Osteology and Arthrology of the Pectoral Girdle and Upper Limb
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
110 Terms
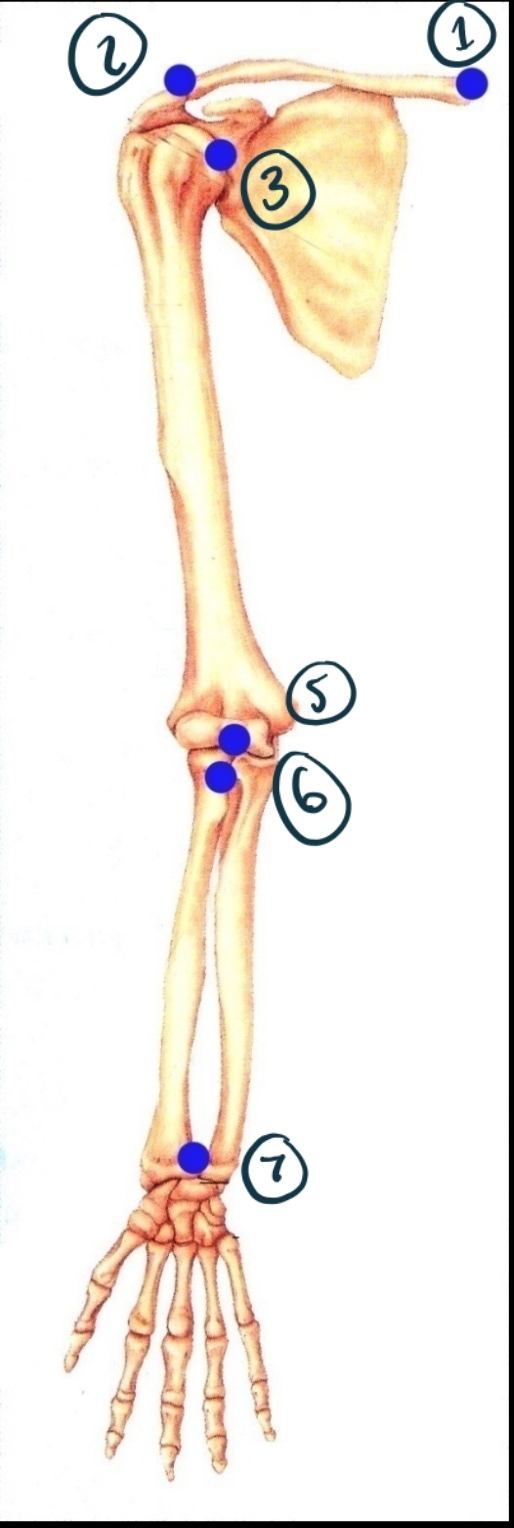
Name Joint 1 Including Structure and Function.
Sternoclavicular joint. Synovial (modified gliding - has some ball + socket/saddle properties). Diarthrosis (multiaxial).
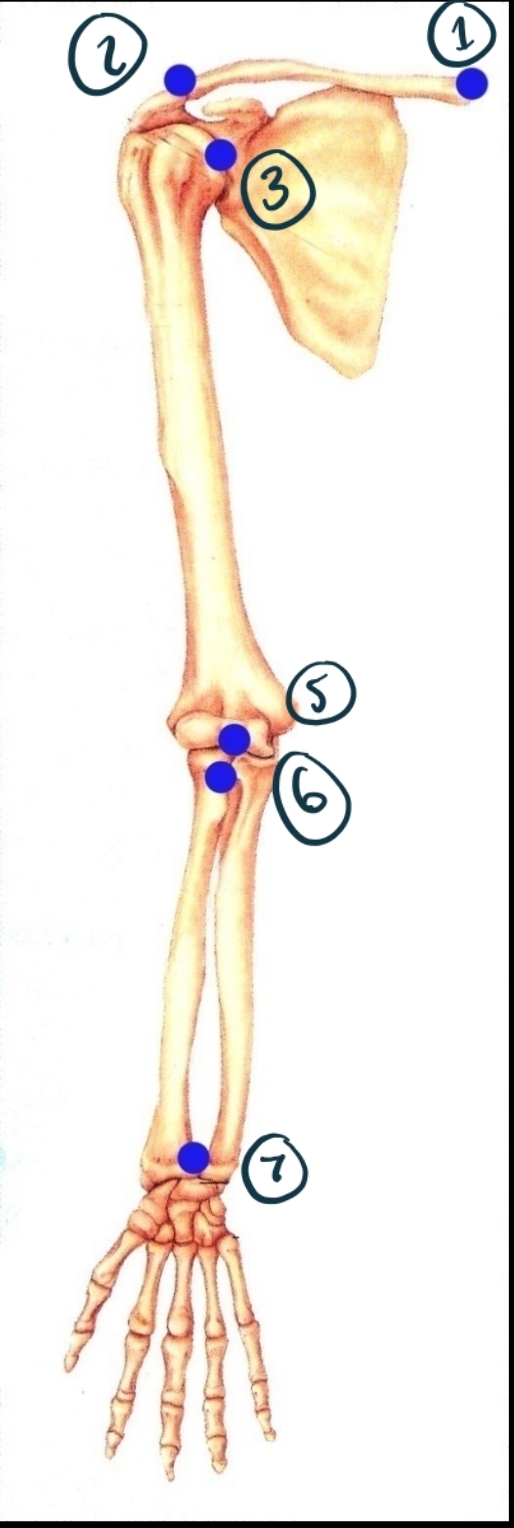
Name joint 2 structure and function.
Acromioclavicular. Synovial (gliding). Diarthrosis (multiaxial?)
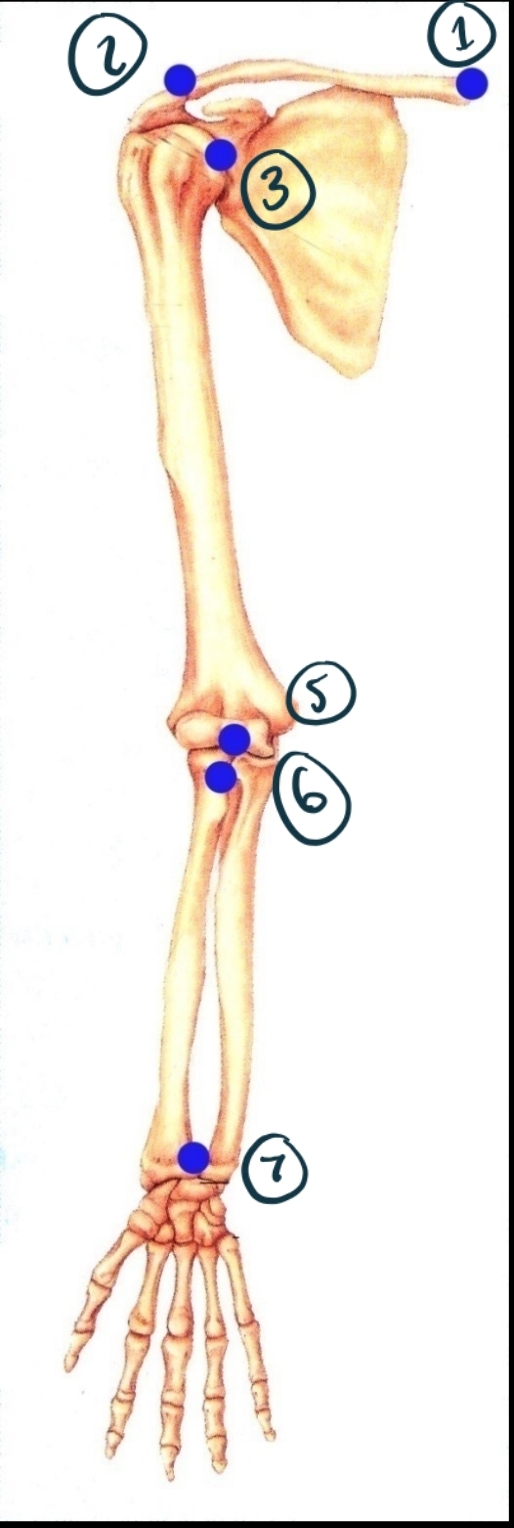
Name joint 3
Glenohumeral. Synovial (ball + socket). Diarthrosis (multiaxial).
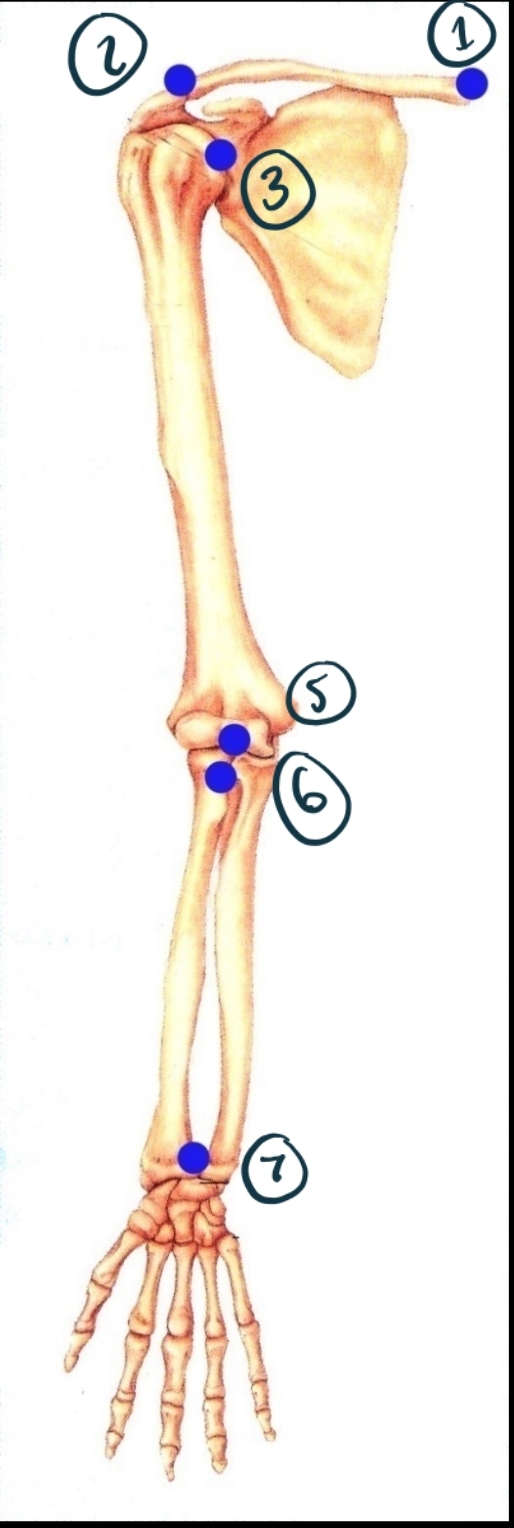
Name joint 5
Humeroulnar (and radial). Synovial (hinge). Diarthrosis (uniaxial).
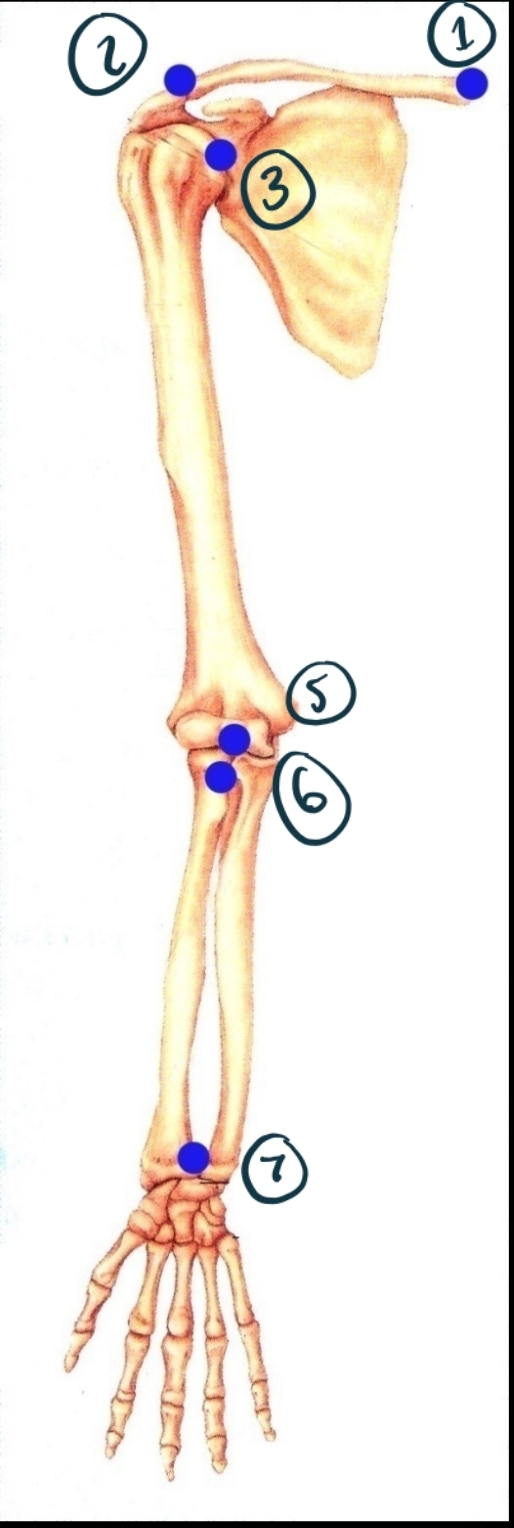
Name joint 6
Proximal radioulnar. Synovial (pivot). Diarthrosis uniaxial.
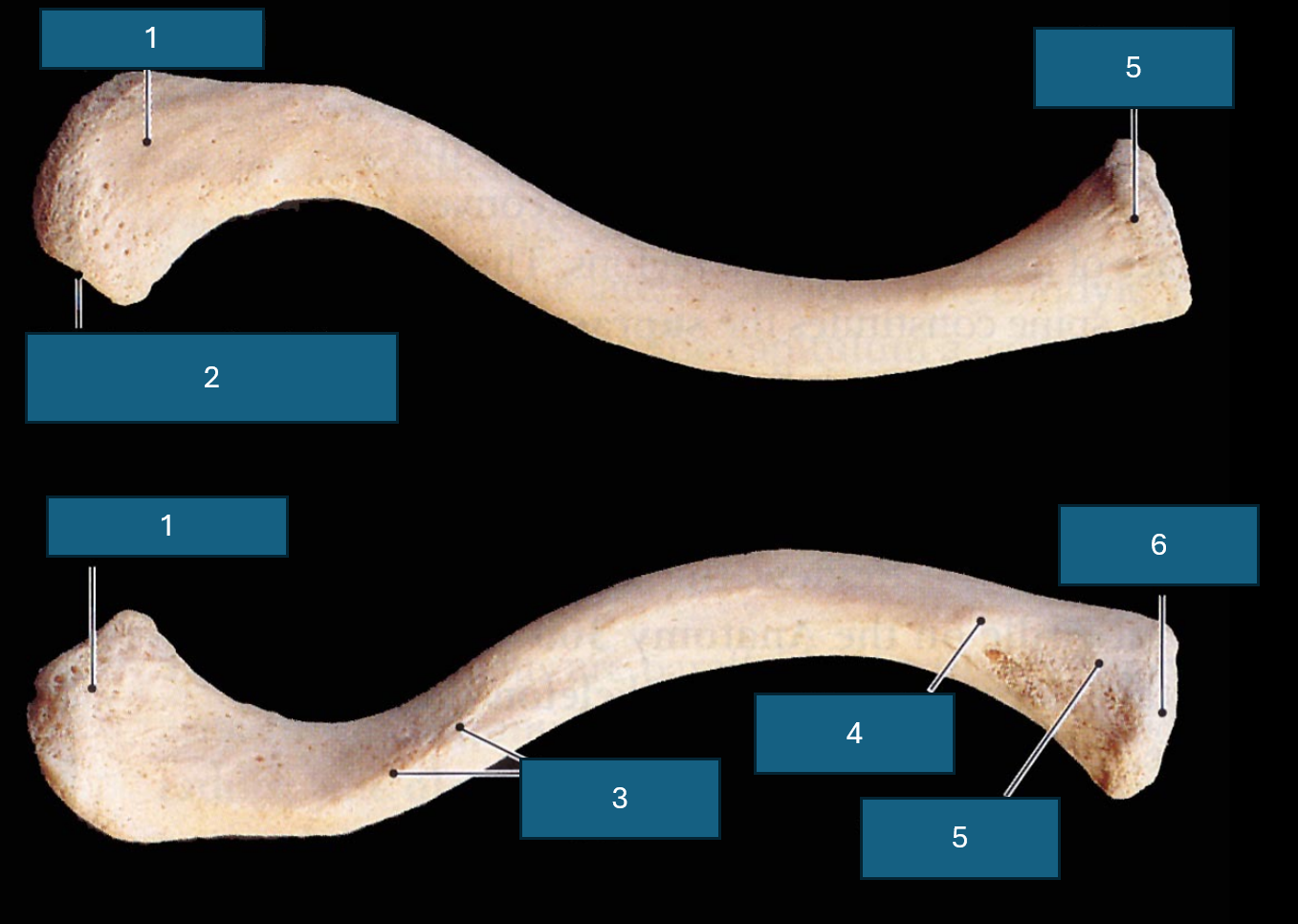

Identify 1
Acromial end (articulates with acromion process of scapula).
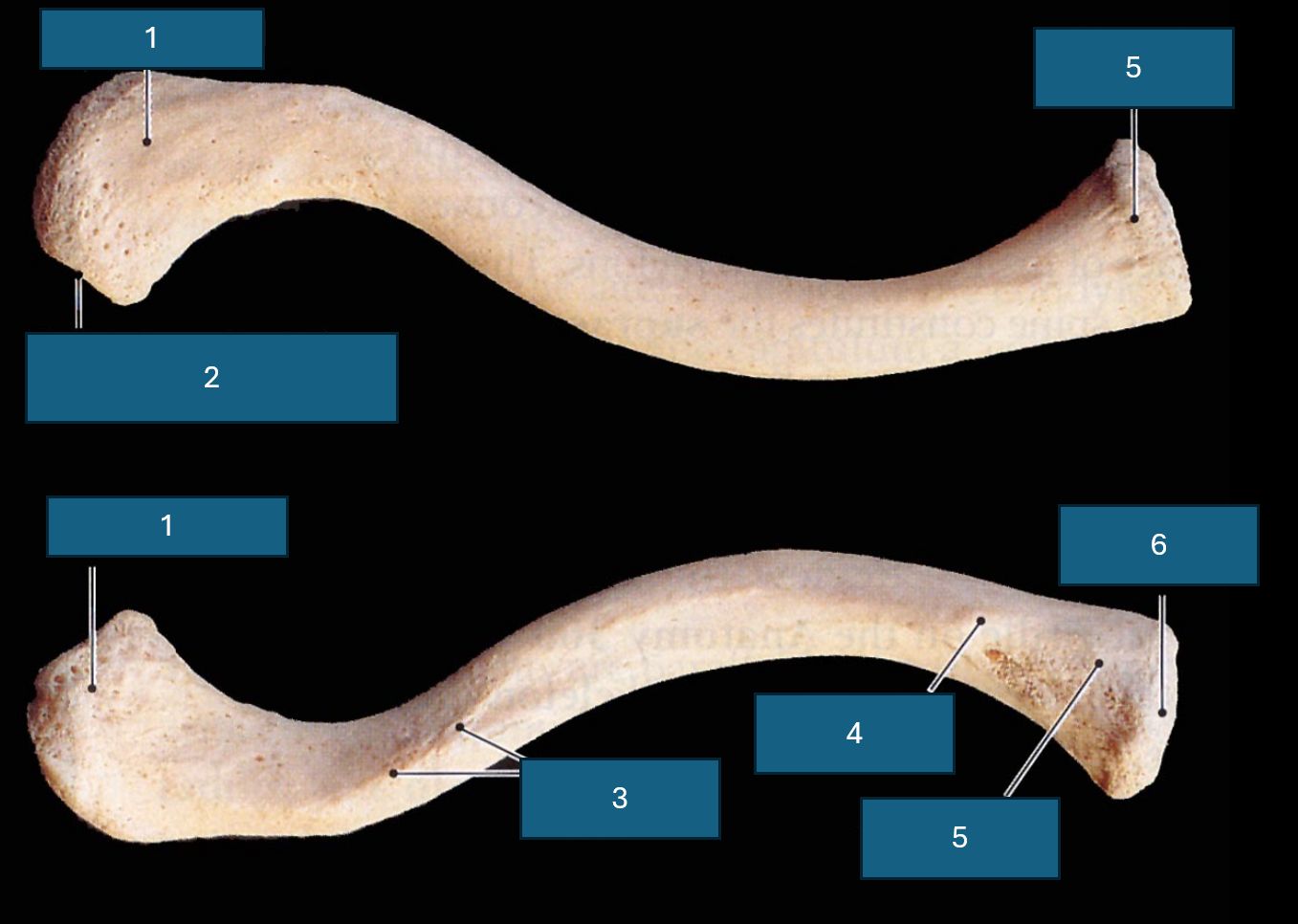

Identify 2
Facet of acromion. (Place of articulation with acromion process)
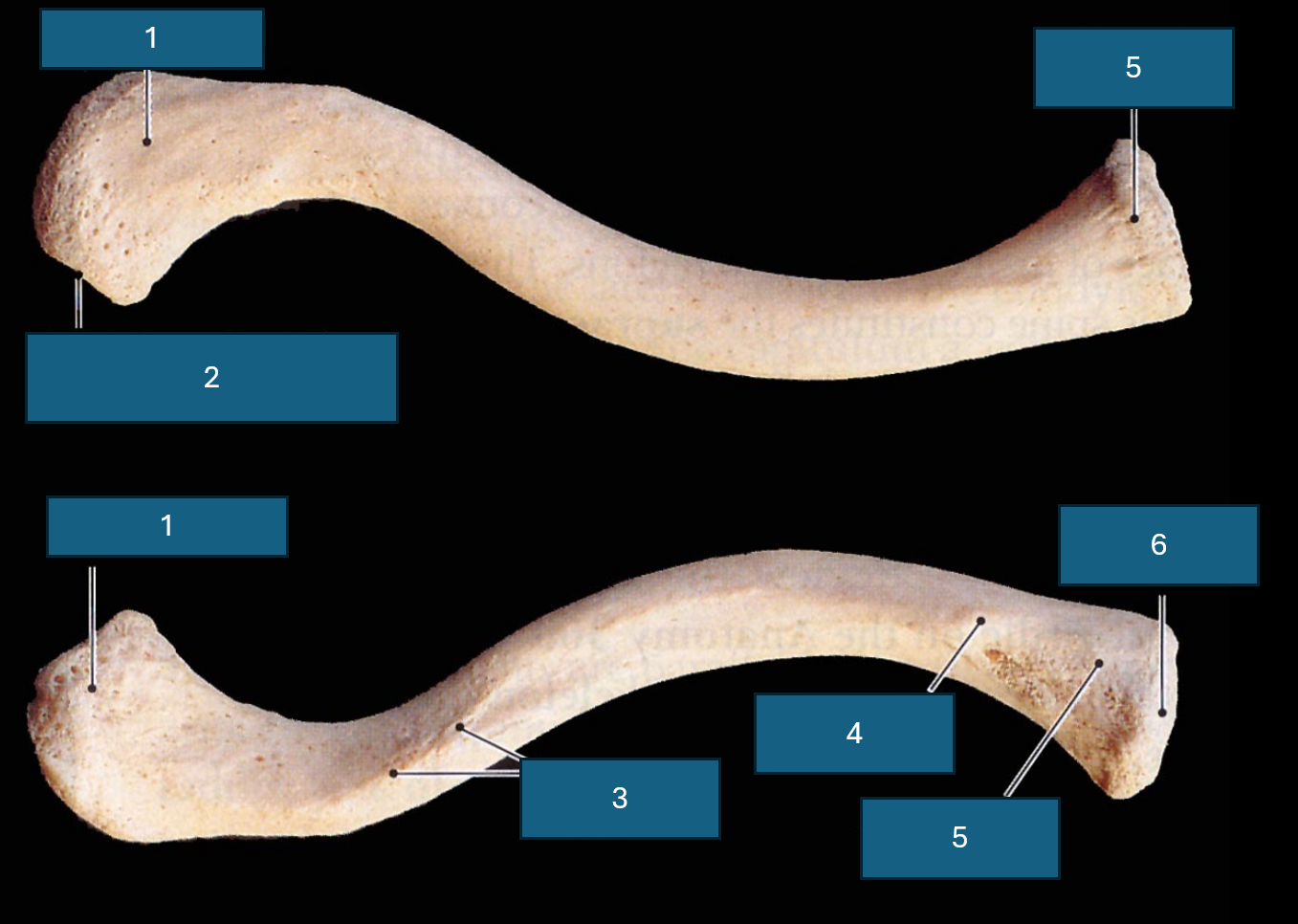

Identify 3
Conoid tubercle. Attachment site of conoid ligament.
