Pathogens-Chapter 7.1
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Pathogens
Any disease causing microorganisms
Bacterias are classified as _____
Prokaryotes - do not have a nucleus
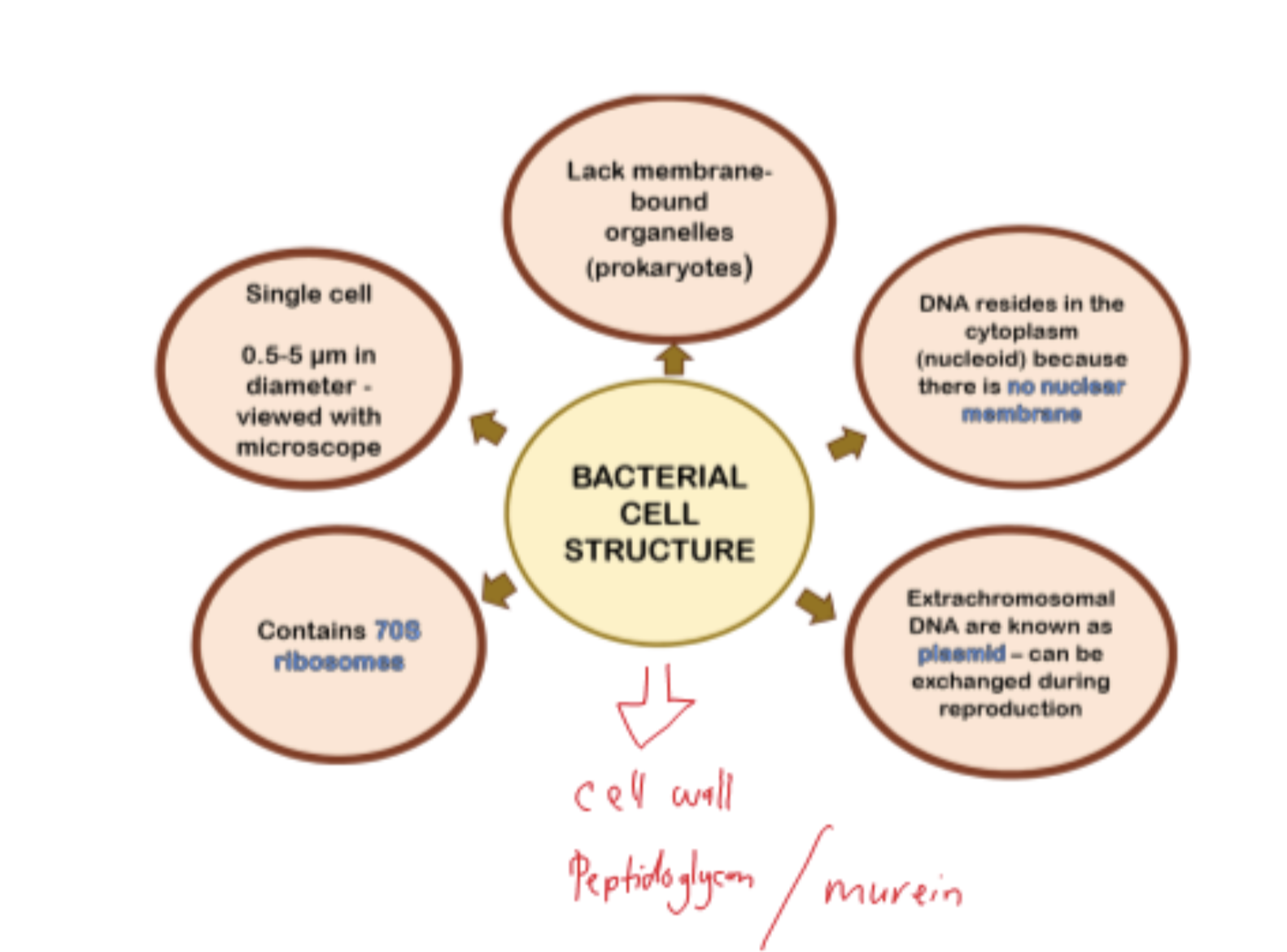
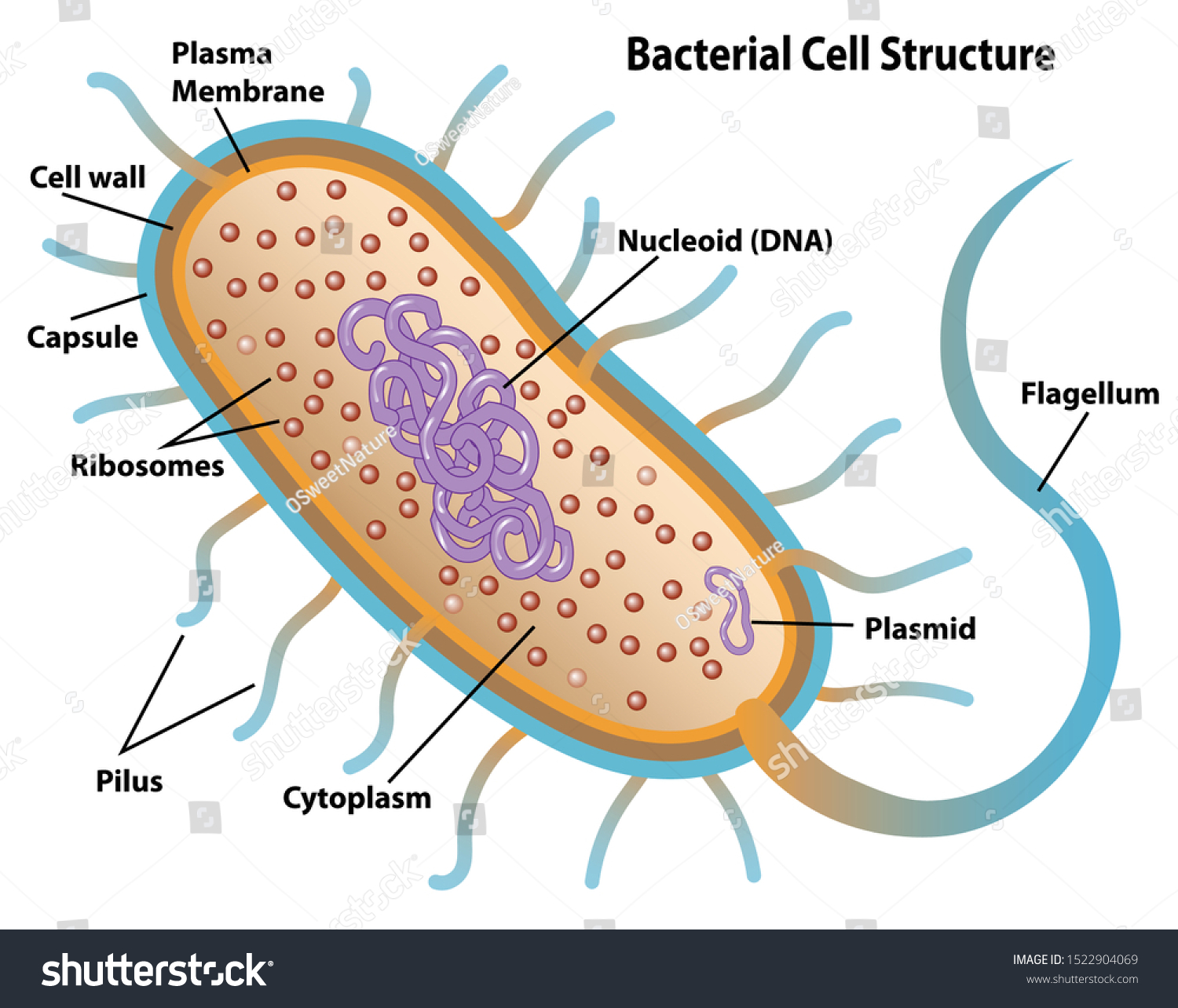
Bacterial cell structure
Common bacterial shapes
Cocci - spherical cells, singly or in pairs
Bacilli - flagella have rod shaped cells
Spirilla - twisted cells
Vibrio - curved rods comma shaped
Bacterial arrangement
Singly
In pairs - diplococci
In chains - streptococci
In clusters - staphylococci
Bacteria cell wall
made out of peptidoglycan/murein (network of carbohydrates cross-linked with polypeptides)
maintain cell shape and structure
Gram positive bacteria
large amount of peptidoglycan (thicker)
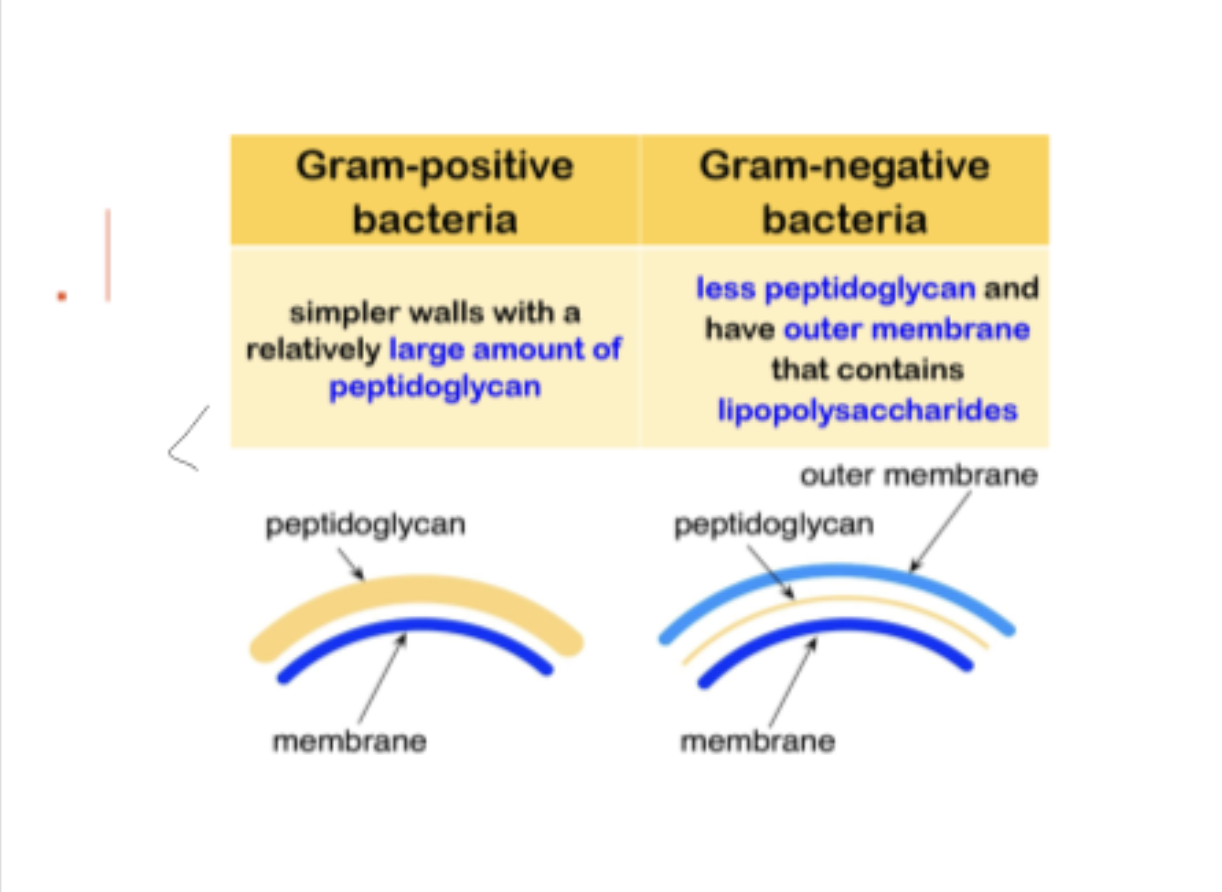
retain crystal violet stain during the decolourization process
Gram negative bacteria
less peptidoglycan and have outer membrane that contains lipopolysaccharides
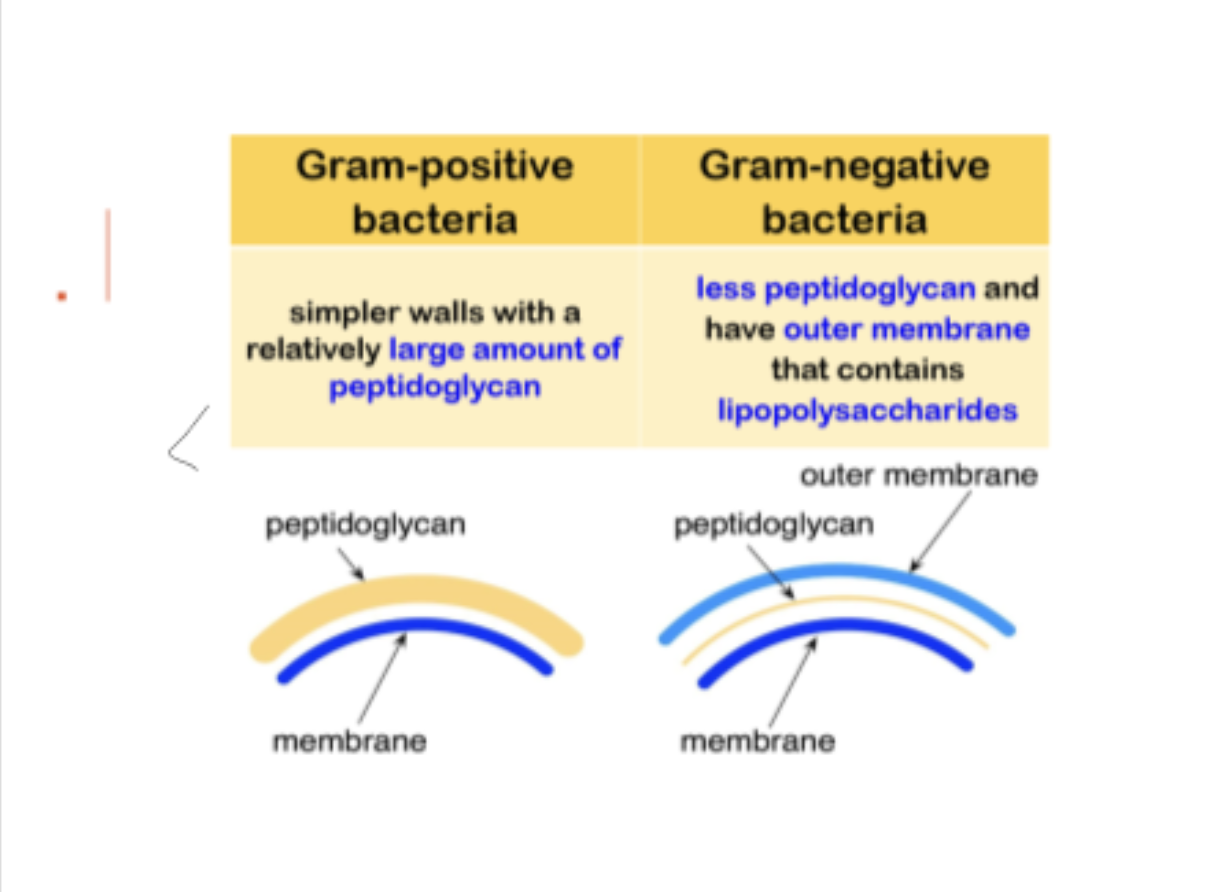
