Innate Immune System
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
external barriers
what is the 1st line of defense?
macrophage, neutrophil, dendritic cell
name the 3 phagocytic cells of innate immunity
neutrophil
most common leukocyte
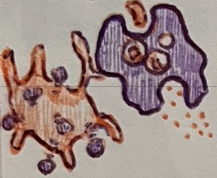
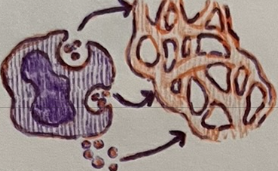
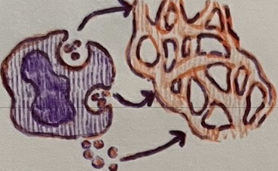
basophils, mast cells
2 pro-inflammatory cells of innate immunity
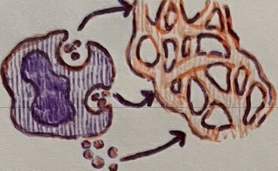
histamine, heparin, eicosanoids
3 chemicals released by pro-inflammatory cells
eicosanoids
which chemical released by basophils and mast cells is described below:
promotes further inflammation
histamine
which chemical released by basophils and mast cells is described below:
increases vasodilation and capillary permeability
heparin
which chemical released by basophils and mast cells is described below:
anticoagulant
neutrophils
__ are the most numerous leukocyte and first responders to site of injury; act as weaker macrophages
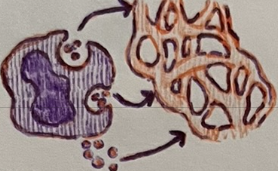
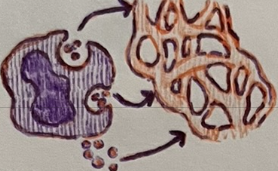
phagolysosome
in phagocytic cells, when the intake vesicle fuses w/ the lysosome, a __ is formed
The following occurs during __.
Intake vesicle fuses with lysosome forming phagolysosome
Digestive enzymes break down unwanted substances
Degraded residue is released by exocytosis
dendritic
__ cells destroy antigens, then present the remaining fragments on their surface to T-cells (APC cells)
initiates adaptive immunity
inflammation
Basophils and mast cells promote __.
phagocytic
macrophages, neutrophils, and dendritic cells are __
basophils
__ are most rare leukocyte (less than 1% of circ. Leukocytes)
mast cells
__ __ reside in connective tissue, mucosa, internal organs
chemotaxis
pro-inflammatory cells like basophils and mast cells release __ chemicals, which attract immune cells
eicosanoids
__ released from the plasma membrane of pro-inflammatory cells promote further inflammation
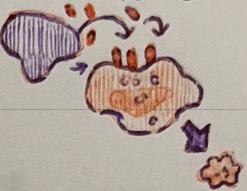
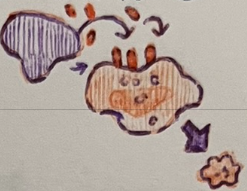
natural killer
__ __ cells are apoptosis-inducing cells that target unhealthy/unwanted cells
natural killer
__ __ cells form in bone marrow, circulate in blood, and accumulate in secondary lymphoid structures
perform immune surveillance
natural killer
__ __ cells perform immune surveillance
natural killer
__ __ cells destroy virus-infected cells, bacterial-infected cells, tumor cells, and cells of transplanted tissue
natural killer
__ __ cells kill by releasing cytotoxic chemicals such as perforin and granzymes
perforin, granzymes
natural killer cells kill by releasing cytotoxic chemicals such as __ and __
perforin
name the cytotoxic chemical described below:
creates a transmembrane pore in the unwanted cell
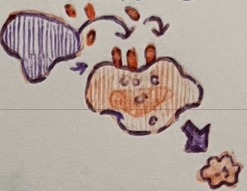
granzymes
name the cytotoxic chemical described below:
enter transmembrane pore and cause apoptosis of the cell
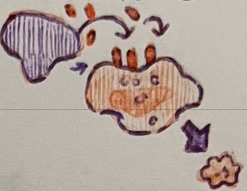
eosinophils
which cell attacks multicellular parasites?
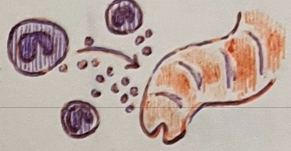
second
macrophages, neutrophils, and dendritic cells are part of the __ line of defense
innate
macrophages, neutrophils, and dendritic cells are part of __ immunity
second
basophils and mast cells are part of the __ line of defense
innate
basophils and mast cells are part of __ immunity
second
natural killer cells are part of the __ line of defense
innate
natural killer cells are part of __ immunity
second
eosinophils are part of the __ line of defense
innate
eosinophils are part of __ immunity
eosinophils
__ degranulate (perforins) and participate in immune responses of allergy/asthma
eosinophils
pattern recognition receptors (toll-like) receptors on the surface of __ bind to patterns on a m/o’s surface
eosinophil
which cell type would respond to a parasitic worm?
