AST, Quiz 2
1/60
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
Antibiotic
a chemical substance, produced by a microorganism, with the capacity to kill or inhibit other microbes
Bacteriostatic
inhibits microbial growth
Bactericidal
kills the organism
Combined Antimicrobial Activity: Indifference
no effect
Combined Antimicrobial Activity: Synergy
combined effect is even greater than the two individual effects added together
Combined Antimicrobial Activity: Antagonism
one drug counteracts the other so that the desired result is less than would be expected
Fox test used to rule out
MRSA (S is not MRSA, R is)
β-Lactamase Inhibitors: Three important in medicine:
Clavulanic acid
• Sulbactam
• Tazobactam
ESBL
Extended Spectrum β-lactamase
and/ or drugs
one test with one drug tells us all results for them
Prophylactic
to prevent infection
Empiric
based on observation and experience of the clinician (etiological agent not proven)
Therapeutic
to treat existing disease
AST Outcomes – Susceptible (S)
Isolates are inhibited by the usually achievable concentrations of antimicrobial agents when the recommended dosage is used for the site of infection.
AST Outcomes – Intermediate (I)
Isolates with antimicrobial MICs usually approach attainable blood and tissue levels, for which response rates may be lower than for susceptible isolates.
Implies clinical efficacy in body sites
where the drugs are physiologically
concentrated or when a higher than
normal dosage can be used.
AST Outcomes – Resistant (R)
Implies isolates are not inhibited by the usually achievable concentrations of the agent with normal dosage schedules and/or:
that demonstrate zone diameters that fall in the range where specific microbial resistance mechanisms are likely
clinical efficacy of the agent against the isolate has not been reliably shown in treatment studies.
Indications for Performing
Susceptibility Testing
Isolate determined to be the probable cause of patient infection
Susceptibility of the isolate to a particular
antimicrobial agents are uncertainStandardized testing methods are
available for the isolate
CLSI Recommendations for Testing and Reporting
Suggested Groups A, B, C, and U
Based on drugs with clinical indications
approved by the FDAUltimately selected by each clinical lab
Group A
Appropriate for inclusion in a routine primary testing panel
as well as for routine reporting of the testing panel
as well as for routine reporting of results for the specific organism groups results in the particular organism groups
Group B
Agents may warrant primary testing. However, they may be reported only selectively, such as they may be reported only selectively, such as
when the organism is resistant to agents of the as in Group A
Group C
Alternative or supplemental agents may require testing in those institutions that harbor require testing in those institutions that harbor endemic or epidemic strains resistant to several of the primary drugs
Group U
Agents that are used only or primarily for treating urinary tract infections
how long until you can read an AST
16 to 18 hour incubation (except Staph
and Enterococci - 24 hrs.)
what antibiotics can you not give kids
flouroquinioles
tetracycline
What is the correct depth of agar for a Meuller-Hinton plate?
4mm
Which of the following is a beta lactamase
inhibitor?
Clavulanic acid
Concentration which will kill >99.9% of
organisms.
Minimum Bacteriocidal Concentration
Vancomycin works on...
Gram Positive organisms only
T/F Beta lactamases can be transported out of the cell and act extracellularly in some organisms.
True
Which antibiotic should you interpret where there is an 80% reduction of interpret where there is an 80% reduction of growth?
Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole
Antibiotics work by targeting all of the following except:
A. Bacterial plasmid DNA
B. DNA replication
C. RNA transcription
D. Bacterial cell wall
A. Bacterial plasmid DNA
The outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria is composed of:
Lipopolysaccharides, phospholipids and porin proteins
T/F: Streptococcus pyogenes is considered universally susceptible to penicillin.
True
Cefoxitin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus is called:
Methicillin-resistant S.aureus
In gram-positive bacteria, this is substantially thicker and more multilayered than in gram-negative bacteria.
Peptidoglycan
Intrinsic mechanisms of resistance are:
Innate characteristics of the bacterium and transmitted to bacterium and transmitted to progeny vertically
T/ F; Efflux is associated with pumping antimicrobial agents out of the cell.
True
T/ F; Changes in penicillin-binding proteins lead to hydrolysis or inactivation of beta-lactam agents.
False
T/F: Changes in porins often limit the amount of drug that can enter the cell to reach the drug's site of action.
True
T/F; Beta lactamases can be transported out of the cell and act extracellularly in some organisms.
True
A 14 year old girl goes to the doctor complaining of sore throat, fever and headache. The doctor does a rapid strep test that is positive for Streptococcus pyogenes (Group A strep). No antibiotic testing is needed because S. pyogenes is:
Universally susceptible to Penicillin
What is CLSI?
