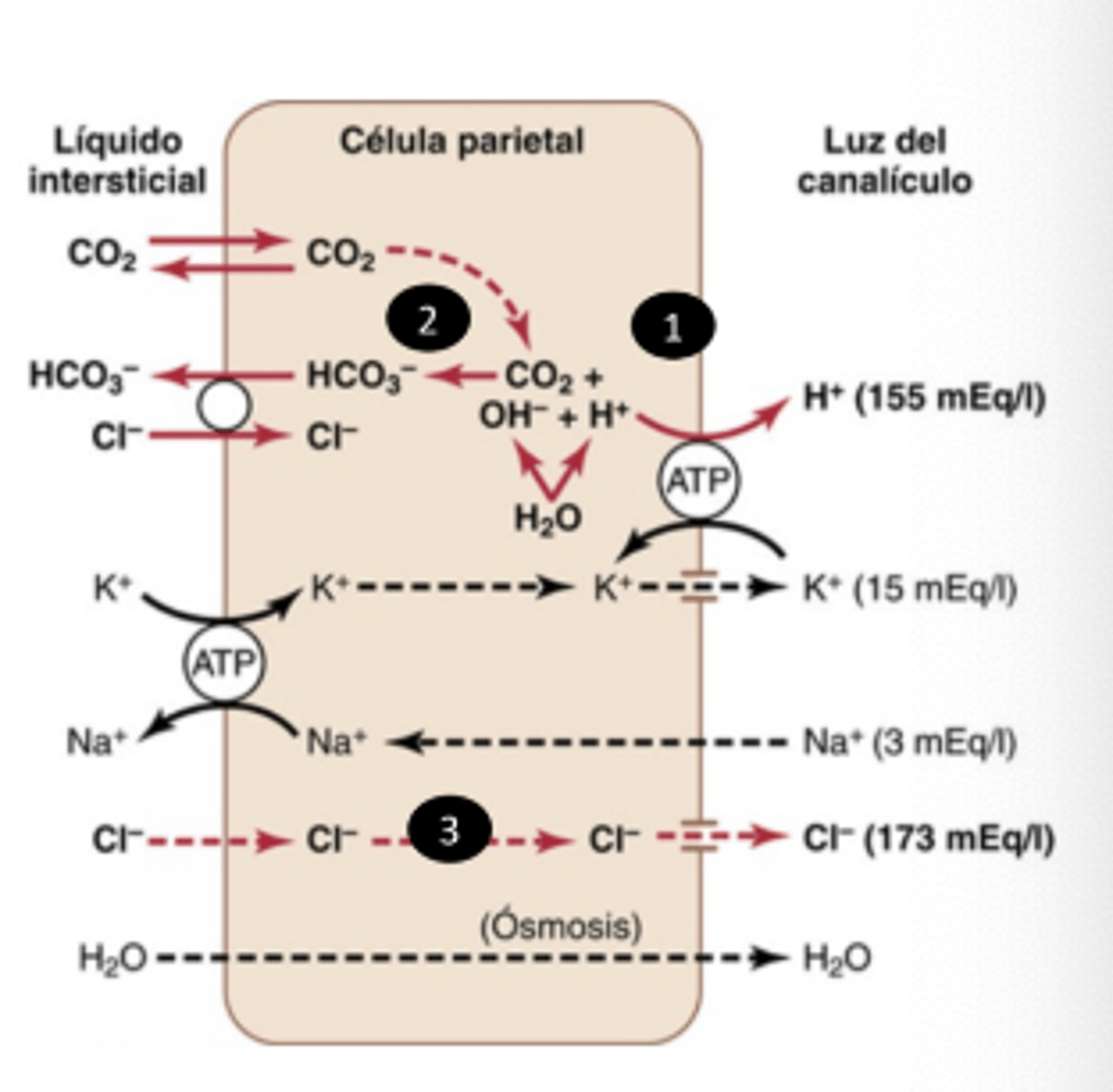
What 3 molecules stimulate acid secretion in parietal cells?
. Acetylcholine,
. Gastrin,
. Histamine
What nerve releases acetylcholine to stimulate parietal cells?
Vagus nerve (parasympathetic)
How does gastrin stimulate HCl secretion?