antimicrobial proteins
__ __ are molecules that destroy cell membranes, impact metabolism, and sequester nutrients
destroy cell walls/membranes
defensins, cathlecidins, protegrins, and lysozymes are anti-microbial proteins that __
defensins
which anti-microbial proteins impact metabolism?
lactoferrins
which anti-microbial proteins sequester nutrients?
interferons
__ are a type of cytokines that non-specifically interfere w/ the spread of intracellular pathogens
interferons
types of __ include IFN-a, IFN-B, and IFN-g
IFN-a, IFN-b
which type of interferons are produced by leukocytes and virus-infected cells?
IFN-a, IFN-b
which type(s) of interferons;
bind to neighboring cells
trigger the synthesis of enzymes that destroy viral nucleic acids
inhibit the synthesis of viral proteins
IFN-a, IFN-b
which type(s) of interferons stimulate NK cells to destroy virus-infected cells?
IFN-g
which type of interferon is produced by t-cells and NK cells?
IFN-g
which type of interferon stimulates macrophages to destroy virus-infected cells?
complement system
the __ __ is a group of > 30 plasma proteins that work w/ antibodies
complement
__ is synthesized in the liver and continuously released in inactive form
enzyme cascade
the complement system is activated via __ __
complement
__ is continuously released inactive by the liver and is activated via enzyme cascade
pathogen
complement activation follows __ entry
classical, alternative, lectin
what are the 3 pathways of complement activation? (CAL)
classical pathway
which complement pathway is described below:
Antibody attaches to foreign substance, then complement binds to antibody
alternative pathway
which complement pathway is described below:
complement binds to polysaccharides of bacterial/fungal cell wall
lectin pathway
which complement pathway is described below:
initiated when mannose-binding lectin binds to mannose
inflammation
which stereotypical response is a local, nonspecific response of vascularized tissue to injury, infection; major response of innate immunity
inflammation
the events of __ are described below
Injured tissue, basophils, mast cells, and infectious organisms release chemicals that initiate responses
released chemicals induce vascular changes: vasodilation, increased capillary permeability, increased endothelial expression of molecules for leukocyte adhesion
leukocyte recruitment: diapedesis, chemotaxis
chemotaxis
leukocytes migrate toward chemicals released from damaged, dead, or pathogenic cells
diapedesis
cells escape blood vessel walls
inflammation
the following vascular changes occur during __
vasodilation
increased capillary permeability
increased endothelial expression of molecules for leukocyte adhesion
exudate
during inflammation, the fluid that moves from blood to the injured/infected area is called __
exudate
__ contains fluid, proteins, and immune cells to eliminate pathogens/promote healing
vasodilation
during inflammation __ brings more blood to the injured/infected area
capillary permeability
during inflammation, the contraction of vessel endothelial cells (opening gaps) increased __ __
fluid reabsorption
the loss of plasma proteins during inflammation decreases capillary osmotic pressure, which then decreases __ __ into the blood
lymphatic capillaries
Extra fluid during inflammation is taken up (“washed”) by __ __ in the area. This allows lymph nodes to monitor the fluid’s contents.
72
Within __ hours inflammation response slows
macrophages eat bacteria, damaged host cells, dying neutrophils
tissue repair: fibroblasts form new connective tissue
redness, heat, swelling, pain, loss of function
cardinal signs of inflammation (red hot sweltering peppers laugh)

redness
increased blood flow during inflammation causes __
heat
increased blood flow and metabolic activity during inflammation cause __
swelling
the increase in fluid loss from capillaries during inflammation causes __
pain
fluid loss and chemical irritants (kinins, prostaglandins, m/o secretions) cause the compression of receptors, which then causes __
loss of function
pain and swelling in severe cases of inflammation may cause __ _ __
fever
abnormal body temperature elevation (>37°C)
fever
the release of pyrogens from immune cells or infectious agents causes __
fever
the events of __ include:
Pyrogens circulate through blood and target hypothalamus
In response, hypothalamus releases prostaglandins
Hypothalamus raises temperature set point leading to fever
fever
the benefits of __ include
Inhibits reproduction of bacteria and viruses
Promotes interferon activity
Stimulates capillary permeability
Increases activity of adaptive immunity
Accelerates tissue repair
103-104
a high grade fever is between __-__°F
104
a dangerous high-grade fever is over __°F
denaturation
high fevers are dangerous because they cause the __ of proteins
106
irreversible brain damage occurs at fevers greater than __°F
108
death is likely to occur if a fever is >__°F
neutrophils
Which innate cell type is typically the first responder at the site of infection?
innate
the 1st and 2nd lines of defense are part of __ immunity
cytokine storm
life-threatening systemic inflammatory syndromes involving elevated levels of circulating cytokines and immune-cell hyperactivation