Family Systems Theory
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/27
Earn XP
Last updated 2:53 AM on 3/22/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
1
New cards
History: Burgess (1926)
1. Defined family as a “unity of interacting personalities”, believe in that the interaction of its members and is a living, changing, growing thing or “super personality”
2. Two family types:
1. Highly integrated - characterized by rituals, discipline, interdependence, and cooperation
2. Uninterrupted - lack of those features
2
New cards
What is a system?
Set of components or processes that interact with one another to achieve a specific object or serve a common purpose or goal
3
New cards
What are the components of a system?
1. Interrelated elements and structure - interact in patterns to serve a common purpose or goal
2. Interact in patterns - to serve a common purpose or goal
3. Have boundaries: open and closed - defining what is inside and outside a system
4. Whole is greater than sum of parts - the behavior of the system as a whole cannot be predicted by analyzing the behavior of its individual parts (?)
5. Messages and rules - systems rely on messages and rules to facilitate communication and interactions between its components
6. Subsystems - within larger system and interact with other subsystems to achieve the larger system’s goals
4
New cards
System Terms: System
* Any set of objects, with their attributes, that relate to each other in a way that creates a new “super entity”
* Boundary-maintained unit
* Interdependent parts, alteration in one part affects all components of system
* Family is a social system
* Can have subsystems, primarily: parental, spousal, and sibling
* Boundary-maintained unit
* Interdependent parts, alteration in one part affects all components of system
* Family is a social system
* Can have subsystems, primarily: parental, spousal, and sibling
5
New cards
System Terms: family roles - specific functions for individuals
Recurring patterns of behavior used to fulfill family functions
1. Mover - initiates action
2. Opposer
3. Follower
4. By standard
1. Mover - initiates action
2. Opposer
3. Follower
4. By standard
6
New cards
System Terms: family roles - dysfunctional families (alcoholic)
Recurring patterns of behavior used to fulfill family functions
1. Dependent
2. Enabler/codependent
3. Hero
4. Delinquent
5. Invisible child
6. Clown
1. Dependent
2. Enabler/codependent
3. Hero
4. Delinquent
5. Invisible child
6. Clown
7
New cards
System Terms: Hierarchy
Rank according to authority/power - family’s arrangement is related to its organization,, communication patterns, decision-making process etc.
8
New cards
System Terms: Boundaries
Lines of demarcation that distinguish a system from its environment and affect the flow of energy and information between the two
1. Open - highly interactive with outside environment, healthy kids
2. Random - no boundaries, few rules exist above defending “family’s territory”, children don’t feel loved
1. Closed - extremely private, result in emotional illness—can’t function on own behalf
1. Open - highly interactive with outside environment, healthy kids
2. Random - no boundaries, few rules exist above defending “family’s territory”, children don’t feel loved
1. Closed - extremely private, result in emotional illness—can’t function on own behalf
9
New cards
Basic Assumptions: The whole is greater than the sum of its parts
Think cake, individual ingredients missing = different quality
10
New cards
Basic Assumptions: society is the environmental context and individual family members are component units
Behavior must be understood in context, both within family context and interaction with other systems context
11
New cards
Basic Assumptions: family is a goal-seeking system
They pursue goals and develop tactics to achieve them, although their degree of goal orientation can vary
12
New cards
Basic Assumptions: a family is a self-reflective and self-regulating system, continually influenced by feedback
Positive (change-sustaining/enhancing) and negative feedback (attempts to return to previous steady state) can be good or bad
13
New cards
Basic Assumptions: family systems are defined by communication
Allows families to create, preserve, and modify a system’s reality. Two levels of messages:
1. Content level
2. Relationship level - what and how it is said/should be interpreted
Meta communication helps articulate needs, clarify misunderstandings, and plan more constructive means for relating to each other
1. Content level
2. Relationship level - what and how it is said/should be interpreted
Meta communication helps articulate needs, clarify misunderstandings, and plan more constructive means for relating to each other
14
New cards
Basic Assumptions: the locus of pathology is not within the person, but is a system of dysfunction
The location of the problem is not within the individual but the system in which they are in is dysfunctional
15
New cards
Bowen Family Systems Theory
* pioneer of FSystemT
* Believes that a family is a unit of complex infractions with emotionally connected members who exhibit emotional interdepence
* Sees the patient as part of the family system and pays attention to the family’s struggle to balance togetherness with individualization
* Believes that a family is a unit of complex infractions with emotionally connected members who exhibit emotional interdepence
* Sees the patient as part of the family system and pays attention to the family’s struggle to balance togetherness with individualization
16
New cards
Triangulation
A 3-person relationship in which a dyad is destabilized by a third party.