Directly and indirectly via histamine release from ECL cells
What system inhibits gastric acid secretion
Sympathetic nervous system
Gastrin is produced in the
G cells in the antrum
What are the 3 phases of gastric secretion?
. Cephalic
. Gastric
. Intestinal
What percentage of acid secretion occurs during the cephalic phase?
30%
What are the stimuli of cephalic phase?
. taste, smell of food, chewing, swallowing or conditional reflexes in anticipation to eating
How is stimulated cephalic phase?
. Direct vagal or indirect (via gastrin to release HCL)
What triggers the gastric phase of acid secretion?
Distension, peptides, amino acids
What is the percentage of gastric secretion?
60%
How is gastric phase stimulated?
. direct or indirect (gastrin) vagal stimulation
What hormone mediates gastric phase stimulation?
Gastrin
What triggers the intestinal phase of acid secretion?
Protein digestion products
What is the percentage of intestinal gastric secretion?
10% of total HCL secretion
Where are the intestinal secretions?
. Duodenum
. Small intestine
. Large intestine
What glands secrete mucus in the duodenum?
Brunner glands
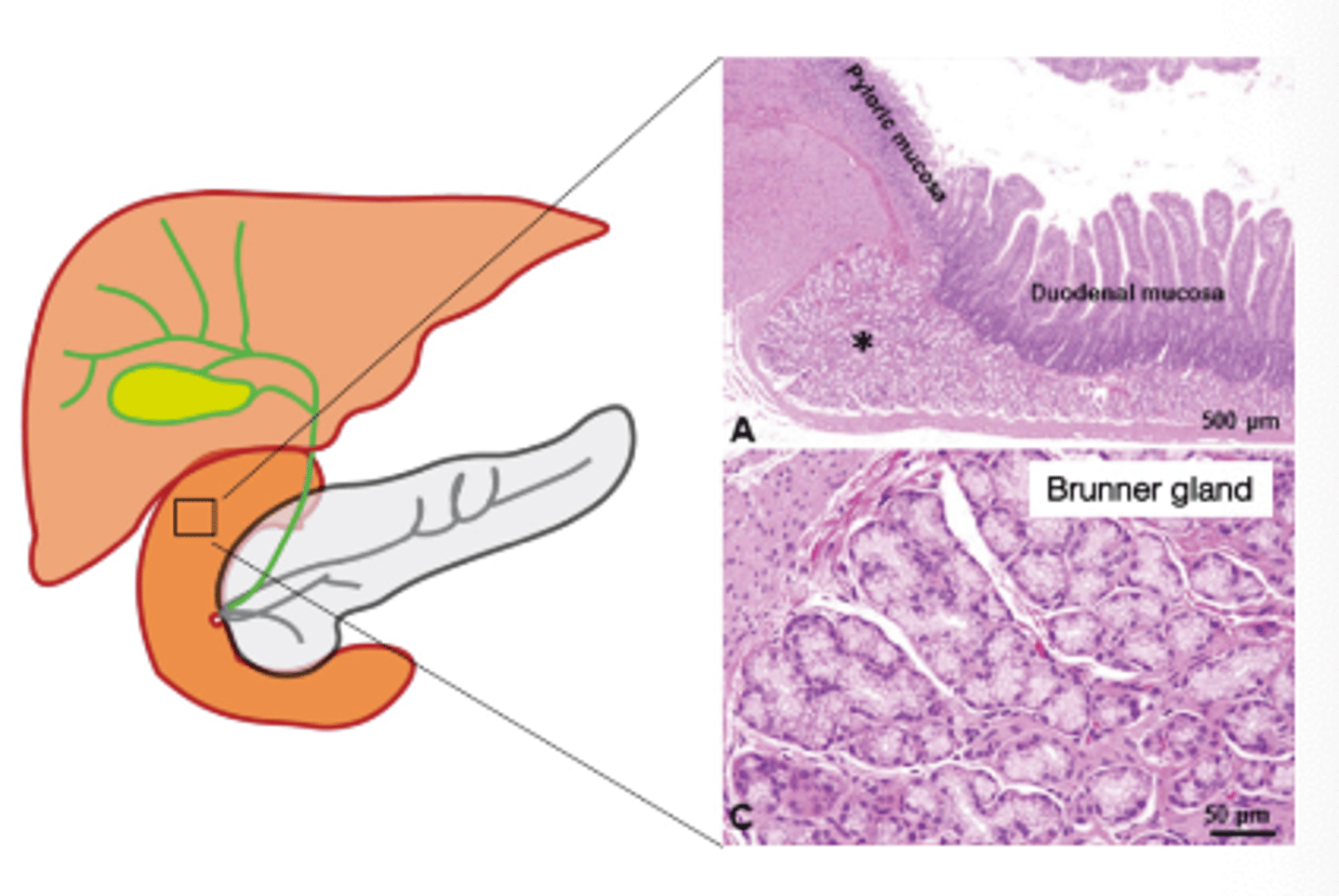
What is the function of Brunner gland secretions?