lose the crystal violet stain and stained by safranin in the final staining process
Gram staining process
Crystal violet
Put iodine (act as a mordant, trap crystal violet inside the bacterial cell wall)
Alcohol wash
Application of safranin (counterstain)
Why are gram negative bacteria more dangerous as disease organisms
Their outer membrane is often hidden by a capsule or slimy layer which hides the antigens of the cell and acts as a camouflage. Harder to kill, quick to develop resistance
Role of capsule in bacteria
Cell wall of some bacteria are covered with a capsule of slime layer (thin)
made of complex carbohydrate
Role: protection
Flagellum
movement
Virus
Extremely small
Non cellular (non-living)
Infectious agents
Virus consists of
Nucleic acid
May be RNA or DNA
Capsid
made of repeating units of capsomere
Membrane envelope
for certain virus
Contain viral proteins
Virus structure (HIV)
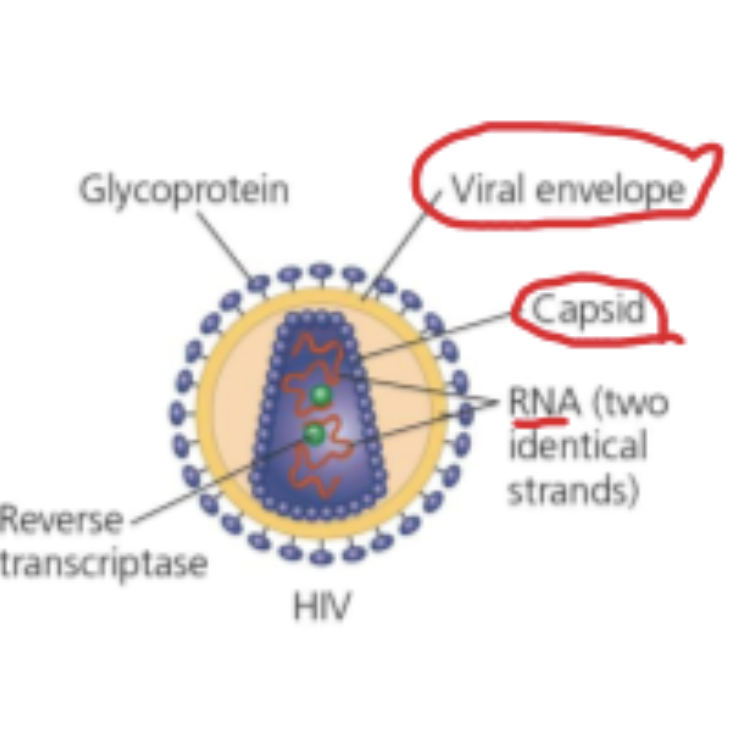
Obligate intracellular parasites
can only replicate/multiply inside hosts cell