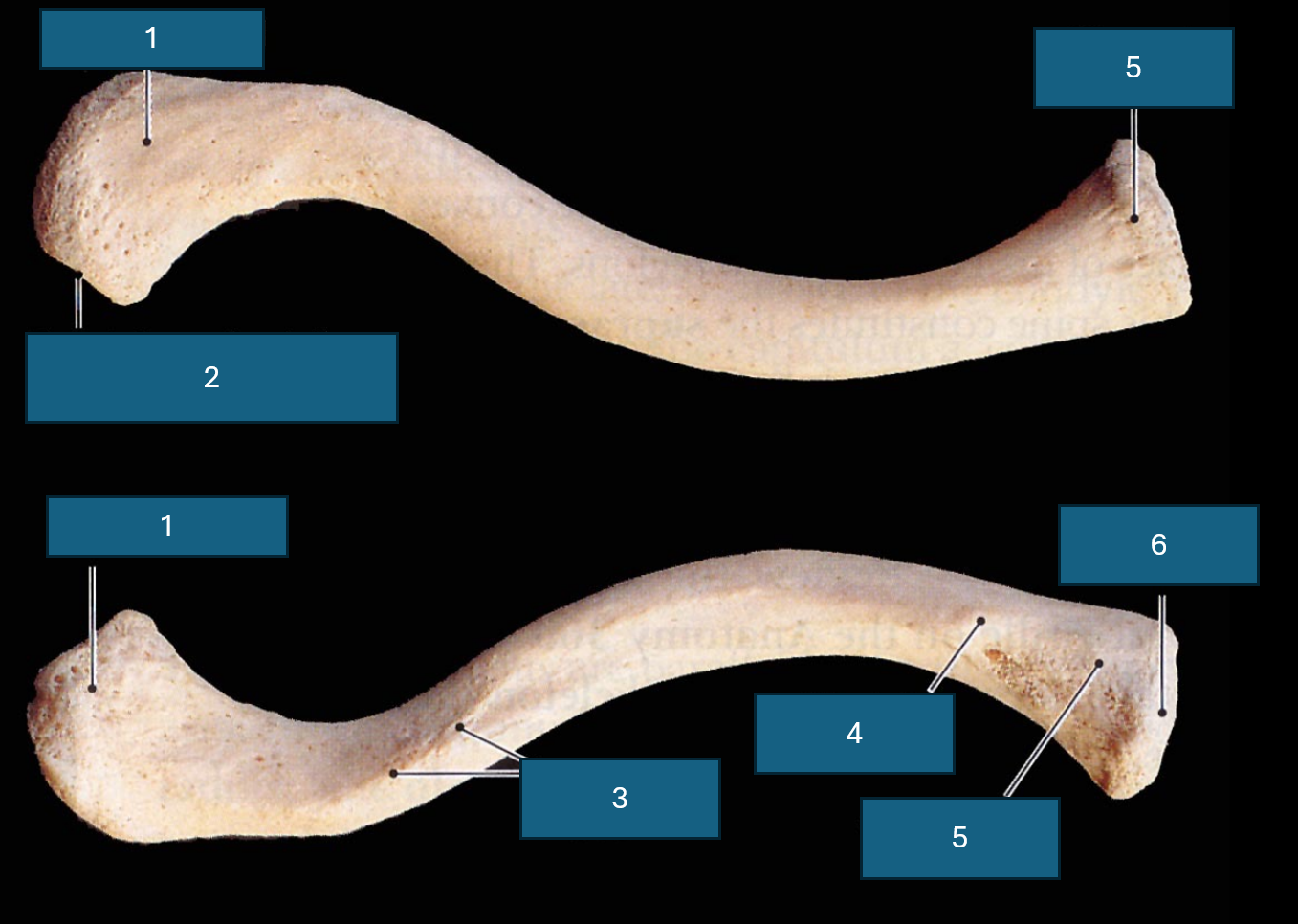

Identify 4
Costal tuberosity
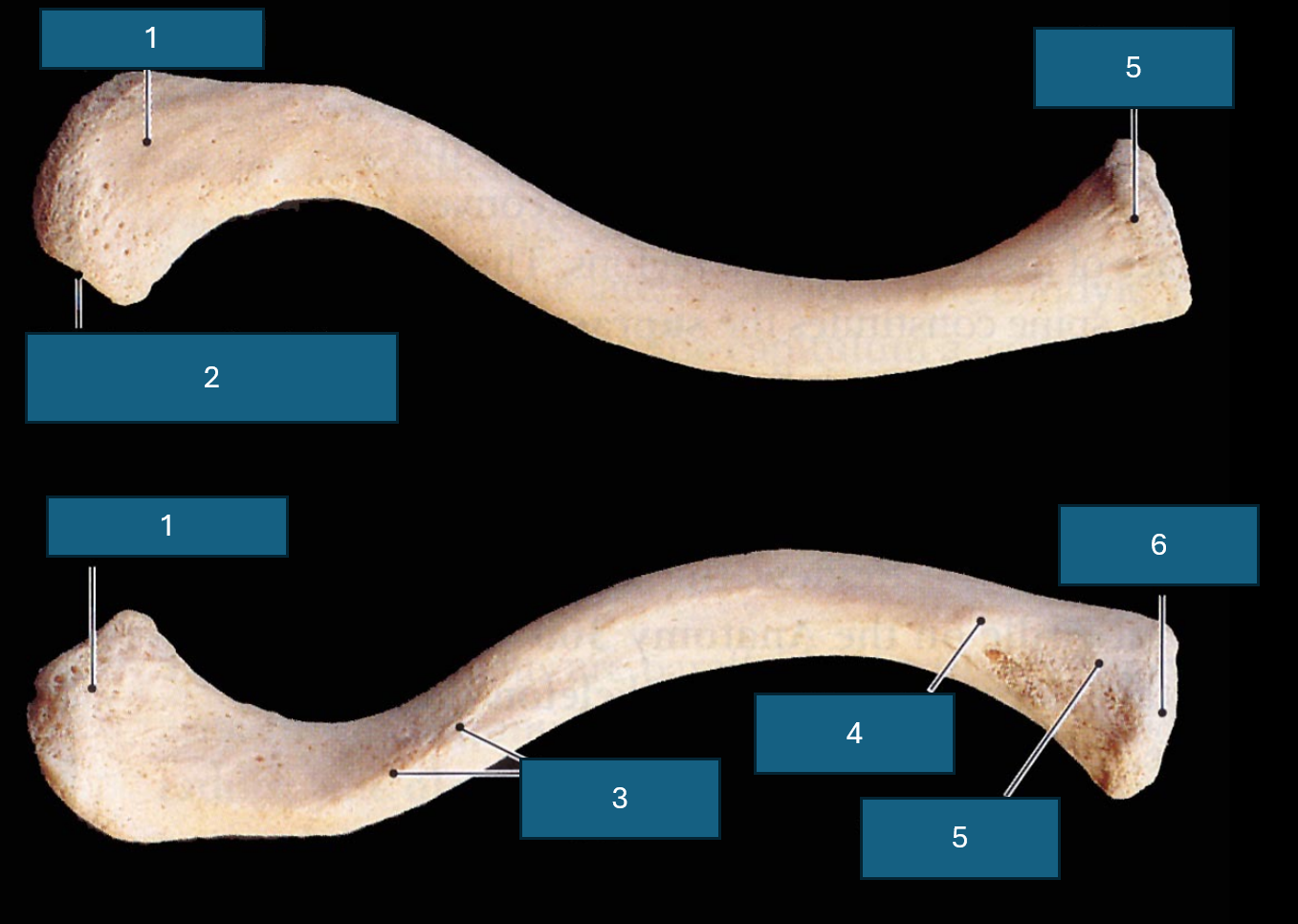

Identify 5
Sternal end
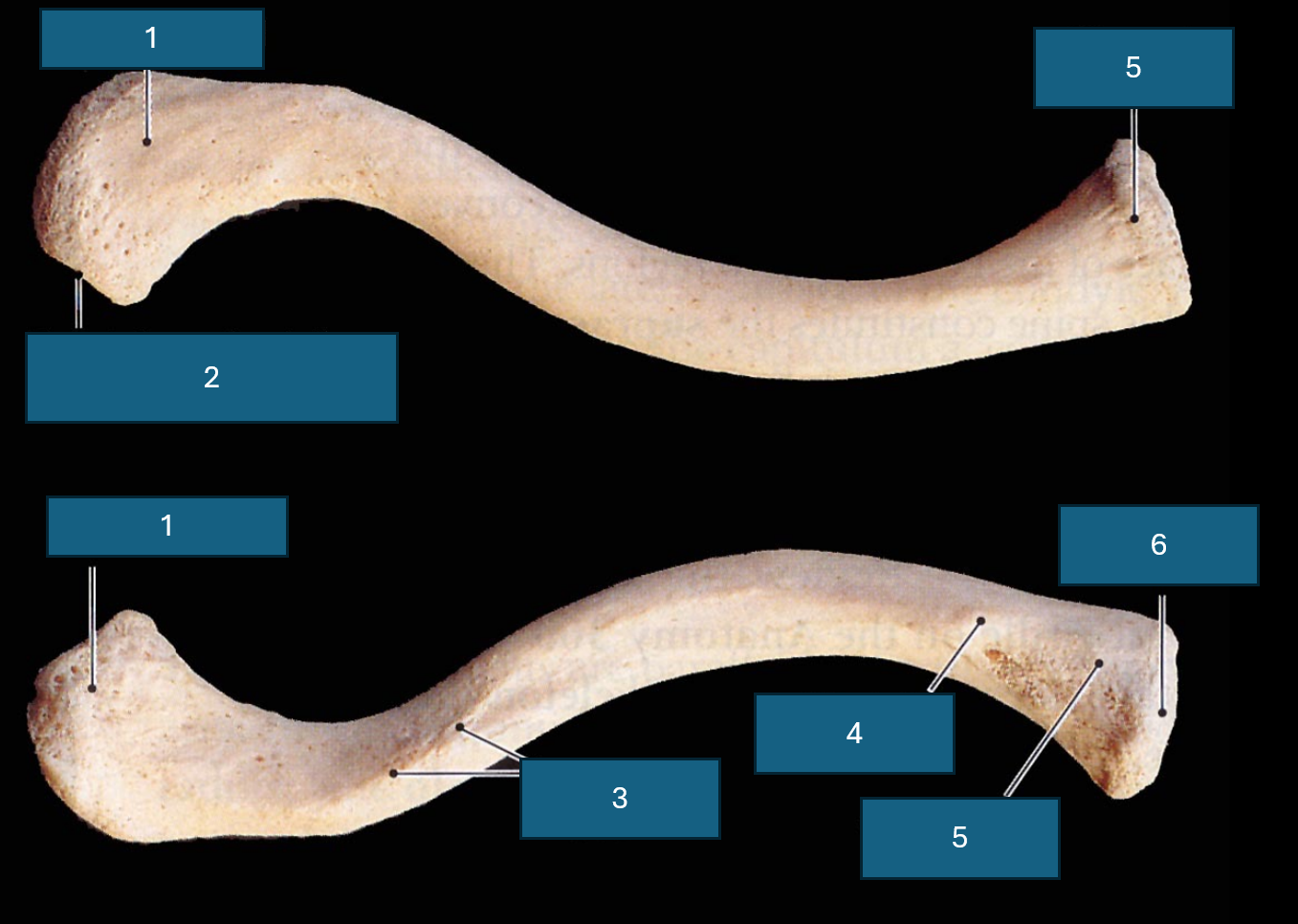

Identify 6
Sternal facet
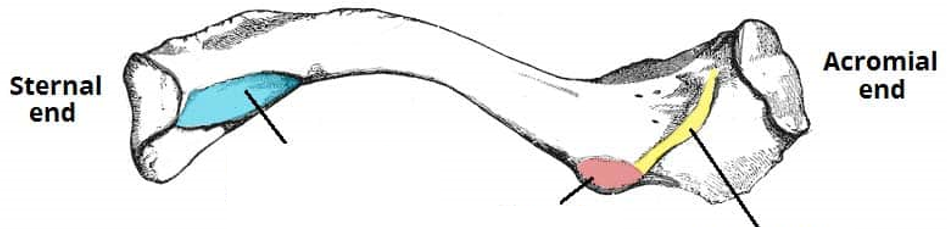
Identify blue
Impression for the costoclavicular ligament
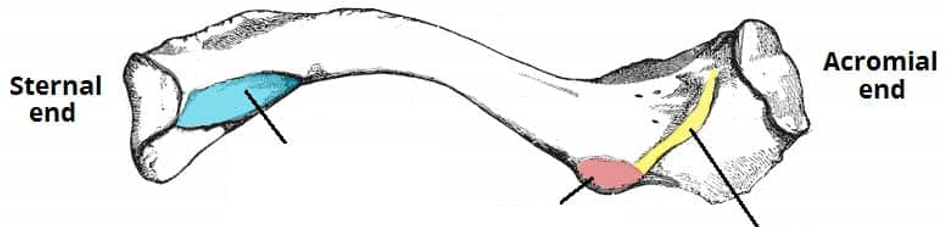
Identify yellow
Trapezoid line. Attachment site of trapezoid ligament.
Distinguishing superior and inferior clavicular surface?
Texture. Inferior is rough due to muscle attachment.
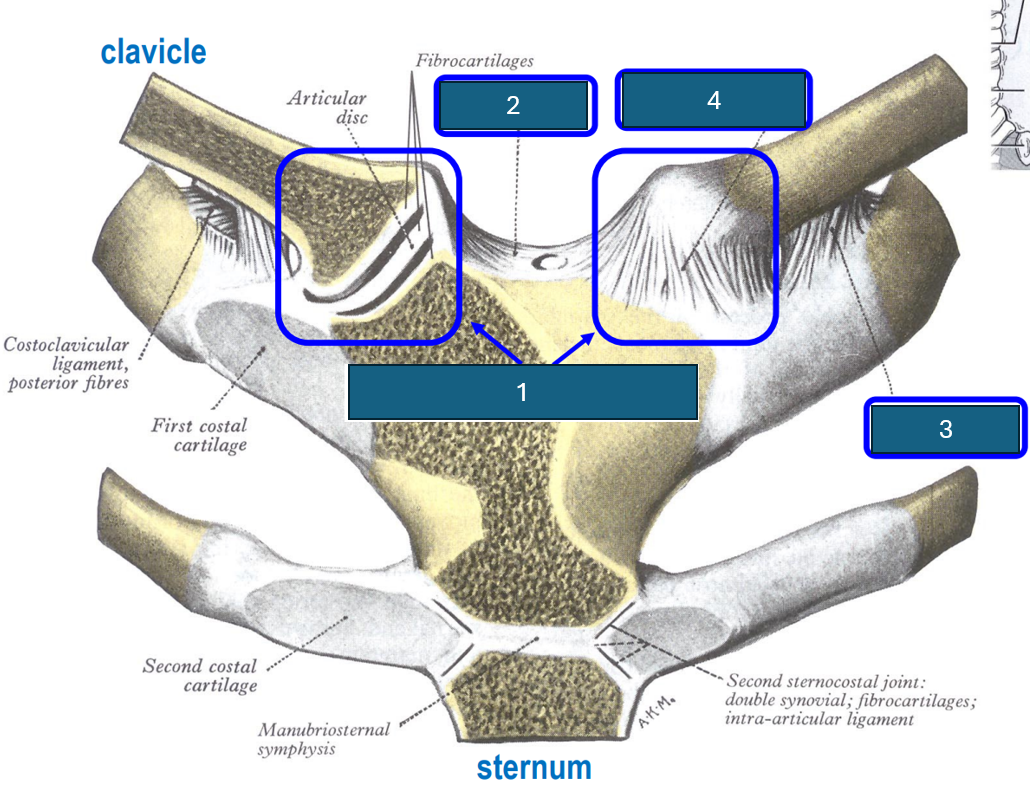
Identify 1
Sternoclavicular joint. Synovial (saddle), diarthrosis (multiaxial).
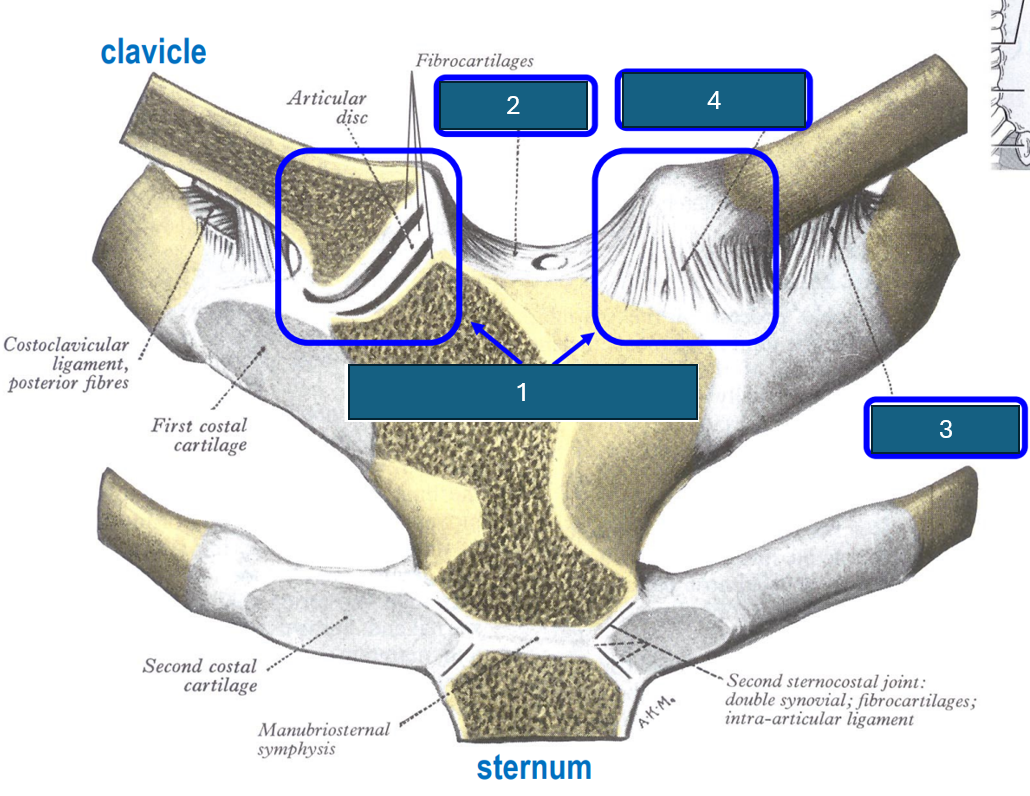
Identify 2
Interclavicular ligament.
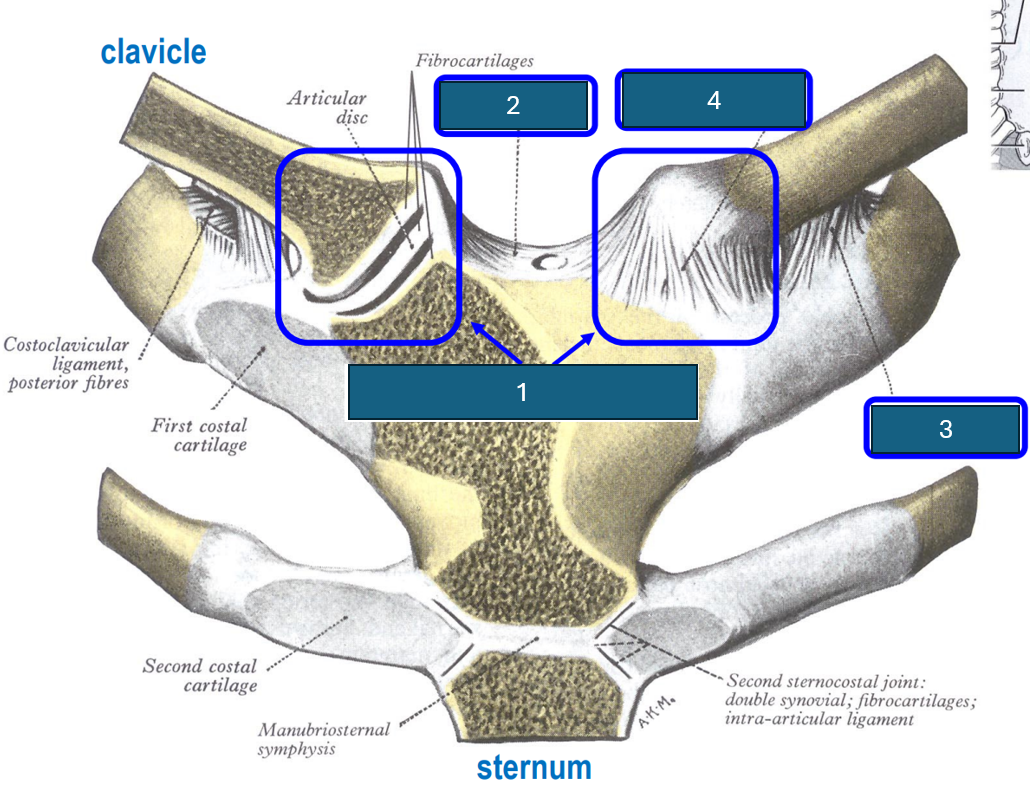
Identify 3
Costoclavicular ligament (inferior surface clavicle to first rib and cartilage).