To protect the duodenum from gastric acid
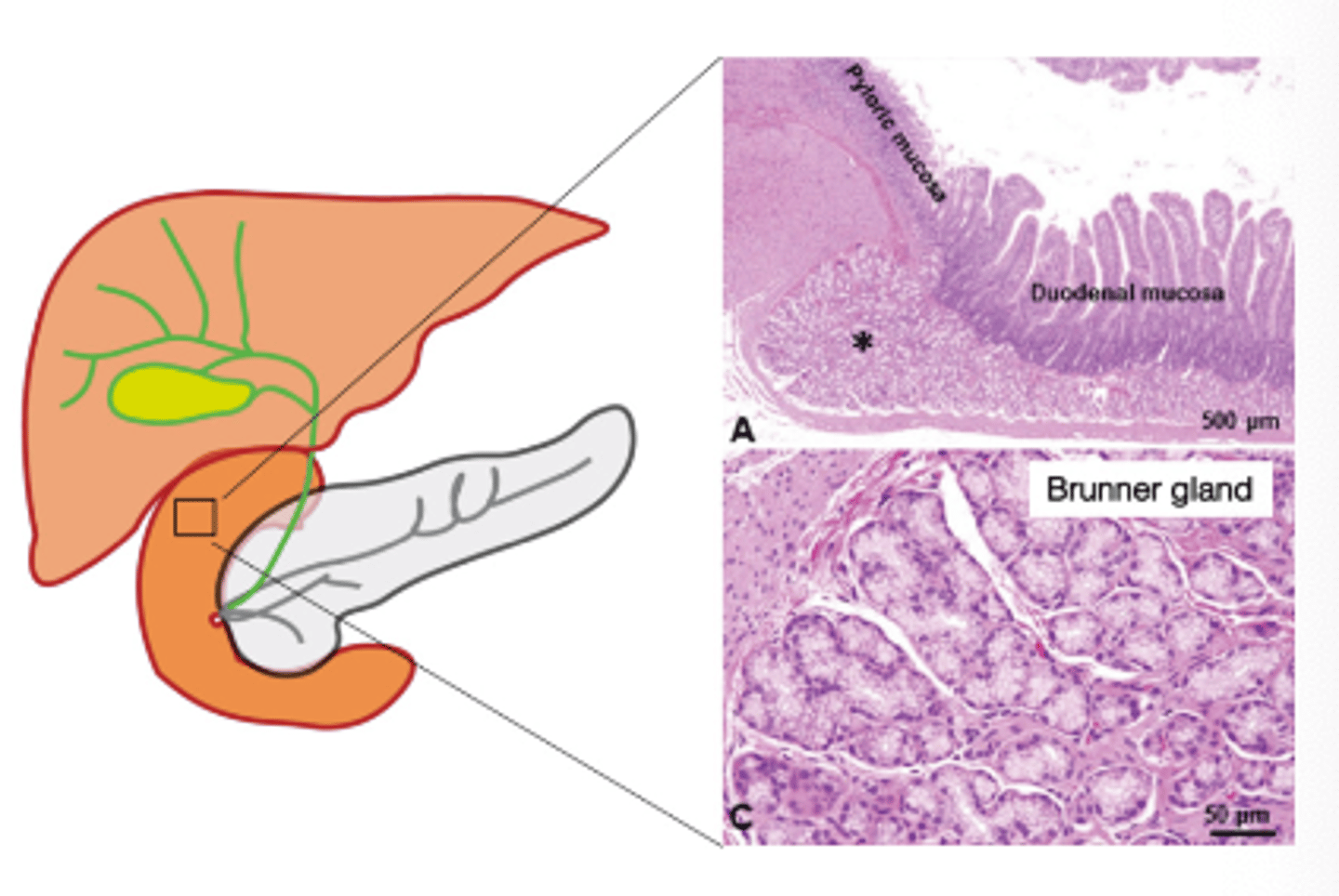
What stimulates Brunner glands?