An organization that promotes the development and use of voluntary laboratory consensus standards and guidelines
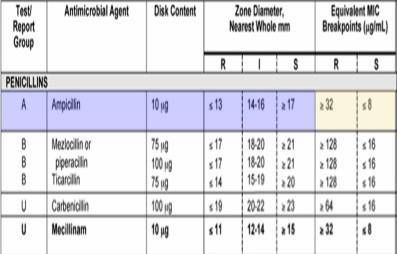
For an E. coli with a resistant zone diameter of 13 mm or less for ampicillin, what would be the equivalent MIC breakpoint for resistance? Use the M100 table exerpt provided.
> or = 32
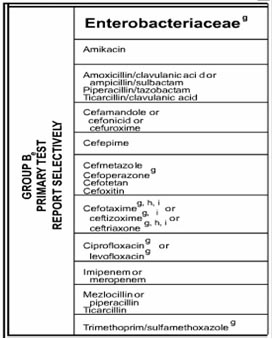
A physician who is treating a patient with a Citrobacter freundii urinary tract infection requests results for levofloxacin. You have already tested ciprofloxacin as susceptible, but not levofloxacin. Based on CLSI recommendations, what should you do?
Report levofloxacin as susceptible
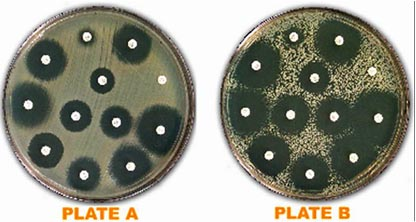
These photos represent testing of the same Enterobacter cloacae isolate on the same day under the same testing conditions but with two different inoculum suspensions. Note the different appearances of the lawns of growth on each plate. Which plate is acceptable to read?
Plate "A"
T/F: The growth pattern seen in this photo may be the result of a mixed culture or possibly a resistant subpopulation of the isolate.
True
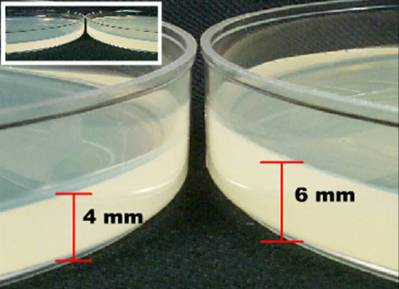
Which one of these plates shows the correct depth for performing disk diffusion testing?
Which of the following is a commercially available beta-lactamase inhibitor?
ampicillin
clavulanate
amikacin
erythromycin
ampicilin
A patient with a heart murmur is given a prescription for an oral antibiotic to take prior having any dental work done. This use of an antimicrobial agent is referred to as:
prophylaxis
For which of the following antibiotics should you interpret where there is an 80% reduction of growth?
Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole
The most important characteristics to be considered when deciding which antimicrobial agents should routinely be tested are:
distribution, absorption, and excretion.
According to CLSI recommendations, which category of drugs should be considered appropriate for inclusion in a routine, primary testing panel, as well as for routine reporting of results for the specific organism groups?
Group A
Advantages of the disk diffusion method for susceptibility testing include all of the following except:
results available in 4-8 hours.

The E-test pictured below is depicts a Staphylococcus aureus isolate tested against vancomycin. What is the interpreted vancomycin MIC for this organism?
2 ug/ml
The term that best describes the interaction of amoxicillin and clavulanate when these drugs are used to treat infections with Klebsiella spp. is:
synergistic
What antibiotics should be reported for urinary tract infections?
Group U antibiotics
When should the antimicrobial susceptibility testing be performed on a bacterial isolate from a clinical specimen?
When the susceptibility of the isolate to particular antimicrobial agents cannot be reliably predicted.
When the isolate is determined to be the probable cause of the patients infection.
When a nitrocefin (beta-lactamase) test is performed on an isolate of Haemophilus influenzae, a red color is observed. This result indicates:
the isolate is resistant to ampicillin
A technologist used the following procedure to perform a disk diffusion test on an isolate of Klebsiella pneumoniae.
1. A broth tube was inoculated with organisms from four similar colonies to achieve a 0.5 McFarland.
2. A MH agar plate was inoculated with this suspension.
3. The antimicrobial disks were placed on the agar surface 1 hour later.
4. the plate was inverted and incubated at 35°C in ambient air for 18 hours.
An evaluation of this procedure indicates that the:
antimicrobial disks were applied too long after plate inoculation
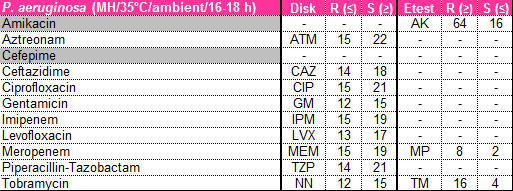
Using the CLSI breakpoints found on your Sacred Heart formulary card, interpret the following result for a Pseudomonas isolate:
Ceftazidime (CAZ): 18 mm
Susceptible
T/F: The faint haze produced by swarming Proteus spp. should be ignored when reading disk diffusion plates.
True