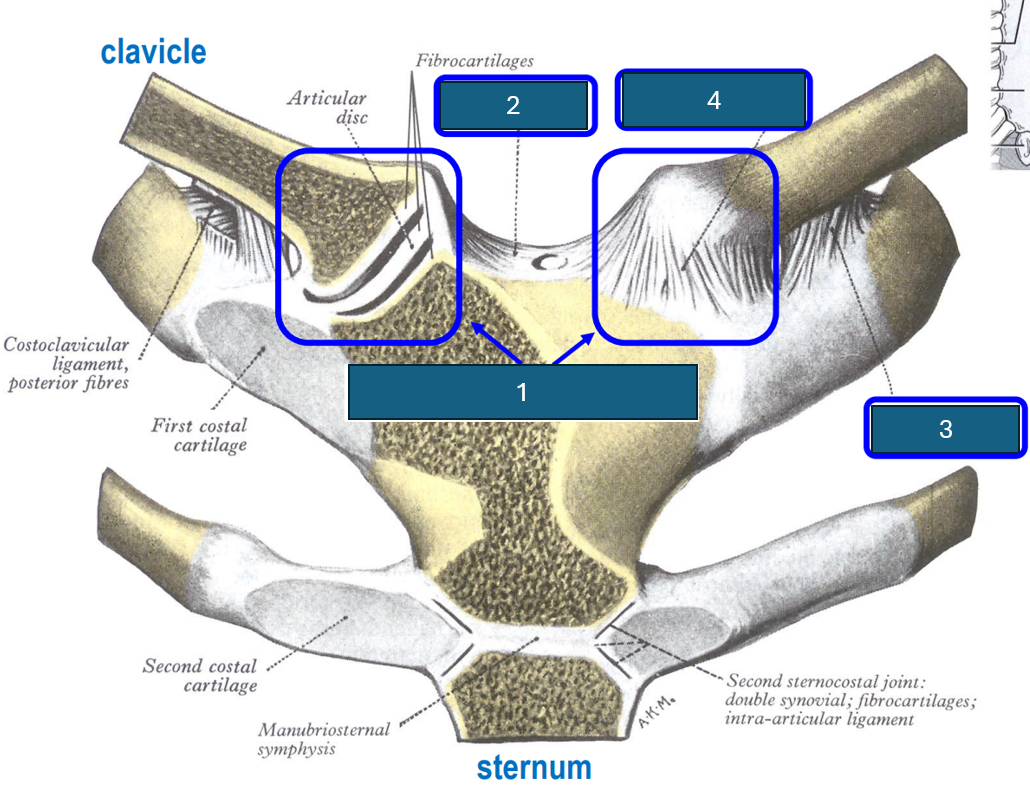
Identify 4
Anterior sternoclavicular ligament
What are the two components of the coracoclavicular ligament?
Trapezoid ligament (lateral) and conoid ligament (medial).
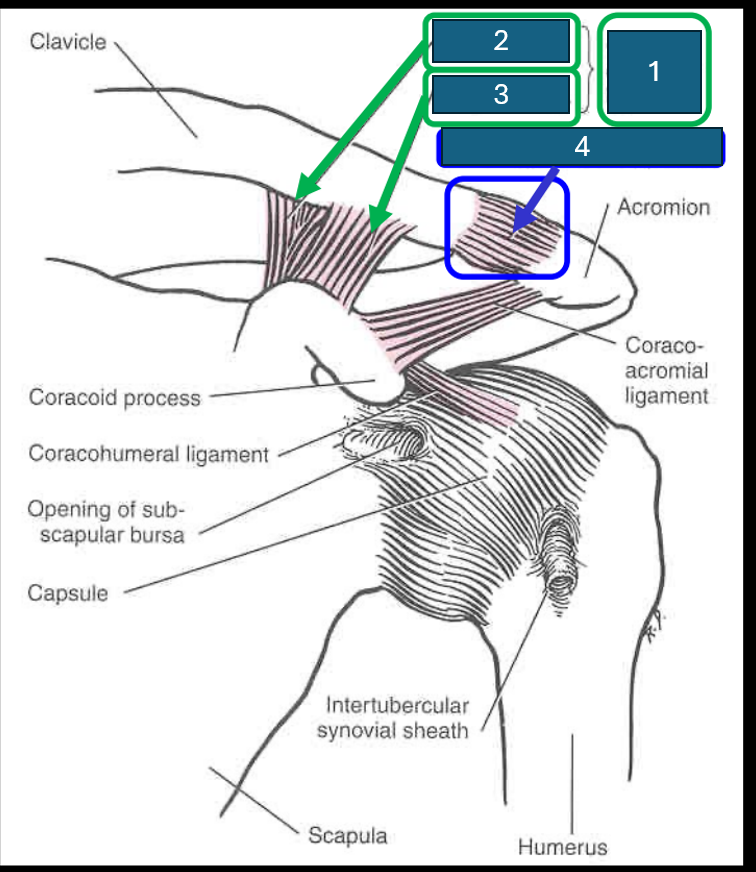
Identify 1
Coracoclavicular ligament
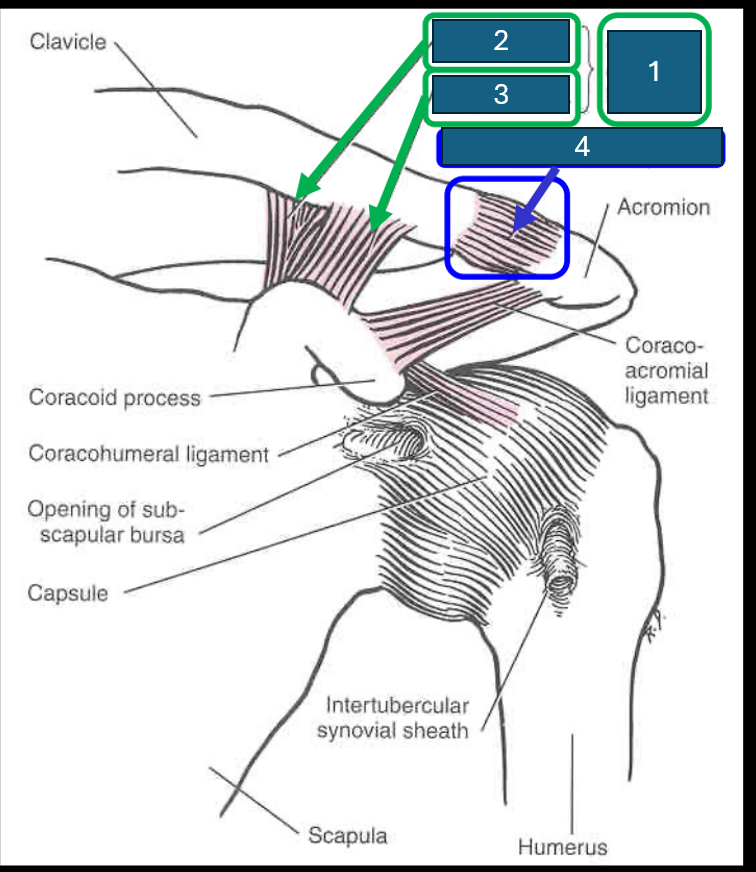
Identify 2
Conoid ligament
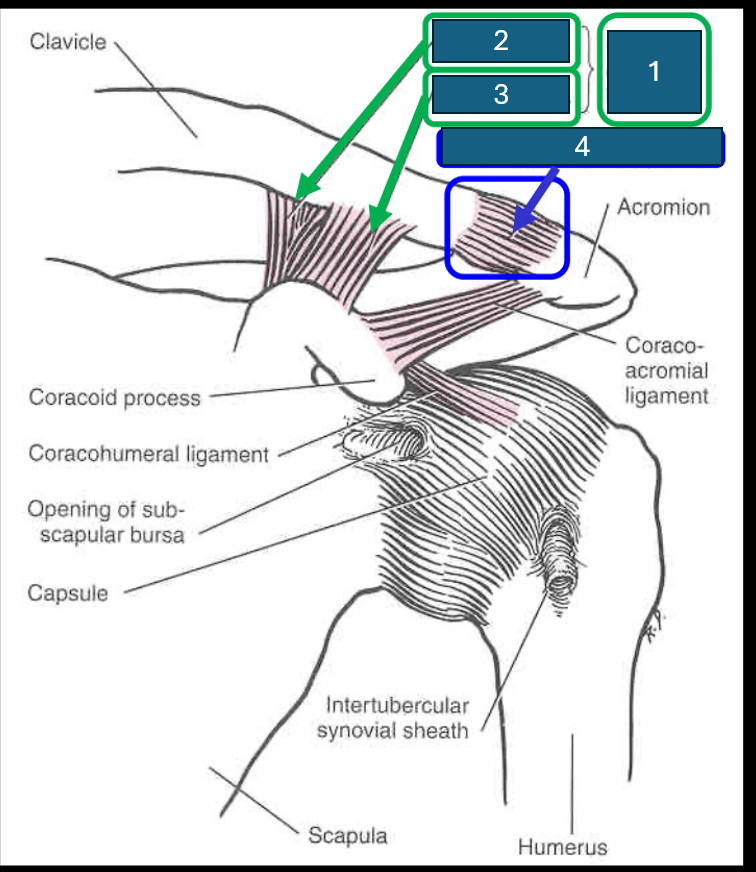
Identify 3
Trapezoid ligament
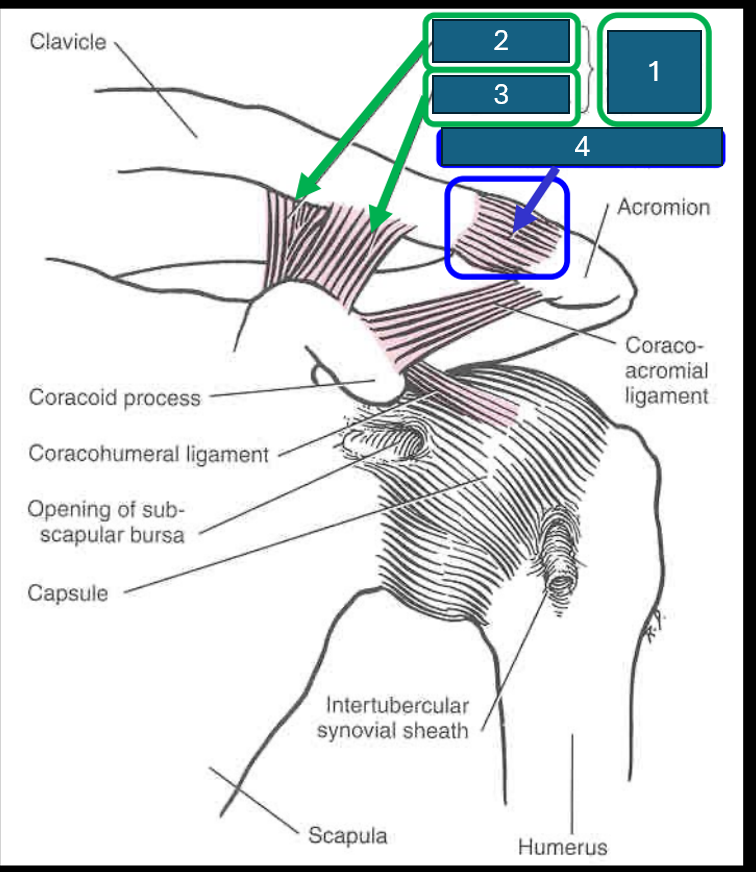
Identify 4 (and the joint it forms)
Acromioclavicular ligament. Forms acromioclavicular joint (synovial - sliding) diarthrosis (multiaxial)
Which surface is this?
Costal surface
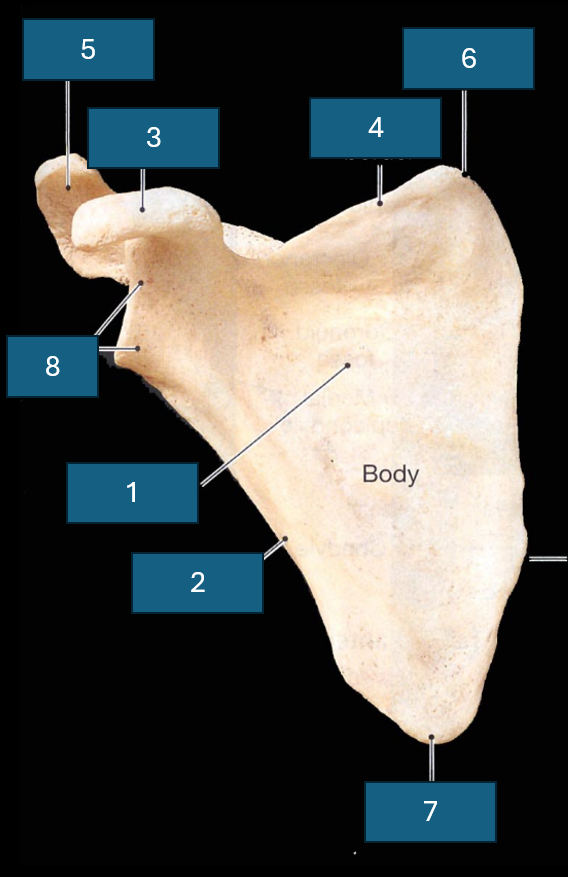
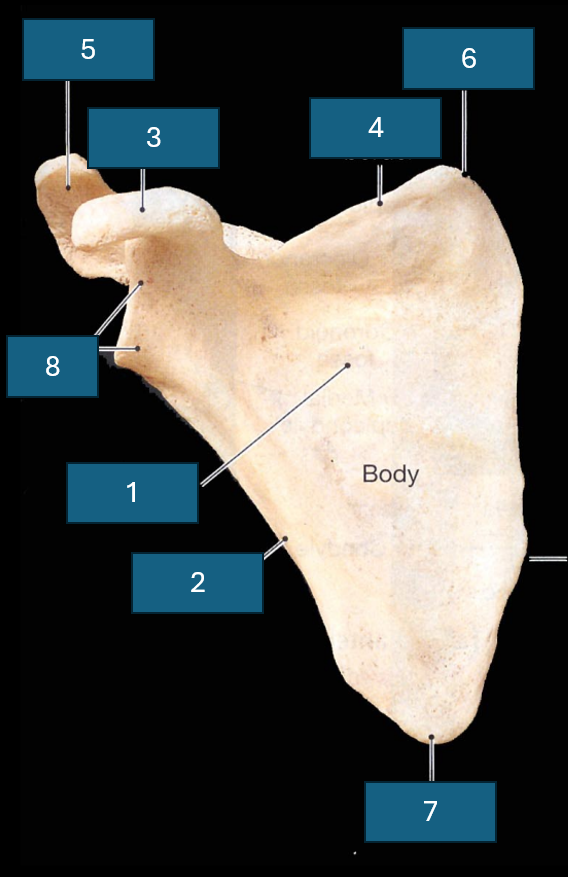
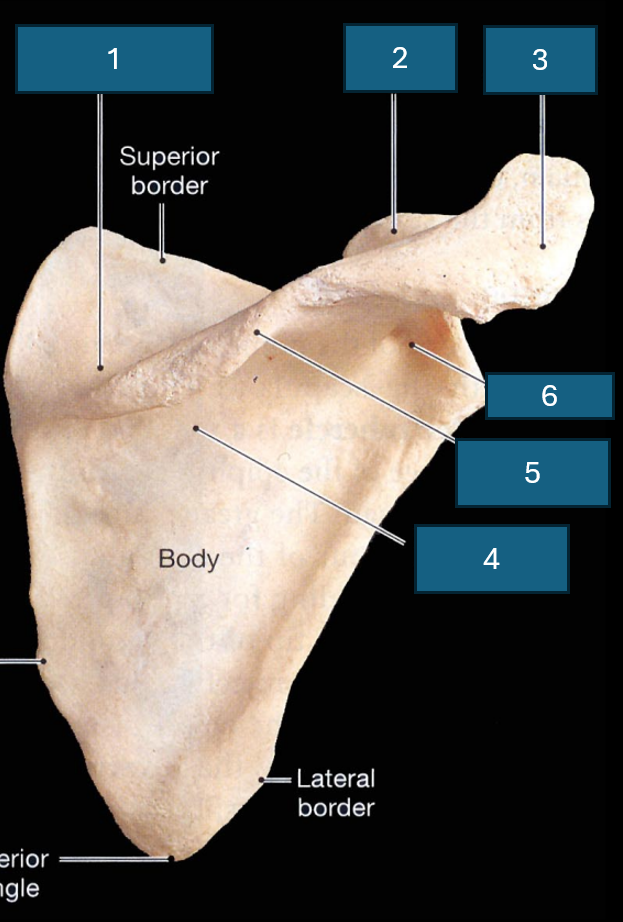
Identify the bone
Scapula
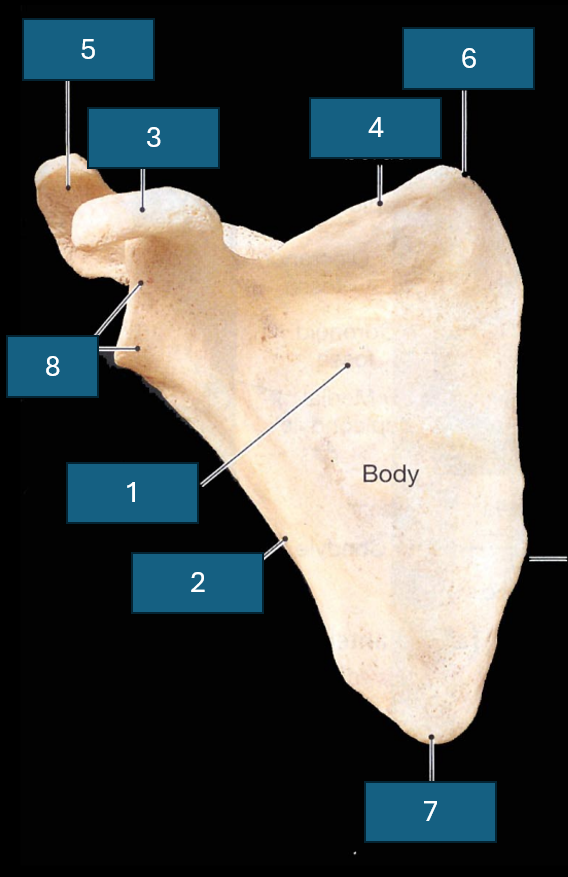
Identify 1
Subscapular fossa
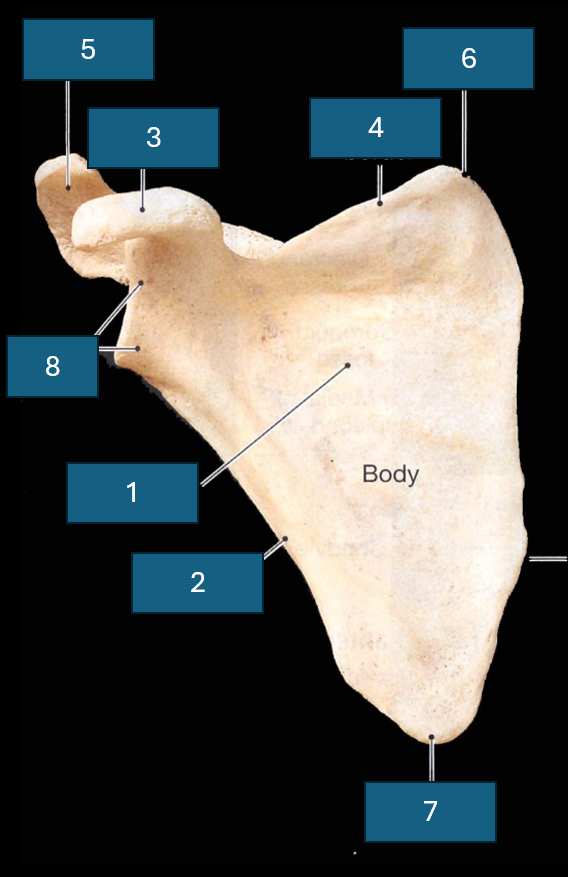
Identify 2
Lateral border
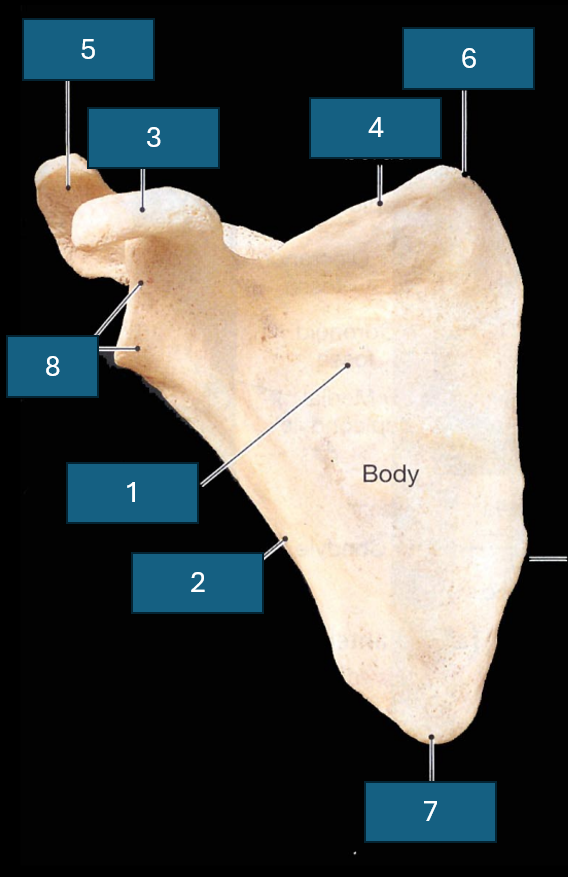