The smallest stable relationship system and a building block of larger emotional system
2-person systems are unstable and can’t tolerate tension
The smallest stable relationship system and a building block of larger emotional system
2-person systems are unstable and can’t tolerate tension
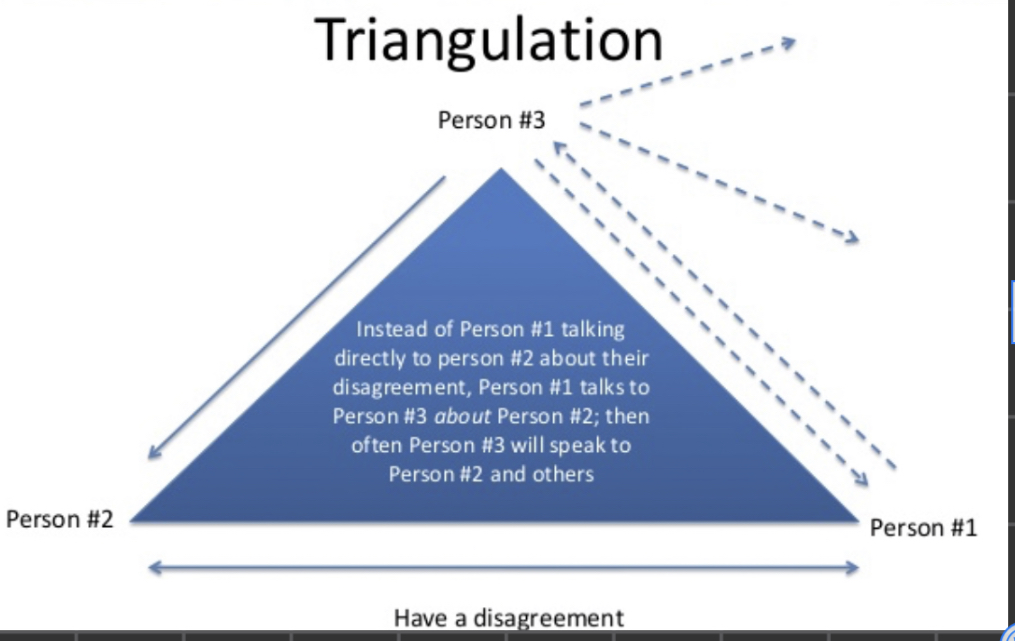
17
New cards
Dysfunctional triangulation
Perpetuates problem
One member is caught between tension between the other two, leading to emotional and psychological distress
Often used to diffuse anxiety and conflict in the system, but ultimately leads to dysfunciton and lack of resolution, #3 talks to both 1 and 2 about the other and also to others outside triangle
One member is caught between tension between the other two, leading to emotional and psychological distress
Often used to diffuse anxiety and conflict in the system, but ultimately leads to dysfunciton and lack of resolution, #3 talks to both 1 and 2 about the other and also to others outside triangle
18
New cards
Functional triangulation
Resolves problem
\#3 is mediator/peacemaker, helping to alleviate tension and conflict between the other two members
Can lead to improved communication, greater emotional maturity, and a stronger, more functional family system
\#3 is mediator/peacemaker, helping to alleviate tension and conflict between the other two members
Can lead to improved communication, greater emotional maturity, and a stronger, more functional family system
19
New cards
Differentiation
The process of becoming an individual and a separate self, while still maintaining emotional connection with others; togetherness vs. separateness—equilibrium
20
New cards
Differentiated self
Less reactive, calm emotions, thoughtful, independent, not vulnerable to stress, decreases triangulation and entanglements/problems, achieves closeness without enmeshment, has better relationships
21
New cards
Undifferentiated self
More reactive, less thoughtful, critical and judgmental, concerned about approval, dependent, increase triangulation, difficulty with decisions, poor communication, repeat problematic relationship
22
New cards
Nuclear Family Problems
1. Marital conflict - significant arguments, disagreements, and tension in relationship
2. Dysfunction in one spouse - one spouse has significant emotional, mental, or behavioral issues that cause distress for the other spouse and children
3. Impairment of one or more children - same as above
4. Emotional distance - feeling disconnected emotionally
5. Tension/anxiety - lead to experience emotional tension/stress, impairs ability (functional—work, school, decision-making etc.), and moves through system (one to another through communication/interaction; dangerous cycle)
23
New cards
Family Projection Process
Parents project emotional responses on children
Can lead to children feeling responsible for others’ well-being’s and increase need for attention/approval
Can lead to children feeling responsible for others’ well-being’s and increase need for attention/approval
24
New cards
Multigenerational Transmission Process
Occurs as child leaves nuclear family to establish own family → changes in family system may occur over time → generations may be very different in family roles, expectations, and functions—may be evident in terms of educational level, occupations, or family structure