Viruses do not have a _____ instead they have a outer layer called _______
cell wall, viral envelope
What gives the virus its structure?
The capsid consists of repeating units of capsomere
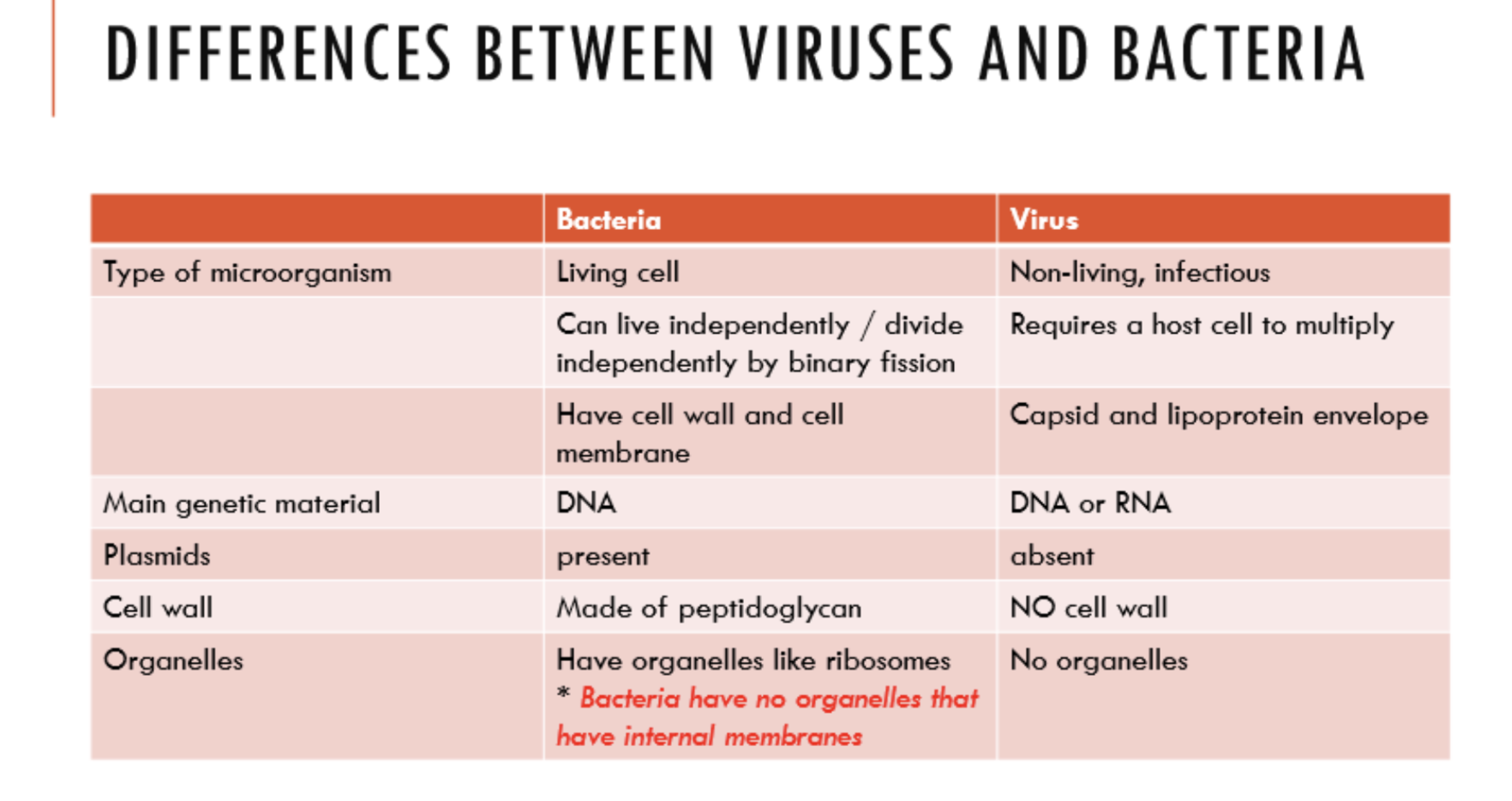
Differences between viruses and bacteria
Airborne
Indirect transmission
When the moisture in exhaled droplets evaporate leaving dried particles of viruses and some bacteria
Suspended in the air by dust particles and inhaled by another uninfected individual
particles remain viable for greater distances compared to droplet transmission
Vectors
Indirect transmission
Transfer of pathogen by other animal
insect that is not affected by the disease transfers the pathogen from an infected individual to an uninfected individual
Ingestion
Indirect transmission
Consumption of contaminated water or food
Droplet
Direct
Tiny droplets of moisture containing pathogens emitted while talking or sneezing remains suspended in the air in droplets of saliva or mucus and inhaled by an uninfected individual