Identify 3
Coracoid process
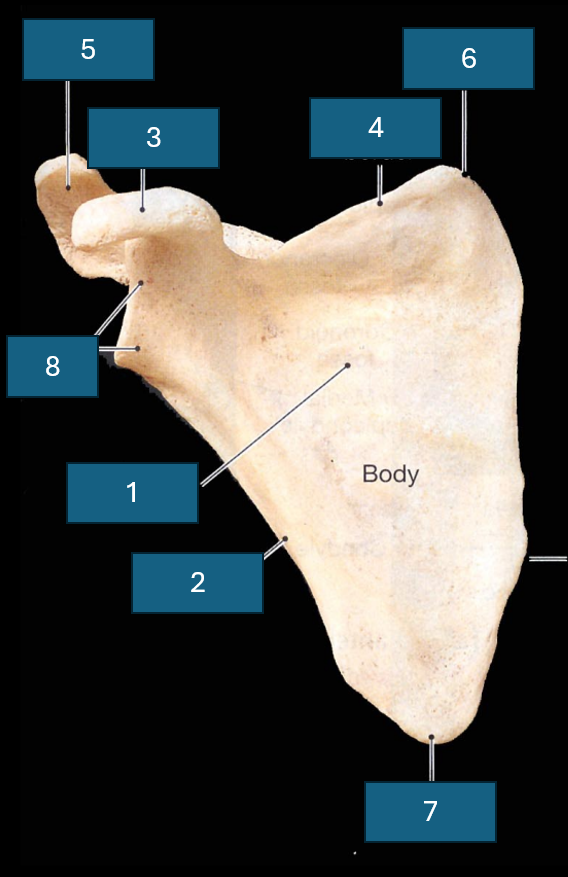
Identify 4
Superior border
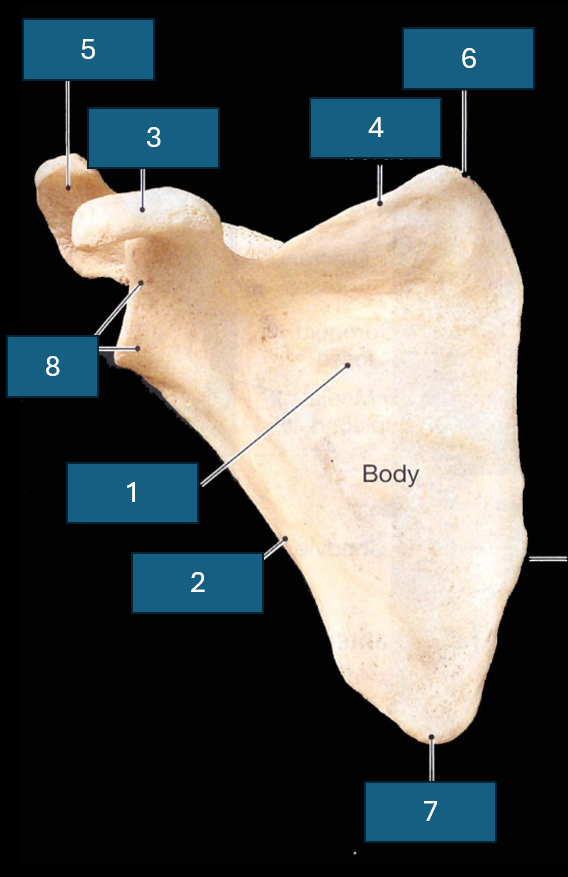
Identify 5
Acromion
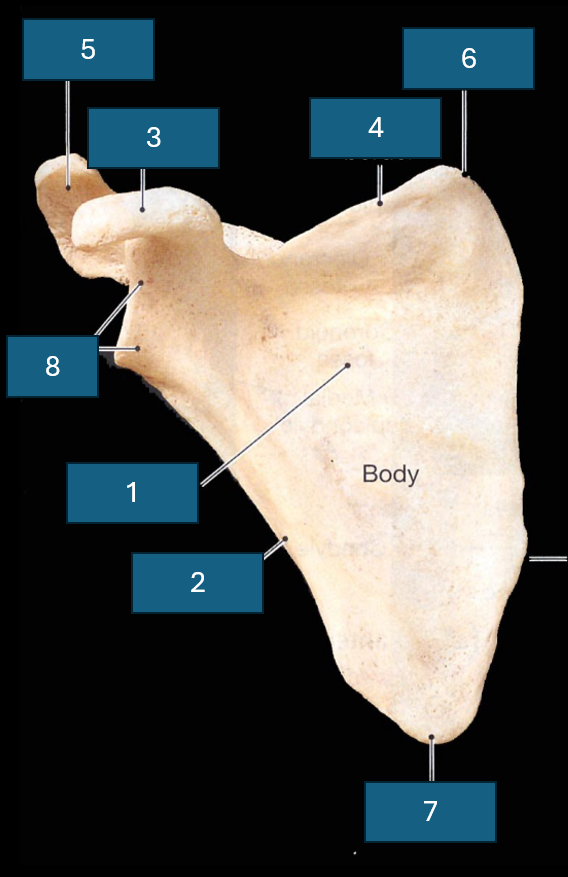
Identify 6
Superior angle
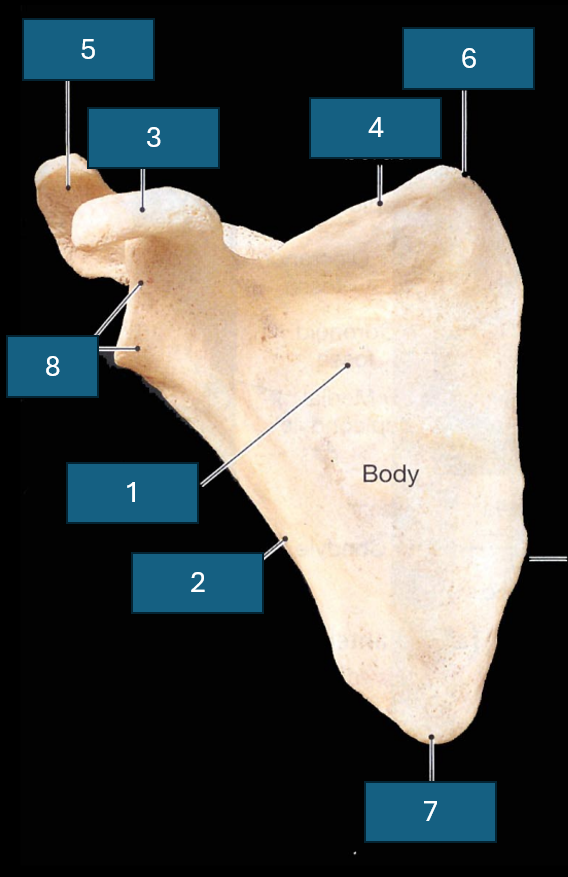
Identify 7
Inferior angle
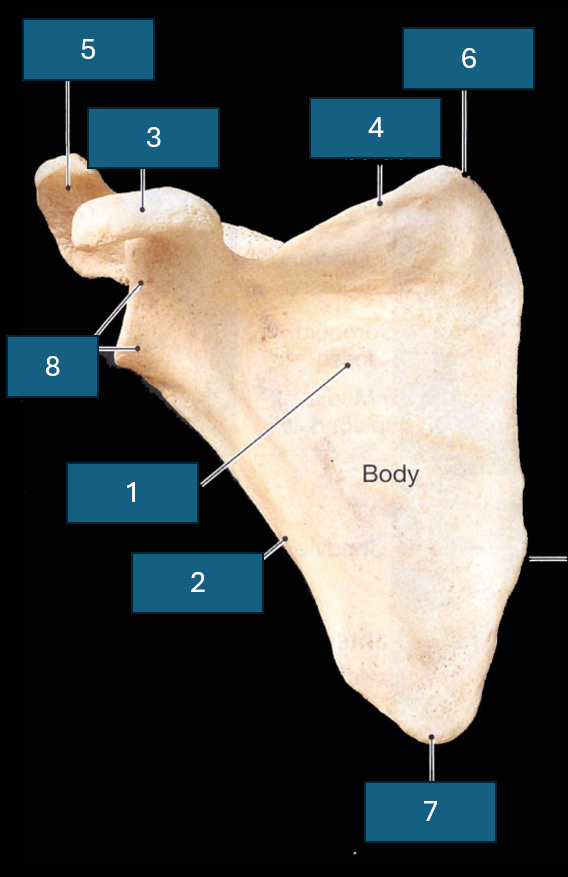
Identify 8
Lateral angle and glenoid cavity
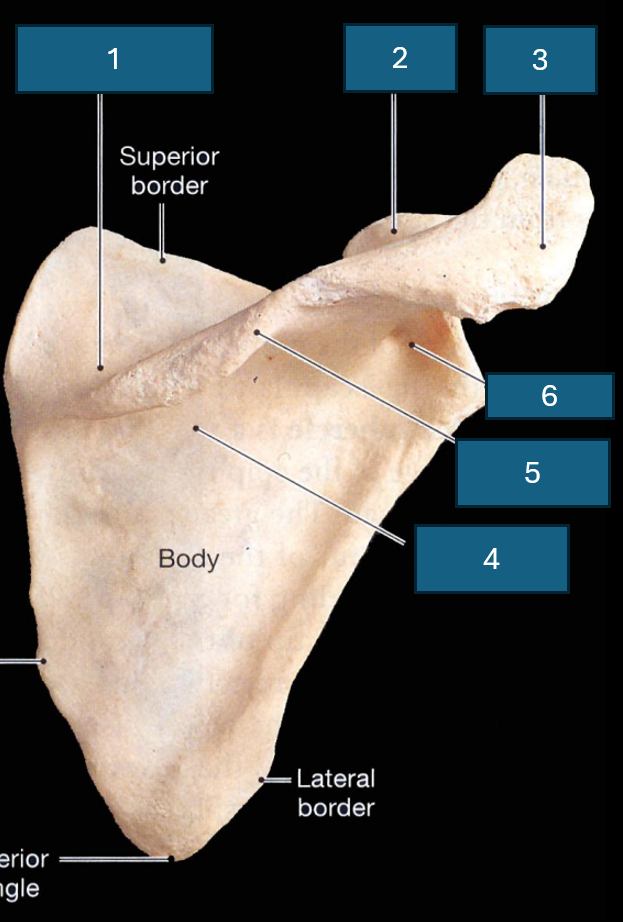
What surface is this
Posterior surface
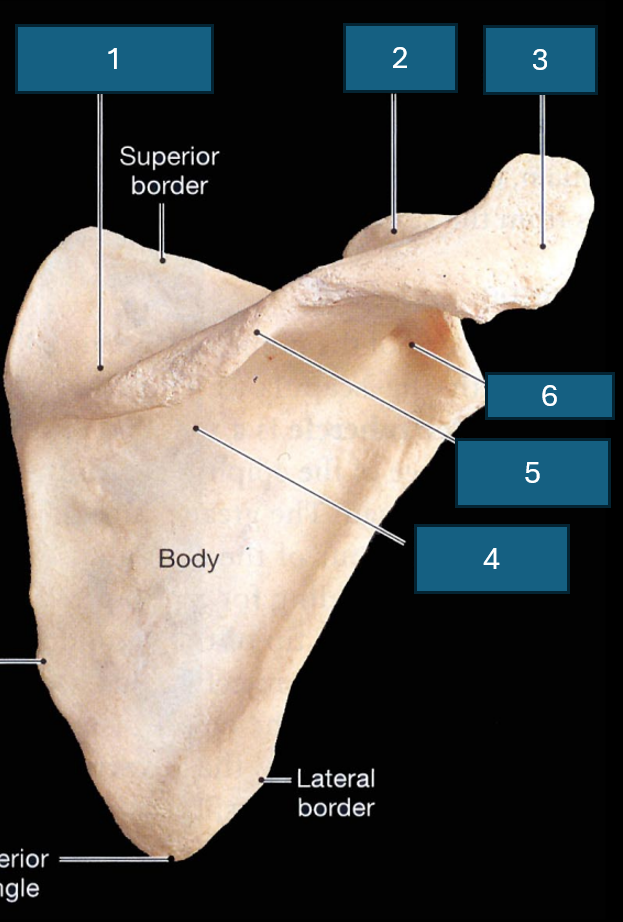
Identify 1
Supraspinous fossa
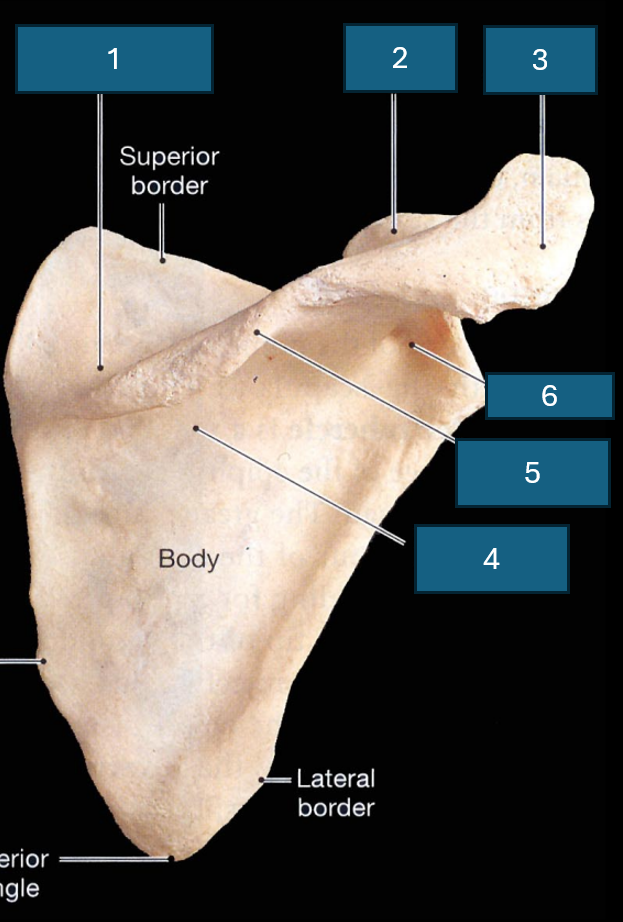
Identify 2
Coracoid process
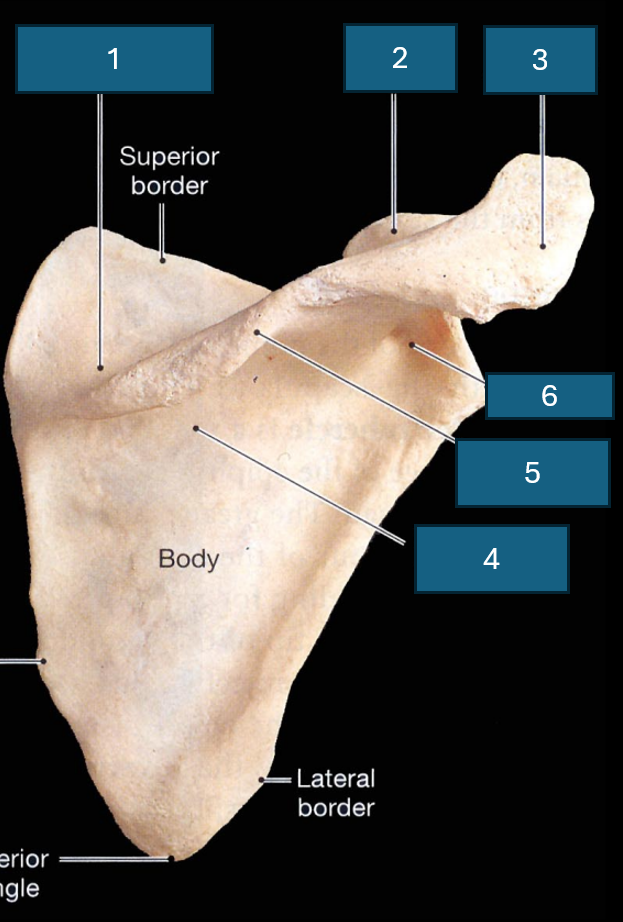
Identify 3
Acromion
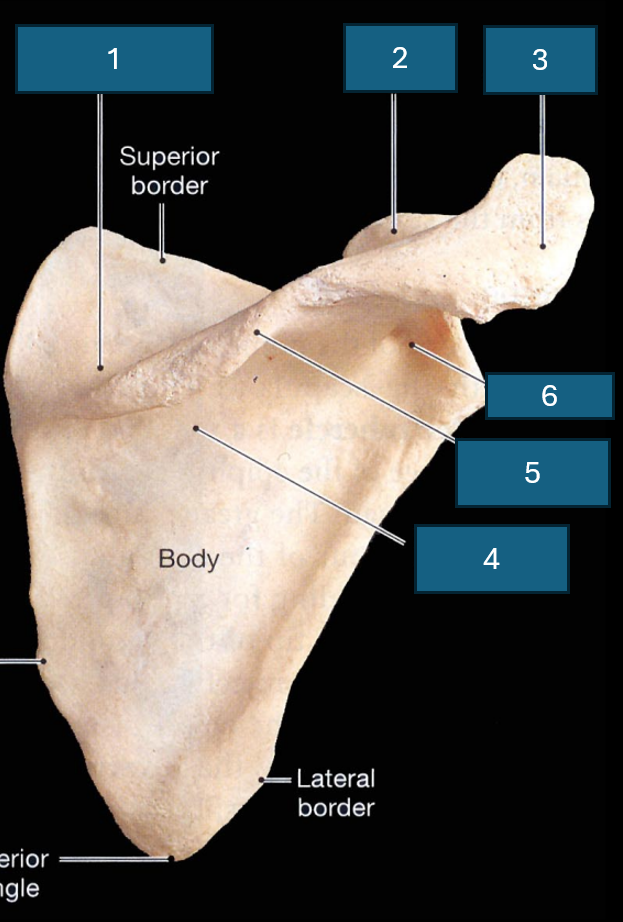
Identify 4
Infraspinous fossa
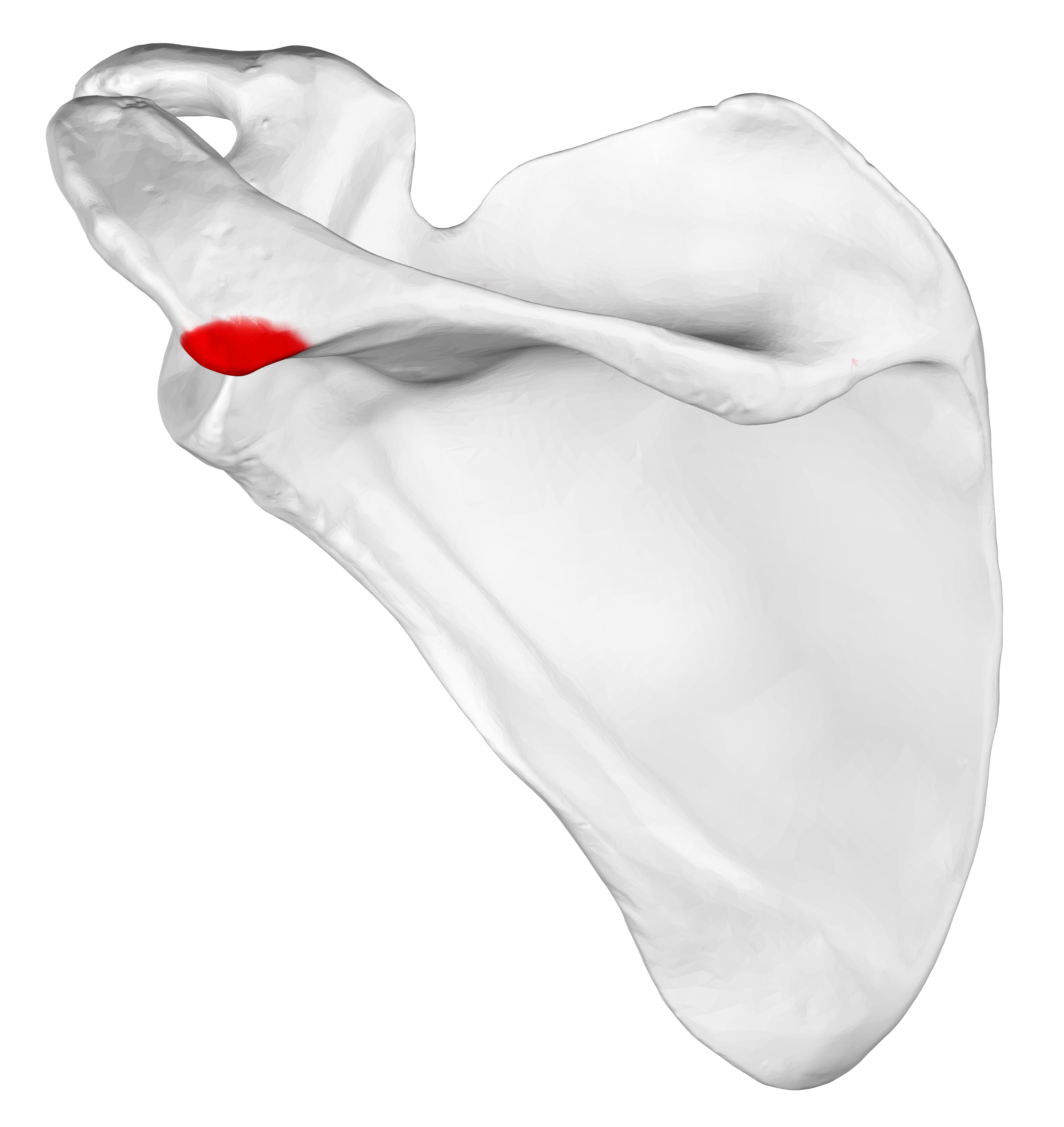
Identify red
Acromial angle
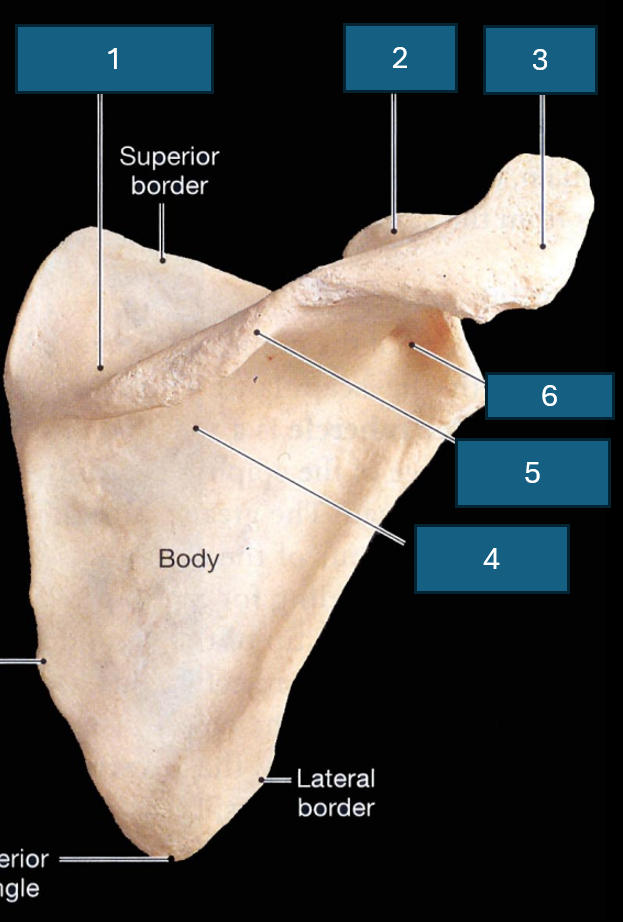
Identify 5
Spine
Identify 6
Neck
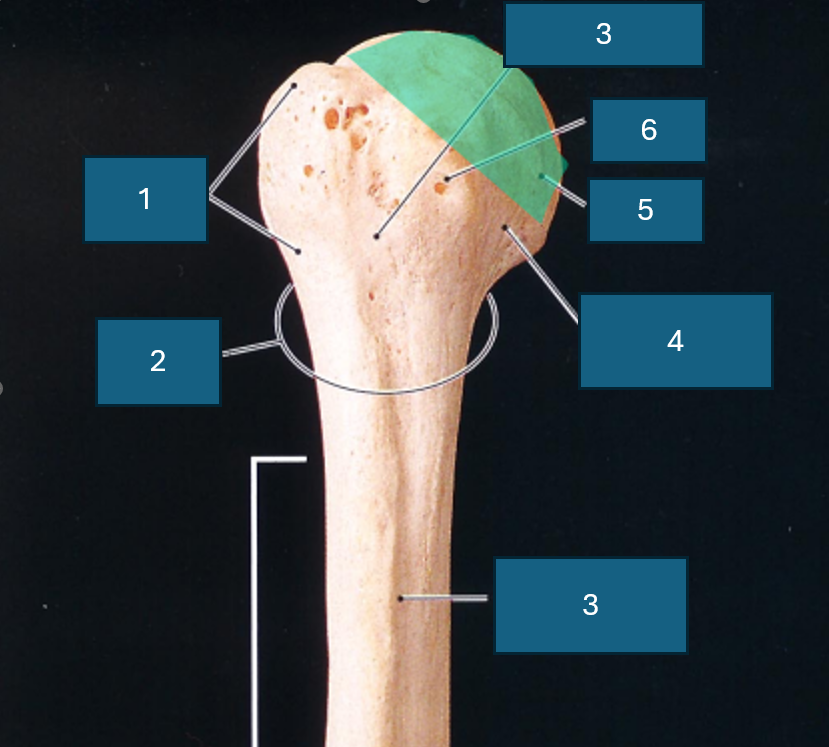
What end of the humerus is this?
