2022 alevel biology paper 1
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
function of nucleus
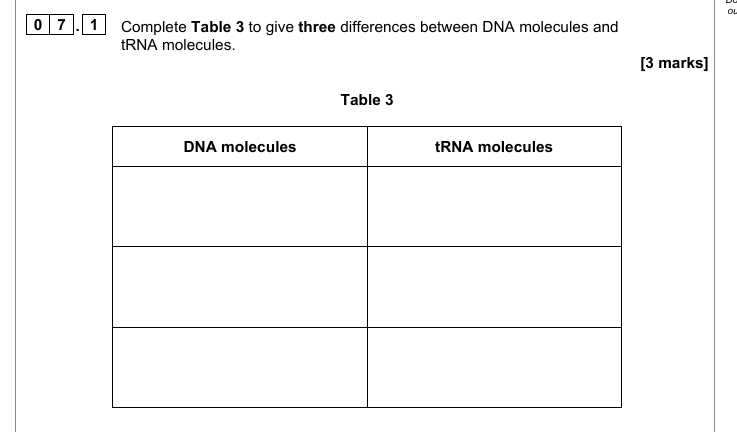
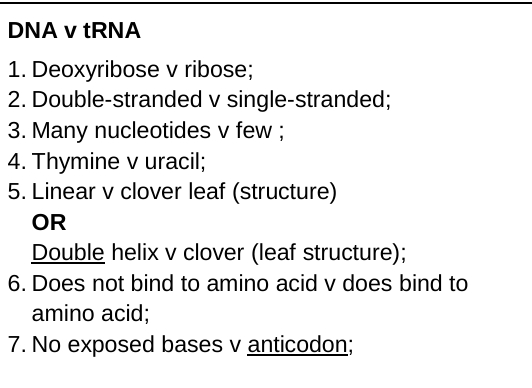
4. (Holds/stores) genetic information/material for polypeptides (production) OR (Is) code for polypeptides
; 5. DNA replication (occurs);
6. Production of mRNA/tRNA OR Transcription (occurs);
7. Production of rRNA/ribosomes;
Name the main polymer that forms the following cell walls. [1]
Cellulose (plants) and Chitin (fungi);
Sometimes farmers stop growing crops on an area of land to allow the natural ecosystem to recover. The plant species index of diversity of these areas previously used to grow crops is different from nearby land that has never been used to grow crops. Suggest and explain how the plant species index of diversity would be different in these areas previously used to grow crops. Use Figure 1 and your knowledge of the effect of farming on biodiversity in your answer.
1. Plant (bio)diversity is lower on (previously used) crop land OR Plant (bio)diversity is higher on land not used (previously to grow crops);
2. Farming reduces (bio)diversity of fungi OR Farming reduces fungal species richness;
Clostridium difficile is a bacterial species that causes disease in humans. Antibiotic-resistant strains of C. difficile have become a common cause of infection acquired when in hospital.
Explain how the use of antibiotics has led to antibiotic-resistant strains of bacteria becoming a common cause of infection acquired when in hospital. [3 marks]
1. (Some bacteria have) alleles for resistance; 2. (Exposure to) antibiotics is the selection pressure Resistant bacteria survive/reproduce;
3. More antibiotics used in hospital (compared with elsewhere) Patients have weakened immune systems
Describe how the scientists could use aseptic techniques to transfer 0.3 cm3 of C. difficile in liquid culture from a bottle onto an agar plate. [3 marks]
1. Wash hands with soap OR Disinfect surfaces; 2. Use sterile pipette/syringe (to transfer bacteria); 3. (Remove bottle lid and) flame neck of bottle; 4. Lift lid of (agar) plate at an angle; 5. Work close to upward air movement; 6. Use sterile spreader; 7. Place pipette/spreader into disinfectant (immediately after use);
Use Figure 2 to evaluate whether more trehalose in the diet could be a factor in the increased number of antibiotic-resistant C. difficile infections. [3 marks]
Against 4. In laboratory not in people;
5. Other disaccharides (in the diet) might affect bacteria;
6. Other bacterial species (in the body) might affect bacteria;
7. No stats test to see if difference/increase is significant;
8. No data for both resistant and non-resistant bacteria growing together;
9. No data for different concentrations of trehalose
For 1. Resistant bacteria grow faster with trehalose; 2. (So) resistant bacteria (likely to) increase in frequency in the population/people;, out competes the non-resistant
Give two features of all prokaryotic cells that are not features of eukaryotic cells. [1 mark]
Prokaryotes have : No membrane-bound organelles/correct example OR (Single,) circular/loop DNA (in cytoplasm) OR DNA free in cytoplasm OR DNA not associated with proteins/histones OR Murein/peptidoglycan (in) cell wall;
The APs damage prokaryotic cells but do not damage the eukaryotic cells in the organisms that produce them. Prokaryotic cell membranes do not contain cholesterol. Assess why the APs do not damage the eukaryotic cells of the organisms that produce them.