25
New cards
Emotional Cutoff
the act of family members disconnecting emotionally from each other as a means of coping with unresolved emotional issues or conflicts
Ex. Adult child cuts off emotionally abusive mom to avoid dealing with issues
Can lead to unresolved emotional pain and distress for all parties and hinder the development of healthy relationships and emotional maturity
Ex. Adult child cuts off emotionally abusive mom to avoid dealing with issues
Can lead to unresolved emotional pain and distress for all parties and hinder the development of healthy relationships and emotional maturity
26
New cards
Sibling Position
Birth order impacts individual responses. Individuals who are in same sibling position have similar personality
1. First born - leader, takes on more responsibility and displays more organized and structured personality
1. Last born - follower, displays more carefree and spontaneous personality being more likely to take risks
1. First born - leader, takes on more responsibility and displays more organized and structured personality
1. Last born - follower, displays more carefree and spontaneous personality being more likely to take risks
27
New cards
Societal Emotional Process
The way societal characteristics, such as cultural norms, economic pressures and political events, impact and influence family systems
Parenting may have become less rule bound due to societal norms
Parenting may have become less rule bound due to societal norms
28
New cards
Article Analysis: Scaffolding or enabling?: Implications of extended parental financial support into adulthood
Major points:
1. Parents provide support to adult children
2. Uses Systems Theory to analyze the situation, which suggests that individuals cannot be understood in isolation but must be viewed in the context of their family system and other systems they are apart of
3. Bowenian Therapy is applied to the family situation, which focuses on understanding how family members are emotionally connected and the ways in which this emotional interdependence can influence their behavior
4. Study found that while parental financial support can be helpful in some situations, it can also create dependency and hinder the development of independence
5. Authors sugges that parents need to set clear boundaries and communicate their expectations to their adult children in order to avoid creating an unhealthy dynamic
1. Parents provide support to adult children
2. Uses Systems Theory to analyze the situation, which suggests that individuals cannot be understood in isolation but must be viewed in the context of their family system and other systems they are apart of
3. Bowenian Therapy is applied to the family situation, which focuses on understanding how family members are emotionally connected and the ways in which this emotional interdependence can influence their behavior
4. Study found that while parental financial support can be helpful in some situations, it can also create dependency and hinder the development of independence
5. Authors sugges that parents need to set clear boundaries and communicate their expectations to their adult children in order to avoid creating an unhealthy dynamic