Touch, distension, irritants, vagus nerve, secretin
What inhibits Brunner gland secretion?
Sympathetic nervous system (ex ; chronic stress causes excessive Sympathetic stimulation = Brunner glands inhibited = duodenal ulcers due to epithelium loses protective amounts of mucus)
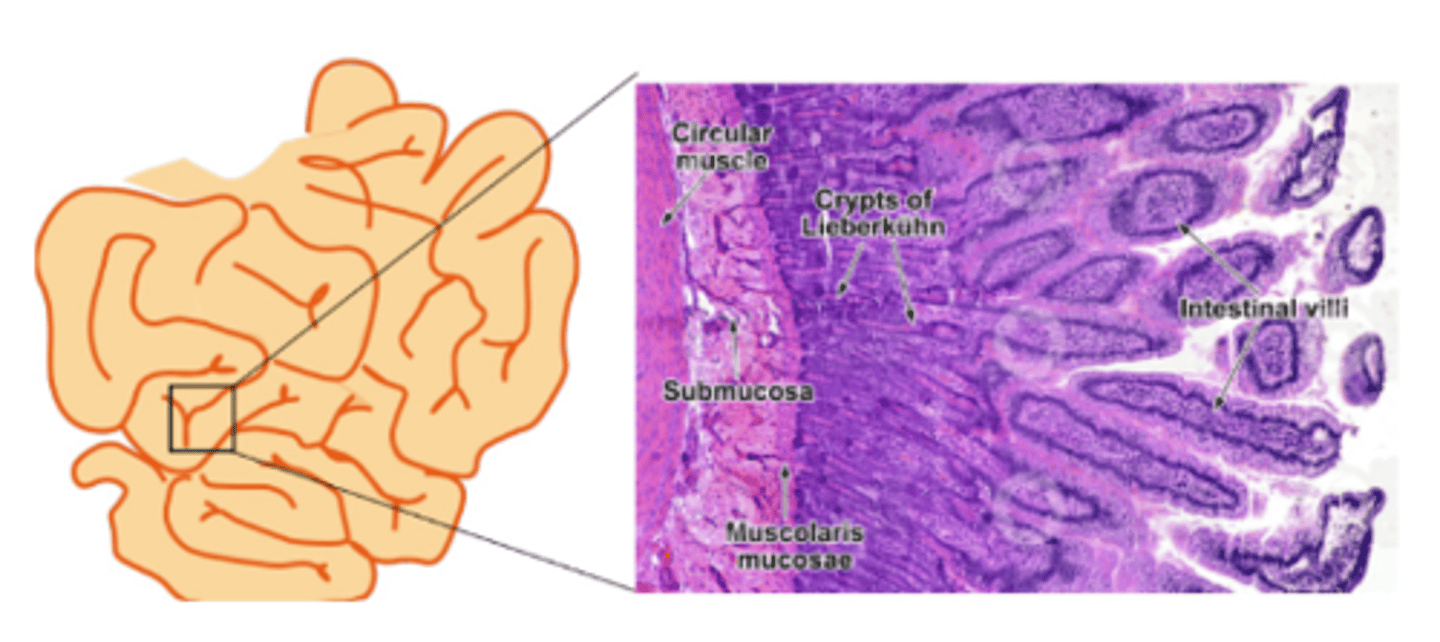
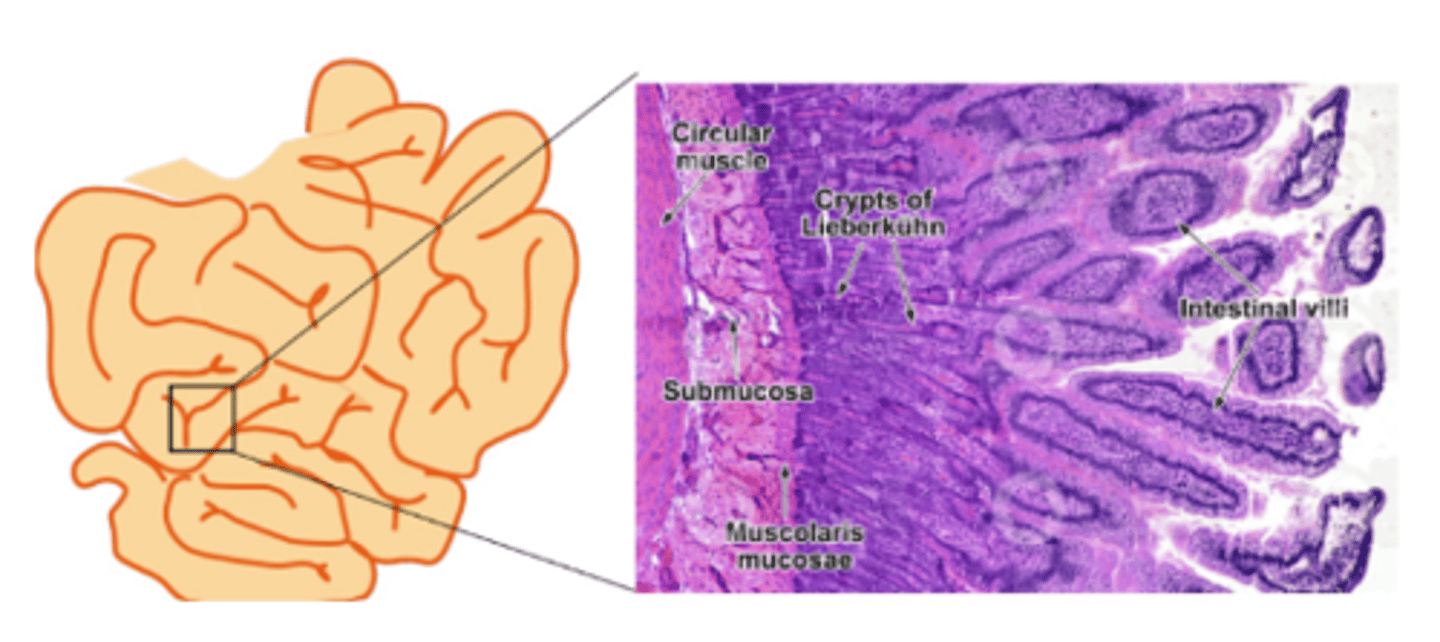
What are the crypts at the base of small intestine villi called?