Indirect
When individuals sneezes and viruses remain on objects and an uninfected individual touches the object and then their eyes or face
Bodily fluids
Direct: bodily fluids from an infected individual comes into contact with the mucous membrane or bloodstream of an uninfected individual
Indirect: sharing of needles with an person infected with _____
Contact
Indirect contact: touching an object touched by an infected individual
Direct contact: touching an infected individual
Characteristic of inflammatory response
Swelling
Redness
Heat
Pain
Roles of inflammatory response (RIP)
Prevent the damage from spreading
Remove damaged tissues and cell debris
Initiate tissue repair mechanism
Inflammatory response occurs when
response to tissue injury (accumulation of tissue fluid)
Antigens
any molecules that stimulates the immune response
Non self antigens
antigens that are not recognized by the immune system as belonging to the host body and will stimulate a further immune response either internal non-specific or specific
Self antigens
antigens that are recognized by the immune system as belonging to the host body and will NOT stimulate a further immune response
Pyrogens
any molecules that will cause a fever
Exogenous pyrogens
pyrogens released by pathogens or non self antigens
Endogenous pyrogens
molecules that are released by our own body such as INTERLEUKIN-1
Fever/Pyrexia
Cytokine induced upward displacement of the thermoregulatory set point
set point of core body temperature set to a higher temperature due to the presence of cytokines
Response due to the release of pyrogens
How does a fever help the body recover from infections?
Increased core body temperature during a fever:
Inhibit bacterial growth by creating an unfavourable environment for bacteria, will not work as well at higher temperatures
Increases metabolic reactions and enzymatic activity of white blood cells
increases the rate of tissue repair by increasing enzymatic activity of WBC
Increases heart rate and blood flow increases the rate of WBC transported to sites of infection
Lymph node contains ______
masses of lymphoid tissue, the cells are criss crossed by a network of fibres
Bacteria are trapped in the mesh of fibres as the lymph nodes flow through the nodes
Macrophage destroy them by phagocytosis
When infections occur, the formation of lymphocytes _____ and the lymph nodes become _____ and ______
increases, swollen and sore
Breaking a fever
Resetting a hypothalamic thermoregulatory setpoint downwards initiates heat loss through vasodilation and sweating
Airborne transmission
Moisture in exhaled droplets evaporate leaving dried particles of viruses and some bacteria
Can be inhaled and remain viable for greater distances compared to droplet transmission
What are modes of transmission that are not passed through direct transmission
V.I.A
Vectors
Ingestion
Airborne
Droplets
tiny droplets of moisture containing pathogens emitted during talking breathing and sneezing are breathed in or ingested with food if particles settle on cutlery