Proximal
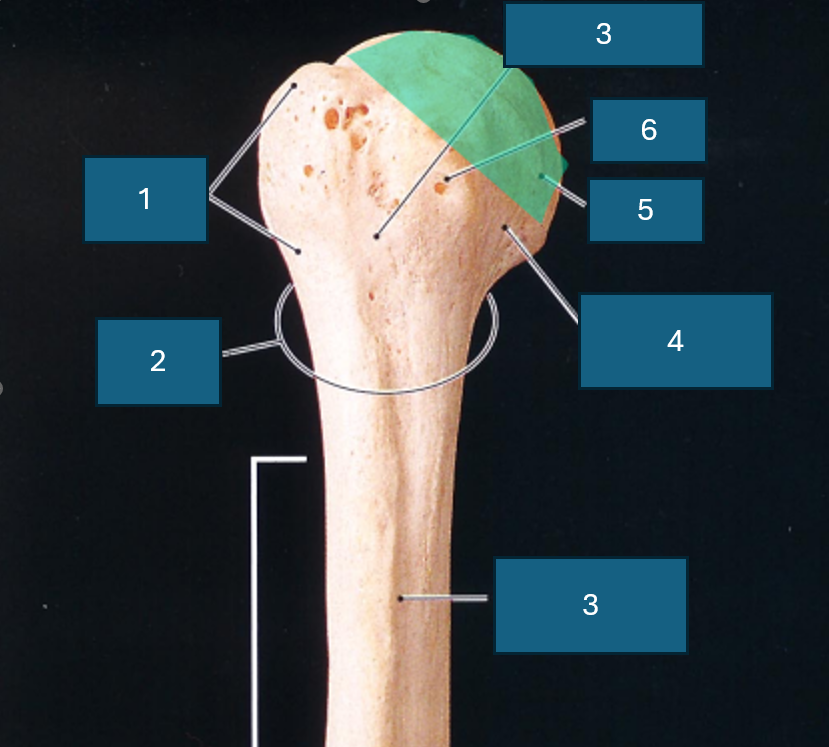
Identify 1
Greater tubercle
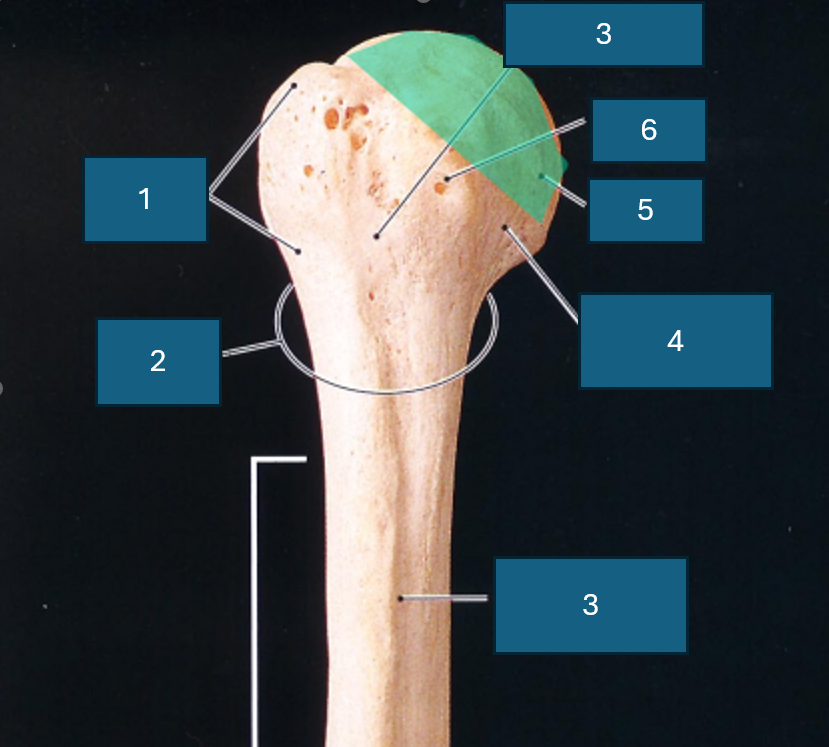
Identify 2
Surgical neck
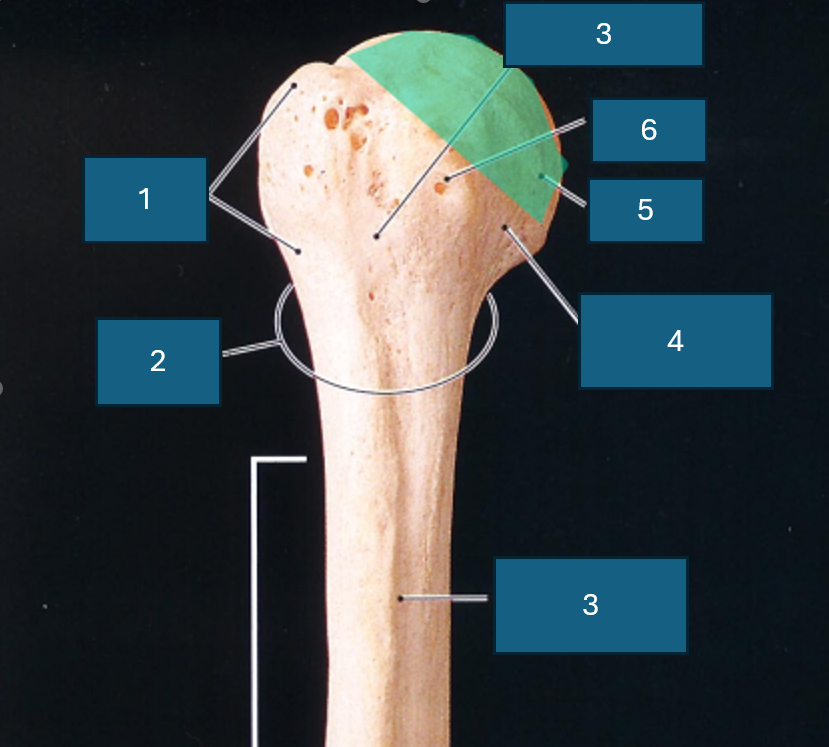
Identify 3
Intertubercular groove
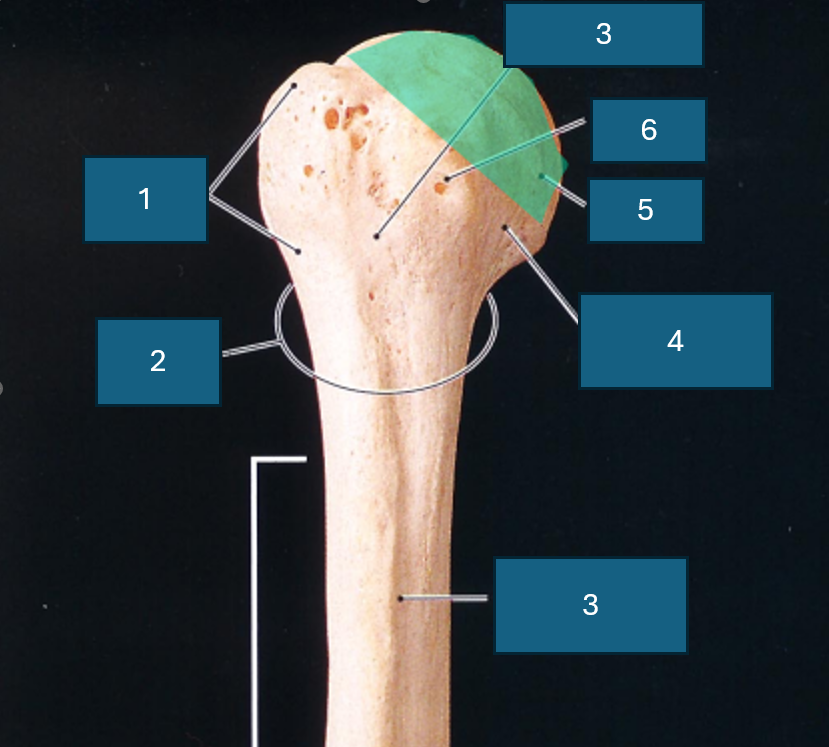
Identify 4
Anatomical neck
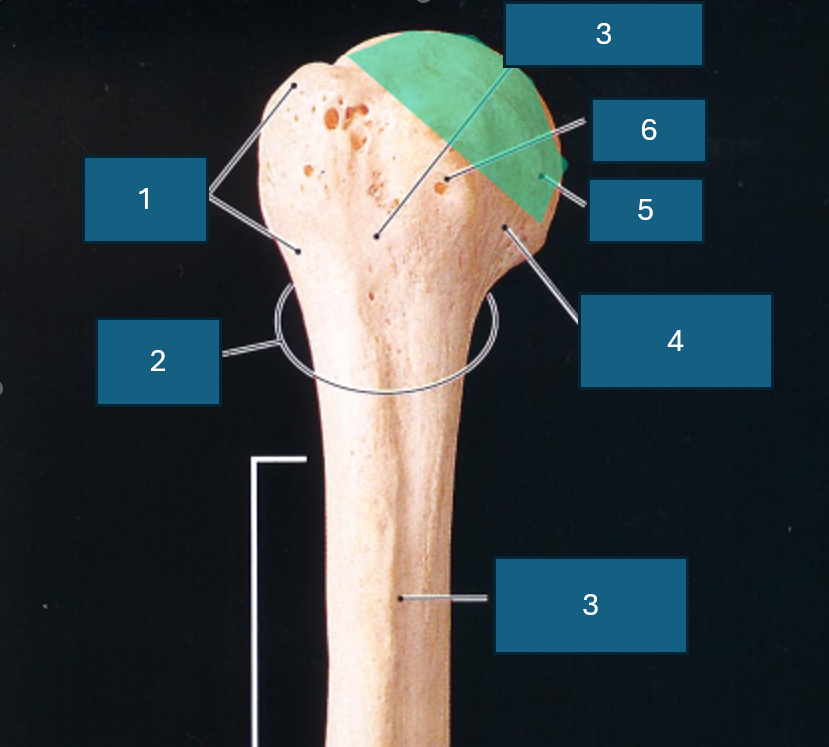
Identify 5
Head
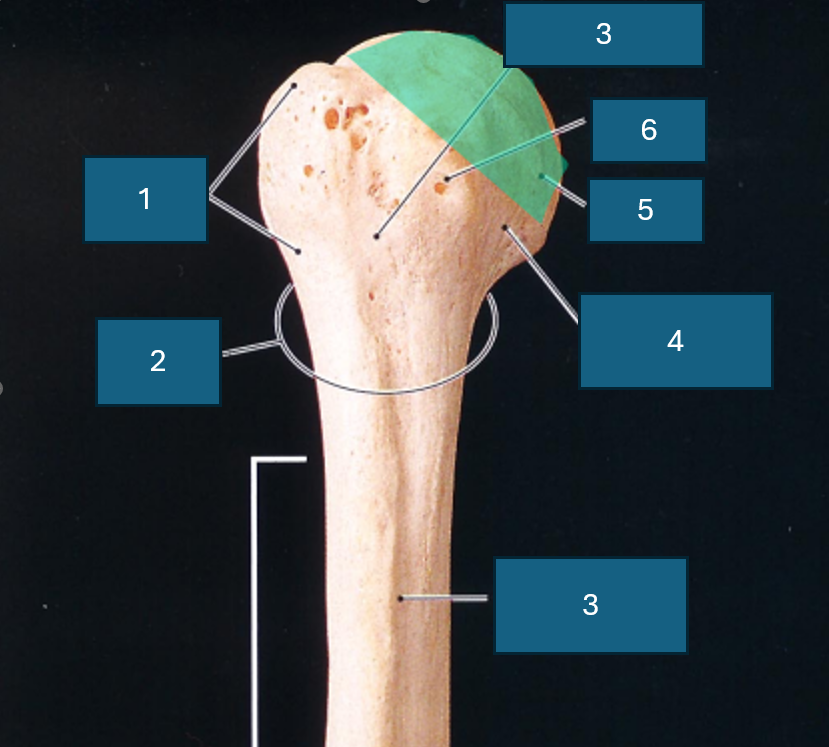
Identify 6
Lesser tubercle
What part of the body is the humerus in?
Brachium (arm)
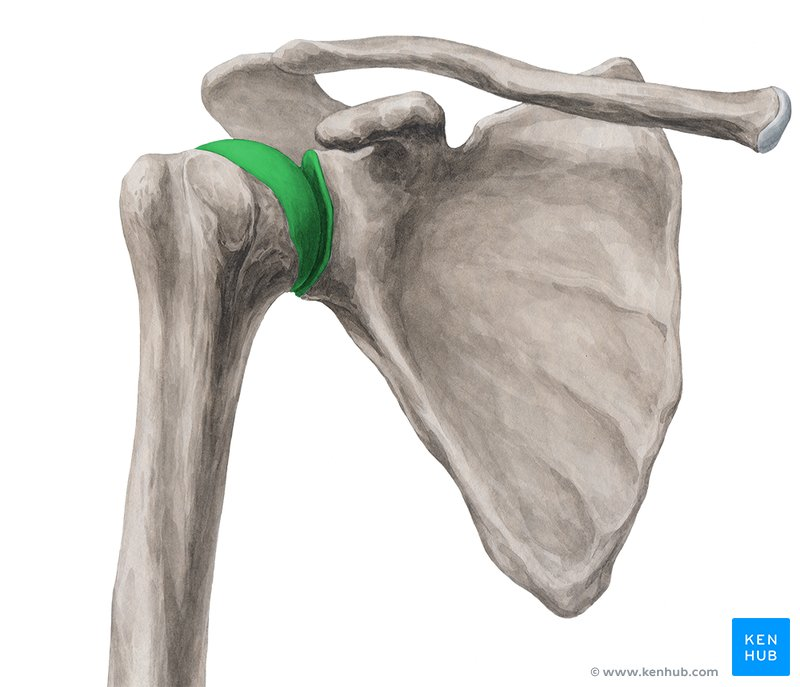
Name the joint including structure and function
Glenohumeral joint (glenoid cavity of scapula and head of humerus). Synovial (ball and socket), diarthrosis (multiaxial).
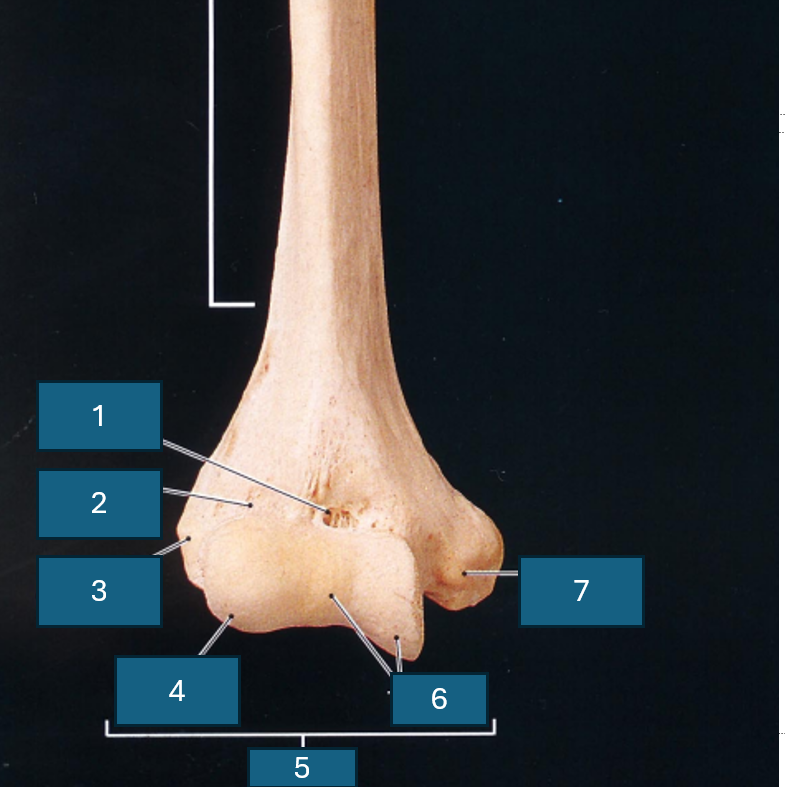
What end of the humerus is this?
Distal
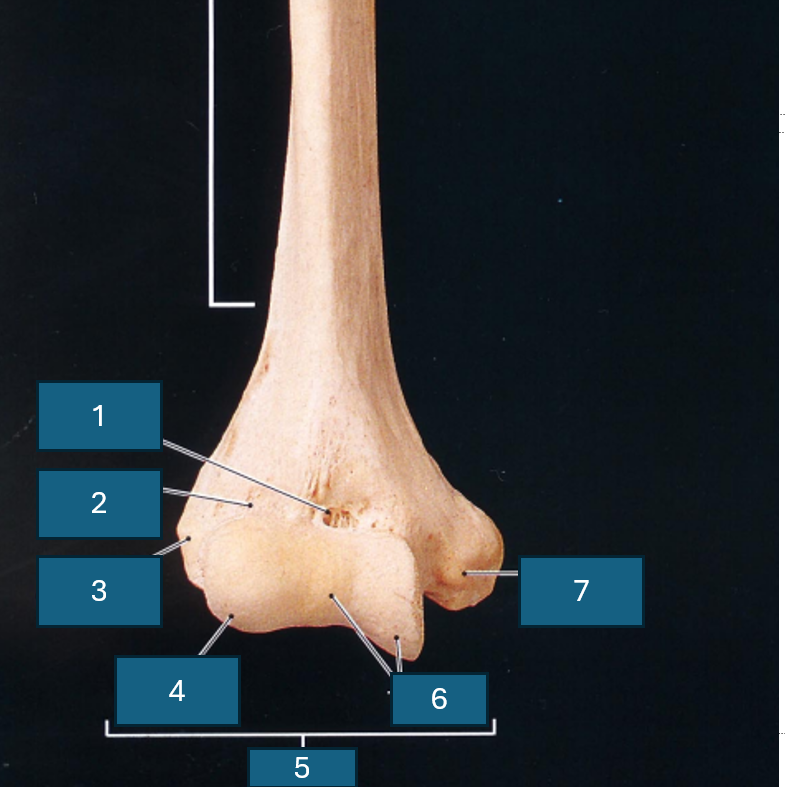
Identify 1
Coronoid fossa
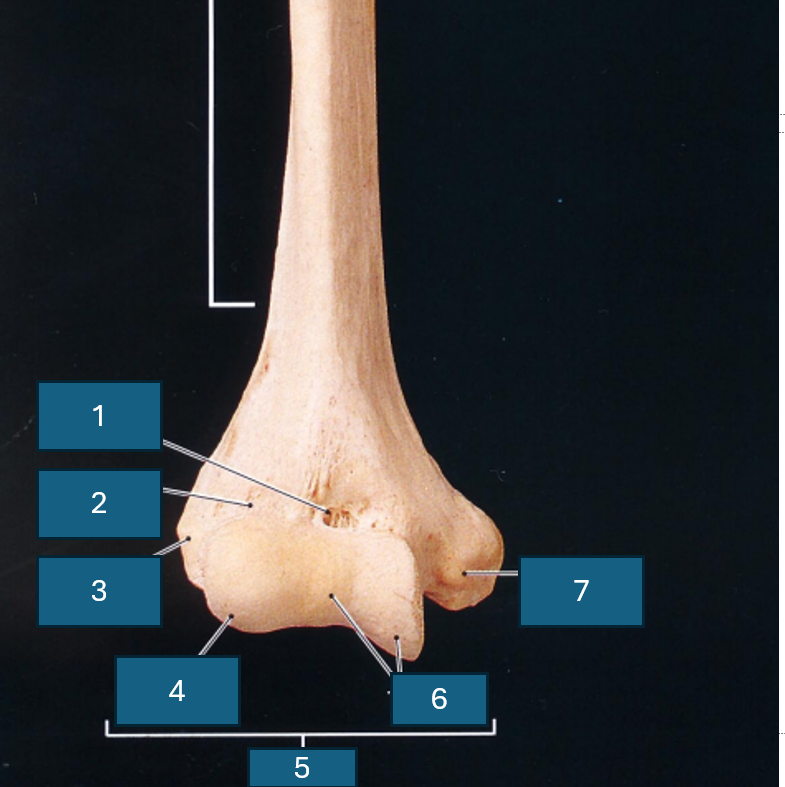
Identify 2
Radial fossa
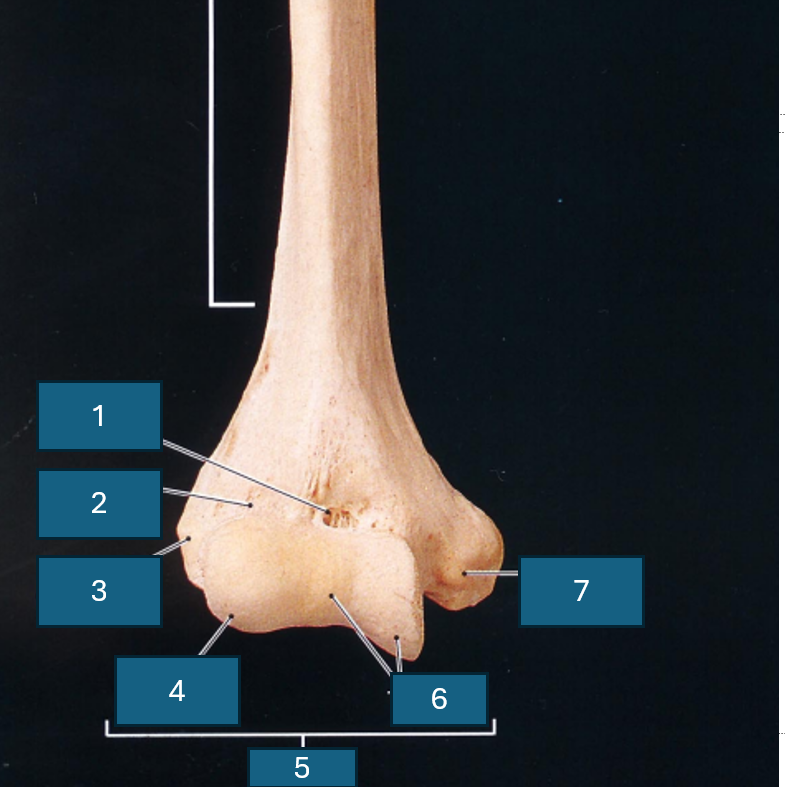
Identify 3
Lateral epicondyle
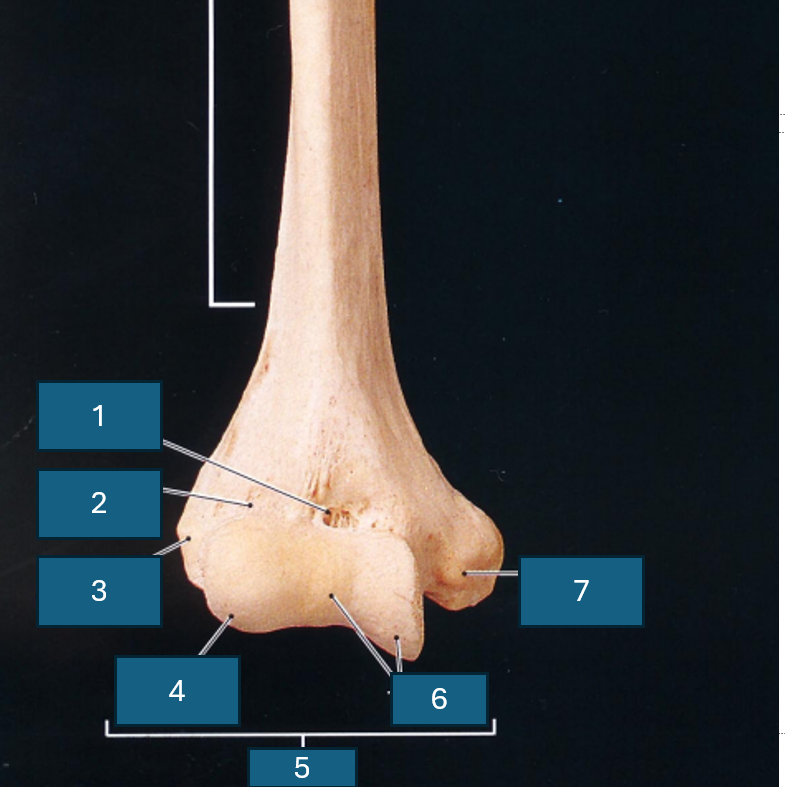
Identify 4
Capitulum