Lieberkühn crypts
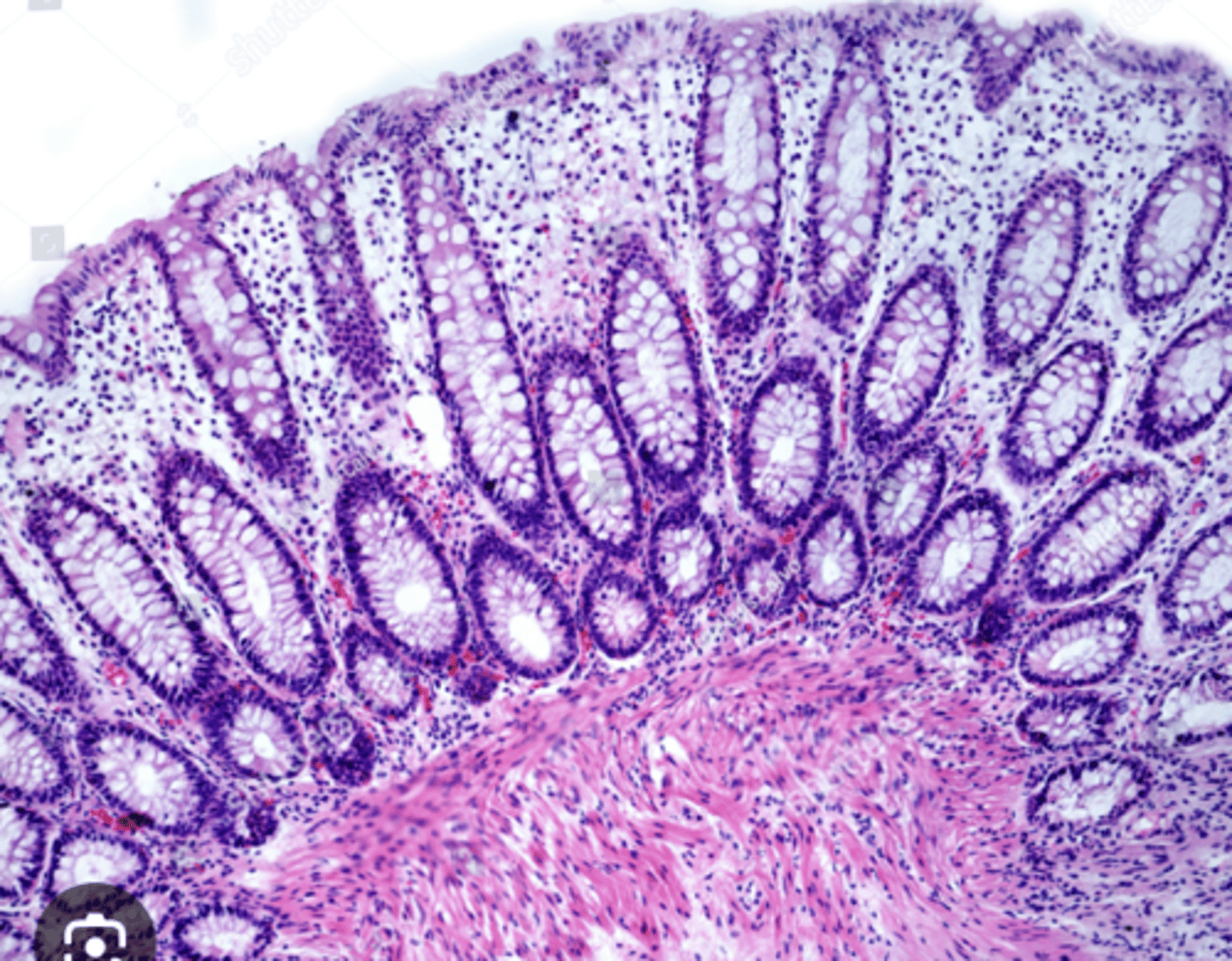
What are the cell types in the crypts?
. Enterocytes
. Goblet cells
. Paneth cells
. Stem cells
. Endocrine cells
What do enterocytes secrete?
Chloride, water, digestive enzymes
What is the function of Paneth cells?
Antimicrobial defense
How often is the intestinal epithelium renewed?
Every 5 days by the stem cells