1. Cholesterol stabilises (the membrane) OR Cholesterol restricts the movement of molecules/phospholipids/fatty acid (tails) (making up the membrane); 2. (So) APs do not make channels in (eukaryotic) membranes
Scientists observed these APs on prokaryotes using a transmission electron microscope. They stained the APs using a monoclonal antibody with gold attached to it. Suggest how these techniques allowed observation of APs on prokaryotes. [3 marks]
1. Antibody binds to AP OR Gold (present) where AP located; 2. (As antibody/tertiary structure is) complementary (to AP); 3. Gold interacts with electrons (in TEM); 4. (T)EM (used as it) has a high resolution
Describe viral replication. [3 marks]
1. Attachment proteins attach to receptors; 2. (Viral) nucleic acid enters cell; 3. Nucleic acid replicated in cell OR Reverse transcriptase makes DNA from RNA; 4. Cell produces (viral) protein/capsid/enzymes; 5. Virus assembled and released (from cell);
Describe what the scientists should place in the control tubes in this investigation. [3 marks]
1. Same volume of (each) buffer/pH solution; 2. Same concentration/mass of substrate (at start); 3. Same concentration/mass of denatured enzyme
Explain the rate of transpiration between 5 am and midday shown in Figure 9. [4 marks]
(Rate of) transpiration/evaporation increases due to increased temperature
(So) increased kinetic energy (causing more water loss)
.Stomata open (at sunrise/after 5 am) allowing gas exchange
. (Some) stomata close at midday/after 11 am (reducing transpiration);
(So) increased water potential gradient (so more water lost)
(Rate of) transpiration/evaporation increases due to decreased humidity
The higher rate of transpiration at high tide shows that the mangrove tree is absorbing water from the sea water surrounding its roots. Describe an experiment that you could do to investigate whether the mangrove root cells have a lower water potential than sea water. You are given: • a piece of fresh mangrove root • sea water • access to laboratory equipment. [4 marks]
1. Record mass/length before and after; 2. Place in sea water for (specified/equal) time; 3. Method to remove surface water; 4. Increase in mass/length shows water has been absorbed by osmosis OR Increase in mass/length shows cells have lower water potential;
The scientists broke open the cells to produce a suspension of cell contents. Describe how the scientists would remove large organelles from this suspension of cell contents. [2 marks]
1. Use centrifuge/centrifugation at slow/low/increasing (sequence of) speed(s); 2. Large/dense organelles (removed) in (first/early) pellet OR Less dense organelles (removed) in supernatant OR Small organelles (removed) in supernatant;
![<p>Explain the position of the bands of ribosomes in tubes A and B in Figure 10. [3 marks]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/8f97ce17-24ef-437c-97b7-a32d03015801.png)
Explain the position of the bands of ribosomes in tubes A and B in Figure 10. [3 marks]
(Tube A) 1. (Ribosomes bound to) rough endoplasmic reticulum; 2. (Are) denser/heavier so move further;(settle low )
Tube B) 3. (Only free ribosomes because) membrane/phospholipids/endoplasmic reticulum dissolved (by detergent);
To observe the fish gills with the optical microscope, the scientists used two different stains. The first stain binds to DNA; the second stain binds to the red blood cells. Explain why a second stain would be needed to stain the red blood cells. Suggest which molecule the stain could bind to in the red blood cells. [2 marks]
1. (Red blood cells) do not have a nucleus/DNA;
2. Haemoglobin;
3. (So) slower gas exchange
Wider/thicker filament/lamella;
2. Longer diffusion pathway
3. (So) slower gas exchange
Describe the transport of carbohydrate in plants. [5 marks]

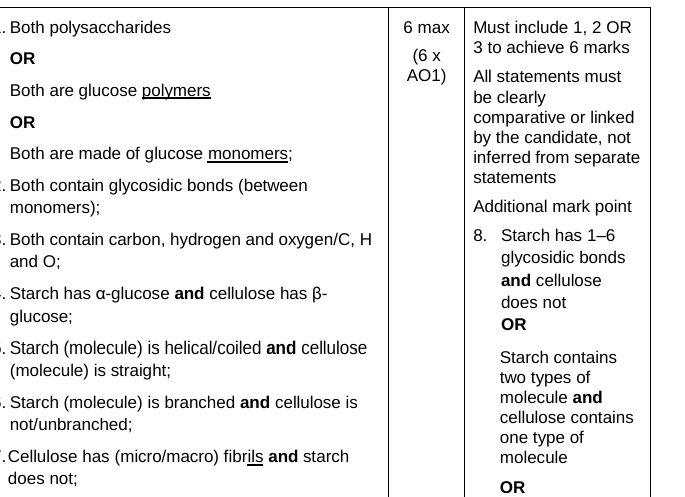
Compare and contrast the structure of starch and the structure of cellulose. [6 marks]
Describe the complete digestion of starch by a mammal. [4 marks]