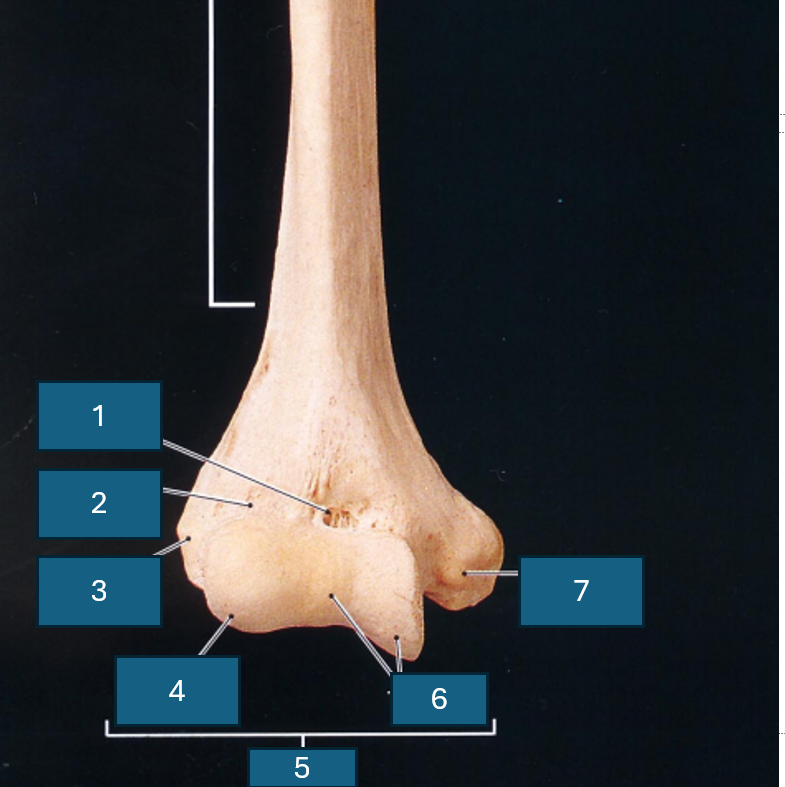
Identify 5
Condyle
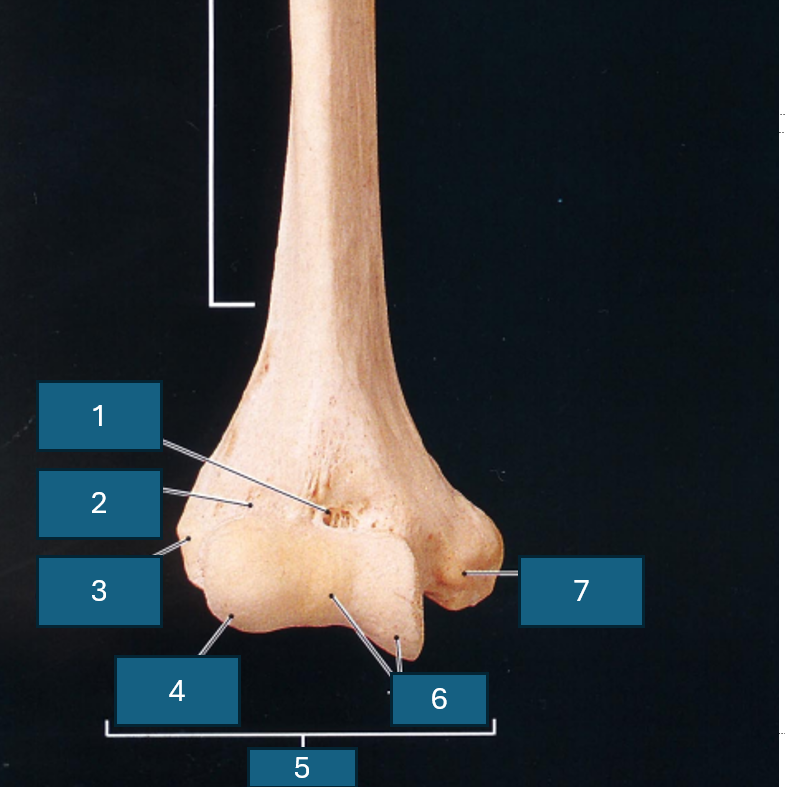
Identify 6
Trochlea
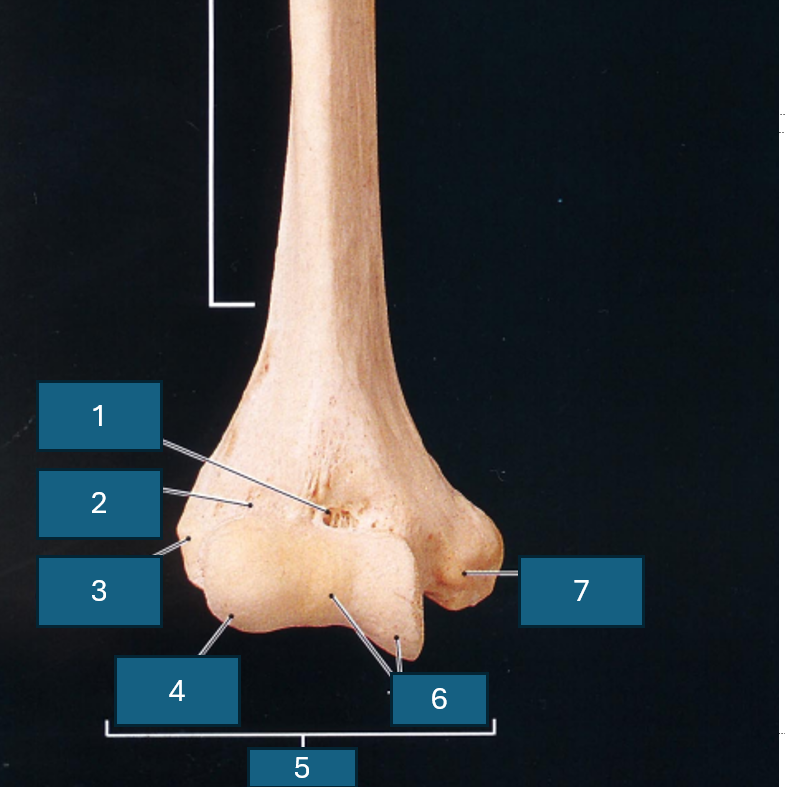
Identify 7
Medial epicondyle
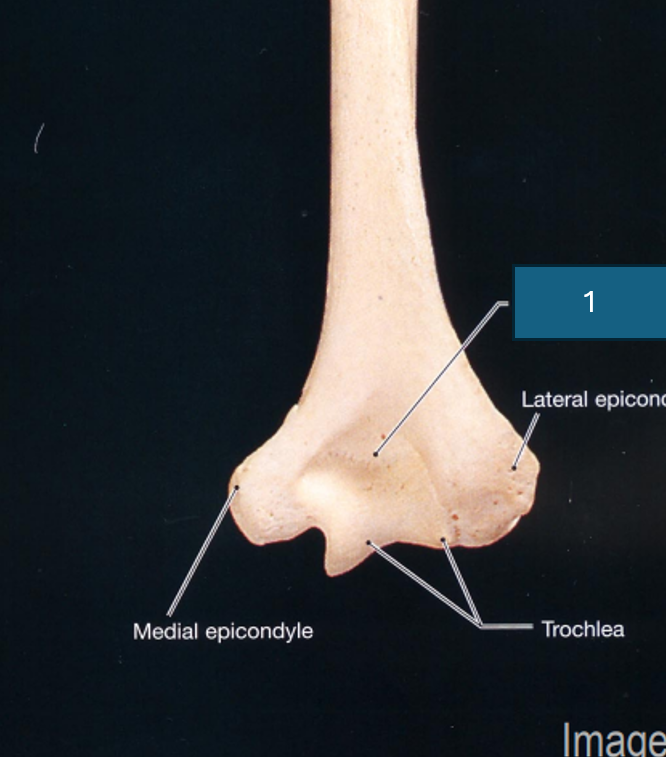
Identify 1
Olecranon fossa
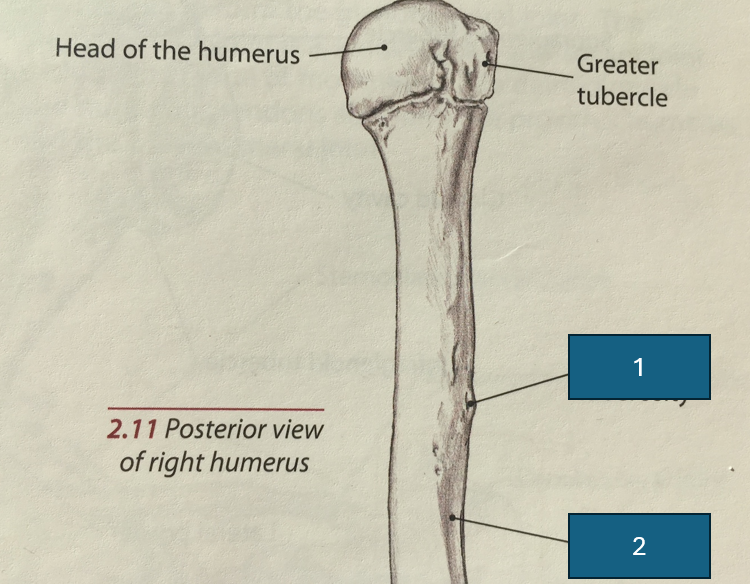
Identify 1
Deltoid tuberosity
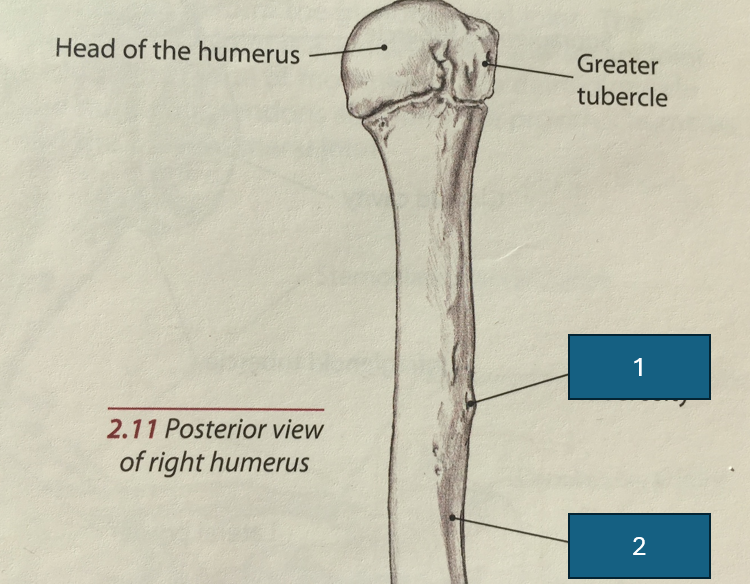
Identify 2
Groove for radial nerve
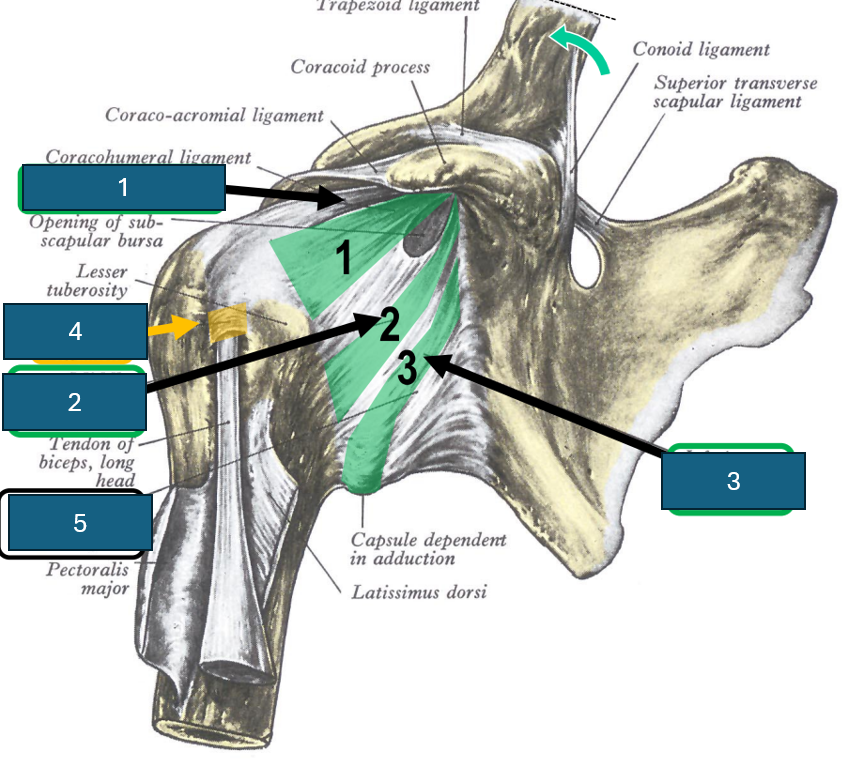
Identify 1
Superior glenohumeral ligament
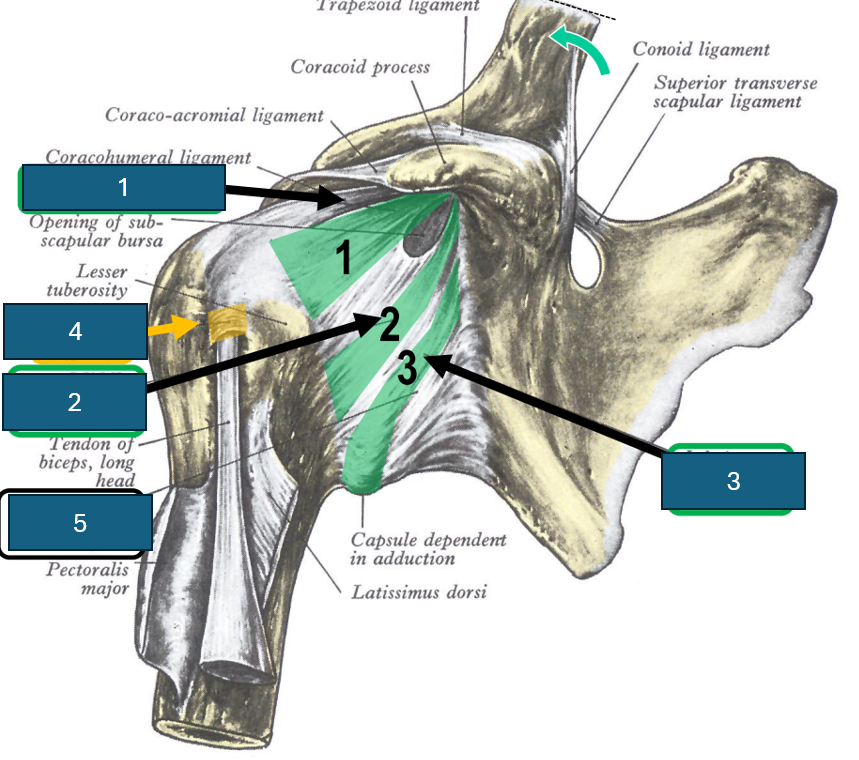
Identify 2
Middle glenohumeral ligament
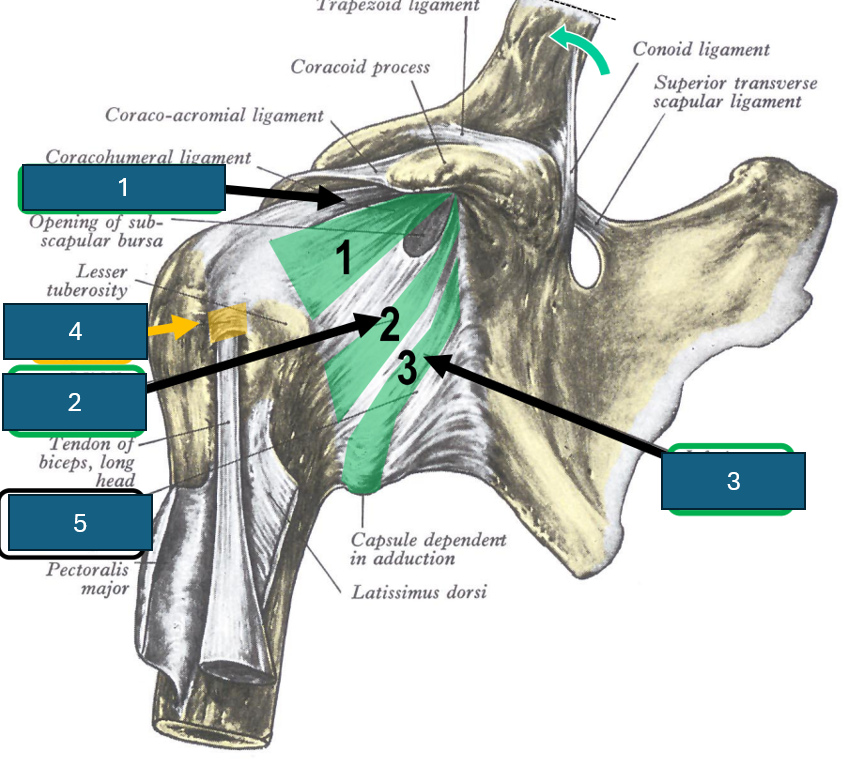
Identify 3
Inferior glenohumeral ligament
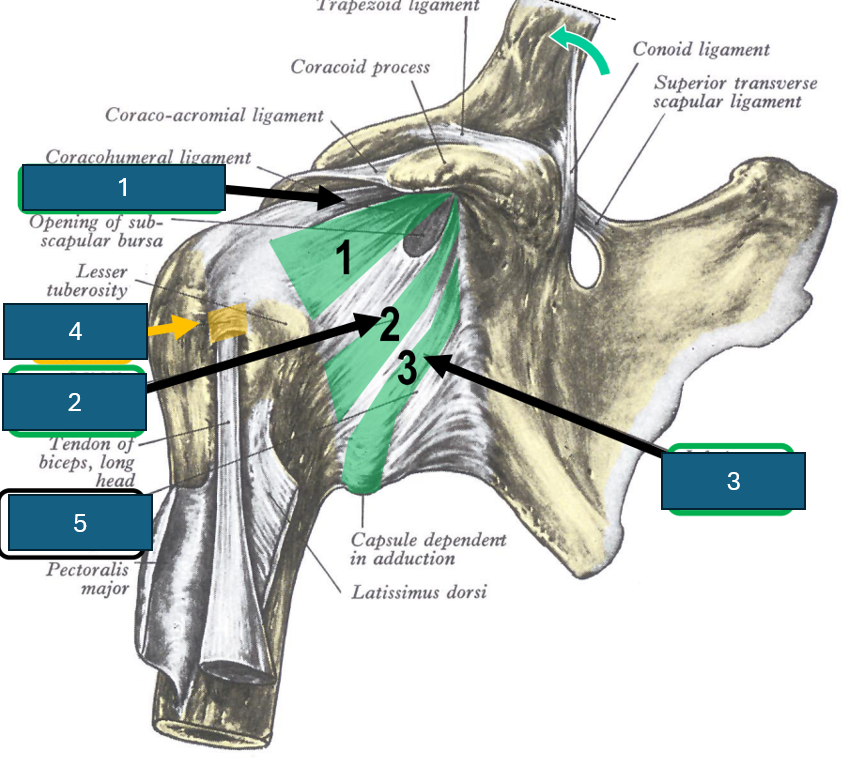
Identify 4
Transverse humeral ligament
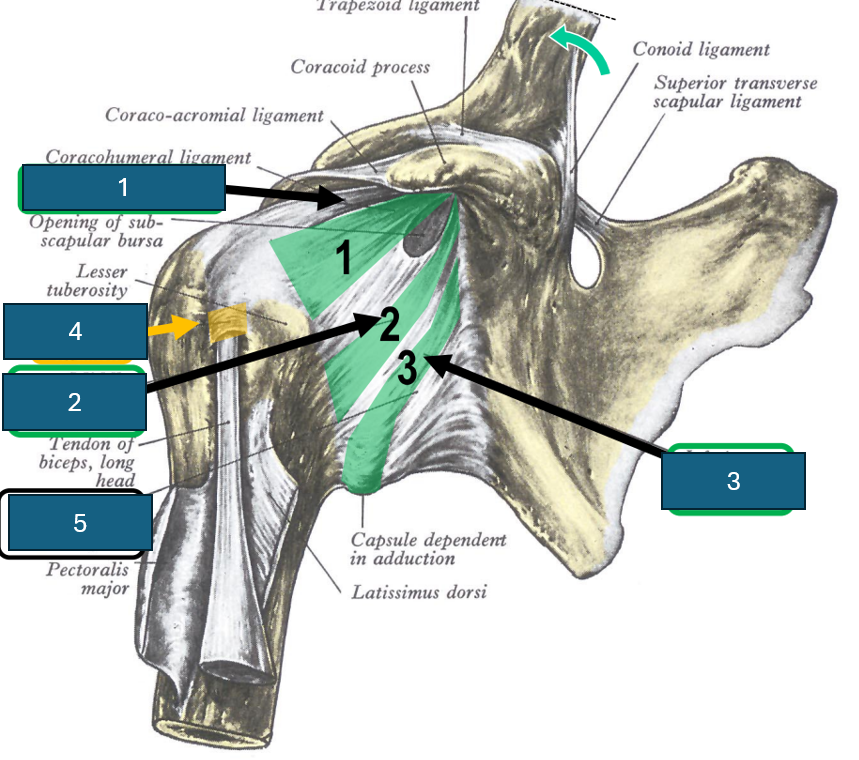
Identify 5
Fibrous capsule of shoulder joint
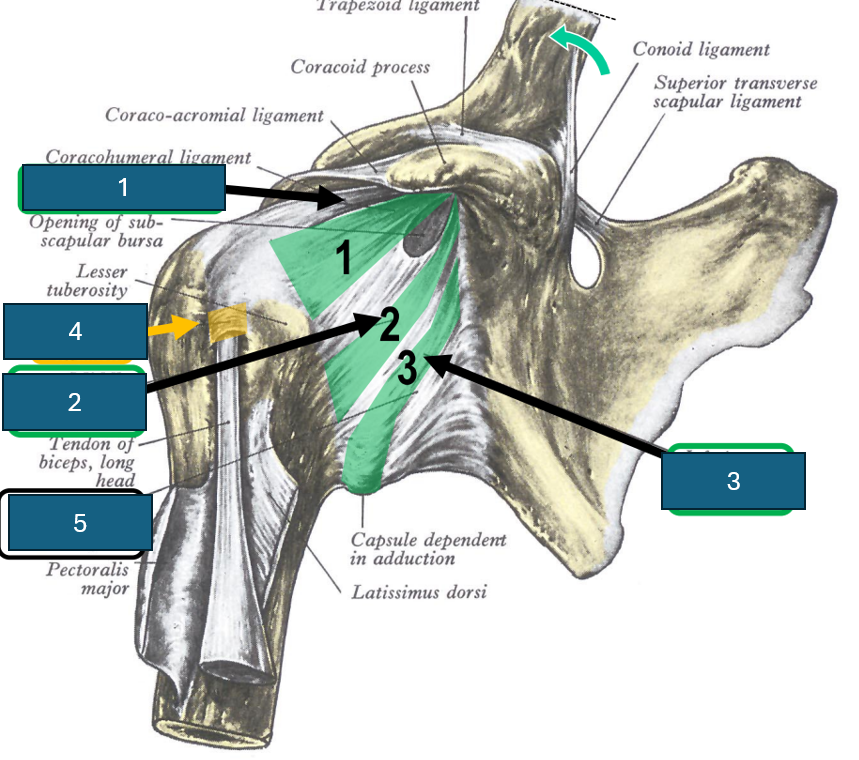
Glenoid labrum
Ring of fibrocartilage that surrounds the glenoid fossa
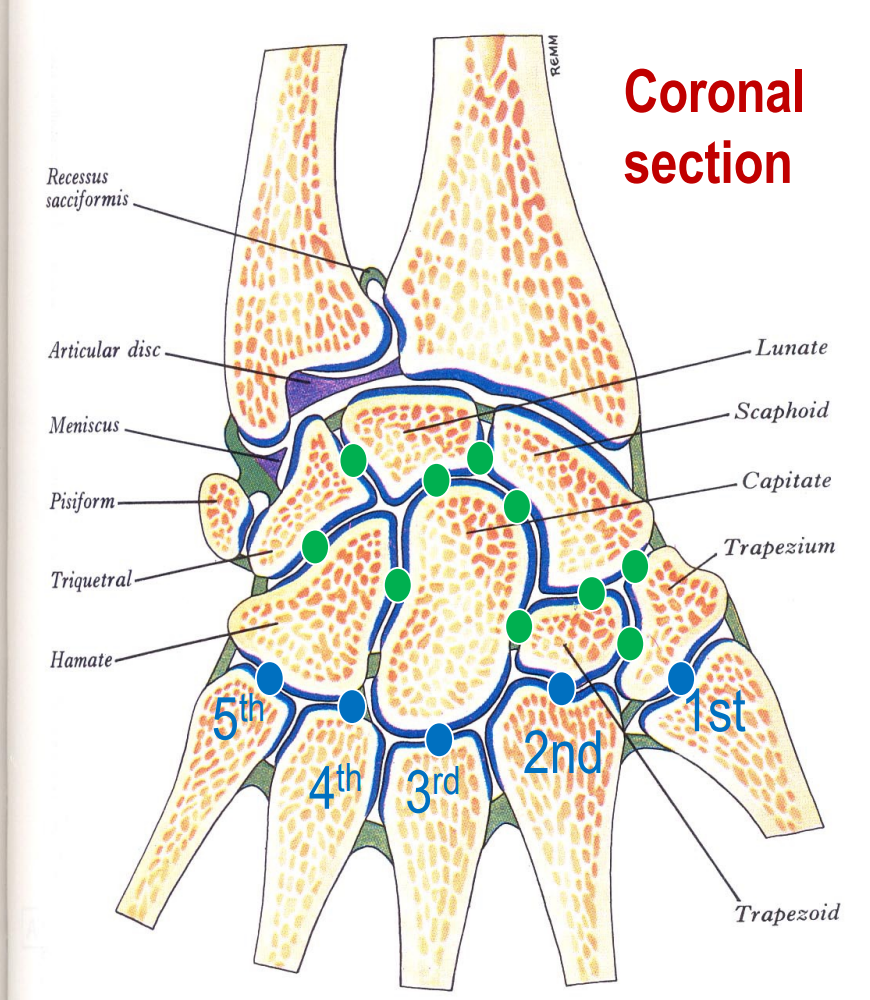
What are the three important features of the carpal bones?