What are the 3 type of endocrine cells?
. S cells (secretin)
. I cells (cholecystokinin)
. D cells (somatostatin)
What hormone is released by S cells?
Secretin
What is the role of cholecystokinin (CCK)
Stimulates pancreatic acini and gallbladder
How do Cl⁻ and HCO₃⁻ enter the intestinal lumen?
Active transport
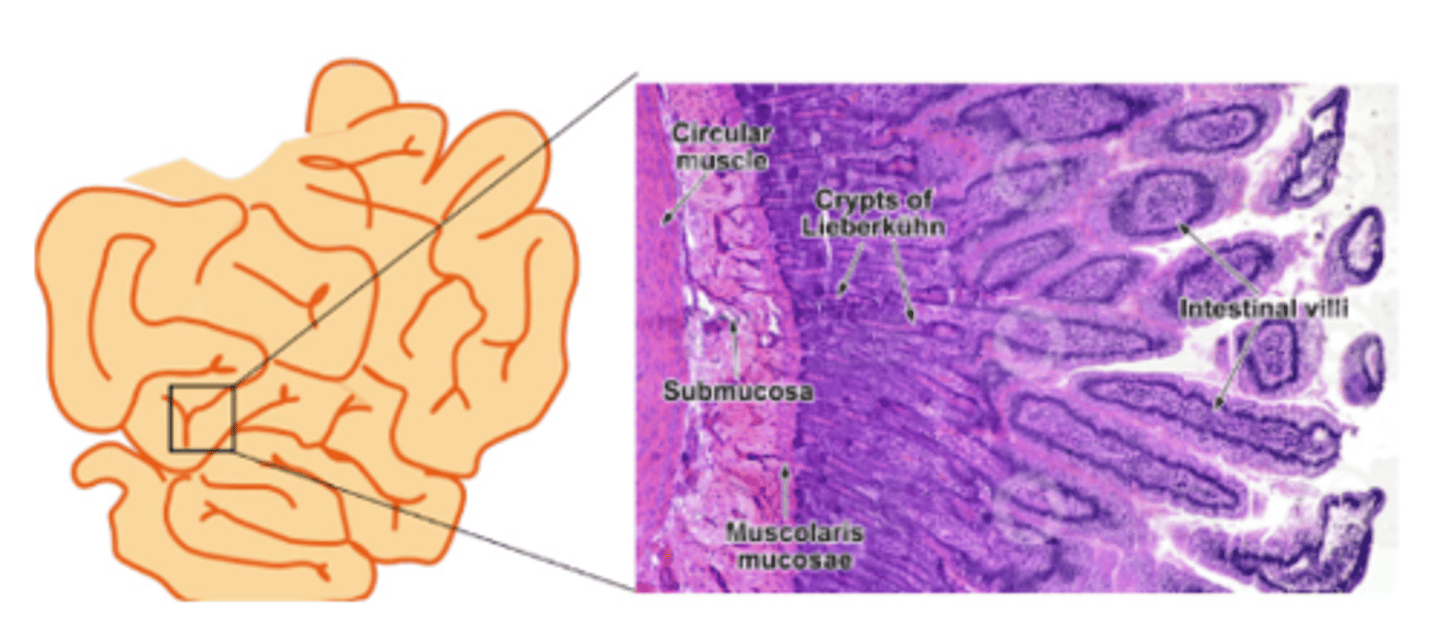
How does water enter the intestinal lumen?
Follows Na⁺ by osmosis
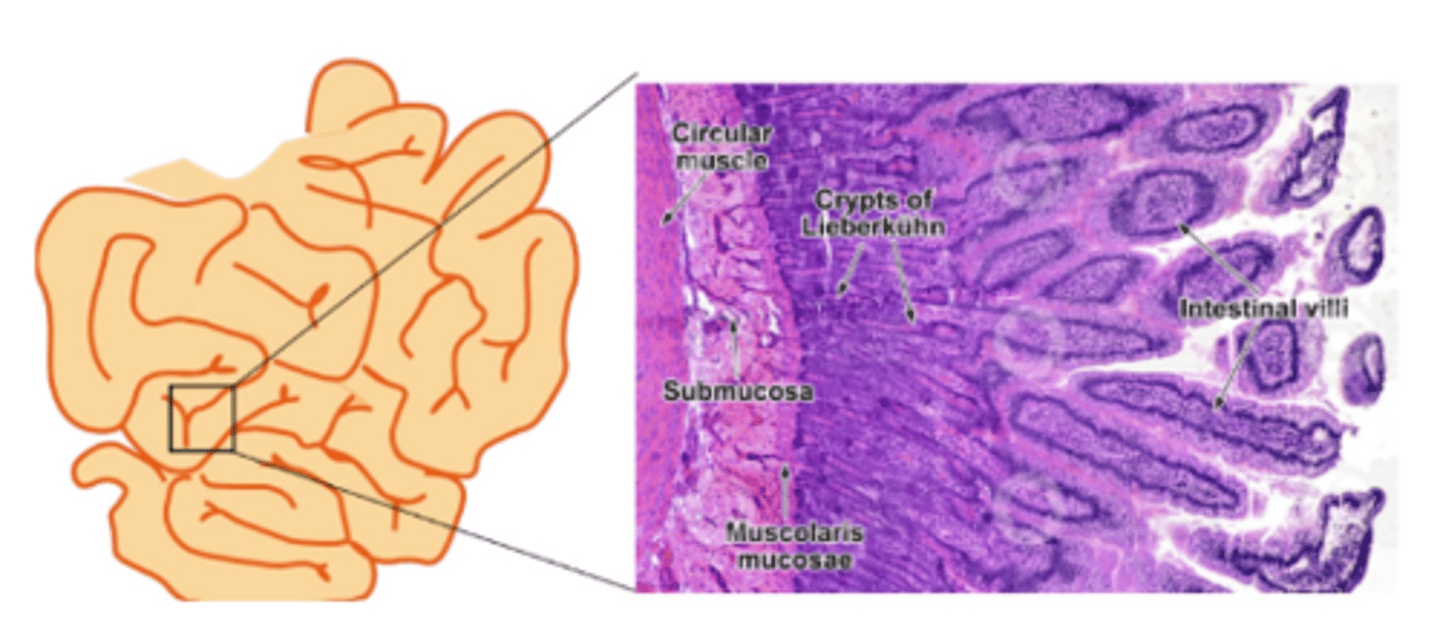
Name 3 carbohydrate-digesting enzymes secreted in the small intestine to break carbohydrates
Sucrase, maltase, lactase
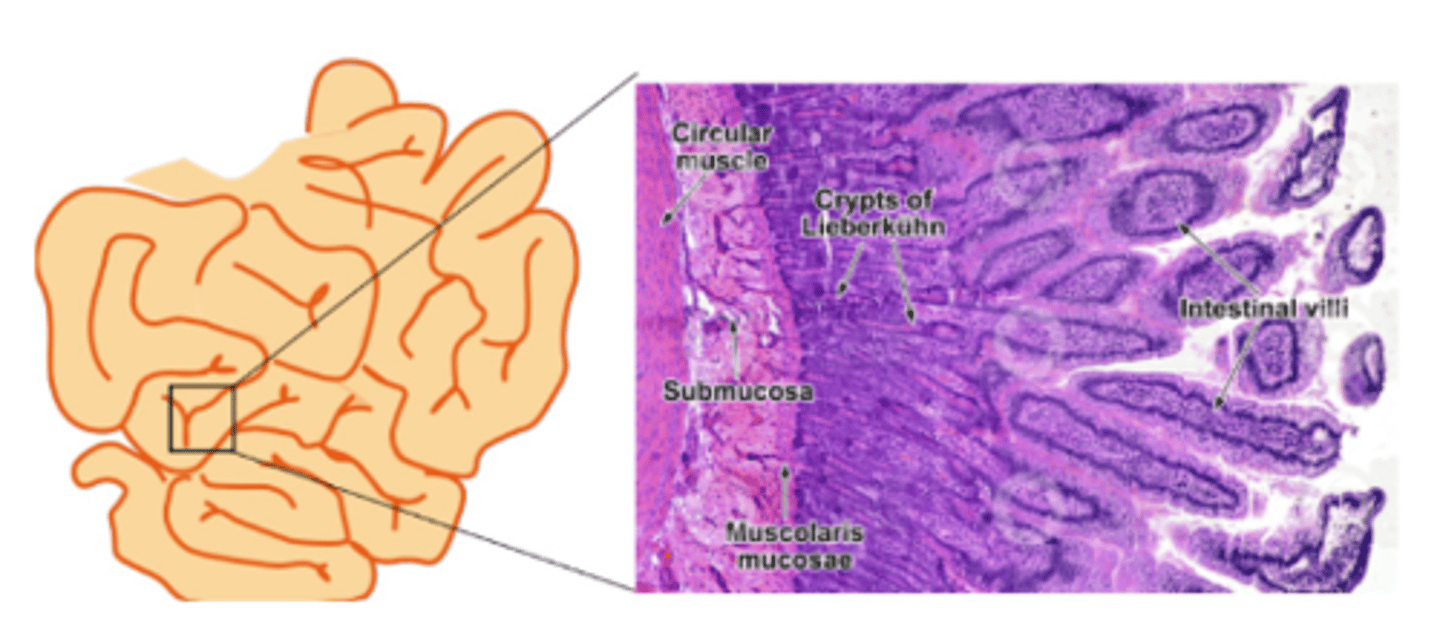
What enzyme breaks down fats in the small intestine
Intestinal lipase
What enzyme breaks down protein in the small intestine
peptidases
Does the large intestine have villi?
No, but there are Lieberkühn crypts
What cells are most abundant in large intestine crypts?
Goblet cells
What is the main function of mucus in the colon
Protection and feces lubrication
What stimulates absorption in the large intestine
Parasympathetic stimulation
What does the colon absorb
Water, electrolytes, and B vitamins
What electrolyte is mainly secreted in the colon
Chloride (Cl⁻)