Tubercle of scaphoid and trapezium and hook of hamate.
What type of bones are metacarpals?
Long bones (head body and shaft).
Important feature of 3rd metacarpal?
Styloid process.
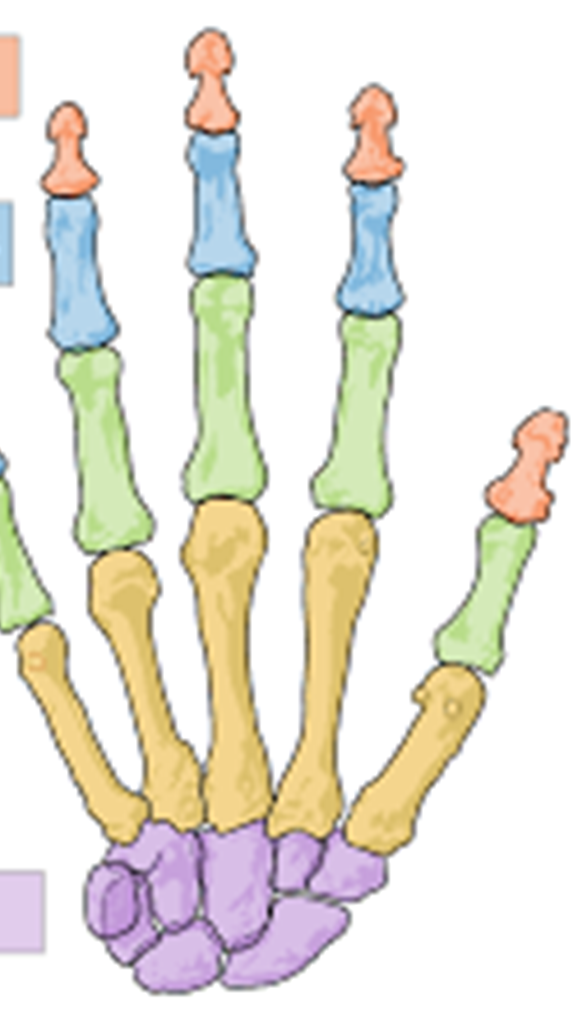
Red
Distal phalanges
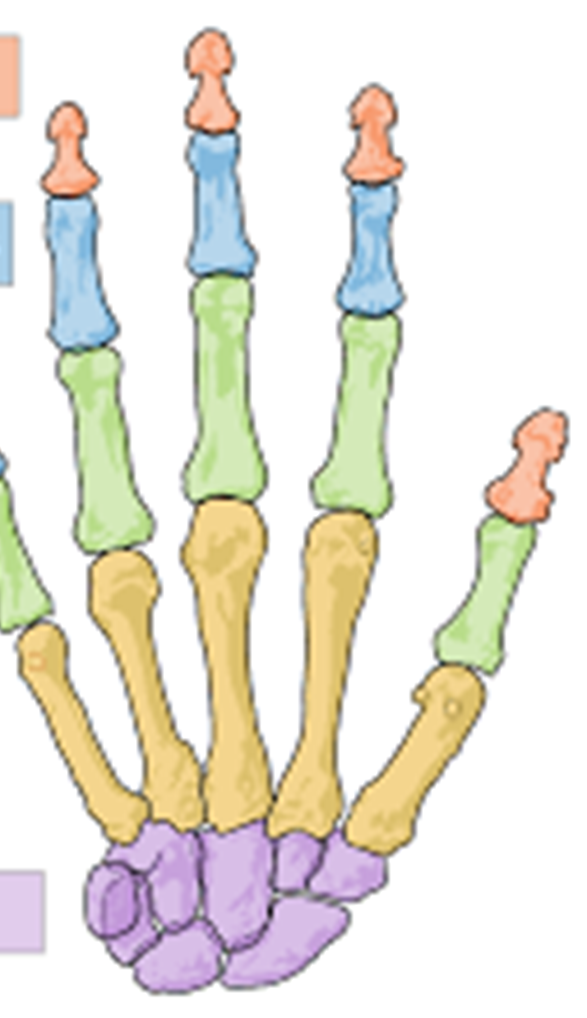
Blue
Middle phalanges
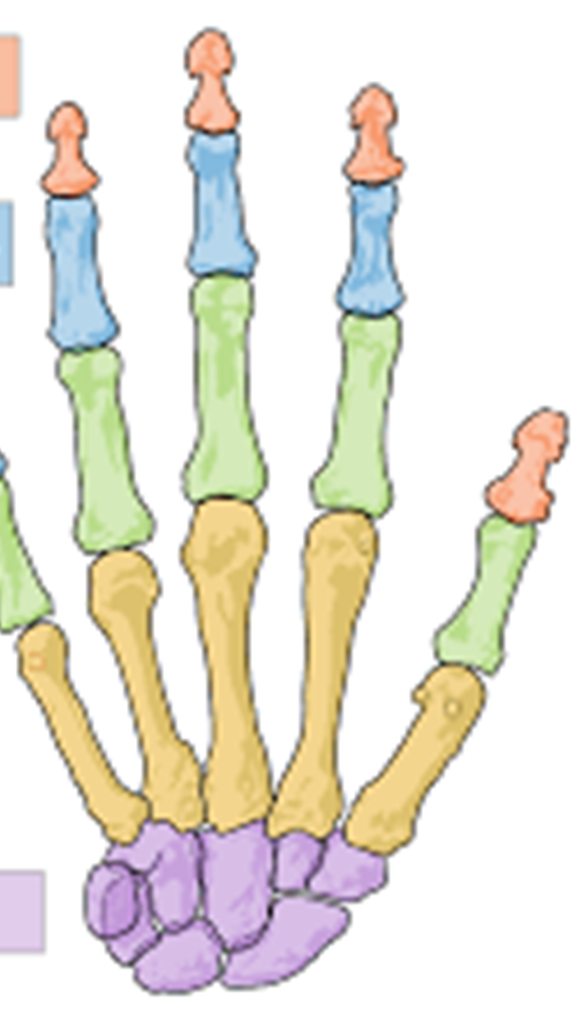
Green
Proximal phalanges
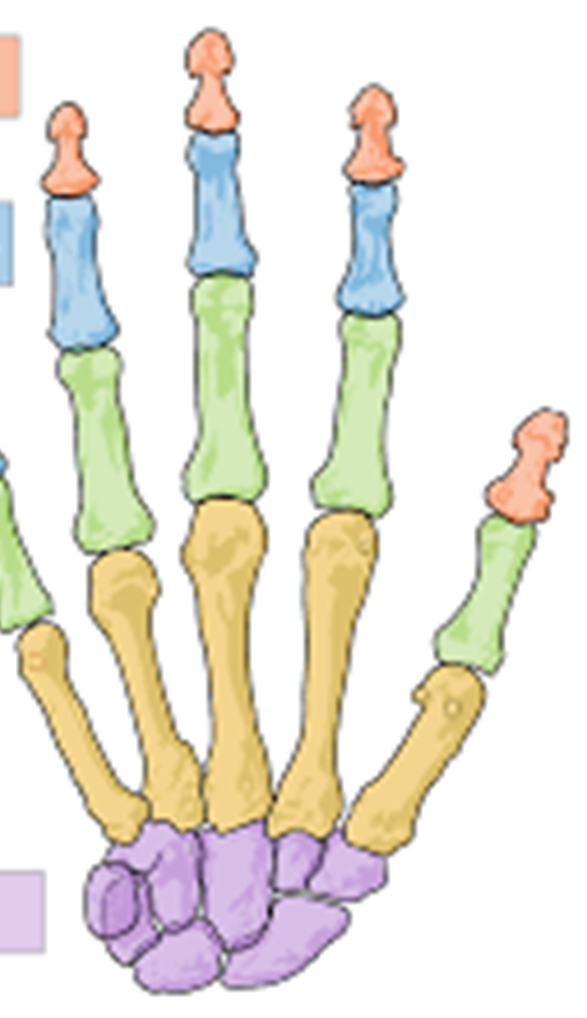
Yellow
Metacarpals
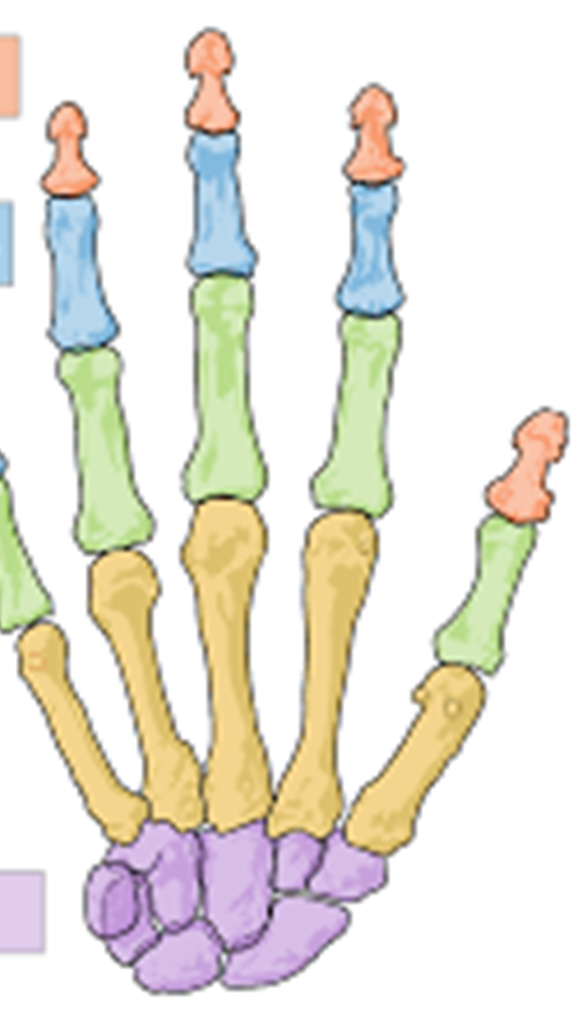
Purple
Carpals
Green
Intercarpal joints. Synovial (plane). Diarthrosis (multiaxial)
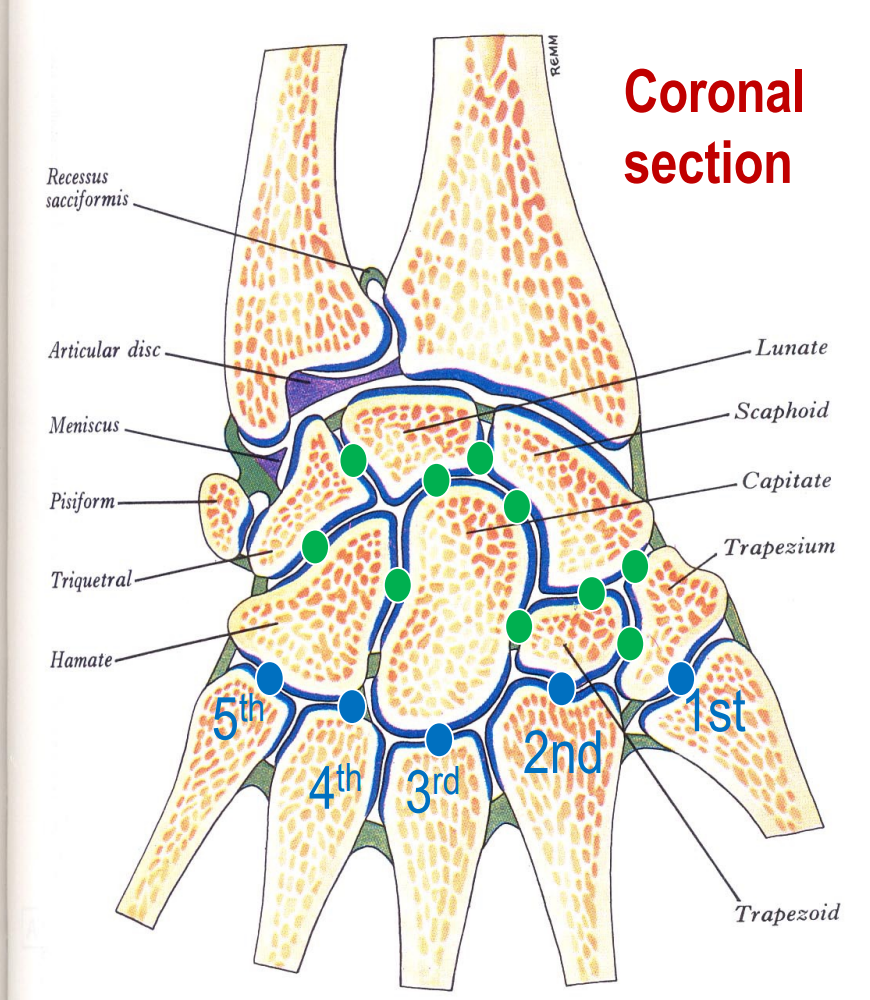
Blue
Carpometacarpal joints. Synovial. 1st - saddle. 2-5 gliding. Diarthrosis. (multiaxial?)
Joint between phalanges
Interphalangeal joints. Synovial (hinge) diarthrosis (uniaxial). Supported by collateral ligaments.
Joint between metacarpals and phalanges
Metacarpophalangeal joints. Synovial (ellipsoidal), diarthrosis (multiaxial)
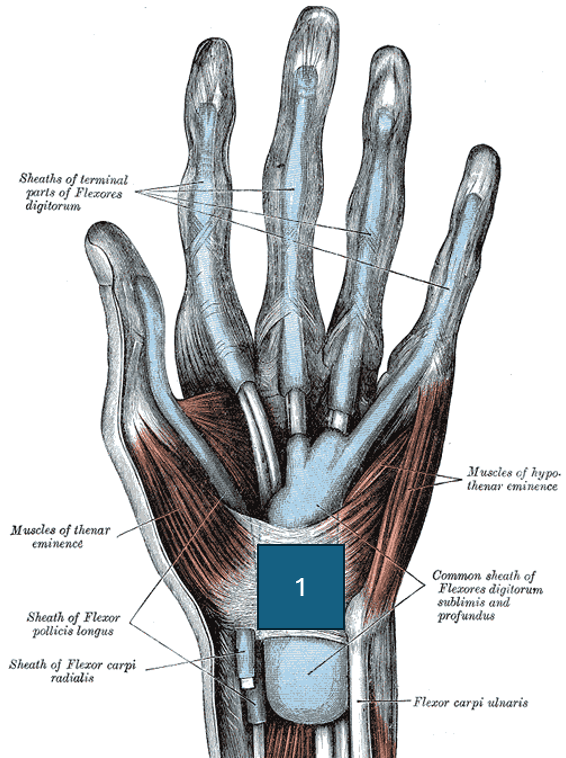
Identify 1
Flexor retinaculum or transverse carpal ligament
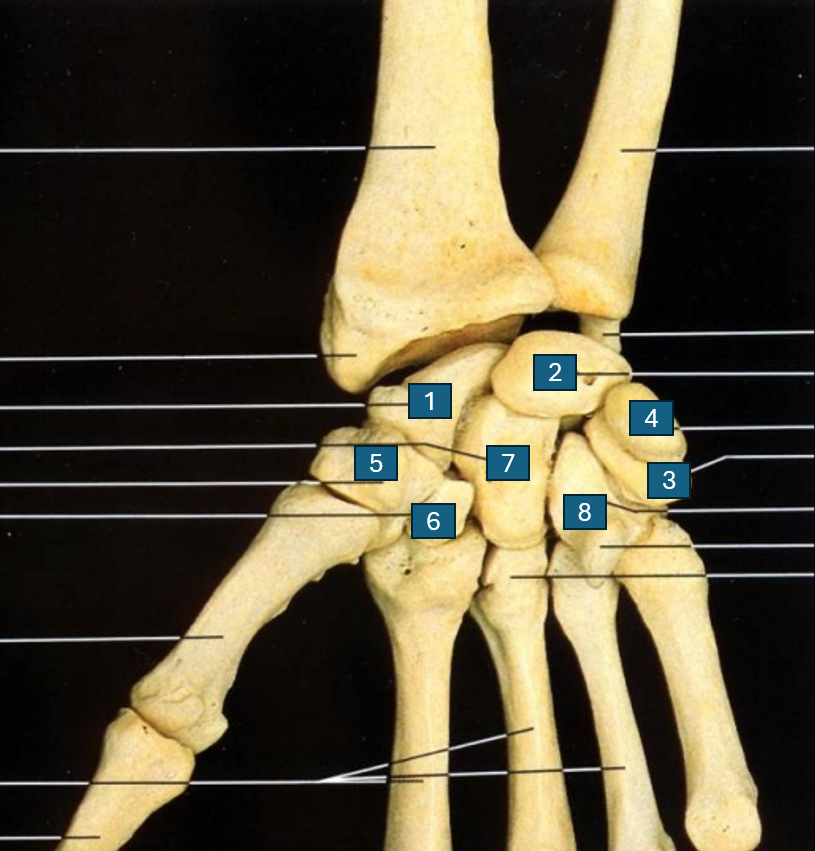
List the carpal bones (in order of rows)
Proximal row: 1.) Scaphoid, 2.) Lunate, 3.) Triquetrum 4.) Pisiform
Distal row: 5.) Trapezium 6.) Trapezoid 7.) Capitate 8.) Hamate
Wrist joint
Radiocarpal joint. Synovial (ellipsoid/condyloid). Diarthrosis (biaxial)
Which finger is digit 1?
Thumb
Elbow joint complex
Humeroulnar (and humeroradial) joint. Synovial (hinge). Diarthrosis (uniaxial).
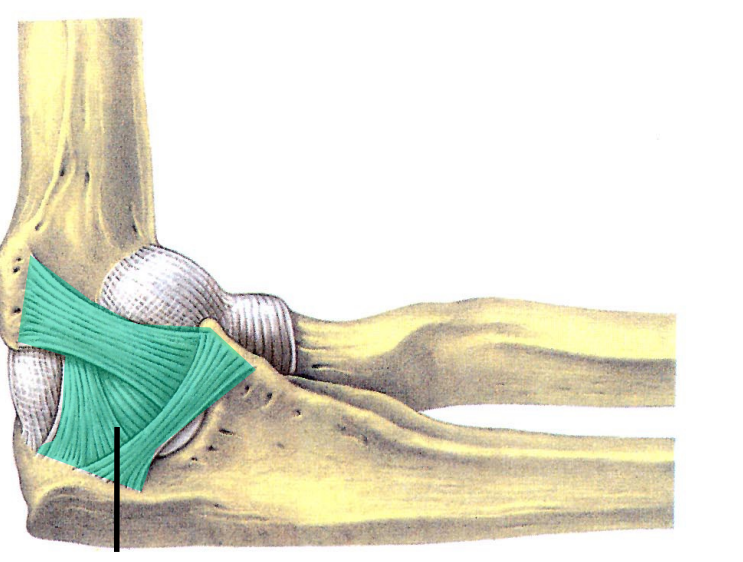
Green
Ulnar (medial) collateral ligament. Holds joint in place (like collateral ligaments of interphalangeal joints).
Green
Radial (lateral) collateral ligament.
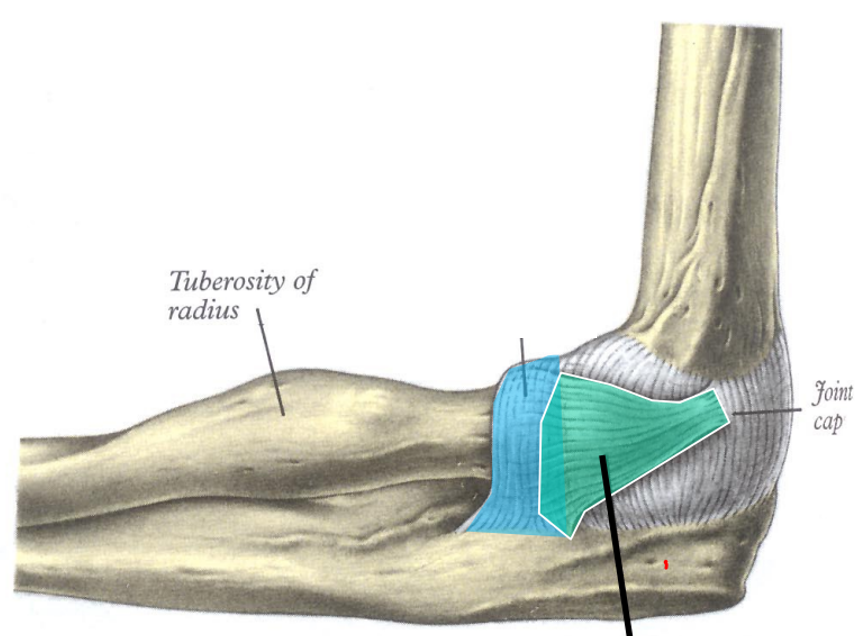
Blue
Annular ligament
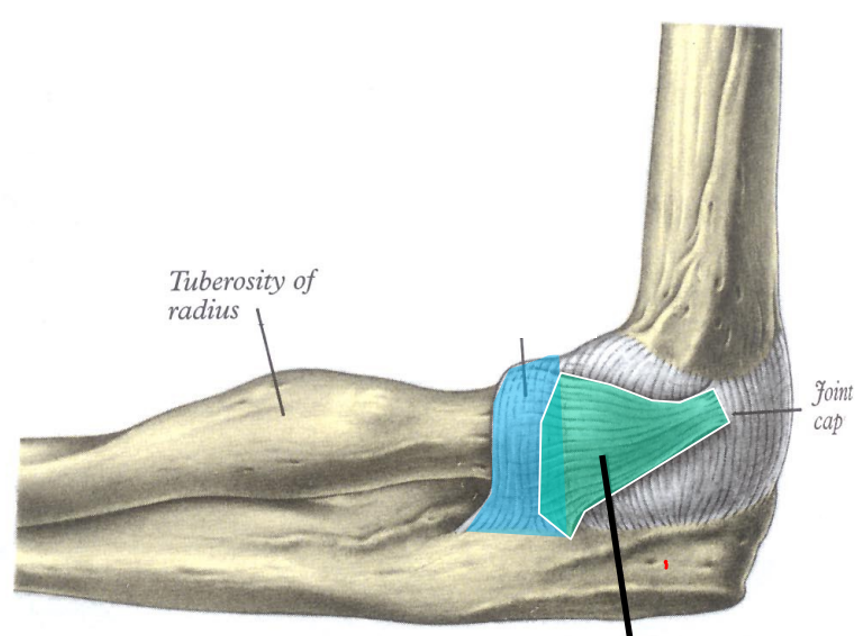
Identify this structure
Middle radioulnar joint. Fibrous (syndesmoses - joints connected by interosseous membrane). Synarthrosis.
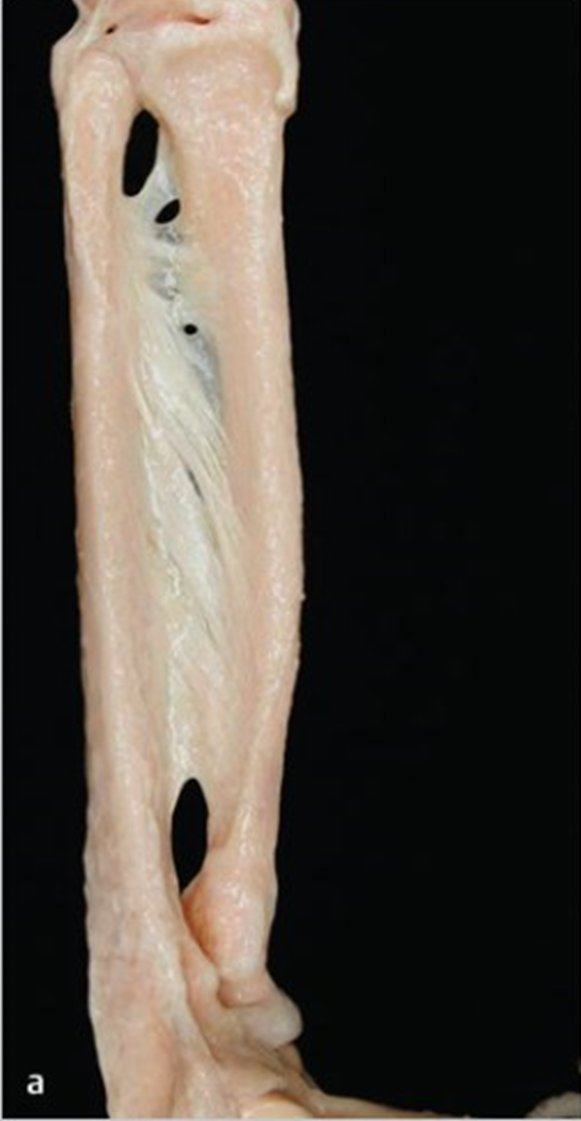
Identify green
Ulna collateral ligament of wrist joint. (Look for pin on ulna in palmar view)
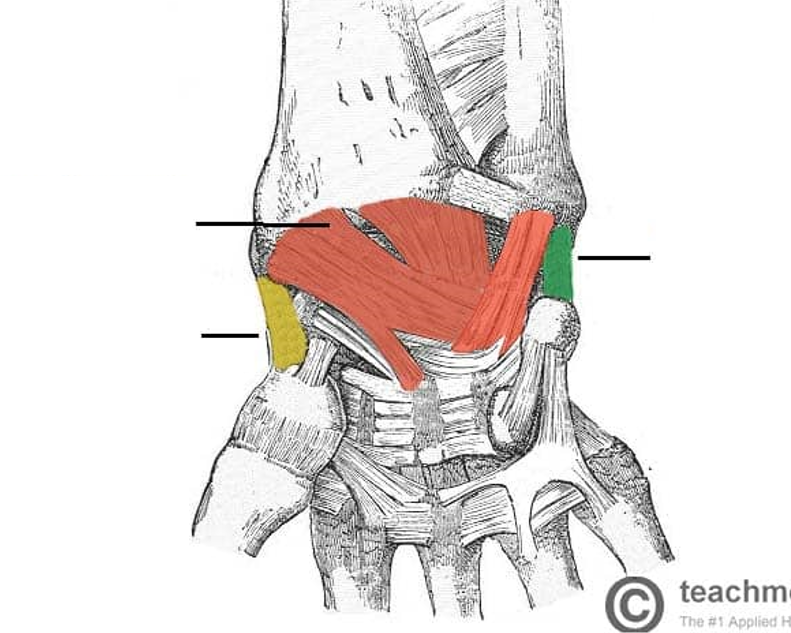
Identify blue
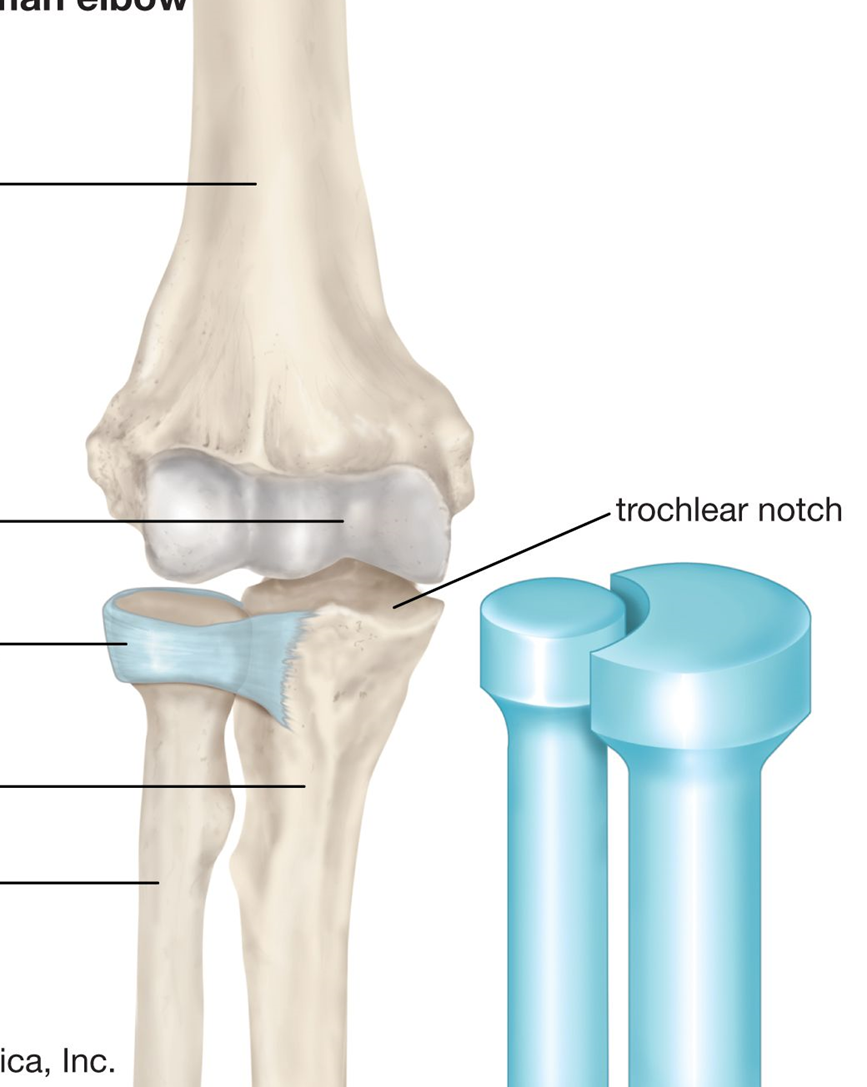
Annular ligament
Identify 1
Proximal radioulnar joint. Synovial (pivot). Diarthrosis (uniaxial)
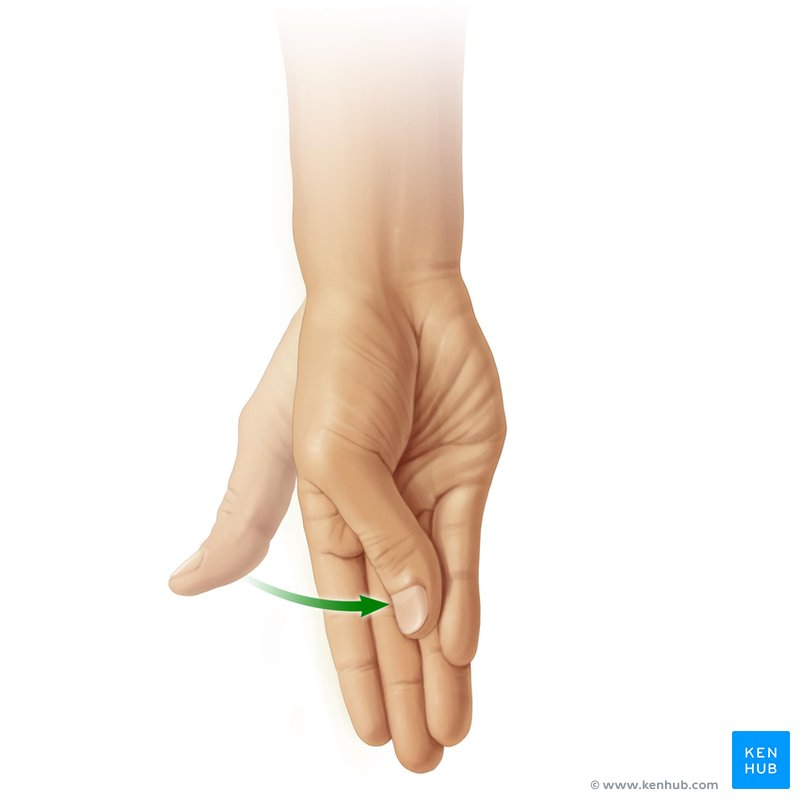
What movement is this?
Opposition and reposition (return to anatomical position)
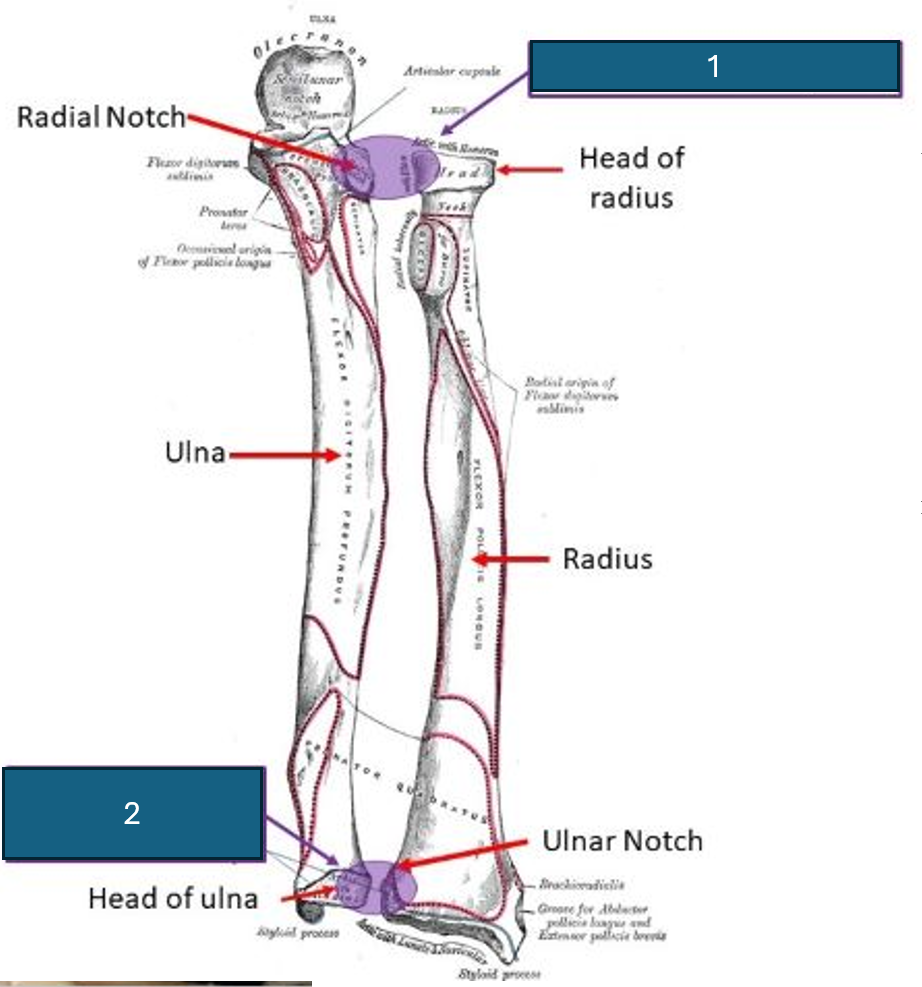
What bone and part of that bone articulates with the carpals?
The carpal articular surface of the radius articulates with scaphoid and lunate.
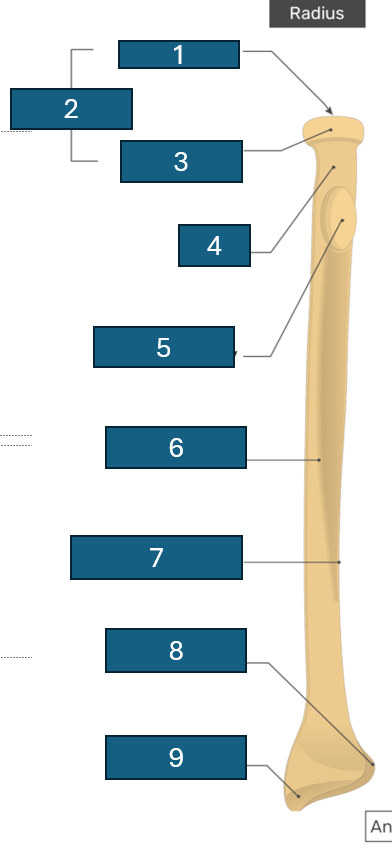
Identify 1
Articular facet/fovea
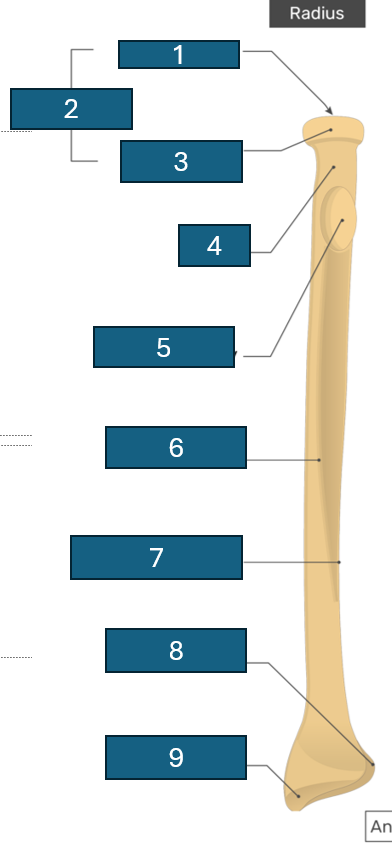
2
Head
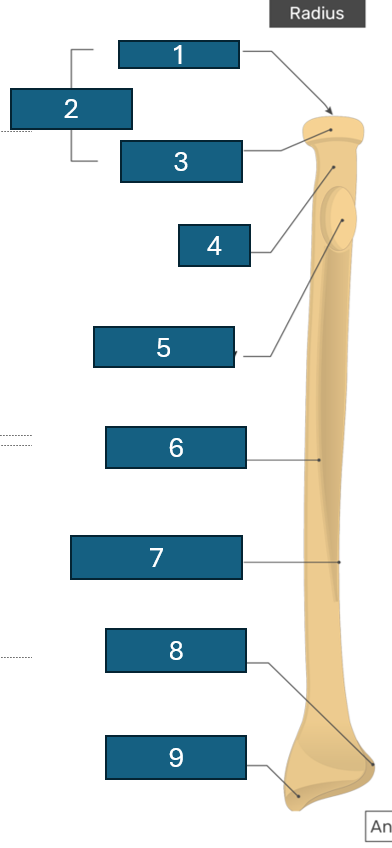
3
Articular circumference
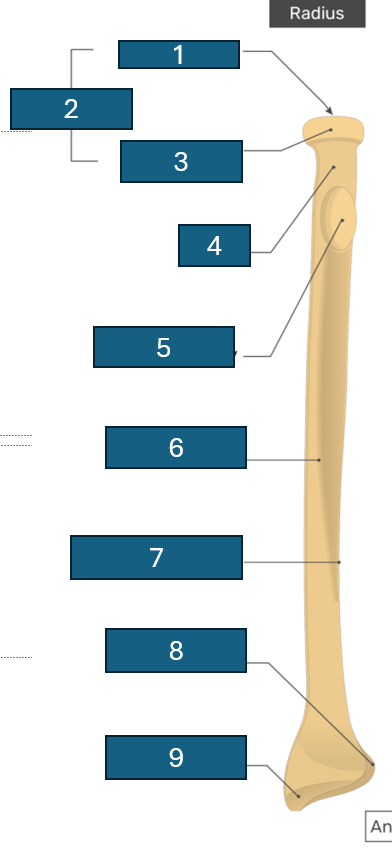
4
Neck
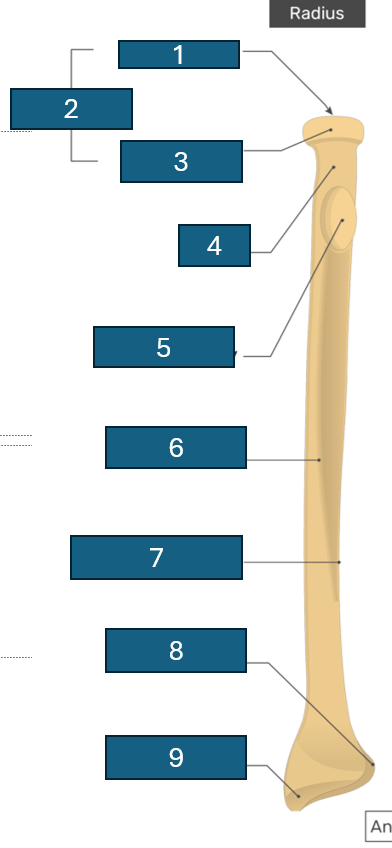
5
Radial tuberosity
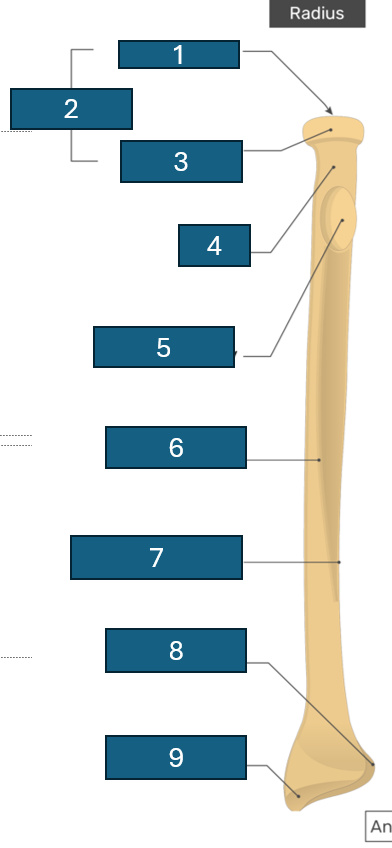
6
Anterior border
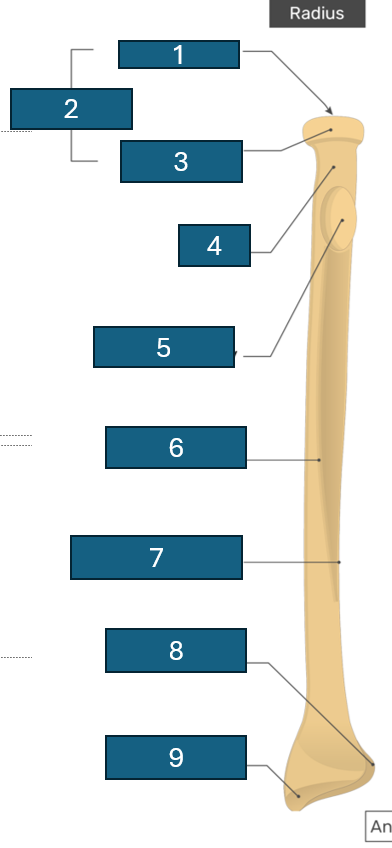
7
Interosseous border